A Review of Advanced Impedance Biosensors with Microfluidic Chips for Single-Cell Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
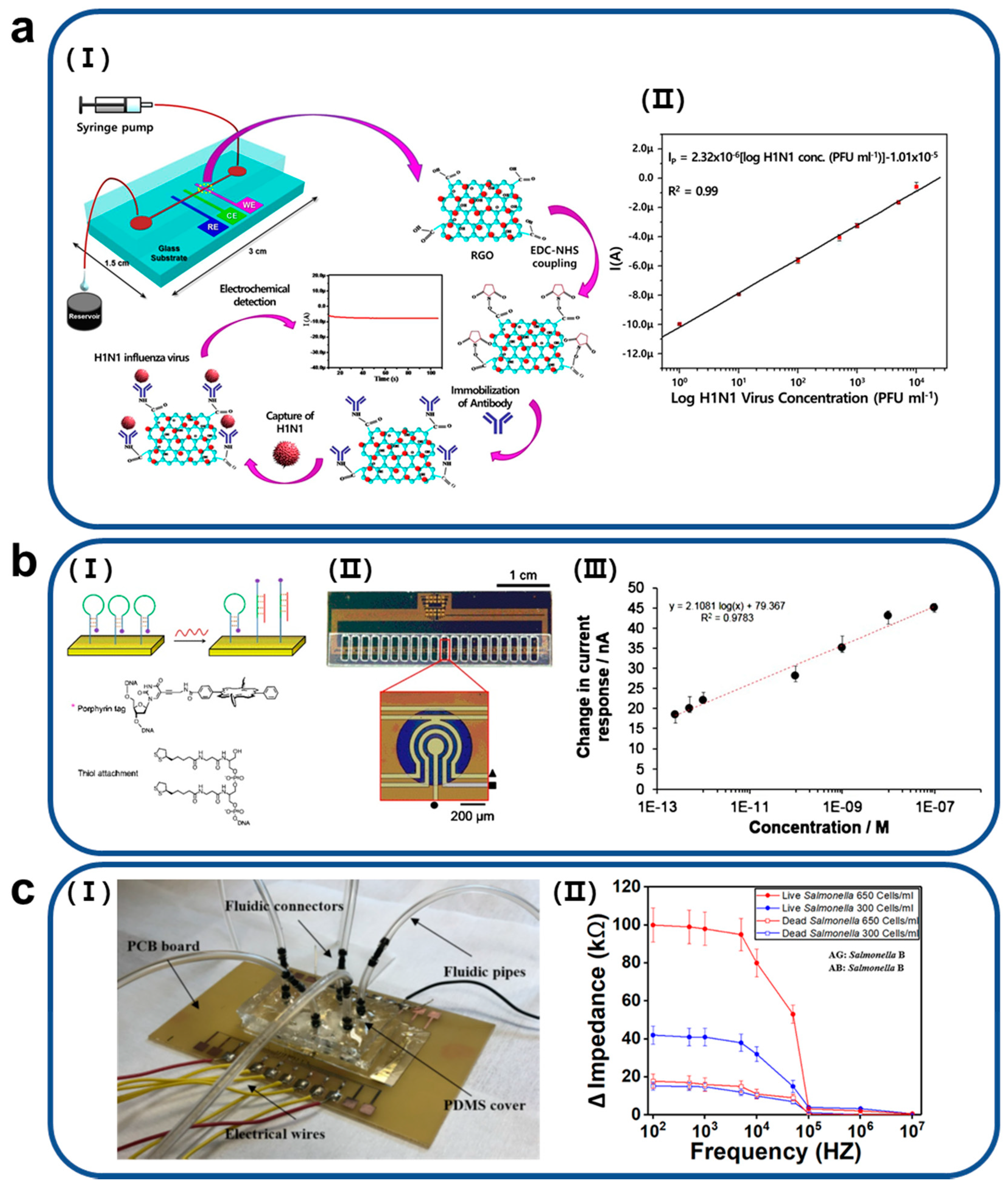
2. Various Applications of Microfluidic Impedance Biosensors
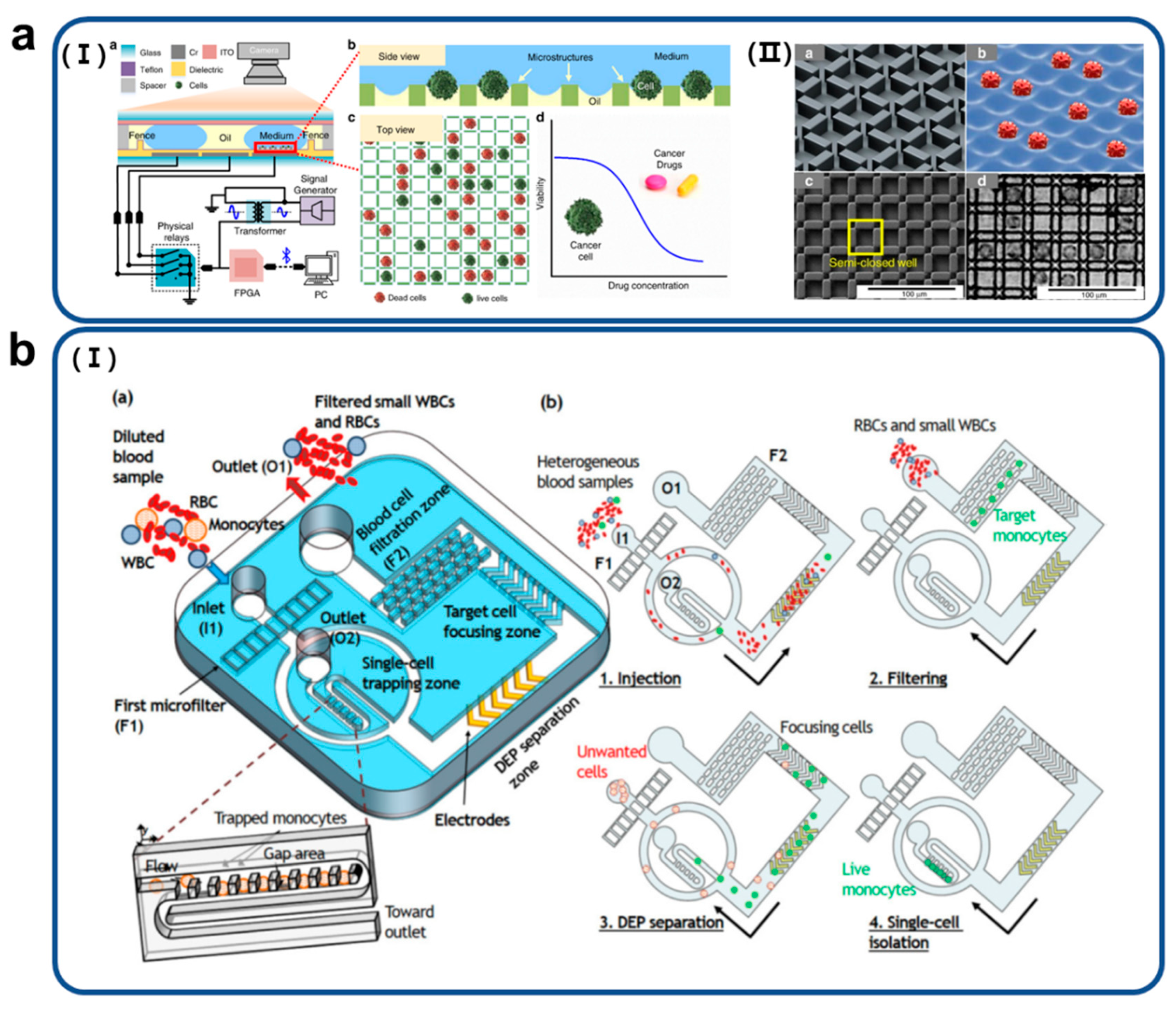
3. Various Technologies of Single-Cell Trapping on Microfluidic Impedance Biosensors
3.1. Dielectrophoretic (DEP)

3.2. Droplet
3.3. Microstructures
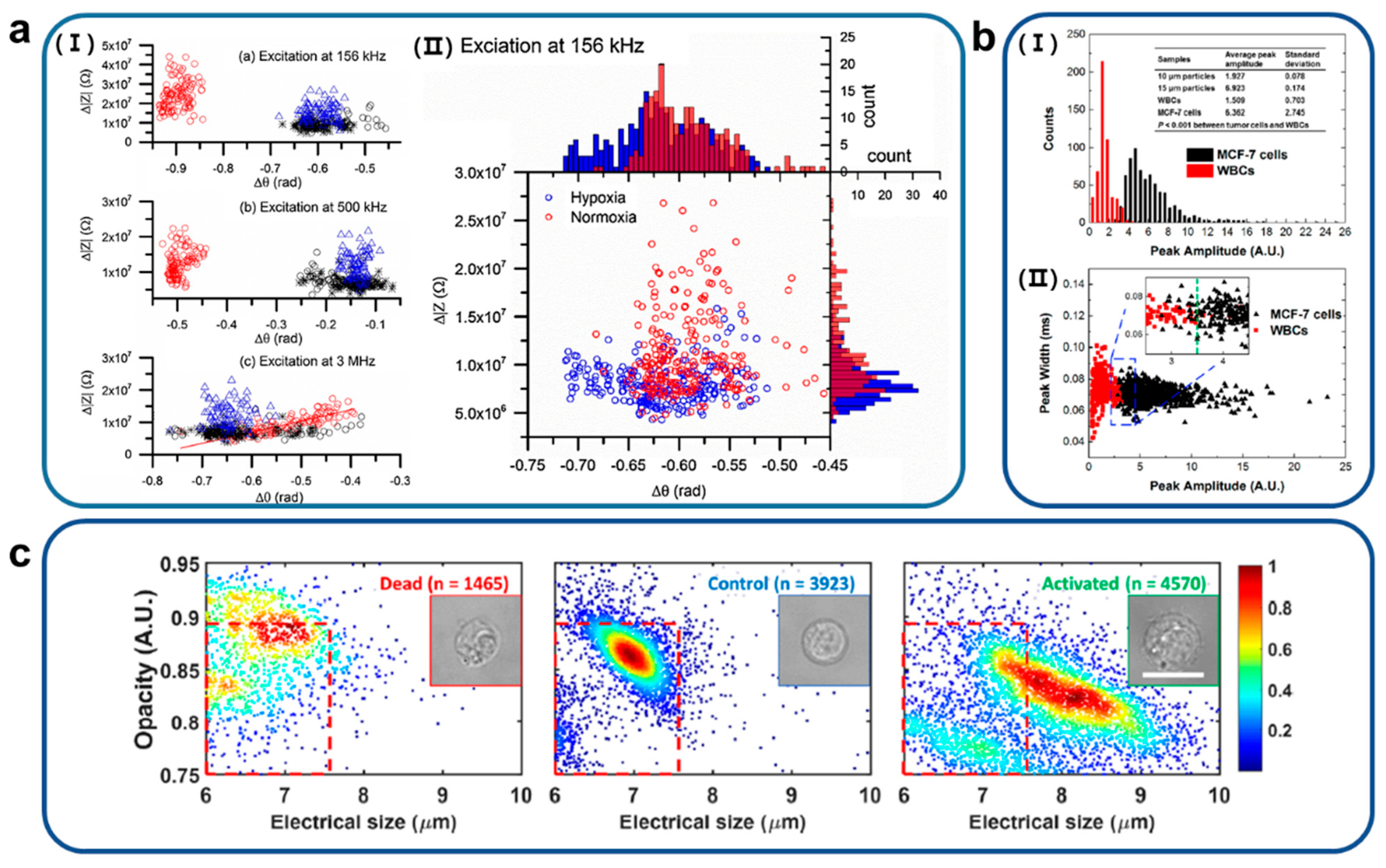
4. Single-Cell Analysis of Microfluidic Impedance Biosensors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Florinel-Gabriel, B. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2012; p. 576. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-free impedance biosensors: Opportunities and challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jasim, I.; Abdullah, A.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, L.; El-Dweik, M.; Zhang, S.; Almasri, M. An integrated impedance biosensor platform for detection of pathogens in poultry products. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Choi, W.M.; Kim, K.; Jeong, W.I.; Seo, J.B.; Park, I. Biopsy needle integrated with electrical impedance sensing microelectrode array towards real-time needle guidance and tissue discrimination. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sui, J.; Foflonker, F.; Bhattacharya, D.; Javanmard, M. Electrical impedance as an indicator of microalgal cell health. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Li, H.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. An electrochemical impedance sensor for simple and specific recognition of G–G mismatches in DNA. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7413–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Lei, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, A.; Lin, X.; et al. Nanoporous gold electrode prepared from two-step square wave voltammetry (SWV) and its application for electrochemical DNA biosensing of lung resistance related protein (LRP) gene. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 840, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chérif, N.; Zouari, M.; Amdouni, F.; Mefteh, M.; Ksouri, A.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B.; Raouafi, N. Amperometric sensing of fish nodavirus RNA using gold nanoparticle/DNA-based bioconjugates. Pathogens 2021, 10, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, M.; Riccò, B. Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for biological analysis and food characterization: A review. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2017, 6, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farré, M.; Kantiani, L.; Barceló, D. Microfluidic devices: Biosensors. In Chemical Analysis of Food: Techniques and Applications, 1st ed.; Picó, Y., Ed.; Elsevier B. V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 177–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chin, S.Y.; Chin, C.D.; Sarik, J.; Harper, M.; Justman, J.; Sia, S.K. Microfluidic CD4+ T-cell counting device using chemiluminescence-based detection. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yu, H.; Wen, Y.; Luo, H.; Jia, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, W.J. Real-time red blood cell counting and osmolarity analysis using a photoacoustic-based microfluidic system. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Q.; Macaraniag, C.; Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Microfluidic systems for hydrodynamic trapping of cells and clusters. Biomicrofluidics 2020, 14, 031502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Feng, Y.; Liang, F.; Wang, W. A microfluidic device enabling deterministic single cell trapping and release. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Mankar, S.; Ajiri, T.; Shirai, K.; Yotoriyama, T. An integrated high-throughput microfluidic circulatory fluorescence-activated cell sorting system (μ-CFACS) for the enrichment of rare cells. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3112–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, S.E.; Doh, J.; Kim, K.; Chung, W.K. User-friendly image-activated microfluidic cell sorting technique using an optimized, fast deep learning algorithm. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 1798–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, D.; Leslie, D.C.; Matthews, B.D.; Fraser, J.P.; Jurek, S.; Hamilton, G.A.; Thorneloe, K.S.; McAlexander, M.A.; Ingber, D.E. A human disease model of drug toxicity–induced pulmonary edema in a lung-on-a-chip microdevice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 159ra147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.I.; Shuler, M.L. UniChip enables long-term recirculating unidirectional perfusion with gravity-driven flow for microphysiological systems. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H.; Kim, D.; Sung, J.H. A Gut-Brain Axis-on-a-Chip for studying transport across epithelial and endothelial barriers. J. Ind. Eng Chem. 2021, 101, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, B.K.; Jeong, G.S.; Hyun, J.K.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, S.H. Three-dimensional brain-on-a-chip with an interstitial level of flow and its application as an in vitro model of Alzheimer’s disease. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.M.; Gumus, A.; Nassar, J.M.; Hussain, M.M. CMOS enabled microfluidic systems for healthcare based applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Alam, M.M.; Shui, L.; Chen, H. Cell elasticity measurement using a microfluidic device with real-time pressure feedback. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Song, H.; Sung, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, K. Microfluidic assay-based optical measurement techniques for cell analysis: A review of recent progress. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lin, J.; Lassiter, K.; Srinivasan, B.; Lin, L.; Lu, H.; Tung, S.; Hargis, B.; Bottje, W.; Berghman, L.; et al. Evaluation study of a portable impedance biosensor for detection of avian influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 178, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, J.; Wang, R.; Lassiter, K.; Srinivasan, B.; Abi-Ghanem, D.; Berghman, L.; Hargis, B.; Tung, S.; Lu, H.; Li, Y. Rapid detection of avian influenza H5N1 virus using impedance measurement of immuno-reaction coupled with RBC amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Hong, S.; Jang, J. Label-free detection of influenza viruses using a reduced graphene oxide-based electrochemical immunosensor integrated with a microfluidic platform. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shafiee, H.; Jahangir, M.; Inci, F.; Wang, S.; Willenbrecht, R.B.M.; Giguel, F.F.; Tsibris, A.M.N.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Acute on-chip HIV detection through label-free electrical sensing of viral nano-lysate. Small 2013, 9, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zin, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, T.; Peng, R.; Li, Z.; Rini, J.M.; Liu, X. Enhancing performance of paper-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy nanobiosensors: An experimental approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanmard, M.; Davis, R.W. A microfluidic platform for electrical detection of DNA hybridization. Sens. Actuator B 2011, 154, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Yoav, H.; Dykstra, P.H.; Bentley, W.E.; Ghodssi, R. A microfluidic-based electrochemical biochip for label-free diffusion-restricted DNA hybridization analysis. Biosens. Bioelecton. 