Emerging Biosensors for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis—A Review Unravelling Their Role in Past and Present Advancements in the Field of Early Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
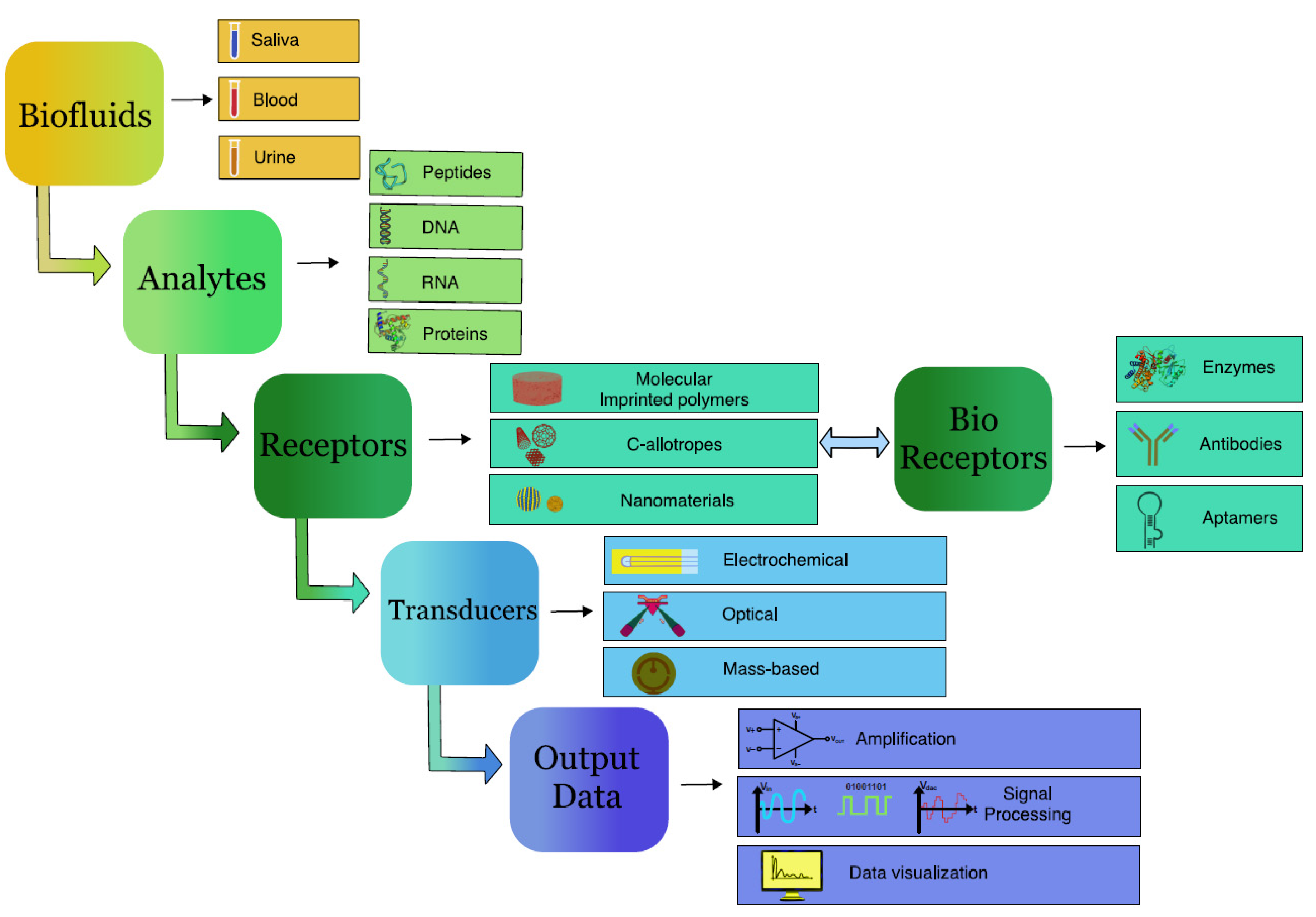
2. Requirement of Biosensors in Diagnostics
3. Various Types of Biosensors Used in Detection of Cancer
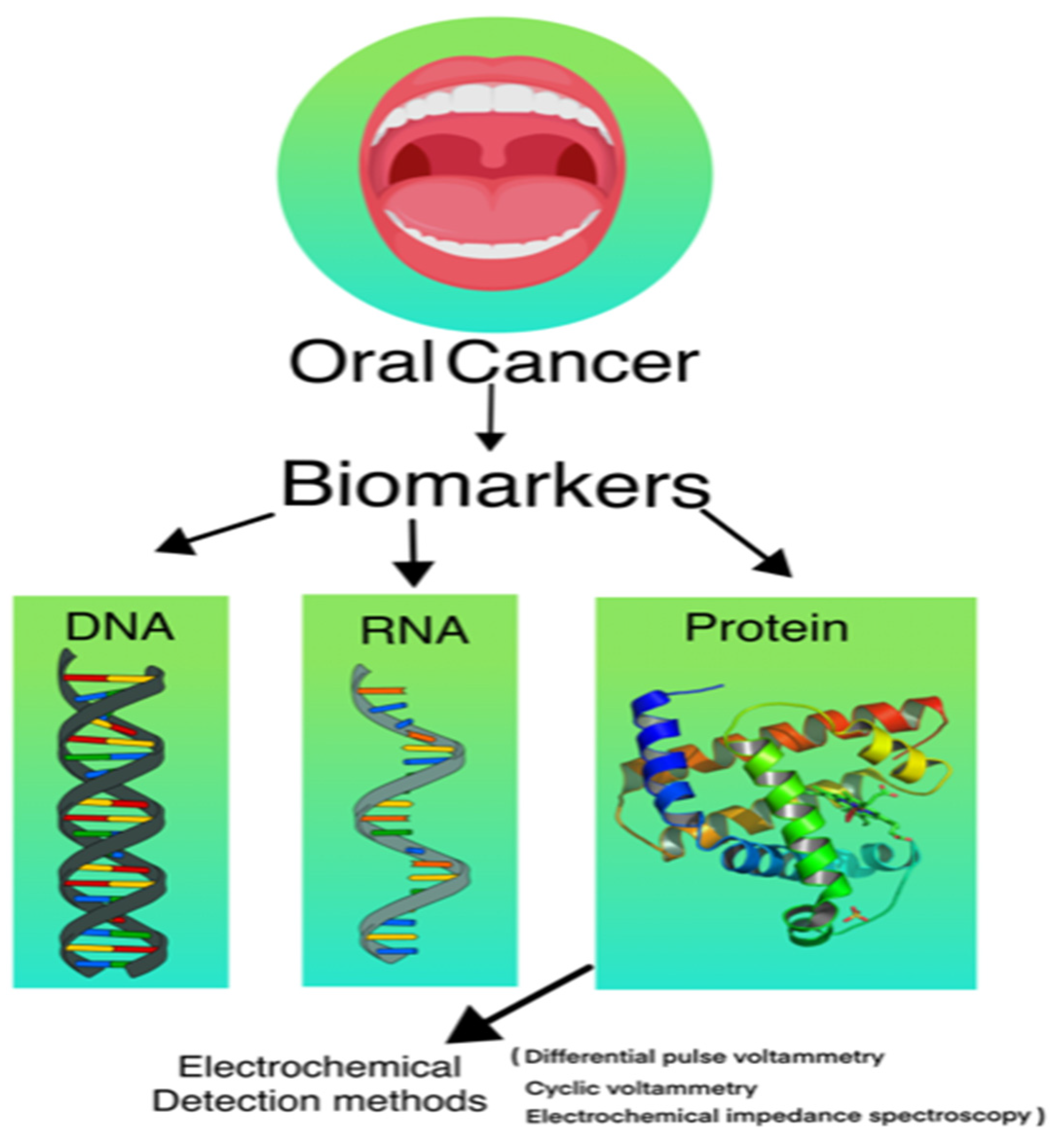
3.1. DNA Biosensor
3.2. RNA Biosensor
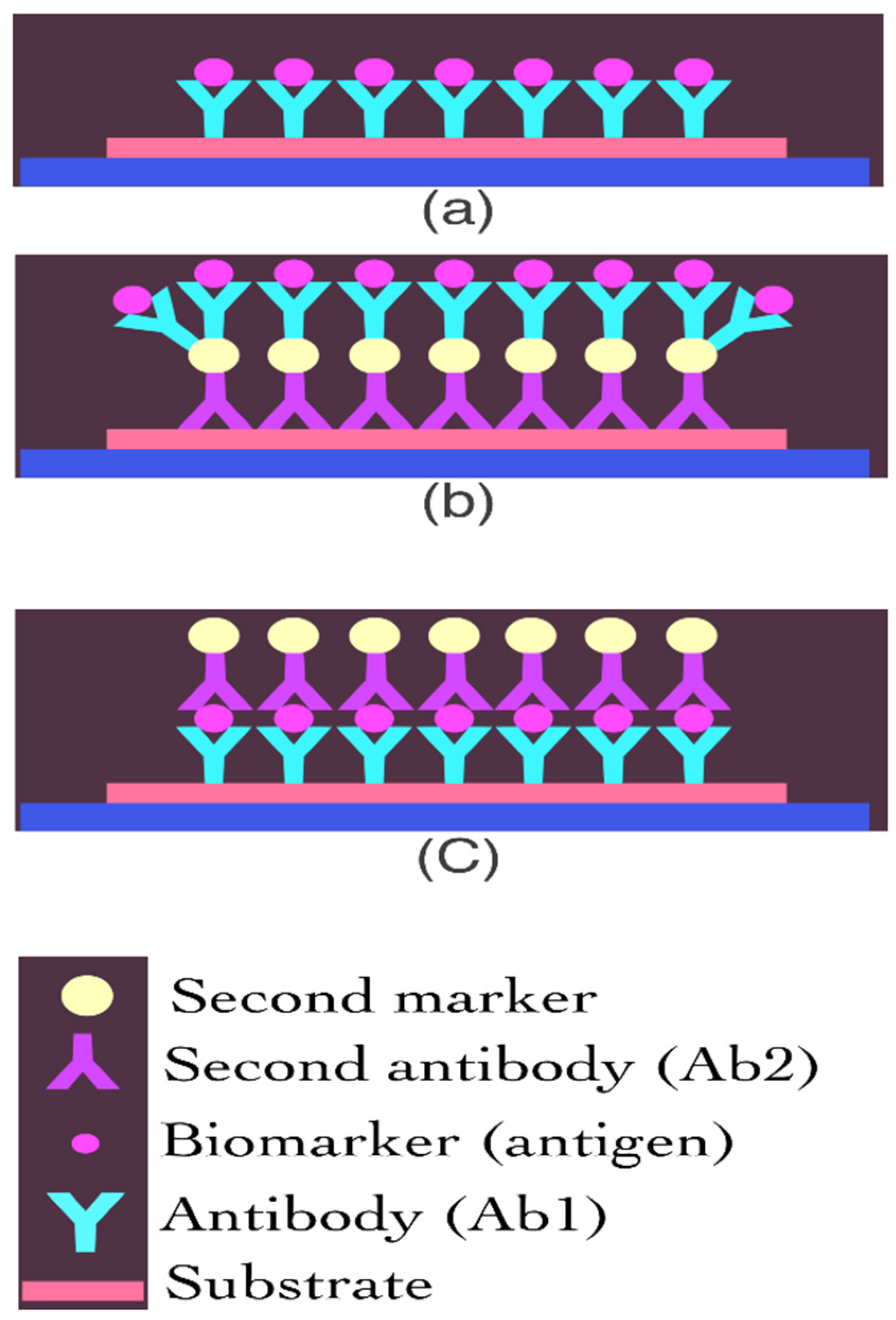
3.3. Protein Biosensor
4. Oral Fluids as Biomedia for Diagnostics
| Sl. No | Biosensor | Method | Source | Advantage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA biosensor | |||||
| 1 | Immobilisation-free, ultra-high selective electrochemical biosensor | Nicking endonuclease-aided target recycling | Saliva | High specificity and good discrimination at single-base mismatch. | [28] |
| 2 | Robust ratiometric electrochemical DNA biosensor | Exo III-assisted target recycling | Saliva | Detect low concentration of biomarkers | [62] |
| 3 | Detection of oral cancer overexpressed 1 | Nuclease-assisted target recycling and DNAzyme | Saliva | Ultra-high discrimination capability with single-base mismatch detection | [63] |
| 4 | Biocompatible DNA dendrimer system | Modified short nanometer of DNA working on the electrode surface | Saliva | Can detect multiple biomarkers at same time | [64] |
| RNA Biosensor | |||||
| 5 | Magnetic controllable electrochemical biosensor | miRNA | Artificial saliva | High sensitivity, detect cancer at early stage | [38] |
| 6 | Ratiometric electrochemical biosensor | Locked nucleic acid | Exosomes | Detect exosomal miR-21 with LOD 2.3 fM | [29] |
| 7 | Single-wall carbon nanotubes | Dendritic Au nanostructure modified fluorine-doped tin oxide | Serum | High sensitivity with LOD 0.01 fmol/mL | [30] |
| Protein Biosensors | |||||
| 8 | Multiplexed electrochemical sensors | Detection of salivary biomarkers | Saliva | Multiplex detection of protein and mRNA IL-8 | [32] |
| 9 | Capacitive aptasensor | Detection of HER2 protein | Serum | Determine the link between capacitance and HER2 concentration | [39,41] |
| 10 | Nano-aptamer sensor | Detect IL-6 | Sweat | Detect low concentration at 0.02 pg/mL | [42] |
5. Saliva-Based Biosensors
5.1. Salivary Metabolomics
5.2. Salivary Proteomics
6. Electrochemical Biosensors
7. Optical Biosensors
8. Nano Biosensors
| Type | Biomarker | Detection Limit | Source | Advantage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical biosensors | |||||
| Electrochemical sandwich-type immunosensor | Interleukin 1 (IL-1) | 5.2 pg/mL | Saliva | Time to obtain results is faster compared to ELISA | [106] |
| Immunosensor by immobilising anti-Cyfra21.1 on a gold electrode modified with cysteamine and glutaraldehyde | Cytokeratin Cyfra21.1 | 2.5 ng/mL | Saliva | Low-cost, dependable, and robust approach for detection of non-invasive salivary Cyfra21.1 | [107] |
| Label-free immunosensor | Interleukin 1 (IL-1) | 7.5 fg/mL | Serum and saliva | 6-phosphonohexanoic acid (PHA) is used as a biomolecule immobilisation matrix. | [108] |
| Magnetic beads-based electrochemical biosensor | Hypoxiainducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1) | 76 pg/mL | Saliva | The biosensor was built in a sandwich shape to require less incubation stages, resulting in a shorter total test time compared to traditional laboratory methods. | [109] |
| A ratio-metric electrochemical sensor | Oral Cancer Overexpressed 1 (ORAOV1) | 12.8 fM | Artificial saliva | This method is to overcome the limitations of traditional electrochemical biosensors with signal-on/signal-off outputs. | [62] |
| Dual SPCE-based immunosensor | IL-1 and TNF | 0.38 for IL-1 and 0.85 for TNF | Serum and saliva | Multiplex and sensitive amperometric biosensor with very low costs. | [110] |
| SiNW sensor array (Silicon nanowire) | TNF- and IL-8 | 100 fg/mL | Saliva | Uses intrinsic opposing charge to enable straightforward differentiation | [45] |
