Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
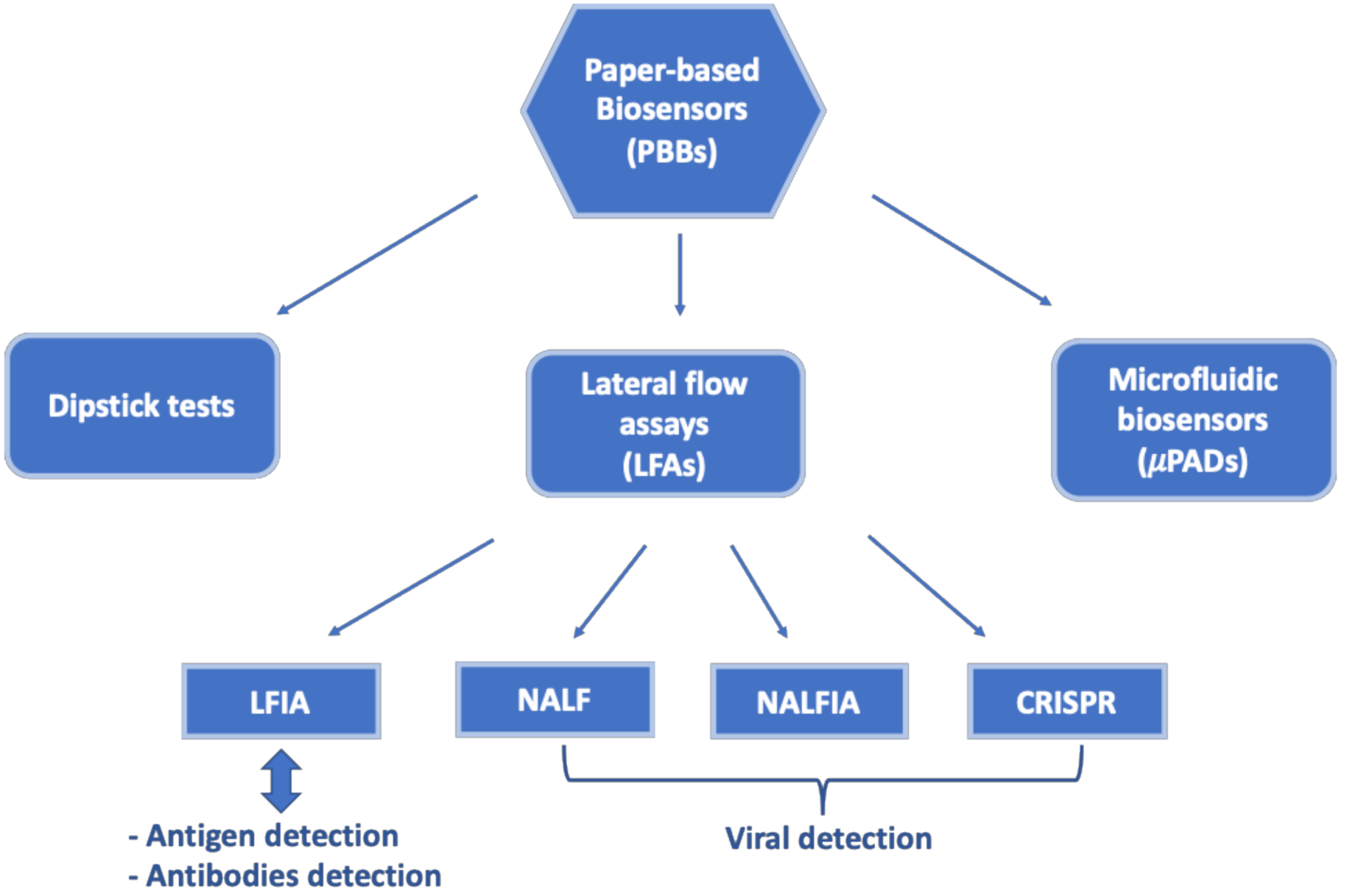
2. Paper-Based Biosensors
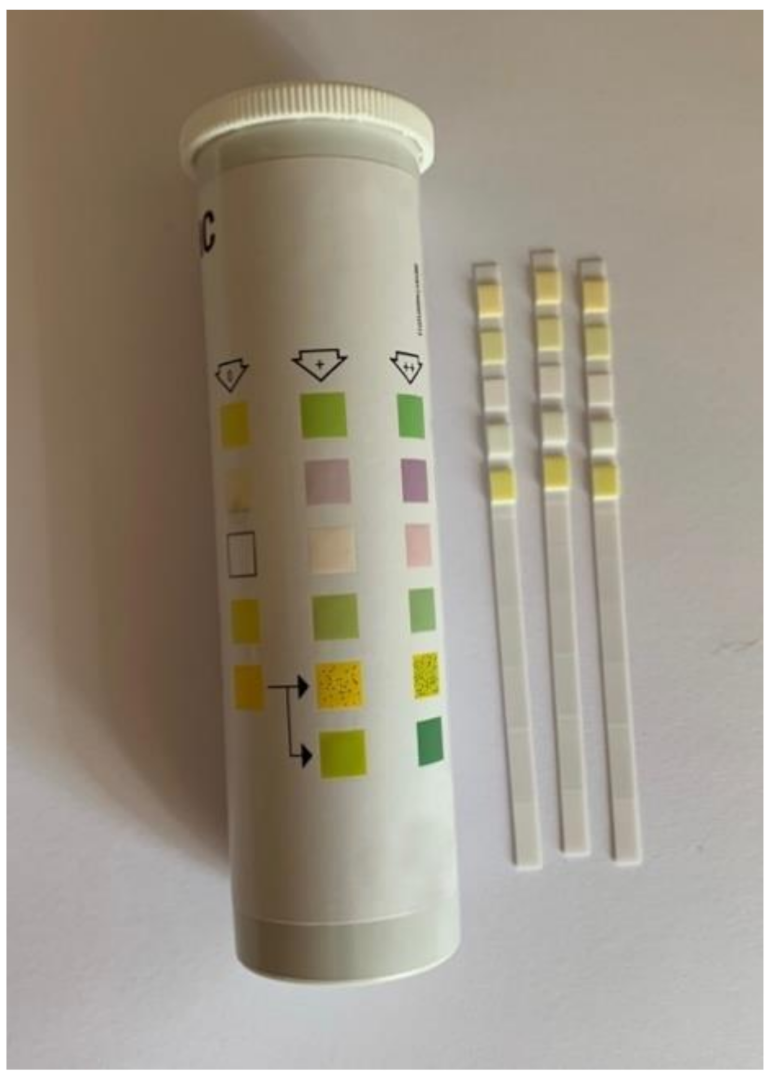
2.1. Dipstick Tests
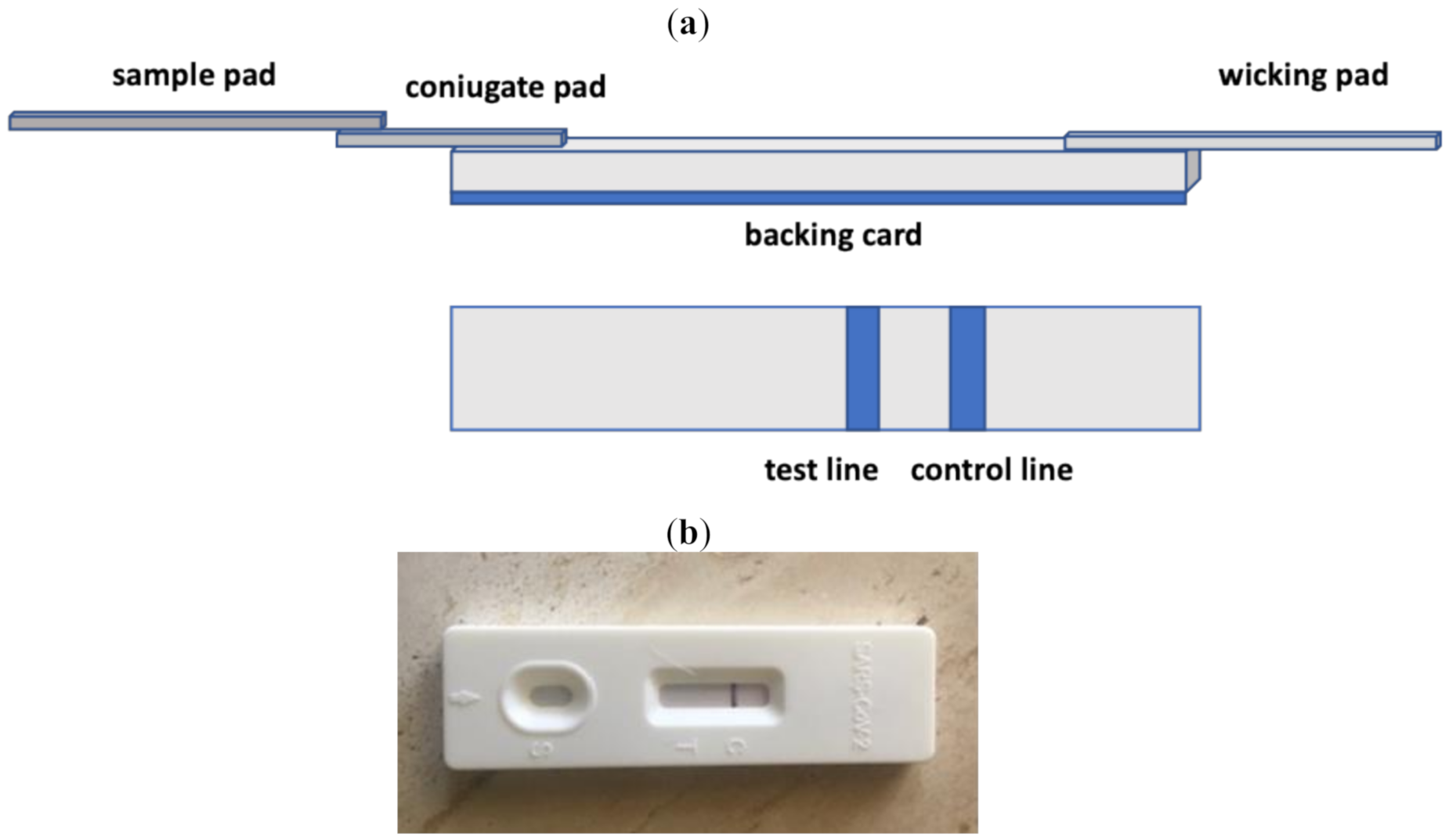
2.2. Lateral Flow Assays
2.2.1. Lateral Flow Immunoassays
2.2.2. Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assays
2.2.3. Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Immunoassays
2.3. Paper-Based Microfluidics
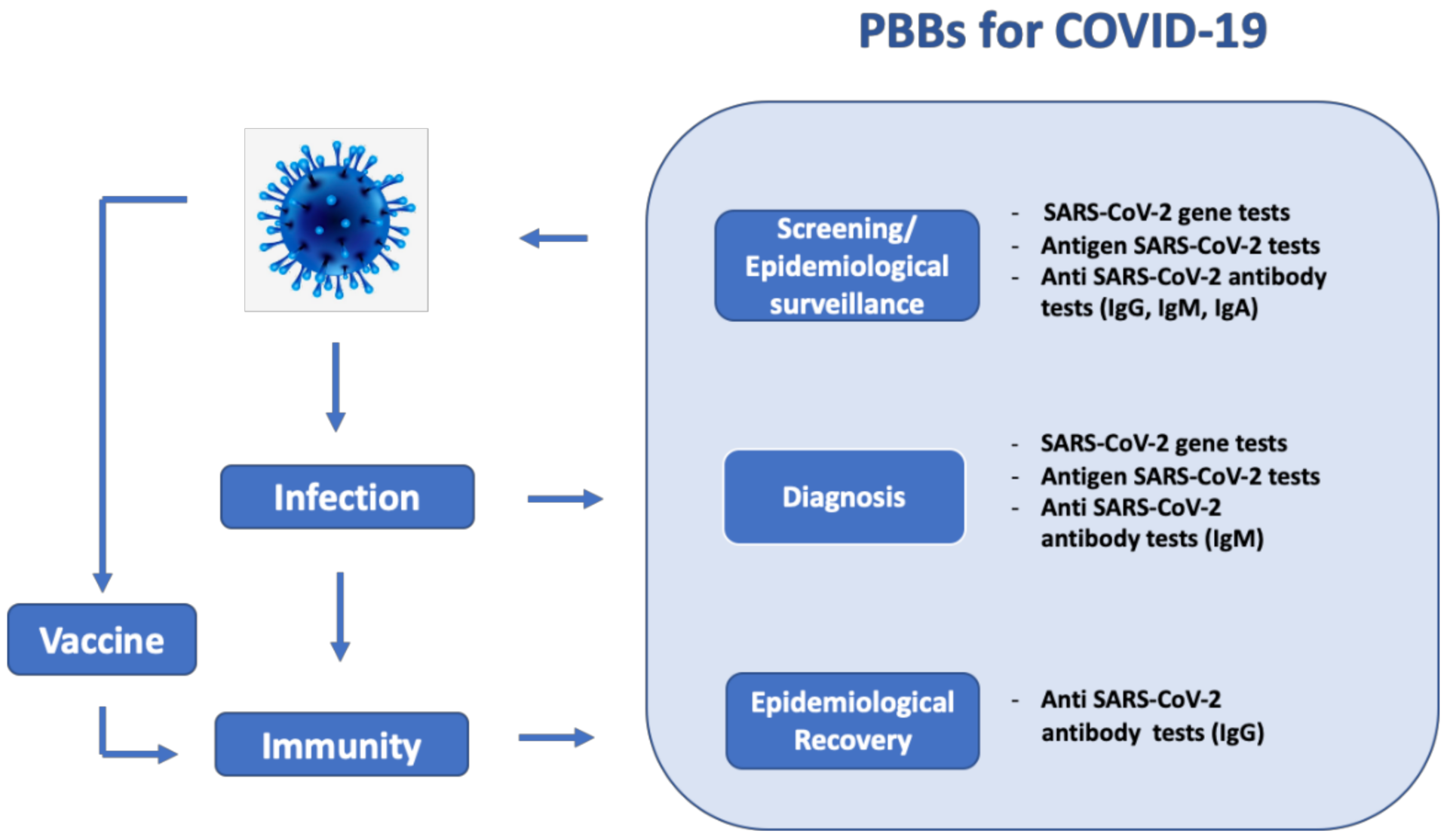
3. Applications of Paper-Based Biosensors for COVID-19 Detection
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Gene Detection
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection
3.4. μPADs for COVID-19 Detection
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Guan, Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S88–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, Q. Insight into 2019 novel Coronavirus-an updated interim review and lessons from SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Situation Report 40. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.C.; Shin, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, R.P. Severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Corona Virus Disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Dangal, G.; Chalise, A.; Bhandari, T.R.; Dangal, O.J. The Coronavirus pandemic: What does the evidence show? Nepal. Health Res. Counc. 2020, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, D.; Liu, Q. Review of the 2019 novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence. Int. J. Ant. Agents 2020, 55, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.S.; Aziz, M.S.; Hussein, R.H.; Othman, H.H.; Omer, S.H.S.; Khalid, E.S.; Abdulrahman, N.A.; Amin, K.; Abdullah, R. The transmission modes and sources of COVID-19: A systematic review. Int. J. Surg. Open 2020, 26, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Huang, L. A familial cluster of infection associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating potential person-to-person transmission during the incubation period. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorelli, C.; Scognamiglio, T.; Odone, A. COVID-19 in Italy: Impact of containment measures and prevalence estimates of infection in the general population. Acta. Bio. Med. 2020, 91, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Udugama, B.; Kadhiresan, P.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Malekjahani, A.; Osborne, M.; Li, V.Y.C.; Chen, H.; Mubareka, S.; Gubbay, J.B.; Chan, W.C.W. Diagnosing COVID-19: The disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, H.S. Diagnostic methods and potential portable biosensors for coronavirus disease. Bios. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.J.; Garner, V.V.; Smoot, J.W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Saveson, C.J.; Sasso, J.M.; Gregg, A.C.; Soares, D.J.; Beskud, T.R. Assay techniques and test development for COVID-19 diagnosis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, P.; Hu, C.; Mao, H. Detecting the Coronavirus (COVID-19). ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C.; Carriere, M.; Fusco, L.; Capua, I.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Pasquali, M.; Scott, J.A.; Vitale, F.; Unal, M.A.; Mattevi, C.; et al. Toward nanotechnology-enabled approaches against the COVID-19 Pandemic. ACS-Nano 2020, 14, 6383–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochia, R. Developments in biosensors for CoV detection and future trends. Bios. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112777. [Google Scholar]
