Abstract
Detection of oncogene mutations has significance for early diagnosis, customized treatment, treatment progression, and drug resistance monitoring. Here, we introduce a rapid, sensitive, and specific mutation detection assay based on the hot-spot-specific probe (HSSP), with improved clinical utility compared to conventional technologies. We designed HSSP to recognize KRAS mutations in the DNA of colorectal cancer tissues (HSSP-G12D (GGT→GAT) and HSSP-G13D (GGC→GAC)) by integration with real-time PCR. During the PCR analysis, HSSP attaches to the target mutation sequence for interference with the amplification. Then, we determine the mutation detection efficiency by calculating the difference in the cycle threshold (Ct) values between HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D. The limit of detection to detect KRAS mutations (G12D and G13D) was 5–10% of the mutant allele in wild-type populations. This is superior to the conventional methods (≥30% mutant allele). In addition, this technology takes a short time (less than 1.5 h), and the cost of one sample is as low as USD 2. We verified clinical utility using 69 tissue samples from colorectal cancer patients. The clinical sensitivity and specificity of the HSSP assay were higher (84% for G12D and 92% for G13D) compared to the direct sequencing assay (80%). Therefore, HSSP, in combination with real-time PCR, provides a rapid, highly sensitive, specific, and low-cost assay for detecting cancer-related mutations. Compared to the gold standard methods such as NGS, this technique shows the possibility of the field application of rapid mutation detection and may be useful in a variety of applications, such as customized treatment and cancer monitoring.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers in the world. It is ranked third in incidence and second in mortality among human cancers [1,2,3,4]. In 2022, 151,030 new cases and 52,580 deaths were estimated in the United States by the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program [5]. This reported rate represented an increase of nearly 10% in both all new cancer cases and all cancer deaths. The metastatic disease will develop in approximately 20% of CRC patients diagnosed [6], and it is associated with lower disease-specific survival, with a less than 14% 5-year survival rate [7]. To increase the survival rate, it is helpful to identify the molecular characteristics of tumors and treat them accordingly. Metastatic CRCs are classified based on their oncogene mutations, such as KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA. Among these, KRAS mutations are discovered in 30–40% of CRCs [8,9]. Ninety percent of the various types of KRAS mutations occur in codons 12 and 13, which leads to constitutive activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) downstream pathways in CRC cells, resulting in cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis, evasion of apoptosis, or angiogenesis. Both the G12D type occurring in codon 12 and the G13D type occurring in codon 13 had a high incidence in CRC. The G12D type has the highest incidence among KRAS mutations, and the G13D type is found most frequently in codon 13 [9]. KRAS mutations have been investigated for their potential as prognostic biomarkers. KRAS wild-type patients showed a therapeutic effects with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) such as cetuximab and panitumumab, whereas patients with KRAS mutations had no significant differences [10,11,12,13]. KRAS mutations are known to activate the rat sarcoma/mitogen-activated protein kinase (RAS/MAPK) signaling pathway downstream of EGFR without ligand binding to the receptor. Thus, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have recommended the use of cetuximab and panitumumab only in KRAS wild-type patients, based on confirmed preclinical and clinical data [11,14,15]. Therefore, detection of KRAS mutations is essential both for managing patients with different types of cancer and for providing customized treatment.
Mutant detection technology for the detection and profiling of rare nucleic acid variants with low allele frequencies, such as cancer mutations or resistance, provides patients with the best-customized treatment, early diagnosis, treatment progression, and tumor drug resistance monitoring [16,17,18]. Current methods for detecting mutations include next-generation sequencing and Sanger sequencing, the amplification refractory mutation system, high-resolution melting analysis, dual priming oligonucleotide, allele-specific hydrolysis, and the dual hybridization probe [19]. The gold standard method for DNA sequencing to detect mutant detection is next-generation sequencing, or Sanger sequencing. However, sequencing techniques are complex, time-consuming, and have high costs. Moreover, the complexity of the clinical sample leads to the missing of mutations by direct sequencing methods, as the sample contains only small numbers of mutant cells mixed with an excess of normal cells. To determine the mutant subgroup through direct sequencing, mutant cells must exist at a minimum concentration of at least 30% of the total gene content [19,20]. BEAMing (Bead, Emulsion, Amplification, and Magnetics) techniques and the Idylla method can detect mutations at a limited sensitivity of 1–5% [21]. The application of these methods in clinical oncology, however, is limited. Although these techniques are more accurate and sensitive than sequencing, they need additional equipment and are complex and therefore not suitable for routine clinical samples. To solve these limitations, many novel methods based on PCR that are designed to detect mutations have been studied and reported, such as PCR restriction fragment length polymorphism mapping, allele-specific PCR, and droplet digital PCR. However, these methods also have a limitation in their simultaneous analysis of different types of mutations [22]. Furthermore, recent studies have shown that detection kits from different manufacturers exhibit inconsistent results, even if the same limit of detection (LOD) is used for mutation detection [23]. Conventional methods for detecting the presence and frequency of mutations by quantitative PCR use fluorescent probes specific to wild-type and mutant alleles. This approach is highly sensitive and reliable but detects only one mutation encoded in the probe [24]. In addition, sequence-selective blockers were used to recognize mutations and increase the discrimination efficiency between different types of mutations or wild-types. Substantial research has been focused on mutation detection methods that use sequence-selective blockers to prevent the amplification of wild-type templates [19,25]. However, the technique is still unsatisfactory as a clinical assay. Therefore, a novel technology would be desirable to overcome the limitations of conventional methods.
