Rational Programming of Cas12a for Early-Stage Detection of COVID-19 by Lateral Flow Assay and Portable Real-Time Fluorescence Readout Facilities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
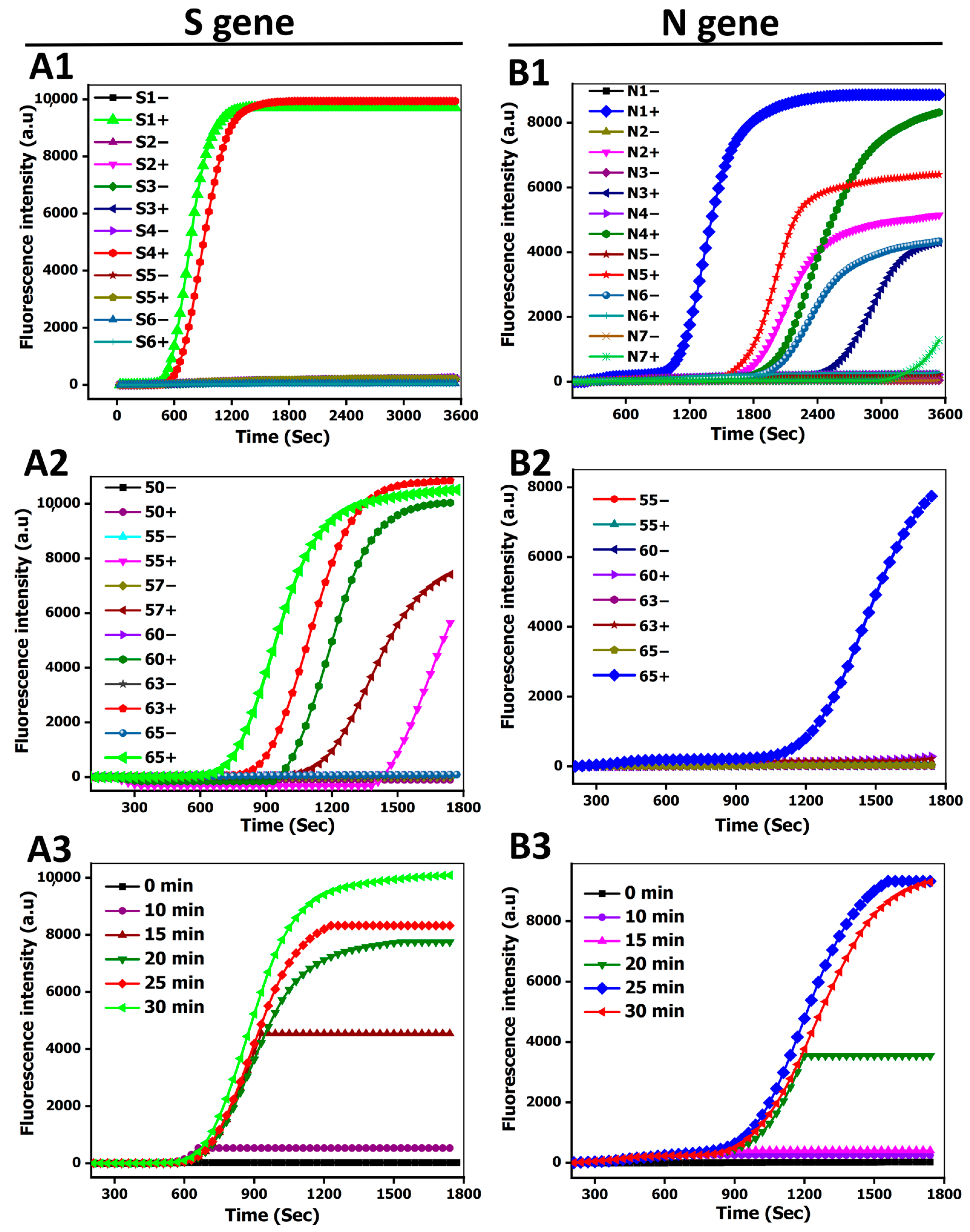
2.2. crRNA Design, Primer Selection, and RT-LAMP Assay
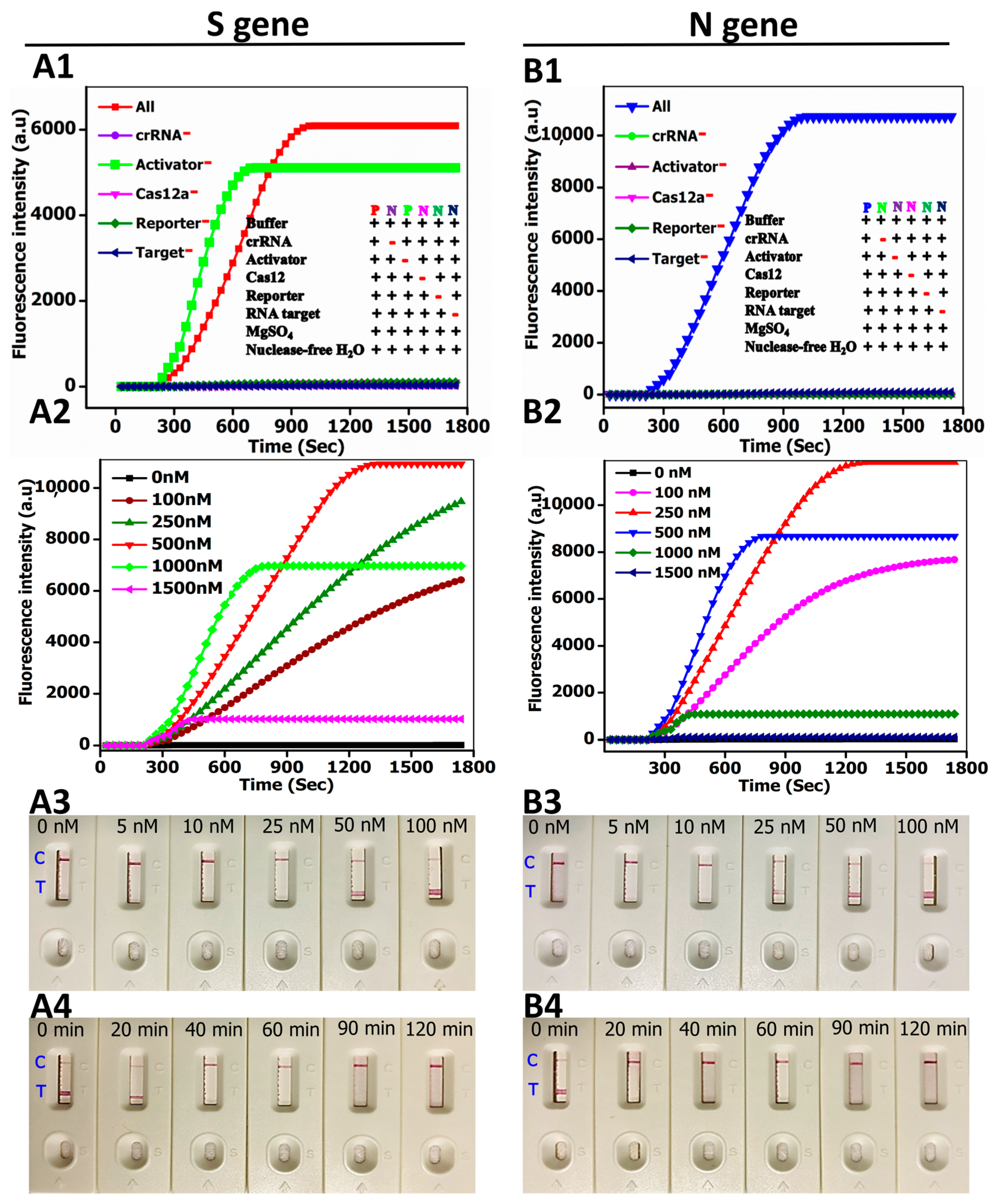
2.3. Target Cleavage, Lateral Flow, and Fluorescence Detection Assays
2.4. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles, Lateral Flow Strip Design, and Assembly
2.5. Clinical Sample Preparation, RNA Extraction, and Ethics Statement
2.6. RT-qPCR Amplification
3. Results
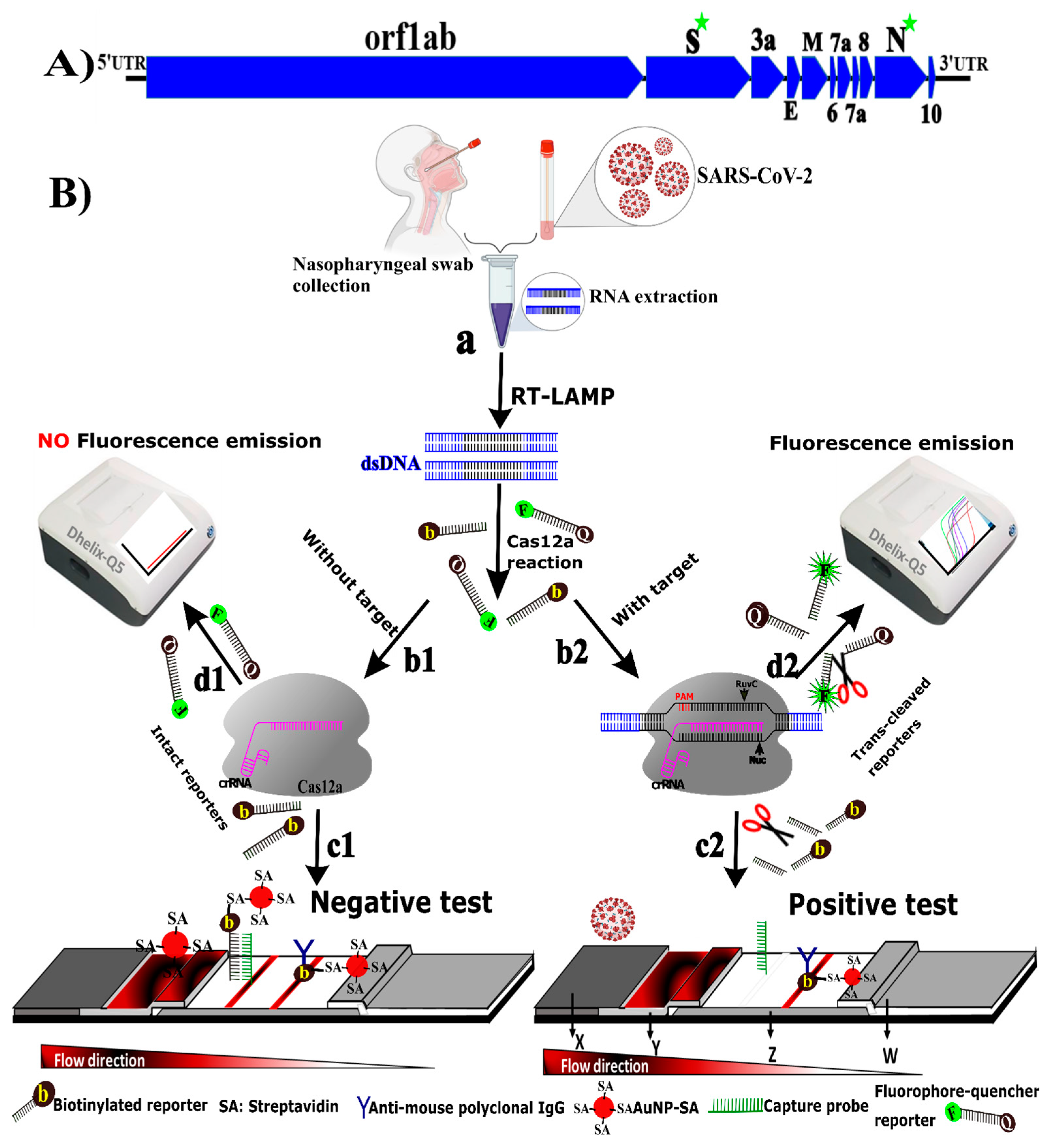
3.1. Principle of CRICOLAP Real-Time Fluorescence and LFS Detection of COVID-19
3.2. Method Performance Optimization
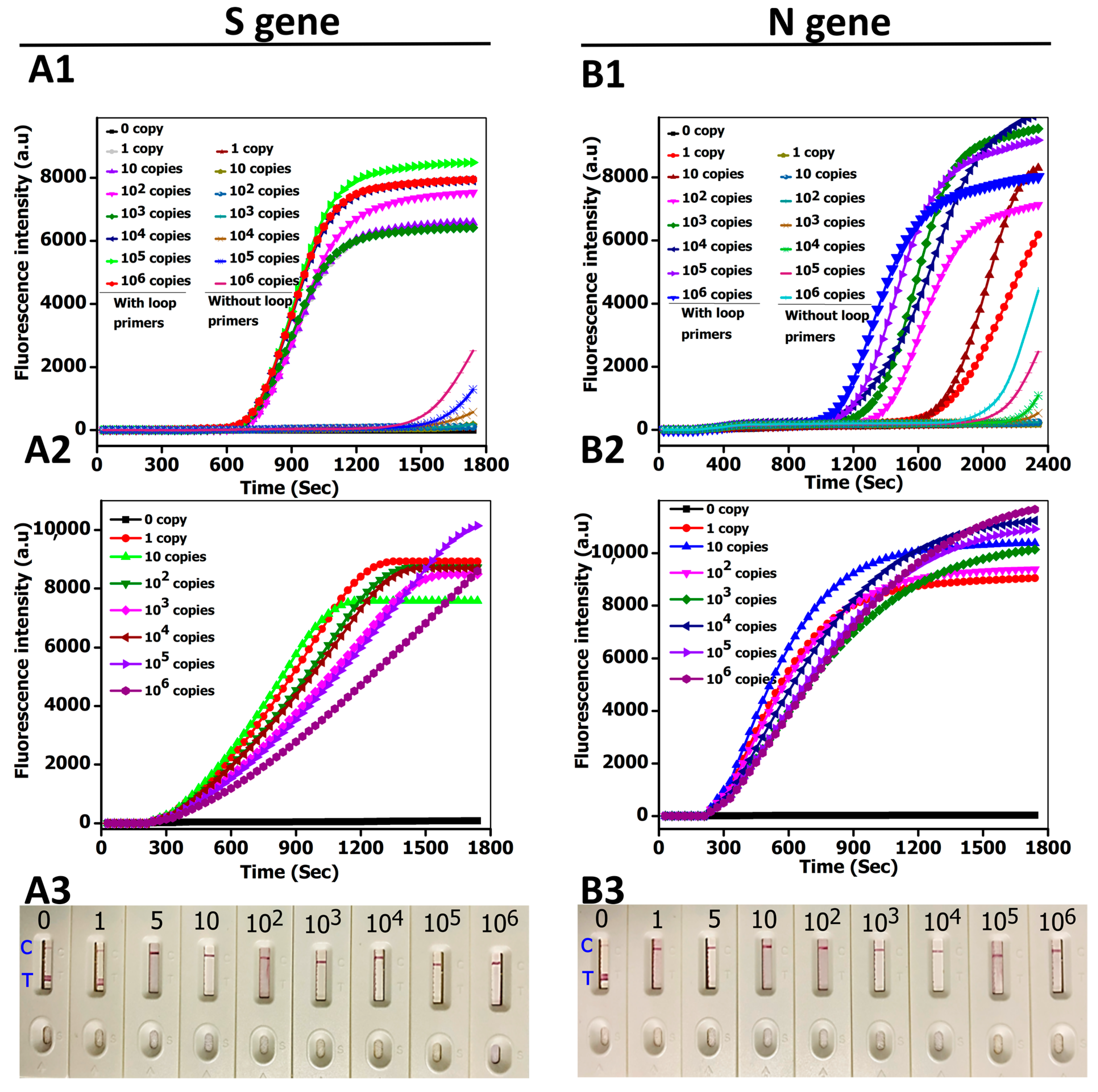
3.3. CRICOLAP Sensitivity
3.4. CRICOLAP Specificity
3.5. CRICOLAP Validation in Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Syncytia formation during SARS-CoV-2 lung infection: A disastrous unity to eliminate lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2019–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, C.S.; Park, K.-H.; Ahn, W.-C.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kwon, O.S.; Yong, D.; Kang, T.; Woo, E. Detection of Infectious Viruses Using CRISPR-Cas12-Based Assay. Biosensors 2021, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. FDA. FDA COVID-19 Response At-A-Glance Summary as of July 19, 2021, FDA (2021). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137005/download (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Phan, L.M.; Tieu, M.-V.; Pham, T.-T.; Cho, S. Clinical Utility of Biosensing Platforms for Confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 In-fection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-C.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Yen, M.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, S.; Priesemann, V. Risking further COVID-19 waves despite vaccination. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 745–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udugama, B.; Kadhiresan, P.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Malekjahani, A.; Osborne, M.; Li, V.Y.C.; Chen, H.; Mubareka, S.; Gubbay, J.B.; Chan, W.C.W. Diagnosing COVID-19: The Disease and Tools for Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Newbigging, A.M.; Le, C.; Pang, B.; Peng, H.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Abbas, G.; Song, J.; Wang, D.-B.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of COVID-19: Challenges and Research Needs. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10196–10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Augustine, S.; Narayan, T.; O’Riordan, A.; Das, A.; Kumar, D.; Luong, J.; Malhotra, B. Point-of-Care PCR Assays for COVID-19 Detection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Hao, X.; Dong, X.; Mao, L.; Pelechano, V.; Chen, W.-H.; Yin, X. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Coronavirus Using a Reverse Transcriptional Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) Diagnostic Platform. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, L.; Zhou, M.; Liang, D. CRISPR/Cas12a-Based Ultrasensitive and Rapid De-tection of JAK2 V617F Somatic Mutation in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Biosensors 2021, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Q.; He, B.; Geng, G.; Wang, Z.; Cao, B.; Dong, X.; Bai, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Programmable RNA editing with compact CRISPR–Cas13 systems from uncultivated microbes. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freije, C.A.; Sabeti, P.C. Detect and destroy: CRISPR-based technologies for the response against viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. Development of CRISPR-Cas systems for genome editing and beyond. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 52, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kivrak, E.; Pauzaite, T.; Copeland, N.A.; Hardy, J.G.; Kara, P.; Firlak, M.; Yardimci, A.I.; Yilmaz, S.; Palaz, F.; Ozsoz, M. Detection of CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Mutations Using a Carbon Nanotube-Modified Electrochemical Genosensor. Biosensors 2021, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, R.; Mahas, A.; Mahfouz, M. Nucleic Acid Detection Using CRISPR/Cas Biosensing Technologies. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Park, M.; Lee, J.; Song, Y. Specific Detection of Influenza A and B Viruses by CRISPR-Cas12a-Based Assay. Biosensors 2021, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.X.; Hunnewell, P.; Alfonse, L.E.; Carte, J.M.; Keston-Smith, E.; Sothiselvam, S.; Garrity, A.J.; Chong, S.; Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V.; et al. Functionally diverse type V CRISPR-Cas systems. Science 2019, 363, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Kellner, M.J.; Joung, J.; Collins, J.J.; Zhang, F. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid de-tection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science 2018, 360, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Somoza, R.; Wang, L.; Welter, J.F.; Li, Y.; I Caplan, A.; Liu, C.C. Exploring the Trans-Cleavage Activity of CRISPR-Cas12a (cpf1) for the Development of a Universal Electrochemical Biosensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17399–17405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Ma, E.; Harrington, L.B.; da Costa, M.; Tian, X.; Palefsky, J.M.; Doudna, J.A. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding un-leashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science 2018, 360, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Lee, J.W.; Essletzbichler, P.; Dy, A.J.; Joung, J.; Verdine, V.; Donghia, N.; Daringer, N.M.; Freije, C.A.; et al. Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2. Science 2017, 356, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Accelerated Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) Summary, SARS-COV-2 RNA DETECTR ASSAY (2020). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139937/download (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Sherlock CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 Kit, FDA (2020). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137746/download (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Luo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yu, S.; Tai, J.; Wang, Y. Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and Highly Specific Diagnosis of COVID-19 by CRISPR-Based Detection. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchsung, M.; Jantarug, K.; Pattama, A.; Aphicho, K.; Suraritdechachai, S.; Meesawat, P.; Sappakhaw, K.; Leelahakorn, N.; Ruenkam, T.; Wongsatit, T. Clinical validation of a Cas13-based assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. 2020, 4, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A. CRISPR–Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, Z.; Aman, R.; Mahas, A.; Rao, G.S.; Tehseen, M.; Marsic, T.; Salunke, R.; Subudhi, A.K.; Hala, S.M.; Hamdan, S.M.; et al. iSCAN: An RT-LAMP-coupled CRISPR-Cas12 module for rapid, sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2. Virus Res. 2020, 288, 198129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Smith, B.M.; Jain, P.K. Enhancement of trans-cleavage activity of Cas12a with engineered crRNA enables amplified nucleic acid detection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, K.H.; Liu, M.M.; Tay, J.W.D.; Teo, S.Y.; Kaewsapsak, P.; Jin, S.; Lee, C.K.; Hou, J.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Lin, W.; et al. An engineered CRISPR-Cas12a variant and DNA-RNA hybrid guides enable robust and rapid COVID-19 testing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Kan, L.