Current Challenges and Future Trends of Enzymatic Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Abstract
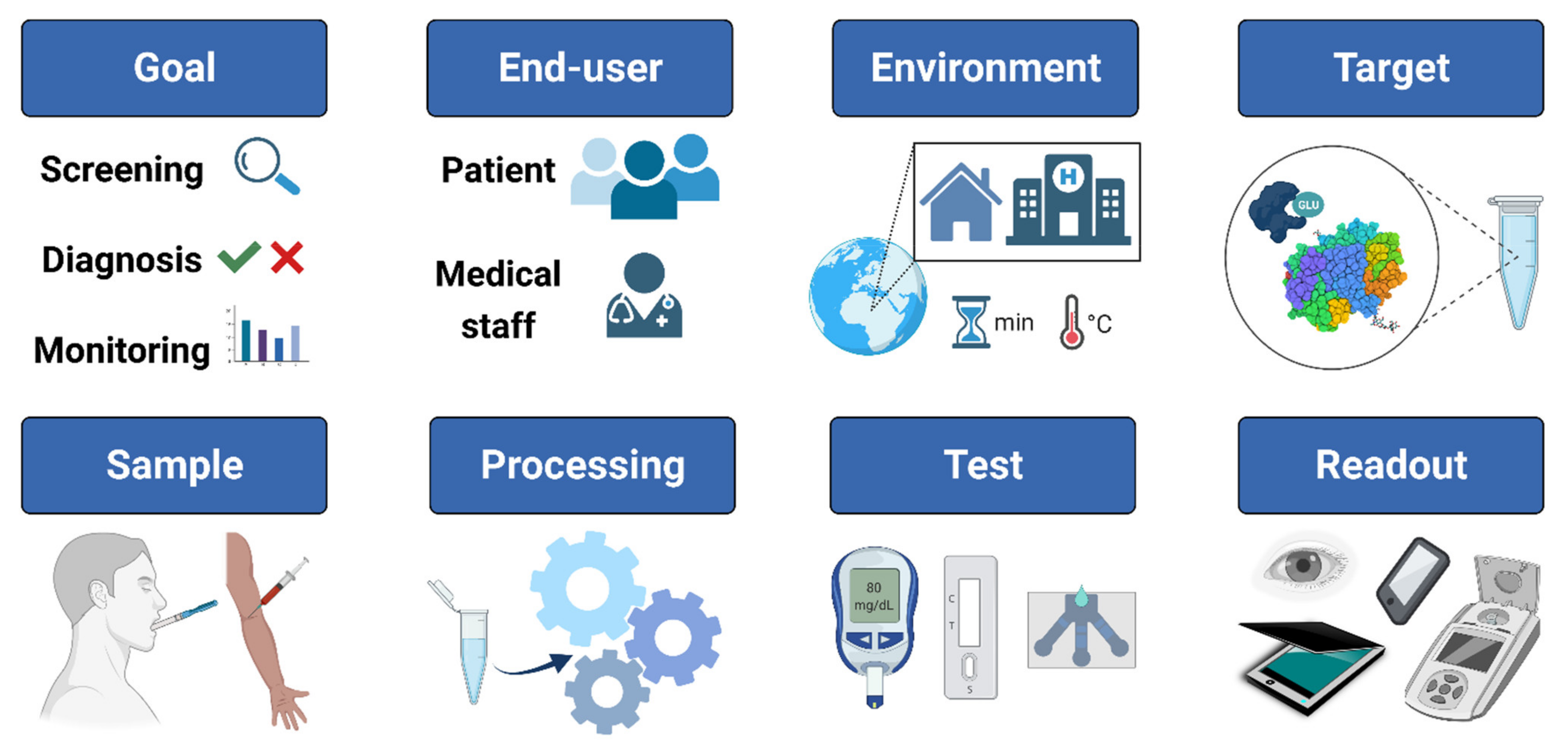
:1. Introduction
2. Main Components of Paper-Based Point-of-Care Platforms
2.1. Platform Design and Fabrication
2.2. Detection Technologies
2.2.1. Colorimetric
2.2.2. Fluorescent
2.2.3. Chemiluminescence and Luminescence
2.2.4. Electrochemical
2.3. Applications
3. Paper-Based Point-of-Care Platforms for Screening and Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
4. Current Challenges and Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suntornsuk, W.; Suntornsuk, L. Recent applications of paper-based point-of-care devices for biomarker detection. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.; Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.E. Recent progress, challenges, and prospects of fully integrated mobile and wearable point-of-care testing systems for self-testing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1812–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi-Aghdam, A.; Majidi, M.R.; Omidi, Y. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (µPADs) for fast and ultrasensitive sensing of biomarkers and monitoring of diseases. BioImpacts 2018, 8, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S. Simultaneous quantification of multiple biomarkers on a self-calibrating microfluidic paper-based analytic device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1097, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, V.A.O.P.; de Freitas, R.C.; de Oliveira, P.R.; Moreira, R.C.; Marcolino-Júnior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Janegitz, B.C. Microfluidic paper-based device integrated with smartphone for point-of-use colorimetric monitoring of water quality index. Measurement 2020, 164, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Niu, J.C.; Du, X.L.; Fang, F.; Wu, Z.Y. Novel field amplification for sensitive colorimetric detection of microalbuminuria on a paper-based analytical device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1080, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Pu, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, D. A convenient and rapid method for detecting D-glucose in honey used smartphone. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksorn, J.; Teepoo, S. Development of the simultaneous colorimetric enzymatic detection of sucrose, fructose and glucose using a microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Talanta 2020, 207, 120302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, A.; van de Vyver, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Hall, D.R.; Mason, D.; Conradie, M. A comparison between point-of-care testing and venous glucose determination for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus 6–12 weeks after gestational diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisi, F.; Peterson, J.R.; Gooding, J.J. The application of personal glucose meters as universal point-of-care diagnostic tools. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.D.; Linder, V.; Sia, S.K. Commercialization of microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2118–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosack, C.S.; Page, A.L.; Klatser, P.R. A guide to aid the selection of diagnostic tests. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E. Diagnostics for the Developing World: Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. From Bench to Bedside: Setting a Path for the Translation of Improved STI Diagnostics into Health Care Delivery in the Developing World an Informal Consultation Jointly Organised and Sponsored By; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía; Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública; Secretaría de Salud. Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición. Ensanut 2018, 1, 47. [Google Scholar]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; ISBN 9782930229874. [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddy, D.M.; Delerive, P.; Summers, R.J.; Sexton, P.M.; Langmead, C.J. G protein–coupled receptors targeting insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubala, V.; Harris, L.F.; Ricco, A.J.; Tan, M.X.; Williams, D.E. Point of Care Diagnostics: Status and Future. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.P.; Mace, C.R. Usability as a guiding principle for the design of paper-based, point-of-care devices—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1140, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Khanra, K.; Chowdhury, A.R.; Datta, P. Lab-on-a-chip sensing devices for biomedical applications. In Bioelectronics and Medical Devices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 47–95. ISBN 9780081024201. [Google Scholar]
