Colorimetric Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus (COVID-19) in Artificial Saliva Using Polydiacetylene Paper Strips
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of PCDA-NHS Monomer
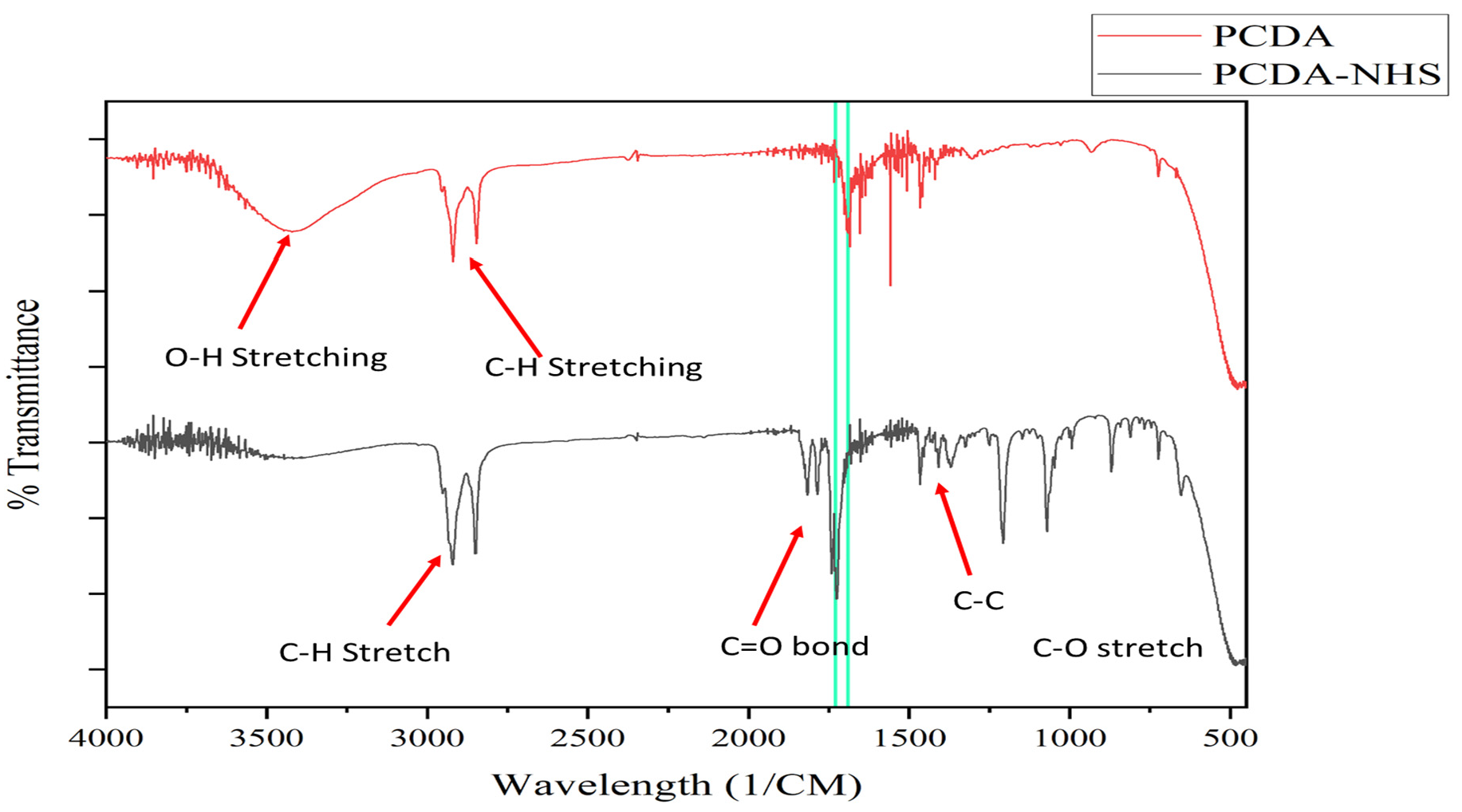
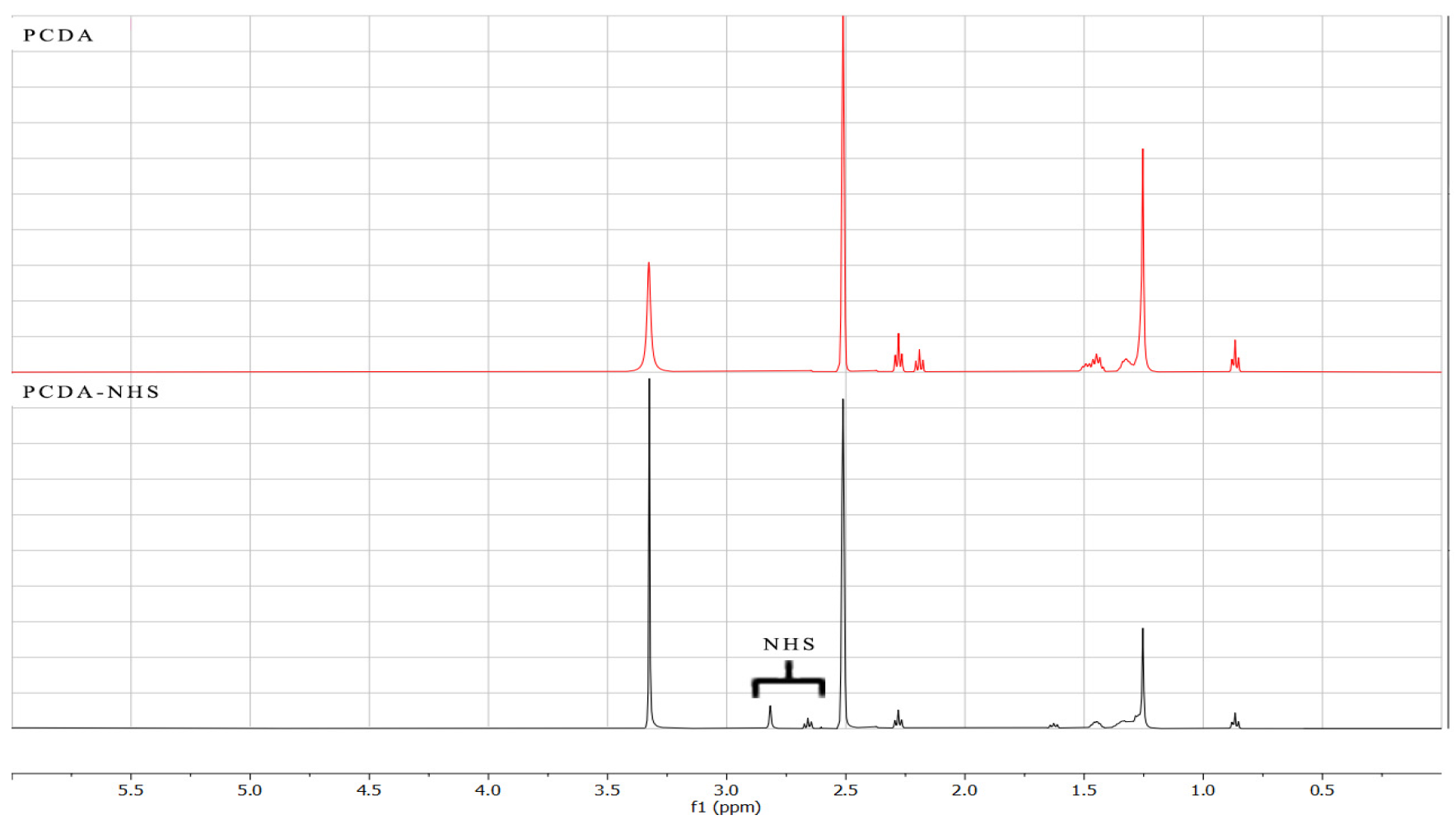
2.3. Characterization of PCDA and PCDA-NHS
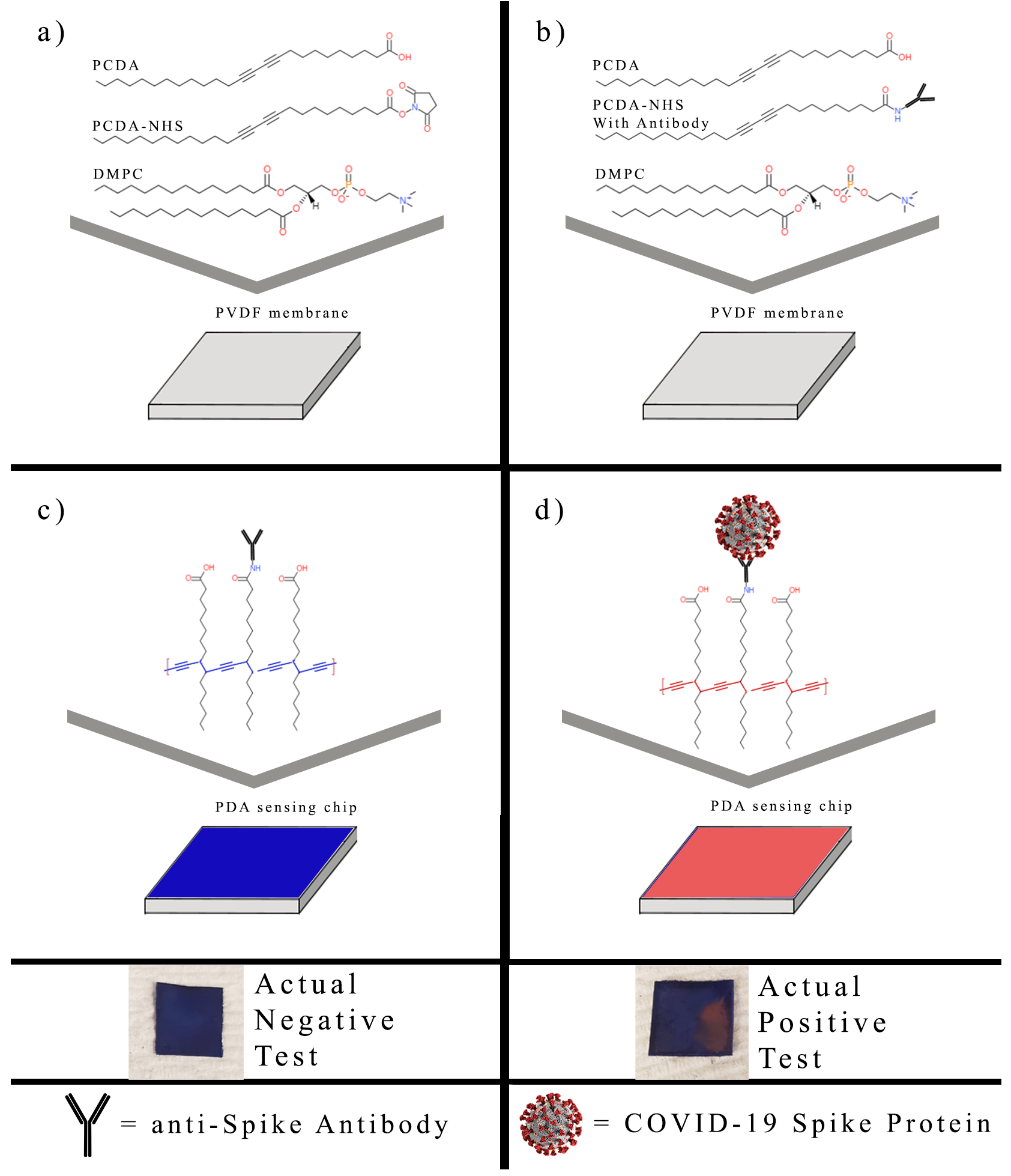
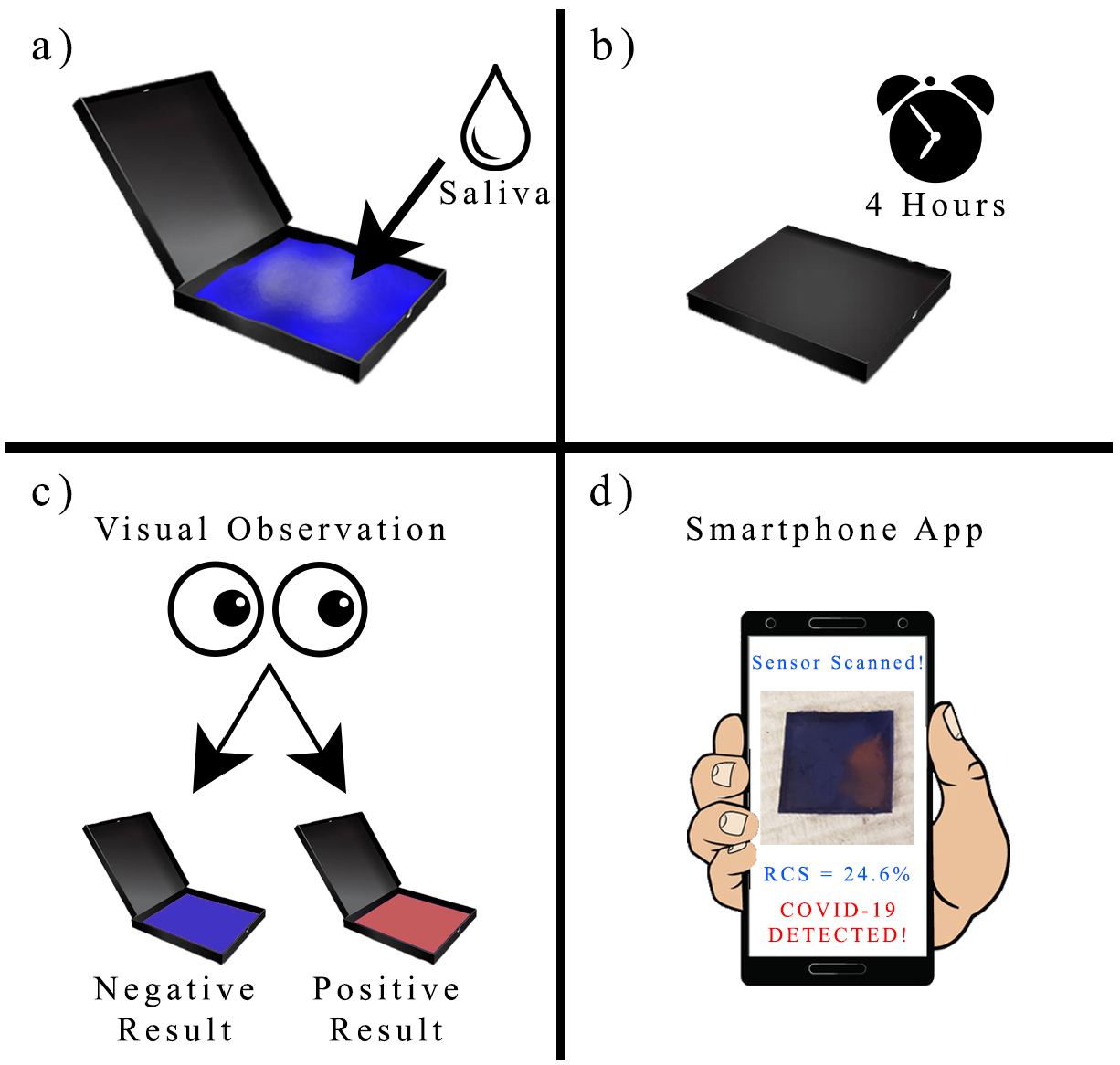
2.4. Preparation of Polydiacetylene Sensing Chips
2.5. PDA Sensor Response to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
2.6. Specificity of Sensor to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in the Presence of the MERS-CoV Spike Protein
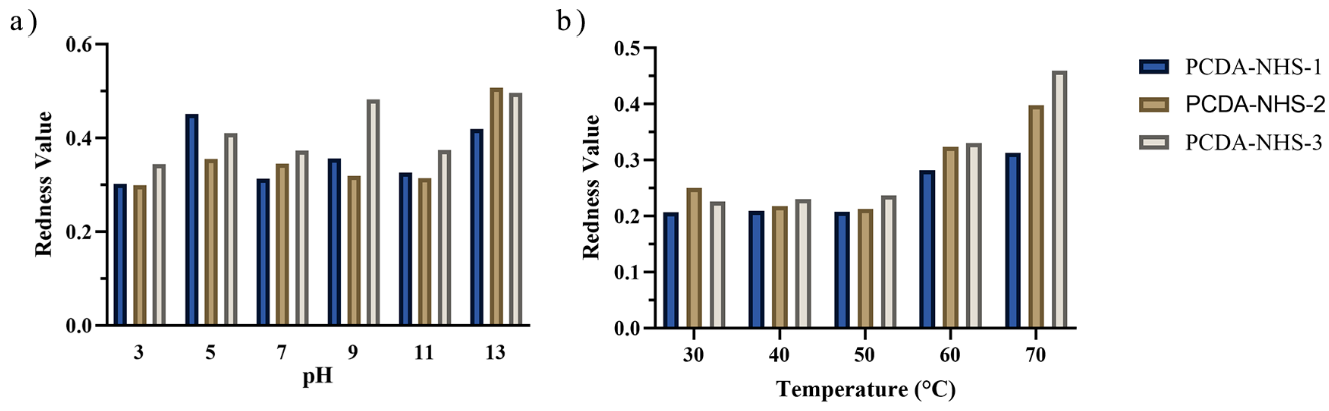
2.7. Effects of Temperature and pH on the Performance of the Sensor
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PCDA-NHS
3.2. Effect of Environmental Factors on PDA Sensor
3.3. PDA Biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 Detection
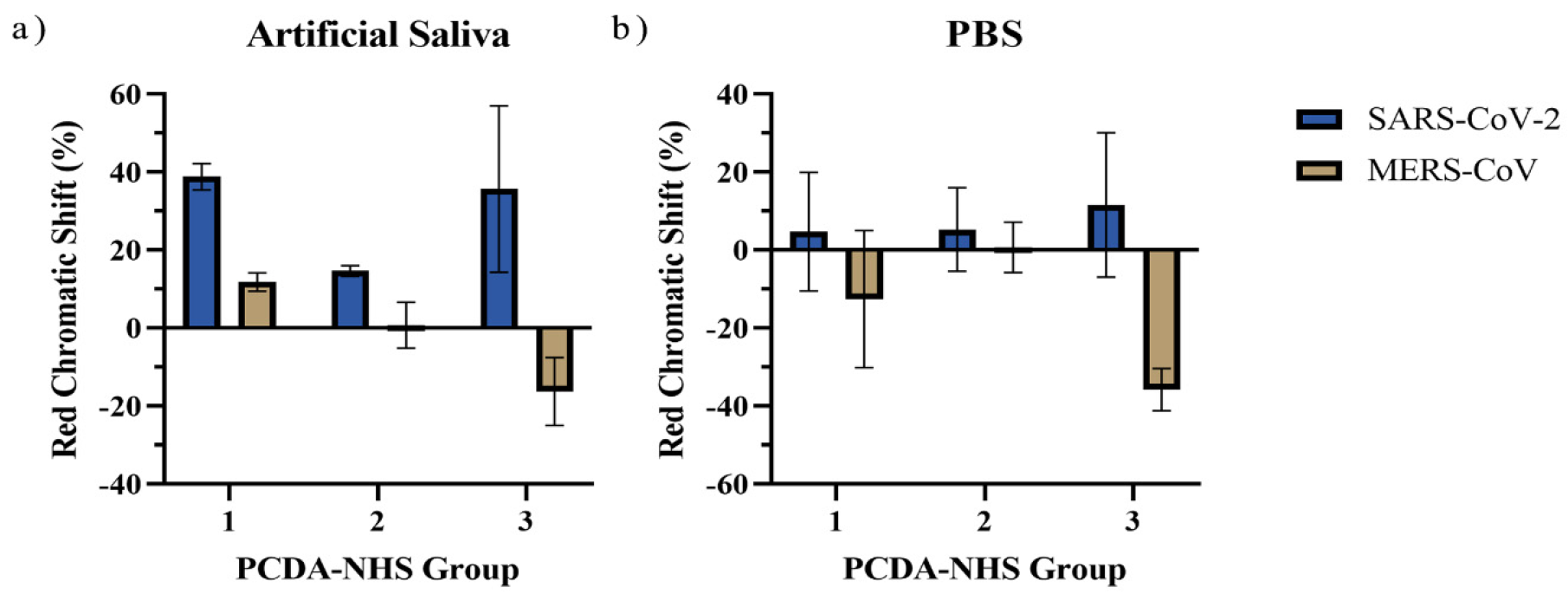
3.4. Specificity of the PDA Sensor
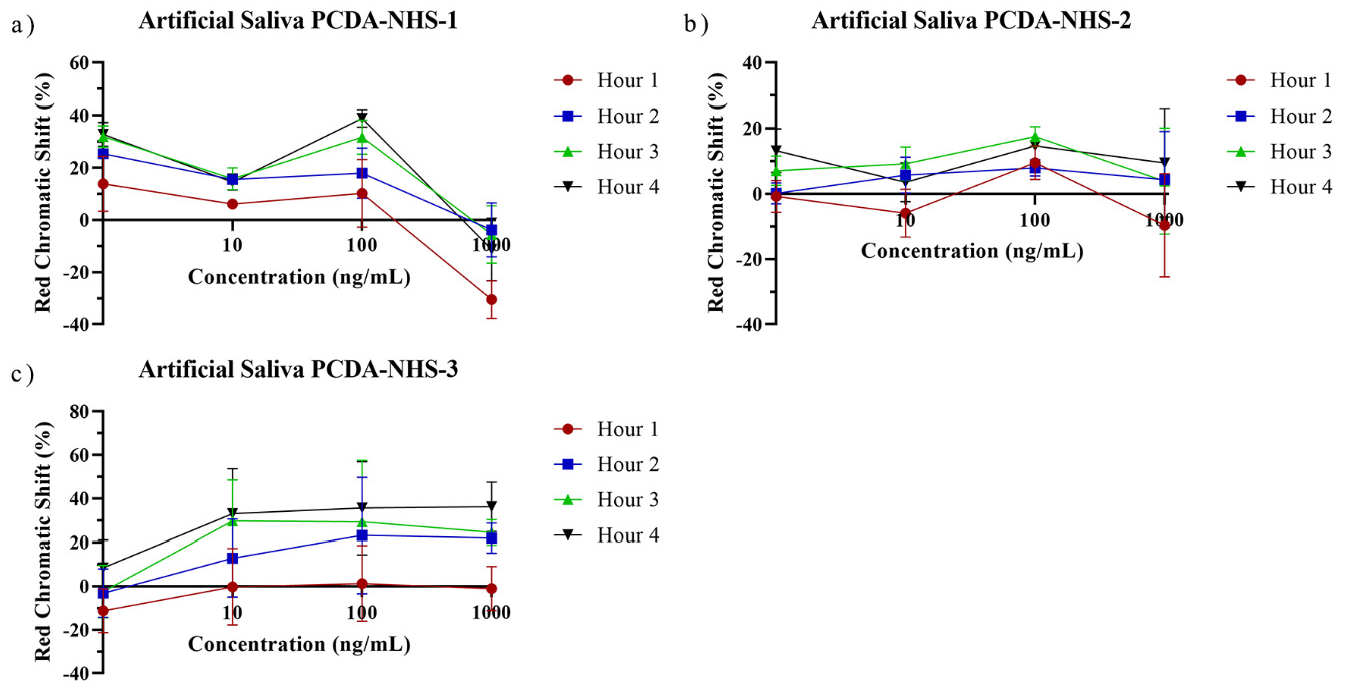
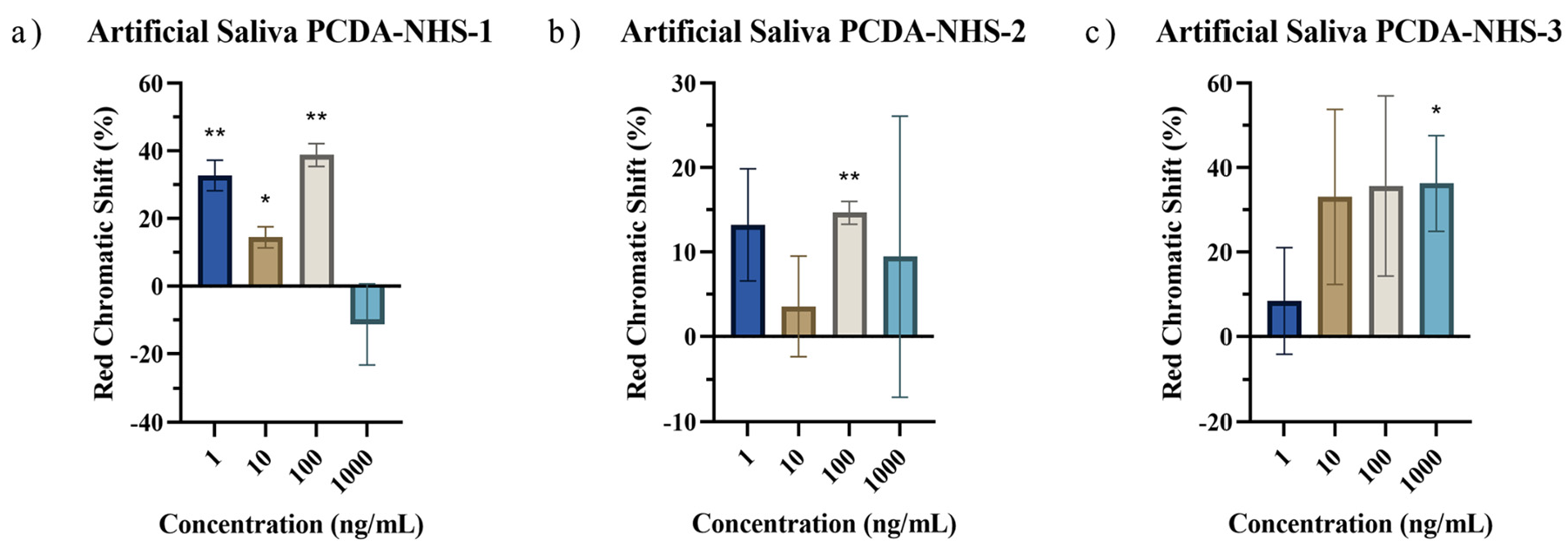
3.5. Performance of PDA Sensor for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Artificial Saliva
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, M.P.; Papenburg, J.; Desjardins, M.; Kanjilal, S.; Quach, C.; Libman, M.; Dittrich, S.; Yansouni, C.P. Diagnostic testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus 2: A narrative review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-Y.; Ma, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Xie, X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Deb, R.; Suklabaidya, S.