In this study, we report the clinical utility of a hot-spot-specific probe (HSSP) for the detection of specific mutations. We designed HSSP for testing the detection efficiency of KRAS mutations that occur specifically in CRC (HSSP-G12D (GGT→GAT) and HSSP-G13D (GGC→GAC)). We demonstrate the capability of HSSP to discriminate mutant target sequences directly. For the determination of the mutation status, we used both HSSPs and measured the differences in the cycle threshold (Ct) values between HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D. HSSP can be easily integrated with conventional methods, such as real-time PCR (qPCR) and direct sequencing, for mutation detection in clinical specimens. Using this assay, the LOD to detect KRAS mutations (G12D and G13D) was 5–10% of the mutant allele in wild-type populations. It is superior to the conventional methods (≥30% mutant allele). Next, 69 tissue samples from CRC patients were used for testing clinical utility. The clinical sensitivity and specificity of the HSSP assay were higher than those of the direct sequencing assay. Therefore, HSSP is a rapid, low-cost, sensitive, and specific assay to detect mutant alleles. It would be possible to provide a fast and correct delivery of patient-customized treatment using this mutation detection assay.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Primer and HSSP
The primer and HSSP sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The primer has an amplification product size of 133 bp, suitable for use in qPCR. The mutation is contained within 133 bp. The reverse primers are designed near the point mutations. HSSP overlaps eight nucleotides with the 3′-end of the reverse primer and includes the mutations, so it is designed to attach only to the target mutation. It was also modified with a C3 spacer at the 3′-end of HSSP because it should not be amplified. Adding this modification to the 3′-end can prevent elongation during PCR without significantly affecting the annealing properties [26,27]. Thus, HSSP competitively interferes with the primers to prevent DNA amplification.
2.2. HSSP with qPCR
The qPCR process conditions consisted of an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 15 min, followed by three-step cycling: 45 cycles at 95 °C for 10 s, 63 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 20 s, and melting steps at 95 °C for 30 s, 65 °C for 30 s, and 95 °C for 30 s. PCR amplification was performed in a total volume of 20 µL, containing 5 µL DNA, 10 µL of AccuPower 2X GreenStar qPCR Master Mix (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea), 2.5 µM of each primer, and 25 µM HSSP on a QuantStudio 3 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA), following the manufacturer′s instructions. An optimization experiment was conducted to determine the concentration of HSSP. The optimal concentration was 10 times that of a primer.
2.3. Cancer Cell Line
A cell line with KRAS mutation was used to confirm the operation and efficiency of HSSP. The G12D point mutation was confirmed in a gastric adenocarcinoma cell line (AGS; ATCC CRL-1739), and the G13D point mutation was confirmed in a human CRC cell line (HCT116; ATCC CCL-247). The cells were cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco′s modified Eagle′s medium (DMEM, HyClone, Logan, UT, USA), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, HyClone) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). The cell culture was maintained in plastic culture dishes and incubated in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Subcultures were done at a ratio of 1:3 when the cell density reached 80–90% every 3 or 4 days.
2.4. Conventional PCR and Sequencing Analysis
The end-point PCR process was comprised of an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 15 min, followed by 45 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, 63 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, as well as a final elongation step at 72 °C for 5 min on a T100TM Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Five microliters of DNA were amplified in a total volume of 25 µL, containing 10X PCR buffer (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM of deoxynucleotide triphosphate, 2.5 µM of each primer, and 1 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Qiagen). PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel. The gel was visualized using a ChemiDoc XRS+ System (Bio-Rad). For direct sequencing of DNA, all the DNA samples were amplified and were then purified using the Expin PCR SV (GeneAll, Seoul, Korea). Using the forward primer, the purified samples were directly sequenced on an ABI 3730XL system (Applied Biosystems) at the Macrogen sequencing center (Macrogen, Inc. Seoul, Korea).