- Luppa, P.B.; Müller, C.; Schlichtiger, A.; Schlebusch, H. Point-of-care testing (POCT): Current techniques and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sher, M.; Zhuang, R.; Demirci, U.; Asghar, W. Paper-based analytical devices for clinical diagnosis: Recent advances in the fabrication techniques and sensing mechanisms. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochia, R. Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease. Biosensors 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillscher, L.M.; Liebich, V.J.; Avrutina, O.; Biesalski, M.; Kolmar, H. Functional paper-based materials for diagnostics. ChemTexts 2021, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-M.; Wang, Y.-N. Detection methods and applications of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, A.P.; Rudolf, F.; Ponti, A. pyPOCQuant—A tool to automatically quantify Point-Of-Care Tests from images. SoftwareX 2021, 15, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.; Liang, T.; Spicar-Mihalic, P.; Houghtaling, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Yager, P. A two-dimensional paper network format that enables simple multi-step assays for use in low-resource settings in the context of malaria antigen detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4574–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutz, B.R.; Trinh, P.; Ball, C.; Fu, E.; Yager, P. Two-dimensional paper networks: Programmable fluidic disconnects for multi-step processes in shaped paper. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrell, C.; Kava, A.; Nguyen, M.; Menger, R.; Munshi, Z.; Call, Z.; Nussbaum, M.; Henry, C. Beyond the lateral flow assay: A review of paper-based microfluidics. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 206, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, X.; Jin, D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Y.; An, Y. Paper-based immunosensors: Current trends in the types and applied detection techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, R.A.G.; Camargo, F.; Pesquero, N.C.; Faria, R.C. A simple method to produce 2D and 3D microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for clinical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 957, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, E.; Ramsey, S.A.; Kauffman, P.; Lutz, B.; Yager, P. Transport in two-dimensional paper networks. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2011, 10, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Pasquale, G.; Zappulla, L.; Scaltrito, L.; Bertana, V. Numerical and experimental evaluation of SLA polymers adhesion for innovative bio-MEMS. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, Z.Z.; Fang, C.; Gao, A.X.; Li, C.M.; Yu, L. Versatile microfluidic complement fixation test for disease biomarker detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 916, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Böck, F.C.; Helfer, G.A.; da Costa, A.B.; Dessuy, M.B.; Ferrão, M.F. PhotoMetrix and colorimetric image analysis using smartphones. J. Chemom. 2020, 34, e3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, Ö.B.; Kılıç, V.; Şen, M. Machine learning-based colorimetric determination of glucose in artificial saliva with different reagents using a smartphone coupled μPAD. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, H.R.; Prabhu, A.; Giri Nandagopal, M.S.; Dheivasigamani, T.; Mani, N.K. One-dollar microfluidic paper-based analytical devices: Do-It-Yourself approaches. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xiang, X.; Luo, M.; Ji, X.; He, Z. Determination of glucose and uric acid with bienzyme colorimetry on microfluidic paper-based analysis devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puiu, M.; Mirceski, V.; Bala, C. Paper-based diagnostic platforms and devices. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderinezhad, F.; Amin, R.; Temirel, M.; Yenilmez, B.; Wentworth, A.; Tasoglu, S. High-throughput rapid-prototyping of low-cost paper-based microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyasit, Y.; Chailapakul, O.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. A multiplexed three-dimensional paper-based electrochemical impedance device for simultaneous label-free affinity sensing of total and glycated haemoglobin: The potential of using a specific single-frequency value for analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Deng, R.; Guo, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Yu, H.-Z. A WiFi scanner in conjunction with disposable multiplex paper assay for the quantitation of disease markers in blood plasma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 4625–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badu-Tawiah, A.K.; Lathwal, S.; Kaastrup, K.; Al-Sayah, M.; Christodouleas, D.C.; Smith, B.S.; Whitesides, G.M.; Sikes, H.D. Polymerization-based signal amplification for paper-based immunoassays. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendez, M.A.; Calahorrano, A.; Costa-Vera, C.; Sanchez, R.; Montero-Oleas, A. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for reliable and low-cost point-of-care applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fourth Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), Guayaquil, Ecuador, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, N.; Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Smartphone-based fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay platform for highly sensitive point-of-care detection of Zika virus nonstructural protein 1. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1055, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Chu, W.; Chen, Y. Paper-based laser induced fluorescence immunodevice combining with CdTe embedded silica nanoparticles signal enhancement strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Akram, M.S.; Lowe, C.R. Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2210–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Kricka, L.J. Prospects for the commercialization of chemiluminescence-based point-of-care and on-site testing devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, E.L.; Silva, T.A.; do Prado, T.M.; de Moraes, F.C.; Faria, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Electrochemical paper-based microfluidic device for high throughput multiplexed analysis. Talanta 2019, 203, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrettoni, C.; Berneschi, S.; Bernini, R.; Giannetti, A.; Grimaldi, I.A.; Persichetti, G.; Testa, G.; Tombelli, S.; Trono, C.; Baldini, F. Optical Monitoring of Therapeutic Drugs with a Novel Fluorescence-Based POCT Device. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padayattil Jose, S.; Banzato, A.; Carraro, P.; Haleh, A.; Rossi, K.; Nante, G.; Denas, G.; Zoppellaro, G.; Pengo, V. Point of Care Testing (POCT) to assess drug concentration in patients treated with non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs). Thromb. Res. 2018, 163, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Su, W.; Ding, X. A review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for glucose detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Enter, B.J.; Von Hauff, E. Challenges and perspectives in continuous glucose monitoring. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5032–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, E.W.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Jönsson-Niedziólka, M. Electrochemical glucose sensing: Is there still room for improvement? Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11271–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Global Health Observatory. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/2380 (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabák, A.G.; Herder, C.; Rathmann, W.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimäki, M. Prediabetes: A high-risk state for diabetes development. Lancet 2012, 379, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Chang, S.J.