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Hussain, S.A. Polydiacetylene a unique material to design biosensors. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2765–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.C.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Jung, O.-S.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, S. Visual simultaneous detection and real-time monitoring of cadmium ions based on conjugated polydiacetylenes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31254–31261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.U.; Seo, S.B.; Jang, S.; Choi, J.; Lim, J.-w.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, H.; Seo, S.; Kang, T.; Jung, J. Naked-eye detection of pandemic influenza a (pH1N1) virus by polydiacetylene (PDA)-based paper sensor as a point-of-care diagnostic platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Peng, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Luo, J. Detection and analysis of nucleic acid in various biological samples of COVID-19 patients. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 37, 101673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.J.; Garner, L.V.; Smoot, J.W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Saveson, C.J.; Sasso, J.M.; Gregg, A.C.; Soares, D.J.; Beskid, T.R. Assay techniques and test development for COVID-19 diagnosis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Kumar, B.K.; Deekshit, V.K.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Detection technologies and recent developments in the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.Y.; Bukhari, F.D.M.; Zulkefli, N.Z.; Ismail, I.; Mustapa, N.I.; Soh, T.S.T.; Hassan, A.H.; Peariasamy, K.M.; Lee, Y.L.; Suppiah, J. Colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 by uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 120, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.; Pandey, S.; Shrestha, R.; Pokharel, K.; Ligler, F.S.; Neupane, B.B. Review of analytical performance of COVID-19 detection methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. Jama 2020, 323, 1843–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, A.T.; Tong, Y.X.; Zhang, S. Profile of RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary study from 56 COVID-19 patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2249–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdas, K.; Darzi, A.; Jain, S. ‘Test, re-test, re-test’: Using inaccurate tests to greatly increase the accuracy of COVID-19 testing. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 810–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drain, P.K.; Hyle, E.P.; Noubary, F.; Freedberg, K.A.; Wilson, D.; Bishai, W.R.; Rodriguez, W.; Bassett, I.V. Diagnostic point-of-care tests in resource-limited settings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liana, D.D.; Raguse, B.; Gooding, J.J.; Chow, E. Recent advances in paper-based sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 11505–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.T.; Lantigua, D.; Meka, A.; Taing, S.; Pandher, M.; Camci-Unal, G. based sensors: Emerging themes and applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, E.; Jankelow, A.; Lim, J.; Kindratenko, V.; Ganguli, A.; White, K.; Kumar, J.; Bashir, R. COVID-19 point-of-care diagnostics: Present and future. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7899–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, A.L.; Fournier, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Campbell, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Warren, J.L.; Geng, B.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.J. Saliva or nasopharyngeal swab specimens for detection of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, A.; Mostafa, A.; Berger, J.; Lim, J.; Araud, E.; Baek, J.; Stewart de Ramirez, S.A.; Baltaji, A.; Roth, K.; Aamir, M.; et al. Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva and Viral Transport Medium Clinical Samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7797–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Städler, B. Recent developments in polydiacetylene-based sensors. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1196–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Städler, B. Polydiacetylene-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Viruses and Related Biomolecules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Luo, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, C.; Jin, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Jiang, L.; He, H. Development and evaluation of a polydiacetylene based biosensor for the detection of H5 influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 219, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-p.; Cho, E.; Yun, D.; Kim, T.; Lee, I.-S.; Jung, S. Label-free colorimetric detection of influenza antigen based on an antibody-polydiacetylene conjugate and its coated polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. Polymers 2017, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, S.Y. Recent trends in nanomaterials-based colorimetric detection of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Khazi, M.I.; Lee, D.G.; Kim, J.-M. Intrinsically porous dual-responsive polydiacetylenes based on tetrahedral diacetylenes. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 10312–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.T.; Viravathana, P.; Ingel, B.; Roper, C.; Tsutsui, H. Polydiacetylene-coated sensor strip for immunochromatic detection of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa. Slas Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2017, 22, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinsky, R.; Kliger, M.; Sheynis, T.; Kolusheva, S.; Jelinek, R. Glass-supported lipid/polydiacetylene films for colour sensing of membrane-active compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3247–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penczek, J.; Boynton, P.A.; Splett, J.D. Color error in the digital camera image capture process. J. Digit. Imaging 2014, 27, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Peng, S.; Spevak, W.; Charych, D. Color and chromism of polydiacetylene vesicles. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolusheva, S.; Boyer, L.; Jelinek, R. A colorimetric assay for rapid screening of antimicrobial peptides. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-l.; Li, J.