2.5. DNA Template Preparation
To confirm the LOD and efficiency for HSSP, mutation DNA templates were made using DNA extracted from the AGS and HCT116 cell lines. The DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen). In addition, a template was made with DNA obtained from a sample of a patient diagnosed with the wild-type. The DNA template has a length of 777 bp containing KRAS mutation. DNA templates were made by PCR analysis using a designed primer and were then purified using the Expin PCR SV (GeneAll). The concentration and quality of the produced DNA templates were assessed using a Qubit 3 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and the DNA copy number was calculated using the EndMemo DNA/RNA copy number calculator. The DNA template was stored at –20 °C until use.
2.6. Clinical Sample Collection
To confirm the efficacy in clinical samples, we used a total of 69 cancer samples, including 25 with the G12D mutation, 25 with the G13D mutation, and 19 with the wild-type. Based on frozen tissue availability, these samples were obtained from the Bio-Resource Center (BRC) of Asan Medical Center (Seoul, Korea) after approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB No. 2016–0809). The colorectal cancer stage characteristics of all patients are shown in Supplementary Table S2. There is no stage I sample (0%). The CRC stages of these samples provided 4 (5.8%) in stage II and 13 (18.8%) in stage III, with the largest number of patients 52 (75.4%) in stage IV [28]. The genomic DNAs from the tissues were extracted using ATL buffer with proteinase K from a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer′s instructions. The samples were eluted using 100 µL of elution buffer. The eluted DNA was stored at –20 °C until use.
3. Results
3.1. Principles of HSSP
The operating principles of HSSP are illustrated in Figure 1. HSSP overlaps the target primer sequence, includes a single mutation, and is modified with a C3 spacer at the 3′-end to prevent amplification by qPCR. When a mutant sequence exists, the HSSP competitively attaches to the target mutant sequence, thereby preventing the primer from binding to the target mutant sequence; subsequently, the sequence is not amplified. We designed HSSP for testing the detection efficiency of KRAS mutations that occur specifically in CRC, namely, G12D (GGT→GAT) and G13D (GGC→GAC). In the case of wild-type with no KRAS mutations, the KRAS sequences were amplified by the primers; the HSSPs (HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D) could not block the amplification. If the G12D mutation exists, HSSP-G12D blocks the target amplification. However, HSSP-G13D does not block the amplification in the G12D target DNAs. Conversely, if the G13D mutation exists, HSSP-G13D blocks the target amplification. However, HSSP-G12D does not block the amplification in the G13D target DNAs (Figure 1-upper). For the determination of the mutation status, we measured the differences in the Ct values between HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D. In the wild-type sequence, the difference (ΔCt) was 2 to −2 based on the equation:
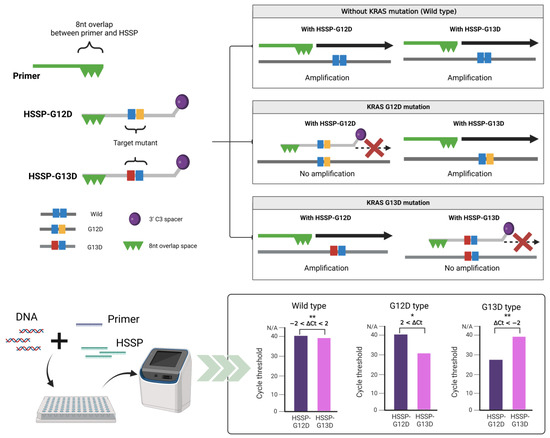
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the principle of HSSP. The hot spot-specific probe (HSSP) is designed to overlap with PCR primers and contains a specific sequence of single mutations. DNA of the target mutation sequence competitively attaches to the HSSP before the primer binds, which prevents amplification. In the case of sequences different from HSSP, the primer is attached and amplified. In the case of HSSP with qPCR, mutants can be checked by detecting a mutation from the difference in the Ct values within 1.5 h. Calculation of the difference between the Ct values when using HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D. If it is higher than 2, it has the G12D mutant; if it is lower than −2, it has the G13D mutant. A value between 2 and −2 is considered wild-type; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
When the G12D mutation exists, ΔCt is greater than 2. In the case of G13D mutation, ΔCt is less than −2. This method is a simple and easy approach that allows the distinguishing of mutations within 1.5 h and is a rapid and robust assay compared to the commonly used qPCR and sequencing methods.
