High-Density Gold Nanoparticles Implanted on Mg/Fe LDH Nanoflowers Assisted Lateral Flow Immuno-Dipstick Assay for Visual Detection of Human Epididymal Protein 4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Biological Reagents
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Preparation of Mg/Fe LDH Nanoflowers
2.4. Synthesis of OLM Capped Gold Nanoparticles (Au NPs)
2.5. Preparation of MF@Au@PEI Nanoflowers
2.6. Preparation of Ab2-MF@Au@PEI
2.7. Fabrication of the MF@Au@PEI−LFIA Test Strips
2.8. Detection of HE4 with the MF@Au@PEI−LFIA
3. Results and Discussion
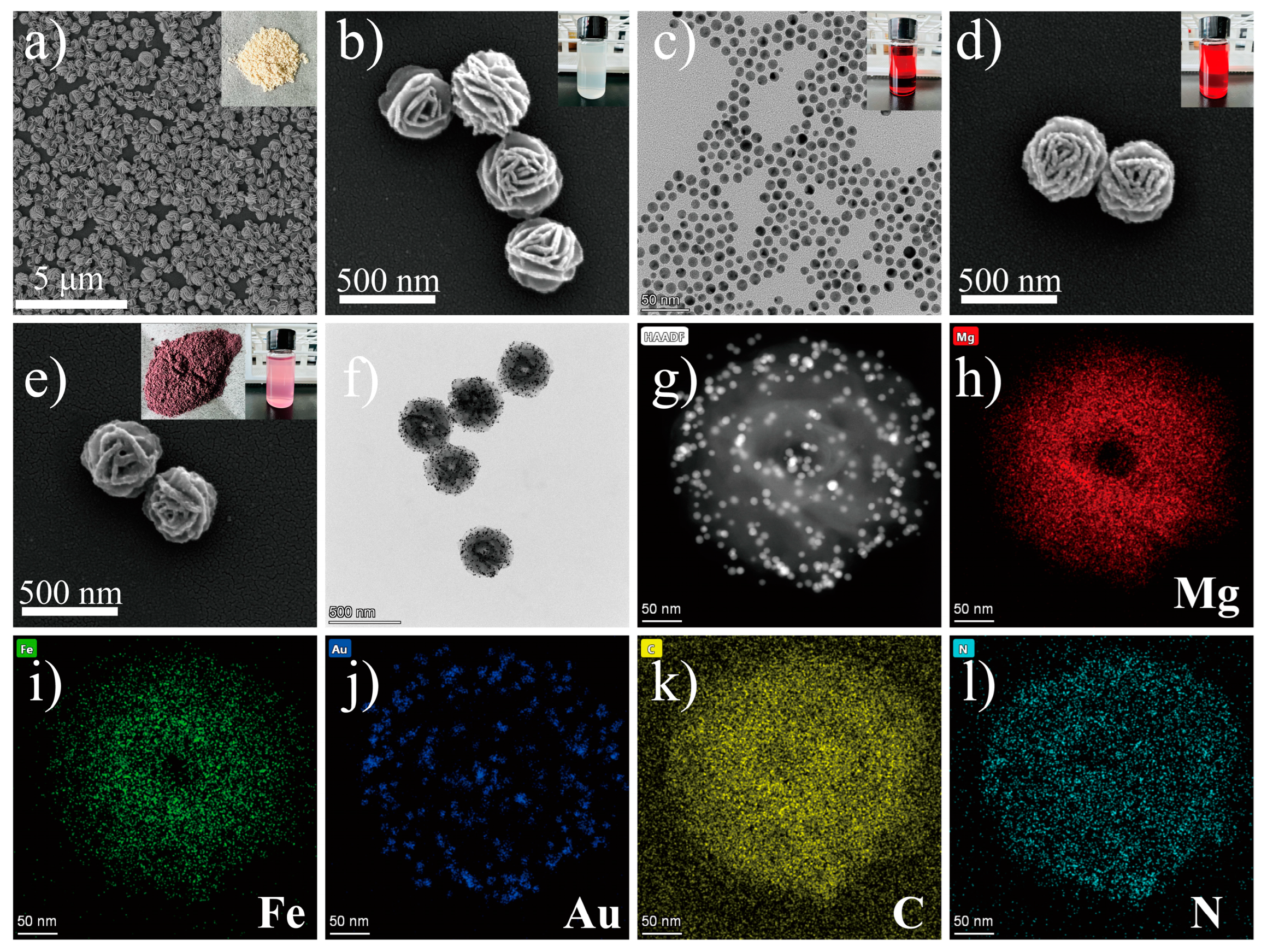
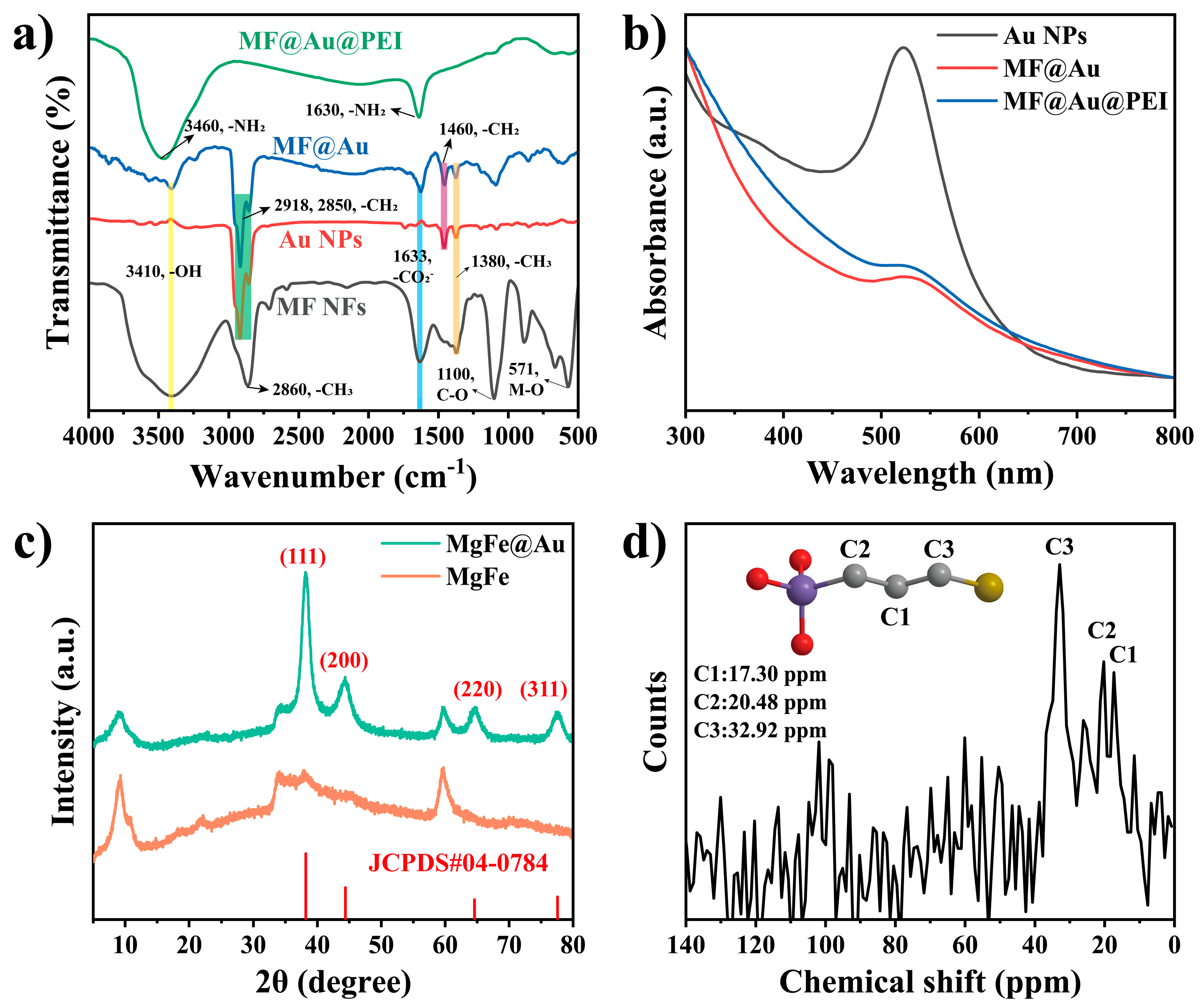
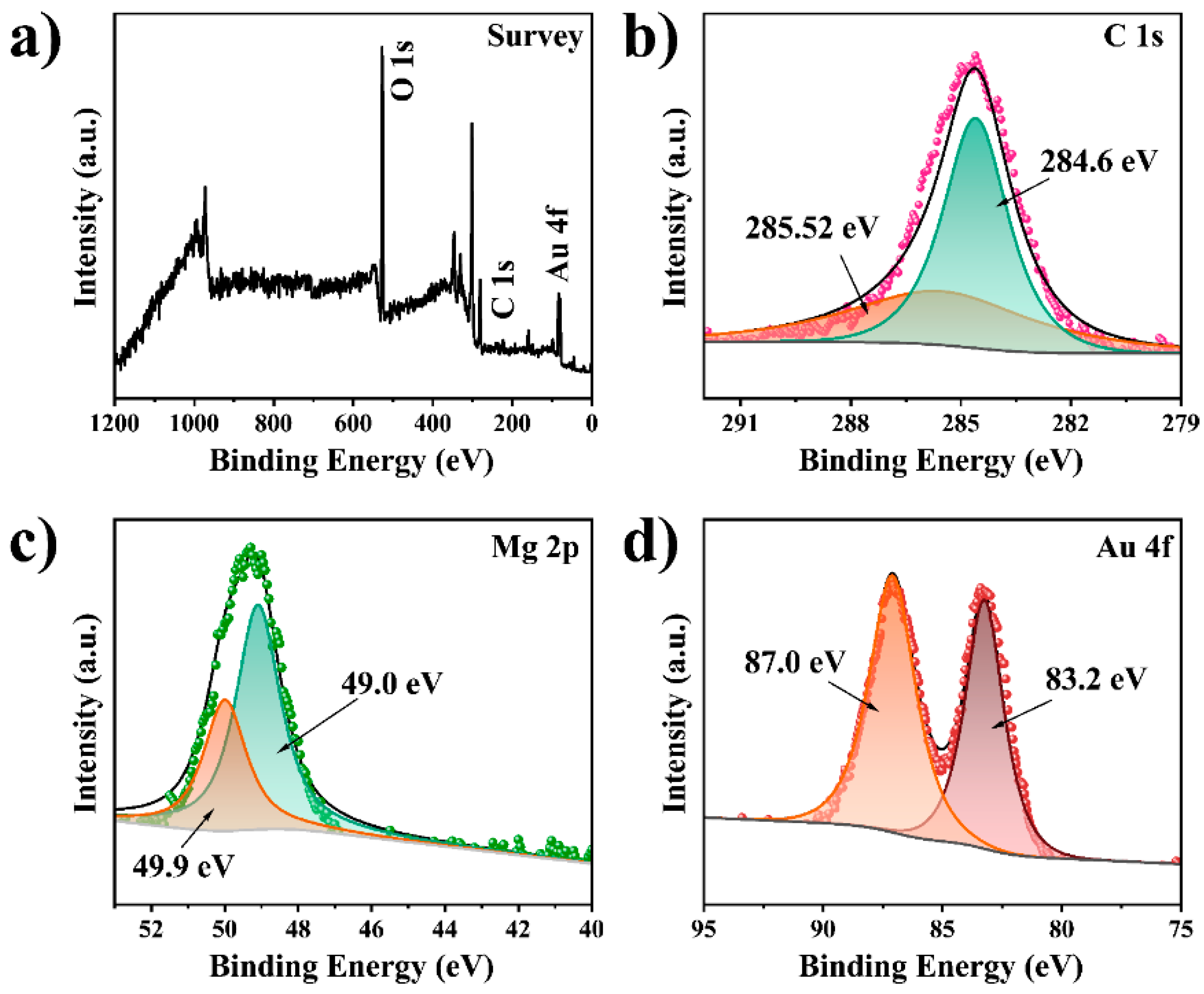
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the MF@Au@PEI NFs
3.2. Performance of MF@Au@PEI−LFIA for HE4 Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morice, P.; Gouy, S.; Leary, A. Mucinous Ovarian Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lheureux, S.; Braunstein, M.; Oza, A.M. Epithelial ovarian cancer: Evolution of management in the era of precision medicine. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 280–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anp, P. The American Cancer Society’s Facts & Figures: 2020 Edition. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2020, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Cui, C.; Shi, O.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.-K.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Incidence and mortality of ovarian cancer at the global, regional, and national levels, 1990–2017. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dowdy, S.; Tipton, T.; Podratz, K.; Lu, W.-G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, S.-W. HE4 as a biomarker for ovarian and endometrial cancer management. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnana, M.; Danese, E.; Giudici, S.; Franchi, M.; Guidi, G.C.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. HE4 in ovarian cancer: From discovery to clinical application. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 55, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.-E.; Qu, J.-Y.; He, F. The diagnosis and pathological value of combined detection of HE4 and CA125 for patients with ovarian cancer. Open Med. 2016, 11, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaletta, G.; Plotti, F.; Luvero, D.; Capriglione, S.; Montera, R.; Miranda, A.; Lopez, S.; Terranova, C.; De Cicco Nardone, C.; Angioli, R. The role of novel biomarker HE4 in the diagnosis, prognosis and follow-up of ovarian cancer: A systematic review. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrer, D.; Grégoire, J.; Turcotte, S.; Plante, M.; Bachvarov, D.; Trudel, D.; Têtu, B.; Douville, P.; Bairati, I. Performance of preoperative plasma tumor markers HE4 and CA125 in predicting ovarian cancer mortality in women with epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kong, D.; Li, J.; Gao, L.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Jin, X. HE4 level in ascites may assess the ovarian cancer chemotherapeutic effect. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, L.; Jiao, Z. The diagnostic value of human epididymis protein 4 for endometrial cancer is moderate. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellström, I.; Raycraft, J.; Hayden-Ledbetter, M.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Schummer, M.; McIntosh, M.; Drescher, C.; Urban, N.; Hellström, K.E. The HE4 (WFDC2) protein is a biomarker for ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3695–3700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wender, R.C.; Brawley, O.W.; Fedewa, S.A.; Gansler, T.; Smith, R.A. A blueprint for cancer screening and early detection: Advancing screening’s contribution to cancer control. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 50–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Tok, K.; Moulahoum, H.; Harmanci, D.; Hanoglu, S.B.; Durmus, C.; Zihnioglu, F.; Evran, S.; Cicek, C.; Sertoz, R.; et al. Dye-Loaded Polymersome-Based Lateral Flow Assay: Rational Design of a COVID-19 Testing Platform by Repurposing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Cocktail and Antigens Obtained from Positive Human Samples. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wei, J.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhang, C.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Ultrasensitive label-free immunochromatographic strip sensor for Salmonella determination based on salt-induced aggregated gold nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ren, S.; Gao, Z.; Chen, A. Dual-competitive lateral flow aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B1 in food and feedstuffs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xue, S.; Ji, R.; Li, B.; Li, J. Localized surface plasmon resonance for enhanced electrocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12070–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-García, V.; Squillaci, M.A.; Diez-Castellnou, M.; Ong, Q.K.; Stellacci, F.; Samorì, P. Chemical sensing with Au and Ag nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1269–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jin, R. Atomically precise alloy nanoclusters: Syntheses, structures, and properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6443–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-M.; Chen, M.