| Optical Biosensors | |||||
| Fluorescent immunosensor | Cyfra21.1 | 0.5 ng/mL | Clinical saliva | The 3DN-CNT sensor enhances the sensitivity of Cyfra 21-1 detection by increasing the density of immobilised antibodies through its high surface area. | [111] |
| Microfluidic biosensor | IL-8, IL-1, and MMP-8 | 80 pg/mL | Saliva | Multiplexed detection of salivary biomarkers | [112] |
| Fluorescent biosensor with magnetic and fluorescence bioprobes (MFBPs) | CD63 proteins | Lower than 500 particles/mL | Saliva | One-step quantification with less assay time; achieved high sensitivity with low limit of detection | [113] |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borse, V.; Konwar, A.N.; Buragohain, P. Oral cancer diagnosis and perspectives in India. Sensors Int. 2020, 1, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Singh, A.; Chien, C.Y.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Tobacco related oral cancer. BMJ 2019, 365, l2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, A.; Sharp, L.; Hanly, P.; Barchuk, A.; Bray, F.; de Camargo Cancela, M.; Gupta, P.; Meheus, F.; Qiao, Y.L.; Sitas, F.; et al. Productivity losses due to premature mortality from cancer in Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa (BRICS): A population-based comparison. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 53, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, P.H.; Patel, S.G. Cancer of the oral cavity. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollaers, K.; Hinton-Bayre, A.; Friedland, P.L.; Farah, C.S. AJCC 8th edition oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma staging—Is it an improvement on the AJCC 7th edition? Oral Oncol. 2018, 82, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoran, L.; Jun, G.; Eugene, M.; Lei, Y. Biomaterials in Translational Medicine; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 213–255. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.P.; Karube, I.; Wilson, G.S. Biosensors Fundamentals and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kokbas, U.; Kaynn, L.; Tuli, A. Biosensors and their medical applications. Arch. Med. Rev. J. 2013, 22, 499–513. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.C., Jr.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, K.R.; Nelakurthi, H.; Kumar, A.S.; Sudarshan, A.; Rudraraju, A. Oral fluid-based biosensors: A novel method for rapid and noninvasive diagnosis. Ind. J. Dent. Sci. 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, M.A.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Recent advances in the development and analytical applications of biosensing probes. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem 1988, 20, 149–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohunicky, B.; Mousa, S.A. Biosensors: The new wave in cancer diagnosis. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Perumal, V.; Hashim, U. Advances in Biosensors: Principle, architecture and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothill, I.E. Biosensors for cancer marker diagnosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.T.; Darvishi, S.; Preet, A.; Huang, T.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Girault, H.H.; Lin, T.E. A review: Electrochemical biosensors for oral cancer. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soper, S.A.; Brown, K.; Ellington, A.; Frazier, B.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Gau, V.; Gutman, S.I.; Hayes, D.F.; Korte, B.; Landers, J.L.; et al. Point-of-care biosensor systems for cancer diagnostics/prognostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical Biosensors: Towards point-of-care cancer diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitra, C.; Veena, K.; Rao, S.; Sharan, P. SPR based biosensors for detection of abnormal growth of tissues. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nextgen Electronic Technologies: Silicon to Software (ICNETS2), Chennai, India, 23–25 March 2017; pp. 