Circularly Permuted Far-Red Fluorescent Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Materials and Methods
2.2. Circular Permutation, Library Construction, and Screening
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. In Vitro Characterization
3. Results
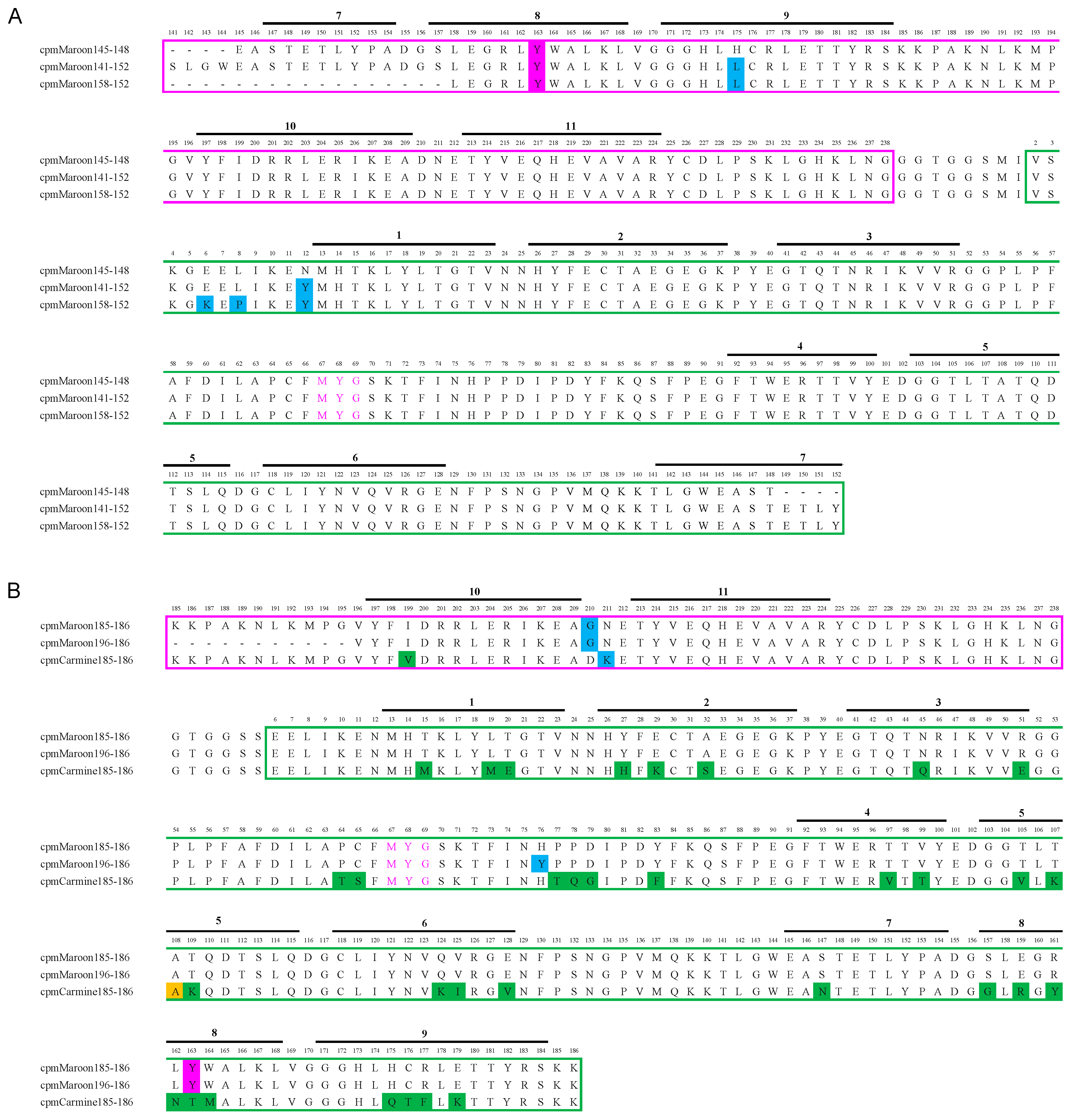
3.1. Circular Permutation of mMaroon1 and mCarmine
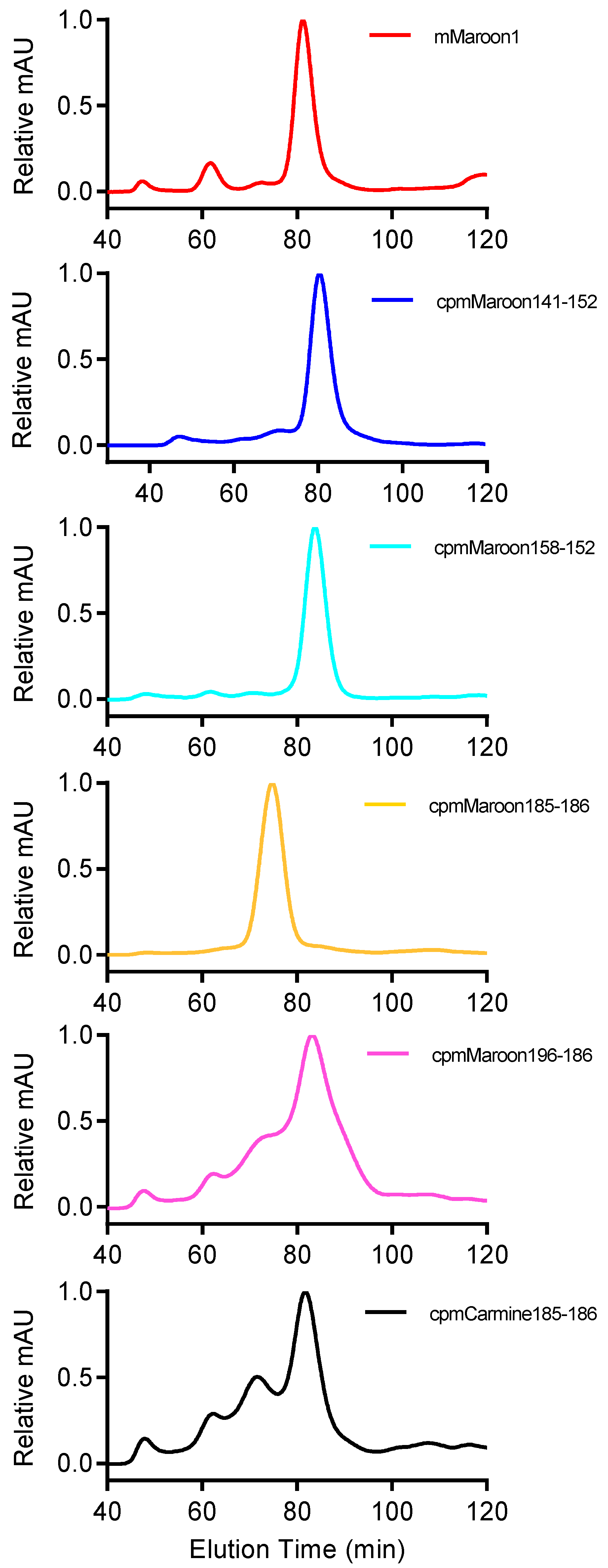
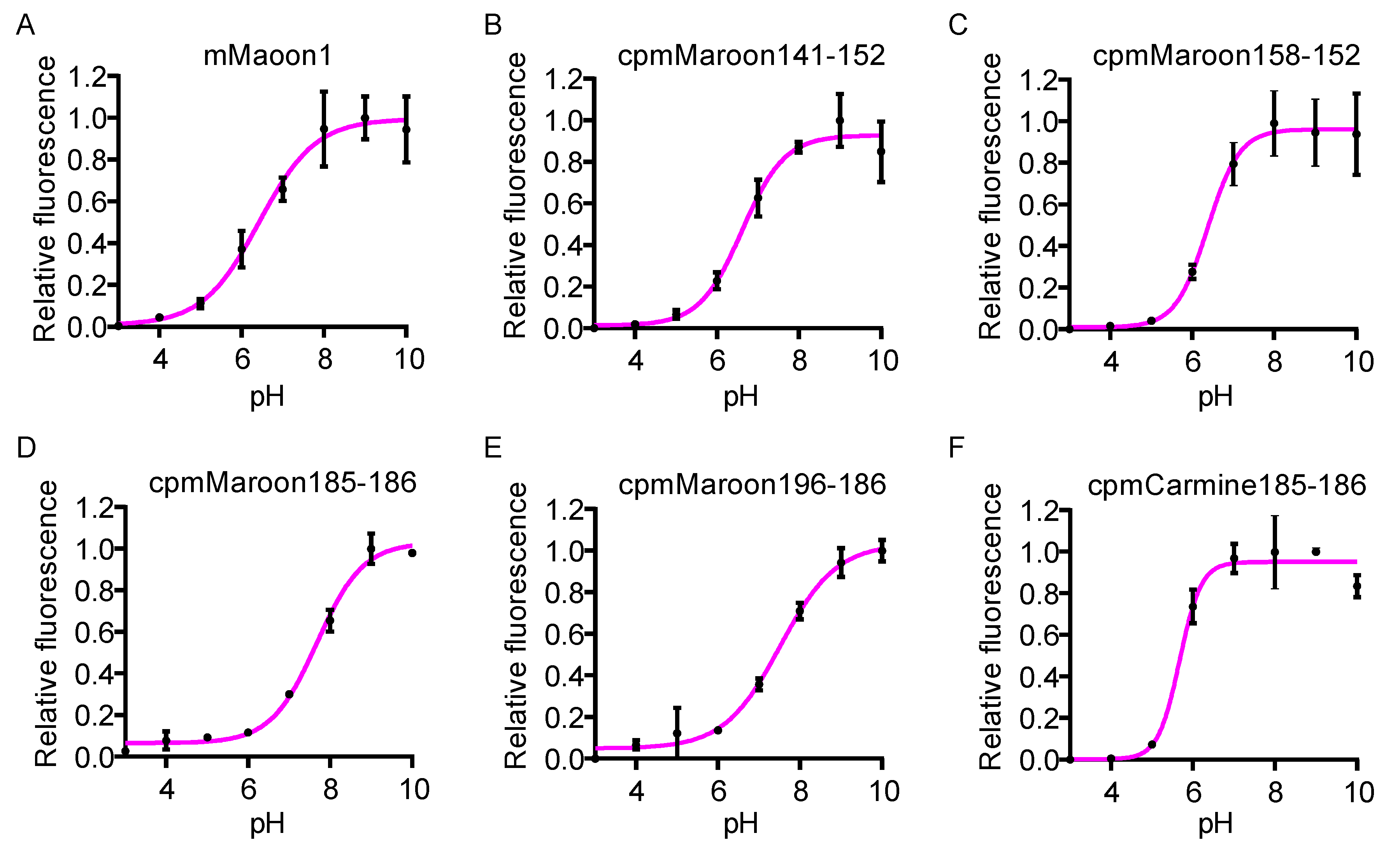
3.2. Characterization of Circularly Permuted mMaroon1 and mCarmine Variants
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, Q.; Mehta, S.; Zhang, J. Live-cell imaging of cell signaling using genetically encoded fluorescent reporters. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y. Lighting Up Live-Cell and In Vivo Central Carbon Metabolism with Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Sensors. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 13, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kramer, L.; Campbell, R.E. Structure- and mechanism-guided design of single fluorescent protein-based biosensors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, E.P.S.; Damon, L.J.; Anson, K.J.; Palmer, A.E. Tools and techniques for illuminating the cell biology of zinc. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ai, H.W. Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Redox Indicators for Unveiling Redox Signaling and Oxidative Toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1826–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, B.L.; Tian, L. Imaging Neurotransmitter and Neuromodulator Dynamics In Vivo with Genetically Encoded Indicators. Neuron 2020, 108, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, E.C.; Mehta, S.; Zhang, J. Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Biosensors Illuminate the Spatiotemporal Regulation of Signaling Networks. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11707–11794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.S.; Qian, Y.; Wu, J.; Shen, Y.; Campbell, R.E.; Drobizhev, M.; Hughes, T.E. Understanding the Fluorescence Change in Red Genetically Encoded Calcium Ion Indicators. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ai, H.W. Fluorescent-protein-based probes: General principles and practices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Araki, S.; Wu, J.; Teramoto, T.; Chang, Y.-F.; Nakano, M.; Abdelfattah, A.S.; Fujiwara, M.; Ishihara, T.; Nagai, T.; et al. An Expanded Palette of Genetically Encoded Ca2+ Indicators. Science 2011, 333, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Dana, H.; Abdelfattah, A.S.; Patel, R.; Shea, J.; Molina, R.S.; Rawal, B.; Rancic, V.; Chang, Y.