Design and Realization of MEMS Heart Sound Sensor with Concave, Racket-Shaped Cilium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principles and Methods
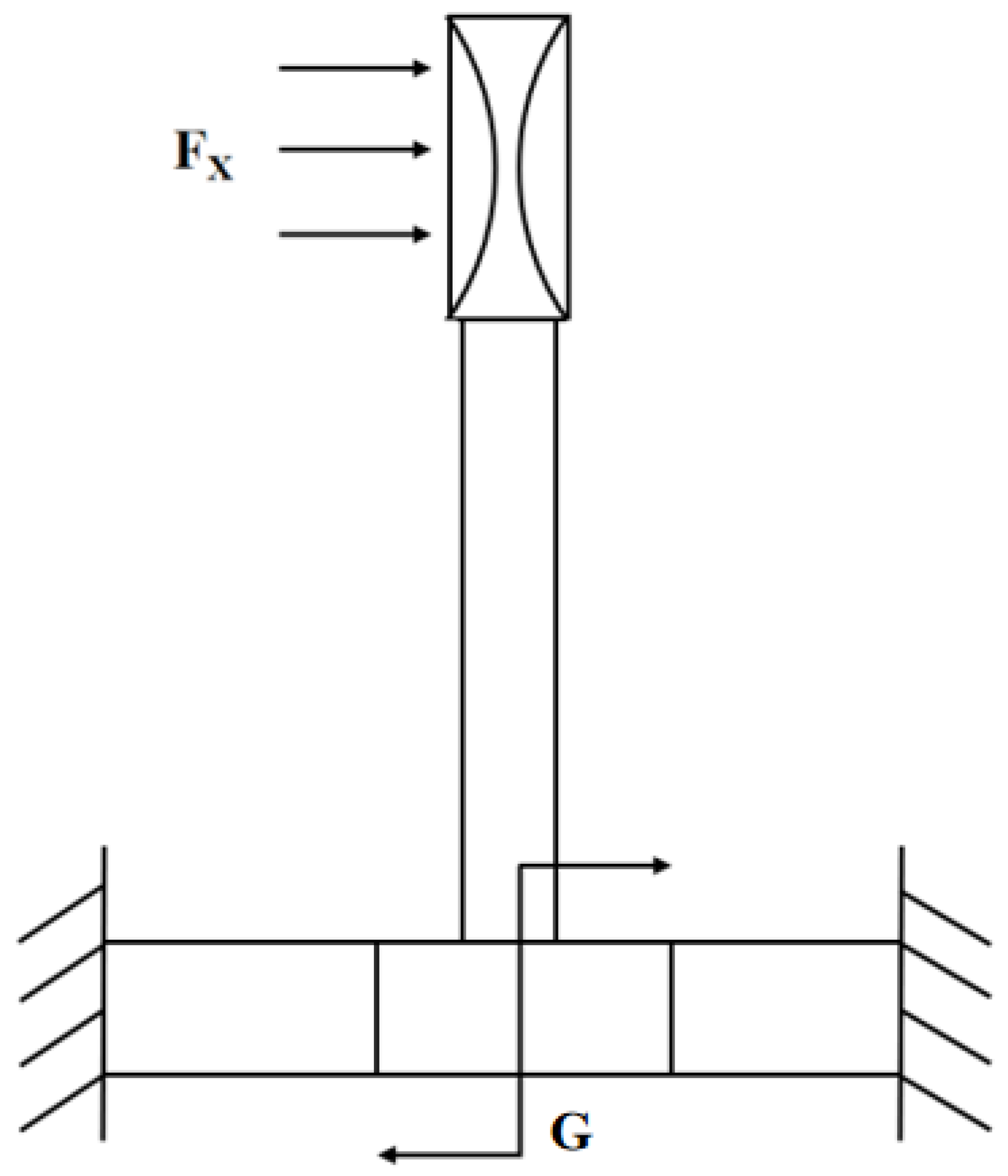
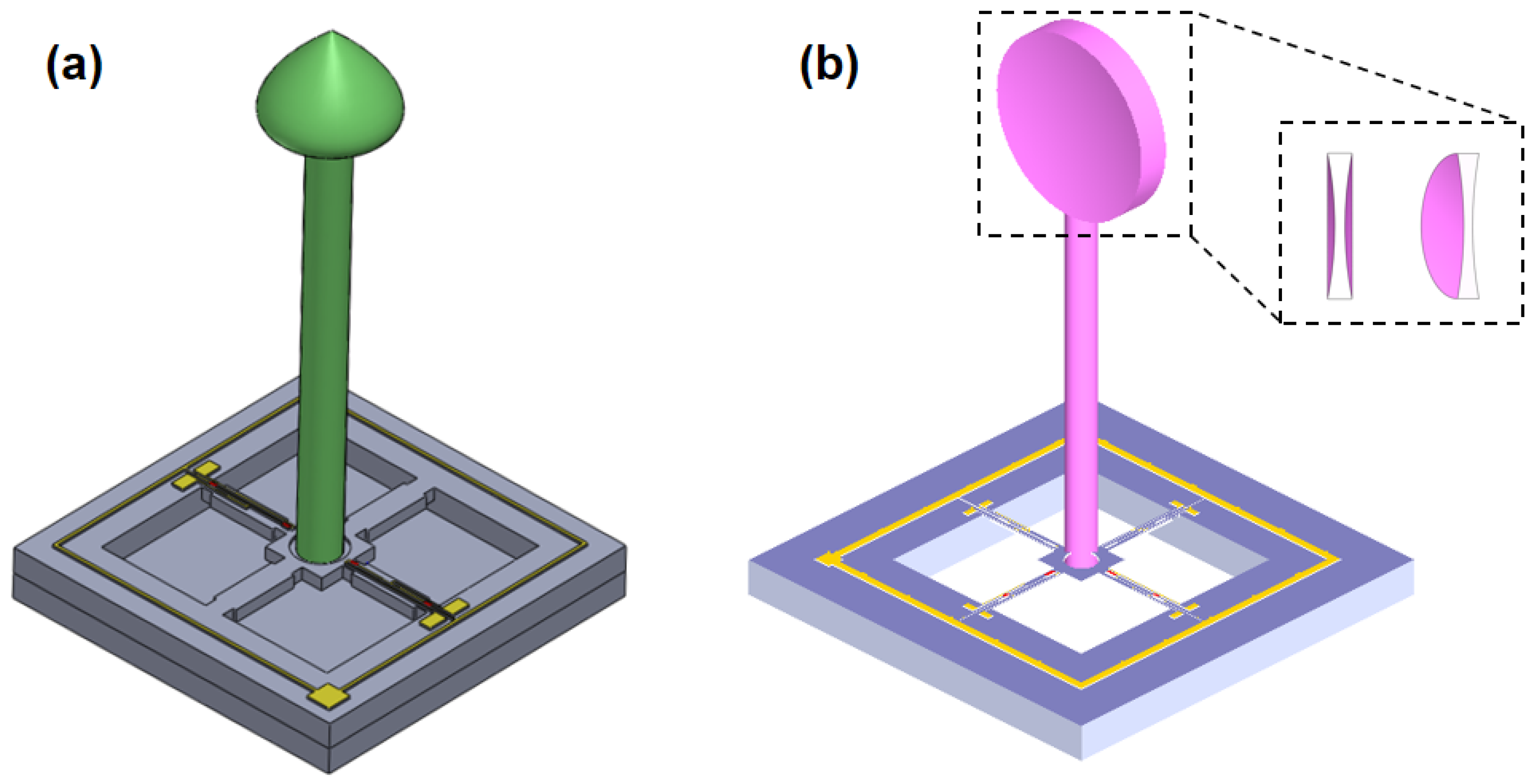
2.1. Principle and Structure
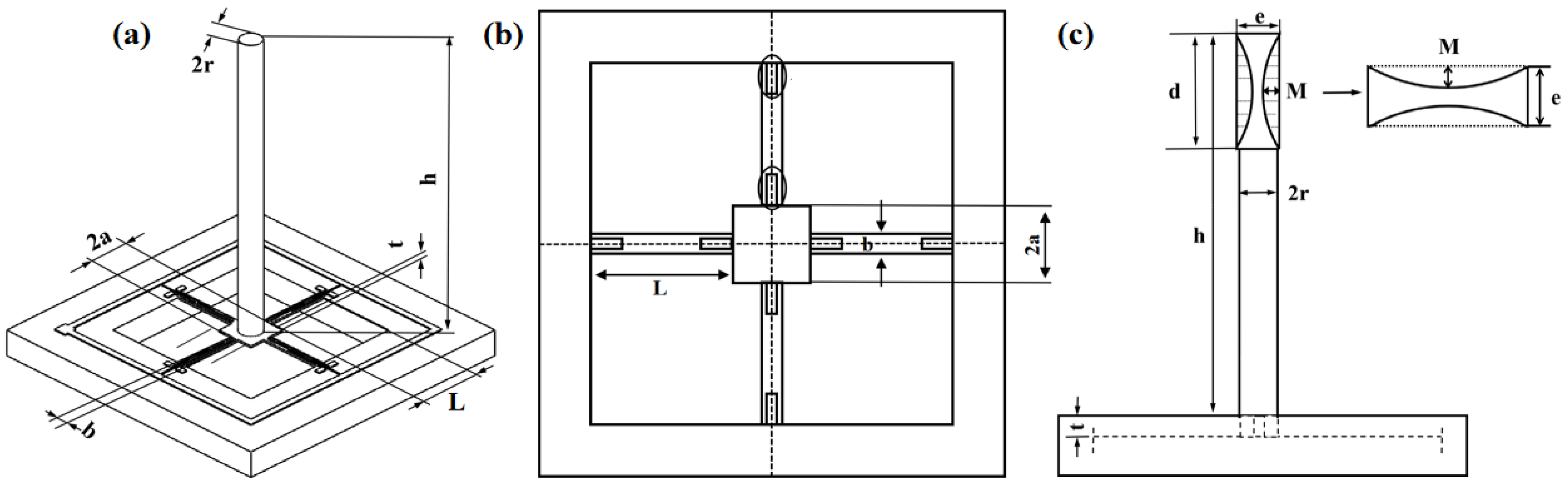
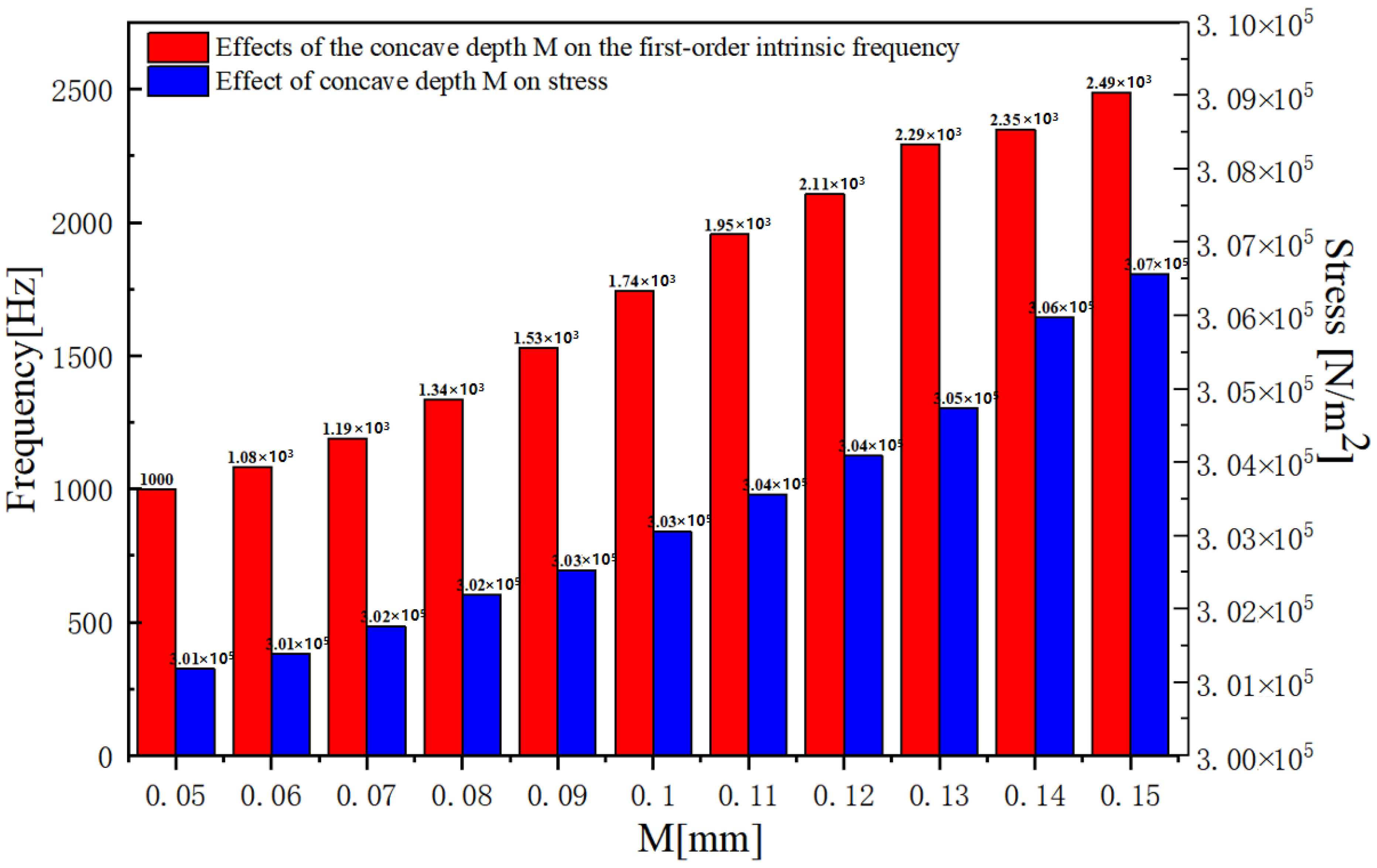
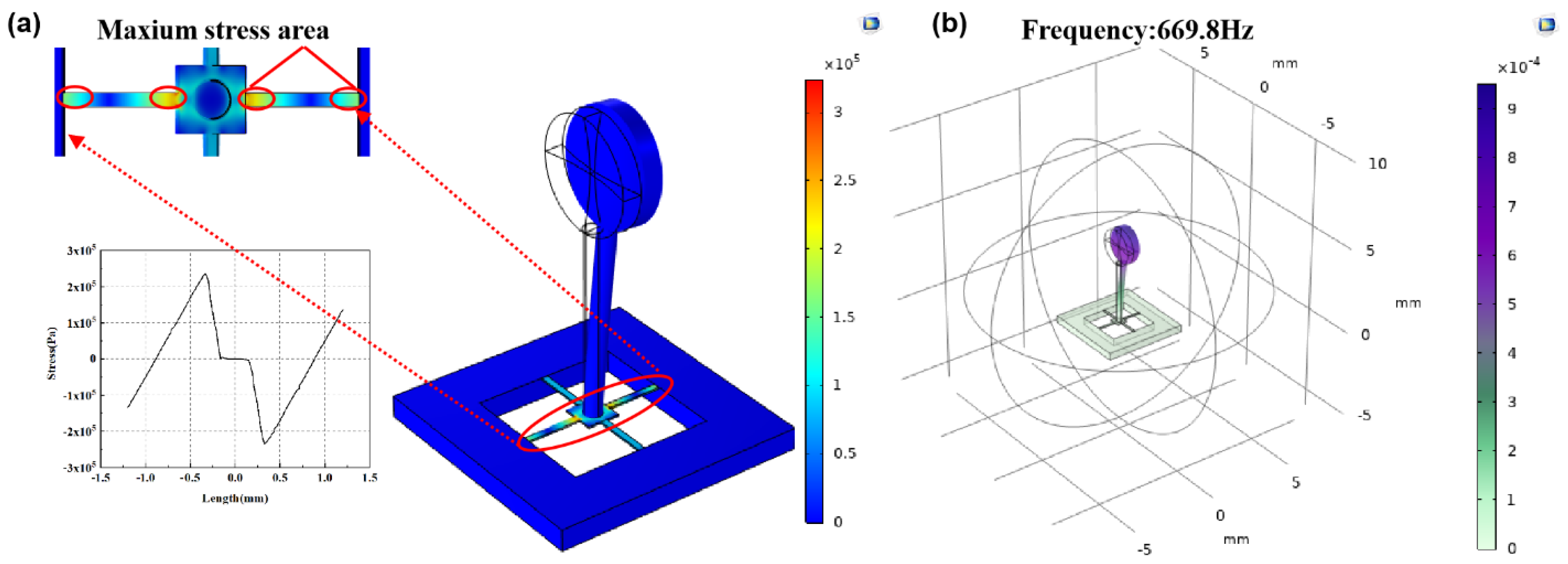
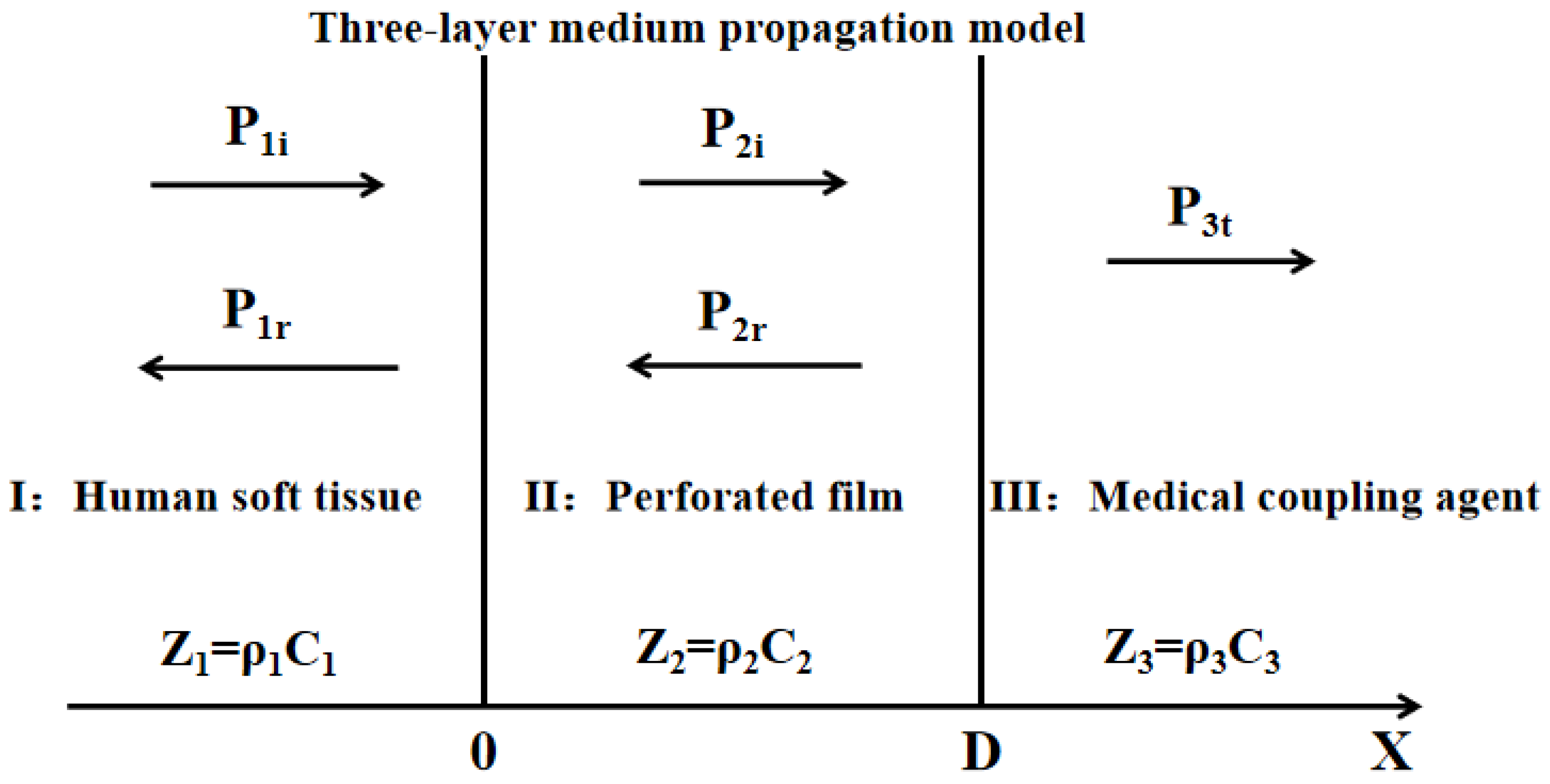
2.2. Design and Optimization of Structure
2.3. Sensor Microstructure Manufacturing Process
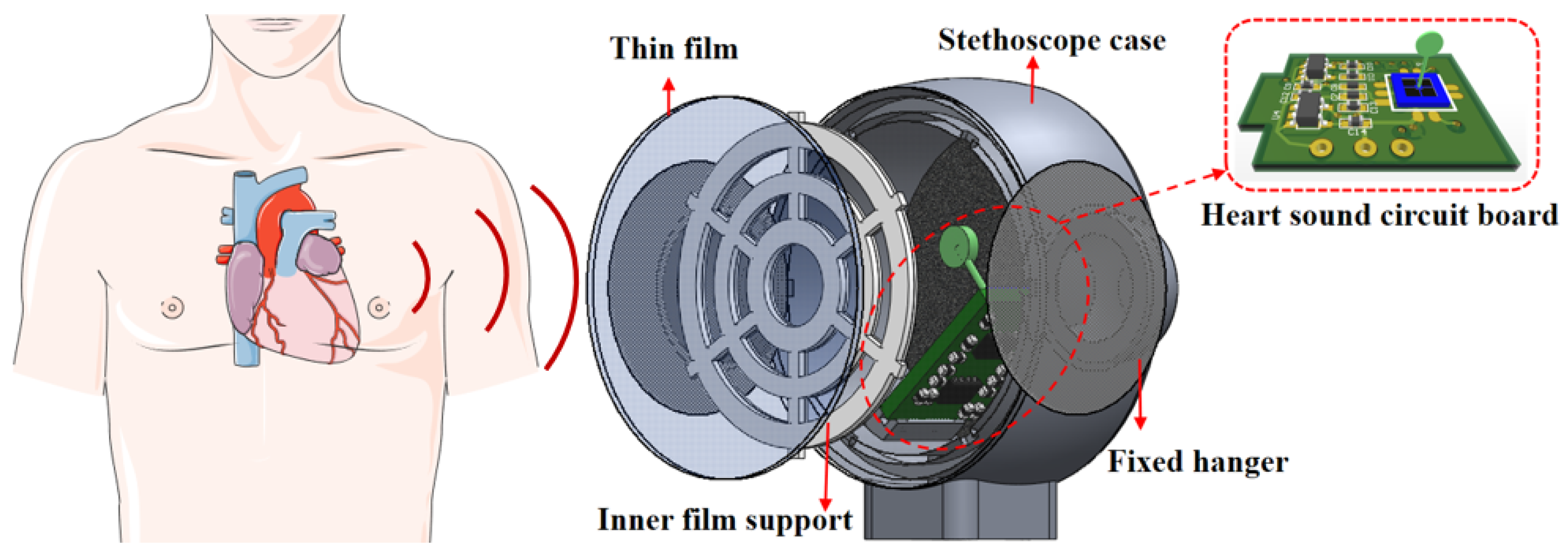
3. Sensor Integration Package and Test
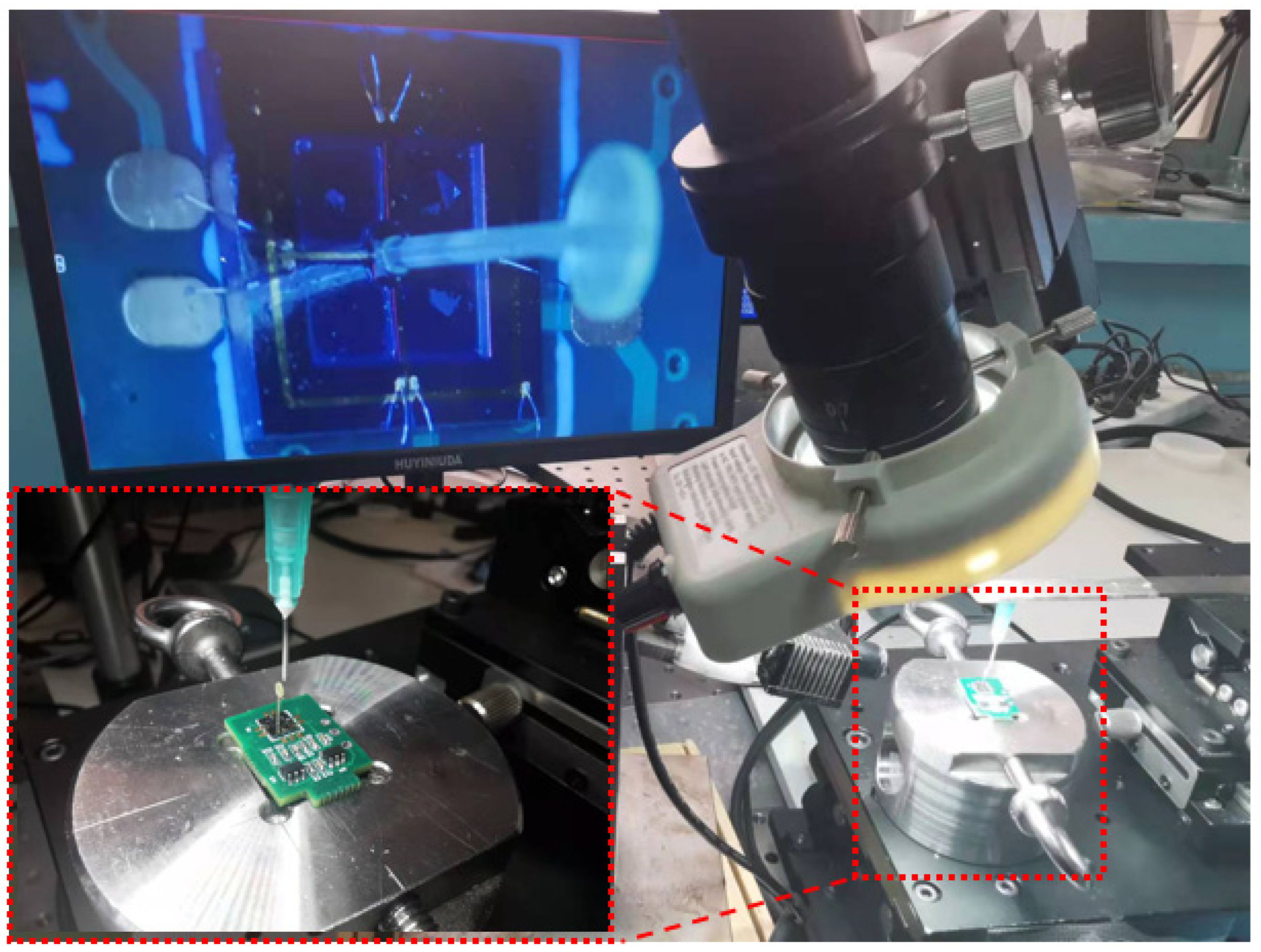
3.1. Sensor Package and Experiment Test
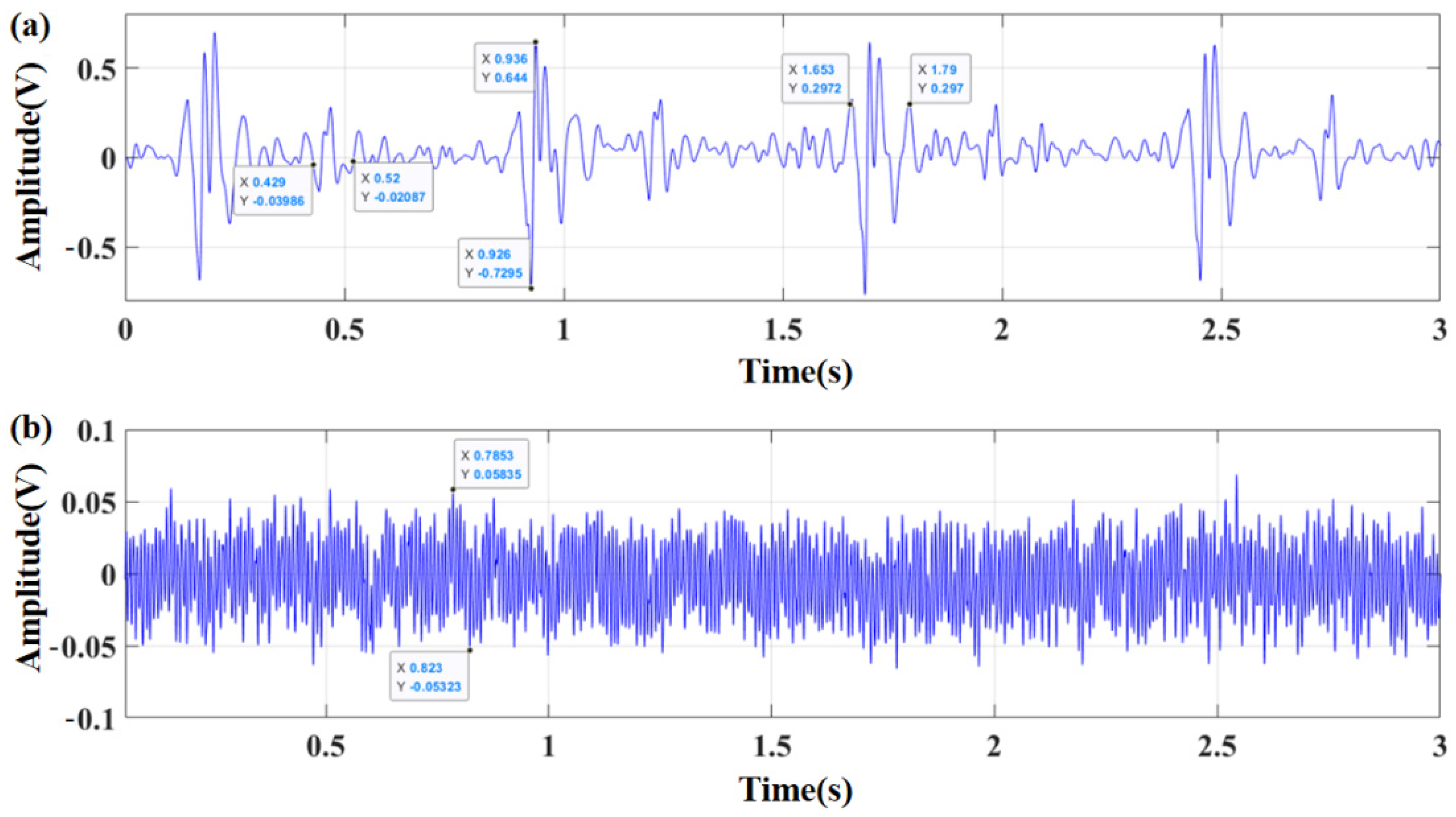
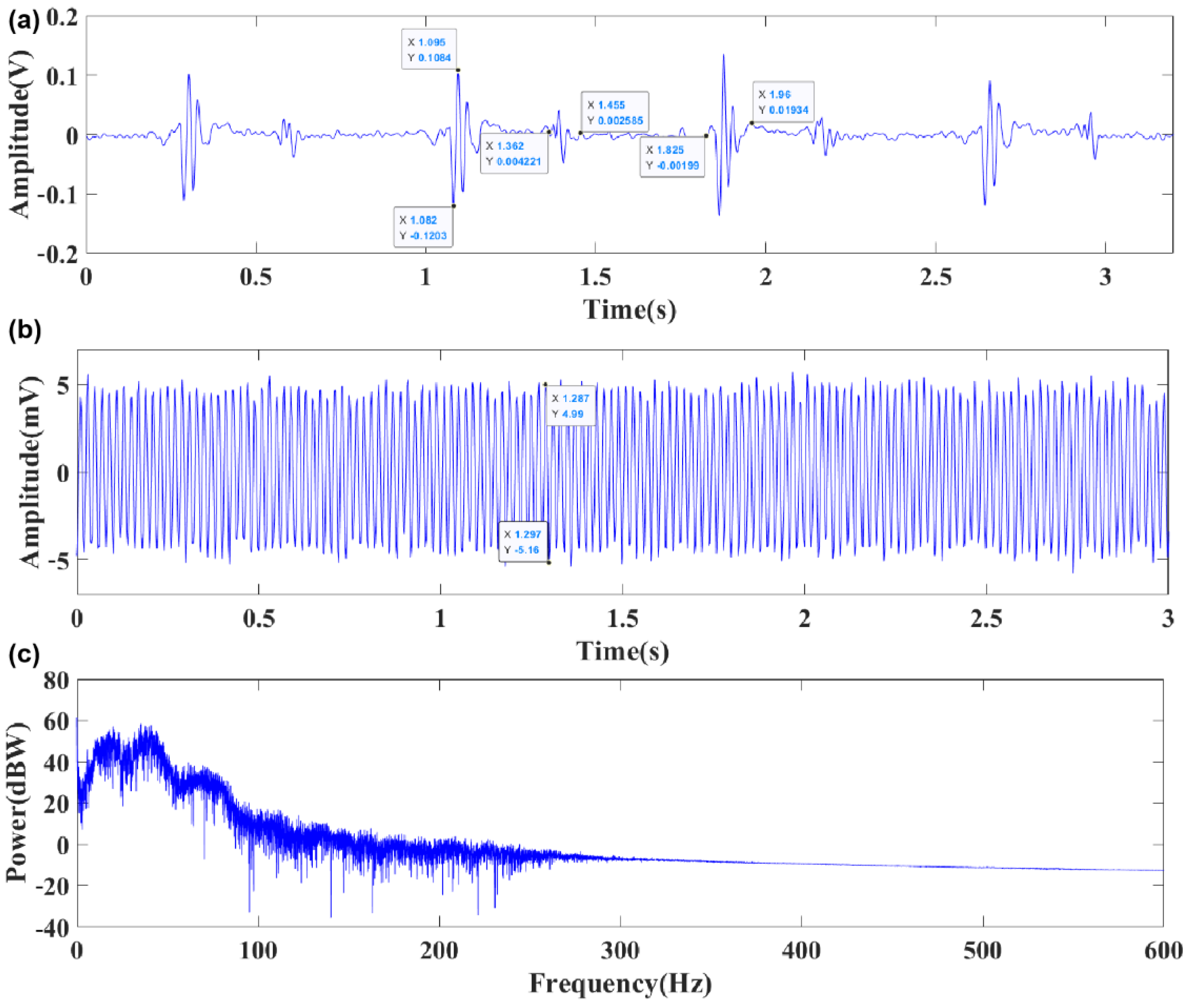
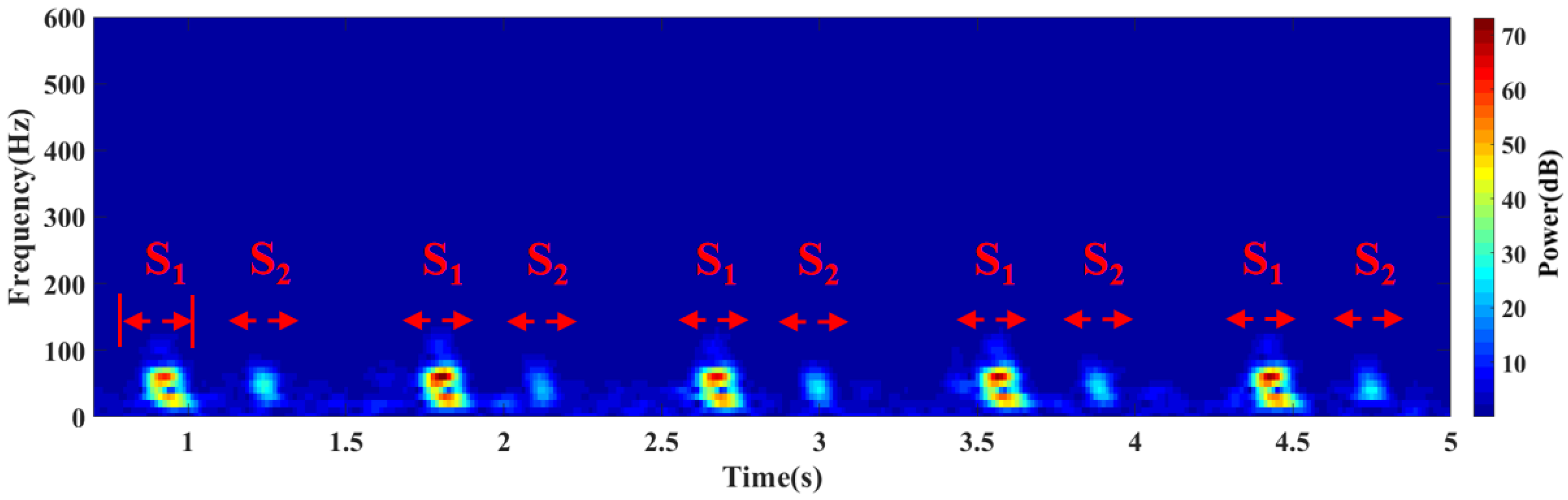
3.2. Comparison and Analysis of Sensor Performance
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montinari, M.R.; Minelli, S. The first 200 years of cardiac auscultation and future perspectives. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2019, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.; Wang, W.; Zhong, N.S.; Liu, Y.M. The invention and evolution of the stethoscope. Zhonghua Yi Shi Za Zhi 2010, 40, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Norton, J.J.; Qazi, R.; Zou, Z.; Ammann, K.R.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Tran, P.L.; Jang, K.I.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Epidermal mechano-acoustic sensing electronics for cardiovascular diagnostics and human-machine interfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tourtier, J.P.; Libert, N.; Clapson, P.; Tazarourte, K.; Borne, M.; Grasser, L.; Debien, B.; Auroy, Y. Auscultation in flight: Comparison of conventional and electronic stethoscopes. Air Med. J. 2011, 30, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anumukonda, M.; Chowdhury, S.R. Heart sound sensing through MEMS Microphone. Sens. Everyday Life 2016, 22, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fattah, S.A.; Rahman, N.M.; Maksud, A.F.; Foysal, A. Stetho-phone: Low-cost Digital Stethoscope for Remote Personalized Healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC), San Jose, CA, USA, 19–22 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Cui, J.; Xu, Q.; Duan, S. Design of a high SNR electronic heart sound sensor based on a MEMS bionic hydrophone. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.J.; Liu, M.R.; Guo, N.; Zhang, W.D. Design of the MEMS Piezoresistive Electronic Heart Sound Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.F.; Lan, J.H. Piezoelectric Sensors, 2nd ed.; Yang, L.J., Ed.; Electronic Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, G.; Rajamani, R.; Erdman, A. Vibro-acoustic model of a piezoelectric-based stethoscope for chest sound measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 095701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedder, G.K. Top-Down design of MEMS. In Proceedings of the Technical Proceedings of the MSM 2000 