A Salmonella Microfluidic Chip Combining Non-Contact Eddy Heater and 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer with Recombinase Aided Amplification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
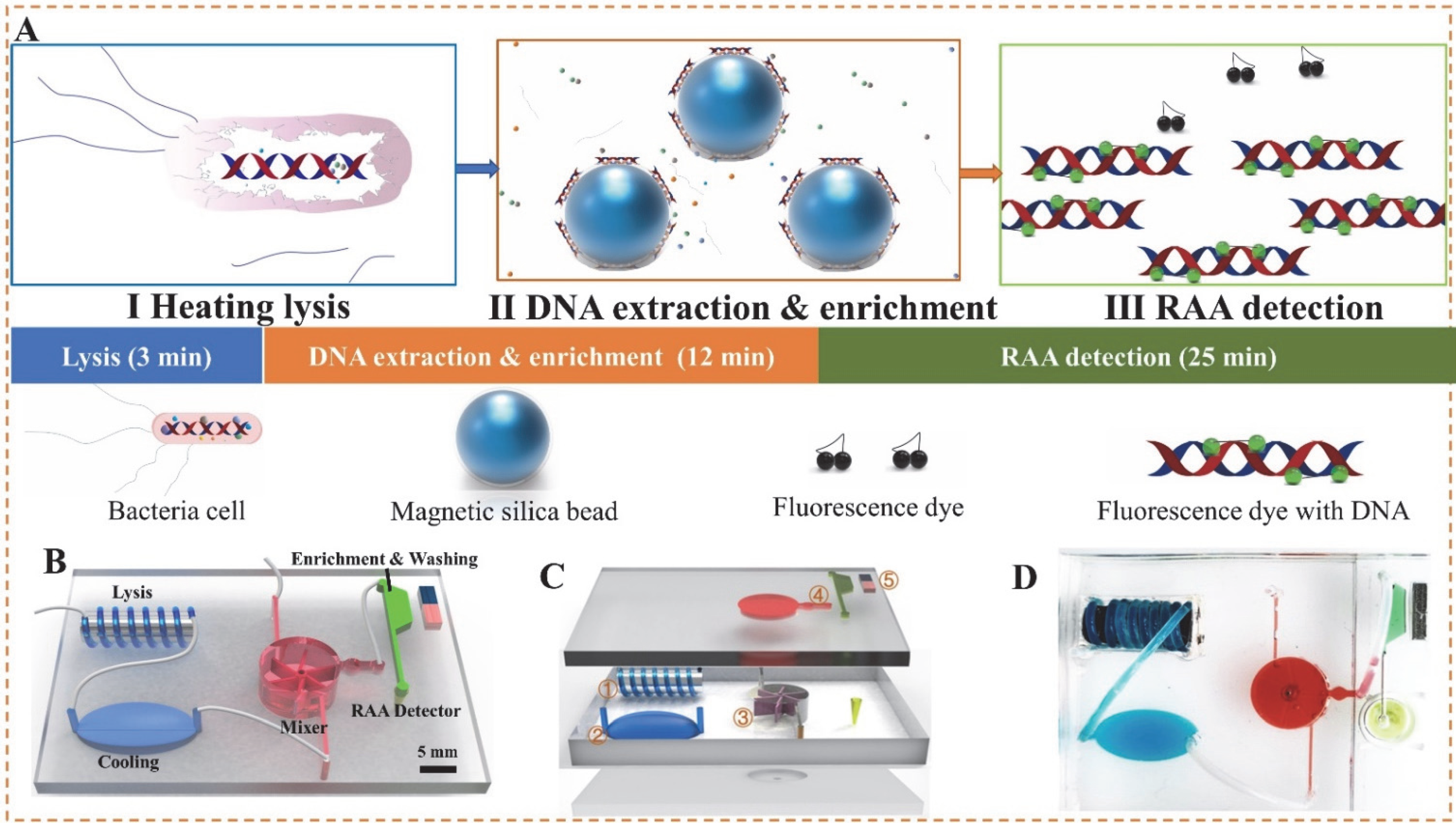
2.2. Development of Microfluidic Chip
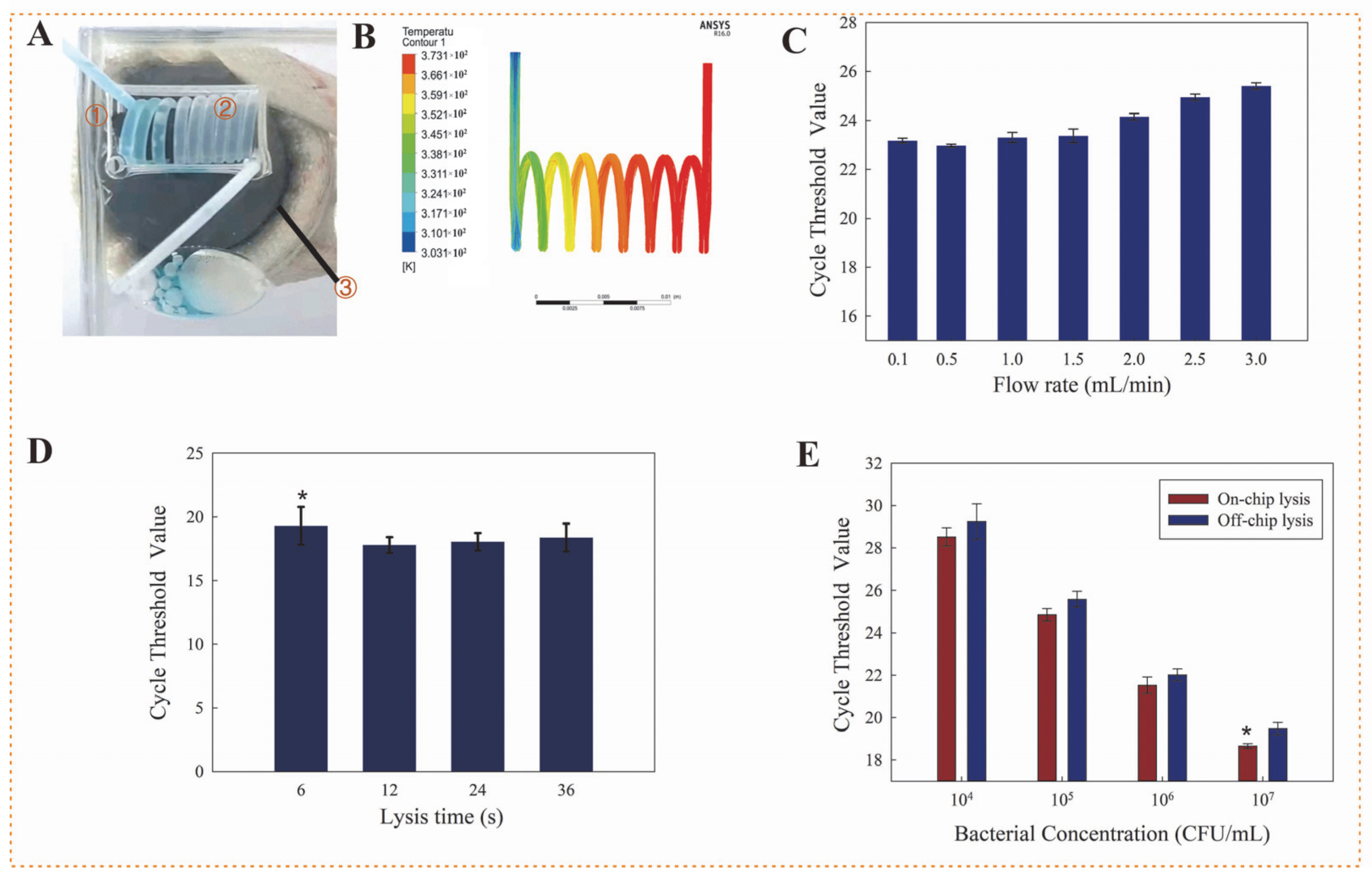
2.3. Bacterial Cells Lysis and DNA Extraction
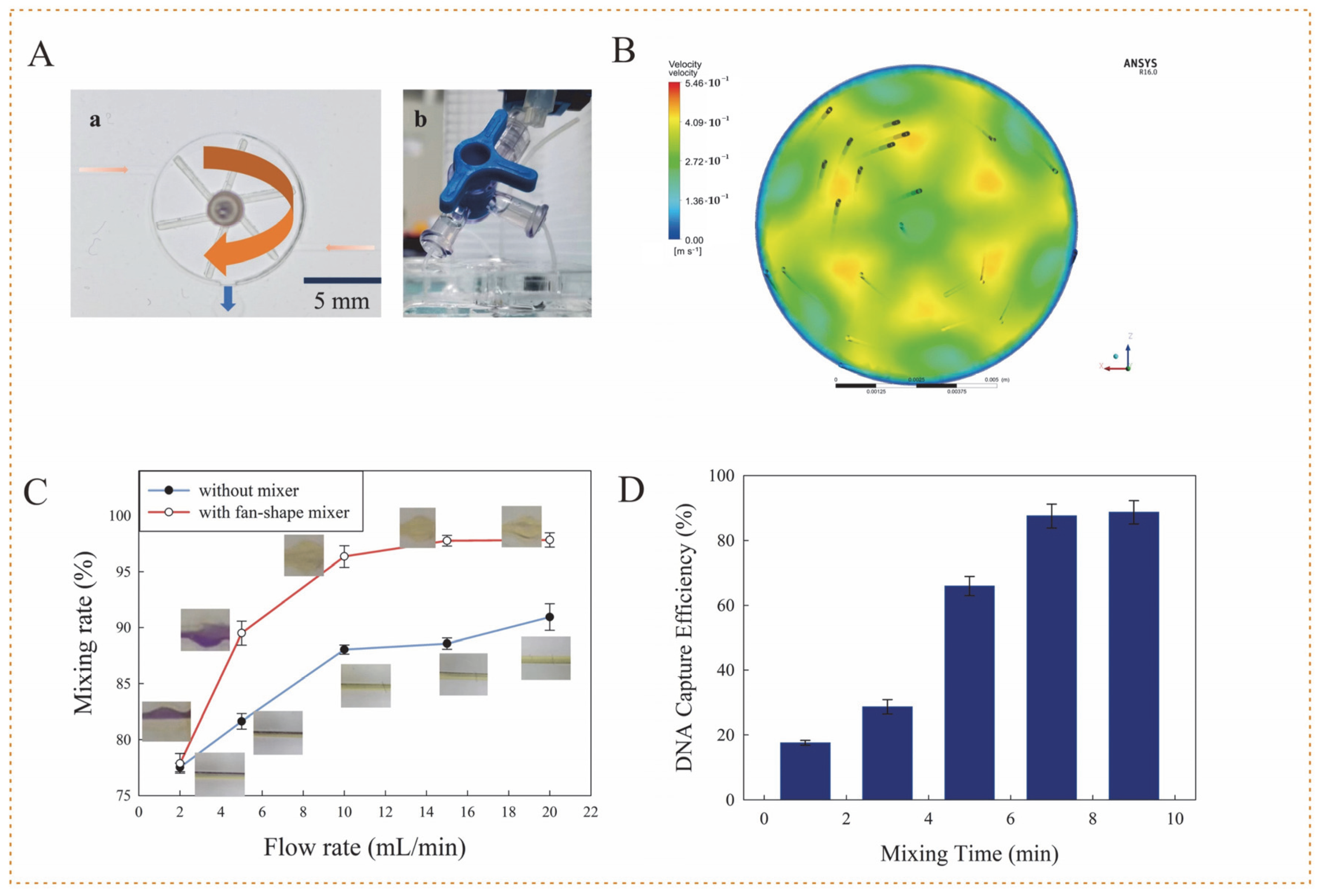
2.4. DNA Separation and RAA Detection
2.5. Spiked Sample Preparation and Detection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Eddy Heating for Bacterial Cells Lysis
3.2. Performance of 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer
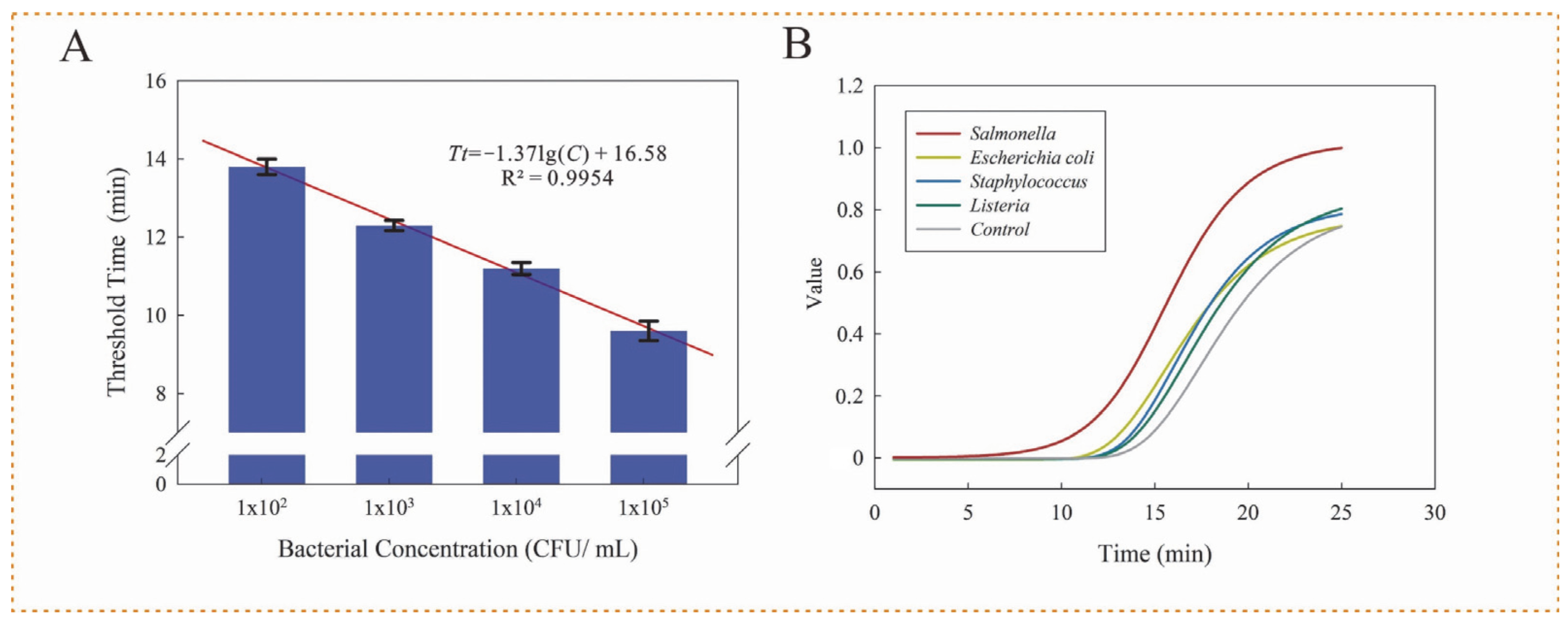
3.3. Performance of Microfluidic Chip
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Alali, W. Editorial: Recent Discoveries in Human Serious Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria: Resurgence, Pathogenesis, and Control Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, M.T.; Cox, C.E.; Teplitski, M. Salmonella Interactions with Plants and Their Associated Microbiota. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procaccianti, M.; Motta, A.; Giordani, S.; Riscassi, S.; Guidi, B.; Ruffini, M.; Maffini, V.; Esposito, S.; Dodi, I. First Case of Typhoid Fever Due to Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhi in Italy. Pathogens 2020, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; van Asselt, E.D.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Towards a Resilient Food Supply Chain in the Context of Food Safety. Food Control 2021, 125, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousalkar, K.; Sims, S.; McWhorter, A.; Khan, S.; Sexton, M. The Effect of Sanitizers on Microbial Levels of Chicken Meat Collected from Commercial Processing Plants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.; Guo, X.; Tokman, J.I.; Roof, S.; Trmcic, A.; Baker, R.C.; Tang, S.; Markwell, P.; Wiedmann, M.; Kovac, J. Extended Enrichment Procedures Can Be Used to Define False-Negative Probabilities for