A Variable Height Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Immunoassay Analysis of Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bead-Based Quantum Dot-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (QLISA) Design
2.2. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) QLISA
2.3. Measurement of GFAP in Clinical Serum Samples
2.4. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) QLISA
2.5. Interleukin-8 (IL-8) QLISA
2.6. Limit of Detection and Coefficient of Variation
2.7. Variable Height Device Fabrication
2.8. Variable Height Device QLISA Analysis
2.9. Fluorescent Image Analysis
2.10. Multiplexed QLISA Analysis
2.11. Assay Bead Size Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
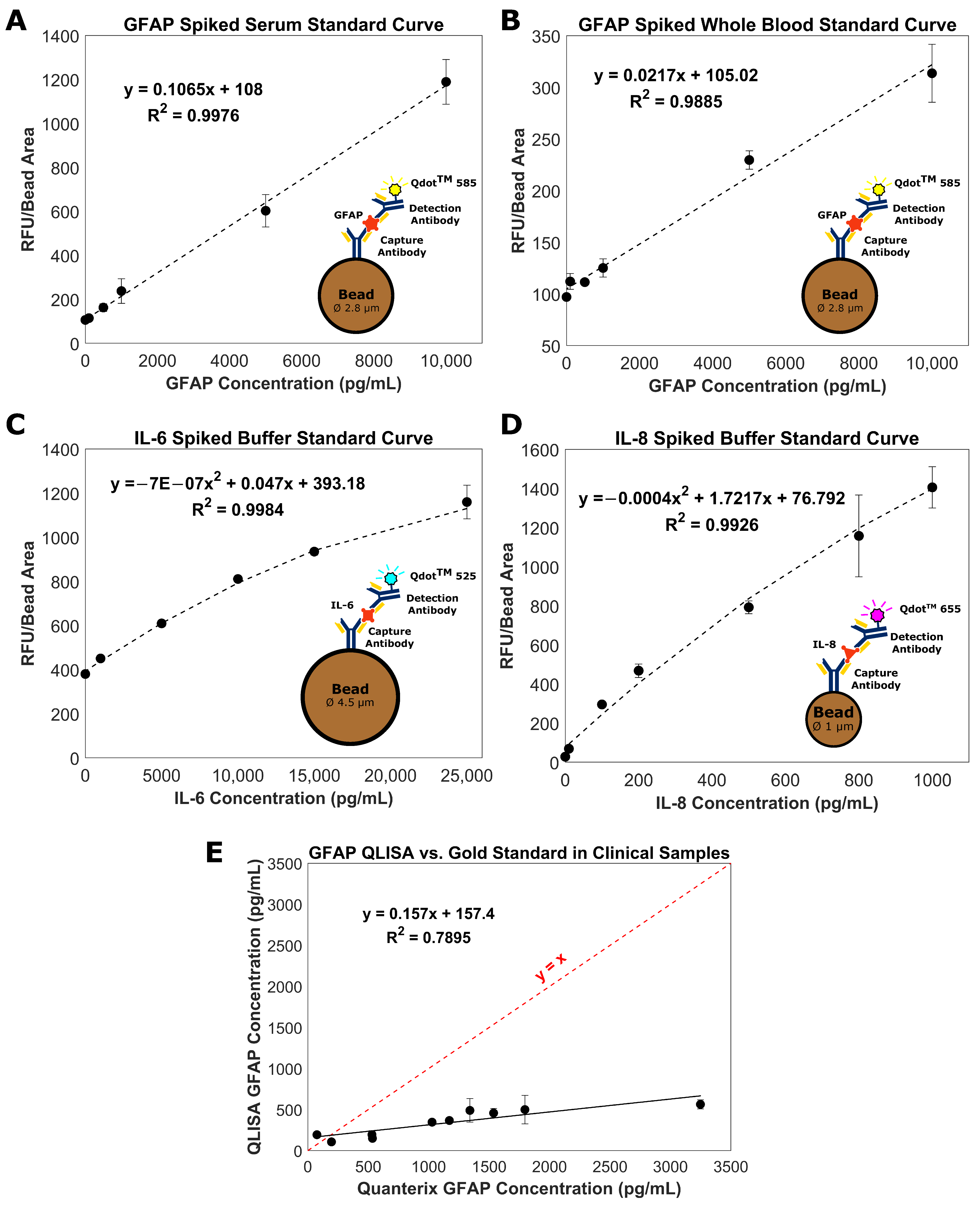
3.1. Bead-Based QLISA Development
3.2. Measurement of GFAP in Clinical Serum Samples
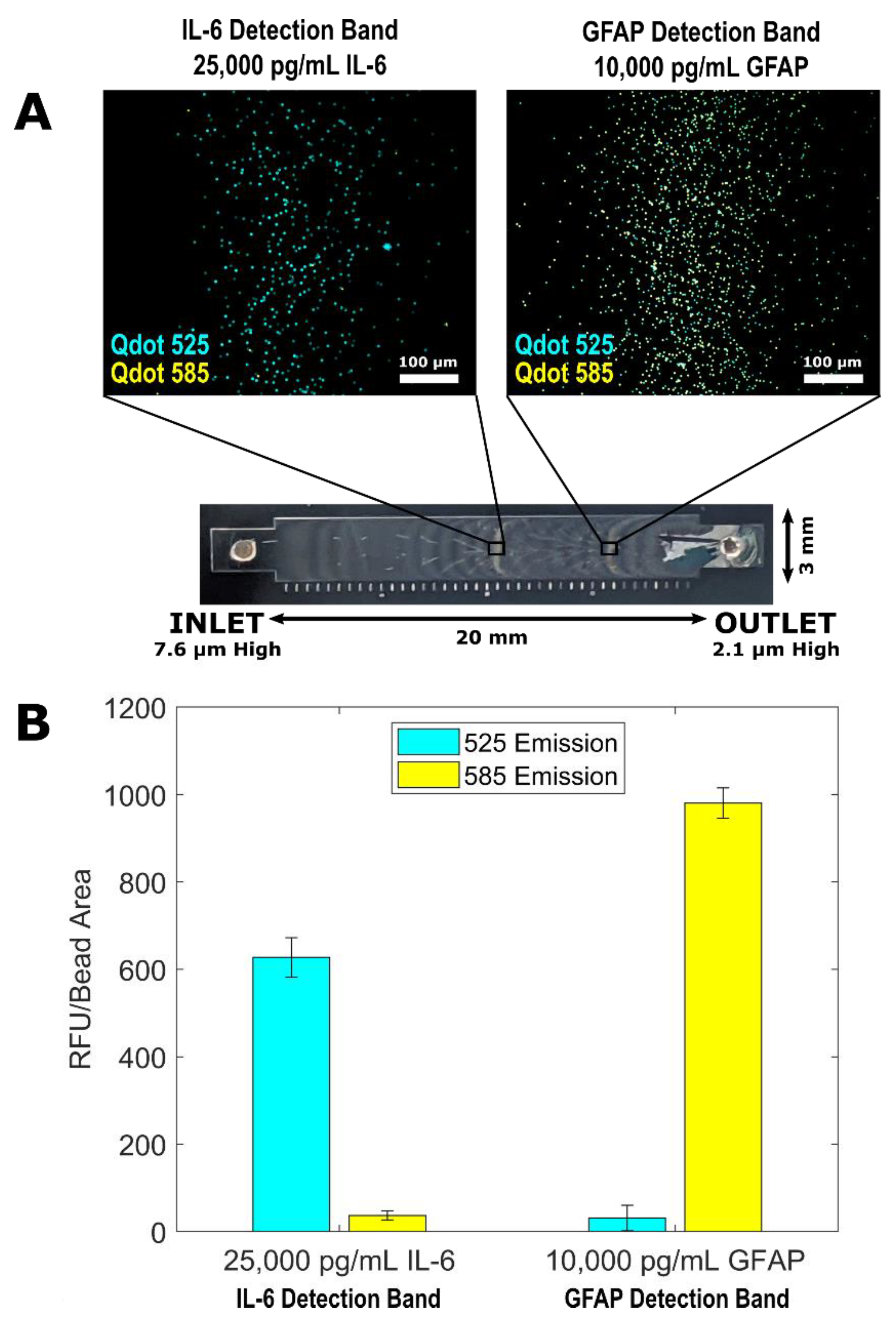
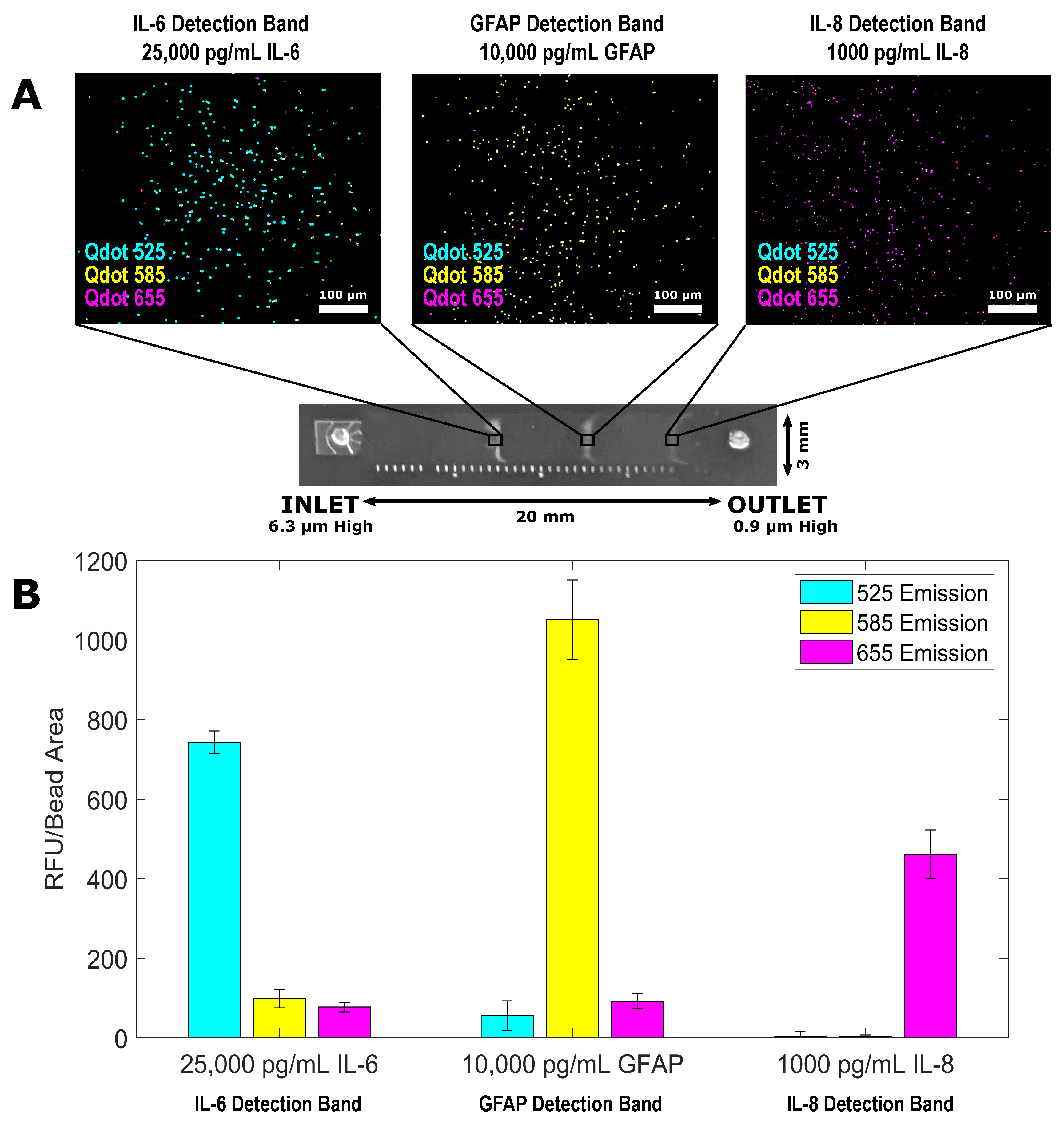
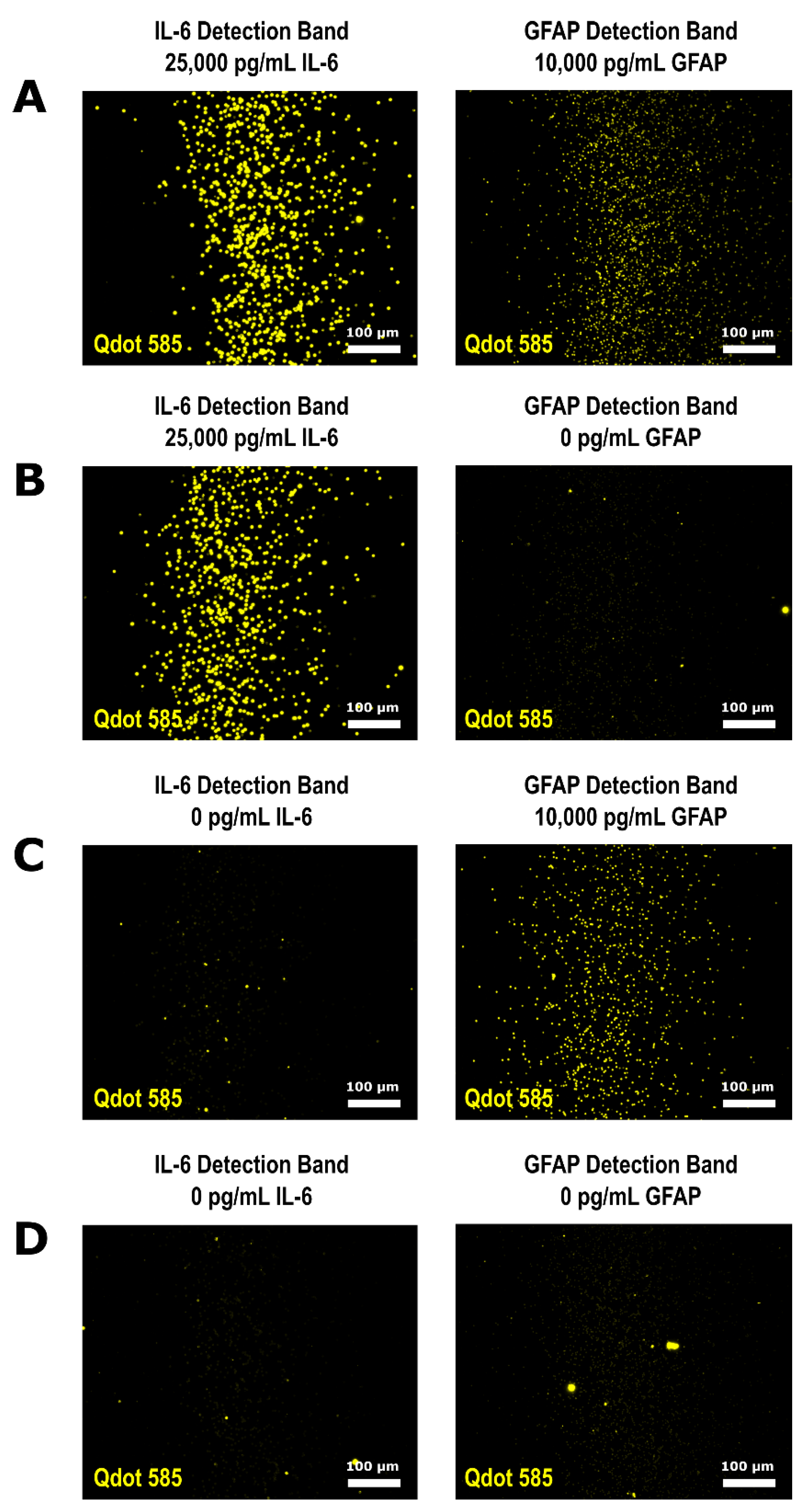
3.3. Multiplexed QLISA Analysis Using the Variable Height Microfluidic Device
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mondello, S.; Muller, U.; Jeromin, A.; Streeter, J.; Hayes, R.L.; Wang, K.K. Blood-based diagnostics of traumatic brain injuries. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 11, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peterson, A.B.; Xu, L.; Daugherty, J.; Breiding, M.J. Surveillance Report of Traumatic Brain Injury-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, United States, 2014. 2019. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/78062 (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Mohamadpour, M.; Whitney, K.; Bergold, P.J. The importance of therapeutic time window in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogoslovsky, T.; Gill, J.; Jeromin, A.; Davis, C.; Diaz-arrastia, R. Fluid Biomarkers of Traumatic Brain Injury and Intended Context of Use. Diagnostics 2016, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckee, C.A.; Lukens, J.R. Emerging