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, J.T. Non-invasive blood glucose monitoring technology: A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.H.; Lee, S.Y. Glucose biosensors: An overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juska, V.B.; Pemble, M.E. A Critical Review of Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Evolution of Biosensor Platforms Based on Advanced Nanosystems. Sensors 2020, 20, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Awan, T.; Salim, H.; Arshad, F.; Hassan, I.U.; Pedram, M.Z.; Ahmed, W.; Faruck, H.L.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; et al. Fourth-generation glucose sensors composed of copper nanostructures for diabetes management: A critical review. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, e10248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, A. Smartphone for glucose monitoring. In Smartphone Based Medical Diagnostics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 45–65. ISBN 9780128170441. [Google Scholar]
- Teymourian, H.; Barfidokht, A.; Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: An updated review (2010–2020). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7671–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tarso Garcia, P.; Garcia Cardoso, T.M.; Garcia, C.D.; Carrilho, E.; Tomazelli Coltro, W.K. A handheld stamping process to fabricate microfluidic paper-based analytical devices with chemically modified surface for clinical assays. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37637–37644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xia, J.; Jiang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, S. Cellulose-Based Strips Designed Based on a Sensitive Enzyme Colorimetric Assay for the Low Concentration of Glucose Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 15461–15468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. An innovative blood plasma separation method for a paper-based analytical device using chitosan functionalization. Analyst 2020, 145, 5491–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, H.; Jang, H.; Oh, J.; Han, G.R.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.G. Simultaneous Detection of Serum Glucose and Glycated Albumin on a Paper-Based Sensor for Acute Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11530–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Park, C.; Jeon, J.; Park, S. Three-Dimensional Paper-Based Microfluidic Analysis Device for Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Biomarkers with a Smartphone. Biosensors 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.X.; Tang, C.; Han, X.X.; Zhang, H.C.; Guo, F.N.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.H. Simultaneous and sensitive detection of multiple small biological molecules by microfluidic paper-based analytical device integrated with zinc oxide nanorods. Talanta 2021, 232, 122499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.H.; Park, M.; Jeong, K.H. Colorimetric Schirmer strip for tear glucose detection. BioChip J. 2017, 11, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Jha, S.K. Smartphone based non-invasive salivary glucose biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 996, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Jiménez, L.; Márquez-Lucero, A.; Osuna, V.; Estrada-Moreno, I.; Dominguez, R. Naked-Eye Detection of Glucose in Saliva with Bienzymatic Paper-Based Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaquer, A.; Barón, E.; de la Rica, R. Detection of low glucose levels in sweat with colorimetric wearable biosensors. Analyst 2021, 146, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Microfluidic Chip-Based Wearable Colorimetric Sensor for Simple and Facile Detection of Sweat Glucose. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14803–14807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.-J.; Pan, S.-W.; Yang, J.-H.; Chang, T.-L.; Lin, P.-Y.; Wu, C.-L.; Liu, W.-F.; Huang, X.-R.; Koshevoy, I.; Chou, P.-T.; et al. Detecting Glucose Levels in Blood Plasma and Artificial Tear by Au(I) Complex on the Carbopol Polymer: A Microfluidic Paper-Based Method. Polymers 2018, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinkova, P.; Brtnicky, M.; Kynicky, J.; Pohanka, M. Fast and simple glucose assay based on filter paper as enzymes carrier using phone camera detection. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jha, S.K. Fabrication and Validation of a Handheld Non-Invasive, Optical Biosensor for Self-Monitoring of Glucose Using Saliva. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 8332–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobbari, M.L.; Rad, M.B.; Jahanshahi, A.; Ghourchian, H. A sample volume independent paper microfluidic device for quantifying glucose in real human plasma. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2020, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granica, M.; Tymecki, Ł. Prussian Blue (bio)sensing device for distance-based measurements. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1136, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, A. A low-cost mobile platform for whole blood glucose monitoring using colorimetric method. Microchem. J. 2021, 162, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Jha, S.K. A paper strip based non-invasive glucose biosensor for salivary analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.F.; Sann, E.E.; Lou, X.; Liu, R.; Dai, J.; Zuo, X.; Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Naked-eye point-of-care testing platform based on a pH-responsive superwetting surface: Toward the non-invasive detection of glucose. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, G.M.; Silva, W.R.; Barreto, D.N.; Lamarca, R.S.; Lima Gomes, P.C.F.; da S Petruci, J.F.; Batista, A.D. Novel approaches for colorimetric measurements in analytical chemistry—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1135, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M.; Balkau, B.; Bonora, E.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Buse, J.B.; Colagiuri, S.; Davidson, M.B.; DeFronzo, R.; Genuth, S.; Holman, R.R.; et al. International Expert Committee Report on the Role of the A1C Assay in the Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnchanasorn, R.; Huang, J.; Ou, H.-Y.; Feng, W.; Chuang, L.-M.; Chiu, K.C.; Samoa, R. Comparison of the Current Diagnostic Criterion of HbA1c with Fasting and 2-Hour Plasma Glucose Concentration. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, D.M.; Griffin, A.; Perez, F.M.; Basque, E.; Do, L.; Steiner, B. Accuracy of a Point-of-Care Hemoglobin A1c Assay. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubach, I.L.; Christ, E.R.; Diem, P. HbA1c-testing: Evaluation of two point-of-care analysers. Prim. Care Diabetes 2019, 13, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, J.A.; McLellan, J.H.; Price, C.P.; English, E.; Feakins, B.G.; Stevens, R.J.; Farmer, A.J. Performance of point-of-care HbA1c test devices: Implications for use in clinical practice—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenters-Westra, E.; English, E. Evaluation of Four HbA1c Point-of-Care Devices Using International Quality Targets: Are They Fit for the Purpose? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupuy, A.M.; Badiou, S.; Bargnoux, A.S.; Russelo, J.; Cristol, J.P. Evaluation of Point of Care Analyzer for Hemoglobin A1c. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, W.D.; Kupfer, K.; Little, R.R.; Amar, M.; Horowitz, B.; Godbole, N.; Swensen, M.H.; Li, Y.; San George, R.C. Accuracy and Precision of a Point-of-Care HbA1c Test. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.D.M.; Moon, J.M.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Park, D.S.; Choi, C.S.; Shim, Y.B. Separation detection of hemoglobin and glycated hemoglobin fractions in blood using the electrochemical microfluidic channel with a conductive polymer composite sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shajaripour Jaberi, S.Y.; Ghaffarinejad, A.; Omidinia, E. An electrochemical paper based nano-genosensor modified with reduced graphene oxide-gold nanostructure for determination of glycated hemoglobin in blood. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1078, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M.; Kasayama, S. Clinical impact of glycated albumin as another glycemic control marker. Endocr. J. 2010, 57, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorcely, B.; Katz, K.; Jagannathan, R.; Chiang, S.S.; Oluwadare, B.; Goldberg, I.J.; Bergman, M. Novel biomarkers for prediabetes, diabetes, and associated complications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paroni, R.; Ceriotti, F.; Galanello, R.; Leoni, G.B.; Panico, A.; Scurati, E.; Paleari, R.; Chemello, L.; Quaino, V.; Scaldaferri, L.; et al. Performance characteristics and clinical utility of an enzymatic method for the measurement of glycated albumin in plasma. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Glycated Albumin Versus HbA1c in the Evaluation of Glycemic Control in Patients With Diabetes and CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vernon Roohk, H.; Zaidi, A.R. A review of glycated albumin as an intermediate glycation index for controlling diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatada, M.; Wilson, E.; Khanwalker, M.; Probst, D.; Okuda-Shimazaki, J.; Sode, K. Current and future prospective of biosensing molecules for point-of-care sensors for diabetes biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 351, 130914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsare, S.; Coté, G. Development of a colorimetric paper fluidic dipstick assay for measurement of glycated albumin to monitor gestational diabetes at the point-of-care. Talanta 2021, 223, 121728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatada, M.; Tsugawa, W.; Kamio, E.; Loew, N.; Klonoff, D.C.; Sode, K. Development of a screen-printed carbon electrode based disposable enzyme sensor strip for the measurement of glycated albumin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatada, M.; Loew, N.; Okuda-Shimazaki, J.; Khanwalker, M.; Tsugawa, W.; Mulchandani, A.; Sode, K. Development of an Interdigitated Electrode-Based Disposable Enzyme Sensor Strip for Glycated Albumin Measurement. Molecules 2021, 26, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleicher, E.D.; Vogt, B.W. Standardization of serum fructosamine assays. Clin. Chem. 1990, 36, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.R.; Johnson, R.N.; Scott, D.J. Serum fructosamine concentrations in patients with type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus during changes in management. BMJ 1984, 288, 1484–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonyasit, Y.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. A microfluidic paper-based analytical device for the assay of albumin-corrected fructosamine values from whole blood samples. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, E.; Rawlings, A.M.; Grams, M.; Klein, R.; Sharrett, A.R.; Steffes, M.; Coresh, J. Fructosamine and glycated albumin for risk stratification and prediction of incident diabetes and microvascular complications: A prospective cohort analysis of the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoury, Z.H.H.; Illesca, P.; Sultan, A.S.S. Salivary Fructosamine as a Noninvasive Glycemic Biomarker: A Systematic Review. JDR Clin. Transl. Res. 2021, 6, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, X. Simultaneous monitoring of glucose and uric acid on a single test strip with dual channels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manbohi, A.; Ahmadi, S.H. Chitosan–Fe3O4 nanoparticle enzymatic electrodes on paper as an efficient assay for glucose and uric acid detection in biological fluids. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 2675–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, N.S.; Chagas, C.L.S.; Oliveira, K.A.; Duarte-Junior, G.F.; de Souza, F.R.; Santhiago, M.; Garcia, C.D.; Kubota, L.T.; Coltro, W.K.T. Fabrication of microwell plates and microfluidic devices in polyester films using a cutting printer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1119, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Tsai, F.-J.; Zeng, Y.-T.; Wang, J.-C.; Hong, C.P.; Huang, P.-H.; Chuang, H.-L.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chan, C.-T.; Ko, Y.-C.; et al. Fast and Effective Turn-on Paper-based Phosphorescence Biosensor for Detection of Glucose in Serum. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2016, 63, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, E.L.; Milani, M.I.; Lima, L.S.; Pezza, H.R. Paper microfluidic device using carbon dots to detect glucose and lactate in saliva samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 248, 119285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, W.; Pan, Y.; Long, Y.; Zheng, H. Glucose detection based on the photothermal effect of OxTMB using a thermometer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davaji, B.; Lee, C.H. A paper-based calorimetric microfluidics platform for bio-chemical sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colletes, T.C.; Garcia, P.T.; Campanha, R.B.; Abdelnur, P.V.; Romão, W.