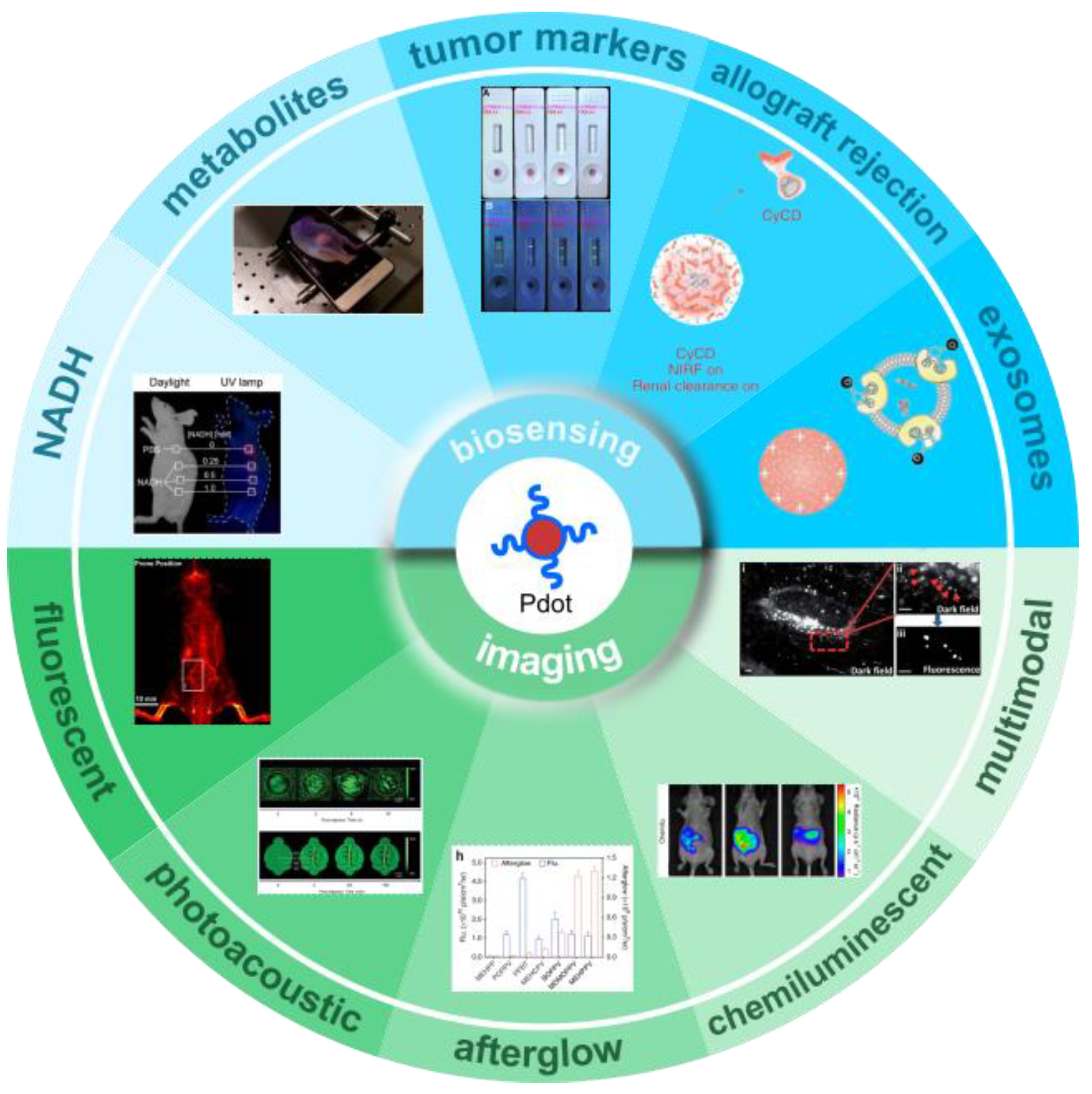
Semiconducting Polymer Dots for Point-of-Care Biosensing and In Vivo Bioimaging: A Concise Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Semiconducting Polymer Dots
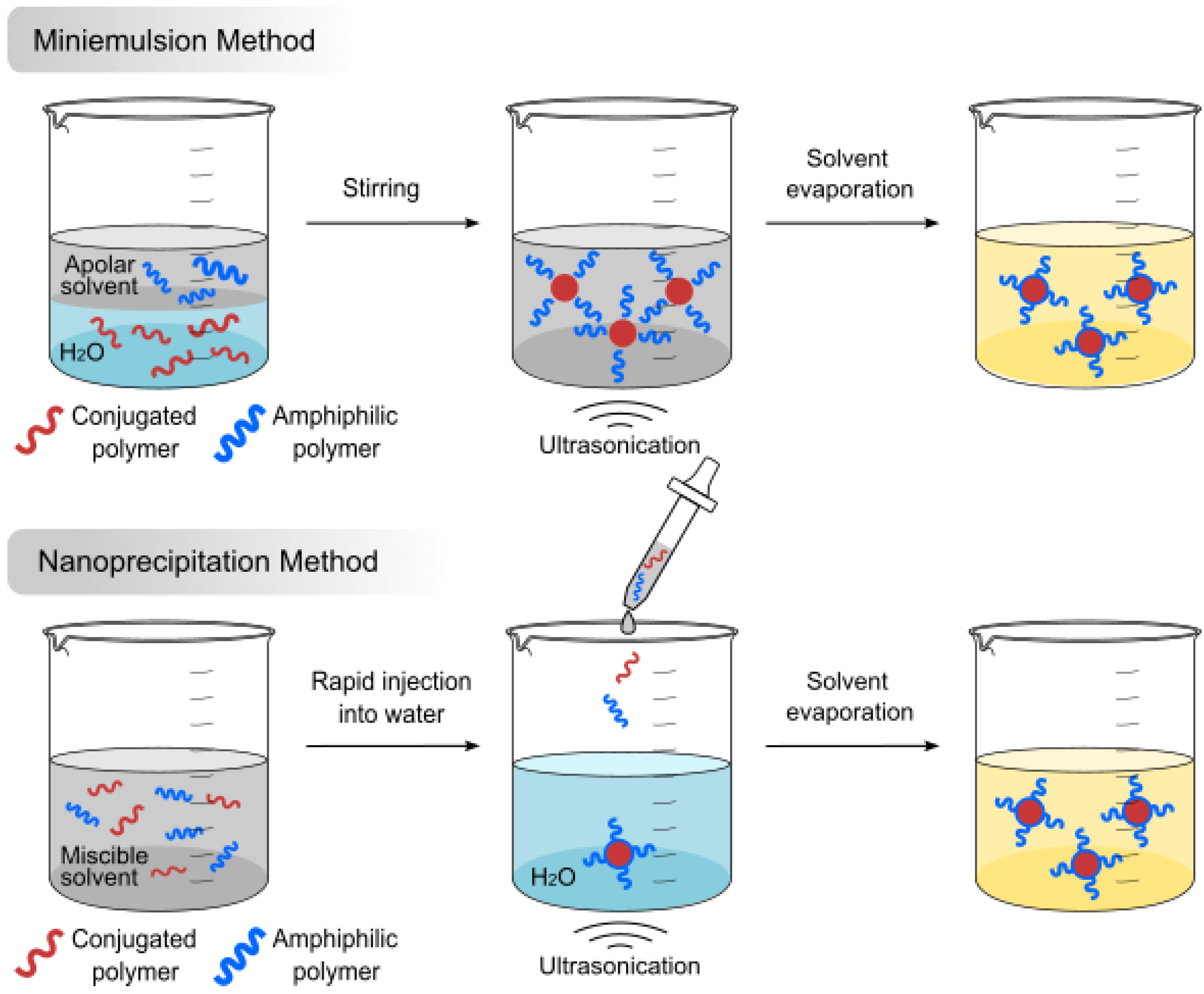
2.1. Methods of Preparation
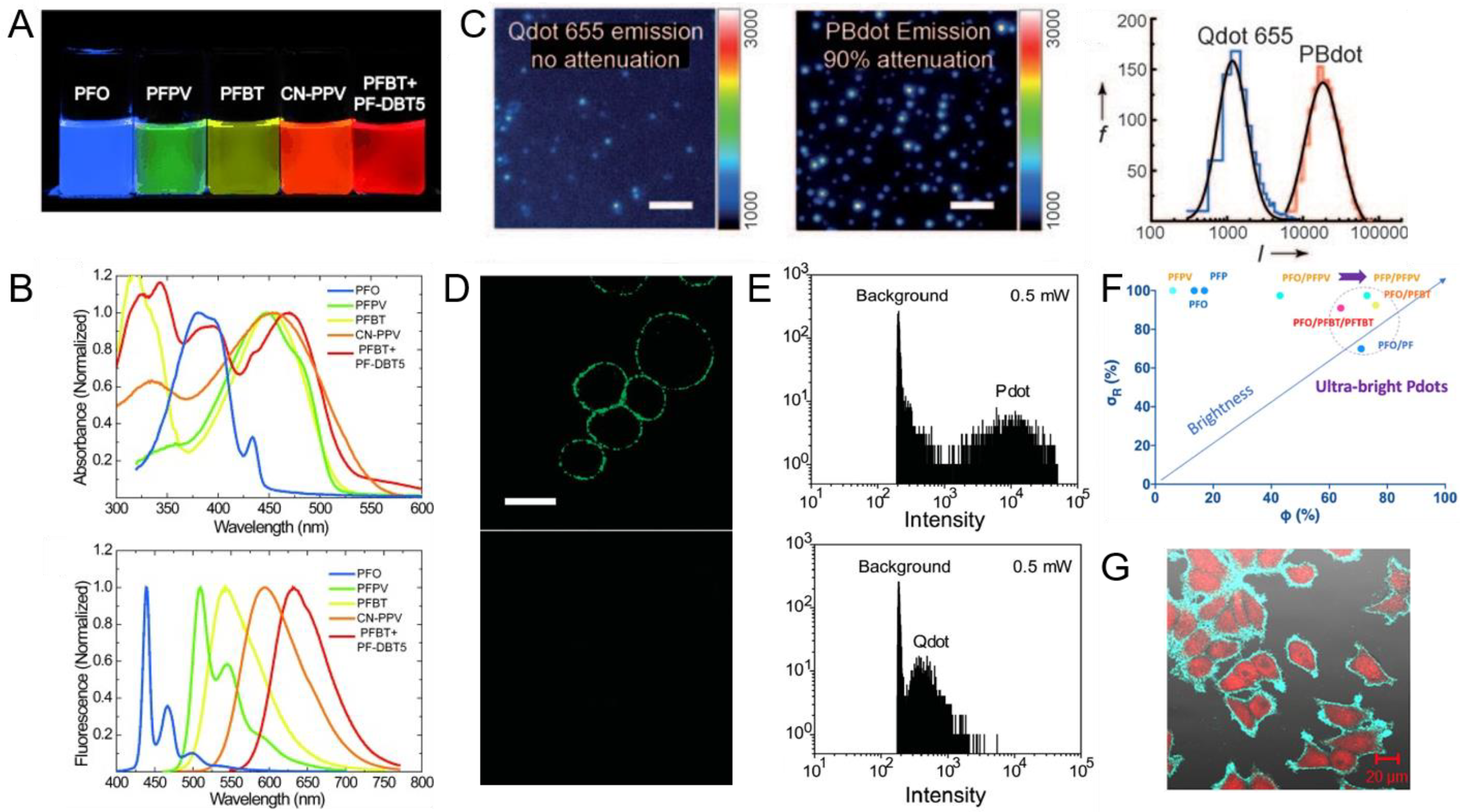
2.2. Properties and Performance
2.3. Surface Modification and Biological Functionalization
2.3.1. Encapsulation Method
2.3.2. Amphiphilic Polymer Coprecipitation Method
2.3.3. Direct Functionalization

3. Application of Pdots Biosensors in Point-of-Care Diagnostics
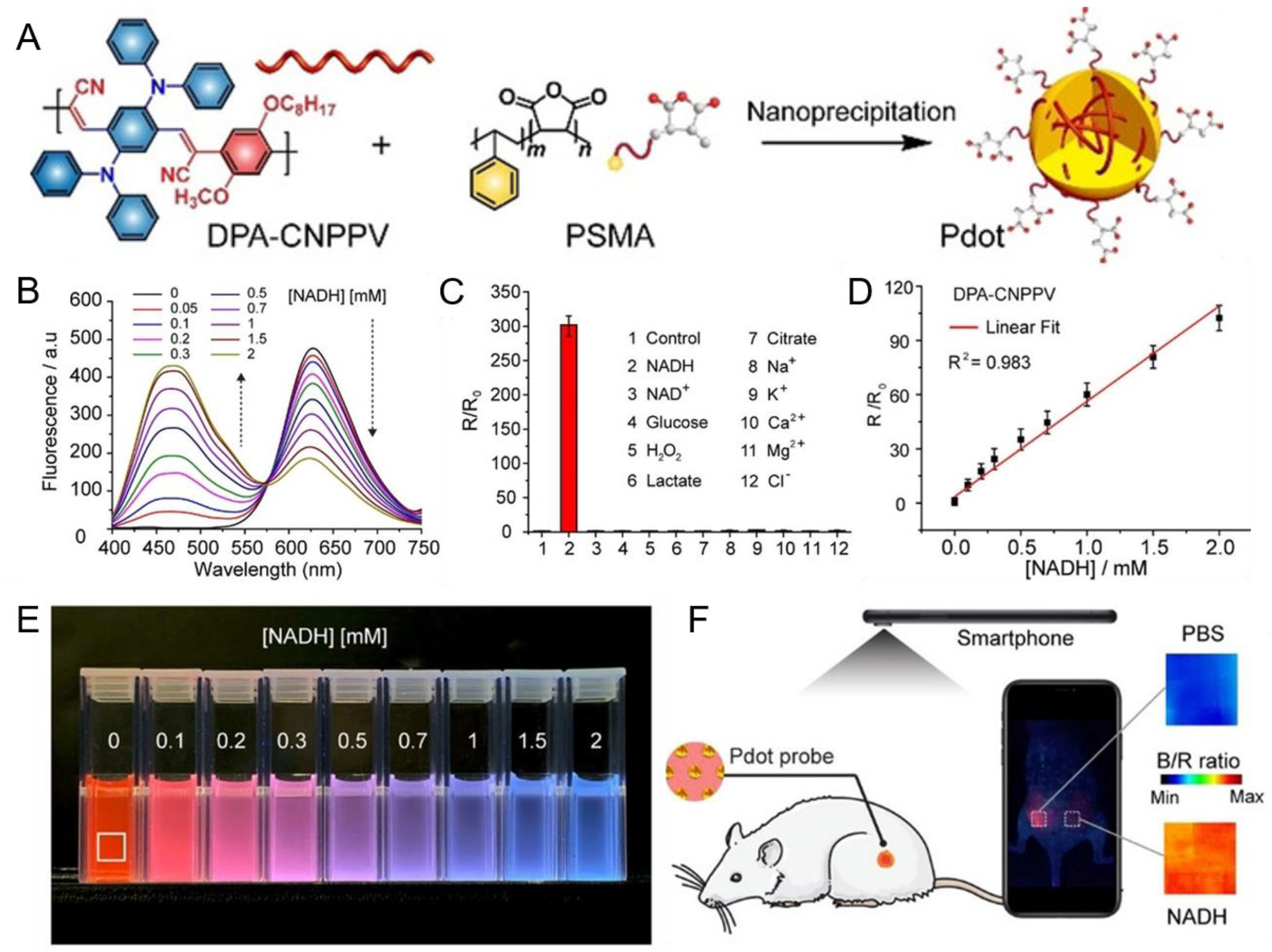
3.1. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (Oxidized Form: NAD+; Reduced Form: NADH)
3.2. Disease-Related Metabolites
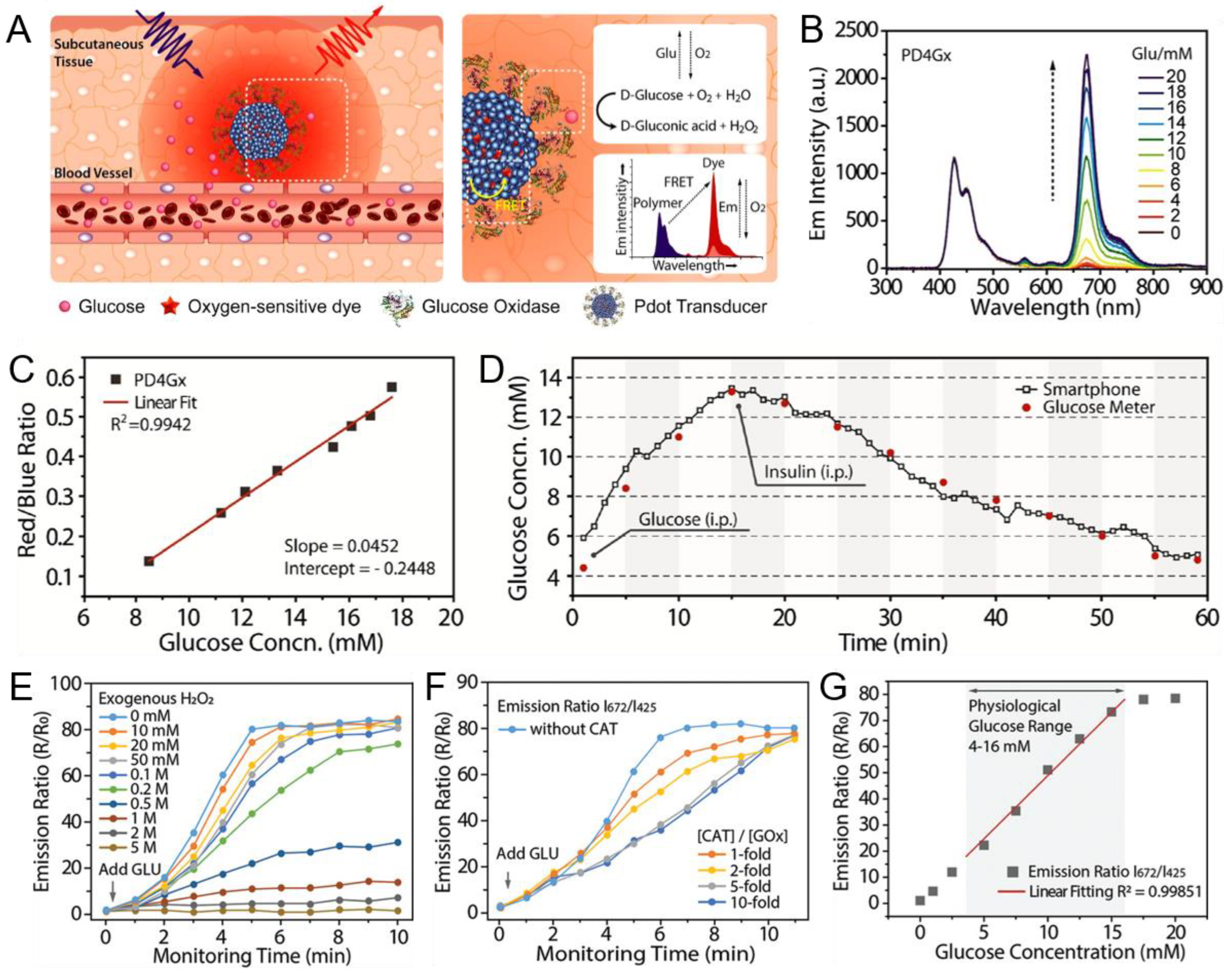
3.2.1. Glucose
3.2.2. Phenylalanine
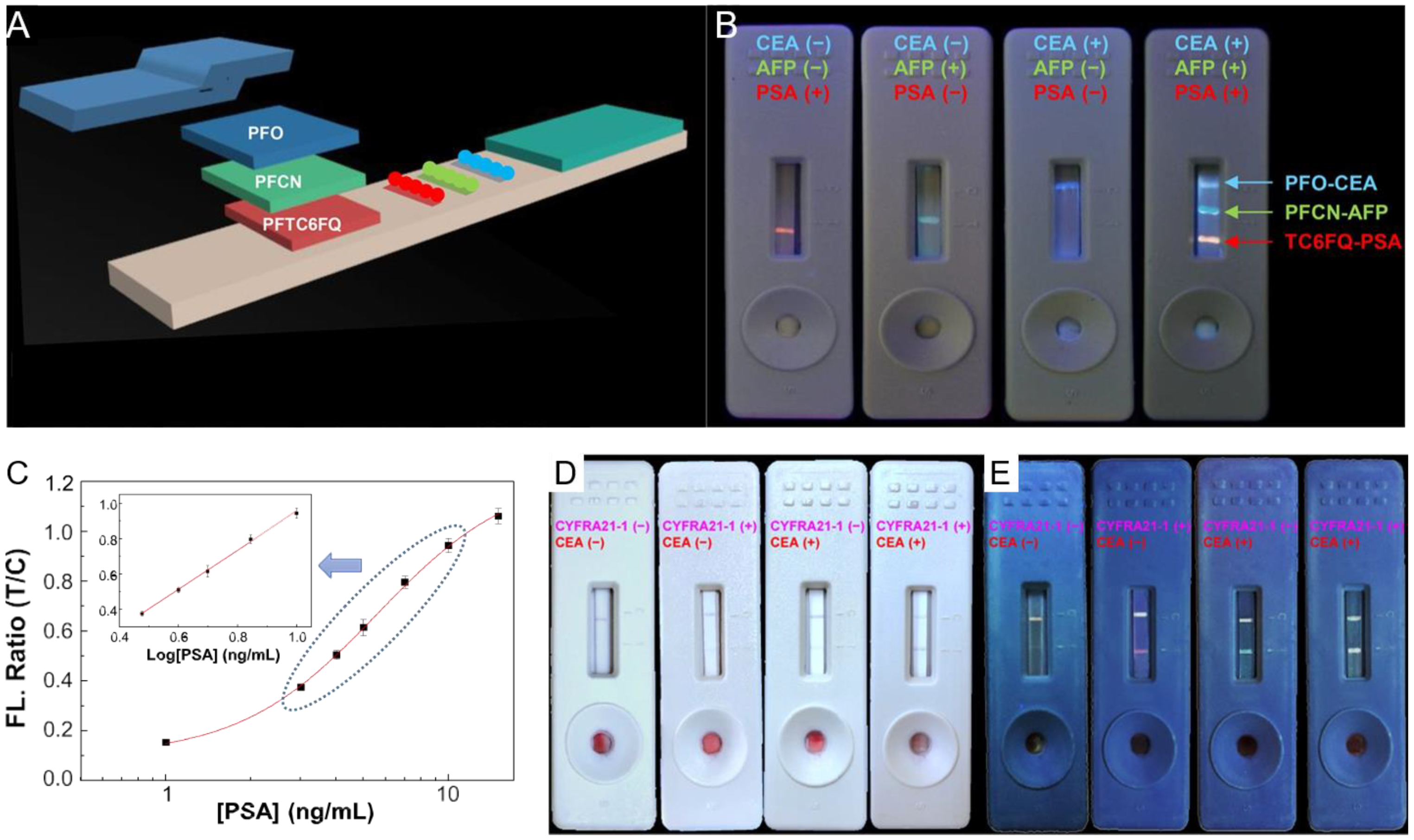
3.3. Tumor Markers
3.4. Cancer and Allograft Rejection
3.5. Exosomes
4. Application of Pdots Optical Probes in Bioimaging
4.1. Pdots for Fluorescence Imaging
4.2. Pdots for Photoacoustic Imaging
4.2.1. Amplification of PA Signal from Pdots
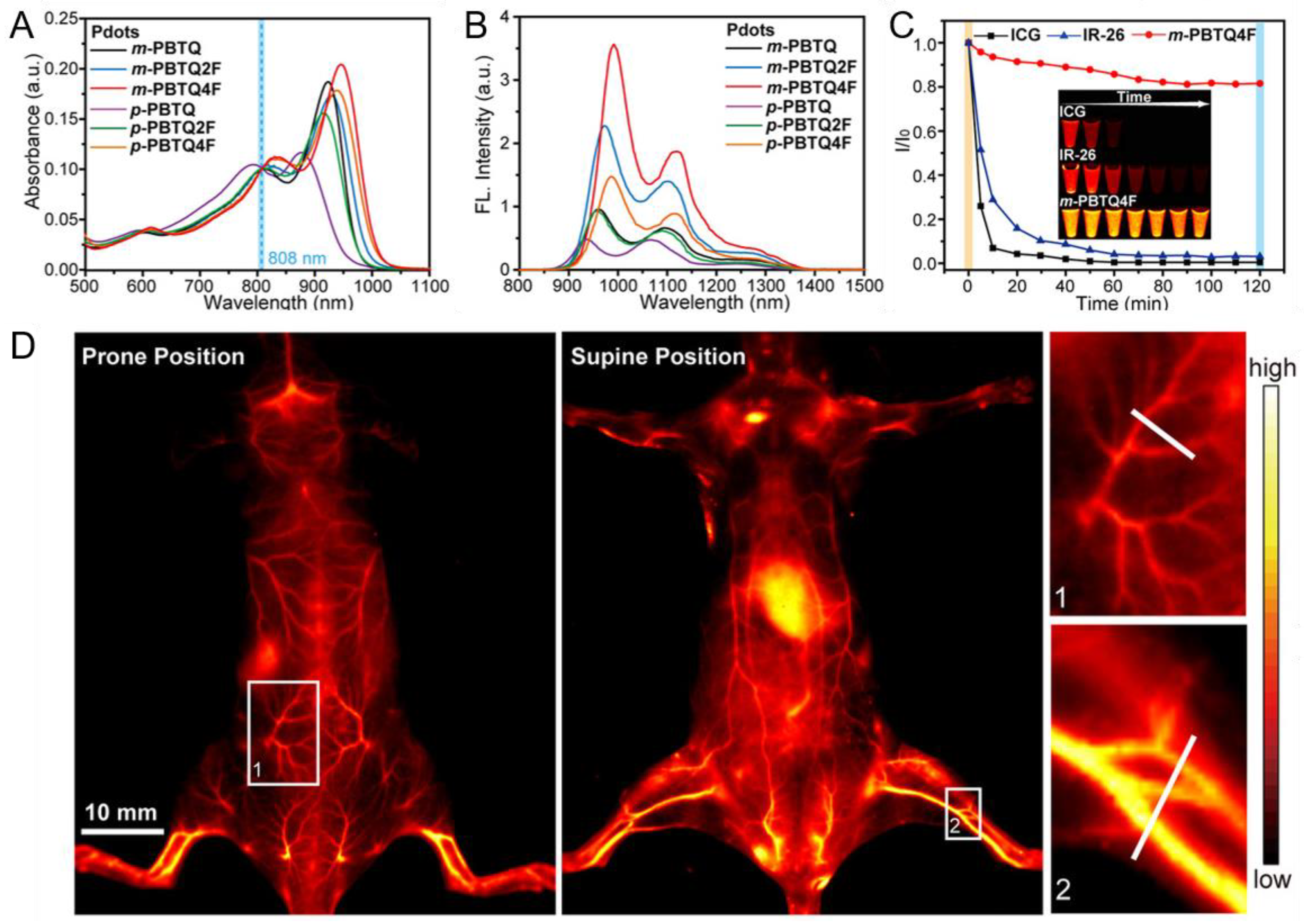
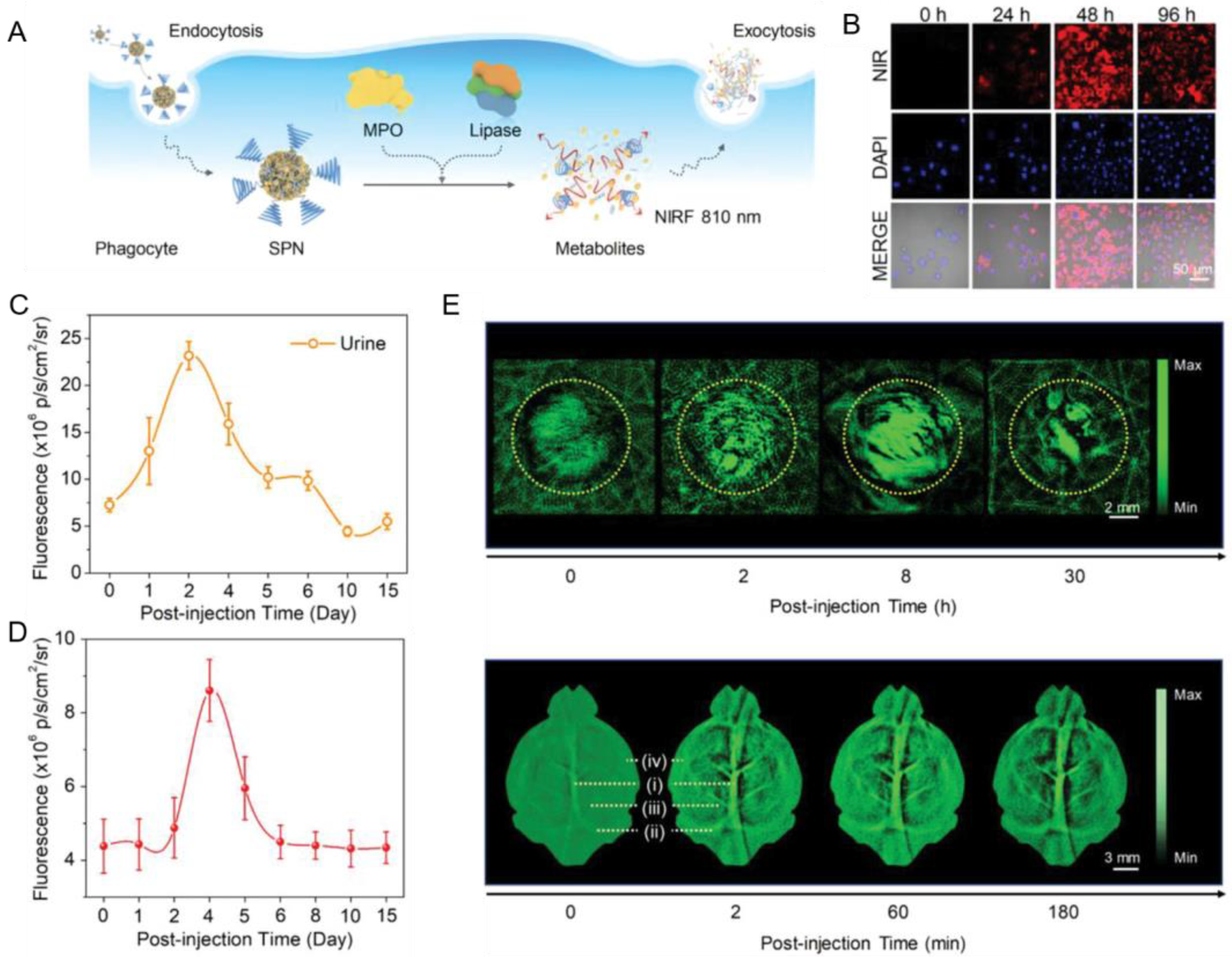
4.2.2. Pdots for NIR-II PAI
4.3. Pdots for Afterglow Imaging
4.4. Pdots for Chemiluminescent Imaging
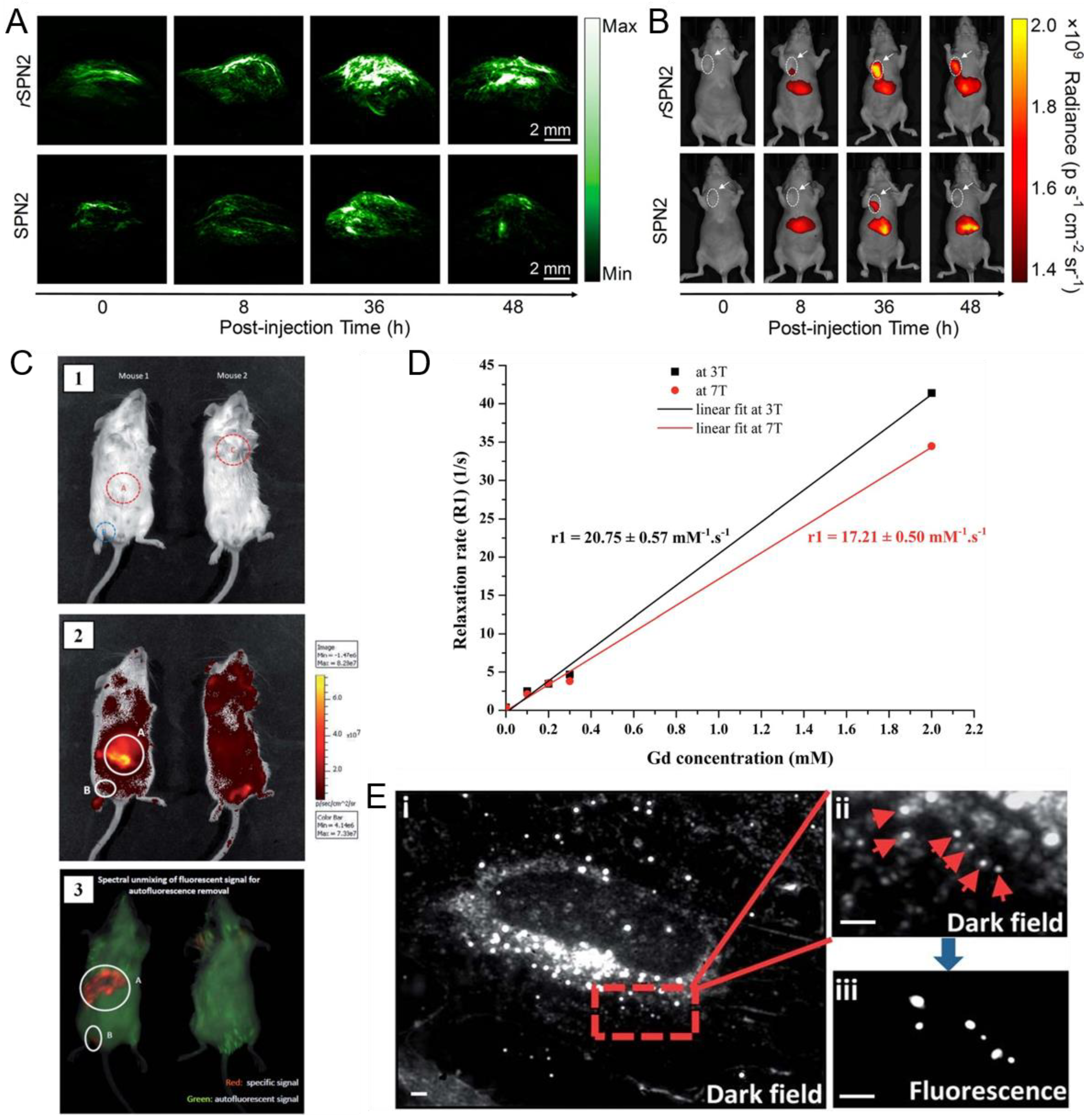
4.5. Pdots for Multimodal Imaging
5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatia, S.N.; Chen, X.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Lammers, T. Cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lázaro, I.; Mooney, D.J. Obstacles and opportunities in a forward vision for cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Roy, I.; Yang, C.; Prasad, P.N. Nanochemistry and nanomedicine for nanoparticle-based diagnostics and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2826–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, J.A.; O’Malley, W.; Kubeil, M.; Graham, B.; Stephan, H.; Spiccia, L. Nanomaterials: Applications in cancer imaging and therapy. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H18–H40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giljohann, D.A.; Mirkin, C.A. Drivers of biodiagnostic development. Nature 2009, 462, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Lai, Y.H.; Lim, J.C.; Huang, N.T.; Lin, C.T.; Huang, J.J. Review of integrated optical biosensors for point-of-care applications. Biosensors 2020, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, F.T.; Falcão, I.R.d.A.; da Souza, J.E.S.; Rocha, T.G.; de Sousa, I.G.; Cavalcante, A.L.; de Oliveira, A.L.; de Sousa, M.C.; dos Santos, J.C. Designing of nanomaterials-based enzymatic biosensors: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Electrochem 2021, 2, 149–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, B. Recent advances of optical imaging in the second near-infrared window. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802394. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, K.; Medina Rangel, P.X.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Antibody mimics for bioimaging and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Pu, K. Activatable molecular probes for fluorescence-guided surgery, endoscopy and tissue biopsy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 566–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, J.; Ji, H.; Qin, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, L.; Zhou, X. Conjugated polymers-based luminescent probes for ratiometric detection of biomolecules. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7309–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, J.; Cardoso dos Santos, M.; Hildebrandt, N. Multiplexed biosensing and bioimaging using lanthanide-based time-gated forster resonance energy transfer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahin, C.; Meares, A.; Esemoto, N.N.; Ptaszek, M.; LaScola, M.; Pandala, N.; Lavik, E.; Yang, M.; Stacey, G.; Hu, D.; et al. Hydroporphyrin-doped near-infrared-emitting polymer dots for cellular fluorescence imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 20790–20801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tang, B.Z. Near-infrared luminescent probes for bioimaging and biosensing. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3377–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Inorganic nanomaterials with rapid clearance for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8669–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Chen, Y.; Sun, C.; Fan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; et al. X-ray-activated persistent luminescence nanomaterials for NIR-II imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chizhik, A.I.; Chu, S.; Jin, D. Single-particle spectroscopy for functional nanomaterials. Nature 2020, 579, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Cai, H.; Steinmetz, N.F. Viral nanoparticles for drug delivery, imaging, immunotherapy, and theranostic applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 214–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ali, M.R.; Chen, K.; Fang, N.