Roles for the Immune System in Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korley, F.K.; Datwyler, S.A.; Jain, S.; Sun, X.; Beligere, G.; Chandran, R.; Marino, J.A.; McQuiston, B.; Zhang, H.; Caudle, K.L.; et al. Comparison of GFAP and UCH-L1 Measurements from Two Prototype Assays: The Abbott i-STAT and ARCHITECT Assays. Neurotrauma Rep. 2021, 2, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Fluid biomarkers for mild traumatic brain injury and related conditions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, H.; Mårten, K.; Salla, N. Biomarkers of Traumatic Brain Injury: Temporal Changes in Body Fluids. eNeuro 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papa, L.; Brophy, G.M.; Welch, R.D.; Lewis, L.M.; Braga, C.F.; Tan, C.N.; Ameli, N.J.; Lopez, M.A.; Haeussler, C.A.; Mendez Giordano, D.I.; et al. Time Course and Diagnostic Accuracy of Glial and Neuronal Blood Biomarkers GFAP and UCH-L1 in a Large Cohort of Trauma Patients With and Without Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korley, F.K.; Yue, J.K.; Wilson, D.H.; Hrusovsky, K.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Ferguson, A.R.; Yuh, E.L.; Mukherjee, P.; Wang, K.K.W.; Valadka, A.B.; et al. Performance Evaluation of a Multiplex Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Four Clinically Relevant Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.; Michel, B.; Delamarche, E. Micromosaic immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Vermesh, O.; Srivastava, A.; Yen, B.K.H.; Qin, L.; Ahmad, H.; Kwong, G.A.; Liu, C.C.; Gould, J.; Hood, L.; et al. Integrated barcode chips for rapid, multiplexed analysis of proteins in microliter quantities of blood. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henares, T.G.; Funano, S.I.; Terabe, S.; Mizutani, F.; Sekizawa, R.; Hisamoto, H. Multiple enzyme linked immunosorbent assay system on a capillary-assembled microchip integrating valving and immuno-reaction functions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 589, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostranec, J.M.; Xiang, Q.; Farcas, G.A.; Lee, J.A.; Rhee, A.; Lafferty, E.I.; Perrault, S.D.; Kain, K.C.; Chan, W.C.W. Convergence of quantum dot barcodes with microfluidics and signal processing for multiplexed high-throughput infectious disease diagnostics. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2812–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Song, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; Fishburn, M.W.; Shao, Q.; Piech, T.; Ferrell, E.P.; Meyer, R.E.; Campbell, T.G.; et al. Multiplexed single molecule immunoassays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Colour-barcoded magnetic microparticles for multiplexed bioassays. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodbane, M.; Stucky, E.C.; Maguire, T.J.; Schloss, R.S.; Shreiber, D.I.; Zahn, J.D.; Yarmush, M.L. Development and validation of a microfluidic immunoassay capable of multiplexing parallel samples in microliter volumes. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3211–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giacoppo, S.; Bramanti, P.; Barresi, M.; Celi, D.; Foti Cuzzola, V.; Palella, E.; Marino, S. Predictive Biomarkers of Recovery in Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurocrit. Care 2012, 16, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti-Kossman, M.C.; Lenzlinger, P.M.; Hans, V.; Stahel, P.; Csuka, E.; Ammann, E.; Stocker, R.; Trentz, O.; Kossmann, T. Production of cytokines following brain injury: Beneficial and deleterious for the damaged tissue. Mol. Psychiatry 1997, 2, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayakata, T.; Shiozaki, T.; Tasaki, O.; Ikegawa, H.; Inoue, Y.; Toshiyuki, F.; Hosotubo, H.; Kieko, F.; Yamashita, T.