LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Pathogen Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of the LAMP Assay
2.1. Principle
2.2. Primer Design
2.3. Features for Rapid Pathogen Detection
3. LAMP Detection Methods
3.1. End-Point Detection
3.1.1. Colorimetric Detection

3.1.2. Electrochemical Detection
3.1.3. Lateral Flow Assay Detection
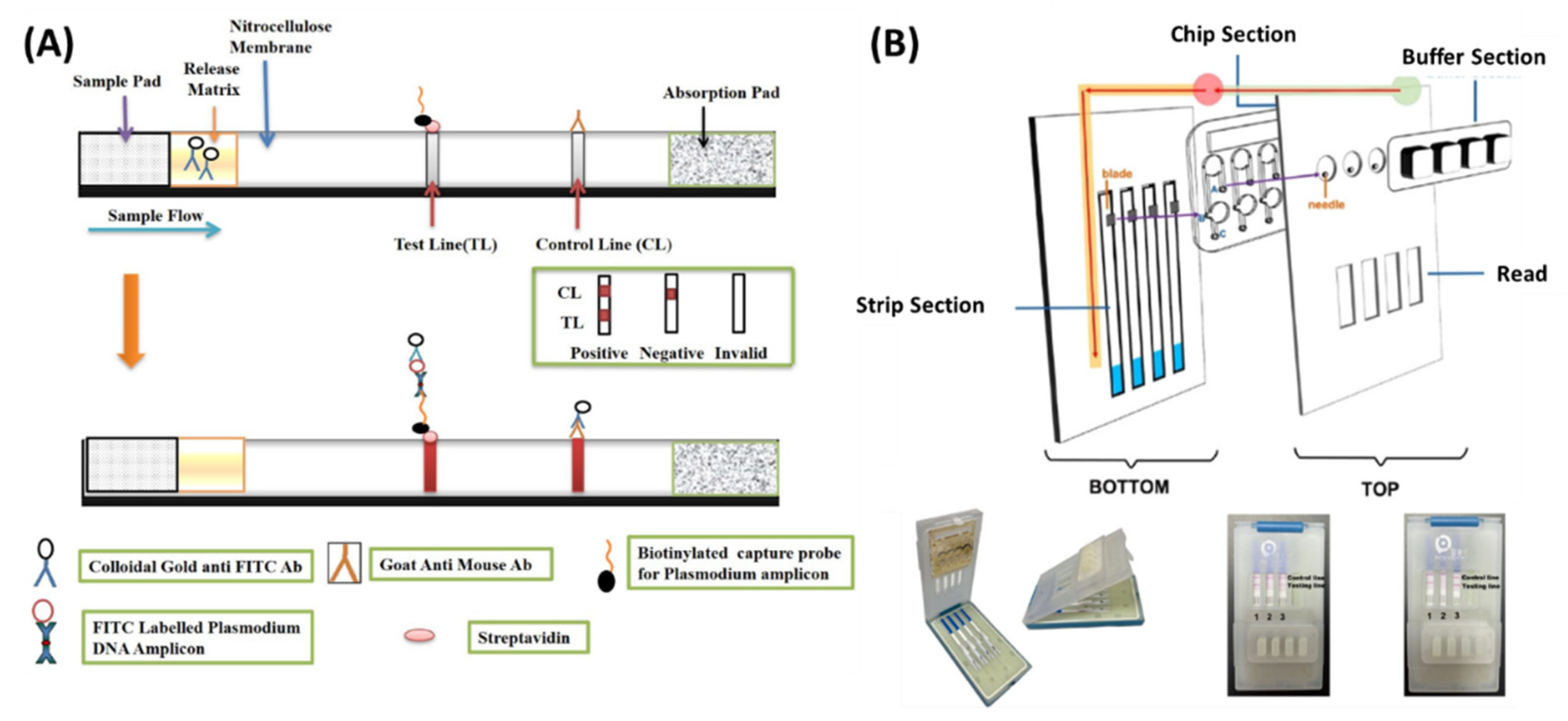
3.1.4. Optical Detection
3.1.5. Diffusometric Method
3.2. Real-Time Detection
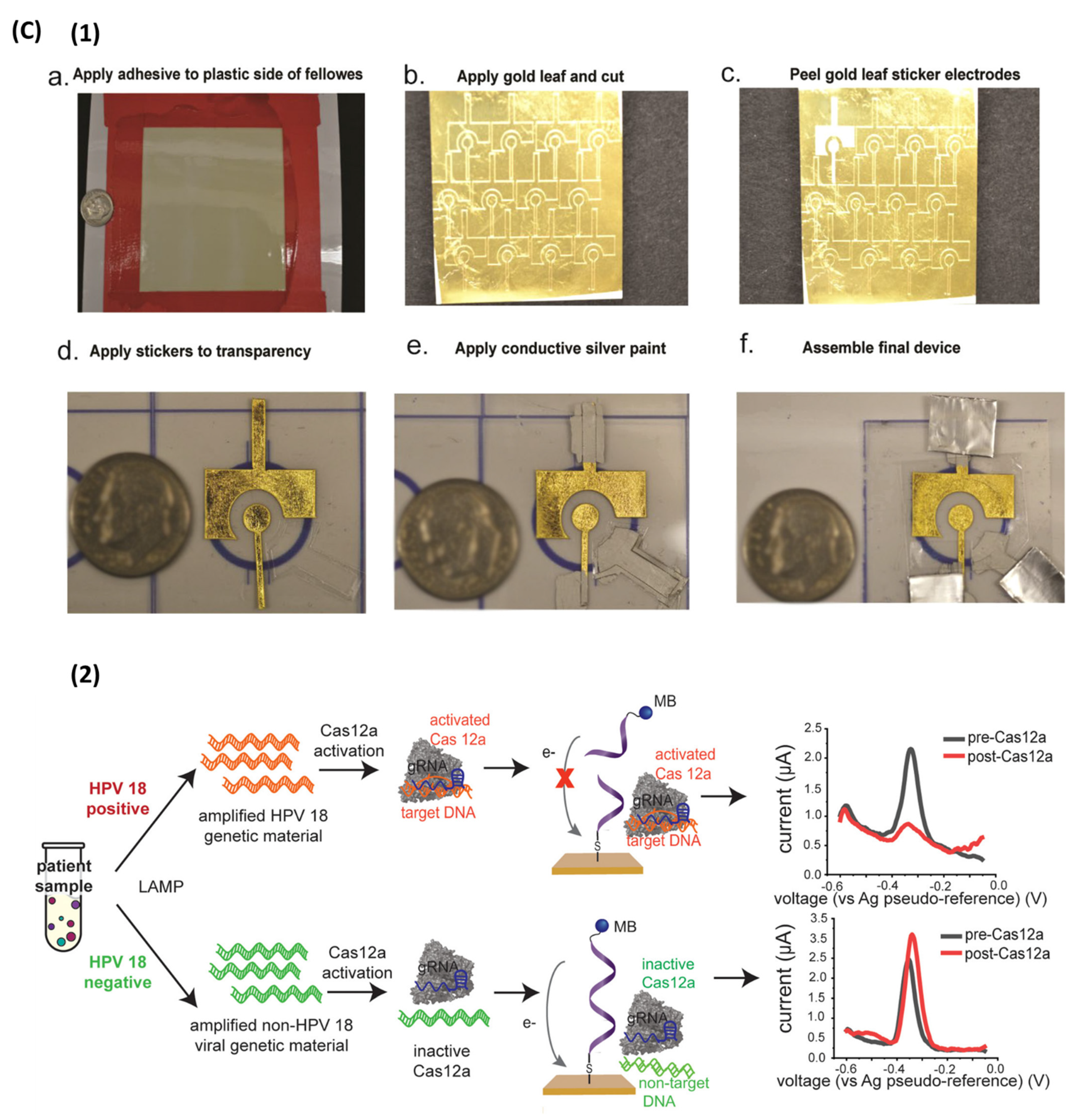
3.2.1. Electrochemical Detection
3.2.2. Smartphone-Based Real-Time Detection
| Technique | Pathogen | Signal Transduction Material | Detection Method | Time | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical | Salmonella | Bis-NQIM-R (naphthoquinone- imidazole) | Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) | 10 min | 1 copy/reaction | [113] |
| Flavobacterium columnare | [Os-(bpy)2dppz]2+, PhP and MB and Ru(NH3)63+ | Square wave voltammetry (SWV) | 30 min | 2 copies/reaction | [109] | |
| E. coli O157:H7 S. enterica | Methylene blue | Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) | 30 min | 10 copies/reaction 1 copy/reaction | [112] | |
| Hepatitis B virus | Methylene blue | Square wave voltammetry (SWV) | 60 min | 6.18 fg/µL | [111] | |
| Smartphone-based | E. coli O157:H7 | Eriochrome Black T (EBT) | Colorimetric | 60 min | 10 copies/μL | [118] |
| N. gonorrhoeae | SYTO | Fluorescence | 40 min | 3.5 copies per 10 μL | [115] | |
| SARS-CoV-2 | SYBR | Fluorescence | 65 min | 20 copies/ μL | [120] |

4. LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors
4.1. LAMP-on-a-Chip
4.1.1. Classical Microfluidic Chip
4.1.2. Paper-Based Chips
4.1.3. Fully Integrated Chips


| Technique | Target | Pathogen | Material | Readout | Time | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical | DNA | Salmonella spp. E. coli O157:H7 | Polycarbonate | Colorimetric | 30 min | 2.5 × 102 copies/mL | [121] |
| DNA | E. coli and Enterococcus spp. | PMMA | Colorimetric | 35 min | 4 copies/well | [122] | |
| DNA | V. parahaemolyticus | PMMA | Fluorescence | 80 min | 3.1 × 101 copies/reaction | [124] | |
| RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | PMMA | Fluorescence | 90 min | 20 copies/µL | [130] | |
| Paper-based | DNA | Sus scrofa (porcine) Bacillus subtilis | Cellulose paper | Colorimetric | 10 min 18 min | 3.43 × 10 −1 copies/μL 2.2 × 103 copies/μL | [133] |
| DNA | Salmonella spp. | Polydopamine coated paper-polycarbonate | Colorimetric | 65 min | 1 × 102 CFU/mL | [137] | |
| DNA | VRE | Paper-PDMS | Colorimetric | 45 min | 102 CFU/mL | [138] | |
| RNA | Zika virus | G4-cellulose paper | Colorimetric | 15 min | 1 copy/µL | [134] | |
| Integrated chips | DNA | E. coli O157:H7, MRSA, MSSA | Silica beads-PMMA | Fluorescence | 2 h | 102 CFU/100 µL | [141] |
| DNA | S. typhimurium and V. parahaemolyticus | Glass microbeads-PPMA | Colorimetric | 80 min | 50 CFU | [143] | |
| DNA | VRE | FTA card-PDMS | Colorimetric | 45 min | 102 CFU/mL | [146] | |
| RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | Magnetic beads | Fluorescence | 82 min | 5000 copies/reaction | [147] |
4.2. Digital LAMP

| Target | Pathogen | Reaction Chamber Type | No. of Chambers | Sample Volume | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA | Streptococcus pneumoniae | Droplet | 6500 | ~2.3 nL | 10 copies/μL | [154] |
| λDNA | EGFR L858R mutation | Droplet | 10,000 | ~1 nL | 1 copy/μL | [155] |
| DNA | N. gonorrhoeae | Droplet | 100,000 | ~10 pL | 600 copies/µL | [153] |
| Plasmid | HPV | Microwells | 4480 | ~4.5 nL | 1 fg/μL | [159] |
| DNA | VRE | Microwells | 736 | ~22.6 nL | 11 copies/30 μL | [152] |
| DNA | Β-lactin | Microwells | 384 | ~6 nL | -- | [150] |
5. Application of LAMP in Clinical Diagnosis
FDA-Approved LAMP-Based Devices
| Method | Target Gene | Time | Sensitivity | Specimen (Swab Type) | LOD | EUA by FDA | Price Per Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STOP Covid [161] | N gene | 70 min | 91.6% | Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs | 100 copies/reaction | No | $40 USD |
| Penn-RAMP [160] | ORF1ab and N gene | 60 min | 84% | Nasopharyngeal swab and saliva | 5 copies/reaction | No | NA |
| DETECTR [162] | N and E gene | 40 min | 95% | Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs | 10 copies/µL | No | NA |
| iSCAN [168] | N and E gene | 60 min | 86% | Nasopharyngeal swab | 10 copies/sample | No | $2–5 USD |
| iLACO [169] | ORF1ab gene | 40 min | 89.9% | -- | 10 copies/µL | No | NA |
| Lucira Check-it [165] | N gene | 30 min | 98% | Nasal swab | 2700 copies/swab | Yes | $68 USD |
| Detect COVID-19 test [166] | ORF1ab gene | 65 min | 95% | Nasal swab | 800 copies/mL | Yes | $55 USD |
| Metrix COVID-19 test [170] | ORF1ab and N gene | 30 min | 95% | Nasal swabs and saliva | 667 copies/mL | Yes | NA |
| DxLab COVID-19 test [171] | M gene | 25 min | 95% | Nasal swab | 3000 copies/swab | Yes | NA |
6. Limitations of LAMP
6.1. Cross-Interference in Multiplex Detection
6.2. Uncertainty of Primer Design
6.3. Carry-Over Contamination
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
7.1. Alternative Methods
7.2. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Rothman, R. PCR-based diagnostics for infectious diseases: Uses, limitations, and future applications in acute-care settings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeke, T.; Jenkins, G.R. Influence of DNA extraction methods, PCR inhibitors and quantification methods on real-time PCR assay of biotechnology-derived traits. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 396, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zeng, D.; Yan, C.; Chen, W.; Ren, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xue, F.; Ji, D.; Tang, F.; et al. Rapid and accurate detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in beef using microfluidic wax-printed paper-based ELISA. Analyst 2020, 145, 3106–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, P.; Fan, L.; Shi, Y. Highly sensitive multiplex detection of foodborne pathogens using a SERS immunosensor combined with novel covalent organic frameworks based biologic interference-free Raman tags. Talanta 2022, 243, 123369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Choi, S.-W.; Chang, H.-J.; Chun, H.S. Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Fresh Lettuce Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Combined with Immunomagnetic Separation. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, H.O.; Cetin, A.E.; Azimzadeh, M.; Topkaya, S.N. Pathogen detection with electrochemical biosensors: Advantages, challenges and future perspectives. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, C.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Q. Pathogen detection strategy based on CRISPR. Microchem. J. 2022, 174, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesakumar, N.; Lakshmanakumar, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Jbb, A.J.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Principles and Recent Advances in Biosensors for Pathogens Detection. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 10063–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumford, E.A.; Lu, J.; Spaczai, I.; Prasetyo, M.E.; Zheng, E.M.; Zhang, H.; Kamei, D.T. Developments in integrating nucleic acid isothermal amplification and detection systems for point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12491–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.; Armes, N. DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins. PLOS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Daubendiek, S.L.; Zillman, M.A.; Ryan, K.; Kool, E.T. Rolling Circle DNA Synthesis: Small Circular Oligonucleotides as Efficient Templates for DNA Polymerases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Compton, J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature 1991, 350, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.; Xu, Y.; Kong, H. Helicase-dependent isothermal DNA amplification. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suea-Ngam, A.; Bezinge, L.; Mateescu, B.; Howes, P.D.; Demello, A.J.; Richards, D.A. Enzyme-Assisted Nucleic Acid Detection for Infectious Disease Diagnostics: Moving toward the Point-of-Care. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2701–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Duan, J.; Chen, J.; Ding, S.; Cheng, W. Recent advances in rolling circle amplification-based biosensing strategies-A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1148, 238187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, H.; Kawai, S.; Takahashi, N.; Hirai, M.; Tanabe, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Evaluation of a Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method as a Tool for Diagnosis of Infection by the Zoonotic Simian Malaria Parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Ghani, R.; Al-Mekhlafi, A.M.; Karanis, P. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for malarial parasites of humans: Would it come to clinical reality as a point-of-care test? Acta Trop. 2012, 122, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, L.Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Fang, X.; Kong, J.; Draz, M.S.; Cao, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique: Principle, development and wide application in food safety. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5551–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.-P.; Othman, S.; Lau, Y.-L.; Radu, S.; Chee, H.-Y. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Guan, G.; Du, P.; Gou, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, Q.; et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method based on two species-specific primer sets for the rapid identification of Chinese Babesia bovis and B. bigemina. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-J.; Xiong, C.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.-S.; Zhou, X.-W. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): Emergence as an Alternative Technology for Herbal Medicine Identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parida, M.; Sannarangaiah, S.; Dash, P.K.; Rao, P.V.L.; Morita, K. Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A new generation of innovative gene amplification technique; perspectives in clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev. Med. Virol. 2008, 18, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, J.N.; Steenberg, C.D.; Bois, J.S.; Wolfe, B.R.; Pierce, M.B.; Khan, A.R.; Dirks, R.M.; Pierce, N.A. NUPACK: Analysis and design of nucleic acid systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, P.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A novel rapid detection platform for pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Alexandrou, G.; Toumazou, C.; Kalofonou, M. Automating the Design of Cancer Specific DNA Probes Using Computational Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society, Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, C.; Lu, X.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.-Y.; Wei, C. GLAPD: Whole Genome Based LAMP Primer Design for a Set of Target Genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savonnet, M.; Aubret, M.; Laurent, P.; Roupioz, Y.; Cubizolles, M.; Buhot, A. Kinetics of Isothermal Dumbbell Exponential Amplification: Effects of Mix Composition on LAMP and Its Derivatives. Biosensors 2022, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craw, P.; Balachandran, W. Isothermal nucleic acid amplification technologies for point-of-care diagnostics: A critical review. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2469–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Chen, W.-L.; Chuang, H.-S. Rapid and Sensitive Pathogen Detection by DNA Amplification Using Janus Particle-Enabled Rotational Diffusometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13945–13951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-J.; Orlova, N.; Oakes, B.L.; Ma, E.; Spinner, H.B.; Baney, K.L.M.; Chuck, J.; Tan, D.; Knott, G.J.; Harrington, L.B.; et al. CasX enzymes comprise a distinct family of RNA-guided genome editors. Nature 2019, 566, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, K.; Najib, M.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Mohamad, S.; Palaz, F.; Ozsoz, M.; Aziah, I. RT-LAMP CRISPR-Cas12/13-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Methods. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Lee, J.W.; Essletzbichler, P.; Dy, A.J.; Joung, J.; Verdine, V.; Donghia, N.; Daringer, N.M.; Freije, C.A.; et al. Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2. Science 2017, 356, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatoum-Aslan, A. CRISPR Methods for Nucleic Acid Detection Herald the Future of Molecular Diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1681–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, A.; Bumbrah, G.S.; Ruwali, M.; Hameed, S.; Fatima, Z. Diagnostic efficiency of RT-LAMP integrated CRISPR-Cas technique for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2022, 116, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Luo, X.; Xue, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Tao, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Sensitive and rapid on-site detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a gold nanoparticle-based high-throughput platform coupled with CRISPR/Cas12-assisted RT-LAMP. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Sahu, U.; Kar, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Development of a Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique for specific and early detection of Mycobacterium leprae in clinical samples. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, R.; Shearer, J.; Sun, F. Rapid Detection of Clostridium botulinum in Food Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Yan, C.; Du, B.; Zhao, H.; Xue, G.; Zheng, P.; Feng, Y.; Cui, J.; Gan, L.; Feng, J.; et al. Development of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Targeting lytA and psaA Genes for Rapid and Visual Diagnosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 816997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, N.; Guo, G.