Paper-Based Substrate for a Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Biosensing Platform—A Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
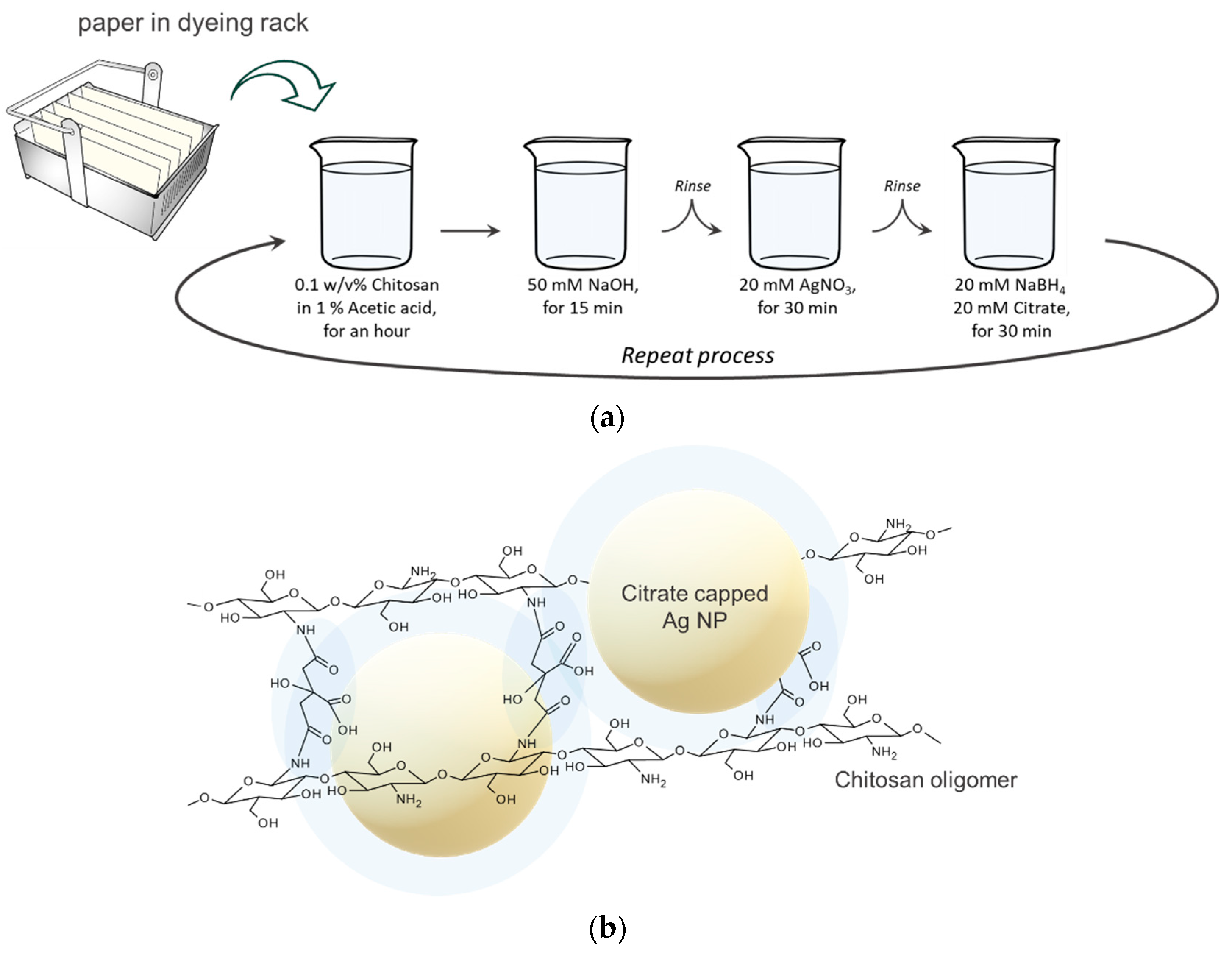
2.2. Fabrication of the Paper SERS Substrate
2.3. Sampling for the Detection of 4-ATP
2.4. Calculation of the Limit of Detection
2.5. Instruments
2.6. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite Layered Paper
3.1.1. Physical Properties
3.1.2. Morphology of the Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite
3.1.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3.2. SERS Measurement
3.2.1. Detection of 4-Aminothiophenol
3.2.2. Application to Biosensing Approaches
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, S.; Zhang, C.; Yuwen, L.; Chao, J.; Zuo, X.; Liu, X.; Song, C.; Fan, C.; Wang, L. Creating SERS hot spots on MoS2 nanosheets with in situ grown gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18735–18741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundare, S.A.; Van Zyl, W.E. A review of cellulose-based substrates for SERS: Fundamentals, design principles, applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6489–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro-Mercado, P.M.; Hernández-Rivera, S.P. Highly sensitive filter paper substrate for SERS trace explosives detection. Int. J. Spectrosc. 2012, 2012, 716527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.; Deprince, A.E.; Demortière, A.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Shevchenko, E.V.; Gray, S.K.; Welp, U.; Vlasko-Vlasov, V.K. Self-assembled large au nanoparticle arrays with regular hot spots for SERS. Small 2011, 7, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restaino, S.M.; White, I.M. A critical review of flexible and porous SERS sensors for analytical chemistry at the point-of-sample. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1060, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantz, K.C.; Meyer, A.F.; Wittenberg, N.J.; Im, H.; Kurtuluş, Ö.; Lee, S.H.; Lindquist, N.C.; Oh, S.-H.; Haynes, C.L. Recent progress in SERS biosensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.; Moody, A.; Payne, T.; Sarabia, G.; Daniel, A.; Sharma, B. In vitro and in vivo SERS biosensing for disease diagnosis. Biosensors 2018, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarrotxena, N.; Liu, B.; Fabris, L.; Bazan, G.C. Antitags: Nanostructured tools for developing SERS-based ELISA analogs. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4954–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Cho, Y.-W.; Kim, T.-H. Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance sensors for sensitive optical detection of pathogens. Biosensors 2022, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidheini, L.; Tiefenauer, R.F.; Gatterdam, V.; Frutiger, A.; Sannomiya, T.; Aramesh, M. Self-assembly of nanodiamonds and plasmonic nanoparticles for nanoscopy. Biosensors 2022, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, H.; Oh, S.-H.; Maier, S.A.; Homola, J. Advances and applications of nanophotonic biosensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Luo, X.; Bazuin, C.G.; Masson, J.-F. In situ growth of AuNPs on glass nanofibers for SERS sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55349–55361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Su, S.; Xu, T.; Zhong, Y.; Zapien, J.A.; Li, J.; Fan, C.; Lee, S.T. Silicon nanowires-based highly-efficient SERS-active platform for ultrasensitive DNA detection. Nano Today 2011, 6, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic single step detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus using gold coated polydimethylsiloxane as the active substrate and aptamer modified gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cai, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Pan, N.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, J.G. Tuning chemical enhancement of SERS by controlling the chemical reduction of graphene oxide nanosheets. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.W.Y.; Silverson, V.A.D.; Mccoy, C.P.; Donnelly, R.F.; Bell, S.E.J. Preaggregated Ag nanoparticles in dry swellable gel films for off-the-shelf surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8106–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarin, A.Y.; Terekhov, S.N.; Kholostov, K.I.; Bondarenko, V.P. SERS-active substrates based on n-type porous silicon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 6969–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarenka, H.; Girel, K.; Zavatski, S.; Panarin, A.; Terekhov, S. Progress in the development of SERS-active substrates based on metal-coated porous silicon. Materials 2018, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Liu, G.