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Changes in CSF S100B and cytokine concentrations in early-phase severe traumatic brain injury. Shock 2004, 22, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, B.; Schwerdtfeger, K.; Mautes, A.; Holanda, M.; Müller, M.; Steudel, W.I.; Marzi, I. Differential release of interleukines 6, 8, and 10 in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma after traumatic brain injury. Shock 2001, 15, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.A.; Pattinson, C.L.; Guedes, V.A.; Peyer, J.; Moore, C.; Davis, T.; Devoto, C.; Turtzo, L.C.; Latour, L.; Gill, J.M. Inflammatory cytokines associate with neuroimaging after acute mild traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, A.; Ignjatovic, V.; Babl, F.E.; Oakley, E.; Greenham, M.; Hearps, S.; Delzoppo, C.; Beauchamp, M.H.; Guerguerian, A.-M.; Boutis, K. Interleukin-8 predicts fatigue at 12 months post-injury in children with traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, S.E.; De Beer, M.P.; McCormick, J.; Habibi, N.; Lahann, J.; Burns, M.A. Variable-height channels for microparticle characterization and display. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausz, A.D.; Dewar, R.; Burns, M.A. Accuracy Evaluation of a Tetrabromophenolphthalein Ethyl Ester Colorimetric Assay for Urinary Albumin. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 4, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, J.J.S.; Di-Pietro, V.; Smith, D.J.; Davies, D.J.; Belli, A.; Oppenheimer, P.G. Rapid optofluidic detection of biomarkers for traumatic brain injury via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, D.O.; Puffer, R.C.; Puccio, A.M.; Yuh, E.L.; Yue, J.K.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Korley, F.K.; Wang, K.K.W.; Sun, X.; Taylor, S.R.; et al. Point-of-Care Platform Blood Biomarker Testing of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein versus S100 Calcium-Binding Protein B for Prediction of Traumatic Brain Injuries: A Transforming Research and Clinical Knowledge in Traumatic Brain Injury Study. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.A.; Panini, N.V.; Martinez, N.A.; Raba, J. Microfluidic immunosensor design for the quantification of interleukin-6 in human serum samples. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 380, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, M.; McClelland, J.F.; Shao, Z.; Lu, M. A photoacoustic immunoassay for biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, D.H.; Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Fournier, D.R.; Piech, T.; Campbell, T.G.; Meyer, R.E.; Fishburn, M.W.; Cabrera, C.; Patel, P.P.; et al. The Simoa HD-1 Analyzer: A Novel Fully Automated Digital Immunoassay Analyzer with Single-Molecule Sensitivity and Multiplexing. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoltewicz, S.J.; Scharf, D.; Yang, B.; Chawla, A.; Newsom, K.J.; Fang, L. Characterization of antibodies that detect human GFAP after traumatic brain injury. Biomark. Insights 2012, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, L.; Lewis, L.M.; Falk, J.L.; Zhang, Z.; Silvestri, S.; Giordano, P.; Brophy, G.M.; Demery, J.A.; Dixit, N.K.; Ferguson, I.; et al. Elevated levels of serum glial fibrillary acidic protein breakdown products in mild and moderate traumatic brain injury are associated with intracranial lesions and neurosurgical intervention. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2012, 59, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.K.W. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: From intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, S.; Hadass, O.; Cohen, M.; Verbarg, J.; Wilsey, J.; Danielli, A. Improving the Sensitivity of Fluorescence-Based Immunoassays by Photobleaching the Autofluorescence of Magnetic Beads. Small 2019, 15, 1803751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barteneva, N.S.; Vorob’ev, I.A. Quantum dots in microscopy and cytometry: Immunostaining applications. Microsc. Sci. Technol. Appl. Educ. 2010, 1, 710–721. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, J.E.; Mason, D.; Lévy, R. Evaluation of quantum dot conjugated antibodies for immunofluorescent labelling of cellular targets. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Figure | Inlet Height (µm) | Outlet Height (µm) | Assay Beads |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2A | 3.675 ± 0.081 | 1.386 ± 0.053 | DynabeadsTM M-270 |
| 2B | 4.066 ± 0.006 | 1.313 ± 0.041 | DynabeadsTM M-270 |
| 2C | 7.008 ± 0.278 | 1.848 ± 0.020 | DynabeadsTM M-450 |
| 2D | 3.157 ± 0.045 | 0.856 ± 0.035 | DynabeadsTM MyOneTM |
| 2E | 3.653 ± 0.044 | 1.368 ± 0.018 | DynabeadsTM M-270 |
| 3A | 7.583 ± 0.177 | 2.077 ± 0.007 | DynabeadsTM M-450 and M-270 |
| 4A | 6.342 ± 0.035 | 0.963 ± 0.057 | DynabeadsTM M-450, M-270, and MyOneTM |
| 5A–E | 7.583 ± 0.177 | 2.077 ± 0.007 | DynabeadsTM M-450 and M-270 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krausz, A.D.; Korley, F.K.; Burns, M.A. A Variable Height Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Immunoassay Analysis of Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers. Biosensors 2021, 11, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090320
Krausz AD, Korley FK, Burns MA. A Variable Height Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Immunoassay Analysis of Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers. Biosensors. 2021; 11(9):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090320
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrausz, Alyse D., Frederick K. Korley, and Mark A. Burns. 2021. "A Variable Height Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Immunoassay Analysis of Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers" Biosensors 11, no. 9: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090320
APA StyleKrausz, A. D., Korley, F. K., & Burns, M. A. (2021). A Variable Height Microfluidic Device for Multiplexed Immunoassay Analysis of Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers. Biosensors, 11(9), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090320