3.2. Optimization and Application of HSSP
Prior to the use of HSSP, the efficiency of the target primer was confirmed. The LOD of the primers was tested with either the G12D mutant DNA obtained from the AGS cell line, the G13D mutant DNA obtained from the HCT116 cell line, or the wild-type DNA without mutations. It was confirmed that the LOD of the primers was 1 × 102 copies of the DNA from each of the three types (Figure 2A). In addition, we used DNA templates from the cell lines AGS and HCT116 to confirm the limit of detection with HSSP. The DNAs were obtained by serial dilution of cell concentrations from the two cell lines. Detection was confirmed with sample sizes down to 10 cells when the test was performed under the same conditions with cells from the two cell lines (Supplementary Figure S1). Therefore, by using HSSP, the mutations can be detected and classified even in small numbers of cells or by DNA.
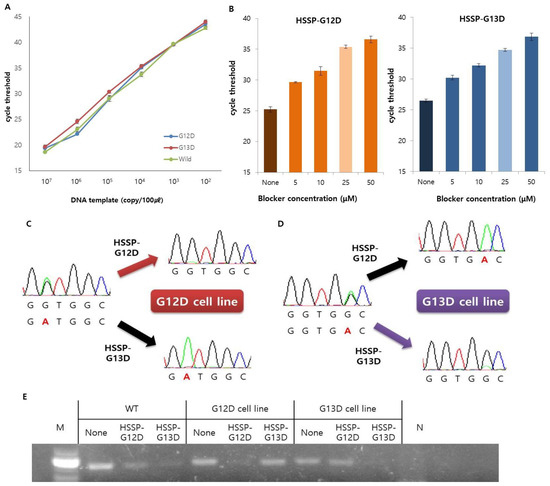
Figure 2.
Optimization and application of the KRAS mutations primer and HSSP. (A) Serial dilution of DNA template was used to test the detection limit of the PCR primer. In the same way, up to 102 copies can be detected in three types. Data are presented as mean ± SD, based on at least three independent experiments. (B) Efficiency of the HSSP depends on the concentration. It showed the largest difference at the highest concentration and the most stable value at 25 µM. This is marked in light colors. Controls without HSSP are displayed in deeper colors. Data are presented as mean ± SD, based on at least three independent experiments. (C–E) Operation of the HSSP was confirmed from direct sequencing and electrophoresis after end-point PCR. This shows that mutations were not amplified in DNA with the same sequence as the HSSP. (C,D) These render direct sequencing results to confirm the operation of the HSSP on (C) G12D cell line and (D) G13D cell line. (E) Electrophoresis results after end-point PCR confirmed the operation of the HSSP.
Next, to find out the optimal concentration of HSSP, we used the serially diluted HSSP-G12D or HSSP-G13D (5–50 µM) for detection of the KRAS 12 or 13 mutation. The ΔCt value of qPCR was larger in 50 µM HSSP (Figure 2B) than in other concentrations, indicating that higher HSSP concentration could block the target DNA amplification by interfering with the binding of the primer to the target sequence. Although the Ct value with 50 µM HSSP was higher than that with 25 µM HSSP, the difference was not significant. Therefore, we selected 25 µM HSSP for HSSP-G12D (Figure 2B-left) and HSSP-G13D (Figure 2B-right) with good stability, efficiency, and low cost.
After the optimization, we conducted the direct sequencing and gel electrophoresis assays to confirm the utility of HSSP as a mutant blocker (Figure 2C–E). We used the direct sequencing assay to confirm heterozygous G12D and G13D mutations in the AGS and HCT116 cell lines, respectively. Working with HSSP-G12D in the AGS cell line, the G12D mutant signal (GGT→GAT) was significantly reduced. Conversely, working with HSSP-G13D, the G12D mutant signal was enhanced by reducing the wild-type signal (Figure 2C). In the case of the G13D type mutation in the HCT116 cell line, the G13D mutant signal (GGC→GAC) was significantly reduced when HSSP-G13D was used. However, the G13D mutant signal was enhanced by reducing the wild-type signal when HSSP-G12D was used (Figure 2D). Therefore, HSSP reduces the signal of the target mutation, and the wild-type signal is also reduced, so that the mutation signal is comparatively enhanced. The results from direct sequencing were similar to the results of the gel electrophoresis assay (Figure 2E). When we used HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D in the wild-type target, both HSSPs interfered the target amplification. In the case of G12D and G13D cell lines, HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D interfered with the target mutant amplification only (Figure 2E). Taken together, the HSSPs specifically blocked the target mutant amplification in cellular applications.