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles in biological optical imaging. Nano Today 2019, 24, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Hou, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, C. Therapeutic considerations and conjugated polymer-based photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1700614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García de Arquer, F.P.; Talapin, D.V.; Klimov, V.I.; Arakawa, Y.; Bayer, M.; Sargent, E.H. Semiconductor quantum dots: Technological progress and future challenges. Science 2021, 373, eaaz8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wang, F. Emerging frontiers of upconversion nanoparticles. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Shuai, Z. Molecular mechanism of aggregation-induced emission. Aggregate 2021, 2, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayder, D.M.; Tonge, C.M.; Nguyen, G.D.; Tran, M.V.; Tom, G.; Darwish, G.H.; Gupta, R.; Lix, K.; Kamal, S.; Algar, W.R.; et al. Polymer dots with enhanced photostability, quantum yield, and two-photon cross-section using structurally constrained deep-blue fluorophores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16976–16992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Chiu, D.T.; McNeill, J. Dual-mode superresolution imaging using charge transfer dynamics in semiconducting polymer dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 16173–16180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Sun, K.; Sun, Z.; Chen, D.; Xu, G.; Xi, P.; Wu, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. Small photoblinking semiconductor polymer dots for fluorescence nanoscopy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, S. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for imaging, cell activity regulation, and therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.S.; Chiu, D.T. Soft fluorescent nanomaterials for biological and biomedical imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4699–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhi, E.; Hasanzadeh, M. Recent advances on the biosensing and bioimaging based on polymer dots as advanced nanomaterial: Analytical approaches. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Mei, H.; Gao, F. Ratiometric detection of copper ions and alkaline phosphatase activity based on semiconducting polymer dots assembled with rhodamine B hydrazide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. Highly fluorescent semiconducting polymer dots for biology and medicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3086–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, M.; Wu, M.; Conroy, E.M.; Algar, W.R. Mind your P’s and Q’s: The coming of age of semiconducting polymer dots and semiconductor quantum dots in biological applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabok, A.; Shamsipur, M.; Yeganeh-Faal, A.; Molaabasi, F.; Molaei, K.; Sarparast, M. A highly selective semiconducting polymer dots-based “off–on” fluorescent nanoprobe for iron, copper and histidine detection and imaging in living cells. Talanta 2019, 194, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.M.; Mei, L.P.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.W.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Energy transfer between semiconducting polymer dots and gold nanoparticles in a photoelectrochemical system: A case application for cathodic bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4277–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.Y.; Li, H.H.; Wu, P.J.; Chen, C.P.; Huang, Y.C.; Chan, Y.H. Dual colorimetric and fluorescent sensor based on semiconducting polymer dots for ratiometric detection of lead ions in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4765–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Deng, L.; Huang, X.; Ren, J. Catalytic chemiluminescence polymer dots for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging of intrinsic reactive oxygen species in mice. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6929–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Ma, M.; Zai, H.; Zhang, L.; Fu, N.; Huang, W.; Wang, L. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for label-free and bioconjugate-Recognized DNA sensing in serum. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1400009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Ju, H. Potential-and color-resolved electrochemiluminescence of polymer dots for array imaging of multiplex microRNAs. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5327–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Tang, K.; Ding, C.; Chen, H.; Yu, S. Fluorescent polymer dots and graphene oxide based nanocomplexes for “off-on” detection of metalloproteinase-9. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 20903–20909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Hou, W.