- Yuce, M.; Filiztekin, E.; Ozkaya, K.G. COVID-19-A review of current methods. Bios. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, J.; AL-Maskri, A.A.A.; Kang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Cai, S. Recent advances and perspectives of nucleic acid detection for Coronavirus. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashir, J.; Yaqinuddin, A. Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays as a rapid diagnostic for COVID-19. Med. Hypoteses 2020, 141, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.E.; Lim, B.; Hsu, C.; Xiong, D.; Wu, W.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, M.; et al. RT-LAMP for rapid diagnosis of coronavirus SARS-CoV-. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Hao, X.; Dong, X.; Mao, L.; Pelechano, V.; Chen, W.; Yin, X. Rapid detection of COVID-19 coronavirus using a reverse transcriptional loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) diagnostic platform. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Ku, K.; Baek, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.; Maeng, J. Development of Reverse Transcription Loop-mediated Iso3hermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) Assays Targeting SARS-CoV-. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Blumenfeld, N.R.; Laksanasopin, T.; Sia, S.K. Point-of-care diagnostics: Recent developments in a connected age. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanat, F.; Stadbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J.; et al. A serological assay to detect SARS- CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Kou, G.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q.; Tan, L.; Wu, W.; Tang, S.; et al. Evaluation of Nucleocapsid and Spike Protein-based ELISAs for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00461–e20. [Google Scholar]
- Okba, N.M.; Muller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Yan, M.; Li, H.; Liu, T.; Lin, C.; Huang, S.; Shen, C. Evaluation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Colloidal Gold- Immunochromatographic Assay Kit for Detection of Novel Corona- virus (SARS-Cov-2) Causing an Outbreak of Pneumonia (COVID-19). medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E.; Wolfe, P.; Stahura, C.; Edwards, K.A. Technical considerations to development of serological tests for SARS-CoV-2. Talanta 2021, 224, 121883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drain, P.K.; Hyle, E.P.; Noubary, F.; Freedberg, K.A.; Wilson, D.; Bishai, W.; Rodriguez, W.; Bassett, I.V. Evaluating Diagnostic Point-of-Care Tests in Resource-Limited Settings. Lancet Inf. Dis. 2014, 14, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gubala, V.; Harris, L.F.; Ricco, A.J.; Tan, M.X.; Williams, D.E. Point of care diagnostics: Status and future. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, B. A perspective on the sensitivity of paper-analytical devices for bioanalysis. J. Appl. Bionalysis 2016, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswandi, B.; Ensafi, A.A. Paper-based Biosensors: Trending topic in clinical diagnostics development and commercialization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, K.; Stobiecka, M. High-performance modified cellulose paper-based biosensors for medical diagnostics and early cancer screening: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.R. Principles of Affinity-Based Biosensors. Mol. Biotechnol. 2000, 14, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochia, R.; Favero, G.; Conti, M.E.; Mazzei, F.; Tortolini, C. Affinity-based biosensors for pathogenic bacteria detection. Int. J. Environmental. Technol. Manag. 2015, 18, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Korvink, J.G.; Mager, D.; Land, K. The potential of paper-based diagnostics to meet the ASSURED criteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, C.