3.3. Detection Limit of HSSP in Mixed-Cell Populations
To check whether HSSP can distinguish the single-point mutation (G12D or G13D) in mixed-cell populations, we used serially diluted DNA samples from both AGS and HCT116 cell lines. Genomic DNA was obtained from the cell mixtures containing 0–100% of the mutant DNAs in the wild-type DNA. When HSSP-G12D and HSSP-G13D were used to amplify the mutations using qPCR, the mutant target could be amplified in the mixture containing 10% of both G12D (Figure 3A) and G13D (Figure 3B). A previous report confirmed that PCR and direct sequencing could not detect the mutant allele in the mixed population containing >30% mutant templates [28]. In contrast, the qPCR assay with HSSP could detect the mutant allele in the mixed samples containing 10% mutant templates in mixed sample populations. For accurate detection, we set an accurate standard for the ΔCt value of qPCR. When the level of the mutant template was 10%, the average difference value was 1.8 in G12D and −2.4 in G13D. In addition, using a wild-type DNA template, we checked from 105 to 10 copies and found that the ΔCt values were 0.662, 1.29, 1.43, 0.84, and 0.47, respectively. The maximum value was about 1.5, and the average difference value was about 0.98 (Supplementary Table S3). As a result, we have confirmed that the wild-type is included within the sequence range based on the case with a 10% mutant template. Thus, the ΔCt value range of the mutation detection criteria was determined at between 2 and −2.
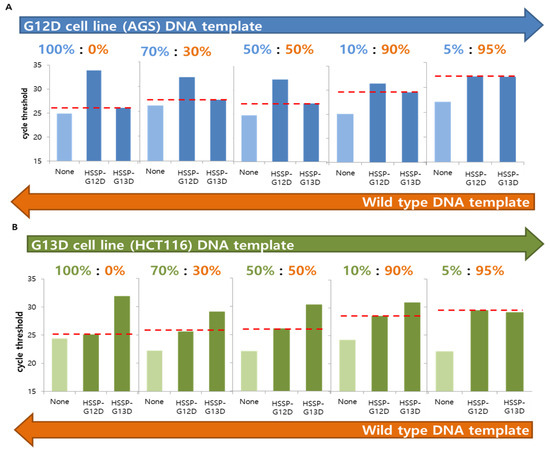
Figure 3.
Analysis of the KRAS mutations, with a serially diluted mixed DNA template, using HSSP with qPCR. (A) G12D cell line (AGS) DNA template was mixed by serial dilution with wild-type DNA template, and the detection limit of the mutant was checked. (B) G13D cell line (HCT116) DNA template was mixed by serial dilution with wild-type DNA template, and the detection limit of the mutant was checked. In both cases, the value was indicated by a red line based on the case of using the non-target HSSP; the Ct value using HSSP-G13D in G12D mutation and the Ct value using HSSP-G12D in G13D mutation offer visual confirmation of the difference in Ct values. Concentrations of 10% and above produce a difference in the Ct value, indicating that the mutations can be detected using HSSP with qPCR.
In the case of serial dilution, when the level of the mutant template was 5%, the same pattern was shown as the wild-type. For more sensitive detection of the mutant DNAs, we conducted a direct sequencing assay with HSSP. When direct sequencing was used to detect the G12D and G13D mutations, the mutant sequences could be identified at a 1% mutant template using HSSP (Supplementary Figure S2). The wild-type strand cannot be amplified; only the mutation strand is emphasized. This confirmed that HSSP could detect nearly 1% of mutations using direct sequencing with both HSSP-G12D (Supplementary Figure S2A) and HSSP-G13D (Supplementary Figure S2B).