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.T.; Ashab-Uddin, M. Biosensors, the Emerging Tools in the Identification and Detection of Cancer Markers. JGWH 2017, 5, 555667. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Sabet, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Klokkevold, P.R.; Wong, D.T.; Ho, C.M. Optical Protein sensors for detecting cancer markers in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Duan, R.; Yang, H.; Luo, X.; Xi, M. Detection of serum human epididymis secretory protein 4 in patients with ovarian cancer using a label-free biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumeria, T.; Kurkuri, M.D.; Diener, K.R.; Parkinson, L.; Losic, D. Label-free reflectometric interference microchip biosensor based on nanoporous alumina for detection of circulating tumour cell. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malima, A.; Siavoshi, S.; Musacchio, T.; Upponi, J.; Yilmaz, C.; Somu, S.; Hartner, W.; Torchilin, V.; Busnaina, A. Highly sensitive microscale in vivo sensor enabled by electrophoretic assembly of nanoparticles for multiple biomarker detection. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4748–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Gamella, M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical bioplatforms for the simultaneous determination of interleukin (IL)-8 MRNA and IL-8 protein oral cancer biomarkers in raw saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, F.; Zaiss, I.; Herzog, D.; Götte, K.; Naim, R.; Hörmann, K. Serum levels of interleukin-6 in patients with primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Ilkhani, H.; Sarparast, M.; Noori, A.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Mousavi, M.F. Electrochemical aptamer/antibody based sandwich immunosensor for the detection of EGFR, a cancer biomarker, using gold nanoparticles as a signaling probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhao, M.; Qiu, B.; Guo, L.; Lin, Z.; Yang, H.H. Ultraselective homogeneous electrochemical biosensor for DNA species related to oral cancer based on nicking endonuclease assisted target recycling amplification. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9204–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, T.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. A ratiometric electrochemical DNA biosensor for detection of exosomal MicroRNA. Talanta 2020, 207, 120298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabahi, A.; Salahandish, R.; Ghaffarinejad, A.; Omidinia, E. Electrochemical nanogenosensor for highly sensitive detection of miR-21 biomarker based on SWCNTgrafted dendritic Au nanostructure for early detection of prostate cancer. Talanta 2020, 209, 120595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluoch, A.O.; Sadik, O.A.; Bedi, G. Development of an oral biosensor for salivary amylase using a monodispersed silver for signal amplification. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 340, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Liao, W.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wong, D.T.; Ho, C.M. Bio/Abiotic interface constructed from nanoscale DNA dendrimer and conducting polymer for ultrasensitive biomolecular diagnosis. Small 2009, 5, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, R.; Patel, V.; Vaqué, J.P.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for oral cancer biomarker IL-6 using carbon nanotube forest electrodes and multilabel amplification. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, S.; Sankhla, B.; Sundaragiri, K.; Bhargava, A. A review of salivary biomarker: A tool for early oral cancer diagnosis. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2017, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malon, R.S.P.; Sadir, S.; Balakrishnan, M.; Córcoles, E.P. Saliva-based biosensors: Noninvasive monitoring tool for clinical diagnostics. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 962903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markopoulos, A.K.; Michailidou, E.Z.; Tzimagiorgis, G. Salivary markers for oral cancer detection. Open Dent. J. 2010, 4, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otieno, B.A.; Krause, C.E.; Latus, A.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Faria, R.C.; Rusling, J.F. On-line protein capture on magnetic beads for ultrasensitive microfluidic immunoassays of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Yang, W.J.; Xu, L.J.; Chen, J.H.; Fu, F.F. A novel electrically magnetic-controllable electrochemical biosensor for the ultra sensitive and specific detection of attomolar level oral cancer-related microRNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Label-free capacitance based aptasensor platform for the detection of HER2/ErbB2 cancer biomarker in serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.E.; Chen, W.H.; Shiang, Y.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Colorimetric detection of platelet-derived growth factors through competitive interactions between proteins and functional gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Godolphin, W.; Jones, L.A.; Holt, J.A.; Wong, S.G.; Keith, D.E.; Levin, W.J.; Stuart, S.G.; Udove, J.; Ullrich, A.; et al. Studies of the HER-2/Neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989, 244, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.S.S.; Wang, X.; Hagen, J.; Naik, R.; Papautsky, I.; Heikenfeld, J. Label free nano-aptasensor for interleukin-6 in protein-dilute bio fluids such as sweat. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3440–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.A.; Schnell, F.; Kaveh-Baghbaderani, Y.; Berensmeier, S.; Schwaminger, S.P. Immunomagnetic separation of microorganisms with iron oxide nanoparticles. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evtugyn, G.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical immuno- and aptasensors for mycotoxin determination. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Xu, L.; Ning, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, G.J. Silicon nanowire biosensor for highly sensitive and multiplexed detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma biomarkers in saliva. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, J.G.; Maji, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanostructured zirconia decorated reduced graphene oxide based efficient biosensing platform for non-invasive oral cancer detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilescu, A.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Titoiu, A.M.; Porumb, R.; Epure, P. Progress in electrochemical (bio)sensors for monitoring wine production. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shellaiah, M.; Sun, K.W. Review on nanomaterial-based melamine detection. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakaria, A.B.M.; Leszczynska, D. Electrochemically prepared unzipped single walled carbon nanotubes-MnO2 nanostructure composites for hydrogen peroxide and glucose sensing. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Tiwari, S.; Augustine, S.; Srivastava, S.; Yadav, B.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Highly sensitive protein functionalized nanostructured hafnium oxide based biosensing platform for non-invasive oral cancer detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Bagbi, Y.; Sarkar, T.; Solanki, P.R. L-Cysteine capped lanthanum hydroxide nanostructures for non-invasive detection of oral cancer biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Yadav, P.; Singh, A.; Kaur, S.; Ramirez-Vick, J.; Chandra, P.; Arora, K.; Singh, S.P. CD 59 targeted ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for fast and noninvasive diagnosis of oral cancer. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Bansal, V.; Garg, S.; Atreja, G.; Bansal, S. The diagnostic role of saliva: A review. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2011, 3, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. Areview of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.A.; Porto-Figueira, P.; Taware, R.; Sukul, P.; Rapole, S.; Câmara, J.S. Unravelling the potential of salivary volatile metabolites in oral diseases. A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Martin Carreras-Presas, C.; Aro, K.; Tu, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics—Current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sapienza, C.; Lee, J.; Powell, J.; Erinle, O.; Yafai, F.; Reichert, J.; Siraj, E.S.; Madaio, M. DNA methylation profiling identifies epigenetic differences between diabetes patients with ESRD and diabetes patients without nephropathy. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehrlich, M.; Lacey, M. DNA hypomethylation and hemimethylation in cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 754, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langie, S.A.; Szarc Vel Szic, K.; Declerck, K.; Traen, S.; Koppen, G.; van Camp, G.; Schoeters, G.; Vanden Berghe, W.; de Boever, P. Whole-genome saliva and blood DNA methylation profiling in individuals with a respiratory allergy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, D.O.; Jeffries, C.D.; Jarskog, L.F.; Thomson, J.M.; Woods, K.; Newman, M.A.; Parker, J.S.; Jin, J.; Hammond, S.M. microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.H.; Parker, E.K.; Williamson, V.; McMichael, G.O.; Fanous, A.H.; Vladimirov, V.I. Experimental validation of candidate schizophrenia gene ZNF804A as target for hsa-miR-137. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 141, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, R.N.; Wang, L.L.; Wang, H.F.S.; Jia, L.P.; Zhang, W.; Shang, L.; Xue, Q.W.; Jia, W.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, H.F.S. Highly sensitive ratiometric electrochemical DNA biosensor based on homogeneous exonuclease III-assisted target recycling amplification and one-step triggered dual-signal output. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 269, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, F.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, G. An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for detection of DNA species related to oral cancer based on nuclease-assisted target recycling and amplification of DNAzyme. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8004–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Patel, P.; Liao, W.; Chaudhry, K.; Zhang, L.; Arellano-Garcia, M.; Hu, S.; Elashoff, D.; Zhou, H.; Shukla, S.; et al. Electrochemical sensor for multiplex biomarkers detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4446–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franzmann, E.J.; Reategui, E.P.; Pedroso, F.; Pernas, F.G.; Karakullukcu, B.M.; Carraway, K.L.; Hamilton, K.; Singal, R.; Goodwin, W.J. Soluble CD44 is a potential marker for the early detection of head and neck cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prevent. 2007, 16, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagler, R.; Bahar, G.; Shpitzer, T.; Feinmesser, R. Concomitant analysis of salivary tumor markers—A new diagnostic tool for oral cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3979–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.-P.; Zhang, C.-P.; Zheng, J.-W.; Li, J.; Chen, W.-T.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Increased Cyfra 21-1 concentration in saliva from primary oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, Y.J.; Lin, C.D.; Lai, C.H.; Tang, C.H.; Huang, S.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Kao, J.Y.; Lin, C.W. Salivary zinc fnger protein 510 peptide as a novel biomarker for detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma in early stages. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayake, N.; Åkerman, S.; Klinge, B.; Lundegren, N.; Jansson, H.; Tryselius, Y.; Sorsa, T.; Gustafsson, A. Salivary biomarkers for detection of systemic diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Wang, C.P.; Tu, M.; Wong, D.T. Oral biofluid biomarker research: Current status and emerging frontiers. Diagnostics 2016, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Garon, E.; Wong, D.T. Salivary diagnostics. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2009, 12, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootveld, M.; Algeo, D.; Silwood, C.J.; Blackburn, J.C.; Clark, A.D. Determination of the Illicit Drug Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (Ghb) in human saliva and beverages by 1 H NMR analysis. Biofactors 2006, 27, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootveld, M.; Silwood, C.J. 1H NMR analysis as a diagnostic probe for human saliva. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 329, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H.; Shimizu, H.; Maeiwa, M. 1H-NMR of human saliva. An application of NMR spectroscopy in forensic science. Forensic Sci. Int. 1987, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Silwood, C.J.; Lynch, E.J.; Seddon, S.; Sheerin, A.; Claxson, A.W.; Grootveld, M.C. 1H-NMR analysis of microbial-derived organic acids in primary root carious lesions and saliva. NMR Biomed. 1999, 12, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.C.; Brennan, L.; Malthouse, J.P.; Roche, H.M.; Gibney, M.J. Effect of acute dietary standardization on the urinary, plasma, and salivary metabolomic profiles of healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada-Nosaka, A.; Fukutomi, S.; Uemura, S.; Hashida, T.; Fujishita, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kyogoku, Y. Preliminary nuclear magnetic resonance studies on human saliva. Arch. Oral Biol. 1991, 36, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, I.; Stretch, C.; Barnaby, P.; Bhatnager, K.; Rankin, K.; Fu, H.; Weljie, A.; Jha, N.; Slupsky, C. Understanding the human salivary metabolome. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, R.; de Morais Guedes, S.; Ferreira, R.; Lobo, M.J.C.; Duarte, J.; Ferrer-Correia, A.J.; Tomer, K.B.; Domingues, P.M.; Amado, F.M. Two-dimensional electrophoresis study of in vitro pellicle formation and dental caries susceptibility. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2006, 114, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shu, R.; Luo, L.J.; Ge, L.H.; Xie, Y.F. Initial comparison of proteomic profiles of whole unstimulated saliva obtained from generalized aggressive periodontitis patients and healthy control subjects. J. Periodontal Res. 2009, 44, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Giusti, L.; Ciregia, F.; Da Valle, Y.; Giacomelli, C.; Donadio, E.; Ferro, F.; Galimberti, S.; Donati, V.; Bazzichi, L.; et al. Correspondence between salivary proteomic pattern and clinical course in primary sjogren syndrome and non-hodgkin’s lymphoma: A case report. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Wang, J. Non-invasive wearable electrochemical sensors: A review. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Wang, J. Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jia, W.; Wang, J. Tattoo-based wearable electrochemical devices: A review. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Wang, M.; Gao, W. The era of digital health: A review of portable and wearable affinity biosensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, T.; Jeddy, N.; Nithya, S.; Muthumeenakshi, R.M. Salivary biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma—An insight. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 6, S51–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lai, Y.-H.; Lim, J.-C.; Huang, N.-T.; Lin, C.-T.; Huang, J.