A Novel Microfluidic-Based OMC-PEDOT-PSS Composite Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Dopamine Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of OMC and PEDOT-PSS Modified Electrodes
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
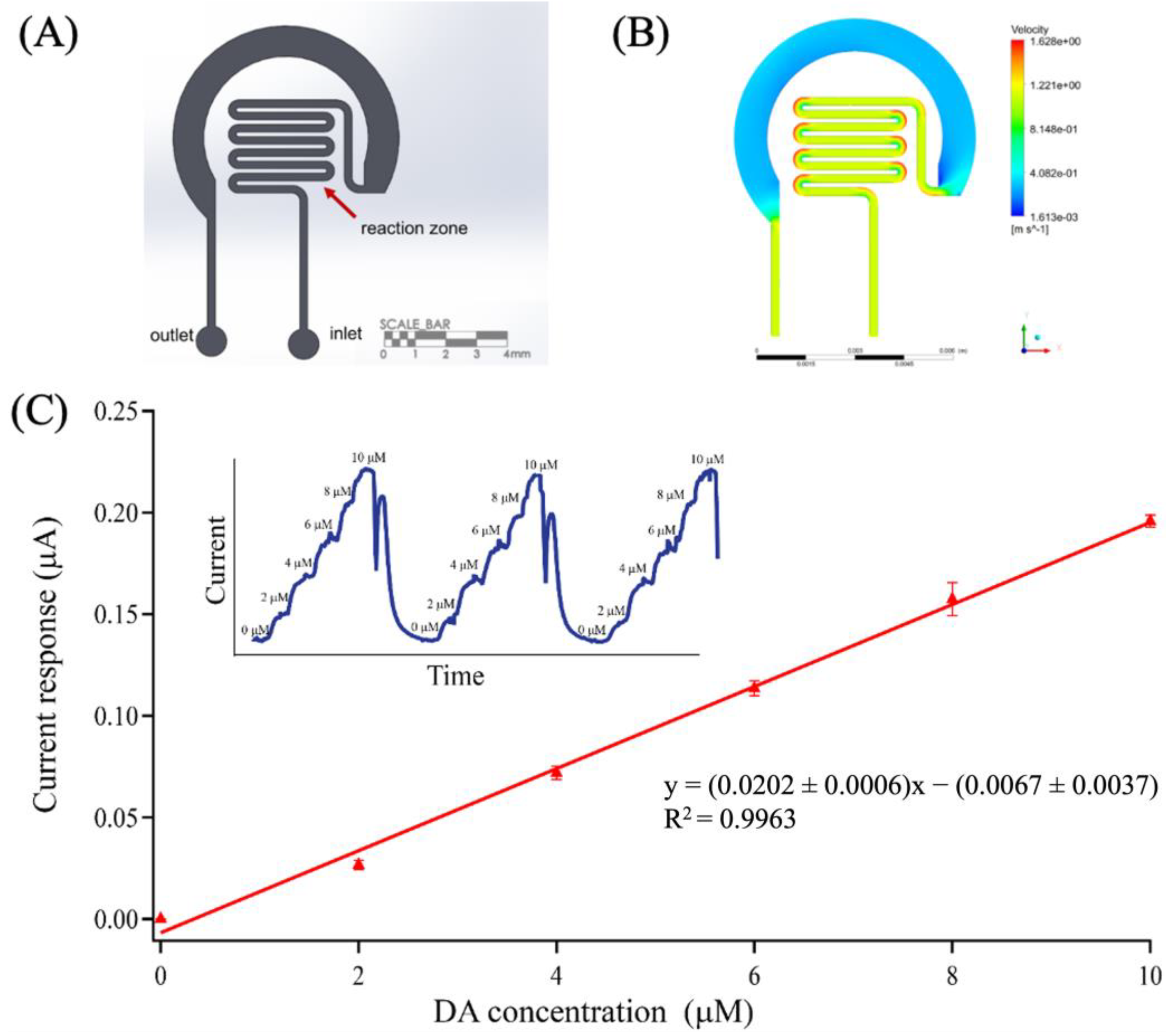
2.4. Design, Simulation, and Fabrication of Microfluidics
2.5. On-Chip Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
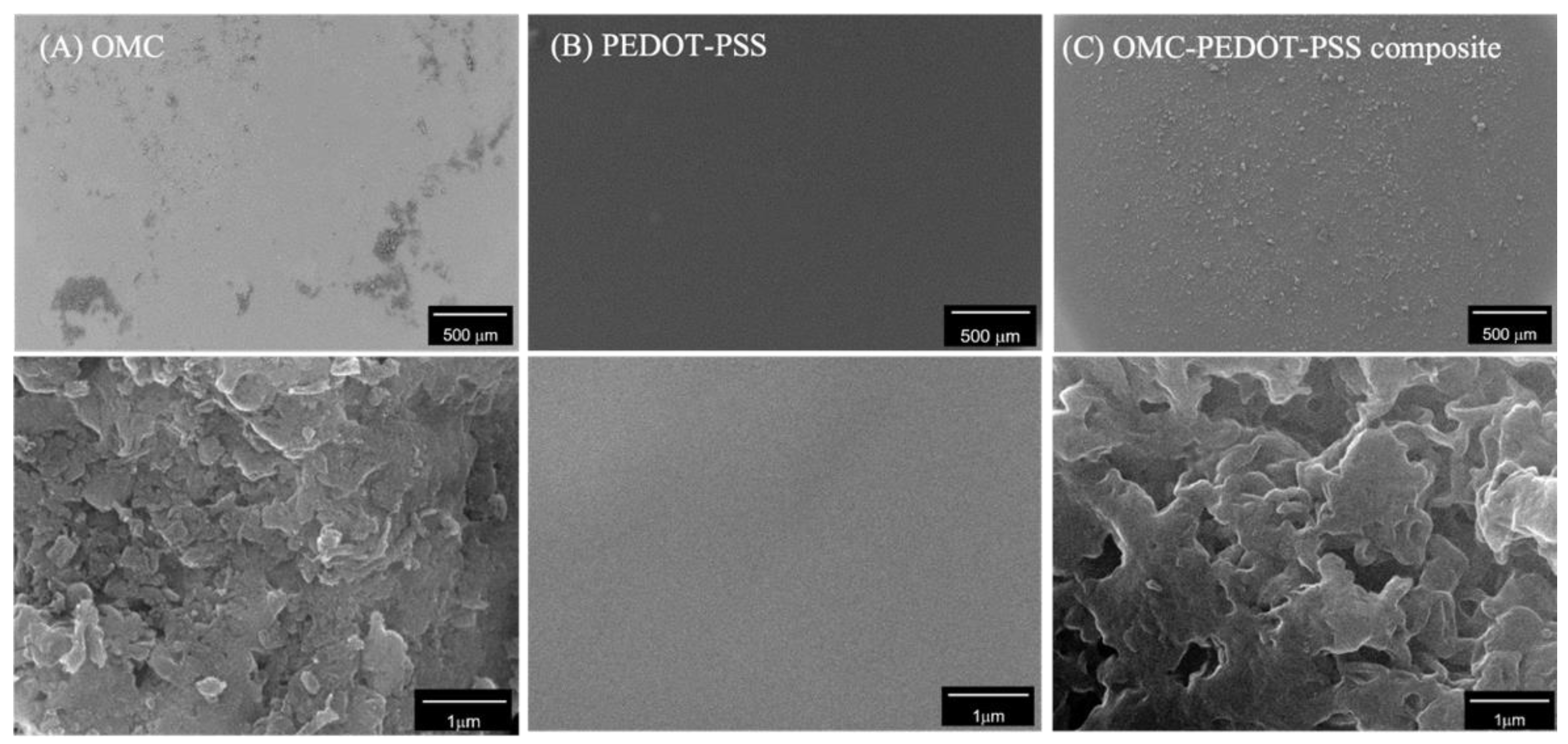
3.1. Surface Characterization
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
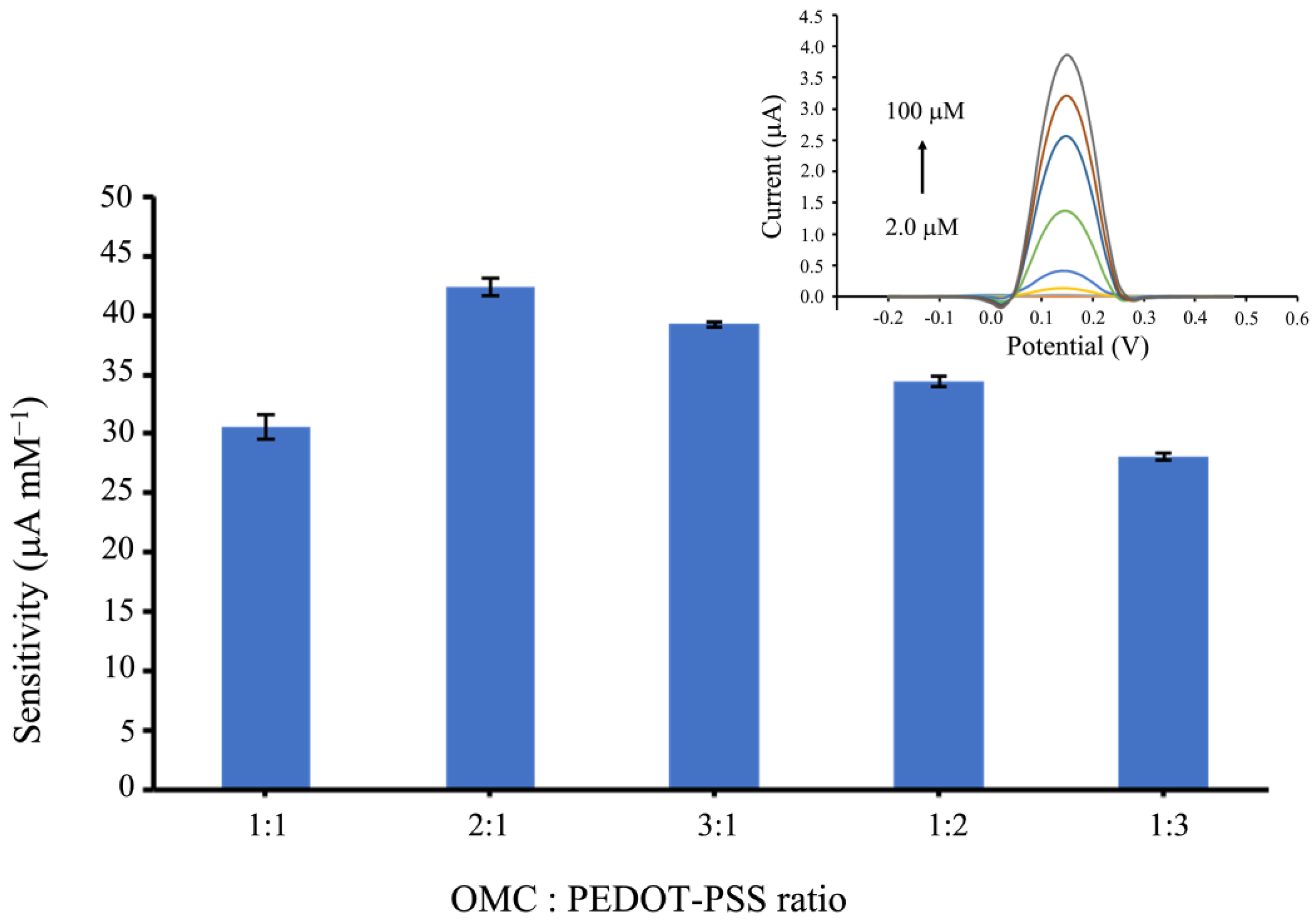
3.3. Effect of OMC: PEDOT-PSS Composite Ratios
3.4. Interference Study
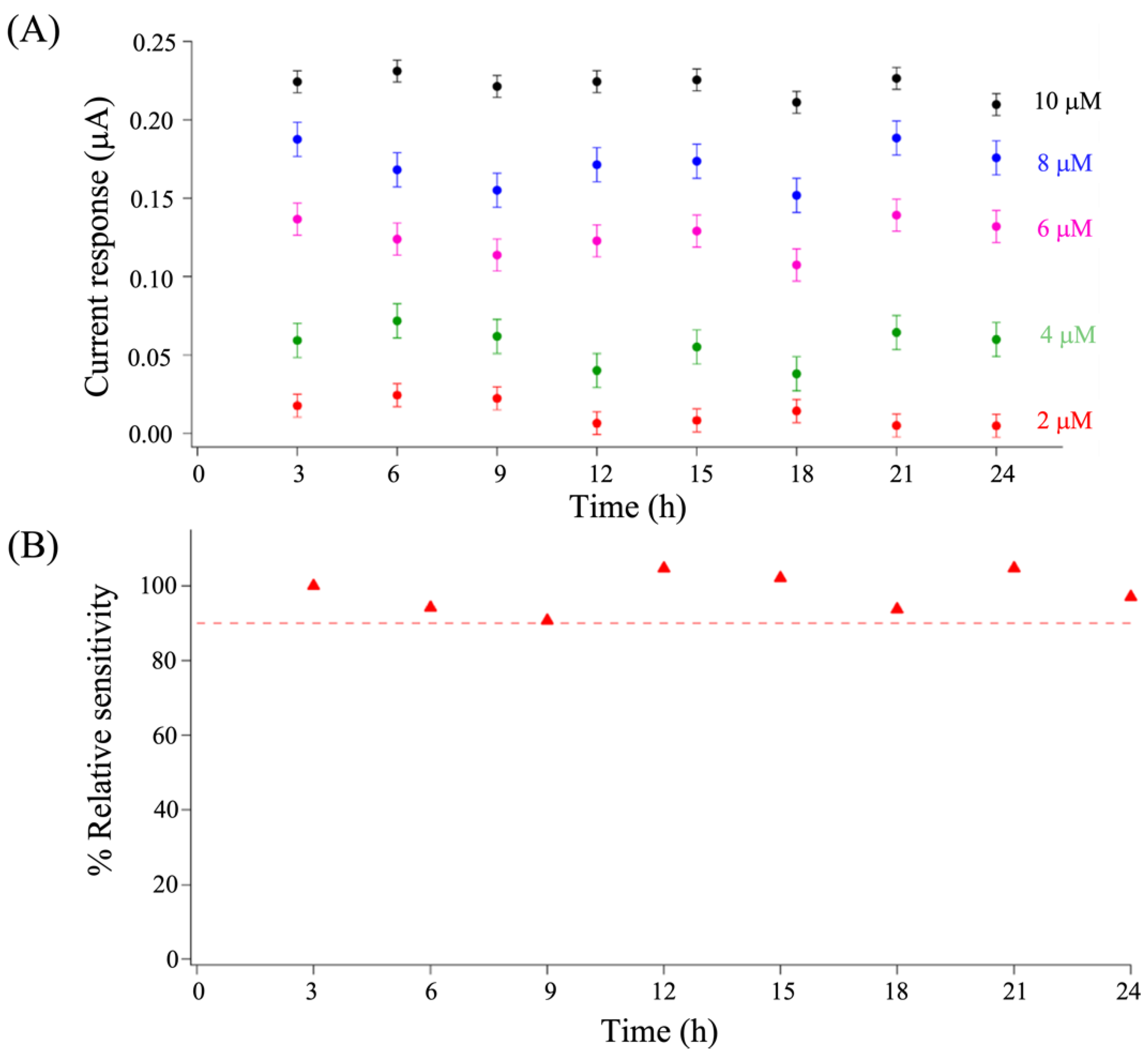
3.5. Dopamine Determination Using a Microfluidic Platform
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booth, M.A.; Gowers, S.A.N.; Leong, C.L.; Rogers, M.L.; Samper, I.C.; Wickham, A.P.; Boutelle, M.G. Chemical Monitoring in Clinical Settings: Recent Developments toward Real-Time Chemical Monitoring of Patients. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K. Brain neurochemical monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.L.; Kahn, R.S.; Ko, G.; Davidson, M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: A review and reconceptualization. Am. J. Psychiatry 1991, 148, 1474–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, B.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Role of Dopamine in the Pathophysiology of Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchon, A.; Feng, L.; Drake, H.F.; Joseph, E.A.; Zhou, H.-C. From fundamentals to applications: A toolbox for robust and multifunctional MOF materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8611–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Tehrani, F.; Longardner, K.; Mahato, K.; Podhajny, T.; Moon, J.-M.; Kotagiri, Y.G.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Litvan, I.; Wang, J. Closing the loop for patients with Parkinson disease: Where are we? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, M.V.; Gutorova, S.V.; Berseneva, D.A.; Apyari, V.V.; Zaitsev, V.D.