3.4. Clinical Utility of HSSP
To validate clinical utility, we randomly selected 69 frozen tissue samples from patients with CRC treated at the BRC of Asan Medical Center. Among the 69 samples, 25 with the G12D mutation (36.2%), 25 with the G13D mutation (36.2%), and 19 with no mutation (27.6%) were examined at the BRC and were used as a reference [28]. HSSP with qPCR results in 69 clinical samples showed differences in Ct values (Figure 4A). After applying the ΔCt range (−2, 2), most wild-type patients had a value between 2 and −2, most G12D type patients had a value of more than 2, and most G13D type patients showed a value of less than −2. For comparison with the conventional method, the direct sequencing method was also performed using the same samples. From the results of HSSP with qPCR, twenty-one samples were detected as true positives (TP) and four as false negatives (FN), out of twenty-five samples with the G12D mutation. Among the twenty-five samples with the G13D mutation, twenty-three were detected as TP, and two as FN. In the case of the nineteen wild-type samples, seventeen were detected as TP and two as FN. With the direct sequencing assay, twenty samples were detected as TP and five as false positives (FP), out of twenty-five samples with the G12D mutation. In twenty-five samples with the G13D mutation, twenty were detected as TP and five as FN. In the case of the wild-type samples, nineteen out of nineteen patients were detected as TP. Detailed data for each patient′s results can be confirmed in Supplementary Table S4. Based on these results, the clinical specificity and sensitivity were calculated (Table 1). When we compared the clinical specificity and sensitivity of the two methods, HSSP with the qPCR assay showed higher sensitivity: 84% and 92% for G12D and G13D mutations, respectively. The specificity of HSSP with the qPCR assay was comparable to that of the direct sequencing assay. Looking at these results, it was possible to see the high sensitivity and specificity of HSSP with the qPCR assay for mutation detection. Therefore, the HSSP assay showed more accuracy in diagnosing mutations. By accelerating the diagnosis, the HSSP assay is expected to allow faster and more appropriate treatment for patients with cancer.
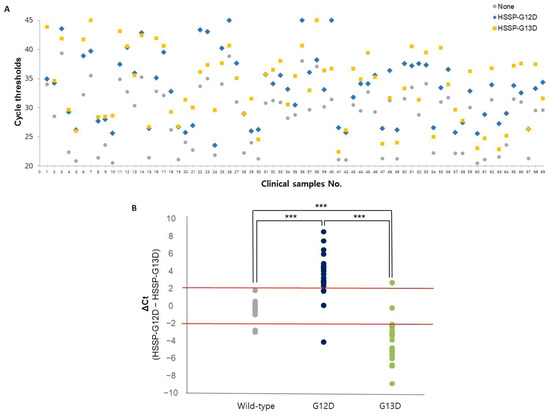
Figure 4.
Application of the KRAS mutations detection in 69 clinical samples. (A) Ct values using HSSP with qPCR in 69 clinical samples. The colors represent HSSP-G12D (blue), HSSP-G13D (yellow), and without HSSP (gray). (B) Mutation detection using ΔCt range (2, −2). Based on the type of sample by BRC, wild-type (gray), G12D type (deep blue), and G13D type (green). The standard for the mutation classification is ΔCt range (2, −2). Significant differences between groups are indicated; *** p < 0.001.

Table 1.
Comparison of specificity and sensitivity of HSSP and direct sequencing for KRAS mutation detection in clinical samples.
4. Discussion
Mutant detection is important for the potential clinical prognostic in cancer monitoring, ranging from customized treatment to tumor drug resistance monitoring. Various technologies to detect single-point mutation have been developed and modified for rapid and highly sensitive detection for clinical use. In this study, we present a rapid and simple technique for mutant detection using a novel probe, HSSP. The presented technology shows a good efficiency compared to existing widely used methods, such as real-time PCR and direct sequencing (Table 2). Other methods are relatively time-consuming, expensive, or reliant on specialized equipment. The HSSP with qPCR test can detect the mutation rapidly (within 1.5 h). This takes less time than does the direct sequencing assay, which takes at least several days to deliver the result, and is faster than other PCR-based methods. In addition, in terms of cost, it is less than USD 2 per sample, which is cheaper than other methods. Differences in Ct values can easily be checked using this analysis technique, so it can be easily used to detect other mutations, and this helps with rapid analysis. The LOD of HSSP (5–10% of mutant allele) is higher than those of other assays, such as qPCR and direct sequencing (≥30% of mutant allele). Hence, HSSP with qPCR is highly useful for the detection of hot spot mutations in clinical specimens, more so than any sequencing assay.

Table 2.
Comparison of mutation detection technologies for KRAS mutation.
In this study, 69 tissue samples were used to detect KRAS mutation. As a result, the clinical sensitivity of HSSP with the qPCR assay was shown to be superior to that of the direct sequencing assay (Table 1). In particular, the detection of wild-type showed higher specificity than in the direct sequencing assay. The HSSP with qPCR method will improve efficiency, especially when treating KRAS wild-type, including those requiring anti-EGFR MoAbs. Therefore, these results show significant potential for rapid and accurate mutation detection in clinical samples. In addition, this HSSP mutation detection assay will be of great help to patient-customized treatment.