-r.; Jiang, L. Chromatic immunoassay based on polydiacetylene vesicles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 38, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Razavi Bazaz, S.; Zhand, S.; Sayyadi, N.; Jin, D.; Stewart, M.P.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M. Point of Care Diagnostics in the Age of COVID-19. Diagnostics 2020, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, L.; Saroglia, M.; Galatà, G.; De Santis, R.; Fillo, S.; Luca, V.; Faggioni, G.; D’Amore, N.; Regalbuto, E.; Salvatori, P. Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: A reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.-H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.-S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G. Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, D.N.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, Y.J.; Heo, M.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.; Do, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, I.K. Flexible and highly biocompatible nanofiber-based electrodes for neural surface interfacing. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2961–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakoh, A.; Pimpitak, U.; Rengpipat, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Chaiyo, S. based electrochemical biosensor for diagnosing COVID-19: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Long, F. Rapid and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody in serum using optofluidic point-of-care testing fluorescence biosensor. Talanta 2021, 235, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yuan, M.; Song, G.; Beutler, N.; Shaabani, N.; Huang, D.; He, W.-t.; Zhu, X.; Callaghan, S.; Yong, P. A human antibody reveals a conserved site on beta-coronavirus spike proteins and confers protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabi9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.A.; Amin, Z.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Saallah, S.; Shaarani, S.M.; Sarker, S.; Siddiquee, S. Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Poultry Farming: Vaccination, Immune Response and Measures for Mitigation. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Jung, K.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Deltacoronavirus evolution and transmission: Current scenario and evolutionary perspectives. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 626785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PCDA | PCDA-NHS | DMPC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCDA-NHS-1 Group | 561.9 mg (1.5 mmol) | 146.9 mg (0.3 mmol) | 813.5 mg (1.2 mmol) |
| PCDA-NHS-2 Group | 449.5 mg (1.2 mmol) | 293.8 mg (0.6 mmol) | 813.5 mg (1.2 mmol) |
| PCDA-NHS-3 Group | 337.1 mg (0.9 mmol) | 440.7 mg (0.9 mmol) | 813.5 mg (1.2 mmol) |
| Sensor Design | Detection Target | Sample Type | Detection Limit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic beads-based biosensor | Spike (S) protein and nucleocapsid (N) protein | Saliva | 19 ng/mL for S protein, 8 ng/mL for N protein | Fabiani et al. [33] |
| Field-effect transistor | Spike protein | Nasal samples | 100 fg/mL | Seo et al. [34] |