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. Spectroscopic methods for determination of catecholamines: A mini-review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2018, 54, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Lin, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Z.; Rao, Y. Simultaneous determination of N-ethylpentylone, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and their metabolites in rat brain microdialysis by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, R.; Lin, L.; Guo, G.; Lin, J.M. Determination of l-ascorbic acid in human serum by chemiluminescence based on hydrogen peroxide-sodium hydrogen carbonate-CdSe/CdS quantum dots system. Talanta 2010, 81, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Shi, H.; Kang, W. Determination of monoamine neurotransmitters and metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography based on Ag(III) complex chemiluminescence detection. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 593, 113594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Gamella, M.; Serafín, V.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Beyond sensitive and selective electrochemical biosensors: Towards continuous, real-time, antibiofouling and calibration-free devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.-F.; Hashemi, P.; Boutelle, M.G. Analytical science in neurochemistry. Analyst 2020, 145, 3774–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.J.; Kang, K.; Niu, L.M.; Kang, W.J. Electroanalysis of neurotransmitters via 3D gold nanoparticles and a graphene composite coupled with a microdialysis device. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 834, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, C.S.; Müller, M.; Bashaw, E.D.; Benfeldt, E.; Bolinder, J.; Bullock, R.; Bungay, P.M.; De Lange, E.C.M.; Derendorf, H.; Elmquist, W.F.; et al. AAPS-FDA workshop white paper: Microdialysis principles, application and regulatory perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.L.; Cheng, W.L.; Hsu, T.K.; Chang, C.W.; Chang, J.L.; Zen, J.M. Ultrasensitive and highly stable nonenzymatic glucose sensor by a CuO/graphene-modified screen-printed carbon electrode integrated with flow-injection analysis. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 30, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneş, M.; Karakaya, S.; Dilgin, Y. Development of an interference-minimized amperometric-FIA glucose biosensor at a pyrocatechol violet/glucose dehydrogenase-modified graphite pencil electrode. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 1923–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.; Witt, C.E.; Keen, D.; Buchanan, A.M.; Batey, L.; Hersey, M.; Hashemi, P. Glutamate Electropolymerization on Carbon Increases Analytical Sensitivity to Dopamine and Serotonin: An Auspicious In Vivo Phenomenon in Mice? Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 10762–10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Speicher, L.M.; Länge, K. Microfluidic integration for electrochemical biosensor applications. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 29, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phairatana, T.; Leong, C.L.; Gowers, S.A.N.; Patel, B.A.; Boutelle, M.G. Real-time detection of carboplatin using a microfluidic system. Analyst 2016, 141, 6270–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, I.C.; Gowers, S.A.N.; Booth, M.A.; Wang, C.; Watts, T.; Phairatana, T.; Vallant, N.; Sandhu, B.; Papalois, V.; Boutelle, M.G. Portable Microfluidic Biosensing System for Real-Time Analysis of Microdialysate in Transplant Kidneys. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14631–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowers, S.A.N.; Samper, I.C.; Murray, D.-S.R.K.; Smith, G.K.; Jeyaprakash, S.; Rogers, M.L.; Karlsson, M.; Olsen, M.H.; Moeller, K.; Boutelle, M.G. Real-time neurochemical measurement of dynamic metabolic events during cardiac arrest and resuscitation in a porcine model. Analyst 2020, 145, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senel, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Alhassen, S.; Dervisevic, M.; Alachkar, A.; Cadarso, V.J.; Voelcker, N.H. Microfluidic Electrochemical Sensor for Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood Dopamine Detection in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12347–12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Cui, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhi, Y.; Ding, X.