Despite the advantages of this technique, the limitations of this study should be addressed in future studies. First, HSSP can be easily applied to qPCR. However, the latter was performed twice for the detection of a single mutation to compare the differences in Ct values from two other mutations. The HSSP method can be difficult to perform with a large number of samples at once. Second, the technique is a negative selection assay, one which blocks the target mutation by HSSP. For example, HSSP-G12D binds with the mutant allele to interfere with the amplification, and other wild-type alleles could then be amplified with HSSP-G13D. Based on the Ct values, the mutation can be determined. Therefore, both target and non-target HSSP must be used for the detection, and there is a limitation in the fact that it is difficult to detect mutations other than those designed. Third, the clinical samples are not enough to validate this technique. To overcome this limitation, further study would be desired with a larger cohort of clinical samples, varying by cancer stages as well as other samples, such as tissue and liquid biopsy, for testing the versatility of the HSSP. Finally, this HSSP assay should be applied to sample preparation techniques for clinical diagnostic systems [29,30,31]. Overall, this method is expected to be able to detect not only KRAS mutations but also other mutations by selectively designing a different sequence. We envision that HSSP will be useful in a variety of applications, such as customized treatment and cancer monitoring.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/bios12080597/s1, Figure S1: Detection limit of the PCR primer in the cell line.; Figure S2: Analysis of the KRAS mutations with serially diluted mixed DNA template using HSSP with direct sequencing.; Table S1: Sequences of primers and HSSP.; Table S2: Disease stage characteristics of the study patients according to colorectal cancer.; Table S3: Differences in the Ct value when using the HSSP in the wild-type DNA template from 105 to 10 copies.; Table S4: Results of HSSP with qPCR, direct sequencing assays in 69 clinical samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S.; methodology, H.J.L. and B.K.; validation, H.J.L., B.K., and Y.O.J.; analysis, H.J.L., B.K., Y.O.J., H.L., and T.N.T.D.; investigation, H.J.L., B.K., Y.O.J., H.L., and T.N.T.D.; resources, S.-B.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.J.L. and B.K.; writing—review and editing, H.J.L., B.K., and Y.S.; supervision, Y.S.; project administration, Y.S.; funding acquisition, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2020R1A2C2007148); supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (HI22C0306), Republic of Korea; and also supported by the Yonsei University Research Fund of 2022-22-0113, Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Sauer, A.G.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Comprehensive review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer State Facts: Colorectal Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html. (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, A.I.; Buchanan, D.D.; Makar, K.W.; Win, A.K.; Baron, J.A.; Lindor, N.M.; Potter, J.D.; Newcomb, P.A. KRAS-mutation status in relation to colorectal cancer survival: The joint impact of correlated tumour markers. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imamura, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Liao, X.Y.; Lochhead, P.; Kuchiba, A.; Yamauchi, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Nishihara, R.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Haigis, K.M.; et al. Specific Mutations in KRAS Codons 12 and 13, and Patient Prognosis in 1075 BRAF Wild-Type Colorectal Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4753–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timar, J.; Kashofer, K. Molecular epidemiology and diagnostics of KRAS mutations in human cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent-Puig, P.; Pekin, D.; Normand, C.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Nizard, P.; Perez-Toralla, K.; Rowell, R.; Olson, J.; Srinivasan, P.; Le Corre, D.; et al. Clinical Relevance of KRAS-Mutated Subclones Detected with Picodroplet Digital PCR in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Treated with Anti-EGFR Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walther, A.; Johnstone, E.; Swanton, C.; Midgley, R.; Tomlinson, I.; Kerr, D. Genetic prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. Drug therapy: EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tougeron, D.; Lecomte, T.; Pages, J.C.; Villalva, C.; Collin, C.; Ferru, A.; Tourani, J.M.; Silvain, C.; Levillain, P.; Karayan-Tapon, L. Effect of low-frequency KRAS mutations on the response to anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, F.; Felicioni, L.; Buscarino, M.; De Dosso, S.; Buttitta, F.; Malatesta, S.; Movilia, A.; Luoni, M.; Boldorini, R.; Alabiso, O.; et al. Increased Detection Sensitivity for KRAS Mutations Enhances the Prediction of Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody Resistance in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4901–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karapetis, C.S.; Khambata-Ford, S.; Jonker, D.J.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Tu, D.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Simes, R.J.; Chalchal, H.; Shapiro, J.D.; Robitaille, S.; et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.R.; Chen, S.X.; Wu, Y.; Patel, A.A.; Zhang, D.Y. Multiplexed enrichment of rare DNA variants via sequence-selective and temperature-robust amplification. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Xiao, M.S.; Yang, H.H.; Li, L.; Fan, C.H.; Pei, H. Circularized blocker-displacement amplification for multiplex detection of rare DNA variants. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 12331–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, W.; Zhong, C. Mutation detection and molecular targeted tumor therapies. STEMedicine 2020, 1, e11. [Google Scholar]