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Y.; Ghafoor, S.; Huang, W.; Zu, Z.; Lu, Y. A porous Au–Ag hybrid nanoparticle array with broadband absorption and high-density hotspots for stable SERS analysis. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9587–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xiao, T.-H.; Luo, Z.; Kitahama, Y.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kishimoto, N.; Itoh, T.; Cheng, Z.; Goda, K. Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, G.; Li, H. Effect of nanostructured silicon on surface enhanced Raman scattering. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6629–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Ansah, I.B.; Park, J.S.; Dang, H.; Choi, N.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Yoo, S.M.; et al. Early and direct detection of bacterial signaling molecules through one-pot au electrodeposition onto paper-based 3D SERS substrates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-J.; Chiang, W.-H. Ag microplasma-engineered nanoassemblies on cellulose papers for surface-enhanced raman scattering and catalytic nitrophenol reduction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 6364–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, W.A.; Su, W.-N.; Beyene, A.B.; Huang, W.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hwang, B.-J. Flexible hydrophobic filter paper-based SERS substrate using silver nanocubes for sensitive and rapid detection of adenine. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Oh, K.; Choi, H.-K.; Lee, S.G.; Youn, H.J.; Lee, H.L.; Jeong, D.H. Subnanomolar sensitivity of filter paper-based SERS sensor for pesticide detection by hydrophobicity change of paper surface. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Hyung, J.; Noh, H. Rationalization of in-situ synthesized plasmonic paper for colorimetric detection of glucose in ocular fluids. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebe, H.S.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Browne, W.R.; Bell, S.E.J. Filter paper based SERS substrate for the direct detection of analytes in complex matrices. Analyst 2021, 146, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; White, I.M. Inkjet printed surface enhanced raman spectroscopy array on cellulose paper. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9626–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torul, H.; Çiftçi, H.; Çetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Boyacı, I.H.; Tamer, U. Paper membrane-based SERS platform for the determination of glucose in blood samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8243–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Foda, M.F.; Zhu, Y. Strawberry-like SiO2/Ag nanocomposites immersed filter paper as SERS substrate for acrylamide detection. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Bai, S.; Tu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lu, J.; He, D. Highly sensitive and stable SERS substrate fabricated by co-sputtering and atomic layer deposition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, Y.; Yabu, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Ijiro, K.; Shimomura, M. Arrays of triangular shaped pincushions for SERS substrates prepared by using self-organization and vapor deposition. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Xu, F.; Wei, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Shi, X. Electrochemical synthesis of chitosan/silver nanoparticles multilayer hydrogel coating with pH-dependent controlled release capability and antibacterial property. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 202, 111711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chook, S.W.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Neoh, H.M.; Jamal, R. Effective immobilization of silver nanoparticles on a regenerated cellulose–chitosan composite membrane and its antibacterial activity. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 5061–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Lin, M.; Lin, H.; Huang, M. Facile synthesis of cellulose nanofiber nanocomposite as a SERS substrate for detection of thiram in juice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, M.; Excoffier, S.; Mermet, J.M. A study of the relation between the limit of detection and the limit of quantitation in inductively coupled plasma spectrochemistry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 1997, 52, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinteza, L.; Scomoroscenco, C.; Voicu, S.; Nistor, C.; Nitu, S.; Trica, B.; Jecu, M.