International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystem, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–29 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Yang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, G.; Duan, S. Design and verification of magnetic-induction electronic stethoscope based on MEMS technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shen, W.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Li, N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, G.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W. Design and implementation of a jellyfish otolith-inspired MEMS vector hydrophone for low-frequency detection. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J. The Research of Cilium MEMS Vector Hydrophone. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Cui, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, B. Design and Implementation of Bionic MEMS Electronic Heart Sound Stethoscope. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Imtiaz, S.A.; Rodriguez-Villegas, E. Acoustic Sensing as a Novel Wearable Approach for Cardiac Monitoring at the Wrist. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghees, V.N.; Ramachandran, K.I. Effective Heart Sound Segmentation and Murmur Classification Using Empirical Wavelet Transform and Instantaneous Phase for Electronic Stethoscope. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3861–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglė, K.; Haroldas, R.; Morse, D.J.; Maxey, G.E.; Naudziunas, A. A Comparison of Electronic and Traditional Stethoscopes in the Heart Auscultation of Obese Patients. Medicina 2019, 55, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Yang, S.; Ho, L.; Tsai, K.; Chen, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Wang, S.; Tsao, Y.; Wu, C. S1 and S2 Heart Sound Recognition using Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2016, 64, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, D. Heart sound classification with signal instant energy and stacked autoencoder network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102211. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, Y.Y. Research on Portable Electronic Heart Sounds and Lung Sounds Stethoscope. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, L.J.; Nowak, K.M. Sound differences between electronic and acoustic stethoscopes. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klum, M.; Leib, F.; Oberschelp, C.; Martens, D.; Pielmus, A.; Tigges, T.; Penzel, T.; Orglmeister, R. Wearable Multimodal Stethoscope Patch for Wireless Biosignal Acquisition and Long-Term Auscultation. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2019), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 5781–5785. [Google Scholar]






| Parameters | Dimensions | Parameters | Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of cantilever beams | L (1 mm) | Thickness of cantilever beams | t (0.03 mm) |
| Width of beams | b (0.12 mm) | Mass block length | a (0.3 mm) |
| Material | Density (Kg/m3) | Poisson’s Ratio | Young’s Modulus (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic resin | 1.2 × 103 | 0.41 | 4.2 × 109 |
| Beam structure (Si) | 2.33 × 103 | 0.27 | 1.6 × 1011 |
| Medium | Density [ρ (Kg/m3)] | Acoustic Characteristic Impedance [z (Pa·s/m)] |
|---|---|---|
| Air (20 °C) | 1.21 | 415 |
| Water (20 °C) | 998 | 1.48 × 106 |
| Blood | 1055 | 1.656 × 106 |
| Soft tissue | 1016 | 1.524 × 106 |
| Muscle | 1074 | 1.684 × 106 |
| Medical coupling agent | 1016 | 1.5~1.7 × 106 |
| Parameter | S1 (ms) | S2 (ms) | VP-P (mV) | Background Noise (mV) | SNR (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3M electronic stethoscope | 137 | 91 | 1373.5 | 111.58 | 21.80 |
| Traditional bionic ciliated MEMS heart sound sensor | 134 | 105 | 210 | 11 | 25.62 |
| Integrated concave ciliated MEMS heart sound sensor | 135 | 93 | 228.7 | 10.15 | 27.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Cui, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Wang, S. Design and Realization of MEMS Heart Sound Sensor with Concave, Racket-Shaped Cilium. Biosensors 2022, 12, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070534
Yang Y, Wang B, Cui J, Zhang G, Wang R, Zhang W, He C, Li Y, Shi P, Wang S. Design and Realization of MEMS Heart Sound Sensor with Concave, Racket-Shaped Cilium. Biosensors. 2022; 12(7):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070534
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuhua, Bo Wang, Jiangong Cui, Guojun Zhang, Renxin Wang, Wendong Zhang, Changde He, Yirui Li, Pengcheng Shi, and Shuotong Wang. 2022. "Design and Realization of MEMS Heart Sound Sensor with Concave, Racket-Shaped Cilium" Biosensors 12, no. 7: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070534
APA StyleYang, Y., Wang, B., Cui, J., Zhang, G., Wang, R., Zhang, W., He, C., Li, Y., Shi, P., & Wang, S. (2022). Design and Realization of MEMS Heart Sound Sensor with Concave, Racket-Shaped Cilium. Biosensors, 12(7), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070534