| Colorimetric bioassay utilizing surface plasmon resonance | Nucleic acid | Isolated RNA | 180 ng/mL | Moitra et al. [35] |
| Paper-based electrochemical biosensor | Antibody | Human serum | 1 ng/mL | Yakoh et al. [36] |
| Optofluidic fluorescence biosensor | Antibody | Human serum | 12.5 ng/mL | Song et al. [37] |
| Polydiacetylene-based paper biosensor | Spike protein | Saliva | 1 ng/mL | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prainito, C.D.; Eshun, G.; Osonga, F.J.; Isika, D.; Centeno, C.; Sadik, O.A. Colorimetric Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus (COVID-19) in Artificial Saliva Using Polydiacetylene Paper Strips. Biosensors 2022, 12, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100804
Prainito CD, Eshun G, Osonga FJ, Isika D, Centeno C, Sadik OA. Colorimetric Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus (COVID-19) in Artificial Saliva Using Polydiacetylene Paper Strips. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100804
Chicago/Turabian StylePrainito, Christopher D., Gaddi Eshun, Francis J. Osonga, Daniel Isika, Cynthia Centeno, and Omowunmi A. Sadik. 2022. "Colorimetric Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus (COVID-19) in Artificial Saliva Using Polydiacetylene Paper Strips" Biosensors 12, no. 10: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100804
APA StylePrainito, C. D., Eshun, G., Osonga, F. J., Isika, D., Centeno, C., & Sadik, O. A. (2022). Colorimetric Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus (COVID-19) in Artificial Saliva Using Polydiacetylene Paper Strips. Biosensors, 12(10), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100804