Cultural Gold Standard Methods for Salmonella Detection, Facilitating Comparisons between Gold Standard and Alternative Methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 83, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Boone, I.; Jansen, W.; Fohler, S.; Klein, G.; Dieckmann, R.; Al Dahouk, S. Overview of Validated Alternative Methods for the Detection of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Ji, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; González-Sapienza, G.; Wang, Y. Development of a Streptavidin-Bridged Enhanced Sandwich ELISA Based on Self-Paired Nanobodies for Monitoring Multiplex Salmonella Serogroups. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1203, 339705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, S.; Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xiong, Y. Large-Volume Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes and Listeria Ivanovii in Lettuce. Food Control 2016, 59, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseri, E.; Biggel, M.; Goossens, H.; Moons, P.; van der Wijngaart, W. Digital Dipstick: Miniaturized Bacteria Detection and Digital Quantification for the Point-of-Care. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Suo, Y.; Zou, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Darland, D.; Zhao, J.X.; Mu, Y. Integrated Microfluidic Systems with Sample Preparation and Nucleic Acid Amplification. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2769–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichaibun, V.; Kanchanaphum, P. Quantitative LAMP and PCR Detection of Salmonella in Chicken Samples Collected from Local Markets around Pathum Thani Province, Thailand. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 8833173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, W.; Hao, Y.; Lin, J. Slipchip-Based Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Rapid Detection of Bacillus Cereus with Tetracycline Resistance Gene TetL in Pasteurized Milk. Food Control 2022, 140, 109122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hice, S.A.; Clark, K.