Trends in Application of SERS Substrates beyond Ag and Au, and Their Role in Bioanalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pt/Pd and Other Noble Metals as SERS Substrates
| Substrate | Average EF (Min; Max) | Average LOD, M (Min; Max) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic | Geometric | Arithmetic | Geometric | ||
| Si without metals | [65,66,67,68,69,70] | ||||
| Si with metals | [50,55,66,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134] | ||||
| Overall Si | [50,55,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134] | ||||
| Pt | [55,56,62,63,64,97,101,135,136,137,138,139] | ||||
| Pd | [55,57,61,62,98,99,100,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149] | ||||
| Overall Pt/Pd | [55,56,57,61,62,63,64,97,98,99,100,101,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149] | ||||
| Pure Al | 3.4 × 105 (5 × 103; 106) | 1.27 × 105 (5 × 103; 106) | 1.03 × 10−6 (10−7; 2 × 10−6) | 5.85 × 10−7 (10−7; 2 × 10−6) | [150,151,152,153,154,155,156] |
| Al + Au (R6G analyte) | 8.1 × 106 (only one EF) | 7 × 10−10 (10−10; 10−9) | 3.16 × 10−10 (10−10; 10−9) | [157,158,159,160] | |
| Al + Ag (R6G analyte) | 5.39 × 107 (107; 9.77 × 107) | 3.13 × 107 (107; 9.77 × 107) | 2.50 × 10−7 (10−15; 10−6) | 1.78 × 10−11 (10−15; 10−6) | [161,162,163,164,165] |
| Pure Cu | 7.36 × 106 (104; 4.70 × 107) | 1.25 × 106 (104; 4.70 × 107) | 4.46 × 10−7 (10−9; 10−6) | 7.2 × 10−8 (10−9; 10−6) | [44,45,166,167,168,169,170] |
| Cu + Au | 2.52 × 105 (1.2 × 103; 5.0 × 105) | 7.81 × 104 (1.2 × 103; 5.0 × 105) | 3.33 × 10−4 (10−10; 10−3) | 10−7 (10−10; 10−3) | [171,172,173,174,175] |
| Cu + Ag | 6.97 × 1010 (1.19 × 105; 4.88 × 1011) | 1.76 × 107 (1.19 × 105; 4.88 × 1011) | 5.01 × 10−9 (10−21; 3.30 × 10−8) | 5.3 × 10−12 (10−21; 3.30 × 10−8) | [169,176,177,178,179,180,181] |
| Other metals (Zn, Ti, Fe, Co, Mo, Cr, Hf + Au, Ag) | 6.85 × 107 (2.70 × 107; 9.40 × 107) | 6.14 × 107 (2.70 × 107; 9.40 × 107) | 2.96 × 10−7 (10−12; 2.0 × 10−6) | 4.43 × 10−8 (10−12; 1.0) | [182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191] |
| Au | (, | (, | [50,192,193,194] | ||
| Ag | ( | ( | [195,196,197,198] | ||
| Overall Au/Ag | ( | [199,200] | |||
3. Copper
| Substrate | Analyte | Analytical Parameters | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu nanowire-coated carbon fibers | Designer drugs | EF 106–107 | Halouzka et al., 2017 [166] |
| Cu/Cu2O core-shell NPs | CV, MB (532 nm) | EF 104 RSD < 28% | H. Dizajghorbani et al., 2019 [44] |
| Cu films on the microstructural mantis wing (Cu/MW) | R6G, 4-ATP, CV | LOD 10−6 M EF 1.19 × 105 RSD < 28% | Li et al., 2018 [45] |
| Copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles | RhB | EF 1.5 × 105 RSD 12% | Behzad Sardari & Meriç Özcan 2017 [220] |
| Copper triangle plates (CTPs) | RhB | EF 4.5 × 106 | Chang Li, Mingqiang Chen 2020 [167] |
| Cu nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxides (CuNPs/rGO) | R6G | LOD 10−8 M EF 2.75 × 106 RSD < 10% | He et al., 2016 [168] |
| Cu-coated fabric | CV | LOD 10−8 M EF 2 × 106 | Dai et al., 2021 [169] |
| The geometric mean for LOD: 4.22 × 10−8 M, geometric mean for EF: 1.59 × 106 | |||
Copper with Nanostructured Silver and Gold
4. Silicon
4.1. Two Groups of Si Comparison
4.2. Overall Si and Ag/Au Discussion
4.3. Application of Silicon as a Substrate for a Sandwich SERS Immunoassay
5. Aluminum
5.1. Limitations and Disadvantages of Al-Based Substrates
5.2. Aluminum with Nanostructured Ag and Au
5.3. Application of Aluminum Foil for Biosensing
6. Other Metals and Alloys
7. Performance Comparison with Gold and Silver Substrates
7.1. R6G (Rhodamine 6G) Detection by SERS
7.2. TNT (2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene) Detection by SERS
7.3. Adenine Detection by SERS
8. SERS Clinical Applications
| Substrates | Average Sensitivity | Average Specificity | Average Accuracy | N of Samples | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 95.7% | 95.1% | 94.4% | All: 56 (17, 116) | [70,130,131,132,133,273,274,275,276,277,278,279,280,281] |
| Only Al | 83% | 83% | 83.3% | All: 60 (30; 30). | [282] |
| Ag@Al | 91.3% (85%; 98%) | 99.5% | 94.2% (91%; 98%) | All: 108 (28; 190). | [283,284,285,286,287,288,289] |
| Au | 94.7% (80.7%; 100%) | 95.5% (84.1%; 100%) | 92.8% (81.2%; 100%) | All: 127 (18; 280). | [272,290,291,292,293,294,295] |
| Ag | 93.0% (80.9%; 100%) | 95.3% (87.5 %; 100%) | 94.2% (84.1%; 100%) | All: 145 (75; 220). | [271,283,296,297,298,299,300] |
8.1. Prostate Cancer Clinical Diagnosis by SERS
8.2. Lung Cancer Diagnosis by SERS
8.3. SARS-CoV-2 Detection by SERS
8.4. Clinical Diagnostics of Other Bio-Analytes on Si and Al-Based SERS Substrates
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrecht, M.G.; Creighton, J.A. Anomalously intense Raman spectra of pyridine at a silver electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 5215–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanmaire, D.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1977, 84, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.-I.; Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R.P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Park, H.Y.; Lipert, R.J.; Porter, M.D. Mixed monolayers on gold nanoparticle labels for multiplexed surface-enhanced Raman scattering based immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9643–9650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.W.; Coulston, R.J.; Biedermann, F.; Mahajan, S.; Baumberg, J.J.; Scherman, O.A. In Situ SERS Monitoring of Photochemistry within a Nanojunction Reactor. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5985–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, S.; Jamieson, L.E.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for in vivo biosensing. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.-K.; Jeon, K.-S.; Kim, H.M.; Nam, J.-M.; Suh, Y.D. Nanogap-engineerable Raman-active nanodumbbells for single-molecule detection. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.-Y.; Nawaz, M.A.H.; Liu, N.; Zhou, H.-P.; Hussain, E.; Wen, X.; Gou, X.-Y.; Jin, X.; Yu, C. A Nile red-based near-infrared fluorescent probe for the detection of superoxide radical anion in living cells. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, E.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhuo, H.; Shahzad, S.A.; Ali, S.; Ismail, M.; Qi, H.; Yu, C. Benzo[ghi]perylene and coronene as ratiometric fluorescence probes for the selective sensing of nitroaromatic explosives. Talanta 2020, 207, 120316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlucker, S. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Concepts and chemical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4756–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziuk, D.; Moehwald, H. Prospects for plasmonic hot spots in single molecule SERS towards the chemical imaging of live cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21072–21093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, A.J.; Harpster, M.H.; Johnson, P.A. The development of surface-enhanced Raman scattering as a detection modality for portable in vitro diagnostics: Progress and challenges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 20415–20433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Jia, Y.; Song, X.; Lu, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.; Han, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. Giant Gold Nanowire Vesicle-Based Colorimetric and SERS Dual-Mode Immunosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Vibrio parahemolyticus. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6124–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Huang, P.; Duan, H.; Chen, X. Plasmonic Vesicles of Amphiphilic Nanocrystals: Optically Active Multifunctional Platform for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, L.A.; Qian, X.; Nie, S. SERS Nanoparticles in Medicine: From Label-Free Detection to Spectroscopic Tagging. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10489–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubisha, D.S.; Lipert, R.J.; Park, H.Y.; Driskell, J.; Porter, M.D. Femtomolar detection of prostate-specific antigen: An immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering and immunogold labels. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5936–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorson, R.A.; Vikesland, P.J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for environmental analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7749–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Emory, S.R. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, K.; Wang, Y.; Kneipp, H.; Perelman, L.T.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Single Molecule Detection Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camden, J.P.; Dieringer, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Masiello, D.J.; Marks, L.D.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Probing the structure of single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot spots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12616–12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.C.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.G.; Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Aizpurua, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Chemical mapping of a single molecule by plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering. Nature 2013, 498, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverberi, R.; Reverberi, L. Factors affecting the antigen-antibody reaction. Blood Transfus 2007, 5, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, E.; Fendler, J.H. Exploitation of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1685–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, P.L.; Dieringer, J.A.; Shah, N.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, H.T.; Haes, A.J. What Does Nanoparticle Stability Mean? J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 2019, 123, 16495–16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, L.; Graham, D. Molecularly-mediated assemblies of plasmonic nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7085–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H. Bimetallic core shelled nanoparticles (Au@AgNPs) for rapid detection of thiram and dicyandiamide contaminants in liquid milk using SERS. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosslick, H.; Sauer, H.; Just, T.; Vick, U.; Fulda, G.; Jonas, L. Biodegradation of gold and platinum implants in rats studied by electron microscopy. Int. J. 2019, 2766, 2748. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Si, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, D.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Man, B.; Jiang, S. Sensitive, reproducible, and stable 3D plasmonic hybrids with bilayer WS2 as nanospacer for SERS analysis. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 21626–21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaghias, G.; Eliades, G.; Vougiouklakis, G. In vivo corrosion behavior of gold-plated versus titanium dental retention pins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 67, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Tsuneda, S.; Nishida, N.; Hara, M.; Sasabe, H.; Knoll, W. Surface-Conditioning Effect of Gold Substrates on Octadecanethiol Self-Assembled Monolayer Growth. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4638–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, A.; Nuutinen, T.; Itkonen, T.; Heinilehto, S.; Puustinen, J.; Hiltunen, J.; Lappalainen, J.; Karioja, P.; Vahimaa, P. Atmospheric oxidation and carbon contamination of silver and its effect on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, C.G.; Linton, R.W. Removing sulfur from gold using ultraviolet/ozone cleaning. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 1995, 13, 2281–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, J.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguie, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.J.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and Future of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, M.W.; King, N.S.; Liu, L.; Everitt, H.O.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Aluminum for plasmonics. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudun, K.; Elemessova, Z.; Khamkhash, L.; Ralchenko, E.; Bukasov, R. Commercial Gold Nanoparticles on Untreated Aluminum Foil: Versatile, Sensitive, and Cost-Effective SERS Substrate. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukanova, Z.; Gudun, K.; Elemessova, Z.; Khamkhash, L.; Ralchenko, E.; Bukasov, R. Detection of Paracetamol in Water and Urea in Artificial Urine with Gold Nanoparticle@Al Foil Cost-efficient SERS Substrate. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2018, 34, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, K.B.; Guhlke, M.; Kneipp, J.; Kadkhodazadeh, S.; Wagner, J.B.; Palanco, M.E.; Kneipp, H.; Kneipp, K. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering on aluminum using near infrared and visible excitation. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2014, 50, 3744–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergiienko, S.; Moor, K.; Gudun, K.; Yelemessova, Z.; Bukasov, R. Nanoparticle-nanoparticle vs. nanoparticle-substrate hot spot contributions to the SERS signal: Studying Raman labelled monomers, dimers and trimers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 4478–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuz, A.; Sultangaziyev, A.; Rapikov, A.; Kunushpayeva, Z.; Bukasov, R. How gap distance between gold nanoparticles in dimers and trimers on metallic and non-metallic SERS substrates can impact signal enhancement. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukasov, R.; Kunushpayeva, Z.; Rapikov, A.; Zhunussova, S.; Sultangaziyev, A.; Filchakova, O. High Contrast Surface Enhanced Fluorescence of Carbon Dot Labeled Bacteria Cells on Aluminum Foil. J. Fluoresc. 2020, 30, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultangaziyev, A.; Akhmetova, A.; Kunushpayeva, Z.; Rapikov, A.; Filchakova, O.; Bukasov, R. Aluminum foil as a substrate for metal enhanced fluorescence of bacteria labelled with quantum dots, shows very large enhancement and high contrast. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 28, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejkova, J.; Prokopec, V.; Brazdova, S.; Kokaislova, A.; Matejka, P.; Stepanek, F. Characterization of copper SERS-active substrates prepared by electrochemical deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7864–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizajghorbani Aghdam, H.; Moemen Bellah, S.; Malekfar, R. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering studies of Cu/Cu2O Core-shell NPs obtained by laser ablation. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 223, 117379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Chang, C. Decoration of Cu films on the microstructural mantis wing as flexible substrates for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Optik 2018, 172, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.E.; Mahajan, S.; Bartlett, P.N.; Baumberg, J.J.; Russell, A.E. SERS at structured palladium and platinum surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7399–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Jiang, X.X.; Su, S.; Wei, X.P.; Lee, S.T.; He, Y. Silicon-based reproducible and active surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates for sensitive, specific, and multiplex DNA detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 203104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosovic, M.; Balarin, M.; Ivanda, M.; Derek, V.; Marcius, M.; Ristic, M.; Gamulin, O. Porous Silicon Covered with Silver Nanoparticles as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate for Ultra-Low Concentration Detection. Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 69, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upender, G.; Sathyavathi, R.; Raju, B.; Bansal, C.; Narayana Rao, D. SERS study of molecules on Ag nanocluster films deposited on glass and silicon substrates by cluster deposition method. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1012, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunushpayeva, Z.; Rapikov, A.; Akhmetova, A.; Sultangaziyev, A.; Dossym, D.; Bukasov, R. Sandwich SERS immunoassay of human immunoglobulin on silicon wafer compared to traditional SERS substrate, gold film. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, C.; Lee, S.-T. Silicon nanostructures for bioapplications. Nano Today 2010, 5, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Tabor, C.E.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.L. A new catalytically active colloidal platinum nanocatalyst: The multiarmed nanostar single crystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4590–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, Y.; Yin, G.; Lin, Y. Carbon nanotubes decorated with Pt nanoparticles via electrostatic self-assembly: A highly active oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2826–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Han, W.; Yao, L.; Lin, J.; Wei, S.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, T.; Xia, X. One-step synthesis and catalytic properties of porous palladium nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17604–17611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Whale, A.; Padalkar, S. Exploring the Efficacy of Platinum and Palladium Nanostructures for Organic Molecule Detection via Raman Spectroscopy. Sensors 2018, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.-Q.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.-Y. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: From Noble to Transition Metals and from Rough Surfaces to Ordered Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9463–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.-L.; Cui, L.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.-Q. Electrochemically Roughened Palladium Electrodes for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Methodology, Mechanism, and Application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1770–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Ren, B.; Mao, B.; Quan, C.; Tian, Z. A Preliminary Investigation of SERS Effect at Roughened Platinum Electrodes. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 1996, 12, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Q.; Ren, B.; Li, J.F.; Yang, Z.L. Expanding generality of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with borrowing SERS activity strategy. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2007, 34, 3514–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Weaver, M.J. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering on uniform transition-metal films: Toward a versatile adsorbate vibrational strategy for solid-nonvacuum interfaces? Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.-P.; Li, J.-F.; Yang, Z.-L.; Li, L.-M.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.-Q. Optimization of SERS activities of gold nanoparticles and gold-core-palladium-shell nanoparticles by controlling size and shell thickness. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 39, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Johnson, R.P.; Lin, X.; Yang, Z.; Russell, A.E. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering on Uniform Pd and Pt Films: From Ill-Defined to Structured Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24843–24850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, H.B.; Yoon, J.K.; Shin, D.; Shin, K.S. Ag Nanoparticle-Mediated Raman Scattering of 4-Aminobenzenethiol on a Pt Substrate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 13589–13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Fan, C.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Liang, E.; Chao, M. Surface enhanced Raman scattering of 4-aminothiophenol sandwiched between Ag nanocubes and smooth Pt substrate: The effect of the thickness of Pt film. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 044312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsai, E.; Kuchmizhak, A.; Pustovalov, E.; Sergeev, A.; Mironenko, A.; Bratskaya, S.; Linklater, D.P.; Balcytis, A.; Ivanova, E.; Juodkazis, S. Chemically non-perturbing SERS detection of a catalytic reaction with black silicon. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9780–9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galopin, E.; Barbillat, J.; Coffinier, Y.; Szunerits, S.; Patriarche, G.; Boukherroub, R. Silicon nanowires coated with silver nanostructures as ultrasensitive interfaces for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, P.K.; Ramgir, N.S.; Bhansali, S. Metal-Decorated Silica Nanowires: An Active Surface-Enhanced Raman Substrate for Cancer Biomarker Detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellacani, P.; Torres-Costa, V.; Agullo-Rueda, F.; Vanna, R.; Morasso, C.; Manso Silvan, M. Laser writing of nanostructured silicon arrays for the SERS detection of biomolecules with inhibited oxidation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.A.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Tan, B. Programmable SERS active substrates for chemical and biosensing applications using amorphous/crystalline hybrid silicon nanomaterial. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, M.; Tan, B.; Venkatakrishnan, K. Label-Free SERS Quantum Semiconductor Probe for Molecular-Level and in Vitro Cellular Detection: A Noble-Metal-Free Methodology. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34886–34904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Li, S.; Deng, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, C. Flexible, Transparent, and Free-Standing Silicon Nanowire SERS Platform for in Situ Food Inspection. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, A.; Inya-Agha, O.; Forster, R.J.; Keyes, T.E. Chemically bound gold nanoparticle arrays on silicon: Assembly, properties and SERS study of protein interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaminska, A.; Szymborski, T.; Jaroch, T.; Zmyslowski, A.; Szterk, A. Gold-capped silicon for ultrasensitive SERS-biosensing: Towards human biofluids analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 84, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymborski, T.; Stepanenko, Y.; Niciński, K.; Piecyk, P.; Berus, S.M.; Adamczyk-Popławska, M.; Kamińska, A. Ultrasensitive SERS platform made via femtosecond laser micromachining for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Yan, J. A split-type structure of Ag nanoparticles and Al2O3@Ag@Si nanocone arrays: An ingenious strategy for SERS-based detection. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 4359–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, N.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; He, Y. Silicon nanohybrid-based SERS chips armed with an internal standard for broad-range, sensitive and reproducible simultaneous quantification of lead(ii) and mercury(ii) in real systems. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4010–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Agarwal, A.; Widjaja, E.; Garland, M.V.; Wong, S.M.; Linn, L.; Khalid, N.M.; Salim, S.M.; Balasubramanian, N. Metallization of Silicon Nanowires and SERS Response from a Single Metallized Nanowire. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3542–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virga, A.; Rivolo, P.; Frascella, F.; Angelini, A.; Descrovi, E.; Geobaldo, F.; Giorgis, F. Silver Nanoparticles on Porous Silicon: Approaching Single Molecule Detection in Resonant SERS Regime. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 20139–20145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virga, A.; Rivolo, P.; Descrovi, E.; Chiolerio, A.; Digregorio, G.; Frascella, F.; Soster, M.; Bussolino, F.; Marchiò, S.; Geobaldo, F.; et al. SERS active Ag nanoparticles in mesoporous silicon: Detection of organic molecules and peptide-antibody assays. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, L.A.; Hasan, K.K.; Alwan, A.M. Rapid and Highly Efficient Detection of Ultra-low Concentration of Penicillin G by Gold Nanoparticles/Porous Silicon SERS Active Substrate. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 206, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, N.; Ding, P.; Shi, H.; Zhai, X.; Su, Y.; He, Y. A Graphene-Silver Nanoparticle-Silicon Sandwich SERS Chip for Quantitative Detection of Molecules and Capture, Discrimination, and Inactivation of Bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5646–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dykes, J.; Gilliam, T.; Chopra, N. A new heterostructured SERS substrate: Free-standing silicon nanowires decorated with graphene-encapsulated gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5263–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.; Que, R.; Shao, M.; Cheng, L.; Lee, S.-T. Copper Nanoparticles Grafted on a Silicon Wafer and Their Excellent Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2067–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhibi, A.; Saadaoui, M.; Lorrain, N.; Guendouz, M.; Raouafi, N.; Moadhen, A. Application of Doehlert Matrix for an Optimized Preparation of a Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Substrate Based on Silicon Nanowires for Ultrasensitive Detection of Rhodamine 6G. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, F.; Wu, Z.; Guo, J.; Jia, D. Porous Silicon Photonic Crystals Coated with Ag Nanoparticles as Efficient Substrates for Detecting Trace Explosives Using SERS. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Han, X.; Ou, X.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, X.; Lee, S.T. Silicon nanowire based single-molecule SERS sensor. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8172–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, C.; Petracca, F.; Virga, A.; Rivolo, P.; Ferrero, S.; Chiolerio, A.; Geobaldo, F.; Porro, S.; Giorgis, F. SERS active silver nanoparticles synthesized by inkjet printing on mesoporous silicon. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarin, A.Y.; Chirvony, V.S.; Kholostov, K.I.; Turpin, P.Y.; Terekhov, S.N. Formation of SERS-active silver structures on the surface of mesoporous silicon. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 76, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, A.M.; Wali, L.A.; Yousif, A.A. Optimization of AgNPs/mesoPS Active Substrates for Ultra–Low Molecule Detection Process. Silicon 2018, 10, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, N.R.; Shtenberg, G. N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase biomarker quantification in milk using Ag-porous Si SERS platform for mastitis severity evaluation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 566, 150700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Syadi, A.M.; Faisal, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Jalalah, M.; Alsaiari, M. Immersion-plated palladium nanoparticles onto meso-porous silicon layer as novel SERS substrate for sensitive detection of imidacloprid pesticide. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N.H.; Tuan, D.A.; Thong, T.T.; Long, N.H.; Thanh, N.H.; Tuan Hung, L.V. Preparation of SERS Substrate with Ag Nanoparticles Covered on Pyramidal Si Structure for Abamectin Detection. Plasmonics 2021, 16, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, A.K.; Agarwal, A. A cost-effective identification of tobacco alkaloids using porous Si SERS substrates for forensic and bioanalytical applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, J.; Li, C. Ultrasensitive and recyclable SERS substrate based on Au-decorated Si nanowire arrays. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 14324–14330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Z.; Wang, F.; Xie, S.; Bu, S. Immunoassay for tumor markers in human serum based on Si nanoparticles and SiC@Ag SERS-active substrate. Analyst 2016, 141, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-Y.; Wang, G.; Hong, M. Hybrid structures of Fe3O4 and Ag nanoparticles on Si nanopillar arrays substrate for SERS applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 214, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Ding, S.Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Bai, M.L.; Anema, J.R.; Wang, X.; Wang, A.; Wu, D.Y.; Ren, B.; Hou, S.M.; et al. Extraordinary enhancement of Raman scattering from pyridine on single crystal Au and Pt electrodes by shell-isolated Au nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15922–15925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, A.A.; Alwan, A.M. Efficient detecting of TNT molecules using palladium nanoparticles/ cross shape pores like structure porous silicon. Vib. Spectrosc. 2019, 103, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, A.A.; Alwan, A.M.; Zayer, M.Q.; Bohan, A.J. Efficient single cell monitoring of pathogenic bacteria using bimetallic nanostructures embedded in gradient porous silicon. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 241, 122359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Singha, S.S.; Majumder, S.; Singha, A.; Banerjee, S.; Satpati, B. Electroless Deposition of Pd Nanostructures for Multifunctional Applications as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates and Electrochemical Nonenzymatic Sensors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiansyah, A.; Chen, A.Y.; Liao, H.L.; Yang, M.C.; Liu, T.Y.; Chan, T.Y.; Tsou, H.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.L. Core-shell of FePt@SiO2-Au magnetic nanoparticles for rapid SERS detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, X. Large-Area Au-Nanoparticle-Functionalized Si Nanorod Arrays for Spatially Uniform Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quyen, T.T.B.; Chang, C.C.; Su, W.N.; Uen, Y.H.; Pan, C.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Rick, J.; Lin, K.Y.; Hwang, B.J. Self-focusing Au@SiO2 nanorods with rhodamine 6G as highly sensitive SERS substrate for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quyen, T.T.B.; Su, W.-N.; Chen, K.-J.; Pan, C.-J.; Rick, J.; Chang, C.-C.; Hwang, B.-J. Au@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticle assemblage used for highly sensitive SERS-based determination of glucose and uric acid. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, F.; Cai, Q.; Li, Y.; Lee, S.T.; Shao, M. The effect of dielectric constants on noble metal/semiconductor SERS enhancement: FDTD simulation and experiment validation of Ag/Ge and Ag/Si substrates. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Su, W.N.; Chen, C.H.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B.J. Highly sensitive and stable Ag@SiO2 nanocubes for label-free SERS-photoluminescence detection of biomolecules. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 175, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, F.; Gu, C.; Tang, S.; Jiang, T.; et al. Synergistic effect of a “stellate” mesoporous SiO2@Au nanoprobe and coffee-ring-free hydrophilic–hydrophobic substrate assembly in an ultrasensitive SERS-based immunoassay for a tumor marker. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, X.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. A novel ratiometric SERS biosensor with one Raman probe for ultrasensitive microRNA detection based on DNA hydrogel amplification. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2643–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xu, L.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Gu, B. Rapid, Quantitative, High-Sensitive Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by Gold-Shell Silica-Core Nanospheres-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 596005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panikar, S.S.; Banu, N.; Escobar, E.R.; Garcia, G.R.; Cervantes-Martinez, J.; Villegas, T.C.; Salas, P.; De la Rosa, E. Stealth modified bottom up SERS substrates for label-free therapeutic drug monitoring of doxorubicin in blood serum. Talanta 2020, 218, 121138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Yang, K.H.; Chen, H.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, Q.Y. Innovative fabrication of a Au nanoparticle-decorated SiO2 mask and its activity on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Analyst 2014, 139, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Yu, C.