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, P.; Cui, D. Microfluidic Device Directly Fabricated on Screen-Printed Electrodes for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Sensing of PSA. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumalraj, B.; Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Kannan, R.S. Alumina Polished Glassy Carbon Electrode as a Simple Electrode for Lower Potential Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine in its Sub-micromolar Level. Electroanalysis 2015, 28, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Graphene Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors based on graphene two-dimensional nanomaterials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansuk, S.; Bitziou, E.; Joseph, M.B.; Covington, J.A.; Boutelle, M.G.; Unwin, P.R.; Macpherson, J.V. Ultrasensitive Detection of Dopamine Using a Carbon Nanotube Network Microfluidic Flow Electrode. Anal. Chem. 2012, 85, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomäki, T.; Peltola, E.; Sainio, S.; Wester, N.; Pitkänen, O.; Kordas, K.; Koskinen, J.; Laurila, T. Unmodified and multi-walled carbon nanotube modified tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) films as in vivo sensor materials for sensitive and selective detection of dopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcarius, A. Recent Trends on Electrochemical Sensors Based on Ordered Mesoporous Carbon. Sensors 2017, 17, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preecharueangrit, S.; Thavarungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Numnuam, A. Amperometric sensing of sulfite using a gold electrode coated with ordered mesoporous carbon modified with nickel hexacyanoferrate. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 808, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qiu, P.; Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Cheng, X.; Deng, Y.; Luo, W. Mesoporous materials–based electrochemical biosensors from enzymatic to nonenzymatic. Small 2021, 17, 1904022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, E.; Ma, Y.; Brezesinski, T.; Elm, M.T. Ordered mesoporous metal oxides for electrochemical applications: Correlation between structure, electrical properties and device performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 10706–10735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualandi, I.; Tonelli, D.; Mariani, F.; Scavetta, E.; Marzocchi, M.; Fraboni, B. Selective detection of dopamine with an all PEDOT:PSS organic electrochemical transistor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, R.; Kanagavalli, P.; Senthilkumar, S.; Mathiyarasu, J. Au Nanoparticle-decorated Nanoporous PEDOT Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode: A New Electrochemical Sensing Platform for the Detection of Glutathione. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2020, 25, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, I.M.; Patel, N.A.; Freedman, N.C.; Castagnola, E.; Cui, X.T. Direct in Vivo Electrochemical Detection of Resting Dopamine Using Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Carbon Nanotube Functionalized Microelectrodes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12917–12927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losaria, P.M.; Ko, Y.S.; Yim, J.-H. Preparation of PEDOT-ordered mesoporous carbon hybrid material using vapor phase polymerization. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. Study on an improved bio-electrode made with glucose oxidase immobilized mesoporous carbon in biofuel cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 24451–24457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsine, Z.; Bizid, S.; Mlika, R.; Sauriat-Dorizon, H.; Haj Said, A.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Nanocomposite based on poly (para-phenylene)/chemical reduced graphene oxide as a platform for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sensors 2020, 20, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărieş, E.; Popescu, D.; Popescu, A. The Pulsatory liposomes releasing of the neurotransmitters inside to interneuronal synaptic cleft may be a possible device for the depression treatment. Rom. J. Biophys. 