-J. Review of integrated optical biosensors for point-of-care applications. Biosensors 2020, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounik, R.; Gusmaroli, M.; Misun, P.M.; Viswam, V.; Hierlemann, A.; Modena, M.M. Integration of discrete sensors and microelectrode arrays into open microfluidic hanging-drop networks. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Seoul, Korea, 27–31 January 2019; pp. 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Su, Y.; Dai, C.; Jia, J.; Fan, G.-C.; Jiang, L.-P.; Song, R.-B.; Zhu, J.-J. Plasmon coupling-enhanced raman sensing platform integrated with exonuclease-assisted target recycling amplification for ultrasensitive and selective detection of microRNA-21. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12298–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, M.L.Y.; Mach, K.E.; Wong, P.K.; Liao, J.C. Advances and challenges in biosensor-based diagnosis of infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Diag. 2014, 14, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, L.; Wei, D.; Wang, M.; Yao, J. The terahertz electromagnetically inducedtransparency-like metamaterials for sensitive biosensors in the detection of cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Viveka, T.S.; Arvind, K.; Shyamsundar, V.; Kanchan, M.; Alex, S.A.; Mukherjee, A. A facile gold nanoparticle-based ELISA system for detection of osteopontin in saliva: Towards oral cancer diagnostics. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 477, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krampa, F.D.; Aniweh, Y.; Kanyong, P.; Awandare, G.A. Recent advances in the development of biosensors for malaria diagnosis. Sensors 2020, 20, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.K.; Umar, A.; Lohia, P.; Albargi, H.; Castañeda, L.; Dwivedi, D.K. 2D Nanomaterial-based surface plasmon resonance sensors for biosensing applications. Micromachines 2020, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M. Design, optimization and application of small molecule biosensor in metabolic engineering. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mostafa, S.; Behafarid, F.; Croy, J.R.; Ono, L.K.; Li, L.; Yang, J.C.; Frenkel, A.I.; Cuenya, B.R. Shape-dependent catalytic properties of Pt nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15714–15719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, M.A. Small is diferent: Shape-, size-, and composition-dependent properties of some colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: The infuence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phy. Chem. B. 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: Applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H. Shape-dependent plasmon resonances of gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2415–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Chauhan, D.; Renugopalakrishnan, V.; Malhotra, B.D. Biofunctionalized nanodot zirconia-based efcient biosensing platform for noninvasive oral cancer detection. MRS Commun. 2020, 10, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Xiong, C.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, R. Wavelength-resolved simultaneous photoelectrochemical bifunctional sensor on single interface: A newly in vitro approach for multiplexed DNA monitoring in cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, W.; He, Y.; Fu, F. A microfuidic chip-based fuorescent biosensor for the sensitive and specifc detection of label-free single-base mismatch via magnetic beads-based “sandwich” hybridization strategy. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.C.; Chen, C.W.; Chan, M.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chang, W.M.; Chi, L.H.; Hsiao, M. MMP2-sensing up-conversion nanoparticle for fuorescence biosensing in head and neck cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-C.; Chan, M.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Liu, R.-S.; Hsiao, M.; Tsai, D.P. Near-infrared-activated fuorescence resonance energy transfer-based nanocomposite to sense MMP2-overexpressing oral cancer cells. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, S.; Agüí, L.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Design of electrochemical immunosensors using electro-click chemistry. Application to the detection of IL-1β cytokine in saliva. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 133, 107484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, M.; Hasanzadeh, M. Non-invasive bioassay of cytokeratin Fragment 21.1 (Cyfra 21.1) protein in human saliva samples using immunoreaction method: An efficient platform for early-stage diagnosis of oral cancer based on biomedicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Adisposable and ultrasensitive ITO based biosensor modified by 6-phosphonohexanoic acid for electrochemical sensing of IL-1β in human serum and saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1039, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Magnetic beadsbased electrochemical immunosensing of HIF-1α, a biomarker of tumoral hypoxia. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tirado, E.; Salvo, C.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Langa, F.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical immunosensor for simultaneous determination of interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha in serum and saliva using dual screen printed electrodes modified with functionalized double–Walled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 959, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.K.; Oh, E.; Kang, M.S.; Shin, B.S.; Han, S.Y.; Jung, M.; Lee, E.S.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Sung, M.M.; Ng, W.B.; et al. Fluorescence-based immunosensor using three-dimensional CNT network structure for sensitive and reproducible detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma biomarker. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1027, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Pires, N.M.M. Immunodetection of salivary biomarkers by an optical microfluidic biosensor with polyethyleniminemodified polythiophene-C70 organic photodetectors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Q.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, G.; Chen, G.; Bian, Z. One-step quantification of salivary exosomes based on combined aptamer recognition and quantum dot signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umapathy, V.R.; Natarajan, P.M.; Swamikannu, B.; Moses, J.; Jones, S.; Chandran, M.P.; Anbumozhi, M.K. Emerging Biosensors for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis—A Review Unravelling Their Role in Past and Present Advancements in the Field of Early Diagnosis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070498
Umapathy VR, Natarajan PM, Swamikannu B, Moses J, Jones S, Chandran MP, Anbumozhi MK. Emerging Biosensors for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis—A Review Unravelling Their Role in Past and Present Advancements in the Field of Early Diagnosis. Biosensors. 2022; 12(7):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070498
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmapathy, Vidhya Rekha, Prabhu Manickam Natarajan, Bhuminathan Swamikannu, Johnson Moses, Sumathi Jones, Manoj Prathap Chandran, and Madurai Kannan Anbumozhi. 2022. "Emerging Biosensors for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis—A Review Unravelling Their Role in Past and Present Advancements in the Field of Early Diagnosis" Biosensors 12, no. 7: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070498
APA StyleUmapathy, V. R., Natarajan, P. M., Swamikannu, B., Moses, J., Jones, S., Chandran, M. P., & Anbumozhi, M. K. (2022). Emerging Biosensors for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis—A Review Unravelling Their Role in Past and Present Advancements in the Field of Early Diagnosis. Biosensors, 12(7), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070498