-F.; Wu, L. A genetically encoded Ca2+ indicator based on circularly permutated sea anemone red fluorescent protein eqFP578. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, Y.; Furuta, T.; Nagai, T.; Horikawa, K. Red fluorescent cAMP indicator with increased affinity and expanded dynamic range. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akerboom, J.; Calderon, N.C.; Tian, L.; Wabnig, S.; Prigge, M.; Tolo, J.; Gordus, A.; Orger, M.B.; Severi, K.E.; Macklin, J.J.; et al. Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.Z.; McKeown, M.R.; Ng, H.-L.; Aguilera, T.A.; Shaner, N.C.; Campbell, R.E.; Adams, S.R.; Gross, L.A.; Ma, W.; Alber, T.; et al. Autofluorescent Proteins with Excitation in the Optical Window for Intravital Imaging in Mammals. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, X.; Royant, A.; Lin, M.Z.; Aguilera, T.A.; Lev-Ram, V.; Steinbach, P.A.; Tsien, R.Y. Mammalian expression of infrared fluorescent proteins engineered from a bacterial phytochrome. Science 2009, 324, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, E.A.; Tran, G.N.; Gross, L.A.; Crisp, J.L.; Shu, X.; Lin, J.Y.; Tsien, R.Y. A far-red fluorescent protein evolved from a cyanobacterial phycobiliprotein. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shcherbakova, D.M.; Baloban, M.; Verkhusha, V.V. Near-infrared fluorescent proteins engineered from bacterial phytochromes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 27, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonov, G.S.; Piatkevich, K.D.; Ting, L.M.; Zhang, J.; Kim, K.; Verkhusha, V.V. Bright and stable near-infrared fluorescent protein for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, N.; Kuypers, B.E.; Nassif, B.; Thomas, E.E.; Alnahhas, R.N.; Segatori, L.; Silberg, J.J. Tolerance of a Knotted Near-Infrared Fluorescent Protein to Random Circular Permutation. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 3763–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.; Piatkevich, K.D.; Mc Larney, B.; Abdelfattah, A.S.; Mehta, S.; Murdock, M.H.; Gottschalk, S.; Molina, R.S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. A genetically encoded near-infrared fluorescent calcium ion indicator. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Cosio, D.M.O.; Piatkevich, K.D.; Aufmkolk, S.; Su, W.C.; Celiker, O.T.; Schohl, A.; Murdock, M.H.; Aggarwal, A.; Chang, Y.F.; et al. Improved genetically encoded near-infrared fluorescent calcium ion indicators for in vivo imaging. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, Z.T.; Brockway, N.L.; Tobias, Z.J.C.; Pajarla, J.; Boardman, I.S.; Ippolito, H.; Nkoula, S.N.; Weissman, T.A. Combining near-infrared fluorescence with Brainbow to visualize expression of specific genes within a multicolor context. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecinos-Franjola, F.; Lin, J.Y.; Rodriguez, E.A. Fluorescent proteins for in vivo imaging, where’s the biliverdin? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkseven, S.; Kruger, A.; Mingone, C.J.; Kaminski, P.; Inaba, M.; Rodella, L.F.; Ikehara, S.; Wolin, M.S.; Abraham, N.G. Antioxidant mechanism of heme oxygenase-1 involves an increase in superoxide dismutase and catalase in experimental diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H701–H707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, T.; Daiber, A. Direct antioxidant properties of bilirubin and biliverdin. Is there a role for biliverdin reductase? Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedlak, T.W.; Saleh, M.; Higginson, D.S.; Paul, B.D.; Juluri, K.R.; Snyder, S.H. Bilirubin and glutathione have complementary antioxidant and cytoprotective roles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5171–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajar, B.T.; Lam, A.J.; Badiee, R.K.; Oh, Y.H.; Chu, J.; Zhou, X.X.; Kim, N.; Kim, B.B.; Chung, M.; Yablonovitch, A.L.; et al. Fluorescent indicators for simultaneous reporting of all four cell cycle phases. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabritius, A.; Ng, D.; Kist, A.M.; Erdogan, M.; Portugues, R.; Griesbeck, O. Imaging-Based Screening Platform Assists Protein Engineering. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Bi, L.; Cui, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.-E. Mutagenesis of mNeptune red-shifts emission spectrum to 681–685 nm. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesbeck, O.; Baird, G.S.; Campbell, R.E.; Zacharias, D.A.; Tsien, R.Y. Reducing the environmental sensitivity of yellow fluorescent protein. Mechanism and applications. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29188–29194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, L.A.; Baird, G.S.; Hoffman, R.C.; Baldridge, K.K.; Tsien, R.Y. The structure of the chromophore within DsRed, a red fluorescent protein from coral. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11990–11995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, R.E.; Tour, O.; Palmer, A.E.; Steinbach, P.A.; Baird, G.S.; Zacharias, D.A.; Tsien, R.Y. A monomeric red fluorescent protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7877–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Sierra, A.M.; Ai, H.W.; Campbell, R.E. Identification of sites within a monomeric red fluorescent protein that tolerate peptide insertion and testing of corresponding circular permutations. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalfie, M.; Kain, S.R. Green Fluorescent Protein: Properties, Applications and Protocols; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 47. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.; Haynes, R.D.; Corbel, S.Y.; Li, P.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, E.; Burg, J.S.; Ataie, N.J.; Lam, A.J.; Cranfill, P.J.; Baird, M.A.; et al. Non-invasive intravital imaging of cellular differentiation with a bright red-excitable fluorescent protein. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakai, J.; Ohkura, M.; Imoto, K. A high signal-to-noise Ca2+ probe composed of a single green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topell, S.; Hennecke, J.; Glockshuber, R. Circularly permuted variants of the green fluorescent protein. FEBS Lett. 1999, 457, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, G.S.; Zacharias, D.A.; Tsien, R.Y. Circular permutation and receptor insertion within green fluorescent proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11241–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shui, B.; Wang, Q.; Lee, F.; Byrnes, L.J.; Chudakov, D.M.; Lukyanov, S.A.; Sondermann, H.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Circular permutation of red fluorescent proteins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gautam, S.; Perron, A.; Mutoh, H.; Knopfel, T. Exploration of fluorescent protein voltage probes based on circularly permuted fluorescent proteins. Front. Neuroeng. 2009, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagai, T.; Sawano, A.; Park, E.S.; Miyawaki, A. Circularly permuted green fluorescent proteins engineered to sense Ca2+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3197–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalangin, R.; Drobizhev, M.; Molina, R.S.; Aggarwal, A.; Patel, R.; Abdelfattah, A.S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Podgorski, K.; Schreiter, E.R.; et al. Far-red fluorescent genetically encoded calcium ion indicators. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.D.; Chinenov, Y.; Kerppola, T.K. Visualization of interactions among bZIP and Rel family proteins in living cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallrabe, H.; Periasamy, A. Imaging protein molecules using FRET and FLIM microscopy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miesenböck, G.; De Angelis, D.A.; Rothman, J.E. Visualizing secretion and synaptic transmission with pH-sensitive green fluorescent proteins. Nature 1998, 394, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Rosendale, M.; Campbell, R.E.; Perrais, D. pHuji, a pH-sensitive red fluorescent protein for imaging of exo- and endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 207, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.E.; Ai, H.W.; Wong, P.; Young, J.D.; Campbell, R.E.; Casey, J.R. Red fluorescent protein pH biosensor to detect concentrative nucleoside transport. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20499–20511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| FrFP Variant | λEx (nm) | λEm (nm) | pKa | Φ | Alkaline Denaturation | Pierce™ 660 nm Protein Assay | Folding and Chromophore Maturation Efficiency § (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ε‡ (M−1 cm−1) | Brightness † | Ε‡ (M−1 cm−1) | Brightness † | ||||||||
| (mM−1 cm−1) | (%) | (mM−1 cm−1) | (%) | ||||||||
| mMaroon1 | 610 | 658 | 6.4 | 0.11 | 70,616 | 7.8 | 100 | 31,977 | 3.5 | 100 | 45 |
| cpmMaroon141-152 | 606 | 642 | 6.6 | 0.14 | 64,507 | 9.0 | 116 | 9954 | 1.4 | 40 | 15 |
| cpmMaroon158-152 | 606 | 660 | 6.4 | 0.11 | 86,667 | 9.5 | 123 | 32,624 | 3.6 | 103 | 37 |
| cpmMaroon185-186 | 610 | 648 | 7.7 | 0.11 | 54,018 | 5.9 | 76 | 4705 | 0.5 | 15 | 9 |
| cpmMaroon196-186 | 608 | 642 | 7.5 | 0.09 | 29,792 | 2.7 | 35 | 1574 | 0.1 | 3 | 5 |
| cpmCarmine185-186 | 606 | 680 | 5.7 | 0.07 | 44,457 | 3.1 | 40 | 6340 | 0.4 | 11 | 14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.; Pang, Y.; Ai, H.-w. Circularly Permuted Far-Red Fluorescent Proteins. Biosensors 2021, 11, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110438
Wu T, Pang Y, Ai H-w. Circularly Permuted Far-Red Fluorescent Proteins. Biosensors. 2021; 11(11):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110438
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Tianchen, Yu Pang, and Hui-wang Ai. 2021. "Circularly Permuted Far-Red Fluorescent Proteins" Biosensors 11, no. 11: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110438
APA StyleWu, T., Pang, Y., & Ai, H.-w. (2021). Circularly Permuted Far-Red Fluorescent Proteins. Biosensors, 11(11), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110438