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-Based Nanobiosensors for Diagnostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Asiri, A.M.; Du, D.; Wen, W.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y. Nanomaterial-enhanced paper-based biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 58, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Brimer, A.; Slocik, J.M.; Tian, L.M.; Naik, R.R. Multifunctional analytical platform on a paper strip: Separation, preparation, and subattomolar detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3977–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Shin, J.H.; Park, J.K. Pressed Paper-Based Dipstick for Detection of Foodborne Pathogens with Multistep Reactions. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezginturk, M.K. Lateral flow assays: Principles, designs and labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngom, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Bi, D. Development and application of lateral flow test strip technology for detection of infectious agents and chemical contaminants: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Joo, C. Recent advances in high-sensitivity detection methods for paper-based lateral-flow assay. Bios. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Cavalera, S.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C. Multiplex lateral flow immunoassay: An overview of strategies towards high-throughput point-of-need testing. Biosensors 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Macdonald, J. Multiplexed lateral flow biosensors: Technological advances for radically improving point-of-care diagnoses. Bios. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.W.; De Puig, H.; Tam, J.O.; Gomez-Marquez, J.; Bosch, I.; Hamad-Schifferli, K.; Gehrke, L. Multicolored silver nanoparticles for multiplexed disease diagnostics: Distinguishing Dengue, yellow fever, and Ebola viruses. Lab Chip. 2015, 15, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; Liao, Y.; Li, Q. Fluorescent probe-based lateral flow assay for multiplex nucleic acid detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5611–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, E.M.; Hawamdeh, G.; Jarrad, N.A.; Yasin, O.; Al-Gharabli, S.I.; Shadfan, R. Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) Hormone using Digital Lateral Flow Immunoassay. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andryukov, B.G. Six decades of lateral flow immunoassay: From determining metabolic markers to diagnosing COVID-19. AIMS Microb. 2020, 6, 280–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.C.; Tse, H.Y. Lateral Flow Immunoassay; Humana Press, Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, J.D.; Hsieh, H.V.; Gasperino, D.J.; Weigl, B.H. Sensitivity enhancement in lateral flow assays: A systems perspective. Lab Chip. 2019, 19, 2486–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, J.H.; Chan, H.M.; Ying, J.Y. Strategies for developing sensitive and specific nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays as point-of-care diagnostic device. Nano Today 2020, 30, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; TYang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W.; Yan, L.; Li, B. Improvement in Detection Limit for Lateral Flow Assay of Biomacromolecules by Test-Zone Pre-enrichment. Scient. Rep. 2020, 10, 9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.R.; Hu, J.; Feng, S.; Abas, W.A.B.W.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Xu, F. Sensitive biomolecule detection in lateral flow assay with a portable temperature–humidity control device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, N.; Huang, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y. Nucleic acid biosensor synthesis of an all-in-one universal blocking linker recombinase polymerase amplification with a peptide nucleic acid-based lateral flow device for ultrasensitive detection of food pathogens. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Choi, J.R.; Gong, Y.; Hu, J.; Feng, S.; Pinguann-Murphy, B.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. Improved sensitivity of lateral flow assay using paper-based sample concentration technique. Talanta 2016, 152, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, R.Y.T.; Thach, A.V.; Wu, C.M.; Wu, B.M.; Kamei, D.T. An aqueous two-phase system for the concentration and extraction of proteins from the interface for detection using the lateral-flow immunoassay. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadavalli, T.; Shukla, D. Role of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tools for Highly Prevalent Viral Infections. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; Van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno)assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, J.; Ma, X. Nanomaterial Labels in Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Point-of-Care-Testing. J. Mat. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, C.; De la Escosura-Muniz, A.; Merkoci, A. Enhanced lateral flow immunoassay using gold nanoparticles loaded with enzymes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Narvaez, E.; Naghdi, T.; Zor, E.; Merkoci, A. Photoluminescent lateral-flow immunoassay revealed by graphene oxide: Highly sensitive paper-based pathogen detection. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8573–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolo, C.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Bergua, J.F.; Calucho, E.; Fuentes-Chust, C.; Hu, L.; Rivas, L.; Alvarez-Diduk, R.; Nguyen, E.P.; Cinti, S.; et al. Tutorial: Design and fabrication of nanoparticle-based lateral-flow immunoassays. Nature Protocols 2020, 15, 3788–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, L.; Guo, S.Z.; Song, F.; Gong, Y.; Xu, F.; Boulware, D.R.; McAlpine, M.C.; Chan, W.C.W.; Bischof, J.C. The role of nanoparticle design in determining analytical performance of lateral flow immunoassays. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7207–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D. The Immunoassay Handbook: Theory and Applications of Ligand Binding, ELISA, and Related Techniques, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK; Waltham, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, A.; Michelini, E.; Zangheri, M.; Di Fusco, M.; Calabria, D.; Simoni, P. Smartphone-based biosensors: A critical review and perspectives. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisin, L.; Amarit, R.; Somboonkaew, A.; Gajanandana, O.; Himananto, O.; Sutapun, B. Significant Sensitivity Improvement for Camera-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay Readers. Sensors 2018, 18, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, C.; Phogat, N.; Laufer, S.; Kohl, M.; Deigner, H.P. A smartphone readout system for gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays: Application to monitoring of digoxigenin. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borse, V.; Srivatsava, R. Process parameter optimization for lateral flow immunosensing. Mat. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; Van Amerongen, A. Development of a competitive later flow immunoassay for progesterone: Influence of coating conjugates and buffer components. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Lie, P.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, Z. Lateral flow biosensors for the detection of nucleic acid. In Nucleic Acid Detection. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols); Kolpashchikov, D., Gerasimova, Y., Eds.; Humana Press, Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1039, pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Jauset-Rubio, M.; Svobodová Mairal, T.; McNeil, C.; Keegan, N.; Saeed, A.; Abbas, M.N.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O.´ Sullivan, C.K. Ultrasensitive, rapid and inexpensive detection of DNA using paper based lateral flow assay. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Broyles, D.; Hunt, E.A.; Dikici, E.; Daunert, S.; Deo, S.K. A paper-based platform for detection of viral RNA. Analyst 2017, 142, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristov, D.R.; Rodriguez-Quijada, C.; Gomez-Marquez, J.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Designing paper-based immunoassays for biomedical applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, G. Disposable nucleic acid biosensors based on gold nanoparticle probes and lateral flow strip. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Xu, H.; Takalkar, S.; Gurung, A.S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Baloda, M.; Baryeh, K.; Liu, G. Carbon nanotube-based lateral flow biosensor for sensitive and rapid detection of DNA sequence. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, G.B.; Wichers, J.H.; Skouridou, V.; Amerongen, A.V.; Masip, L. Nucleic acid lateral flow assays using a conjugate of a DNA binding protein and carbon nanoparticles. Michrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochia, R. Nanobiosensors as new diagnostic tools for SARS, MERS and COVID-19: From past to perspectives. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Gong, Y.; You, M.; Liu, Z.; Choi, J.R.; Wen, T.; Qu, Z.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. A fully disposable and integrated paper-based device for nucleic acid extraction, amplification and detection. Lab. Chip. 2017, 17, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Safenkova, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Nucleic acid lateral flow assay with recombinase polymerase amplification: Solutions for highly sensitive detection of RNA virus. Talanta 2020, 210, 120616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, S.C.; Power, J.B.; Cocking, E.C.; Davey, M.R. Strategies for signal amplification in nucleic acid detection. Mol. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Craw, P.; Balachandran, W. Isothermal nucleic acid amplification technologies for point-of-care diagnostics: A critical review. Lab. Chip. 2012, 12, 2469–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akineden, O.; Wittwer, T.; Geister, K.; Plotz, M.; Usleber, E. Nucleic acid lateral flow immunoassay (NALFIA) with integrated DNA probe degradation for the rapid detection of Cronobacter sakazakii and Cronobacter malonaticus in powdered infant formula. Food Control. 2020, 109, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchia, S.; Da Lio, D. Development of a rapid PCR-Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Immunoassay (PCR-NALFIA) based on rDNA IGS sequence analysis for the detection of Macrophomina phaseolina in soil. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2018, 151, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, J.F.; Ho, A.H.; Turner, A.P.; Mak, W.C. Integrated printed microfluidic biosensors. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, L.; Medina-Sánchez, M.; De la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Merkoçi, A. Improving sensitivity of gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays by using wax-printed pillars as delay barriers of microfluidics. Lab. Chip. 2014, 14, 4406–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Si, J.; Li, Z. Fabrication techniques for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices and their applications for biological testing: A review. Biosens. Bioelectr. 