-C.; Wu, T.-C.; Chen, J.-W.; Lai, C.-H. Lectin-Triggered Aggregation of Glyco-Gold Nanoprobes for Activity-based Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide by the Naked Eye. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, L.; Liu, B.; Ni, H.; Sun, L.; Su, E.; Chen, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, X. Quantitative and ultrasensitive detection of multiplex cardiac biomarkers in lateral flow assay with core-shell SERS nanotags. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Joo, J.; Kwon, S.G.; Jang, Y.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis of Monodisperse Spherical Nanocrystals. ChemInform 2007, 38, 4630–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, G.; Prasad, P.N.; Swihart, M.T. Synthesis of Monodisperse Au, Ag, and Au–Ag Alloy Nanoparticles with Tunable Size and Surface Plasmon Resonance Frequency. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 4098–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J. Multifunctional Colloids with Optical, Magnetic, and Superhydrophobic Properties Derived from Nucleophilic Substitution-Induced Layer-by-Layer Assembly in Organic Media. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5417–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Wang, D.; Cho, J. Layer-by-Layer Growth of Polymer/Quantum Dot Composite Multilayers by Nucleophilic Substitution in Organic Media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.; Jang, Y.; Kim, S.-W.; An, K.; Yu, J.H.; Hyeon, T. Generalized Fabrication of Multifunctional Nanoparticle Assemblies on Silica Spheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4789–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán, G.; Martí-Gastaldo, C.; Ribera, A.; Coronado, E. Hybrid Materials Based on Magnetic Layered Double Hydroxides: A Molecular Perspective. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, M.; Jeon, H.; Islam, M.S.; Yoon, C.; Bae, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, H.-J. One-pot synthesis of layered double hydroxide hollow nanospheres with ultrafast removal efficiency for heavy metal ions and organic contaminants. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Li, K.; Tian, R.; Lin, Y.; Lu, C. Highly dispersed layered double oxide hollow spheres with sufficient active sites for adsorption of methyl blue. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 23191–23197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, X.; Liu, L. Facile synthesis of ZnAl-layered double hydroxide microspheres with core–shell structure and their enhanced adsorption capability. Mater. Lett. 2015, 156, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.-R.; Yan, L.-G.; Yang, Y.