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Vaz, B.G. A new insert sample approach to paper spray mass spectrometry: A paper substrate with paraffin barriers. Analyst 2016, 141, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, S.V.; De Souza, F.R.; Rodrigues Neto, J.C.; Vasconcelos, G.A.; Abdelnur, P.V.; Vaz, B.G.; Henry, C.S.; Coltro, W.K.T. Uncovering the Formation of Color Gradients for Glucose Colorimetric Assays on Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices by Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11949–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, L.F.; de Freitas, S.V.; Duarte, L.C.; de Souza, J.A.C.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Coltro, W.K.T. Salivary diagnostics on paper microfluidic devices and their use as wearable sensors for glucose monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Salazar, J.R.; Rodrigues Cruz, K.; MaterónVásques, E.M.M.; de Oliveira, O.N., Jr. Microfluidic Point-of-Care Devices: New Trends and Future Prospects for eHealth Diagnostics. Sensors 2020, 20, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdem, Ö.; Eş, I.; Akceoglu, G.A.; Saylan, Y.; Inci, F. Recent Advances in Microneedle-Based Sensors for Sampling, Diagnosis and Monitoring of Chronic Diseases. Biosensors 2021, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, S.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Park, S. From Diagnosis to Treatment: Recent Advances in Patient-Friendly Biosensors and Implantable Devices. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1960–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Sharma, S.; Cass, A.E.G.; Tasca, F.; Antiochia, R. Minimally Invasive Glucose Monitoring Using a Highly Porous Gold Microneedles-Based Biosensor: Characterization and Application in Artificial Interstitial Fluid. Catalysts 2019, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tasca, F.; Tortolini, C.; Bollella, P.; Antiochia, R. Microneedle-based electrochemical devices for transdermal biosensing: A review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ni, S.; Korabečná, M.; Yobas, L.; Neuzil, P. The vision of point-of-care PCR tests for the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.L.; Wang, J.; Maruthamuthu, M.K.; Dextre, A.; Pascual-Garrigos, A.; Mohan, S.; Putikam, S.V.S.; Osman, F.O.I.; McChesney, D.; Seville, J.; et al. A paper-based colorimetric molecular test for SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2021, 9, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Davis, R.W.; Saha, A.K. Microfluidic Point-of-Care Testing: Commercial Landscape and Future Directions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolo, C.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-based nanobiosensors for diagnostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisowski, P.; Zarzycki, P.K. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) and micro total analysis systems (μTAS): Development, applications and future trends. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grand View Research. Paper Diagnostics Market Analysis Report by Device Type (Diagnostics, Monitoring), by Application, by Product (Lateral Flow Assays, Paper Based Microfluidics), by End Use, and Segment Forecasts, 2018–2025. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/paper-diagnostics-market (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Chin, C.D.; Linder, V.; Sia, S.K. Lab-on-a-chip devices for global health: Past studies and future opportunities. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luong, J.H.T. Point-of-Care Technologies Enabling Next-Generation Healthcare Monitoring and Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-11415-2. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.; Korvink, J.G.; Mager, D.; Land, K. The potential of paper-based diagnostics to meet the ASSURED criteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34012–34034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishat, S.; Jafry, A.T.; Martinez, A.W.; Awan, F.R. Paper-based microfluidics: Simplified fabrication and assay methods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 336, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobphahom, S.; Nguyet Ly, M.; Soum, V.; Pyun, N.; Kwon, O.