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Brehm-Stecher, B.F. Capture, Concentration, and Detection of Salmonella in Foods Using Magnetic Ionic Liquids and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.S.; Pan, J.; Li, F.; Zhu, M.; Xu, M.; Zhu, H.; Yu, Y.; Su, G. Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Coupled with CRISPR-Cas12a for Facile and Highly Sensitive Colorimetric SARS-CoV-2 Detection. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4126–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, T.; Xie, Y.-N.; Li, F.; Jiang, X.; Hou, X.; Wu, P. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Coupled with a Photosensitization Colorimetric Assay for Fast Salmonella Spp. Testing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6559–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; He, L. Enzyme-Free Colorimetric Detection of DNA by Using Gold Nanoparticles and Hybridization Chain Reaction Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7689–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X. Reagents-Loaded, Automated Assay That Integrates Recombinase-Aided Amplification and Cas12a Nucleic Acid Detection for a Point-of-Care Test. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14846–14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, B.; Cui, J.; Yan, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; et al. Reverse-Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9699–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Zhou, D.; Xie, G.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Q.; Feng, X.; Xu, H. The Fluorescent Probe-Based Recombinase-Aided Amplification for Rapid Detection of Escherichia Coli O157:H7. Mol. Cell. Probes 2021, 60, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Ma, R.; Cong, L.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Xue, S.; Zheng, W.; Tang, S. Rapid Detection of Salmonella with Recombinase Aided Amplification. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 139, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayaka, A.C.; Ngo, T.A.; Kant, K.; Engelsmann, P.; Dave, V.P.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. Rapid Detection of Salmonella Enterica in Food Samples by a Novel Approach with Combination of Sample Concentration and Direct PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Privorotskaya, N.; Liu, Y.-S.; Lee, J.; Zeng, H.; Carlisle, J.A.; Radadia, A.; Millet, L.; Bashir, R.; King, W.P. Rapid Thermal Lysis of Cells Using Silicon–Diamond Microcantilever Heaters. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Han, J. One-Step Nucleic Acid Purification and Noise-Resistant Polymerase Chain Reaction by Electrokinetic Concentration for Ultralow-Abundance Nucleic Acid Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10981–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Han, D.H.; Hwang, S.-H.; Park, J.-K. Reciprocating Flow-Assisted Nucleic Acid Purification Using a Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Device. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3346–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.S.; Quigley, M. A Rapid Boiling Method for the Preparation of Bacterial Plasmids. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 114, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, S. A 3D-Printed Millifluidic Platform Enabling Bacterial Preconcentration and DNA Purification for Molecular Detection of Pathogens in Blood. Micromachines 2018, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Qian, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, J. A Reversible Valve-Assisted Chip Coupling with Integrated Sample Treatment and CRISPR/Cas12a for Visual Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Shang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Q.; Ye, Q.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q. A Microfluidic Genoserotyping Strategy for Fast and Objective Identification of Common Salmonella Serotypes Isolated from Retail Food Samples in China. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1201, 339657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Peng, N. Smartphone-Based Droplet Digital LAMP Device with Rapid Nucleic Acid Isolation for Highly Sensitive Point-of-Care Detection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2258–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, F.; Ye, Q.; Shang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B.; Suo, H.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q. High-Throughput Microfluidic Strategy Based on RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a Dual Signal Amplification for Accurate Identification of Pathogenic Listeria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Shang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B.; Suo, H.; Chen, M.; Gu, Q.; Ding, Y.; et al. A Salmonella Serogroup Rapid Identification System for Food Safety Based on High Throughput Microfluidic Chip Combined with Recombinase Aided Amplification. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 357, 131402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Gai, Z.; Huo, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Xing, S.; Shi, G.; Shi, F.; et al. Comparison between Digital PCR and Real-Time PCR in Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.U.; Jo, E.-J.; Noh, Y.; Mun, H.; Ahn, Y.-D.; Kim, M.-G. Adenosine Triphosphate Bioluminescence-Based Bacteria Detection Using Targeted Photothermal Lysis by Gold Nanorods. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10171–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsougeni, K.; Kaprou, G.; Loukas, C.M.; Papadakis, G.; Hamiot, A.; Eck, M.; Rabus, D.; Kokkoris, G.; Chatzandroulis, S.; Papadopoulos, V.; et al. Lab-on-Chip Platform and Protocol for Rapid Foodborne Pathogen Detection Comprising on-Chip Cell Capture, Lysis, DNA Amplification and Surface-Acoustic-Wave Detection. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 320, 128345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methods | Targets | Lysis Time | Amount/Volume | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photothermal lysis | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | 6 min | 5.0 × 105 CFU/50 μL | [32] |