2012, 38, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursey, J.P.; Chen, Y.; Stulz, E.; Park, M.K.; Kongsuphol, P. Microfluidic electrochemical multiplex detection of bladder cancer DNA markers. Sens. Actuator B 2017, 251, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teengram, P.; Siangproh, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Electrochemical impedance-based DNA sensor using pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acids for tuberculosis detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1044, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabbagh, K.; Hornung, T.; Voigt, A.; Sadir, S.; Rajabi, T.; Länge, K. Microfluidic impedance biosensor chip with DNA-based self-assembled monolayers for label-free detection of cardiac biomarker troponin I. MDPI 2020, 60, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, F.; Leung, P.H.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Ye, W.; Zhang, X.; Yi, L.; Yang, M. A PDMS microfluidic impedance immunosensor for E. coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus detection via antibody-immobilized nanoporous membrane. Sens. Actuator B 2011, 159, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastider, S.G.; Abdullah, A.; Jasim, I.; Yuksek, N.S.; Dweik, M.; Almasri, M. Low concentration E. coli O157:H7 bacteria sensing using microfluidic MEMS biosensor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jasim, I.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Dweik, M.; Zhang, S.; Almasri, M. A microfluidic based biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella in food products. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X. A PDMS microfluidic impedance immunosensor for sensitive detection of pesticide residues in vegetable real samples. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 4155–4164. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Yin, T.