Recent Advances in Digital Biosensing Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Digital ELISA (dELISA)
2.1. Technical Needs for dELISA
2.2. Methods and Technology for Compartmentalizing the Solid Supports in dELISA
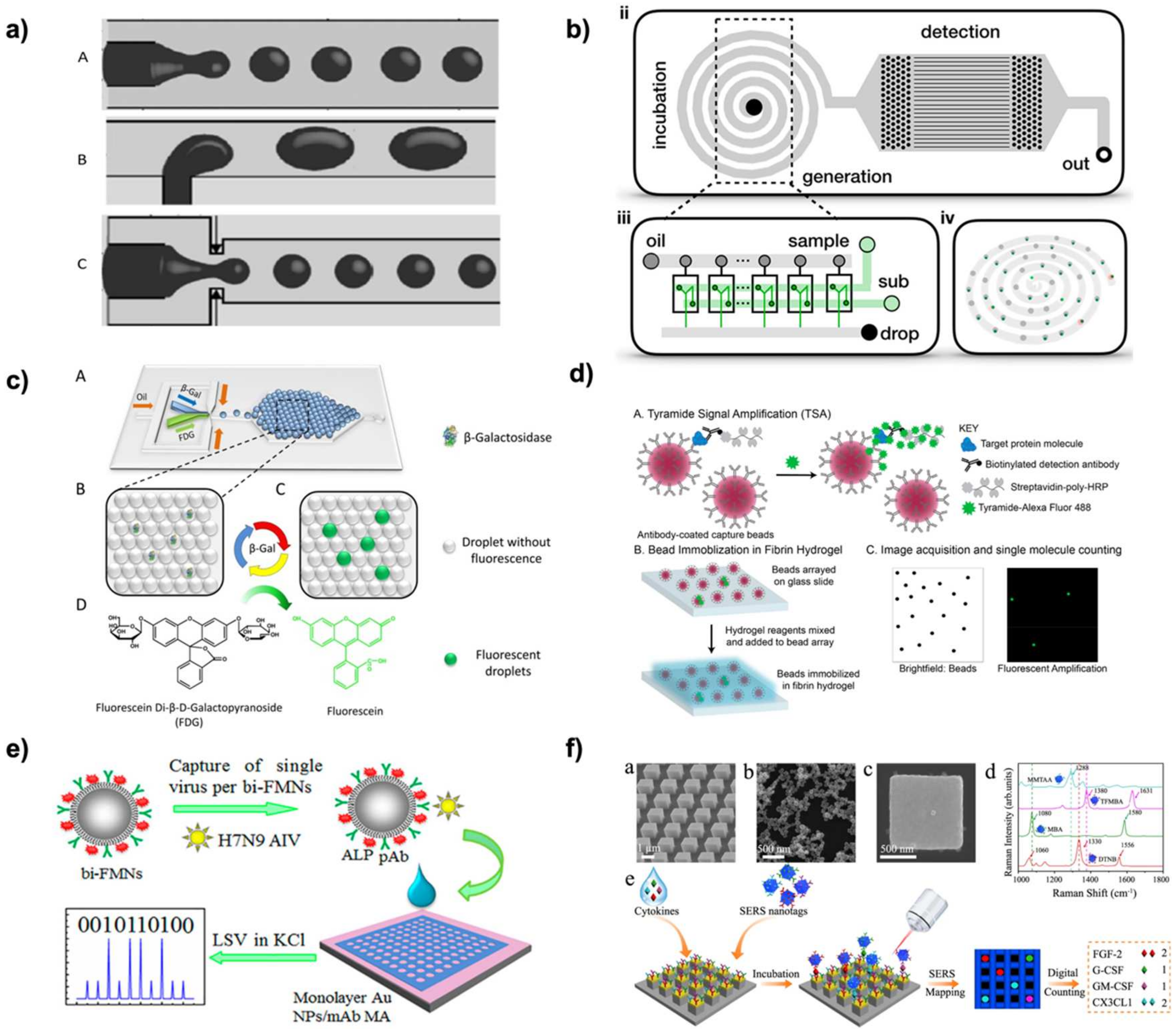
2.2.1. Droplet Microarrays
2.2.2. Microwell Arrays
2.2.3. Microstructure Arrays
2.2.4. Microfluidics
2.3. Readout Methods for dELISA
2.3.1. Fluorescence
2.3.2. Electrical
2.3.3. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS)
| Target | Platform | Generation Method | Readout | Limit of Detection | Range | Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-8 | Microdroplet Array | Vortex system | Fluorescence | 0.793 pM buffer 1.54 pM whole blood | 0–300 pg/mL | N/A | [13] |
| Aβ42 peptide | Microdroplet array | Flow cell | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [10] |
| Influenza A | Microdroplet Array | Droplet SETS | Fluorescence | 0.032 hemagglutination units/reaction | N/A | 40 min | [11] |
| IgA | Microdroplet Array | Inkjet printing | Fluorescence | N/A | 6 ng/mL to 50 ng/mL | N/A | [12] |
| Cytokines | Nanopillar | Manual loading | SERS | 0.044 ng/mL | N/A | 30 min | [27] |
| cardiac troponin I (cTnI) | Micropillar array | Pumping | Fluorescence | 9.75 pg/mL | 0 to 1500 pg/mL | 10–15 min | [29] |
| amyloid B | Micropillar Array | Manual loading with magnetic actuation | Fluorescence | 10 pg/mL | 12.5–200 pg/mL | 45 min | [28] |
| SARS-CoV-2-IL6 | Microwell Array | Programmed microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 0.4 pg/mL | sub-pg/mL to ng/mL | 9 min | [60] |
| PSA | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 0.093 pg/mL | 0.1 pg/mL to 200 pg/L | 1.5 h | [54] |
| PSA and bhCG | Microwell Array | Manual loading | Bright field imaging |
0.060 pg mL−1, 2.84 pg mL−1 | N/A | N/A | [61] |
| TNF-α | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 3.0 aM | Max concentration 240 fM | N/A | [25] |
| Influenza A | Microwell Array | Hydrophobic-hydrophilic interaction | Fluorescence | 4 ± 1 fM | 0 to 100 fM | ~2 h | [15] |
| TSH | Microwell Array | EWOD | Fluorescence | 0.0013 μIU/mL | N/A | N/A | [18] |
| Tau | Microwell Array | Magnetic actuation | Fluorescence | 24 ± 7 aM | 1 × 10−16 to 1 × 1013 | ~20 min | [16] |
| β-galactosidase | Microwell array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 100 fM | N/A | N/A | [19] |
| TNF-a, IL-6, IL-1a, and IL-1b | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 21 fg/mL, 3 fg/mL, 5 fg/mL, 43 fg/mL | N/A | N/A | [20] |
| IL-4, IL-6, and IFN-γ. | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 0.183 pg, 0.175 pg, 0.084 pg | N/A | N/A | [53] |
| Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) | Microwell Array | Flow Cell | Nanoparticle Enhanced | 0.059 pg/mL | N/A | N/A | [62] |
| Interleukin 6 (IL6) | Microwell Array | Flow Cell | Nanoparticle Enhanced | 0.039 pg/mL | N/A | N/A | [62] |
| PSA | Microwell array on a disk | Centrifugal Force | Fluorescence | 10 zM and 2 aM | 0.011 pg/mL up to 100 pg/mL | N/A | [22] |
| β-galactosidase and PSA | Microwell Array | Flow Cell | Fluorescence | 2.0 aM and 10 zM | 10 zM to 1 fM and 0 to 200 aM | 10 min to 5 h | [14] |
| proteins—PSA and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)—to | Microwell Array | Centrifugal Force | Fluorescence | 50 aM and 150 aM | N/A | N/A | [6] |
| PSA | Microwell Array | Centrifugal Force | Fluorescence | 0.008 pg/mL | 8 fg/mL to 100 pg/mL | N/A | [63] |
| alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 1 fg/mL | 1 to 100 fg/mL | N/A | [64] |
| β-galactosidase and TNF-α | Microwell Array | Flow Cell | Fluorescence | 930 zM and 50.48 fg/mL | 1 aM to 1 fM | 30 min | [17] |
| Cytokine | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | N/A | 104 | 30 min | [23] |
| IL17a, 1L12p70, p24, interferon alpha | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 0.7 aM 0.092 aM, 9.1 aM 45.9 aM | N/A | N/A | [9] |
| β-galactosidase and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [19] |
| IGF-1R | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 0.011 pg/mL and 0.016 pg/mL | 10 fg/mL to 1 ng/mL | N/A | [24] |
| Up to 16 targets | Microwell Array | Centrifugal force | Fluorescence | 0.07 IU mL−1 | fg/mL to pg/mL | <1.5 h | [21] |
| IgA | Microwell Array | Inkjet dispensing | Fluorescence | N/A | 0 to 50 ng/mL | 3 min | [65] |
| IL-6 | Microfluidic | Microwell | Electrical impedance | 21.8 aM | six orders or magnitude | ~1 h | [56] |
| H7N9 virus | Microarray | Manual loading | Ectrochemical | of 7.8 fg/mL | 0.01 to 1.5 pg/mL | 1 h | [36] |
| IL-6 | Microarray | Bead immobilization | Fluorescence | 1 fM | 0.1 fM to 100 fM | N/A | [35] |
| HBsAg | Magnetic Beads | Droplet free | Fluorescence | 0.09 mIU/mL | 4 orders of magnitude | ~1 h | [55] |
| IL-6 and HBsAg | Magnetic Beads | Droplet free | Fluorescence | 0.1 pg/mL and 0.013 IU/mL | N/A | N/A | [66] |
| GM-CSF and IL6 | Microfluidic | Parallel droplets generator | Fluorescence | 0.0045 pg/mL (320 aM) and 0.0070 pg/mL (350 aM) | 0–8 pg/mL | 10 min | [39] |
| Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | SERS tags | <0.1 ng/mL | 0.05 to 200 ng/mL | 174 droplets per minute | [50] |
| Dual of free-PSA and total-PSA | Microfluidic | T-junction | SERS tags | <0.1 ng/mL | 0.05 to 100 ng/mL | 10 min | [58] |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Microfluidic | T-junction | SERS tags | 0.22 PFU/mL | 0 to 100 PFU/mL | ≤10 min | [41] |
| Zika virus NS1 | Microfluidic | Parallel flow focusing generation | Fluorescence | 62.5 ng/mL | N/A | ~9 min | [67] |
| Vesicles | Microfluidic | Parallel droplets generator | Fluorescence | 9 EVs/μL | 2 orders of magnitude | 5 min | [33] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | Microfluidic | T junction | SERS | 0.22 PFU/mL | log 0.8 to 2 | 10 min | [41] |
| IL-6 and mTOR | Microfluidic | T-junction | Fluorescence | 25 pmol/L and 800 pmol/L | N/A | Incubation time down to 27 min | [52] |
| IL-10 | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 0.14 pg/mL | N/A | N/A | [43] |
| teatnus protein | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 0.1 IU/mL | 0.1 IU/mL to 1 IU/mL | ~30 min | [44] |
| β-galactosidase | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | 4 h | [34] |
| IL-6 | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 6 pg/mL | 10 pg/mL to 2 ng/mL | N/A | [68] |
| IFNγ and IL-2 | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 30 aM and 20 aM | 0 to 100 fM | N/A | [69] |
| TSH | Microfluidic | Injection | Fluorescence | 40 pM | 5 miIU/L | N/A | [45] |
| AFP and β-galactosidase | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 5 fM to 250 fM | ~3 h | [42] |
| glucose, LDH, bile acids | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 70 μM | N/A | N/A | [38] |
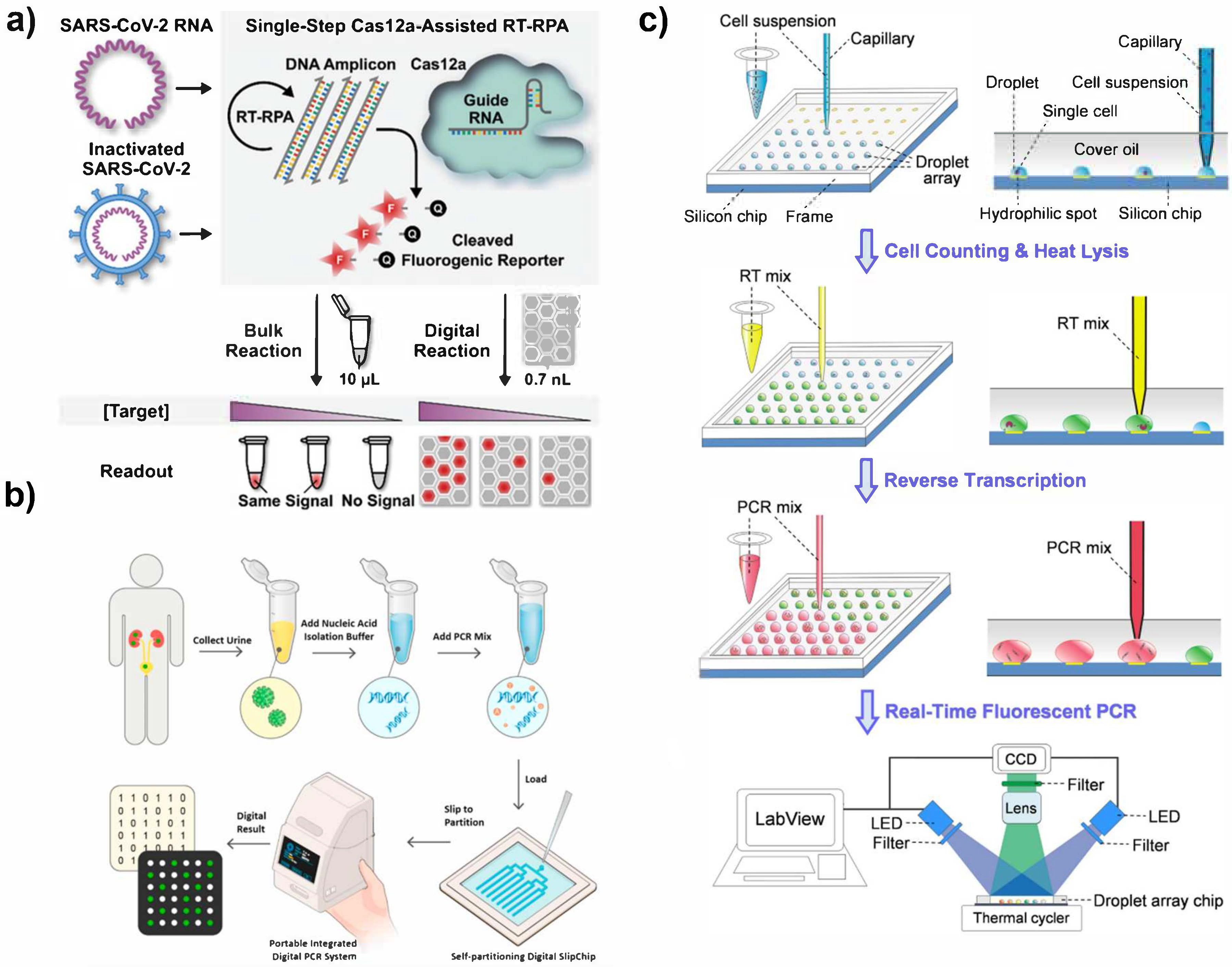
3. Digital Biosensing for Nucleic Acids
3.1. Technical Needs for Digital PCR
3.2. Methods and Technology for Compartmentalizing dPCR
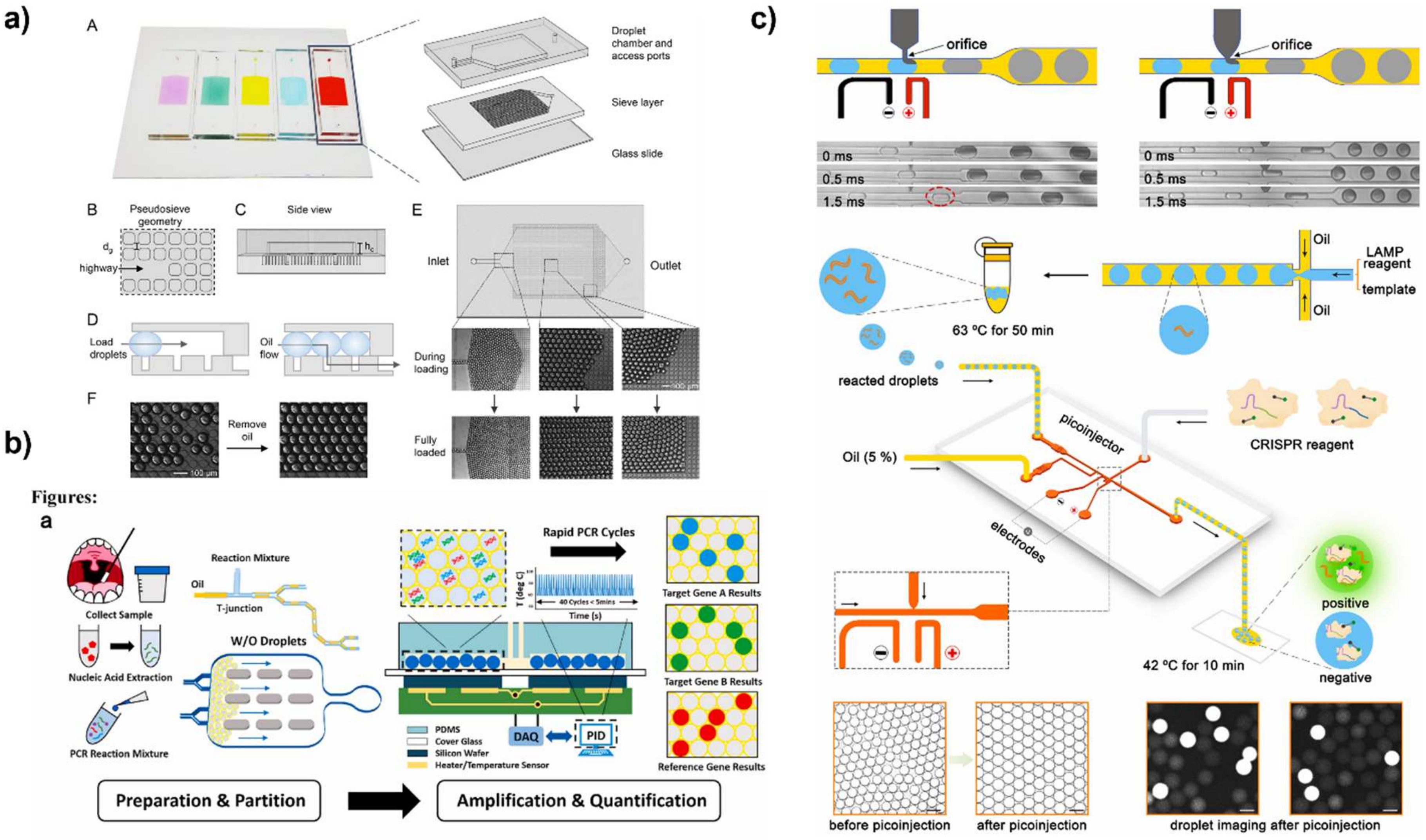
3.2.1. Microwell and Microdroplet Arrays
3.2.2. Droplet Microfluidics
3.2.3. Unconventional Compartmentalization Techniques for dPCR
3.3. Readout Methods for Nucleic Acid Detection
3.3.1. Fluorescence
3.3.2. Colorimetric
| Target | Amplification Type | Platform | Generation Method | Readout | Limit of Detection | Range | Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | CRISPR | Microwell array | Flow cell | Fluorescence | 5 fM | N/A | <5 min | [91] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | CRISPR | Microwell Array | Manual loading | Fluorescence | 1 GE/µL RNA | N/A | 30 min | [90] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | CRISPR | Microwell Array | Manual loading | Fluorescence | 5 copies/μL | N/A | ~1.5 h | [137] |