2015, 25, 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Nuh, S.; Kwanyuang, A.; Konthapakdee, N.; Chirasatitsin, S.; Phairatana, T. Leakage-Free Bonding of a Serpentine PDMS Microfluidics Directly on a Screen-Printed Electrode. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Ubon Ratchathani, Thailand, 19–22 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Extraction and enrichment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by ordered mesoporous carbon reinforced hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, Z.; Yang, G.; Shen, H.; Zhu, L. Electrochemical properties of ordered mesoporous carbon and its electroanalytical application for selective determination of dopamine. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgrishi, N.; Rountree, K.; McCarthy, B.D.; Rountree, E.; Eisenhart, T.T.; Dempsey, J.L. A Practical Beginner’s Guide to Cyclic Voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 95, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Gao, F.; Wu, Q.-A.; Xu, P.-Y.; Wang, S.-S.; Gao, N.-N.; Wang, Q.-X. A highly sensitive dopamine sensor based on a polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide/Nafion nanocomposite. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Jarjes, Z.A.; Desprez, V.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Sensitive, selective, disposable electrochemical dopamine sensor based on PEDOT-modified laser scribed graphene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonklam, K.; Wannapob, R.; Sriwimol, W.; Thavarungkul, P.; Phairatana, T. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer PMB/MWCNTs sensor for highly-sensitive cardiac troponin T detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 308, 127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, L.M.; Li, Y.; Lim, G.N.; Wairegi, S.G.; Ross, A.E. A microfluidic electrochemical flow cell capable of rapid on-chip dilution for fast-scan cyclic voltammetry electrode calibration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6287–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Kang, E.