2016, 77, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Hahn, Y.K.; Kim, M.S. Review Recent Advances of Fluid Manipulation Technologies in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices (µPADs) toward Multi-Step Assays. Micromachines 2020, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Sinton, D. Turning the page: Advancing paper-based microfluidics for broad diagnostic application. Chem Rev. 2017, 117, 8447–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Min, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Cao, H.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z. Paper-based microfluidics for rapid diagnostics and drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, B.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lin, L.; Sun, J. Point-of-care-testing of nucleic acids by microfluidics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.; Devadhasan, J.P.; Howse, R.; Kim, J. A chemically patterned microfluidic paper-based analytical device (C-μPAD) for point-of-care diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Carrilho, E.; Thomas, S.W.; Sindi, H.; Whitesides, G.M. Simple telemedicine for developing regions: Camera phones and paper-based microfluidic devices for real- time, off-site diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Nimse, S.B.; Kim, J.; Song, K.S.; Kim, T. Development of a Lateral Flow Strip Membrane Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14139–14144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Multiplex reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Bios. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.D. Development of Point-of-Care Biosensors for COVID-. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Lei, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, L. Rapid lateral flow immunoassay for the fluorescence detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaz, F.; Kalkan, A.K.; Tozluyurt, A.; Ozsoz, M. CRISPR-based tools: Alternative methods for the diagnosis of COVID-. Clin. Biochem. 2021, (in press). [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Liang, C.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Q.; Dai, M.; Qu, B.; Fang, S.; Yihuan Mao, Y. SARS-CoV-2 detection with CRISPR diagnostics. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abduljalil, J.M. Laboratory diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2: Available approached and limitations. New Microbe. New Inf. 2000, 36, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.N.T.; McCarthy, C.; Lantigua, D.; Camci-Unal, G. Development of Diagnostic Tests for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A. CRISPR–Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, P.; Dang, L.; Meng, Q.; Wan, W.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, G. Rapid and sensitive detection of COVID-19 using CRISPR/Cas12a-based detection with naked eye readout, CRISPR/Cas12a-NER. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Curti, L.; Pereyra-Bonnet, F.; Gymenez, C.A. An ultrasensitive, rapid, and portable coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 sequence detection method based on CRISPR-Cas12. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Gootenberg, J.S. A protocol for detection of COVID-19 using CRISPR. Diagnostics 2020, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock-Biosciences, Instructions for Use for Sherlock™ CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 Kit. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137746/download (accessed on 13 September 2020).