| HPV | LAMP | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | 1.5 h | [141] |
| pMD 18-T-HA β-actin DNA | LAMP | Microwell Array | Vacuum assisted loading and oil sealing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | 1.5 h | [142] |
| S. aureus and E. coli | PCR | Microwell Array | Droplet Magnetofluidic Cartridge | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [143] |
| Chicken DNA | PCR | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | 30 min | [96] |
| E. coli | LAMP | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 1 pg/μL | N/A | ~1 h | [144] |
| VRE | LAMP | Microwell Array | Microfluidic loading | Fluorescence | 11 copies | N/A | 30 min | [145] |
| S. agalactiae, P. mirabilis, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, and E. coliare | PCR | Microwell Array | Vacuum assisted loading and oil driven digitization | Fluorescence | N/A | 104 to 107 CFU | 4 h | [93] |
| λDNA | PCR | Microwell Array | Pressure actuation | Fluorescence | 10 copies/µL | 10 copies to 3600 copies/µL | N/A | [97] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | PCR | Microwell Array | Dispensing robot | Fluorescence | 3.9 copies/μL | 8 aM–30 fM | 10 min | [99] |
| BK Virus | PCR | SlipChip | Self-partitioning | Fluorescence | 3.0 × 102 copies/mL | 3.0 × 104 to 1.5 × 108 copies/mL | N/A | [100] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | LAMP/CRISPR | SlipChip | Self-partitioning | Fluorescence | 4 × 102 copies/mL. | N/A | 1 h | [102] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | LAMP | SlipChip | Self-partitioning | Fluorescence | 344 to 901 copies/mL | 2.74 to 4.81 log10 | ~30 min | [101] |
| HPV | LAMP | SlipChip | Self-partitioning | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | ~1 h | [146] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | PCR | Microchamber array | Manual pipetting | Fluorescence | 3.8 (N target region) and 3.0 (ORF1ab target region) copies per 20 μL | 4 to 1000 copies | 1.5 h | [147] |
| KRAS Gene | PCR | Microdroplet array | Manual loading | Fluorescence | N/A | 3 to 3 × 103 copies | 5 min | [94] |
| miRNA-122 | PCR | Microdroplet array | Capillary loading | Fluorescence | 6 copies/droplet | 3061 copies/cell to 79,998 copies/cell | N/A | [98] |
| λDNA | LAMP | Microdroplet array | Manual loading | Fluorescence | 1 copy/μL | 1 copy to 500 copies/μL | 30 min | [148] |
| OLR1 gene | RCA | Microdroplet array | Hydrophobic hydrophilic patterning | Fluorescence | N/A | 3 × 106 to 3 × 103 copies | 30 min | [111] |
| Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | 10 CFU/mL | N/A | 1 h | [149] |
| E. coli | PCR | Microfluidic | Wire guided droplet manipulation | Fluorescence | 103 genomic copies | 5.2 × 105−103 genomic copies | 15 min | [150] |
| Human Genomic DNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | Single copy to 100,000 copies | N/A | [123] |
| HBV | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 101 to 104 copies | 60 min | [151] |
| λDNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | Single copy | 1.5, 0.5, 0.15 copy/droplet | N/A | [152] |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis, Trepo-nema denticola and Tannerela forsythia | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | 125 CFU/µL | N/A | 5 min | [153] |
| HER2 | PCR | Microfluidic | Step emulsification | Fluorescence | 10 copies/µL | 4 log10 | N/A | [118] |
| CDO1 | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | 0.8 copies/µL | N/A | N/A | [124] |
| E. coli | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | 0.01 ng/µL | N/A | <1 h | [122] |
| λDNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 4 copies/µL to 86.69 × 103 copies/μL to 6.69 × 107 copies/μL | N/A | [115] |
| PSA cDNA | PCR | Microfluidic | T-junction | Fluorescence | N/A | 5 × 102 to ∼5.5 × 104 copies | <1 h | [113] |
| HPV | PCR | Benchtop reactor | Inkjet printing | Fluorescence | N/A | range 4 orders of mag | N/A | [129] |
| E. coli | PCR | Microfluidic | Co-flow | Fluorescence | N/A | 1:105 to 1:102 | ~1 h | [118] |
| EpCAM cancer biomarker gene | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | ~1 h | [154] |
| 16S E. coli | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | 1.56 nM | N/A | N/A | [155] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow-Focusing | Fluorescence | 10 copies/test | 4 orders of magnitude | 15 min | [156] |
| Bovine DNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Co-flow and step emulsification | Fluorescence | 20 copies | 20 to 50,000 copies/μL | 15 min | [119] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | PCR | Microfluidic | T-junction | Fluorescence | 5 copies/test | 10 copies to 1000 copies | <5 min | [126] |
| KRAS g12S | PCR | Microfluidic | Manual loading | Fluorescence | 5 copies/test | 5 copies per μL to 5 × 104 copies per μL | N/A | [92] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Manual loading | Fluorescence | 10 copies/µL | 10 copies to 10,000 copies/µL | 80 min | [95] |
| ACTB gene | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 5000, 1500, 1000, 100, and 10 copies/μL | 30 min | [125] |
| KRAS G12D | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [157] |
| circulating cell free DNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 0.25 ng/mL to 11 ng/mL | N/A | [158] |
| PSA | PCR | Microfluidic | Dispenser | Fluorescence | 0.48 ng/mL | 0.5 to 30 ng/mL | ~2 h | [159] |
| miRNA-21 | PCR | Microfluidic | T junction | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | <20 min | [114] |
| PCR | Microfluidic | T junction | flow cytometry or gel | 1 × 10−7 | Five log10 | N/A | [160] | |
| O. europaea | PCR | Microfluidic | T junction | Fluorescence | 10 nM | N/A | N/A | [161] |
| E. coli and L. monocytogenes | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 10 CFU/mL | 10 to 104 CFU/mL | N/A | [105] |
| AOX gene | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | 13 min | [162] |
| HBV | PCR | Microfluidic | T junction | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [163] |
| ACTB gene | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 90 to 9000 copies/µL | 45 min | [106] |
| miRNA | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 10 copies/µL | 105 copies/μL to 10 copies/μL | <30 min | [107] |
| miRNA | PCR | Microfluidic | T junction | Fluorescence | N/A | 300 to 3000 templates/µL | N/A | [110] |
| HIV | PCR | Microfluidic | Droplet printing | Fluorescence | 10 copies/test | N/A | N/A | [164] |
| N/A | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [165] |
| PBMCs | PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [166] |
| Salmonella | LAMP | Microfluidic | T junction | Fluorescence | 3 fM | N/A | ~1 h | [127] |
| Salmonella typhimurium | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 1 positive droplet per 250 CFU of S. typhimurium | N/A | 30 min | [167] |
| Virus RNAs | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 4 copies | N/A | N/A | [134] |
| HIV | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | 120 min | [168] |
| HBV | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 1 × 101 to 1 × 104 copies/μL | N/A | [169] |
| mRNA | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | N/A | N/A | [170] |
| E. coli, E. faecalis, and Salmonella Typhi | LAMP | Membrane | Peel off process | Fluorescence | N/A | 11 to 1.1 × 105 copies/μL | N/A | [112] |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | ~600 copies per μL. | N/A | N/A | [108] |
| E. coli | LAMP | Microfluidic | Emulsified by centrifugation | Fluorescence | N/A | 15–1500 copies/μL | 1.5 h | [171] |