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Rehman, N.U.; Zheng, L.; Wang, P.; Han, S.; et al. Investigation of Streptococcus agalactiae using pcs B-based LAMP in milk, tilapia and vaginal swabs in Haikou, China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 128, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, M.; Honda, E.; Ogura, A.; Nomoto, A.; Hanaki, K.-I. Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. BioTechniques 2009, 46, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-S.; Shao, N.; Chen, J.-W.; Qi, W.-B.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y.-J.; Bian, S.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, S.-C. Multiplex and visual detection of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) based on Hive-Chip and direct loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1140, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Jing, W.; Liu, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, Z.; Xia, H.; Sui, G. A self-powered rapid loading microfluidic chip for vector-borne viruses detection using RT-LAMP. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2021, 333, 129521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, H.; Zou, B.; Zhou, G. Multiplex detection of blood-borne pathogens on a self-driven microfluidic chip using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Ding, G.; Li, G.; Yang, G.; Han, Y.; Hao, N.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, W. Rapid detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens using visual high-throughput microfluidic chip. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Jayawardena, A.; Chan, J.; Tan, S.M.; Alan, T.; Kwan, P. An ultra-portable, self-contained point-of-care nucleic acid amplification test for diagnosis of active COVID-19 infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, P.; Gatto, F.; Cortimiglia, C.; Bassi, D.; Lucchini, F.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Pompa, P.P. Colorimetric Point-of-Care Detection of Clostridium tyrobutyricum Spores in Milk Samples. Biosensors 2021, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Xu, J.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Equipment-free nucleic acid extraction and amplification on a simple paper disc for point-of-care diagnosis of rotavirus A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1018, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Coulter, F.J.; Yang, M.; Smith, J.L.; Tafesse, F.G.; Messer, W.B.; Reif, J.H. A lyophilized colorimetric RT-LAMP test kit for rapid, low-cost, at-home molecular testing of SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid detection of Fusarium proliferatum causing ear and kernel rot on maize. Crop Prot. 2020, 132, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Dai, Z.; Tian, X.; Jiang, X. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on combined aptamers magnetic capture and loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Food Control 2018, 85, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish Kumar, T.; Navaneeth Krishnan, A.; Joseph Sahaya Rajan, J.; Makesh, M.; Jithendran, K.P.; Alavandi, S.V.; Vijayan, K.K. Visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for the rapid diagnosis of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) infection. 2018, 117, 1485–1493. (EHP) Infection 2018, 117, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Rapid detection of milk vetch dwarf virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 261, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, S.; Pal, V.; Tripathi, N.K.; Goel, A.K. Development of a set of three real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays for detection of Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, K.G.; Estrela, P.F.N.; Mendes, G.D.M.; dos Santos, C.A.; Silveira-Lacerda, E.D.P.; Duarte, G.R.M. Rapid molecular diagnostics of COVID-19 by RT-LAMP in a centrifugal polystyrene-toner based microdevice with end-point visual detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanas, C.; Alam, M.; Loeb, J.C.; Lednicky, J.A.; Wu, C.-Y.; Fan, Z.H. A Valve-Enabled Sample Preparation Device with Isothermal Amplification for Multiplexed Virus Detection at the Point-of-Care. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokelmann, L.; Nickel, O.; Maricic, T.; Pääbo, S.; Meyer, M.; Borte, S.; Riesenberg, S. Point-of-care bulk testing for SARS-CoV-2 by combining hybridization capture with improved colorimetric LAMP. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.S.; Hsieh, K.; Soh, H.T.; Plaxco, K.W. Electrochemical real-time nucleic acid amplification: Towards point-of-care quantification of pathogens. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surucu, O.; Öztürk, E.; Kuralay, F. Nucleic Acid Integrated Technologies for Electrochemical Point-of-Care Diagnostics: A Comprehensive Review. Electroanalysis 2021, 34, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Yang, J.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Label-Free and Amplified Electrochemical Detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Folded Nucleic Acid Secondary Structures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B880–B884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.H.J.; Hsieh, K.; Patterson, A.S.; Ferguson, B.S.; Eisenstein, M.; Plaxco, K.W.; Soh, H.T. Accurate Zygote-Specific Discrimination of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Using Microfluidic Electrochemical DNA Melting Curves. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 3227–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fang, X.; Ye, D.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Kong, J. A real-time microfluidic multiplex electrochemical loop-mediated isothermal amplification chip for differentiating bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi, A.; Mohammadpour, Z.; Zuo, X.; Safavi, A. Nucleic acid-based electrochemical nanobiosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiya, E. Portable Electrochemical DNA Sensors Based on Gene Amplification Reactions to Screen and Identify Pathogen and SNPs. Sensors 2022, 22, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Saito, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Rao, S.R.; Furui, S.; Hino, A.; Takamura, Y.; Takagi, M.; Tamiya, E. Electrochemical genosensor for the rapid detection of GMO using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Analyst 2009, 134, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Inada, M.; Ito, K. A novel voltammetric approach for real-time electrochemical detection of targeted nucleic acid sequences using LAMP. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 539, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Bai, L.; Yuan, R. Development of an electrochemical method for Ochratoxin A detection based on aptamer and loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, F.; Stolowicz, F.; Vojnov, A.