-S.; Baek, S.; Choo, S.-S.; Chung, Y.-H.; Lee, D.; Min, J.; Kim, T.-H. Electrochemical detection of dopamine using periodic cylindrical gold nanoelectrode arrays. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, H.; He, Q.; Gan, N.; Li, T. A microchip-based flow injection-amperometry system with mercaptopropionic acid modified electroless gold microelectrode for the selective determination of dopamine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 625, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Electrode Material | Detection Method | Limit of Detection (nM) | Sensitivity (μA μM−1) | Working Volume (μL) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFμE | FSCV | NR | 0.013 | 50 | [48] |
| AuμE | Amperometry | 0.1 | 3.53 | 2.40 | [23] |
| CAuNE | Amperometry | 5800 | 0.034 | NR | [49] |
| MPA/Au µE | Amperometry | 74 | NR | 0.120 | [50] |
| OMC-PEDOT-PSS/SPCE | Amperometry | 21.6 | 20.2 | 0.675 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuh, S.; Numnuam, A.; Thavarungkul, P.; Phairatana, T. A Novel Microfluidic-Based OMC-PEDOT-PSS Composite Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Dopamine Monitoring. Biosensors 2023, 13, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010068
Nuh S, Numnuam A, Thavarungkul P, Phairatana T. A Novel Microfluidic-Based OMC-PEDOT-PSS Composite Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Dopamine Monitoring. Biosensors. 2023; 13(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuh, Sofwan, Apon Numnuam, Panote Thavarungkul, and Tonghathai Phairatana. 2023. "A Novel Microfluidic-Based OMC-PEDOT-PSS Composite Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Dopamine Monitoring" Biosensors 13, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010068
APA StyleNuh, S., Numnuam, A., Thavarungkul, P., & Phairatana, T. (2023). A Novel Microfluidic-Based OMC-PEDOT-PSS Composite Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Dopamine Monitoring. Biosensors, 13(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010068