-L.; Petcu, C. Chitosan-stabilized Ag nanoparticles with superior biocompatibility and their synergistic antibacterial effect in mixtures with essential oils. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalaivani, R.; Maruthupandy, M.; Muneeswaran, T.; Hameedha Beevi, A.; Anand, M.; Ramakritinan, C.M.; Kumaraguru, A.K. Synthesis of chitosan mediated silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for potential antimicrobial applications. Front. Lab. Med. 2018, 2, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Maclean, N.; Mahiddine, S. Mechanisms of nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in solution. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7610–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, J.; Penlidis, A.; Moresoli, C. Viscoelastic properties of crosslinked chitosan films. Processes 2019, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Kong, X. Review of recent progress of plasmonic materials and Nano-structures for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Materials 2015, 8, 3024–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.H.; Atalla, R.H. Band assignments in the Raman spectra of celluloses. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 160, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.; Eichhorn, S.J. Crystalline and amorphous deformation of process-controlled cellulose-II fibres. Polymer 2005, 46, 6380–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, A.; Hanuza, J.; Wandas, M.; Dymińska, L. Determination of N-acetylation degree in chitosan using Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasekara, N.D.; Michud, A.; Zhu, C.; Rahatekar, S.; Sixta, H.; Eichhorn, S.J. Deformation mechanisms in ionic liquid spun cellulose fibers. Polymer 2016, 99, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.J.; Sirichaisit, J.; Young, R.J. Deformation mechanisms in cellulose fibres, paper and wood. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlinger, N.; Schwanninger, M.; Reinecke, A.; Burgert, I. Molecular Changes during Tensile Deformation of Single Wood Fibers Followed by Raman Microscopy. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quynh, L.M.; Nam, N.H.; Kong, K.; Nhung, N.T.; Notingher, I.; Henini, M.; Luong, N.H. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy study of 4-ATP on gold nanoparticles for basal cell carcinoma fingerprint detection. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2563–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Soni, R.K. Silver nanocube- and nanowire-based SERS substrates for ultra-low detection of PATP and thiram molecules. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, E. Effect of silvernanoplates on Raman spectra of p-aminothiophenol assembled on smooth macroscopic gold and silver surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chin, W.S. Rapid fabrication of a flexible and transparent Ag Nanocubes@PDMS film as a SERS substrate with high performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 37538–37548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier-Boss, P. Review on SERS of bacteria. Biosensors 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azevedo, E.P.; Retarekar, R.; Raghavan, M.L.; Kumar, V. Mechanical properties of cellulose: Chitosan blends for potential use as a~coronary artery bypass graft. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Noh, H. Paper-Based Substrate for a Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Biosensing Platform—A Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite Approach. Biosensors 2022, 12, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050266
Kang Y, Kim HJ, Lee SH, Noh H. Paper-Based Substrate for a Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Biosensing Platform—A Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite Approach. Biosensors. 2022; 12(5):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050266
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Yuri, Hyeok Jung Kim, Sung Hoon Lee, and Hyeran Noh. 2022. "Paper-Based Substrate for a Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Biosensing Platform—A Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite Approach" Biosensors 12, no. 5: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050266
APA StyleKang, Y., Kim, H. J., Lee, S. H., & Noh, H. (2022). Paper-Based Substrate for a Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Biosensing Platform—A Silver/Chitosan Nanocomposite Approach. Biosensors, 12(5), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050266