| JAK2 V617F mutation | LAMP | Microfluidic | Centrifugal force | Fluorescence | N/A | 101 to 104 | 1.5 h | [121] |
| HCT-116 genomic DNA | LAMP | Microfluidic | T junction | Fluorescence | 5 copies/reaction | Five to 500,000 copies/reaction | 1 h | [172] |
| vancomycin-resistant gene (vanA) | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | 1 copy/μL | 50 to 2.5 × 103 copies | ~40 min | [173] |
| Artificial cells | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | 4 copies/droplet | 4 to 8.7 × 109 copies | N/A | [174] |
| HPV | RPA | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | 1.1 copy/μL | 6 orders of magnitude | 10 min | [136] |
| HPV | RPA | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 10 cp/μL | 10 copies to 10,000 copies | 30 min | [175] |
| miRNA | HCR | Microfluidic | Flow Focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 1 nM to 200 nM | ~1 h | [139] |
| L. monocytogenes | RPA | Microfluidic | Centrifugal emulsion | Fluorescence | N/A | 500 copies/μL to 4000 | 30 min | [120] |
| Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Proteus mirabilis | FISH | Microfluidic | Lab disk | Fluorescence | ~3 × 103 bacteria/mL | Upper limit ~3 × 107 bacteria/mL | 1.5 h | [176] |
| miRNA | Auto-catalytic hairpin assembly | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 0.34 pM | N/A | N/A | [177] |
| African swine fever virus, Epstein–Barr virus, and Hepatitis B virus | CRISPR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 0.5 pM | 1750 to 17.5 copies/μL | 1 h | [138] |
| Shigella, Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus pneumophila | LAMP | Microfluidic | Manual generation | Fluorescence | <10 copies/μL | N/A | ~1 h | [178] |
| miRNA 21 | Circle strand displacement | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | N/A | 0.33–1.66 nmol/L | N/A | [109] |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae 16S rRNA | RT PCR | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Fluorescence | 1aM | N/A | N/A | [179] |
| Legionella | LAMP | Microfluidic | Flow focusing | Colorimetric | 100 fg/mL | 100 fg/mL to 106 fg/mL | N/A | [140] |
| L. monocytogenes | PCR | microcentrifuge tube | Centrifugal force | Fluorescence | N/A | Single copy to 2000 copy/µL | <1 h | [128] |
| HER2 | PCR | Well | Vibrating Sharp tip capillary | Fluorescence | 0.25 copies/µL | 6 orders of magnitude | ~1 h | [130] |
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Lei, Y. A critical review: Recent advances in “digital” biomolecule detection with single copy sensitivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.M.; Hsieh, K.; Wang, T. Droplet microfluidics for high-sensitivity and high-throughput detection and screening of disease biomarkers. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging Droplet Microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrabi, S.; Kassir, N.; Moraveji, M.K. Droplet microfluidics: Fundamentals and its advanced applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 27560–27574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engvall, E.; Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry 1971, 8, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorache, M.; Bala, C. Sensitive Aflatoxin B1 Determination Using a Magnetic Particles-Based Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Sensors 2008, 8, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witters, D.; Knez, K.; Ceyssens, F.; Puers, R.; Lammertyn, J. Digital microfluidics-enabled single-molecule detection by printing and sealing single magnetic beads in femtoliter droplets. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Tobos, C.I.; Rissin, D.M.; Wiener, A.D.; Meyer, R.E.; Svancara, D.M.; Comperchio, A.; Warwick, C.; Millington, R.; Collier, N.; et al. Digital enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with sub-attomolar detection limits based on low numbers of capture beads combined with high efficiency bead analysis. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2122–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunding, A.H.; Busk, L.L.; Webb, H.; Klafki, H.W.; Otto, M.; Kutter, J.P.; Dufva, M. Micro-droplet arrays for micro-compartmentalization using an air/water interface. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2797–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.-H.; Ma, Y.-D.; Fu, C.-Y.; Lee, G.-B. A structure-free digital microfluidic platform for detection of influenza a virus by using magnetic beads and electromagnetic forces. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Nakahara, T.; Nakagama, T.; Seino, N.; Shinoda, M.; Uchiyama, K. Development of a Surface-Reaction System in a Nanoliter Droplet Made by an Ink-jet Microchip. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, S.A.; Huynh, T.; Chang, T.C.; Anderson, C.E.; McDermott, J.J.; Oncina, C.I.; Weigl, B.H.; Nichols, K.P. Wash-Free, Digital Immunoassay in Polydisperse Droplets. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3535–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Iwai, S.; Araki, S.; Sakakihara, S.; Iino, R.; Noji, H. Large-scale femtoliter droplet array for digital counting of single biomolecules. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4986–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirs, K.; Kumar, P.T.; Decrop, D.; Pérez-Ruiz, E.; Leblebici, P.; Van Kelst, B.; Compernolle, G.; Meeuws, H.; Van Wesenbeeck, L.; Lagatie, O.; et al. Bioassay Development for Ultrasensitive Detection of Influenza A Nucleoprotein Using Digital ELISA. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8450–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruiz, E.; Decrop, D.; Ven, K.; Tripodi, L.; Leirs, K.; Rosseels, J.; van de Wouwer, M.; Geukens, N.; De Vos, A.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Digital ELISA for the quantification of attomolar concentrations of Alzheimer’s disease biomarker protein Tau in biological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1015, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Gou, T.; Ding, X.; Song, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, G.; Yin, J.; Mu, Y. Power-free polydimethylsiloxane femtoliter-sized arrays for bead-based digital immunoassays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 139, 111339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirs, K.; Dosso, F.D.; Perez-Ruiz, E.; Decrop, D.; Cops, R.; Huff, J.; Hayden, M.; Collier, N.; Yu, K.X.; Brown, S.; et al. Bridging the Gap between Digital Assays and Point-of-Care Testing: Automated, Low Cost, and Ultrasensitive Detection of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8919–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Ichiki, T.; Noji, H. Digital enzyme assay using attoliter droplet array. Analyst 2018, 143, 4923–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Song, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; Fishburn, M.W.; Shao, Q.; Piech, T.; Ferrell, E.P.; Meyer, R.E.; Campbell, T.G.; et al. Multiplexed single molecule immunoassays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.H.; Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Fournier, D.R.; Piech, T.; Campbell, T.G.; Meyer, R.E.; Fishburn, M.W.; Cabrera, C.; Patel, P.P.; et al. The Simoa HD-1 Analyzer: A Novel Fully Automated Digital Immunoassay Analyzer with Single-Molecule Sensitivity and Multiplexing. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Rivnak, A.J.; Campbell, T.G.; Piech, T.; Rissin, D.M.; Mösl, M.; Peterça, A.; Niederberger, H.-P.; Minnehan, K.A.; Patel, P.P.; et al. Isolation and detection of single molecules on paramagnetic beads using sequential fluid flows in microfabricated polymer array assemblies. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sandford, E.; Tian, Y.; Yin, Q.; Kozminski, A.G.; Su, S.-H.; Cai, T.; Ye, Y.; Chung, M.T.; Lindstrom, R.; et al. Rapid single-molecule digital detection of protein biomarkers for continuous monitoring of systemic immune disorders. Blood 2021, 137, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, M.; Dreher, D.D.; Zeng, Y. Ultrasensitive microfluidic solid-phase ELISA using an actuatable microwell-patterned PDMS chip. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4190–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araci, I.E.; Robles, M.; Quake, S.R. A reusable microfluidic device provides continuous measurement capability and improves the detection limit of digital biology. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lim, S.; Kannan, A.; Alford, S.C.; Sunden, F.; Herschlag, D.; Dimov, I.K.; Baer, T.M.; Cochran, J.R. High-throughput analysis and protein engineering using microcapillary arrays. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wuethrich, A.; Sina, A.A.I.; Cheng, H.-H.; Wang, Y.; Behren, A.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Trau, M. A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Kim, M.; Kang, S.M.; Lim, K.T.; Kim, T.S.; Kang, J.Y. Magnetic bead droplet immunoassay of oligomer amyloid β for the diagnosis of Alzheimer′s disease using micro-pillars to enhance the stability of the oil–water interface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Shim, J.S. Microfluidic Adapter Converting a 96-Well Cartridge into an Autonomous Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chem. 2018, 91, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, S.L.; Bontoux, N.; Stone, H.A. Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Drop formation in a co-flowing ambient fluid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, T.; Roberts, R.W.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. Dynamic Pattern Formation in a Vesicle-Generating Microfluidic Device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4163–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Atiyas, Y.; Shen, H.; Siedlik, M.J.; Wu, J.; Beard, K.; Fonar, G.; Dolle, J.P.; Smith, D.H.; Eberwine, J.H.; et al. Ultrasensitive Single Extracellular Vesicle Detection Using High Throughput Droplet Digital Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 4315–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lv, J.; Shen, H.; Yang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. A highly parallel microfluidic droplet method enabling single-molecule counting for digital enzyme detection. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 014110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maley, A.M.; Garden, P.M.; Walt, D.R. Simplified Digital Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Using Tyramide Signal Amplification and Fibrin Hydrogels. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, W.-J.; Bai, Y.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Pang, D.-W.; Zhang, Z.-L. Digital Single Virus Electrochemical Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay for Ultrasensitive H7N9 Avian Influenza Virus Counting. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, S.H.; Yap, Y.F.; Ng, M.Y.; Nguyen, N.-T. Numerical and experimental investigations of the formation process of ferrofluid droplets. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2011, 11, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Han, Y.D.; Choi, J.; Garcia-Cordero, J.L.; Revzin, A. Automated Droplet-Based Microfluidic Platform for Multiplexed Analysis of Biochemical Markers in Small Volumes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5133–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelleswarapu, V.; Buser, J.R.; Haber, M.; Baron, J.; Inapuri, E.; Issadore, D. Mobile platform for rapid sub–picogram-per-milliliter, multiplexed, digital droplet detection of proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4489–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, M.C.; Cigliana, G.; Spoto, G. Ultrasensitive detection of lysozyme in droplet-based microfluidic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 104, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jeon, C.S.; Choi, N.; Moon, J.-I.; Lee, K.M.; Pyun, S.H.; Kang, T.; Choo, J. Sensitive and reproducible detection of SARS-CoV-2 using SERS-based microdroplet sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Du, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Ji, X.; He, Z. Digital analysis with droplet-based microfluidic for the ultrasensitive detection of β-gal and AFP. Talanta 2018, 186, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Fang, X.; Sun, T.; Yi, J.; Kuang, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gu, H.; Xu, H. Breaking through the Poisson Distribution: A compact high-efficiency droplet microfluidic system for single-bead encapsulation and digital immunoassay detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, A.; Yarmush, M.L.; Konry, T. Picoliter droplet microfluidic immunosorbent platform for point-of-care diagnostics of tetanus. Mikrochim. Acta 2013, 180, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Cherif, A.; Begolo, S.; Descroix, S.; Viovy, J.-L.; Malaquin, L. Programmable Magnetic Tweezers and Droplet Microfluidic Device for High-Throughput Nanoliter Multi-Step Assays. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10923–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.H.; Bhuiyan, W.T.; Pang, S.; Warren, B.; Makris, K.; Coleman, S.; Hassan, S.-U.; Niu, X. A portable droplet microfluidic device for cortisol measurements using a competitive heterogeneous assay. Analyst 2021, 146, 4535–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitthamniyom, P.; Zhang, Y. Magnetic digital microfluidics on a bioinspired surface for point-of-care diagnostics of infectious disease. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Hsu, W.; Huang, H.-Y.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-T.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Shieh, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-H.; Yao, D.-J.; Liu, C.-H. Simultaneous detection of two growth factors from human single-embryo culture medium by a bead-based digital microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiao, X.; Xia, L.; Li, G.; Shui, L. Microfluidic Magnetic Analyte Delivery Technique for Separation, Enrichment, and Fluorescence Detection of Ultratrace Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8273–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Demello, A.J.; Choo, J. Wash-free magnetic immunoassay of the PSA cancer marker using SERS and droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Papautsky, I. Heterogeneous Immunoassay Using Channels and Droplets in a Digital Microfluidic Platform. Micromachines 2019, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, L.; Rehbein, U.; Schönberg, J.-N.; Brandstetter, T.; Thedieck, K.; Rühe, J. Breaking the Interface: Efficient Extraction of Magnetic Beads from Nanoliter Droplets for Automated Sequential Immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10283–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-M.; Bi, Q.; Zhang, W.J.; Cui, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, C.; Cui, Y. Highly accurate multiprotein detection on a digital ELISA platform. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akama, K.; Iwanaga, N.; Yamawaki, K.; Okuda, M.; Jain, K.; Ueno, H.; Soga, N.; Minagawa, Y.; Noji, H. Wash- and Amplification-Free Digital Immunoassay Based on Single-Particle Motion Analysis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13116–13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akama, K.; Shirai, K.; Suzuki, S. Droplet-Free Digital Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Based on a Tyramide Signal Amplification System. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7123–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Davis, R.W.; Javanmard, M. Digital microfluidic assay for protein detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, S.; Qiu, B.; Luo, F.; Guo, L.; Lin, Z. Noble Metal Nanoparticle-Based Multicolor Immunoassays: An Approach toward Visual Quantification of the Analytes with the Naked Eye. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Choo, J. Simultaneous immunoassays of dual prostate cancer markers using a SERS-based microdroplet channel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.; Kim, W.; Zhou, W.; You, E.-A. A digital SERS sensing platform using 3D nanolaminate plasmonic crystals coupled with Au nanoparticles for accurate quantitative detection of dopamine. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17340–17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ye, Y.; Su, S.-H.; Stephens, A.; Cai, T.; Chung, M.-T.; Han, M.K.; Newstead, M.W.; Yessayan, L.; Frame, D.; et al. A digital protein microarray for COVID-19 cytokine storm monitoring. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sawaya, P.; Shi, J.; Wang, P. Quantitation of Femtomolar-Level Protein Biomarkers Using a Simple Microbubbling Digital Assay and Bright-Field Smartphone Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13922–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akama, K.; Noji, H. Multiplexed homogeneous digital immunoassay based on single-particle motion analysis. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissin, D.M.; Fournier, D.R.; Piech, T.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Song, L.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; Patel, P.P.; Provuncher, G.K.; et al. Simultaneous Detection of Single Molecules and Singulated Ensembles of Molecules Enables Immunoassays with Broad Dynamic Range. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M.; Mao, G.; Ji, X.; He, Z. A digital quantification method for the detection of biomarkers on a microfluidic array chip. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Nishiwaki, M.; Inoue, Y.; Seino, N.; Nakagama, T.; Uchiyama, K. Rapid ELISA in Droplet on PDMS Dimple with Nanoliter Reagents Dispensed by Ink-jet Microchip. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 536–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akama, K.; Shirai, K.; Suzuki, S. Highly sensitive multiplex protein detection by droplet-free digital ELISA. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2019, 102, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelleswarapu, V.R.; Jeong, H.-H.; Yadavali, S.; Issadore, D. Ultra-high throughput detection (1 million droplets per second) of fluorescent droplets using a cell phone camera and time domain encoded optofluidics. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, L.; Bendali, A.; Pereiro, I.; Azimani, M.; Dumas, S.; Malaquin, L.; Mai, T.D.; Descroix, S. Modular microfluidic system for on-chip extraction, preconcentration and detection of the cytokine biomarker IL-6 in biofluid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.; Cui, N.; Cai, Y.; Garden, P.M.; Li, X.; Weitz, D.A.; Walt, D.R. Single Molecule Protein Detection with Attomolar Sensitivity Using Droplet Digital Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9491–9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, K.; Faloona, F.; Scharf, S.; Saiki, R.; Horn, G.; Erlich, H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: The polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1986, 51, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, A.L.; Mohr, S.; Day, P.J. High-throughput droplet PCR. Methods 2010, 50, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; de Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V.; Mickelsen, P.A.; Murray, B.E.; Persing, D.H.; Swaminathan, B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.; Armes, N.A. DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature 1991, 350, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Daubendiek, S.L.; Zillman, M.A.; Ryan, K.; Kool, E.T. Rolling Circle DNA Synthesis: Small Circular Oligonucleotides as Efficient Templates for DNA Polymerases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.T.; Fraiser, M.S.; Schram, J.L.; Little, M.C.; Nadeau, J.G.; Malinowski, D.P. Strand displacement amplification—An isothermal, in vitro DNA amplification technique. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Xu, Y.; Kong, H. Helicase-dependent isothermal DNA amplification. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupil, C.; Seifert, W.; Zabrocki, K.; Müller, E.; Snyder, G.J. Thermodynamics of Thermoelectric Phenomena and Applications. Entropy 2011, 13, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinca, M.P.; Gheorghe, M.; Aherne, M.; Galvin, P. Fast and accurate temperature control of a PCR microsystem with a disposable reactor. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 065009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, J.; Shimizu, N.; Matsui, Y.; Shiokawa, S. Liquid heating effects by SAW streaming on the piezoelectric substrate. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 1881–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, P.J.R.; Beitel, L.K.; Khan, R.; Lumbroso, R.; Najih, M.; Cheung, M.C.-K.; Thiemann, J.; Veerasubramanian, V.; Trifiro, M.; Chodavarapu, V.P.; et al. Demonstration of a plasmonic thermocycler for the amplification of human androgen receptor DNA. Analyst 2012, 137, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, D.; Venkataraman, V. A portable battery-operated chip thermocycler based on induction heating. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2002, 102, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermér, C.; Nilsson, P.; Larhed, M. Microwave-assisted high-speed PCR. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 18, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Mancuso, M.; Lu, Z.; Akar, G.; Cesarman, E.; Erickson, D. Solar thermal polymerase chain reaction for smartphone-assisted molecular diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for Diagnostic Applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreejith, K.R.; Ooi, C.H.; Jin, J.; Dao, D.V.; Nguyen, N.-T. Digital polymerase chain reaction technology—Recent advances and future perspectives. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3717–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yin, F.; Song, L.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Fan, C.; Zuo, X.; Xia, Q. Nucleic Acid Tests for Clinical Translation. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 10469–10558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Hsieh, K.; Chen, L.; Kaushik, A.; Trick, A.Y.; Wang, T. Digital CRISPR/Cas-Assisted Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, H.; Taguchi, Y.; Nakagawa, R.; Makino, A.; Okazaki, S.; Nakano, M.; Muramoto, Y.; Takahashi, C.; Takahashi, I.; Ando, J.; et al. Amplification-free RNA detection with CRISPR–Cas13. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q.; Li, G. A hand-powered microfluidic system for portable and low-waste sample discretization. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3429–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athamanolap, P.; Hsieh, K.; O’Keefe, C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.