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, N.; Li, X.; Yin, S.; Qin, W.; Wu, C. Measuring cellular uptake of polymer dots for quantitative imaging and photodynamic therapy. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7071–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Tai, X.; Li, X.; Tan, J.; Lee, C.S.; Sun, P.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. Side chain engineering of semiconducting polymers for improved NIR-II fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S. A pH-responsive nanoplatform based on fluorescent conjugated polymer dots for imaging-guided multitherapeutics delivery and combination cancer therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Yuan, Z. Thermosensitive polymer dot nanocomposites for trimodal computed tomography/photoacoustic/fluorescence imaging-guided synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51174–51184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J. Semiconducting polymer dots as fluorescent probes for in vitro biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6248–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Hou, W.; Qin, W.; Wu, C. Recent advances in semiconducting polymer dots as optical probes for biosensing. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pu, K. Semiconducting polymer nanomaterials as near-infrared photoactivatable protherapeutics for cancer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Men, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. Reversible ratiometric NADH sensing using semiconducting polymer dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12007–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yin, S.; Qin, W.; Yu, J.; Chiu, D.T.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C. Ultrabright polymer-dot transducer enabled wireless glucose monitoring via a smartphone. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5176–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.C.; Chou, C.C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wei-Kai, T.; Wang, Y.T.; Chan, Y.H. Multiplexed detection of tumor markers with multicolor polymer dot-based immunochromatography test strip. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, S.; Wang, H.; Pu, K. Renal clearable polyfluorophore nanosensors for early diagnosis of cancer and allograft rejection. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Cui, D.; Huang, J.; Fan, W.; Miao, Y.; Pu, K. Near-nfrared afterglow semiconducting nano-polycomplexes for the multiplex differentiation of cancer exosomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4983–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, F. Highly luminescent and photostable near-infrared fluorescent polymer dots for long-term tumor cell tracking in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qi, W.; Ye, Z.; He, S.; et al. Fluorination enhances NIR-II fluorescence of polymer dots for quantitative brain tumor imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21049–21057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Rao, J. Self-luminescing BRET-FRET near-infrared dots for in vivo lymph-node mapping and tumour imaging. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Du, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, C.; Yuan, Z. Biomimetic semiconducting polymer dots for highly specific NIR-II fluorescence imaging of glioma. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Upputuri, P.K.; Xie, C.; Zeng, Z.; Sharma, A.; Zhen, X.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Pramanik, M.; Pu, K.; et al. Metabolizable semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for second near-infrared photoacoustic imaging. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Men, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, D.; Wu, C.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Ultrasmall semiconducting polymer dots with rapid clearance for second near-infrared photoacoustic imaging and photothermal cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Lyu, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, X.; Jokerst, J.V.; Pu, K. Molecular afterglow imaging with bright, biodegradable polymer nanoparticles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Miao, Q.; Lyu, Y.; Pu, K. Self-assembled semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for ultrasensitive near-infrared afterglow imaging of metastatic tumors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, X.; Zhang, C.; Xie, C.; Miao, Q.; Lim, K.L.; Pu, K. Intraparticle energy level alignment of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles to amplify chemiluminescence for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging of reactive oxygen species. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6400–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Pu, K.; Zhang, R. Semiconducting polymer nanoreporters for near-infrared chemiluminescence imaging of immunoactivation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Zhen, X.; Miao, Y.; Pu, K. Reaction-based semiconducting polymer nanoprobes for photoacoustic imaging of protein sulfenic acids. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, Z.; Green, M.; Chung, P.H.; Suhling, K.; Protti, A.; Phinikaridou, A.; Botnar, R.; Khanbeigi, R.A.; Thanou, M.; Dailey, L.A.; et al. Gd-containing conjugated polymer nanoparticles: Bimodal nanoparticles for fluorescence and MRI imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8376–8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Hayden, S.; Jin, Y.; Rong, Y.; Yu, J.; Ye, F.; Chan, Y.H.; Zeigler, M.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T.; et al. A versatile method for generating semiconducting polymer dot nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7246–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, J.; Mecking, S. Nanoparticles of conjugated polymers. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6260–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieh, A.; Khoee, S.; Mahdavian, A.R. Emulsion and miniemulsion techniques in preparation of polymer nanoparticles with versatile characteristics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 152–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, R.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, X.; Wang, B.; Gao, F.; Wang, L.; et al. Flash nanoprecipitation of ultra-small semiconducting polymer dots with size tunability. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, P.; Krishnan, B.P.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Zeng, R.; Cui, J.; Chen, J. From a molecular toolbox to a toolbox for photoswitchable fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Feng, Z.; Hu, D.; Xu, S.; Middha, E.; Pan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Qian, J.; Sheng, Z.; et al. Precise deciphering of brain vasculatures and microscopic tumors with dual NIR-II fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Schneider, T.; Burnham, D.R.; Smith, P.B.; Chiu, D.T. Ultrabright and bioorthogonal labeling of cellular targets using semiconducting polymer dots and click chemistry. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 9436–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Fang, X.; Jin, Y.; Hu, X.; Yin, M.; Men, X.; Chen, N.; Fan, C.; Chiu, D.T.; Wan, Y.; et al. Semiconducting polymer nanocavities: Porogenic synthesis, tunable host–guest interactions, and enhanced drug/siRNA delivery. Small 2018, 14, 1800239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Men, X.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, C.; McNeill, J. Multimode time-resolved superresolution microscopy revealing chain packing and anisotropic single carrier transport in conjugated polymer nanowires. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Fang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, H. Anisotropic assembly and fluorescence enhancement of conjugated polymer nanostructures. View 2022, 3, 20220020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bull, B.; Szymanski, C.; Christensen, K.; McNeill, J. Multicolor conjugated polymer dots for biological fluorescence imaging. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Szymanski, C.; McNeill, J. Preparation and encapsulation of highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2956–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggeling, C.; Widengren, J.; Rigler, R.; Seidel, C. Photobleaching of fluorescent dyes under conditions used for single-molecule detection: Evidence of two-step photolysis. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, L.P.; Kandel, P.K.; Yu, J.; McNeill, J.; Ackroyd, P.C.; Christensen, K.A. Mechanism of cellular uptake of highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hansen, S.J.; Hou, Q.; Yu, J.; Zeigler, M.; Jin, Y.; Burnham, D.R.; McNeill, J.D.; Olson, J.M.; Chiu, D.T. Design of highly emissive polymer dot bioconjugates for in vivo tumor targeting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3430–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Schneider, T.; Zeigler, M.; Yu, J.; Schiro, P.G.; Burnham, D.R.; McNeill, J.D.; Chiu, D.T. Bioconjugation of ultrabright semiconducting polymer dots for specific cellular targeting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15410–15417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chiu, D.T. Ultrabright pdots with a large absorbance cross section and high quantum yield. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 13631–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.T.; Wu, I.C.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Wu, L.; Chiu, D.T. Improving the photostability of semiconducting polymer dots using buffers. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11785–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.; Lin, W.C.; Jia, C.Y.; Ting, L.Y.; Jayakumar, J.; Elsayed, M.H.; Yang, Y.Q.; Chan, Y.H.; Wang, W.S.; Lu, C.Y.; et al. Low-toxic cycloplatinated polymer dots with rational design of acceptor co-monomers for enhanced photocatalytic efficiency and stability. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ow, H.; Larson, D.R.; Srivastava, M.; Baird, B.A.; Webb, W.W.; Wiesner, U. Bright and stable core−shell fluorescent silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Tan, W. Dual-luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for multiplexed signaling. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Pu, K.Y.; Feng, S.S.; Zhan, R.; Liu, B. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes-containing conjugated polymer loaded PLGA nanoparticles with trastuzumab (herceptin) functionalization for HER2-positive cancer cell detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Pan, J.; Feng, S.S.; Wu, A.W.; Pu, K.Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Generic strategy of preparing fluorescent conjugated-polymer-loaded poly (dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for targeted cell imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, P.; Green, M.; Bowers, A.; Parker, D.; Varma, G.; Kallumadil, M.; Hughes, M.; Warley, A.; Brain, A.; Botnar, R.; et al. Magnetic conjugated polymer nanoparticles as bimodal imaging agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9833–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, P.; Green, M.; Levitt, J.; Suhling, K.; Hughes, M. Phospholipid encapsulated semiconducting polymer nanoparticles: Their use in cell imaging and protein attachment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3989–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Rong, Y.; Ye, F.; Chiu, D.T. Importance of having low-density functional groups for generating high-performance semiconducting polymer dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5429–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Ye, F.; Gallina, M.E.; Rong, Y.; Wu, I.C.; Sun, W.; Chan, Y.H.; Chiu, D.T.; et al. Stable functionalization of small semiconducting polymer dots via covalent cross-linking and their application for specific cellular imaging. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3498–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Sun, W.; Yu, J.; Wu, I.C.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, D.T. Light-induced crosslinkable semiconducting polymer dots. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Men, X.; Sun, K.; Sun, Z.; Fang, X.; Wu, C. Light-induced PEGylation and functionalization of semiconductor polymer dots. ChemNanoMat 2017, 3, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; McNeill, J. Light-harvesting and amplified energy transfer in conjugated polymer nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 838–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Rational construction of a mitochondria-targeted reversible fluorescent probe with intramolecular fret for ratiometric monitoring sulfur dioxide and formaldehyde. Biosensors 2022, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Yu, J.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, C. Near-infrared optical transducer for dynamic imaging of cerebrospinal fluid glucose in brain tumor. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14265–14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, S.; Dong, H.; Wu, C. Ratiometric fluorescent detection of intracellular singlet oxygen by semiconducting polymer dots. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 14629–14634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, I.C.; DuFort, C.C.; Carlson, M.A.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Kuo, C.T.; Qin, Y.; Yu, J.; Hingorani, S.R.; et al. Photostable ratiometric pdot probe for in vitro and in vivo imaging of hypochlorous acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6911–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, K.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Rao, J. Semiconducting polymer nanoprobe for in vivo imaging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10325–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Kuo, C.T.; Jian, T.; Wu, I.C.; Rong, Y.; Chiu, D. Highly photostable wide-dynamic-range pH sensitive semiconducting polymer dots enabled by dendronizing the near-IR emitters. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7236–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Chiu, D.T. Ratiometric temperature sensing with semiconducting polymer dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8146–8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Xie, C.; Pu, K. Temperature-correlated afterglow of a semiconducting polymer nanococktail for imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3938–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, X. Preparation, properties and applications in cell imaging and ions detection of conjugated polymer nanoparticles with alcoxyl bonding fluorene core. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. Copper (II) and iron (II) ion sensing with semiconducting polymer dots. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2820–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Canaveras, J.C.G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, L.; Jang, C.; Mayr, J.A.; Zhang, Z.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Zhan, L.; et al. Serine catabolism feeds NADH when respiration is impaired. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 809–821.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias, A.J.; Perrone, R.; Grozio, A.; Verdin, E. NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, T.S.; Eller, J.M.; Lu, M.J.; Niere, M.; Raith, F.; Perry, C.; Bornstein, M.R.; Oliphint, P.; Wang, L.; McReynolds, M.R.; et al. SLC25A51 is a mammalian mitochondrial NAD+ transporter. Nature 2020, 588, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaremba, M.; Dakineviciene, D.; Golovinas, E.; Zagorskaitė, E.; Stankunas, E.; Lopatina, A.; Sorek, R.; Manakova, E.; Ruksenaite, A.; Silanskas, A. Short prokaryotic Argonautes provide defence against incoming mobile genetic elements through NAD+ depletion. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xue, L.; Hiblot, J.; Griss, R.; Fabritz, S.; Roux, C.; Binz, P.A.; Haas, D.; Okun, J.G.; Johnsson, K. Semisynthetic sensor proteins enable metabolic assays at the point of care. Science 2018, 361, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.; Makaroff, L. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Tang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yin, S.; Qin, W.; Yu, J.; Chiu, D.T.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. In vivo dynamic monitoring of small molecules with implantable polymer-dot transducer. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6769–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Chiu, D.T. Enhancing the long-term stability of a polymer dot glucose transducer by using an enzymatic cascade reaction system. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T.; et al. Improving the accuracy of Pdot-based continuous glucose monitoring by using external ratiometric calibration. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2359–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, K.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, J.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, C.; et al. Long-term in vivo glucose monitoring by polymer-dot transducer in an injectable hydrogel implant. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Spronsen, F.J.; Blau, N.; Harding, C.; Burlina, A.; Longo, N.; Bosch, A.M. Phenylketonuria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, K.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. Monitoring metabolites using an NAD (P) H-sensitive polymer dot and a metabolite-specific enzyme. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19331–19336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, P.Y.; Li, F.C.; Liu, M.H.; Chan, Y.H. Colorimetric and fluorescent dual-mode immunoassay based on plasmon-enhanced fluorescence of polymer dots for detection of PSA in whole blood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9841–9849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Liu, M.H.; Yang, S.M.; Chan, Y.H. Bimodal multiplexed detection of tumor markers in non-small cell lung cancer with polymer dot-based immunoassay. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4255–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Lyu, Y.; Pu, K. Nanoparticle regrowth enhances photoacoustic signals of semiconducting macromolecular probe for in vivo imaging. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, E.; Leung, B.Y.; Helfield, B.L.; Shakiba, M.; Gandier, J.A.; Jin, C.S.; Master, E.R.; Wilson, B.C.; Goertz, D.E.; Zheng, G.; et al. In situ conversion of porphyrin microbubbles to nanoparticles for multimodality imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.J.; Dudani, J.S.; Bhatia, S.N. Ultrasensitive tumour-penetrating nanosensors of protease activity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Andronico, L.A.; Jung, S.R.; Chen, H.; Fujimoto, B.; Vojtech, L.; Chiu, D.T. High-throughput counting and superresolution mapping of tetraspanins on exosomes using a single-molecule sensitive flow technique and transistor-like semiconducting polymer dots. Angew. Chem. 2021, 60, 13470–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Chan, Y.H.; Saha, S.; Liu, M.H. Near-infrared-II semiconducting polymer dots for deep-tissue fluorescence imaging. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, G.; Sun, H.; Yin, S. Recent advances in the development and applications of conjugated polymer dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2995–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Shan, L.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yung, B.C.; Jacobson, O.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, S.; et al. Tumour microenvironment-responsive semiconducting polymer-based self-assembling nanotheranostics. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R.; Schroeder, A.B.; Grudzinski, J.J.; Rosenthal, E.L.; Warram, J.M.; Pinchuk, A.N.