-S.; Rodthongkum, N.; Shin, K. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices toward High-Throughput Screening. Molecules 2020, 25, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gao, L.; Chen, Z. Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of glucose through glucose oxidase and Cu 2+ -catalyzed 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine oxidation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 213, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Yu, L.; Li, C.M. Fast prototyping of a customized microfluidic device in a non-clean-room setting by cutting and laminating Parafilm®. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85468–85472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Substrate | System | Sample | Detection | LOD (mg/dL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wax printing on Whatman chromatography paper 595 | GOD/HRP/ 4-AAP/HBA | Tears | Smartphone camera | NM | [74] |
| Whatman filter paper No. 1 with lamination film | GOD/BP | Saliva | Smartphone camera | 24.6 | [75] |
| Wax printing on qualitative filter paper and Schirmer strips | GOD/Au(I) complex (AuC2C6H4OMe)2 (Ph2P(C6H4)3PPh2) | Simulated tear fluid and blood | Bifurcated optical fiber system | 16.2 (plasma) 1.4 (tear) | [79] |
| Whatman cellulose filter paper No. 1 treated with CH | GOD/HRP/ EDC/o-PD | Urine | Smartphone camera | 18.0 | [80] |
| Whatman filter paper No. 40 stamped with paraffin and treated with CH | GOD/HRP/ TBHBA/4-AAP | Artificial and human saliva | Naked eye | 0.8 | [76] |
| High-purity cellulose membranes | GOD/HRP/TMB | Urine | Digital camera | 8.1 | [69] |
| Whatman filter paper No. 1 with lamination film | GOD/BP | Saliva | Handheld optical biosensor | 32.0 | [81] |
| Wax printing on Whatman filter paper No. 1 | GOD/HRP/ KI or TMB | Plasma | Smartphone camera | 27.0 (KI) 0.9 (TMB) | [82] |
| Wax printing on Whatman filter paper No. 1 treated with CH | GOD/HRP/ 4-AAP/HBA | Blood | Scanner | NM | [70] |
| Whatman qualitative paper No.1 treated with PB | GOD | Serum | Distance-based measurements | 19.8 | [83] |
| Nitrocellulose membranes | GOD/HRP/4-AAP/COL/MADB | Serum | Chemidoc imaging system | 0.2 | [71] |
| Wax printing on Whatman No. 1 cellulose chromatography paper treated with BSA | GOD/HRP/ 4-AAP/DHBS | Serum | Scanner | 5.4 | [4] |
| Whatman qualitative filter paper No. 1 coated with a UV-curable resin | GOD/HRP/ MAOS/4-AAP | Serum | Smartphone camera | 5.4 | [72] |
| Wax printing in Whatman No. 1 chromatography filter paper treated with CH | GOD/HRP/TMB | Blood | Smartphone-based optical platform | 5.0 | [84] |
| Whatman filter paper No. 3 treated with OTS and MTS | GOD/HRP/ phenol/4-AAP | Plasma | Portable scanner | 15.1 | [45] |
| Wax printing in Whatman No. 1 qualitative filter paper loaded with ZnNR | GOD/ 4-AAP/ DHBS | Serum and urine | Smartphone camera | 0.05 | [73] |
| Whatman filter paper No. 41 treated with BSA-Tween | GOD/HRP/TMB | Sweat | Scanner and Smartphone camera | 0.18 | [77] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Martínez, M.; Flores-DelaToba, R.; González-González, M.; Rito-Palomares, M. Current Challenges and Future Trends of Enzymatic Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Biosensors 2021, 11, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120482
Ortiz-Martínez M, Flores-DelaToba R, González-González M, Rito-Palomares M. Current Challenges and Future Trends of Enzymatic Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Biosensors. 2021; 11(12):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120482
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Martínez, Margarita, Raquel Flores-DelaToba, Mirna González-González, and Marco Rito-Palomares. 2021. "Current Challenges and Future Trends of Enzymatic Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2" Biosensors 11, no. 12: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120482
APA StyleOrtiz-Martínez, M., Flores-DelaToba, R., González-González, M., & Rito-Palomares, M. (2021). Current Challenges and Future Trends of Enzymatic Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Biosensors, 11(12), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120482