- Su, N.; Wei, K.; Zhao, N.; Wang, L.; Duan, G.J.; Ren, X.D.; Qu, X.M.; Huang, Q. Sensitive and selective detections of codon 12 and 13 KRAS mutations in a single tube using modified wild-type blocker. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 494, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufort, S.; Richard, M.J.; de Fraipont, F. Pyrosequencing method to detect KRAS mutation in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tumor tissues. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 391, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivancos, A.; Aranda, E.; Benavides, M.; Elez, E.; Gomez-Espana, M.A.; Toledano, M.; Alvarez, M.; Parrado, M.R.C.; Garcia-Barberan, V.; Diaz-Rubio, E. Comparison of the Clinical Sensitivity of the Idylla Platform and the OncoBEAM RAS CRC Assay for KRAS Mutation Detection in Liquid Biopsy Samples. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holm, M.; Andersson, E.; Osterlund, E.; Ovissi, A.; Soveri, L.M.; Anttonen, A.K.; Kytola, S.; Aittomaki, K.; Osterlund, P.; Ristimaki, A. Detection of KRAS mutations in liquid biopsies from metastatic colorectal cancer patients using droplet digital PCR, Idylla, and next generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.H.; Wang, S.J.; Fu, B.Q.; Wang, J. Evaluation of droplet digital PCR and next generation sequencing for characterizing DNA reference material for KRAS mutation detection. Sci. Rep.-UK 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Didelot, A.; Le Corre, D.; Luscan, A.; Cazes, A.; Pallier, K.; Emile, J.F.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Blons, H. Competitive allele specific TaqMan PCR for KRAS, BRAF and EGFR mutation detection in clinical formalin fixed paraffin embedded samples. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2012, 92, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubarov, A.S.; Oscorbin, I.P.; Filipenko, M.L.; Lomzov, A.A.; Pyshnyi, D.V. Allele-Specific PCR for KRAS Mutation Detection Using Phosphoryl Guanidine Modified Primers. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestheim, H.; Jarman, S.N. Blocking primers to enhance PCR amplification of rare sequences in mixed samples-a case study on prey DNA in Antarctic krill stomachs. Front. Zool. 2008, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dames, S.; Margraf, R.L.; Pattison, D.C.; Wittwer, C.T.; Voelkerding, K.V. Characterization of aberrant melting peaks in unlabeled probe assays. J. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 9, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, C.E.; Yeom, S.S.; Koo, B.; Lee, T.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, Y.; Lim, S.B. Rapid and accurate detection of KRAS mutations in colorectal cancers using the isothermal-based optical sensor for companion diagnostics. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83860–83871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zou, Q.; Kim, M.G.; Qiao, Z.; Nguyen, D.T.T.; Koo, B.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, Y.O.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, Y. Homobifunctional Imidoester Combined Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Used as Cofactors for Nucleic Acid Extraction. BioChip J. 2022, 16, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.E.; Koo, B.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, Y. Simple and label-free pathogen enrichment via homobifunctional imidoesters using a microfluidic (SLIM) system for ultrasensitive pathogen detection in various clinical specimens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.E.; Koo, B.; Lee, T.Y.; Han, K.; Lim, S.B.; Park, I.J.; Shin, Y. Simple and Low-Cost Sampling of Cell-Free Nucleic Acids from Blood Plasma for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, A.M.; Bratman, S.V.; To, J.; Wynne, J.F.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Modlin, L.A.; Liu, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Merritt, R.E.; et al. An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuth, C.; Spindler, K.L.G.; Johansen, J.S.; Pallisgaard, N.; Nielsen, D.; Hogdall, E.; Vittrup, B.; Sorensen, B.S. Measuring KRAS Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA by Droplet Digital PCR and Next-Generation Sequencing. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Durkee, K.H.; Moore, K.J.; Goodman, S.N.; Shuber, A.P.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Analysis of mutations in DNA isolated from plasma and stool of colorectal cancer patients. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).