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, M.; Tian, J.; Lin, S.; et al. An enhanced method for nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas12a using phosphorothioate modified primers and optimized gold-nanopaticle strip. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4580–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellows, T.; Ho, L.; Flanagan, S.; Fogel, R.; Ojo, D.; Limson, J. Gold nanoparticle-streptavidin conjugates for rapid and efficient screening of aptamer function in lateral flow sensors using novel CD4-binding aptamers identified through Crossover-SELEX. Analyst 2020, 145, 5180–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Huang, J.; Lie, P.; Xiao, Z.; Ouyang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zeng, L. Lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor for Cu2+ detection in aqueous solution with high sensitivity and selectivity. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9043–9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; Man, S.; Ma, L. Integration of logic gates to CRISPR/Cas12a system for rapid and sensitive detection of pathogenic bacterial genes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1125, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, K. Evaluation of CRISPR/Cas12a-based DNA detection for fast pathogen diagnosis and GMO test in rice. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yin, K.; Li, Z.; Lalla, R.V.; Ballesteros, E.; Sfeir, M.M.; Liu, C. Ultrasensitive and visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 using all-in-one dual CRISPR-Cas12a assay. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, R.; Tang, Z.; Dong, M.; Liu, T.; Kshirsagar, A.; Guan, W. CRISPR-based detection of SARS-CoV-2: A review from sample to result. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Hossain, M.A.; Mozibullah, M.; Mujib, F.A.; Afrose, A.; Shahed-Al-Mahmud, M.; Apu, M.A.I. CRISPR is a useful biological tool for detecting nucleic acid of SARS-CoV-2 in human clinical samples. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Tian, D.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lyon, C.; Lai, W.; Fusco, D.; Drouin, A.; Yin, X.; Hu, T. Ultra-sensitive and high-throughput CRISPR-Powered COVID-19 diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 164, 112316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Biotech. Lateral Flow Readout for CRISPR/Cas-Based Detection Strategies. 2020. Available online: https://www.milenia-biotec.com/uploads/2019/07/Confusion-T-and-C-Line_final.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Teng, F.; Cui, T.; Feng, G.; Guo, L.; Xu, K.; Gao, Q.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, W. Repurposing CRISPR-Cas12b for mammalian genome engineering. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Assay | Target Gene | Amplification Method | Amplification Time | Total Assay Time | Detection Limit | Assay Control | Control Line | Test Line | LFS Source | LFS Price | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRICOLAP | N and S genes | LAMP | 25 min | 60 min | 1 copy/μL | LFB, fluorescence | Biotinylated antibody | ssDNA probe | Designed and assembled by our group | USD 0.095 | This study |
| DETECTR | E and NP genes | LAMP | 30–40 min | 60 min | 10 copies/μL | LFB, fluorescence | Streptavidin | Anti-conjugate antibody | Purchased from Milenia Biotech. | USD < 3 | [27] |
| VaNGuard | ORF1b, S-, and N-genes | LAMP | 22 min | 30 min | 50 copies/reaction | LFB, fluorescence | Streptavidin | Anti-conjugate antibody | Purchased from Milenia Biotech. | USD < 3 | [30] |
| ENHANCE | N gene | LAMP | 20–30 min | 40–60 min | 3 copies/μL | LFB, fluorescence | Avidin | Anti-conjugate antibody | Purchased from Milenia Biotech. | USD < 3 | [29] |