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Larocca, L.; Carrillo, C.; Cortón, E. Towards a versatile and economic Chagas Disease point-of-care testing system, by integrating loop-mediated isothermal amplification and contactless/label-free conductivity detection. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavieh, M.; Kanakasabapathy, M.K.; Tarlan, F.; Ahmed, M.U.; Zourob, M.; Asghar, W.; Shafiee, H. Emerging Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification-Based Microchip and Microdevice Technologies for Nucleic Acid Detection. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based microfluidic chip for pathogen detection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 60, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroenram, W.; Kampeera, J.; Arunrut, N.; Karuwan, C.; Sappat, A.; Khumwan, P.; Jaitrong, S.; Boonnak, K.; Prammananan, T.; Chaiprasert, A.; et al. Graphene-based electrochemical genosensor incorporated loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid on-site detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampeera, J.; Pasakon, P.; Karuwan, C.; Arunrut, N.; Sappat, A.; Sirithammajak, S.; Dechokiattawan, N.; Sumranwanich, T.; Chaivisuthangkura, P.; Ounjai, P.; et al. Point-of-care rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood using loop-mediated isothermal amplification and graphene-based screen-printed electrochemical sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Duan, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Ding, S.; Min, X. A LAMP-based ratiometric electrochemical sensing for ultrasensitive detection of group B. Streptococci with improved stability and accuracy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Robson, J.M.; Fan, A.; Bono, M.S.; Furst, A.L.; Klapperich, C.M. Electrochemical Strategy for Low-Cost Viral Detection. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosik, M.; Jirakova, L.; Anton, M.; Vojtesek, B.; Hrstka, R. Genomagnetic LAMP-based electrochemical test for determination of high-risk HPV16 and HPV18 in clinical samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1042, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, M.; Moranova, L.; Hrstka, R.; Bartosik, M. Application of an electrochemical LAMP-based assay for screening of HPV16/HPV18 infection in cervical samples. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Chavarría, R.G.; Castillo-Villanueva, E.; Alvarez-Serna, B.E.; Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Ramírez-Zamora, R.M.; Buitrón, G.; Alvarez-Icaza, L. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based electrochemical sensor for detecting SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater samples. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Li, J.; Quan, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Shen, A. Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification coupled with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor assay for Mycoplasma pneumoniae detection. AMB Express 2019, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Ma, K.; Yi, X.; Xiong, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. The rapid and visual detection of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification linked to a nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Kang, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, P.; Sun, B. A Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification with a Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor Assay to Detect Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Endophthalmitis. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-Q.; Huang, X.-H.; Guo, L.-Q.; Shen, Z.-C.; Lv, L.-X.; Li, F.-X.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Zhang, A.D.-F. Rapid and Visual Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Aquatic Foods Using blaCARB-17 Gene-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Lateral Flow Dipstick (LAMP-LFD). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Zhai, X.; Lei, C.; Ye, X.; Kang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Development and application of a visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick (LAMP-LFD) method for rapid detection of Salmonella strains in food samples. Food Control. 2019, 104, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Shi, H. Combining loop-mediated isothermal amplification and nanozyme-strip for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of viable Listeria monocytogenes cells and biofilms. LWT 2021, 154, 112641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Cai, S.; Ye, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Quantum Dot Nanobeads-Labelled Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strip for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella typhimurium Based on Strand Displacement Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Engineering 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Tan, Q.; Ying, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, S. A Label-Based Polymer Nanoparticles Biosensor Combined with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Rapid, Sensitive, and Highly Specific Identification of Brucella abortus. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 758564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Bhardwaj, N.; Singh, J.; Kumari, S.; Savargaonkar, D.; Anvikar, A.R.; Das, J. Advanced Multiplex Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (mLAMP) Combined with Lateral Flow Detection (LFD) for Rapid Detection of Two Prevalent Malaria Species in India and Melting Curve Analysis. Diagnostics 2021, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Multiplex reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tang, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Lu, B.; Yu, J.; Zhu, K.; Li, B.; Du, Y. SARS-CoV-2 Point-of-Care (POC) Diagnosis Based on Commercial Pregnancy Test Strips and a Palm-Size Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11956–11964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpartida-Cardenas, K.; Miscourides, N.; Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Yu, L.-S.; Moser, N.; Baum, J.; Georgiou, P. Quantitative and rapid Plasmodium falciparum malaria diagnosis and artemisinin-resistance detection using a CMOS Lab-on-Chip platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.-L.; Wei, S.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-W. A polycarbonate-based surface plasmon resonance sensing cartridge for high sensitivity HBV loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 32, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Fang, J.; de la Chapelle, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Huang, G.; Yang, X.; Fu, W. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering inspired by programmable nucleic acid isothermal amplification technology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Kim, S.; Han, Y.D.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, J.-H.; Yoon, H.; Yoon, H.C. Salmonella typhimurium Sensing Strategy Based on the Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Using Retroreflective Janus Particle as a Nonspectroscopic Signaling Probe. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, K.; Xiao, C.; Tong, Z.; Jin, L.; He, N.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Highly sensitive smartphone-based detection of Listeria monocytogenes using SYTO9. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 33, 1933–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawattanapaiboon, K.; Kiatpathomchai, W.; Santanirand, P.; Vongsakulyanon, A.; Amarit, R.; Somboonkaew, A.; Sutapun, B.; Srikhirin, T. SPR-DNA array for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in combination with loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorgmehr, A.; Yazdanparast, R.; Mollasalehi, H. Non-crosslinking gold nanoprobe-LAMP for simple, colorimetric, and specific detection of Salmonella typhi. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, M.S.; Lu, X. Development of a Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)—Surface Enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) Assay for the Detection of Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis. Theranostics 2016, 6, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Paris, J.L.; Roumani, F.; Diéguez, L.; Prado, M.; Espiña, B.; Abalde-Cela, S.; Garrido-Maestu, A.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L. Multifuntional Gold Nanoparticles for the SERS Detection of Pathogens Combined with a LAMP–in–Microdroplets Approach. Materials 2020, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, K.N.; Berglund, G.D.; Linnes, J.C.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L.; Wereley, S.T. DNA Microviscosity Characterization with Particle Diffusometry for Downstream DNA Detection Applications. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13334–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, K.N.; Moehling, T.; Lee, D.H.; Wereley, S.T.; Linnes, J.C.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L. Particle Diffusometry: An Optical Detection Method for Vibrio cholerae Presence in Environmental Water Samples. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, D.; Hsieh, H.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Chen, W.-L.; Chuang, H.-S. Ultrafast and Sensitive Screening of Pathogens by Functionalized Janus Microbeads-Enabled Rotational Diffusometry in Combination with Isothermal Amplification. Small Sci. 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Lin, C.-W.; Kwon, J.-S.; Chuang, H.-S. Rotational diffusometric sensor with isothermal amplification for ultra-sensitive and rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 nsp2 cDNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehling, T.J.; Lee, D.H.; Henderson, M.E.; McDonald, M.K.; Tsang, P.H.; Kaakeh, S.; Kim, E.S.; Wereley, S.T.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L.; Clayton, K.N.; et al. A smartphone-based particle diffusometry platform for sub-attomolar detection of Vibrio cholerae in environmental water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, A.J.; Co, K.; Lima-Cooper, G.; Lee, D.H.; Clayton, K.N.; Wereley, S.T.; John, C.C.; Linnes, J.C.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L. Towards the use of a smartphone imaging-based tool for point-of-care detection of asymptomatic low-density malaria parasitaemia. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, A.J.; Lee, D.H.; Clayton, K.N.; Wereley, S.T.; Linnes, J.C.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L. PD-LAMP smartphone detection of SARS-CoV-2 on chip. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1203, 339702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Grant, K.B.; Stressmann, F.; Ghigo, J.-M.; Marchal, D.; Limoges, B. Ultimate Single-Copy DNA Detection Using Real-Time Electrochemical LAMP. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, D.; Gougis, M.; Baque, M.; Navarro, F.P.; Belgacem, M.N.; Chaussy, D.; Bourdat, A.-G.; Mailley, P.; Berthier, J. Screen-Printed Polyaniline-Based Electrodes for the Real-Time Monitoring of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Reactions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10124–10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanath, N.Y.; Nguyen, L.T.; Vu, T.T.; Tran, L.D. Development of a portable electrochemical loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) device for detection of hepatitis B virus. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34954–34959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.-T.; Liu, S.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Huang, S.-T. An Integrated Real-time Electrochemical LAMP Device for Pathogenic Bacteria Detection in Food. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-J.; Mani, V.; Huang, S.-T.; Hu, Y.-C.; Shan, H.-C.P. Bisintercalating DNA redox reporters for real-time electrochemical qLAMP. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 129, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priye, A.; Ball, C.S.; Meagher, R.J. Colorimetric-Luminance Readout for Quantitative Analysis of Fluorescence Signals with a Smartphone CMOS Sensor. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12385–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, N.; Zheng, L.; Cai, G.; Lin, J. A lab-on-chip device for the sample-in-result-out detection of viable Salmonella using loop-mediated isothermal amplification and real-time turbidity monitoring. Lab A Chip 2020, 20, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Pandian, V.; Kadimisetty, K.; Zhang, X.; Ruiz, C.; Cooper, K.; Liu, C. Real-time Colorimetric Quantitative Molecular Detection of Infectious Diseases on Smartphone-based Diagnostic Platform. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thio, S.K.; Bae, S.W.; Park, S.-Y. Lab on a smartphone (LOS): A smartphone-integrated, plasmonic-enhanced optoelectrowetting (OEW) platform for on-chip water quality monitoring through LAMP assays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, V.D.; Liu, F.; Seo, T.S. An Integrated Smartphone-Based Genetic Analyzer for Qualitative and Quantitative Pathogen Detection. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22208–22214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen, V.D.; Van Nguyen, H.; Seo, T.S. Quantification of colorimetric isothermal amplification on the smartphone and its open-source app for point-of-care pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Bui, H.K.; Phan, V.M.; Seo, T.S. An internet of things-based point-of-care device for direct reverse-transcription-loop mediated isothermal amplification to identify SARS-CoV-2. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 195, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; La, H.C.; Lee, N.Y. Fully Integrated and Foldable Microdevice Encapsulated with Agarose for Long-Term Storage Potential for Point-of-Care Testing of Multiplex Foodborne Pathogens. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chiang, E.L.C.; Medriano, C.A.D.; Li, L.; Bae, S. Rapid quantification of fecal indicator bacteria in water using the most probable number—Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (MPN-LAMP) approach on a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) microchip. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, R.; Dinh, V.P.; Lee, N.Y. Ultraviolet-induced in situ gold nanoparticles for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases in loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Qian, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhong, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xu, J.; Wu, J. Rotary Valve-Assisted Fluidic System Coupling with CRISPR/Cas12a for Fully Integrated Nucleic Acid Detection. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4048–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Lu, H.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Sui, G.; Guan, M. A LAMP-based microfluidic module for rapid detection of pathogen in cryptococcal meningitis. Talanta 2021, 236, 122827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, P.; Ngamsom, B.; Walter, C.; Dyer, C.E.; Gitaka, J.; Iles, A.; Pamme, N. A lab-on-a-chip platform for integrated extraction and detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in resource-limited settings. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1177, 338758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhou, Y.-R.; Wang, C.-H.; Tsai, H.-P.; Shan, Y.-S.; Lee, G.-B. An integrated microfluidic platform featuring real-time reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of COVID-19. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, N.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y. A portable microfluidic analyzer for integrated bacterial detection using visible loop-mediated amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Duan, L.; Fu, J.; Chai, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shao, X.; Wang, L.; Yan, M.; Su, X.; et al. A real-time LAMP-based dual-sample microfluidic chip for rapid and simultaneous detection of multiple waterborne pathogenic bacteria from coastal waters. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2710–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Phan, V.M.; Seo, T.S. Total integrated centrifugal genetic analyzer for point-of-care COVID-19 testing with automatic and high-throughput capability. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2021, 353, 131088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnes, J.C.; Fan, A.; Rodriguez, N.M.; Lemieux, B.; Kong, H.; Klapperich, C.M. Paper-based molecular diagnostic for Chlamydia trachomatis. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42245–42251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, N.M.; Linnes, J.C.; Fan, A.; Ellenson, C.K.; Pollock, N.R.; Klapperich, C.M. Paper-Based RNA Extraction, in Situ Isothermal Amplification, and Lateral Flow Detection for Low-Cost, Rapid Diagnosis of Influenza A (H1N1) from Clinical Specimens. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7872–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Mohd-Naim, N.F.; Safavieh, M.; Ahmed, M.U. Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Detection on Paper Microchip Using Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification and Crystal Violet Dye. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarj, K.; Akarapipad, P.; Yoon, J.-Y. Simpler, Faster, and Sensitive Zika Virus Assay Using Smartphone Detection of Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification on Paper Microfluidic Chips. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batule, B.S.; Seok, Y.; Kim, M.-G. Paper-based nucleic acid testing system for simple and early diagnosis of mosquito-borne RNA viruses from human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 151, 111998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Fu, K.; Liu, Y.; Ding, X.; Hu, J.; Wu, W.; Xu, K.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Mu, Y.; et al. Development of a self-priming PDMS/paper hybrid microfluidic chip using mixed-dye-loaded loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for multiplex foodborne pathogens detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1040, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; Lee, N.Y. A foldable isothermal amplification microdevice for fuchsin-based colorimetric detection of multiple foodborne pathogens. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; Lee, N.Y. Spinning and Fully Integrated Microdevice for Rapid Screening of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.P.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of a fully integrated paper microdevice for point-of-care testing of infectious disease using Safranin O dye coupled with loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 204, 114080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, Y. A newly developed paper embedded microchip based on LAMP for rapid multiple detections of foodborne pathogens. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yu, T.; He, J.; Liu, F.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q. An integrated microfluidic chip for the detection of bacteria—A proof of concept. Mol. Cell. Probes 2015, 29, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.; Kwok, H.; Leung, C.; Wu, S.; Law, I.; Cheung, Y.; Chin, M.; Kwan, P.; Hui, M.; Kong, S.; et al. Sample-to-answer on molecular diagnosis of bacterial infection using integrated lab-on-a-disc. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.H.; Oh, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Choi, G.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Seo, T.S. An integrated rotary microfluidic system with DNA extraction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and lateral flow strip-based detection for point-of-care pathogen diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, V.D.; Lee, E.Y.; Seo, T.S. Point-of-care genetic analysis for multiplex pathogenic bacteria on a fully integrated centrifugal microdevice with a large-volume sample. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Trinh, T.N.D.; Lee, N.Y. Fully integrated and slidable paper-embedded plastic microdevice for point-of-care testing of multiple foodborne pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; Thai, D.A.; Lee, N.Y. Pop-up paper-based and fully integrated microdevice for point-of-care testing of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-S.; Wang, C.-H.; Tsai, H.-P.; Shan, Y.-S.; Lee, G.-B. Electromagnetically-driven integrated microfluidic platform using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansen, A.; Herrick, A.M.; Dimov, I.K.; Lee, L.P.; Chiu, D.T. Digital LAMP in a sample self-digitization (SD) chip. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Staheli, J.P.; Wu, A.; Kreutz, J.E.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J.; Schneider, T.; Fujimoto, B.S.; Qin, Y.; Yen, G.S.; et al. Detection of 14 High-Risk Human Papillomaviruses Using Digital LAMP Assays on a Self-Digitization Chip. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3266–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yu, B.; Ren, H.; Qiu, L.; Han, S.; Jin, W.; Jin, Q.; Mu, Y. Self-priming compartmentalization digital LAMP for point-of-care. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4755–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, K.; Sun, J.; Song, X.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Vibrio parahemolyticus by the Mixed-Dye-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay on a Self-Priming Compartmentalization Microfluidic. Chip. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11312–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-D.; Chang, W.-H.; Luo, K.; Wang, C.-H.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yen, W.-H.; Lee, G.-B. Digital quantification of DNA via isothermal amplification on a self-driven microfluidic chip featuring hydrophilic film-coated polydimethylsiloxane. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, T.D.; Chen, L.; Zec, H.C.; Wang, T.-H. Microfluidic continuous flow digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Lab Chip 2014, 15, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Tian, J.; Chao, Y.; Chien, Y.-S.; Luo, R.-H.; Guo, J.-Y.; Li, S.; Chou, Y.-J.; Shum, H.C.; Chen, C.-F. Hand-Powered Microfluidics for Parallel Droplet Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2868–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Guo, X.; Mao, P.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; You, M.; Hu, J.; Tian, M.; Yao, C.; Li, F.; et al. A Portable Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Platform Based on Microgel Array and Hand-Held Reader. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3564–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Peng, N. Smartphone-Based Droplet Digital LAMP Device with Rapid Nucleic Acid Isolation for Highly Sensitive Point-of-Care Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 2258–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, L.; Nichols, K.P.; Ismagilov, R.F. SlipChip. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Shen, F.; McCalla, S.E.; Kreutz, J.E.; Karymov, M.A.; Ismagilov, R.F. Mechanistic Evaluation of the Pros and Cons of Digital RT-LAMP for HIV-1 Viral Load Quantification on a Microfluidic Device and Improved Efficiency via a Two-Step Digital Protocol. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Lyu, W.; Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Qu, H.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Han, X.; Lai, D.; Shen, F. Self-partitioning SlipChip for slip-induced droplet formation and human papillomavirus viral load quantification with digital LAMP. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; El-Tholoth, M.; Li, Y.; Graham-Wooten, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Weiss, S.R.; Collman, R.G.; Bau, H.H. Single- and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Point-of-Care, Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13063–13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.; Ladha, A.; Saito, M.; Segel, M.; Bruneau, R.; Huang, M.W.; Kim, N.-G.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Walker, B.D.; et al. Point-of-care testing for COVID-19 using SHERLOCK diagnostics. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; et al. CRISPR–Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucira Health Inc. Meet Lucira Check It. n.d.-b. Available online: https://www.lucirahealth.com/ (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Authorization Letter Lucira COVID-19 All-in-One Test Kit. n.d.-h. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/143810/download (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Authorization Letter Lucira Check-It COVID-19 Test Kit. n.d.-g. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/147492/download (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Detect Inc. The Future of Testing Is in the Home. n.d.-b. Available online: https://detect.com/our-test (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration, 2021c. Authorization Letter Detect COVID-19 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/153663/download (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Ali, Z.; Aman, R.; Mahas, A.; Rao, G.S.; Tehseen, M.; Marsic, T.; Salunke, R.; Subudhi, A.K.; Hala, S.M.; Hamdan, S.M.; et al. iSCAN: An RT-LAMP-coupled CRISPR-Cas12 module for rapid, sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2. Virus Res. 2020, 288, 198129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Hao, X.; Dong, X.; Mao, L.; Pelechano, V.; Chen, W.-H.; Yin, X. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Coronavirus Using a Reverse Transcriptional Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) Diagnostic Platform. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration, 2021c. Authorization Letter Metrix COVID-19 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/162401/download (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration, 2021c. Authorization Letter DxLab COVID-19 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/158977/download (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Sahoo, P.R.; Sethy, K.; Mohapatra, S.; Panda, D. Loop mediated isothermal amplification: An innovative gene amplification technique for animal diseases. Veter. World 2016, 9, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wastling, S.L.; Picozzi, K.; Kakembo, A.S.L.; Welburn, S.C. LAMP for Human African Trypanosomiasis: A Comparative Study of Detection Formats. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Jin, C.; Chen, F. Development of multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification-RFLP (mLAMP-RFLP) to detect Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp. in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 148, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.U.; Schmithausen, R.M.; Li, D.; Jacobs, M.L.; Hollstein, R.; Blumenstock, K.; Liebing, J.; Słabicki, M.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Israeli, O.; et al. LAMP-Seq enables sensitive, multiplexed COVID-19 diagnostics using molecular barcoding. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.B.; Veigas, B.; Carlos, F.F.; Sánchez-Melsió, A.; Balcázar, J.L.; Borrego, C.M.; Baptista, P.V. Water safety screening via multiplex LAMP-Au-nanoprobe integrated approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, M.R.; James, G.; Sultana, Y.; Ginn, A.N.; Outhred, A.C.; Kong, F.; Verweij, J.J.; Iredell, J.R.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, R. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for Strongyloides stercoralis in stool that uses a visual detection method with SYTO-82 fluorescent dye. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, K.; Mage, P.L.; Csordas, A.T.; Eisenstein, M.; Soh, H.T. Simultaneous elimination of carryover contamination and detection of DNA with uracil-DNA-glycosylase-supplemented loop-mediated isothermal amplification (UDG-LAMP). Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, A.; Nakajima, C.; Fukushima, Y.; Tamaru, A.; Sugawara, I.; Kimura, A.; Kawahara, R.; Hu, Z.; Suzuki, Y. A Rapid Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Targeting hspX for the Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 65, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischbach, J.; Xander, N.C.; Frohme, M.; Glökler, J.F. Shining a light on LAMP assays’ A comparison of LAMP visualization methods including the novel use of berberine. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.; Chidambara, V.A.; Andreasen, S.Z.; Golabi, M.; Huynh, V.N.; Linh, Q.T.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. Point-of-care devices for pathogen detections: The three most important factors to realise towards commercialization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiddle, G.; Hardinge, P.; Buttigieg, N.; Gandelman, O.; Pereira, C.; McElgunn, C.J.; Rizzoli, M.; Jackson, R.; Appleton, N.; Moore, C.; et al. GMO detection using a bioluminescent real time reporter (BART) of loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) suitable for field use. BMC Biotechnol. 2012, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, X.; Deng, M.; Yang, H.; Gao, G.; Wang, K.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Cui, D. A novel HBV genotypes detecting system combined with microfluidic chip, loop-mediated isothermal amplification and GMR sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirks, R.M.; Pierce, N.A. Triggered amplification by hybridization chain reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15275–15278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Lv, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Z.-S. Hybridization chain reaction and its applications in biosensing. Talanta 2021, 234, 122637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Wu, M.; Wang, P.; Feng, Q. Novel integrating polymethylene blue nanoparticles with dumbbell hybridization chain reaction for electrochemical detection of pathogenic bacteria. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, M. Hybridization chain reaction circuit-based electrochemiluminescent biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene assay. Talanta 2022, 240, 123207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Yuan, S.; Sun, B.; Sun, R.; Meng, X. A novel method for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on an aptamer and hybridization chain reaction. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 3734–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Mauk, M.G.; Hackett, B.A.; Cherry, S.; Bau, H.H.; Liu, C. Instrument-Free Point-of-Care Molecular Detection of Zika Virus. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7289–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Ragupathy, V.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Vemula, S.V.; El Mubarak, H.S.; Ye, Z.; Landry, M.L.; Hewlett, I. Nanomicroarray and Multiplex Next-Generation Sequencing for Simultaneous Identification and Characterization of Influenza Viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Xing, W.; Yu, X.; Fu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zou, M.; Luo, Z.; Xu, D. Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick for rapid and visual detection of Schistosoma japonicum. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Liu, C.; Mauk, M.G.; Rankin, S.C.; Lok, J.B.; Greenberg, R.M.; Bau, H.H. Two-Stage Isothermal Enzymatic Amplification for Concurrent Multiplex Molecular Detection. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.; Fang, X.; Li, X.; Kong, J. Gold nanoparticle-mediated nucleic acid isothermal amplification with enhanced specificity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1043, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, H.; Feng, W.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiao, H.; Pabbaraju, K.; Tipples, G.; et al. Isothermal Amplification and Ambient Visualization in a Single Tube for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Loop-Mediated Amplification and CRISPR Technology. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 16204–16212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Jiang, X. Microfluidic Synthesis of Functional Nanoparticles. In Nanotechnology and Microfluidics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 319–345. ISBN 978-3-527-81834-1. [Google Scholar]


| Technique | Pathogen | Signal Transduction Material | Readout Method | Time | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetric | SARS-CoV-2 | SYBR Green I | Visual | 10 min | 10−3 copies/reaction | [59] |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Phenol red | 60 min | 100 copies/reaction | [53] | ||
| Rotavirus A | Neutral red | 30 min | 1 × 103 copies/mL | [52] | ||
| Six bacteria | HNB | 60 min | 102–103 CFU/mL | [48] | ||
| HIV, HBV, HCV | Calcein | 65 min | 2 copies/µL | [47] | ||
| Lateral flow | L. monocytogenes | Fe3O4NPs | Visual | 60 min | 10 CFU/mL | [87] |
| S. typhimurium | QBs-labeled LFIAS | 60 min | 103 CFU/mL | [88] | ||
| SARS-CoV-2 | hCG-probe | 120 min | 0.5 copy/µL | [92] | ||
| Electrochemical | V. parahaemolyticus | Hoechst-33258 | Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) | 45 min | 0.3 CFU per 25 g raw seafood | [76] |
| HPV | Benzoquinone (BQ) | Chronoamperometry | 40 min | 0.1 ng | [79] | |
| Group B Streptococci | Methylene blue | Cyclic voltammetry (CV) | 45 min | 0.23 fg/μL | [77] | |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Methylene blue | Square wave voltammetry (SWV) | 30 min | ~2.5 × 10−6 ng/µL | [81] | |
| Optical | L. monocytogenes | SYTO-9 | CMOS | 60 min | 6 copies/μL | [97] |
| Salmonella typhi | AuNPs | SPR | 2 h | 20 CFU/mL | [99] | |
| MRSA | Biotinylated-ssDNA probes | SPR | 60 min | 10 copies/μL | [98] | |
| S. enterica | AuNP-Cy5/DNA | SERS | 40 min | 66 CFU/mL | [100] | |
| L. monocytogenes | Multifunctional AuNPs | SERS | 60 min | 3.6 × 102 CFU/mL | [101] | |
| Diffusometric | Vibrio cholerae | 400 nm green fluorescent particles | CMOS | 35 min | 6 cells/reaction | [106] |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 400 nm green fluorescent particles | CMOS | 35 min | 35 × 104 viral particles/mL | [108] | |
| E. Coli | 1 µm Janus particles | CCD | 10 min | 42.8 fg/µL | [104] | |
| SARS-CoV-2-nsp2 cDNA | 1 µm Janus particles | CCD | 10 min | 70 ag/µL | [105] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, D.; Lin, C.-W.; Chuang, H.-S. LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Pathogen Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121068
Das D, Lin C-W, Chuang H-S. LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Pathogen Detection. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121068
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Dhrubajyoti, Cheng-Wen Lin, and Han-Sheng Chuang. 2022. "LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Pathogen Detection" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121068
APA StyleDas, D., Lin, C.-W., & Chuang, H.-S. (2022). LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Pathogen Detection. Biosensors, 12(12), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121068