-H. Nanoarray Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction with High-Resolution Melt for Enabling Broad Bacteria Identification and Pheno–Molecular Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12784–12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Si, H.; Jing, F.; Sun, P.; Wu, D. A Self-Priming Microfluidic Chip with Cushion Chambers for Easy Digital PCR. Biosensors 2021, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jing, F.; Wan, X.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhuang, S. A rapid nucleic acid concentration measurement system with large field of view for a droplet digital PCR microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3742–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, J.; Wei, C.; Li, S.; Yu, C.; Meng, X.; Li, J. Pre-Degassed Microfluidic Chamber-Based Digital PCR Device for Meat Authentication Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ravichandran, G.C.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y. A microfluidic alternating-pull–push active digitization method for sample-loss-free digital PCR. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 4104–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Liu, W.-W.; Ma, Y.; Fang, Q.; Yao, B. Printing 2-Dimentional Droplet Array for Single-Cell Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR Assay with a Microfluidic Robot. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, H.; Iida, T.; Makino, A.; Yoshimura, M.; Ishikawa, J.; Ando, J.; Murai, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Muramoto, Y.; Nakano, M.; et al. Automated amplification-free digital RNA detection platform for rapid and sensitive SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qu, H.; Alonso, D.G.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhu, T.; Wu, N.; Shen, F. Portable integrated digital PCR system for the point-of-care quantification of BK virus from urine samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 175, 112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, L.; Shen, F. Slip formation of a high-density droplet array for nucleic acid quantification by digital LAMP with a random-access system. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3086–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, L.; Lyu, W.; Shen, F. Parallel multistep digital analysis SlipChip demonstrated with the quantification of nucleic acid by digital LAMP-CRISPR. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 2954–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Du, W.; Kreutz, J.E.; Fok, A.; Ismagilov, R.F. Digital PCR on a SlipChip. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Qu, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, L.; Lv, W.; Wang, H.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Li, M.; Shen, F. Multistep SlipChip for the Generation of Serial Dilution Nanoliter Arrays and Hepatitis B Viral Load Quantification by Digital Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8751–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Jing, F.; Li, G.; Fan, X.; Jia, C.; Zhou, H.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. A microfluidic droplet digital PCR for simultaneous detection of pathogenic Escherichia coli O157 and Listeria monocytogenes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yin, J.; Wu, W.; Liang, H.; Zhu, F.; Mu, Y.; Fan, H.; Zhang, T. Rapid In Situ Photoimmobilization of a Planar Droplet Array for Digital PCR. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8530–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jing, F.; Li, G.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jia, C.; Jin, Q.; Mao, H.; et al. Absolute quantification of lung cancer related microRNA by droplet digital PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, T.; Chen, L.; Zec, H.C.; Wang, T.-H. Microfluidic continuous flow digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Lab Chip 2015, 15, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, M.C.; Zanoli, L.M.; D’Agata, R.; Finotti, A.; Gambari, R.; Spoto, G. Isothermal circular-strand-displacement polymerization of DNA and microRNA in digital microfluidic devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, M.; Wiederkehr, R.S.; Cai, Q.; Majeed, B.; Fiorini, P.; Stakenborg, T.; Matsuno, T. An integrated one-chip-sensor system for microRNA quantitative analysis based on digital droplet polymerase chain reaction. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 04EM05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, J. A microfabrication-free nanoliter droplet array for nucleic acid detection combined with isothermal amplification. Analyst 2015, 140, 4370–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, X.; Urmann, K.; Xie, X.; Hoffmann, M.R. Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification on a Commercial Membrane. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Zeng, X.; Liu, W.; Xue, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. Stable Colloidosomes Formed by Self-Assembly of Colloidal Surfactant for Highly Robust Digital PCR. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6003–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tang, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, F.; Hu, B. Droplet-based PCR in a 3D-printed microfluidic chip for miRNA-21 detection. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3286–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Burns, M.A. Performance of nanoliter-sized droplet-based microfluidic PCR. Biomed. Microdev. 2009, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, D.-K.; Ali, M.M.; Zhang, K.; Huang, S.S.; Peterson, E.; Digman, M.A.; Gratton, E.; Zhao, W. Rapid detection of single bacteria in unprocessed blood using Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Leng, X.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Lu, J.; Yang, C.J. Highly sensitive and quantitative detection of rare pathogens through agarose droplet microfluidic emulsion PCR at the single-cell level. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3907–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Zheng, M.; Li, C.; Shen, F.; Liu, M.; Luo, H.; Song, X.; Lan, Y.; Pan, J.-Z.; Du, W. Assembled Step Emulsification Device for Multiplex Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Meng, J.; Li, T.; Cheng, J.; Pan, F.; Li, J. Easy-to-Operate Co-flow Step Emulsification Device for Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3939–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, F.; Schwemmer, F.; Trotter, M.; Wadle, S.; Zengerle, R.; von Stetten, F.; Paust, N. Centrifugal step emulsification applied for absolute quantification of nucleic acids by digital droplet RPA. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhu, M.; Gao, Z.; Liao, C.; Jia, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, J. A centrifugal microfluidic emulsifier integrated with oil storage structures for robust digital LAMP. Biomed. Microdev. 2020, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, K.G.; Han, D.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.-K. Pushbutton-activated microfluidic dropenser for droplet digital PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hid-dessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-Throughput Droplet Digital PCR System for Absolute Quantitation of DNA Copy Number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, C.M.; Kaushik, A.M.; Wang, T.-H. Highly Efficient Real-Time Droplet Analysis Platform for High-Throughput Interrogation of DNA Sequences by Melt. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11275–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, Z.; Fan, H.; Zhang, T. A photofabricated honeycomb micropillar array for loss-free trapping of microfluidic droplets and application to digital PCR. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3933–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Z.; Shi, N.; Qi, Y.; Jian, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Mao, H. Ultrafast multiplexed detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using a rapid droplet digital PCR system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cao, X.; Meng, Y.; Richards, D.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Demello, A.J. DropCRISPR: A LAMP-Cas12a based digital method for ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liao, P.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Y. Centrifugal micro-channel array droplet generation for highly parallel digital PCR. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Koga, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Nakajima, H.; Lin, J.-M.; Uchiyama, K. Inkjet Printing Based Droplet Generation for Integrated Online Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5329–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, J.; Fike, B.J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Mendis, B.L.; Li, P. A portable droplet generation system for ultra-wide dynamic range digital PCR based on a vibrating sharp-tip capillary. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 191, 113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eischeid, A.C. SYTO dyes and EvaGreen outperform SYBR Green in real-time PCR. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, J.; Pingoud, A. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. ChemBioChem 2003, 4, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, P.S.; Ajioka, R.S.; Kushner, J.P.; Wittwer, C.T. Homogeneous Multiplex Genotyping of Hemochromatosis Mutations with Fluorescent Hybridization Probes. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-L.; Huang, A.-Q.; Tang, L.-J.; Jiang, J.-H. Multiplexed droplet loop-mediated isothermal amplification with scorpion-shaped probes and fluorescence microscopic counting for digital quantification of virus RNAs. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 8445–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Hossain, A.; Mozibullah; Al Mujib, F.; Afrose, A.; Mahmud, S.A.; Apu, A.I. CRISPR is a useful biological tool for detecting nucleic acid of SARS-CoV-2 in human clinical samples. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.X.; Cui, J.Q.; Park, H.; Chan, K.W.; Leung, T.; Tang, B.Z.; Yao, S. Isothermal Background-Free Nucleic Acid Quantification by a One-Pot Cas13a Assay Using Droplet Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5883–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yin, K.; Li, Z.; Sfeir, M.M.; Liu, C. Sensitive quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples using digital warm-start CRISPR assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 184, 113218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Shu, B.; Tian, T.; Xiong, E.; Huang, M.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Droplet Cas12a Assay Enables DNA Quantification from Unamplified Samples at the Single-Molecule Level. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 4643–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lin, W.N.; Hu, Y.; Sun, G.; Phan, D.-T.; Chen, C.-H. Ultrahigh-throughput droplet microfluidic device for single-cell miRNA detection with isothermal amplification. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1914–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, C.; Slesiona, N.; Hentschel, S.; Aehlig, O.; Breitenstein, A.; Csáki, A.; Henkel, T.; Fritzsche, W. Loop-mediated amplification as promising on-site detection approach for Legionella pneumophila and Legionella spp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, J.E.; Wang, J.; Sheen, A.M.; Thompson, A.M.; Staheli, J.P.; Dyen, M.R.; Feng, Q.; Chiu, D.T. Self-digitization chip for quantitative detection of human papillomavirus gene using digital LAMP. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yu, B.; Ren, H.; Qiu, L.; Han, S.; Jin, W.; Jin, Q.; Mu, Y. Self-priming compartmentalization digital LAMP for point-of-care. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddes, D.E.; Lee, P.-W.; Trick, A.Y.; Athamanolap, P.; O’Keefe, C.M.; Puleo, C.; Hsieh, K.; Wang, T.-H. Facile Coupling of Droplet Magnetofluidic-Enabled Automated Sample Preparation for Digital Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing and Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13254–13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-H.; Li, B.-R. Passively driven microfluidic device with simple operation in the development of nanolitre droplet assay in nucleic acid detection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-D.; Chang, W.-H.; Luo, K.; Wang, C.-H.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yen, W.-H.; Lee, G.-B. Digital quantification of DNA via isothermal amplification on a self-driven microfluidic chip featuring hydrophilic film-coated polydimethylsiloxane. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 99, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lyu, W.; Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Qu, H.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Han, X.; Lai, D.; Shen, F. Self-partitioning SlipChip for slip-induced droplet formation and human papillomavirus viral load quantification with digital LAMP. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yadav, V.; Zhang, C.; Huo, X.; Wang, C.; Senapati, S.; Chang, H.-C. Elliptical Pipette Generated Large Microdroplets for POC Visual ddPCR Quantification of Low Viral Load. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6456–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; You, M.; Gao, B.; Xie, X.; Xue, Z.; Peng, P.; Yao, C.; Xu, F. A digitalized isothermal nucleic acid testing platform based on a pump-free open droplet array microfluidic chip. Analyst 2021, 146, 6960–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, T.J.; Cherukury, H.; Ou, C.-Y.; Vu, T.; Toledano, M.; Li, Y.; Grunwald, J.T.; Toosky, M.N.; Tifrea, D.F.; Slepenkin, A.; et al. Rapid bacterial detection and antibiotic susceptibility testing in whole blood using one-step, high throughput blood digital PCR. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, S.; Cho, S.; Harshman, D.K.; Song, J.-Y.; Yoon, J.-Y. A portable, shock-proof, surface-heated droplet PCR system for Escherichia coli detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Peng, N. Smartphone-Based Droplet Digital LAMP Device with Rapid Nucleic Acid Isolation for Highly Sensitive Point-of-Care Detection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2258–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Cui, L.; Yang, C.J. Agarose droplet microfluidics for highly parallel and efficient single molecule emulsion PCR. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2841–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ju, R.; Sekine, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhuang, S.; Yamaguchi, Y. All-in-one microfluidic device for on-site diagnosis of pathogens based on an integrated continuous flow PCR and electrophoresis biochip. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2663–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jenkins, G.