-C.; Hsu, T.-C. Improved performances on surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on electrochemically roughened gold substrates modified with SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Yang, K.-H.; Hsu, T.-C. Improved Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Performances on Silver−Silica Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 8162–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, D.-W.; Li, Y.; Fossey, J.S.; Long, Y.-T. Cyclic electroplating and stripping of silver on Au@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles for sensitive and recyclable substrate of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3688–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.L.; Su, W.-N.; Chen, C.-H.; Hwang, B.-J. Ag@SiO2 nanocube loaded miniaturized filter paper as a hybrid flexible plasmonic SERS substrate for trace melamine detection. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6823–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.A.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.J.; He, L.F.; Wong, T.L.; Chui, Y.S.; Zhang, W.J.; Lee, S.T. Ordered Ag/Si nanowires array: Wide-range surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for reproducible biomolecule detection. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5039–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Jin, M.; Ma, Q.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Akinoglu, E.M.; van den Berg, A.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Ag nano-assemblies on Si surface via CTAB-assisted galvanic reaction for sensitive and reliable surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Q.; Hou, X.; Tian, Y.; Wu, L. Sensitive detection of bisphenol A by coupling solid phase microextraction based on monolayer graphene-coated Ag nanoparticles on Si fibers to surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 187, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, B.; Yu, B.; Huang, N.; Liu, L.; Lu, J.; Jiang, X. Graphene-coated Si nanowires as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 541, 148486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikac, L.; Ivanda, M.; Đerek, V.; Gotić, M. Influence of mesoporous silicon preparation condition on silver clustering and SERS enhancement. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, C.; Faro, M.J.; Bertino, G.; Ossi, P.M.; Neri, F.; Trusso, S.; Musumeci, P.; Galli, M.; Cioffi, N.; Irrera, A.; et al. Decoration of silicon nanowires with silver nanoparticles for ultrasensitive surface enhanced Raman scattering. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 375603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahes, A.; En Naciri, A.; Navvabpour, M.; Jradi, S.; Akil, S. Self-Assembled Ag Nanocomposites into Ultra-Sensitive and Reproducible Large-Area SERS-Active Opaque Substrates. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Liu, G.; Ma, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Cai, W. Fabrication of Ag-nanosheets-built micro/nanostructured arrays via in situ conversion on Cu2O-coated Si nanocone platform and their highly structurally-enhanced SERS effect. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 345302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Xu, J.; Xiao, R. A facile method to fabricate a novel 3D porous silicon/gold architecture for surface enhanced Raman scattering. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 790, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moram, S.S.B.; Shaik, A.K.; Byram, C.; Hamad, S.; Soma, V.R. Instantaneous trace detection of nitro-explosives and mixtures with nanotextured silicon decorated with Ag-Au alloy nanoparticles using the SERS technique. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1101, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Gong, Q.; Teng, J.; Hong, M. Laser hybrid micro/nano-structuring of Si surfaces in air and its applications for SERS detection. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadan, P.; Aggarwal, S.; Anappara, A.A.; Narayana, C.; Barshilia, H.C. Tailored periodic Si nanopillar based architectures as highly sensitive universal SERS biosensing platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J. Graphene-Ag Hybrids on Laser-Textured Si Surface for SERS Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, N.; Lin, D.; Hu, X.; Yang, X. Three-dimensional ordered Ag/ZnO/Si hierarchical nanoflower arrays for spatially uniform and ultrasensitive SERS detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, T.; Petti, L.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, X. Classification analyses for prostate cancer, benign prostate hyperplasia and healthy subjects by SERS-based immunoassay of multiple tumour markers. Talanta 2018, 188, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berus, S.M.; Adamczyk-Poplawska, M.; Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska, B.; Witkowska, E.; Szymborski, T.; Waluk, J.; Kaminska, A. SERS-based sensor for the detection of sexually transmitted pathogens in the male swab specimens: A new approach for clinical diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, A.; Witkowska, E.; Kowalska, A.; Skoczynska, A.; Gawryszewska, I.; Guziewicz, E.; Snigurenko, D.; Waluk, J. Highly efficient SERS-based detection of cerebrospinal fluid neopterin as a diagnostic marker of bacterial infection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4319–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Chen, R.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Cao, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering holography chip for rapid, sensitive and multiplexed detection of human breast cancer-associated MicroRNAs in clinical samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Ding, P.; Shi, Y.; Jin, T.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; He, Y. Portable and Reliable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Silicon Chip for Signal-On Detection of Trace Trinitrotoluene Explosive in Real Systems. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5072–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Chung, C.K. Novel irregular pore peripheral plasmonic mechanism of nanocomposite metal-nanoporous AAO using new facile one-step anodization and pore widening for high SERS enhancement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 580, 152252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Simple, Low-Cost Fabrication of Highly Uniform and Reproducible SERS Substrates Composed of Ag(-)Pt Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, J.; Ge, M.; Iocozzia, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, K.Q.; Lai, Y. Immobilization of Pt Nanoparticles via Rapid and Reusable Electropolymerization of Dopamine on TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Reversible SERS Substrates and Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensors. Small 2017, 13, 1604240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, K. Surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering of rhodamine 6G on Pt nanoaggregates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2005, 36, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bich Quyen, T.T.; Su, W.N.; Chen, C.H.; Rick, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Hwang, B.J. Novel Ag/Au/Pt trimetallic nanocages used with surface-enhanced Raman scattering for trace fluorescent dye detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5550–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvalya, V.; Filipič, G.; Vengust, D.; Zavašnik, J.; Modic, M.; Abdulhalim, I.; Cvelbar, U. Reusable Au/Pd-coated chestnut-like copper oxide SERS substrates with ultra-fast self-recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 517, 146205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Yi, S.I.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Dai, W.; Sinyukov, A.M.; Liang, H. Morphology dependent catalysis and surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) studies using Pd nanostructures in DNA, CTAB and PVA scaffolds. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 9678–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.-J.; Lin, X.-X.; Chen, S.-S.; Huang, H.; Wang, A.-J. Thymine-directed synthesis of highly branched gold-palladium alloy nanobrambles as a highly active surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Chen, C.; You, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, P.; Che, R. Hollow Palladium-Gold Nanochains with Periodic Concave Structures as Superior ORR Electrocatalysts and Highly Efficient SERS Substrates. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1904072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jeong, H.; Choi, K.H.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, J. Electrodeposition of triangular Pd rod nanostructures and their electrocatalytic and SERS activities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3002–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kweon, S.; Kim, J. Electrodeposition of Pt nanostructures with reproducible SERS activity and superhydrophobicity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 23547–23553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvana, T.; Kulkarni, G.U. A SERS-active nanocrystalline pd substrate and its nanopatterning leading to biochip fabrication. Small 2008, 4, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.-C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Han, B.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Chen, Q.-D.; Sun, H.-B. Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing of Plasmonic Ag/Pd Alloy Nanostructures Enables Flexible Integration of Robust SERS Substrates. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, G.; Wu, X.; Shi, G. Electrochemical fabrication of two-dimensional palladium nanostructures as substrates for surface enhanced Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24585–24592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, J. Electrodeposition of nanoflake Pd structures: Structure-dependent wettability and SERS activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7129–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Sigle, D.O.; Herrmann, L.O.; Wolverson, D.; Baumberg, J.J. Nanoimprint lithography of Al nanovoids for deep-UV SERS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17358–17363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Neumann, O.; McClain, M.J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Aluminum Nanocrystals: A Sustainable Substrate for Quantitative SERS-Based DNA Detection. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5071–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigle, D.O.; Perkins, E.; Baumberg, J.J.; Mahajan, S. Reproducible Deep-UV SERRS on Aluminum Nanovoids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, C.L.; Koh, C.S.L.; Wang, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Jiang, R.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Phang, I.Y.; Ling, X.Y. Aluminum nanostructures with strong visible-range SERS activity for versatile micropatterning of molecular security labels. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, A.; Jiang, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Man, B. Aluminum nanoparticle films with an enhanced hot-spot intensity for high-efficiency SERS. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9174–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Fang Lim, S.; Puretzky, A.A.; Riehn, R.; Hallen, H.D. Near-field enhanced ultraviolet resonance Raman spectroscopy using aluminum bow-tie nano-antenna. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 113116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Cardinal, M.F.; Ross, M.B.; Zrimsek, A.B.; Bykov, S.V.; Punihaole, D.; Asher, S.A.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Aluminum Film-Over-Nanosphere Substrates for Deep-UV Surface-Enhanced Resonance Raman Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7968–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Meng, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Z.; Chen, B.; Sun, K. Ag-nanoparticle-decorated Au-fractal patterns on bowl-like-dimple arrays on Al foil as an effective SERS substrate for the rapid detection of PCBs. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2014, 50, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Ren, J.; Bai, X.; Bai, J. SERS activity with tenfold detection limit optimization on a type of nanoporous AAO-based complex multilayer substrate. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5920–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.; Hassing, S.; Albrektsen, O.; Foghmoes, S.; Morgen, P. Fabrication of Large-Area Self-Organizing Gold Nanostructures with Sub-10 nm Gaps on a Porous Al2O3 Template for Application as a SERS-Substrate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14165–14171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Choi, Y.; Hong, S.; Kang, T.; Lee, L.P. Self-organized hexagonal-nanopore SERS array. Small 2010, 6, 1741–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Wu, S.-H. Bi-functional Al-doped ZnO@SnO2 heteronanowires as efficient substrates for improving photocatalytic and SERS performance. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, L.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y. Surface Plasmon Resonance and Interference Coenhanced SERS Substrate of AAO/Al-Based Ag Nanostructure Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 23930–23936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, P.; Sarma, B.K. Ag/ZnO heterostructure fabricated on AZO platform for SERS based sensitive detection of biomimetic hydroxyapatite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 509, 144798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Goswami, L.P.; Gayathri, J.; Tiwari, S.; Saxena, K.; Mehta, D.S. Fabrication of low cost highly structured silver capped aluminium nanorods as SERS substrate for the detection of biological pathogens. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 495301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.J.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, J. Ag nanoparticle decorated MnO2 flakes as flexible SERS substrates for rhodamine 6G detection. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37750–37756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halouzka, V.; Halouzkova, B.; Jirovsky, D.; Hemzal, D.; Ondra, P.; Siranidi, E.; Kontos, A.G.; Falaras, P.; Hrbac, J. Copper nanowire coated carbon fibers as efficient substrates for detecting designer drugs using SERS. Talanta 2017, 165, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, M. Active site-dominated electromagnetic enhancement of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) on a Cu triangle plate. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 42030–42037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Gu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Fu, X.; Tang, J. Hydrophobic ligand-mediated hierarchical Cu nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxides for SERS platform. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 7764–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Zhu, L. Highly Sensitive and Stable Copper-Based SERS Chips Prepared by a Chemical Reduction Method. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizajghorbani-Aghdam, H.; Miller, T.S.; Malekfar, R.; McMillan, P.F. SERS-Active Cu Nanoparticles on Carbon Nitride Support Fabricated Using Pulsed Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakir, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Onses, M.S. SERS-active hydrophobic substrates fabricated by surface growth of Cu nanostructures. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowska, M.; Krajczewski, J.; Dzięcielewski, I.; Kudelski, A.; Weyher, J.L. Au–Cu Alloyed Plasmonic Layer on Nanostructured GaN for SERS Application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; MacFarlane, D.R. Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of urea by highly ordered Au/Cu hybrid nanostructure arrays. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2017, 53, 7949–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Chettri, P.; Basu, J.; Tripathi, A.; Mukherjee, B.; Tiwari, A.; Mandal, R.K. Synthesis of anisotropic Au–Cu alloy nanostructures and its application in SERS for detection of methylene blue. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Krishnan, S.; Esparza, R.; Pal, U. Controlled Fabrication of Flower-Shaped Au-Cu Nanostructures Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Their Performance in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Molecular Sensing. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3699–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodjo, E.K.; Riaz, S.; Li, D.-W.; Qu, L.-L.; Marius, N.P.; Albert, T.; Long, Y.-T. Cu@Ag/β-AgVO3 as a SERS substrate for the trace level detection of carbamate pesticides. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 3785–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Yu, J.; Lei, F.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Man, B. Fast multiphase analysis: Self-separation of mixed solution by a wettability-controlled CuO@Ag SERS substrate and its applications in pollutant detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.K.; Ghildiyal, P.; Radhakrishnan, T.P. In Situ Fabricated Cu–Ag Nanoparticle-Embedded Polymer Thin Film as an Efficient Broad Spectrum SERS Substrate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y. Rationally Designed Graphene/Bilayer Silver/Cu Hybrid Structure with Improved Sensitivity and Stability for Highly Efficient SERS Sensing. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5761–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaja, S.; Nag, A. Bimetallic Ag-Cu Alloy Microflowers as SERS Substrates with Single-Molecule Detection Limit. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13027–13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Shi, X.; Jiang, F.; Xu, X. Superhydrophobic nanostructured copper substrate as sensitive SERS platform prepared by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 501, 144269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, T.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Rapid SERS detection of acid orange II and brilliant blue in food by using Fe3O4@Au core-shell substrate. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lai, H.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Hu, Y. CoFe2O4@HNTs/AuNPs Substrate for Rapid Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction and Efficient SERS Detection of Complex Samples All-in-One. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4607–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, G.; Depero, L.E.; Alessandri, I. Recyclable SERS substrates based on Au-coated ZnO nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2557–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.-E.; Tang, Z.; Zou, M.; Yang, X.; Gong, H.; Yu, Z.; Jin, S.; Liang, P. Ag@MIL-101(Cr) Film Substrate with High SERS Enhancement Effect and Uniformity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 7297–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, H.; Li, D.; Shen, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Li, S.; Fan, H.J. Ordered array of gold semishells on TiO2 spheres: An ultrasensitive and recyclable SERS substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, C.; Wang, L.; Bai, R.; Yang, Z. Label-Free Detecting of the Compaction and Decompaction of ctDNA Molecules Induced by Surfactants with SERS Based on a nanoPAA-ZnCl2-AuLs Solid Substrate. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Armenta, S.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcarcel, M.; Lendl, B. Determination of pyrimidine and purine bases by reversed-phase capillary liquid chromatography with at-line surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic detection employing a novel SERS substrate based on ZnS/CdSe silver-quantum dots. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9391–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zou, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. High-Performance Real-Time SERS Detection with Recyclable Ag Nanorods@HfO2 Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27162–27168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Tang, Z.; Liang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Q.; Huang, J.; Yu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H. ZrO2@Ag@SiO2 Sandwich Structure with High SERS Enhancement Effect and Stability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 25967–25974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippin, N.; Castillo-Seoane, J.; Lopez-Santos, M.C.; Rojas, C.T.; Ostrikov, K.; Barranco, A.; Sanchez-Valencia, J.R.; Borras, A. Plasma-Enabled Amorphous TiO2 Nanotubes as Hydrophobic Support for Molecular Sensing by SERS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50721–50733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, B.; Gu, M.; Petti, L.; Mormile, P. Controllable synthesis and SERS characteristics of hollow sea-urchin gold nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 25601–25608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, A.B.; Hwang, B.J.; Tegegne, W.A.; Wang, J.-S.; Tsai, H.-C.; Su, W.-N. Reliable and sensitive detection of pancreatic cancer marker by gold nanoflower-based SERS mapping immunoassay. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasary, S.S.; Singh, A.K.; Senapati, D.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Gold nanoparticle based label-free SERS probe for ultrasensitive and selective detection of trinitrotoluene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13806–13812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Fan, C.; Mao, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Liang, E.; Chao, M. A monolayer of hierarchical silver hemi-mesoparticles with tunable surface topographies for highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 074703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Zhang, K.; Han, S.; He, Y.; Lee, S.T. Silver nanosheet-coated inverse opal film as a highly active and uniform SERS substrate. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Brodoceanu, D.; Kraus, T.; Voelcker, N.H. Templated silver nanocube arrays for single-molecule SERS detection. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 4288–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrapu, H.; Avasarala, R.; Soma, V.R.; Balivada, S.K.; Podagatlapalli, G.K. Silver nanoribbons achieved by picosecond ablation using cylindrical focusing and SERS-based trace detection of TNT. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41217–41228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Lang, X.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Iwasaki, H.; Inouye, Y.; Xue, Q.; Chen, M. Single molecule detection from a large-scale SERS-active Au(7)(9)Ag(2)(1) substrate. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quyen, T.T.B.; Hwang, B.J. Novel Ag/Au Nanocubes Modified the Negative/Positive Charge on the Surface and Their Application in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Procedia CIRP 2016, 40, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Sigma-Aldrich. Platinum, Nanoparticle Dispersion. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/KZ/en/product/aldrich/773875 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Sigma-Aldrich. Palladium. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/KZ/en/product/aldrich/686468 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Sigma-Aldrich. Silver, Dispersion. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/KZ/en/substance/silverdispersion1078798765 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Sigma-Aldrich. Gold Nanoparticles. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/KZ/en/substance/goldnanoparticles1969798765 (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Chan, G.H.; Zhao, J.; Hicks, E.M.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Plasmonic Properties of Copper Nanoparticles Fabricated by Nanosphere Lithography. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuda, K.M.; Bingham, J.M.; Wustholz, K.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. 3.09—Nanostructures and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. In Comprehensive Nanoscience and Technology; Andrews, D.L., Scholes, G.D., Wiederrecht, G.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 263–301. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.S.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Tunable laser excitation profile of surface enhanced raman scattering from pyridine adsorbed on a copper electrode surface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1980, 75, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mernagh, T.P.; Cooney, R.P. Laser microzone damage in surface-enhanced Raman scattering by pyridine on cooper electrodes. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1985, 16, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, M.R.; Cooney, R.P. Chemical origins of surface-enhanced Raman scattering by cyanide on copper electrodes. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1985, 81, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, C.A.; Kovacs, G.J.; Aroca, R. Fourier transform surface-enhanced Raman scattering of Langmuir-Blodgett monolayers on copper and gold island substrates. Langmuir 2002, 9, 2151–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudelski, A.; Bukowska, J.; Dolata, M.; Grochala, W.; Szummer, A.; Janik-Czachor, M. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) on modified amorphous Cu–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 267, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpati, D.; Spada, E.R.; Pla Cid, C.C.; Sartorelli, M.L.; Aroca, R.F.; Constantino, C.J. Exploring copper nanostructures as highly uniform and reproducible substrates for plasmon-enhanced fluorescence. Analyst 2015, 140, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.Q.; Yue, Z.W.; Yang, D.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, Z.H.; Ge, H.H.; Li, Y.J. Self-assembled monolayer of ammonium pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on copper detected using electrochemical methods, surface enhanced Raman scattering and quantum chemistry calculations. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 6492–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendisová-Vyškovská, M.; Prokopec, V.; Člupek, M.; Matějka, P. Comparison of SERS effectiveness of copper substrates prepared by different methods: What are the values of enhancement factors? J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susman, M.D.; Feldman, Y.; Vaskevich, A.; Rubinstein, I. Chemical Deposition and Stabilization of Plasmonic Copper Nanoparticle Films on Transparent Substrates. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-C.; Li, C.-H. Cu, Cu–Cu2O core–shell, and hollow Cu2O nanodendrites: Structural evolution and reverse surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.D.; Sheremet, E.; Nesterov, M.; Moras, S.; Rahaman, M.; Weiss, T.; Hietschold, M.; Zahn, D.R.T. Aluminum and copper nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: A one-to-one comparison to silver and gold. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Yu, J.-S.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.-W. Nanoporous Copper with Tunable Nanoporosity for SERS Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardari, B.; Ozcan, M. Real-Time and Tunable Substrate for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy by Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles via Electrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, M.; Mondola, R. Synthetic cathinones: Chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of a new class of designer drugs of abuse marketed as “bath salts” or “plant food”. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, A.A.; Kaminska, A.; Adamkiewicz, W.; Witkowska, E.; Tkacz, M. Novel highly sensitive Cu-based SERS platforms for biosensing applications. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudelski, A.; Bukowska, J.; Janik-Czachor, M.; Grochala, W.; Szummer, A.; Dolata, M. Characterization of the copper surface optimized for use as a substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Vib. Spectrosc. 1998, 16, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S. A new route for the formation of Au nanowires and application of shape-selective Au nanoparticles in SERS studies. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Panderi, I.; Yan, D.D.; Szulak, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Ma, H.; Niesen, D.B.; Seeram, N.; Ahmed, A.; et al. A comparative study of hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles and hollow gold nanospheres on degradability and toxicity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8780–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Lin, M.; Chen, G.; Fan, C.; Li, M.; Gu, X.; Cong, S.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, L.; Fang, X.; et al. Photodegradable CuS SERS Probes for Intraoperative Residual Tumor Detection, Ablation, and Self-Clearance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23436–23444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Wang, H.; Hai, J.; He, S.; Chen, F.; Wang, B. Photochemical Synthesis of Porous CuFeSe2/Au Heterostructured Nanospheres as SERS Sensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Lung Cancer Cells and Their Biomarkers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5200–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Berlin, A.A.; Kwon, S.; Sundararajan, N.; Yamakawa, M. Metal Coated Nanocrystalline Silicon as an Active Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Substrate. U.S. Patent 6,970,239, 29 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Mock, J.; Smith, D.; Gao, T.; Sailor, M.J. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering from Silver-Plated Porous Silicon. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11654–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Yasseri, A.A.; Sharma, S.; Li, Z.; Woo, H.Y.; Vak, D.; Bazan, G.C.; Kelley, A.M. Silver nanocrystal-modified silicon nanowires as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman and hyper-Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6279–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Huo, D.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Electrodeposition of rough gold nanoarrays for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 263, 124388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, W.A.; Su, W.-N.; Beyene, A.B.; Huang, W.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hwang, B.-J. Flexible hydrophobic filter paper-based SERS substrate using silver nanocubes for sensitive and rapid detection of adenine. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Chae, J. Methods of reducing non-specific adsorption in microfluidic biosensors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 075015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchitskaya, G.L.; Mohideen, U.; Mostepanenko, V.M. Casimir and van der Waals forces between two plates or a sphere (lens) above a plate made of real metals. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 61, 062107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Vuye, G.; Lopez-Rios, T. Sers of oxygen on Ag surfaces covered by Al submonolayers. Surf. Sci. Lett. 1985, 164, L819–L822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robatjazi, H.; Zhao, H.; Swearer, D.F.; Hogan, N.J.; Zhou, L.; Alabastri, A.; McClain, M.J.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Plasmon-induced selective carbon dioxide conversion on earth-abundant aluminum-cuprous oxide antenna-reactor nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Kadkhodazadeh, S.; Lazzari, M. Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) in the visible range on scalable aluminum-coated platforms. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10638–10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, C.; Schwind, M.; Kasemo, B.; Zorić, I. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonances in Aluminum Nanodisks. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.H.; Zhao, J.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy of Triangular Aluminum Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13958–13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Ding, S.-Y.; Panneerselvam, R.; Tian, Z.-Q. Core–Shell Nanoparticle-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5002–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoumi, A.; Zhang, D.; Tam, F.; Halas, N.J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5523–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Adsorption of DNA onto gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide: Surface science and applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 10485–10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, M.M.; McKeating, K.S.; Faulds, K. Recent developments and future directions in SERS for bioanalysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 5312–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, V.V.; Herrmann, L.O.; Sigle, D.O.; Zhang, T.; Liedl, T.; Baumberg, J.J.; Keyser, U.F. DNA origami based assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Paria, D.; Balasubramanian, K.; Ghosh, A.; Narayanan, R.; Raghavan, S. Directed Microwave-Assisted Self-Assembly of Au–Graphene–Au Plasmonic Dimers for SERS Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gu, H.; Qin, L.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, X. Facile fabrication of adjustable Al/C3N4/Agx nano-micro composites for sensitive SERS detection. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Chuang, K.-W.; Chou, C.-M. A facile method to directly deposit the large-scale Ag nanoparticles on a silicon substrate for sensitive, uniform, reproducible and stable SERS substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibar, G.; Topal, A.E.; Dana, A.; Tuncel, A. Newly designed silver coated-magnetic, monodisperse polymeric microbeads as SERS substrate for low-level detection of amoxicillin. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1119, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, S.; Cantarini, L.; Almaviva, S.; Puiu, A.; Rufoloni, A. Assessment of SERS activity and enhancement factors for highly sensitive gold coated substrates probed with explosive molecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 592, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Pang, S.; He, L. Integration of colorimetric and SERS detection for rapid screening and validation of melamine in milk. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6426–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros Santos, E.; Lima, E.C.N.L.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Sigoli, F.A.; Mazali, I.O. Fast detection of paracetamol on a gold nanoparticle–chitosan substrate by SERS. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3564–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.Y.; Liu, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, Y.; Tsang, Y.H.; Lei, D.Y. In situ SERS monitoring of photocatalytic organic decomposition using recyclable TiO2-coated Ag nanowire arrays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 301, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Z.; Li, Z. Silver Nanoparticles Coated Zinc Oxide Nanorods Array as Superhydrophobic Substrate for the Amplified SERS Effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9977–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Bao, Z.; Jia, F.; Deng, S. Adsorption of CO(2), CH(4), N(2)O, and N(2) on MOF-5, MOF-177, and zeolite 5A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Yaghi, O.M. Storage of hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide in highly porous covalent organic frameworks for clean energy applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8875–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.X.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Shekhah, O.; Jiang, H.; Adil, K.; Cairns, A.J.; Eddaoudi, M. Tunable Rare Earth fcu-MOF Platform: Access to Adsorption Kinetics Driven Gas/Vapor Separations via Pore Size Contraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5034–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, D.; Cui, Y. SERS-Activated Platforms for Immunoassay: Probes, Encoding Methods, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7910–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Rong, Z.; Wang, W.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Magnetic SERS Strip for Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Respiratory Viruses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19495–19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Mo, Y.; Chen, F.; Shi, H.; Zhang, W.; Hu, C.; Chen, J. Electrochemical fabrication of pyramid-shape silver microstructure as effective and reusable SERS substrate. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 274, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, C.X.; Deng, L.; Zhang, G.X.; Xu, H.J.; Sun, X.M. Cicada wing decorated by silver nanoparticles as low-cost and active/sensitive substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 213101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. Synthesis of flexible and stable SERS substrate based on Au nanofilms/cicada wing array for rapid detection of pesticide residues. Opt. Commun. 2018, 425, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, F.D.; Hsu, T.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Yang, K.H.; Chen, B.C. A new strategy to prepare surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active substrates by electrochemical pulse deposition of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2011, 47, 2958–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, S. Snowflake-like gold nanoparticles as SERS substrates for the sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticide residues. Food Control. 2020, 108, 106835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwidyantri, A.; El-Mekki, I.; Lai, C. Tunable plasmonic Au-film over nanosphere SERS substrate by rapid thermal annealing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Sendai, Japan, 22–25 August 2016; pp. 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Yang, K.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Yu, C.C.; Wu, Y.H. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active gold nanoparticles modified with a monolayer of silver film. Analyst 2012, 137, 4943–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Mu, X.; Pang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, D. Ultrasensitive SERS detection of rhodamine 6G and p-nitrophenol based on electrochemically roughened nano-Au film. Talanta 2020, 210, 120631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, Y.; Lin, B.Y. Silver-Based SERS Pico-Molar Adenine Sensor. Biosensors 2020, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.Y.; Chui, H.C.; Tzeng, Y. Electrochemically fabricated self-aligned 2-D silver/alumina arrays as reliable SERS sensors. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 11441–11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wang, K.S.; Tsai, K.T.; Chen, Z.X.; Chang, Y.C.; Tseng, Y.Q.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.L. SERS Detection of Biomolecules by Highly Sensitive and Reproducible Raman-Enhancing Nanoparticle Array. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapandiyan, P.; Yang, J. Photochemical method for decoration of silver nanoparticles on filter paper substrate for SERS application. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2014, 45, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potara, M.; Baia, M.; Farcau, C.; Astilean, S. Chitosan-coated anisotropic silver nanoparticles as a SERS substrate for single-molecule detection. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, K.; Ye, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Chen, R.; Lin, J. Label-free detection of nasopharyngeal and liver cancer using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and partial lease squares combined with support vector machine. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6053–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Lin, T.; Zheng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, P. Rapid and label-free identification of different cancer types based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering profiles and multivariate statistical analysis. J. Cell Biochem. 2021, 122, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dai, E.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Z.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K.; Tu, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Development of a SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in clinical samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Man, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, C. Label-free and stable serum analysis based on Ag-NPs/PSi surface-enhanced Raman scattering for noninvasive lung cancer detection. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4345–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Cheng, H.; Hou, J.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G.; Lü, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, C. Detection of breast cancer based on novel porous silicon Bragg reflector surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy-active structure. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2020, 18, 051701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Lou, B.; Wang, H. An intelligent serological SERS test toward early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis through ultrasensitive nanobiosensing. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5331–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Yan, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Su, Y.; et al. Fabrication of optoplasmonic particles through electroless deposition and the application in SERS-based screening of nodule-involved lung cancer. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 279, 121483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Lin, D.; Lai, S.; Tao, H.; Chen, T.; Peng, M.; Qiu, S.; Feng, S. Highly sensitive and reliable detection of microRNA for clinically disease surveillance using SERS biosensor integrated with catalytic hairpin assembly amplification technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 208, 114236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, P.; Kapil, D.; Pyng, L.; Hann Qian, L.; Dinish, U.S.; Malini, O. Proof of concept clinical study for the rapid diagnosis of Lung cancer from pleural fluid using label free SERS based chemometric approach. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11655, Label-free Biomedical Imaging and Sensing (LBIS), Online, 5 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Buse, B.; Hülya, T.; Müslüm, İ.; Cenk, Y.; Sükrü Numan, B.; Süleyman, Ç.; Meriç, Ö.; Özlem, D.; Önder, E.; Ihsan, S.; et al. Clinical validation of SERS metasurface SARS-CoV-2 biosensor. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11957, Biomedical Vibrational Spectroscopy 2022: Advances in Research and Industry, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Czaplicka, M.; Kowalska, A.A.; Nowicka, A.B.; Kurzydłowski, D.; Gronkiewicz, Z.; Machulak, A.; Kukwa, W.; Kamińska, A. Raman spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) spectra of salivary glands carcinoma, tumor and healthy tissues and their homogenates analyzed by chemometry: Towards development of the novel tool for clinical diagnosis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1177, 338784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.A.; Jenkins, R.A.; Pryse, M.M.; Welsby, K.A.; Jitsumura, M.; Thornton, C.A.; Dunstan, P.R.; Harris, D.A. A high-throughput serum Raman spectroscopy platform and methodology for colorectal cancer diagnostics. Analyst 2018, 143, 6014–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefancu, A.; Moisoiu, V.; Couti, R.; Andras, I.; Rahota, R.; Crisan, D.; Pavel, I.E.; Socaciu, C.; Leopold, N.; Crisan, N. Combining SERS analysis of serum with PSA levels for improving the detection of prostate cancer. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2455–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, Q.; Lin, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, H.; Liu, S. Noninvasive prostate cancer screening based on serum surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and support vector machine. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 091104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, S.; Cui, X.; Xu, W.; Kong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, W. Identifying non-muscle-invasive and muscle-invasive bladder cancer based on blood serum surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 3533–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Jin, S.; Song, Z.; Jiang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z. Label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of serum based on multivariate statistical analysis for the diagnosis and staging of lung adenocarcinoma. Vib. Spectrosc. 2019, 100, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, X.; Zeng, Q.; Li, L.; Lin, L.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Su, C.; Qi, M.; Guo, Z. Classifying low-grade and high-grade bladder cancer using label-free serum surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and support vector machine. Laser Phys. 2018, 28, 035603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jin, M.; Su, C.; Lin, L.; Xu, J.; et al. Characterization and noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer with serum surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and genetic algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Tingting, L.; Yamin, L.; Jiamin, G.; Wei, G.; Xiang, W.; Yun, Y.; Juqiang, L. Label-free detection of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia based on SERS spectroscopy of Plasma. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11900, Optics in Health Care and Biomedical Optics XI, Nantong, China, 9 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Gao, N.; Yue, X.; Zhong, F.; Lv, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Ma, C. Establishment of a reliable scheme for obtaining highly stable SERS signal of biological serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yan, B.; Xue, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Ji, P. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of blood serum based on gold nanoparticles for the diagnosis of the oral squamous cell carcinoma. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Feng, S.; Pan, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, G.; Xie, S.; Zeng, H.; Chen, R. Colorectal cancer detection by gold nanoparticle based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of blood serum and statistical analysis. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 13565–13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Wang, Y.; Hua, L.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Y. New method of lung cancer detection by saliva test using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Mistro, G.; Cervo, S.; Mansutti, E.; Spizzo, R.; Colombatti, A.; Belmonte, P.; Zucconelli, R.; Steffan, A.; Sergo, V.; Bonifacio, A. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of urine for prostate cancer detection: A preliminary study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3271–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; He, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Label-free diagnosis for colorectal cancer through coffee ring-assisted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on blood serum. J. Biophoton. 2020, 13, e201960176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Rong, M.; Shao, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Dong, B.; Xue, W.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Pan, J. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of serum accurately detects prostate cancer in patients with prostate-specific antigen levels of 4-10 ng/mL. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5399–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cai, X.; Yang, H. Research on the difference between patients with coronary heart disease and healthy controls by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 272, 120997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Arteaga, A.; de Jesús Zermeño Nava, J.; Kolosovas-Machuca, E.S.; Velázquez-Salazar, J.J.; Vinogradova, E.; José-Yacamán, M.; Navarro-Contreras, H.R. Diagnosis of breast cancer by analysis of sialic acid concentrations in human saliva by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of silver nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Teng, P.; Xiao, W.; He, G.; Song, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, B.; Li, G.; Hu, L.; Cao, D.; et al. Application of the amplification-free SERS-based CRISPR/Cas12a platform in the identification of SARS-CoV-2 from clinical samples. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, D.; Lin, J.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Feng, S.; Li, B.; Liu, N.; et al. Label-free detection of serum proteins using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for colorectal cancer screening. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 087003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrborn, C.G. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: An overview. Rev. Urol. 2005, 7 (Suppl. S9), S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
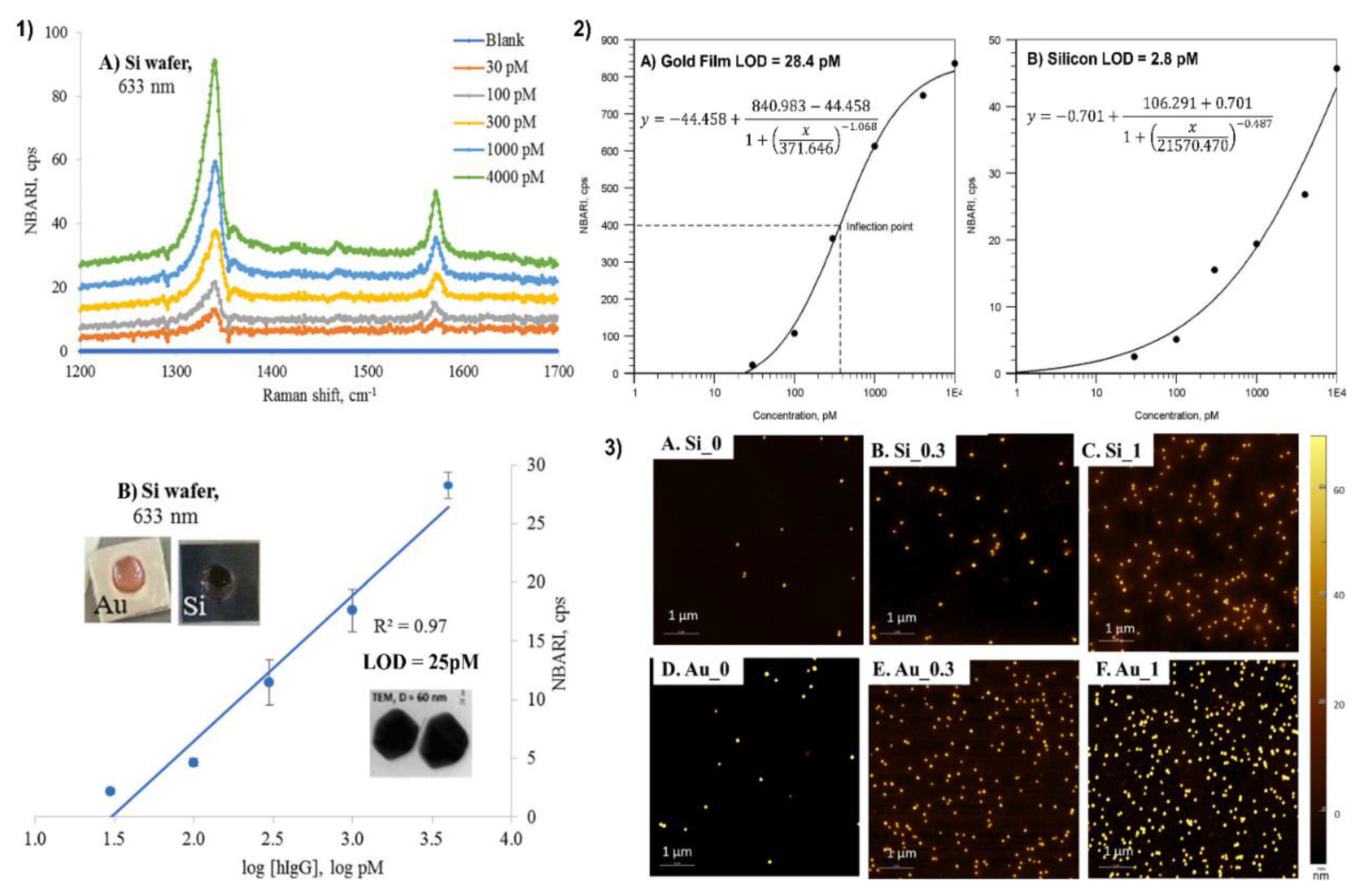
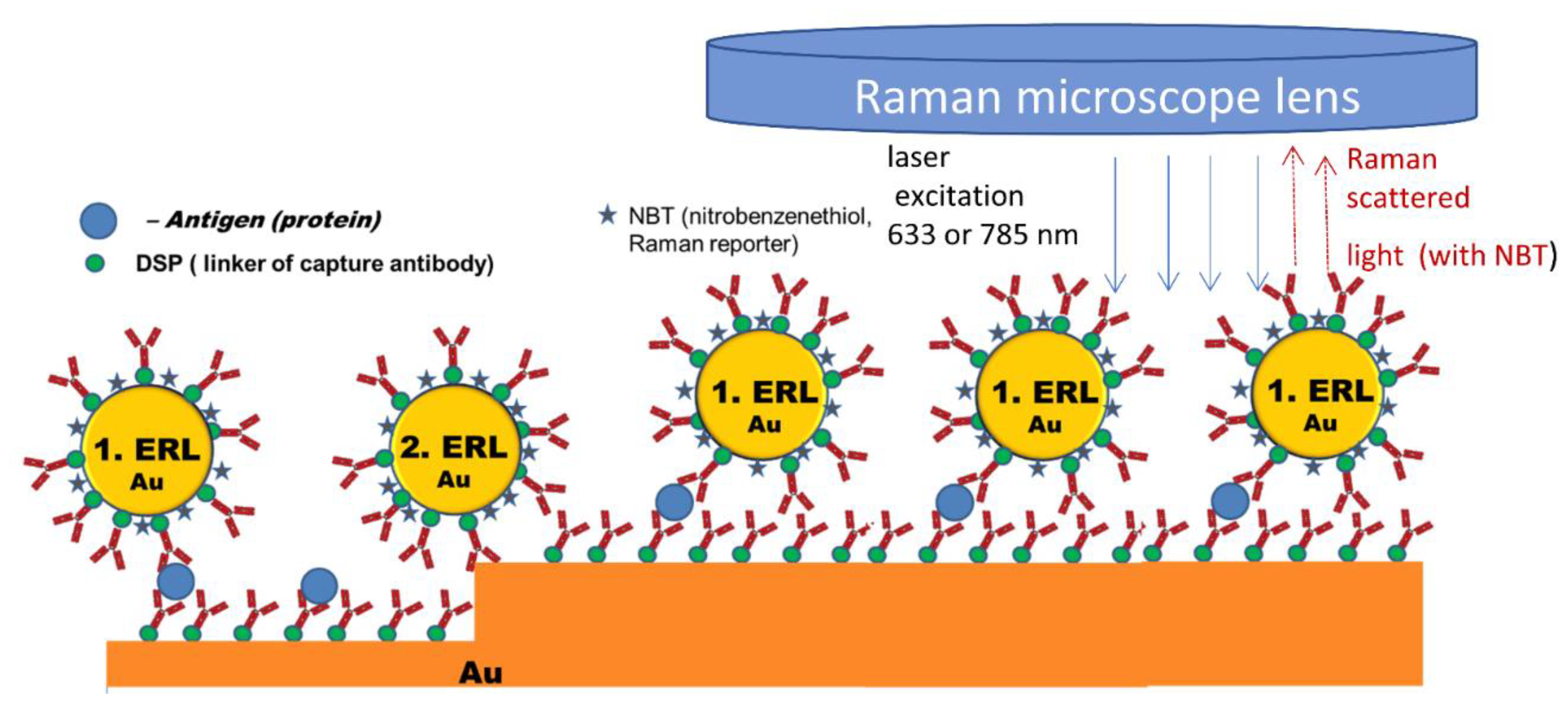

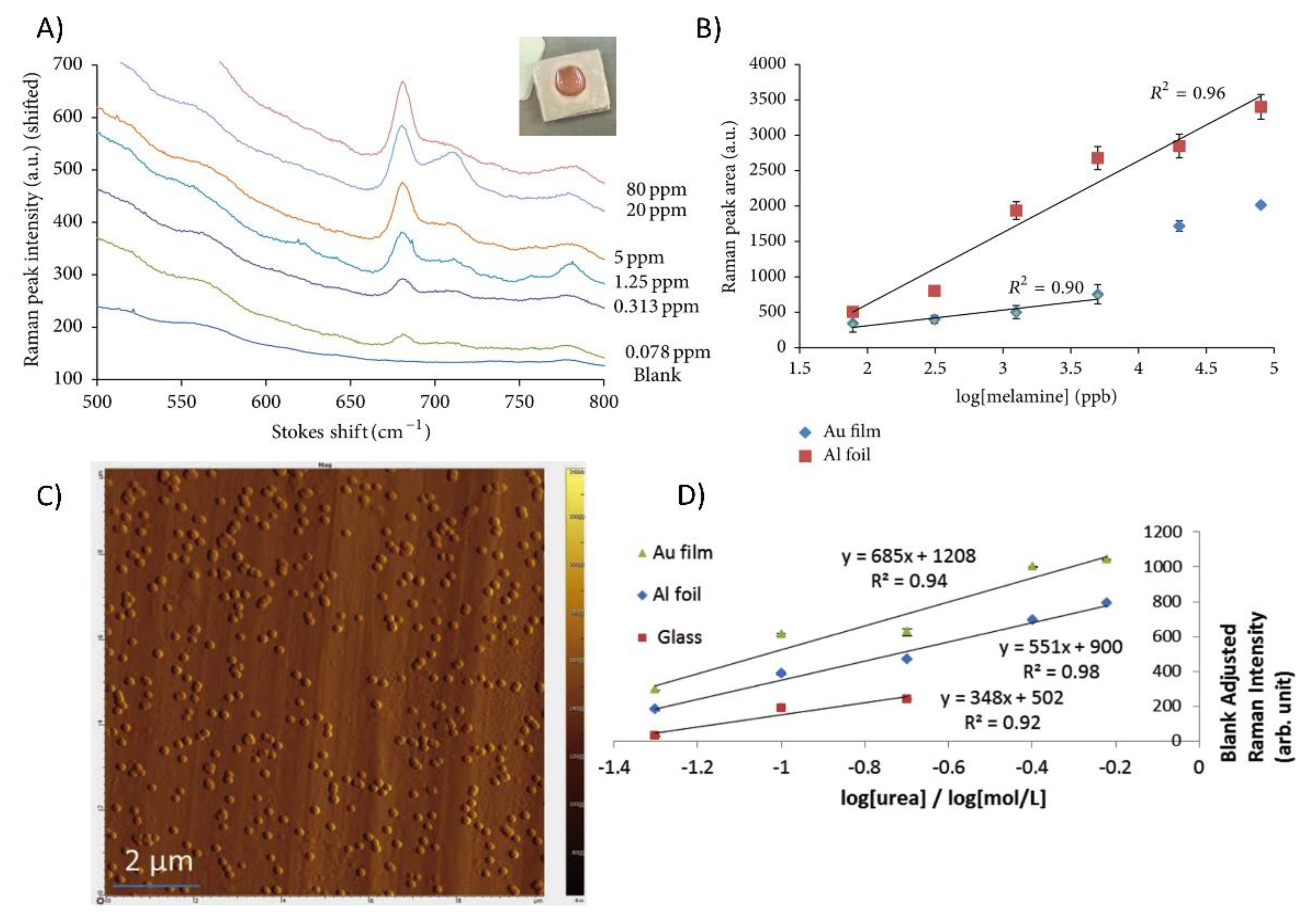
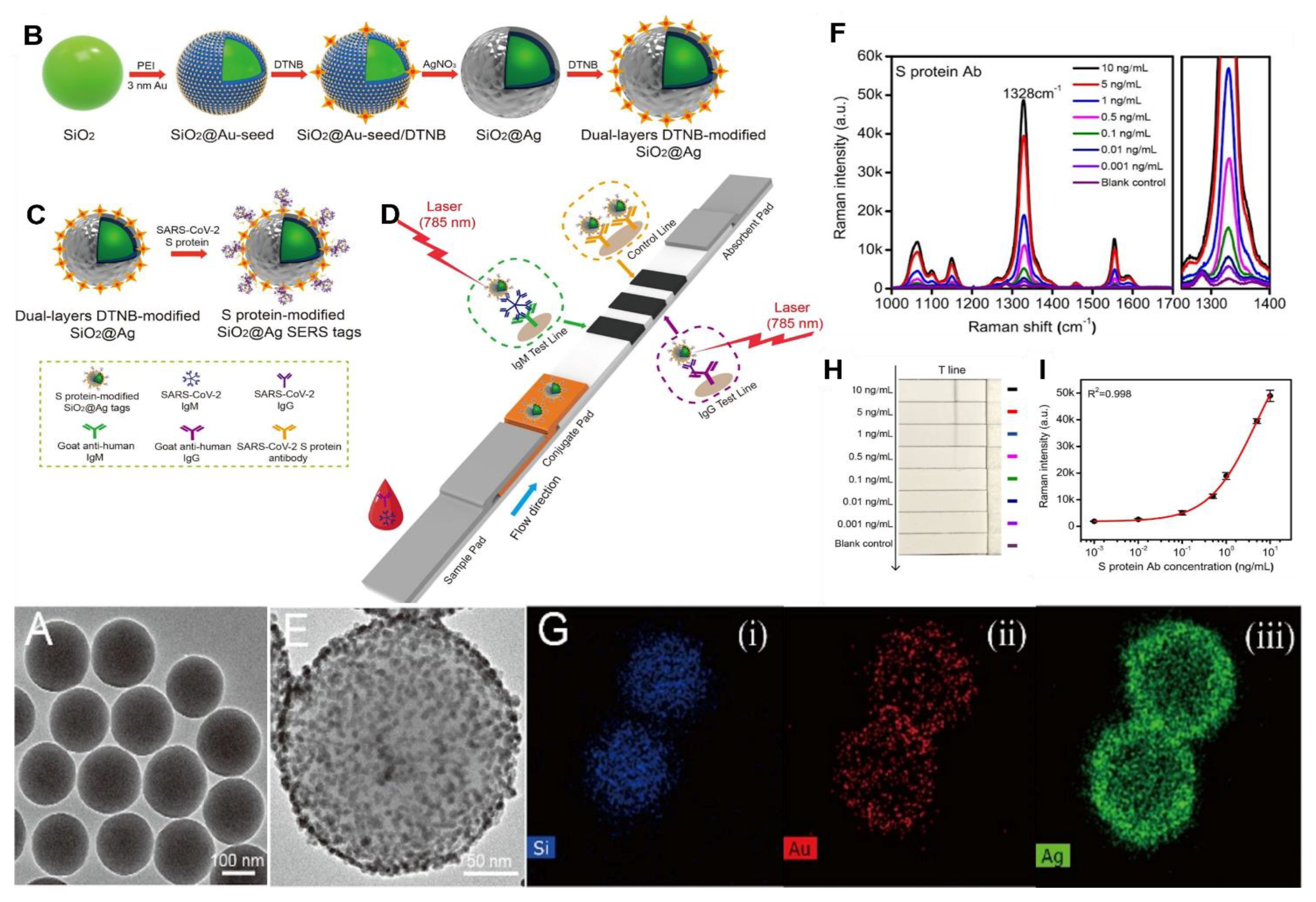
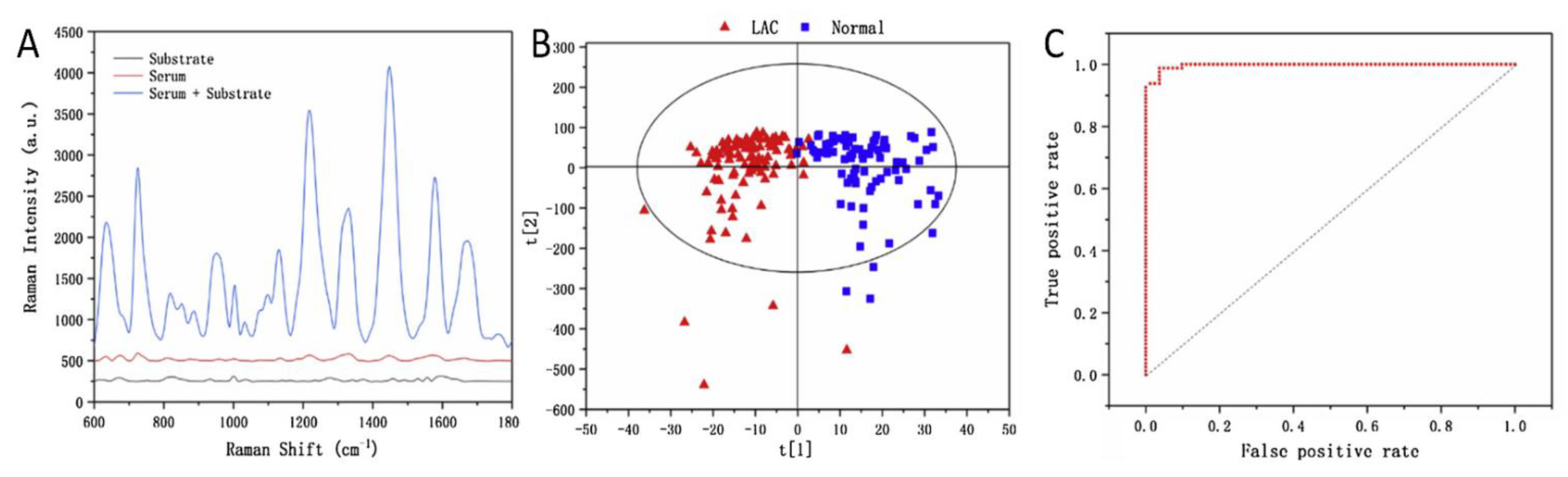
| Substrate | Analytes | Analytical Parsameters | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al NP−film | Adenine, CV (325 nm) | Adenine: EF 3.62 × 105, LOD 10−6 M CV: EF 4.1 × 105, LOD 10−7 | [154] |
| Al nanocrystals | ssDNA (785 nm) | EF 105–106 LOD 2 × 10−6 M | [151] |
| Al nanodots | NAP, TEPS (532 nm) | EF 7 × 104 EF 1.7 × 104 | [153] |
| AlFON | Adenine (229 nm), (Ru(bpy)3)2+ MH (355 nm), BPE (405 nm) | EF 103–105 | [156] |
| Al nanovoids | Adenine (244 nm) | EF 5 × 103 | [150] |
| Al nanovoids | Adenine (488 nm, 785 nm) | EF 106 | [152] |
| Al bow-tie nanoantenna | Liquid benzene (258.8 nm) | EF~105 | [155] |
| Substrate | Analyte | Analytical Parameters | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 NPs @Au nanoshell | acid orange II, brilliant blue | LOD 6.31 × 10−7 M brilliant blue, 2.85 × 10−3 M acid orange II RSD 2.49–3.75%, R2 = 92–98% | Xie et al., 2019 [182] |
| CoFe2O4NPs@HNTs/AuNPs | 4,4′-thioaniline, nitrofurantoin | LOD 1.20 × 10−7 M 4,4′-thioaniline, 5.88 × 10−8 M nitrofurantoin EF 2.7 × 107 | Zhang et al., 2020 [183] |
| Au coated-ZnO NRs | MB | LOD 10−12 M | Sinha et al., 2011 [184] |
| Ag NPs@ZnO | 4-ATP | 3-fold enhancement compared with hydrophilic Ag@ZnO RSD 11% | Xu et al., 2011 [252] |
| Ag NPs@MIL-101(Cr) film | 4-ATP, nitrofurantoin (NFT) | LOD: 10−11 M 4-ATP, 10−7 M NFT RSD 5% | Shao et al., 2021 [185] |
| Au semishells on TiO2 spheres | Rhodamine 6G (R6G), brilliant cresyl blue (BCB) | LOD: BCB 10−7 M, R6G 10−6 M EF 1.4 × 105 RSD 12% | Li et al., 2021 [186] |
| nanoPAA-ZnCl2- AuLs | ctDNA, Surfactant CTAB, SDS, composites ctDNA−CTAB, DNA−CTAB−SDS | LOD: 10−9 M EF 9.18 × 107 | Hao et al., 2020 [187] |
| ZnS capped CdSe Ag-QDs | Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, xanthine, and hypoxanthine | LOD: 2 × 10−6 M RSD 3.0–6.3% R2 = 0.991–0.999 | Carrillo-Carrion et al., 2011 [188] |
| Ag NRs@HfO2 shell | CV, MB;2-NAT and 2MPy | LOD 1.25 × 10−7 M EF 6.1 × 107 RSD 5.14% | Ma et al., 2016 [189] |
| ZrO2@Ag@SiO2 NPs | 4-ATP, R6G | LOD: 10−9 M 4-ATP, 10−8 M R6G RSD 17.4% | Shi et al., 2020 [190] |
| TiO2 NTs@ AgNPs (diameter 10–12 nm) | R6G | LOD 10−12 M EF 9.4 × 107 | Filippin et al., 2020 [191] |
| Substrate | Average EF | Average LOD (M) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic | Geometric | Arithmetic | Geometric | ||
| Si | [55,66,68,71,75,77,78,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,92,93,100,102,103,105,106,117,119,120,121,124,128,129,230,265] | ||||
| Pt/Pd | [55,100,136,137,138,143,147] | ||||
| Au/Ag | [157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,196,197,199,200,258,259,260,261,262,263,264] | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultangaziyev, A.; Ilyas, A.; Dyussupova, A.; Bukasov, R. Trends in Application of SERS Substrates beyond Ag and Au, and Their Role in Bioanalysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110967
Sultangaziyev A, Ilyas A, Dyussupova A, Bukasov R. Trends in Application of SERS Substrates beyond Ag and Au, and Their Role in Bioanalysis. Biosensors. 2022; 12(11):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110967
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultangaziyev, Alisher, Aisha Ilyas, Aigerim Dyussupova, and Rostislav Bukasov. 2022. "Trends in Application of SERS Substrates beyond Ag and Au, and Their Role in Bioanalysis" Biosensors 12, no. 11: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110967
APA StyleSultangaziyev, A., Ilyas, A., Dyussupova, A., & Bukasov, R. (2022). Trends in Application of SERS Substrates beyond Ag and Au, and Their Role in Bioanalysis. Biosensors, 12(11), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110967