| TESTOR | ORF1ab and N gene | RPA | - | 120 min | 5 copies/reaction | LFB, fluorescence | Anti-digoxin antibody | Anti-FAM antibody | Designed by Gong et al. and assembled by Twist Dx Ltd. | USD < 3 | [31] |
| COVID-19 MCCD | ORF1ab and NP genes | MCDA | 35 min | 60 min | 7 copies/μL | LFB, fluorescence | Anti-FITC antibody | Biotin-bovine serum albumin | Designed and assembled by Zhu et al. | - | [25] |
| iSCAN | N and E genes | LAMP | 20 min | 40 min | 10 copies/reaction | LFB, fluorescence | Streptavidin | Anti-conjugate antibody | Purchased from Milenia Biotech. | USD < 3 | [28] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, Z.; de Dieu Habimana, J.; Mukama, O.; Li, Z.; Odiwuor, N.; Jing, H.; Nie, C.; Hu, M.; Lin, Z.; Wei, H.; et al. Rational Programming of Cas12a for Early-Stage Detection of COVID-19 by Lateral Flow Assay and Portable Real-Time Fluorescence Readout Facilities. Biosensors 2022, 12, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010011
Yi Z, de Dieu Habimana J, Mukama O, Li Z, Odiwuor N, Jing H, Nie C, Hu M, Lin Z, Wei H, et al. Rational Programming of Cas12a for Early-Stage Detection of COVID-19 by Lateral Flow Assay and Portable Real-Time Fluorescence Readout Facilities. Biosensors. 2022; 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Zhijian, Jean de Dieu Habimana, Omar Mukama, Zhiyuan Li, Nelson Odiwuor, Hanzhi Jing, Chengrong Nie, Mei Hu, Zuoxian Lin, Hongping Wei, and et al. 2022. "Rational Programming of Cas12a for Early-Stage Detection of COVID-19 by Lateral Flow Assay and Portable Real-Time Fluorescence Readout Facilities" Biosensors 12, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010011
APA StyleYi, Z., de Dieu Habimana, J., Mukama, O., Li, Z., Odiwuor, N., Jing, H., Nie, C., Hu, M., Lin, Z., Wei, H., & Zeng, L. (2022). Rational Programming of Cas12a for Early-Stage Detection of COVID-19 by Lateral Flow Assay and Portable Real-Time Fluorescence Readout Facilities. Biosensors, 12(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010011