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. Massively Parallel Single-Molecule and Single-Cell Emulsion Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Using Agarose Droplet Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, T.D.; Zec, H.C.; Puleo, C.; Lee, A.P.; Wang, T.-H. Droplet microfluidics for amplification-free genetic detection of single cells. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3341–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Tong, Z.; Shen, C.; Xu, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Mao, H. Micro-PCR chip-based multifunctional ultrafast SARS-CoV-2 detection platform. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Toralla, K.; Pereiro, I.; Garrigou, S.; Di Federico, F.; Proudhon, C.; Bidard, F.-C.; Viovy, J.-L.; Taly, V.; Descroix, S. Microfluidic extraction and digital quantification of circulating cell-free DNA from serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Vu, T.; Grunwald, J.T.; Toledano, M.; Zimak, J.; Toosky, M.; Shen, B.; Zell, J.; Gratton, E.; Abram, T.; et al. An ultrasensitive test for profiling circulating tumor DNA using integrated comprehensive droplet digital detection. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W. Development of immunomagnetic droplet-based digital immuno-PCR for the quantification of prostate specific antigen. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3690–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuga, J.; Zeng, Y.; Novak, R.; Lan, Q.; Tang, X.; Rothman, N.; Vermeulen, R.; Li, L.; Hubbard, A.; Zhang, L.; et al. Single molecule quantitation and sequencing of rare translocations using microfluidic nested digital PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, L.M.; Licciardello, M.; D’Agata, R.; Lantano, C.; Calabretta, A.; Corradini, R.; Marchelli, R.; Spoto, G. Peptide nucleic acid molecular beacons for the detection of PCR amplicons in droplet-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 405, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, A.; Bagheri, M.; Shamloo, A.; Ashkezari, A.H.K. A plasmonic gold nanofilm-based microfluidic chip for rapid and inexpensive droplet-based photonic PCR. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Manz, A.; Wu, W. Miniaturized Continuous-Flow Digital PCR for Clinical-Level Serum Sample Based on the 3D Microfluidics and CMOS Imaging Device. Sensors 2020, 20, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucha, R.W.; Hobbs, K.S.; Hanhauser, E.; Hogan, L.E.; Nieves, W.; Ozen, M.O.; Inci, F.; York, V.; Gibson, E.A.; Thanh, C.; et al. High-throughput Characterization of HIV-1 Reservoir Reactivation Using a Single-Cell-in-Droplet PCR Assay. eBioMedicine 2017, 20, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, W. Passive Micropump for Highly Stable, Long-Termed, and Large Volume of Droplet Generation/Transport Inside 3D Microchannels Capable of Surfactant-Free and Droplet-Based Thermocycled Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reactions Based on a Single Thermostatic Heater. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11925–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malic, L.; Daoud, J.; Geissler, M.; Boutin, A.; Lukic, L.; Janta, M.; Elmanzalawy, A.; Veres, T. Epigenetic subtyping of white blood cells using a thermoplastic elastomer-based microfluidic emulsification device for multiplexed, methylation-specific digital droplet PCR. Analyst 2019, 144, 6541–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Zaferani, M.; Cheong, S.H.; Abbaspourrad, A. Pathogenic Bacteria Detection Using RNA-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal-Amplification-Assisted Nucleic Acid Amplification via Droplet Microfluidics. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-L.; Wang, T.; He, J.; Jiang, J.-H. Droplet microfluidic-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification (dLAMP) for simultaneous quantification of multiple targets. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Hu, F.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Tian, H.; Peng, N. An LED-Driven AuNPs-PDMS Microfluidic Chip and Integrated Device for the Detection of Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal DNA Amplification. Micromachines 2020, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.T.; Kurabayashi, K.; Cai, D. Single-cell RT-LAMP mRNA detection by integrated droplet sorting and merging. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, F.; Siber, C.; Hin, S.; Wadle, S.; Paust, N.; Zengerle, R.; von Stetten, F. Digital droplet LAMP as a microfluidic app on standard laboratory devices. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2750–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.; Veigas, B.; Fernandes, A.R.; Águas, H.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Baptista, P.V. Fast Prototyping Microfluidics: Integrating Droplet Digital Lamp for Absolute Quantification of Cancer Biomarkers. Sensors 2020, 20, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-D.; Luo, K.; Chang, W.-H.; Lee, G.-B. A microfluidic chip capable of generating and trapping emulsion droplets for digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification analysis. Lab Chip 2017, 18, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardinge, P.; Baxani, D.K.; McCloy, T.; Murray, J.A.H.; Castell, O.K. Bioluminescent detection of isothermal DNA amplification in microfluidic generated droplets and artificial cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.Q.; Liu, F.X.; Park, H.; Chan, K.W.; Leung, T.; Tang, B.Z.; Yao, S. Droplet digital recombinase polymerase amplification (ddRPA) reaction unlocking via picoinjection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 202, 114019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-T.; Calabrese, S.; Borst, N.; Lehnert, M.; Lai, Y.-K.; Schlenker, F.; Juelg, P.; Zengerle, R.; Garstecki, P.; von Stetten, F. Microfluidic One-Pot Digital Droplet FISH Using LNA/DNA Molecular Beacons for Bacteria Detection and Absolute Quantification. Biosensors 2022, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-P.; Yang, P.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhuo, Y.; Liang, W.-B. One-Step Digital Droplet Auto-Catalytic Nucleic Acid Amplification with High-Throughput Fluorescence Imaging and Droplet Tracking Computation. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 9166–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Tian, J.; Chao, Y.; Chien, Y.-S.; Luo, R.-H.; Guo, J.-Y.; Li, S.; Chou, Y.-J.; Shum, H.C.; Chen, C.-F. Hand-Powered Microfluidics for Parallel Droplet Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2868–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Chen, L.; Rane, T.D.; Wang, T.-H. Droplet Digital Enzyme-Linked Oligonucleotide Hybridization Assay for Absolute RNA Quantification. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curtin, K.; Fike, B.J.; Binkley, B.; Godary, T.; Li, P. Recent Advances in Digital Biosensing Technology. Biosensors 2022, 12, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090673
Curtin K, Fike BJ, Binkley B, Godary T, Li P. Recent Advances in Digital Biosensing Technology. Biosensors. 2022; 12(9):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090673
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurtin, Kathrine, Bethany J. Fike, Brandi Binkley, Toktam Godary, and Peng Li. 2022. "Recent Advances in Digital Biosensing Technology" Biosensors 12, no. 9: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090673
APA StyleCurtin, K., Fike, B. J., Binkley, B., Godary, T., & Li, P. (2022). Recent Advances in Digital Biosensing Technology. Biosensors, 12(9), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090673