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Kuo, J.S.; Weichert, J.P. Beyond the margins: Real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmettre, T.; Devoisselle, J.; Mordon, S. Fluorescence properties and metabolic features of indocyanine green (ICG) as related to angiography. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2000, 45, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitus, M.; Ranjit, S. Cyanine dyes in biophysical research: The photophysics of polymethine fluorescent dyes in biomolecular environments. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 44, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altınoglu, E.I.; Russin, T.J.; Kaiser, J.M.; Barth, B.M.; Eklund, P.C.; Kester, M.; Adair, J.H. Near-infrared emitting fluorophore-doped calcium phosphate nanoparticles for in vivo imaging of human breast cancer. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, D.; Fang, X.; Zheng, J.; Qin, W.; Wu, C. Brightness enhancement of near-infrared semiconducting polymer dots for in vivo whole-body cell tracking in deep organs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26928–26935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Mao, D.; Tomczak, N.; Liu, B. Ultrasmall conjugated polymer nanoparticles with high specificity for targeted cancer cell imaging. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 Who classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Pu, K. Organic semiconducting agents for deep-tissue molecular imaging: Second near-infrared fluorescence, self-luminescence, and photoacoustics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rao, J.; Pu, K. Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Pu, K. Molecular fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared optical window using organic contrast agents. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1700262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, K.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Jokerst, J.V.; Mei, J.; Gambhir, S.S.; Bao, Z.; Rao, J. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as photoacoustic molecular imaging probes in living mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, C. Nanoparticle probes for structural and functional photoacoustic molecular tomography. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 757101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Pu, K.; Jiang, X. Photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles: Signal amplification and second near-infrared construction. Small 2021, 17, 2004723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Chang, K.; Men, X.; Fang, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.; Gao, D.; Yin, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Highly absorbing multispectral near-infrared polymer nanoparticles from one conjugated backbone for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 144, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Sheng, Z.; Hu, D.; Li, A.; Xu, S.; Manghnani, P.N.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Zheng, H.; Liu, B.; et al. Molecular engineering of conjugated polymers for biocompatible organic nanoparticles with highly efficient photoacoustic and photothermal performance in cancer theranostics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10124–10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Wen, K.; Chen, J.; Xie, J.; Fan, W.; Ma, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, F.; Peng, A.; et al. Significant enhancement of photothermal and photoacoustic efficiencies for semiconducting polymer nanoparticles through simply molecular engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Miao, Q.; Zhen, X.; Ding, D.; Pu, K. Intraparticle molecular orbital engineering of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as amplified theranostics for in vivo photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4472–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Feng, X.; Xie, C.; Zheng, Y.; Pu, K. Surface engineering of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for amplified photoacoustic imaging. Biomaterials 2017, 127, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Mao, D.; Liew, W.H.; Guo, B.; Wang, S.; Cai, X.; Thakor, N.; Yao, K.; Zhang, C.J. Photoacoustic and magnetic resonance imaging bimodal contrast agent displaying amplified photoacoustic signal. Small 2018, 14, 1800652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Upputuri, P.K.; Xie, C.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Q.; Pramanik, M.; Pu, K. Broadband absorbing semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging in second near-infrared window. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 4964–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; You, L.; Lan, L.; Lee, H.J.; Chaudhry, S.T.; Li, R.; Cheng, J.X.; Mei, J. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for centimeters-deep photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Sheng, Z.; Hu, D.; Lin, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Liu, B. Biocompatible conjugated polymer nanoparticles for highly efficient photoacoustic imaging of orthotopic brain tumors in the second near-infrared window. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, N.; Middha, E.; Xu, S.; Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, K.; Liu, C.; Liu, B.; et al. High-resolution 3D NIR-II photoacoustic imaging of cerebral and tumor vasculatures using conjugated polymer nanoparticles as contrast agent. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhen, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, C.; Miao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Pu, K.; et al. A generic approach towards afterglow luminescent nanoparticles for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Ye, Z.; Guan, K.; Teng, L.; Wu, J.; Yin, X.; Song, G.; Zhang, X.B. Reactive oxygen correlated chemiluminescent imaging of a semiconducting polymer nanoplatform for monitoring chemodynamic therapy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Walker, J.R.; Park, Y.; Smith, T.P.; Liu, L.X.; Hall, M.P.; Labanieh, L.; Hurst, R.; Wang, D.C.; Encell, L.P.; et al. Novel NanoLuc substrates enable bright two-population bioluminescence imaging in animals. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Huang, X.; Ren, J. Multicolor chemiluminescent resonance energy-transfer system for in vivo high-contrast and targeted imaging. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3042–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Yuan, Z. Multifunctional conjugated polymer nanoparticles for photoacoustic-based multimodal imaging and cancer photothermal therapy. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2019, 12, 1930001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Yuan, Z. Polymer dots for precision photothermal therapy of brain tumors in the second near-infrared window: A mini-review. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4319–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, D.; Ding, M.; Lyu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, J. Radioactive organic semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for multimodal cancer theranostics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 619, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, Z.; Fan, Q.; Pu, K. Grafted semiconducting polymer amphiphiles for multimodal optical imaging and combination phototherapy. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10553–10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Pu, K. Multimodal biophotonics of semiconducting polymer nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pdots | λmaxabs (nm) | λmaxem (nm) | Φ (%) | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPA-CNPPV | 294 | 627 | 10.8 | NADH sensing | [50] |
| PD4Gx | 380 | 425, 672 | 11.5 | Glucose monitoring | [51] |
| PF-TC6FQ | ~360 | ~670 | N.A. | PSA detection | [52] |
| PFCN | ~390 | ~450 | N.A. | AFP detection | [52] |
| PFO | ~350 | ~490 | N.A. | CEA detection | [52] |
| APNs | 700 | 720 | N.A. | Cancer and allograft | [53] |
| ASPNC | ~440 | 680 | N.A. | Exosomes sensing | [54] |
| NIR MEH-PPV | 504 | 776 | N.A. | Fluorescent imaging | [55] |
| m-PBTQ4F | 946 | 1123 | 3.2 | Fluorescent imaging | [56] |
| RET2IR NPs | 503 | 778 | 0.18 | Fluorescent imaging | [57] |
| Pdots-C6 | 745 | 1055 | N.A. | Fluorescent imaging | [58] |
| SPN-PT | 1064 | N.A. | N.A. | Photoacoustic imaging | [59] |
| DPP-BTzTD | ~1000 | N.A. | N.A. | Photoacoustic imaging | [60] |
| SPNs | ~490 | 780 | N.A. | Afterglow imaging | [61] |
| SPPVN | 500, 775 | 775 | 51.0 | Afterglow imaging | [62] |
| SPN-NIR | 452, 773 | 507, 775 | 2.12 | Chemiluminescent imaging | [63] |
| SPNRs | 450, 460, 580 | 520, 540, 700 | 2.7 ± 0.014 | Chemiluminescent imaging | [64] |
| rSPN2 | ~680 | 840 | N.A. | Multimodal imaging | [65] |
| PPE Gd-SPNs | 388 | 440, 470 | 22.0 | Multimodal imaging | [66] |
| Au-NP-Pdots | 525 | ~440, 460 | 18.0 | Multimodal imaging | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H. Semiconducting Polymer Dots for Point-of-Care Biosensing and In Vivo Bioimaging: A Concise Review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010137
Deng S, Li L, Zhang J, Wang Y, Huang Z, Chen H. Semiconducting Polymer Dots for Point-of-Care Biosensing and In Vivo Bioimaging: A Concise Review. Biosensors. 2023; 13(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Sile, Lingfeng Li, Jiaxi Zhang, Yongjun Wang, Zhongchao Huang, and Haobin Chen. 2023. "Semiconducting Polymer Dots for Point-of-Care Biosensing and In Vivo Bioimaging: A Concise Review" Biosensors 13, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010137
APA StyleDeng, S., Li, L., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., & Chen, H. (2023). Semiconducting Polymer Dots for Point-of-Care Biosensing and In Vivo Bioimaging: A Concise Review. Biosensors, 13(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010137