- Rauch, J.N.; Valois, E.; Solley, S.C.; Braig, F.; Lach, R.S.; Baxter, N.J.; Kosik, K.S.; Arias, C.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Wilson, M.Z. A Scalable, easy-to-deploy, protocol for Cas13-based detection of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, T.R.; Dhamdhere, G.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Goudy, L.; Zeng, L.; Chemparathy, A.; Chmura, S.; Heaton, N.S.; Debs, R. Development of CRISPR as a prophylactic strategy to combat novel coronavirus and influenza. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Han, C.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L.; Dan, Y.; et al. Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection by Detection of Nucleocapsid Protein. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.D.; Anderson, C.E.; Williford, J.R.; Alonzo, L.F.; Glukhova, V.A.; Boyle, D.S.; Weigl, B.H.; Nichols, K.P. SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Antigen-Detecting Half-Strip Lateral Flow Assay Toward the Development of Point of Care Tests Using Commercially Available Reagents. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11305–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Products–STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag. Available online: https://sdbiosensor.com/xe/product/7672 (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Products–Sofia2 Flu+SARS Antigen FIA.; Quidel. Available online: https://quidel.com/immunoassays/sofia-2-flu-sars-antigen-fia (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Stadlbauer, D.; Amanat, F.; Chromikova, V.; Jiang, K.; Strohmeier, S.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Tan, J.; Bhavsar, D.; Capuano, C.; Kirkpatrick, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Humans: A detailed protocol for a serological assay, antigen production, and test setup. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2020, 57, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwich, C.; Croxatto, A.; Coste, A.T.; Pojer, F.; André, C.; Pellaton, C.; Farina, A.; Campos, J.; Hacker, D.; Lau, K.; et al. Changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike versus nucleocapsid antibody responses impact the estimates of infections in population-based seroprevalence studies. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01828-20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yi, Y.; Luo, X.; Xiong, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, W. Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Huang, C.; Shi, F.J.; Zeng, X.Y.; Lu, T.; Ding, S.N.; Jiao, Y.J. Development of a lateral flow immunoassay strip for rapid detection of IgG antibody against SARS-CoV-2 virus. Analyst 2020, 145, 5345–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhao, H.; Bian, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, Using Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7226–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalera, S.; Colitti, B.; Rosati, S.; Ferrara, G.; Bertolotti, L.; Nogaro, C.; Guiotto, C.; Cagnazzo, C.; Denina, M.; Fagioli, F.; et al. A multi-target lateral flow immunoassay enabling the specific and sensitive detection of total antibodies to SARS COV-2. Talanta 2021, 223, 121737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd22. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, A.; Cavalera, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Calabria, D.; Rosati, S.; Somini, P.; Colitti, B.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, M.; Anfossi, L. Dual lateral flow optical/chemiluminescence immunosensors for the rapid detection of salivary and serum IgA in patients with COVID-19 disease. Bios. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartanto, H.; Wu, M.; Lam, M.L.; Chen, T.H. Microfluidic immunoassay for detection of serological antibodies: A potential tool for rapid evaluation of immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Biomicrofluidics 2020, 14, 061507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Chavez-Pineda, O.G.; Hernandez-Ortiz, J.A.; Amador-Hernandez, J.U.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Patino-Lopez, L.D.; et al. High-throughput multiplexed microfluidic device for COVID-19 serology assays. Lab. Chip. 2021, 21, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyke, D.A.; Sharma, E.; Sahoo, M.K.; Huang, C.H.; Banaei, N.; Pinsky, B.A.; Santiago, J.G. Electric field-driven microfluidics for rapid CRISPR-based diagnostics and its application to detection of SARS-CoV-2 Ramachandran. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29518–29525. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Balda, M.; Gurung, A.S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G. Ultrasensitive nucleic acid biosensor based on enzyme-gold nanoparticle dual label and lateral flow strip biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Yoo, Y.K.; Han, S.I.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, K.; Hwang, K.S.; Lee, K.H.; Chung, S.; Lee, J.H. Battery operated preconcentration-assisted lateral flow assay. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Tang, R.; Gong, Y.; Feng, S. Polydimethylsiloxane-paper hybrid lateral flow assay for highly sensitive point-of-care nucleic acid testing. Anal Chem. 2016, 88, 6254–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Abbas, N.; Shin, S. A rapid diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 using DNA hydrogel formation on microfluidic pores. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Peng, R.; Baravik, I.K.; Liu, X. Fighting COVID-19: Integrated micro- and nanosystems for viral infection diagnostics. Matter 2020, 3, 628–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Li, P.; Ji, Y.; Ikram, A.; Pan, Q. Cross-reactivity towards SARS-CoV-2: The potential role of low-pathogenic human coronaviruses. Lancet Microbe. 2020, 1, E151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Smartphone-based analytical biosensors. Analyst 2018, 43, 5339–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Zhang, H.; Yankg, Z. The potential of an integrated biosensor system with mobile health and wastewater-based epidemiology (iBMW) for the prevention, surveillance, monitoring and intervention of the COVID-19 pandem. Bios. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; RuChoi, J.; Wang, S.; Gong, Y.; Feng, S.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; JianLu, T.; Xu, F. Multiple test zones for improved detection performance in lateral flow assays. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2017, 243, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PBB Type | Biomarker | Amplification Method | Readout | LOD | Sensitivity and Specificity | Assay Time | POC | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NALF | RdRp, ORF3a, N gene | RT-PCR | fluorescence | 10 copies/test for each gene | 100% 99% | 30 min | no | 98 |
| NALFIA | ORF1ab, N gene | RT-LAMP | colorimetric | 12 copies/reaction | 100% 100% | 1 h | yes | 99 |
| NALFIA | ORF1ab, E gene N gene | none | fluorescence | 500 copies/mL | 100% 99% | <1 h | yes | 101 |
| CRISPR-Cas12 | E gene N gene | RT-LAMP | fluorescence,visual | 10 copies/μL | 95% 100% | ~45 min | no | 106 |
| CRISPR-Cas12 | ORF1a, ORD1b, N gene, E gene | RT-RAA | fluorescence | - | 100% | <1 h | yes | 107 |
| CRISPR-Cas12 | RdRp, ORF1b,ORF1ab | RPA | fluorescence,visual | 10 copies/μL | - | 90 min | yes | 108 |
| CRISPR-Cas13 | S gene ORF1ab | RPA | fluorescence | 10–100 copies/μL | - | <1 h | yes | 109 |
| CRISPR-Cas13 | N gene ORF1ab | RT-LAMP | fluorescence, | 6.75 copies/μL 6\1 | - | 1 h | yes (commercially available) | 110 |
| μPAD | RNA | RT-LAMP | fluorescence | - | - | 30 min | no | 127 |
| PBB Type | Biomarker | Amplification Method | Readout | LOD | Sensitivity and Specificity | Assay Time | POC | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFIA | N-protein antigen | no | Fluorescence | - | 68% 100% | 10 min | yes | 113 |
| LFIA | N-protein antigen | no | fluorescence, visual | 0.65ng/ml | - | - | no | 114 |
| PBB Type | Biomarker | Amplification Method | Readout | LOD | Sensitivity and Specificity | Assay Time | POC | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFIA | IgM/IgG | none | visual | - | - | 15 min | yes | 119 |
| LFIA | IgM/IgG | none | visual | - | - | 15 min | yes | 120 |
| LFIA | IgG | none | fluorescence | - | - | - | yes | 121 |
| LFIA | IgM/ IgG/IgA | none | fluorescence | - | 94.6% 100% | - | yes | 122 |
| LFIA | IgA (also in saliva) | none | colorimetric/chemiluminescence | - | - | 15 min | yes | 124 |
| μPAD | IgG/IgM | none | fluorescence | - | 95% 91% | 6.6 min/assay 5.5 h/50 assays | yes | 126 |
| Target Analyte | Type of Result | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| gene | false negative | possible mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 genome | simultaneous detection of multiple regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome |
| false positive false negative | cross-reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 with other coronaviruses lack of amplification | simultaneous detection of multiple regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome use of isothermal amplification in CRISPR, NALF and NALFIA methods | |
| antigen | false negative | low viral load in the nasopharyngeal swabs | - |
| antibodies | false negative false positive | seroconversion cross-reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 with other coronaviruses | waiting the right time gap before testing using subunit S1 instead of the S-trimer protein which has high sequence similarities with other coronaviruses |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antiochia, R. Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease. Biosensors 2021, 11, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11040110
Antiochia R. Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease. Biosensors. 2021; 11(4):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntiochia, Riccarda. 2021. "Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease" Biosensors 11, no. 4: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11040110
APA StyleAntiochia, R. (2021). Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease. Biosensors, 11(4), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11040110