-M.; Yang, K.; Yu, S.-J.; Yu, H.-Q.; Zhu, B.-C.; Du, B. Highly efficient removal of three red dyes by adsorption onto Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-D.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, S.-N.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Ultrasensitive Detection of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Based on Immunofluorescent Carbon Dots/SiO2 Nanosphere-Based Lateral Flow Assay. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21431–21438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.D.; Zhu, J.; Ding, S.N. Immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid proteins using novel red emission-enhanced carbon dot-based silica spheres. Analyst 2021, 146, 5055–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, M.S.; Kweon, S.H.; Jeong, S.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, M.I.; Lee, J.; Doh, J. Simple and Sensitive Point-of-Care Bioassay System Based on Hierarchically Structured Enzyme-Mimetic Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kweon, S.H.; Cho, S.; An, S.S.A.; Kim, M.I.; Doh, J.; Lee, J. Pt-Decorated Magnetic Nanozymes for Facile and Sensitive Point-of-Care Bioassay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35133–35140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liu, J.; Wei, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, C.; Song, W. Size-selective adsorption of anionic dyes induced by the layer space in layered double hydroxide hollow microspheres. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géraud, E.; Rafqah, S.; Sarakha, M.; Forano, C.; Prevot, V.; Leroux, F. Three Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous Layered Double Hydroxides: Preparation by Templated Impregnation/Coprecipitation and Pattern Stability upon Calcination. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, H.; Yu, L.; Xu, R.; Lim, T.-T.; Lou, X.W. Template-free Formation of Uniform Urchin-like α-FeOOH Hollow Spheres with Superior Capability for Water Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, M.; Islam, M.S.; Yoon, D.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Bae, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J. Flower-like Mg/Fe-layered double oxide nanospheres with ultrahigh adsorption efficiency for anionic organic dyes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 618, 126446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Bastidas, J.M.; Polo, J.L.; Mora, N. Study of the Effect of Acetic Acid Vapor on Copper Corrosion at 40 and 80% Relative Humidity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, B431–B437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, S.; Bianchi, C.L.; Fadoni, M.; Vercelli, B. Magnesium salts and oxide: An XPS overview. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 119, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daware, K.; Kasture, M.; Kalubarme, R.; Shinde, R.; Patil, K.; Suzuki, N.; Terashima, C.; Gosavi, S.; Fujishima, A. Detection of toxic metal ions Pb2+ in water using SiO2@Au core-shell nanostructures: A simple technique for water quality monitoring. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 732, 136635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, B.D.; Lee, M.-M.; Wijeratne, D.; James, T.; Shine, B.; Oke, J.L. Trends in Cancer Antigen 125 testing 2003–2014: A primary care population-based cohort study using laboratory data. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2019, 28, e12914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, F.-G.; Li, Y.-S.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.-H.; Lu, S.-Y.; Ren, H.-L.; Liu, Z.-S. Colloidal gold probe-based immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of brevetoxins in fishery product samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2744–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled Nucleation for the Regulation of the Particle Size in Monodisperse Gold Suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.-Y.; Jiao, Y.-J.; Zhu, J.; Ding, S.-N. Rapid Detection of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus via Colloidal Gold Immunochromatography Assay. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 15399–15406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Wu, M.-X.; Ding, S.-N. High-Density Gold Nanoparticles Implanted on Mg/Fe LDH Nanoflowers Assisted Lateral Flow Immuno-Dipstick Assay for Visual Detection of Human Epididymal Protein 4. Biosensors 2022, 12, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100797
Liu H, Wu M-X, Ding S-N. High-Density Gold Nanoparticles Implanted on Mg/Fe LDH Nanoflowers Assisted Lateral Flow Immuno-Dipstick Assay for Visual Detection of Human Epididymal Protein 4. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100797
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hao, Mei-Xia Wu, and Shou-Nian Ding. 2022. "High-Density Gold Nanoparticles Implanted on Mg/Fe LDH Nanoflowers Assisted Lateral Flow Immuno-Dipstick Assay for Visual Detection of Human Epididymal Protein 4" Biosensors 12, no. 10: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100797
APA StyleLiu, H., Wu, M.-X., & Ding, S.-N. (2022). High-Density Gold Nanoparticles Implanted on Mg/Fe LDH Nanoflowers Assisted Lateral Flow Immuno-Dipstick Assay for Visual Detection of Human Epididymal Protein 4. Biosensors, 12(10), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100797