| Chemical lysis | Salmonella typhimurium | 10 min | 5.0 × 102 CFU/72 μL | [33] |
| Mechanical lysis | Enterococcus faecalis | 6 min | 1.0 × 106 CFU/100μL | [34] |
| Electrical lysis | Salmonella enterica | 40 s | 1.0 × 106 CFU/100 μL | [35] |
| This method | Salmonella typhimurium | 12 s | 1.1 × 107 CFU/100 μL |
| Added Concentration (CFU/mL) | Detected Concentration (CFU/mL) | Recovery Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 110 | 104.3 ± 21.6 | 94.8% ± 19.6% |
| 1100 | 1135.0 ± 189.0 | 103.2% ± 17.2% |
| 11,000 | 9277.2 ± 1544.7 | 84.3% ± 14.0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; Cai, G.; Lin, J.; Yue, X. A Salmonella Microfluidic Chip Combining Non-Contact Eddy Heater and 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer with Recombinase Aided Amplification. Biosensors 2022, 12, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090726
Wu S, Duan H, Zhang Y, Wang S, Zheng L, Cai G, Lin J, Yue X. A Salmonella Microfluidic Chip Combining Non-Contact Eddy Heater and 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer with Recombinase Aided Amplification. Biosensors. 2022; 12(9):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090726
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shangyi, Hong Duan, Yingchao Zhang, Siyuan Wang, Lingyan Zheng, Gaozhe Cai, Jianhan Lin, and Xiqing Yue. 2022. "A Salmonella Microfluidic Chip Combining Non-Contact Eddy Heater and 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer with Recombinase Aided Amplification" Biosensors 12, no. 9: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090726
APA StyleWu, S., Duan, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Zheng, L., Cai, G., Lin, J., & Yue, X. (2022). A Salmonella Microfluidic Chip Combining Non-Contact Eddy Heater and 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer with Recombinase Aided Amplification. Biosensors, 12(9), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090726