-I.; Reyes, D.; Urban, G.A. Microfluidic chip with integrated electrical cell-impedance sensing for monitoring single cancer cell migration in three-dimensional matrixes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11068–11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascoyne, P.R.; Noshari, J.; Anderson, T.J.; Becker, F.F. Isolation of rare cells from cell mixtures by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.V.; Jen, C.P. Impedance detection integrated with dielectrophoresis enrichment platform for lung circulating tumor cells in a microfluidic channel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Antfolk, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Kaneda, S.; Laurell, T.; Fujii, T. Highly efficient single cell arraying by integrating acoustophoretic cell pre-concentration and dielectrophoretic cell trapping. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4356–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macosko, E.Z.; Basu, A.; Satija, R.; Nemesh, J.; Shekhar, K.; Goldman, M.; Tirosh, I.; Bialas, A.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Martersteck, E.M.; et al. Highly parallel genome-wide expression profiling of individual cells using nanoliter droplets. Cell 2015, 161, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babahosseini, H.; Misteli, T.; Devoe, D.L. Microfluidic on-demand droplet generation, storage, retrieval, and merging for single-cell pairing. Lab Chip 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.T.; Kurabayashi, K.; Cai, D. Single-cell RT-LAMP mRNA detection by integrated droplet sorting and merging. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh-Barforoushi, A.; Law, A.M.K.; Hejri, A.; Asadnia, M.; Ormandy, C.J.; Gallego-Ortega, D.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M. Static droplet array for culturing single live adherent cells in an isolated chemical microenvironment. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Yen, G.S.; Thompson, A.M.; Burnham, D.R.; Chiu, D.T. Self-digitization of samples into a high-density microfluidic bottom-well array. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10417–10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J. Integration of a microfluidic chip with a size-based cell bandpass filter for reliable isolation of single cells. Lab A Chip 2015, 15, 4128–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, M.A.; Takeuchi, M.; Nakajima, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ahmad, M.R. Electrical impedance spectroscopy for detection of cells in suspensions using microfluidic device with integrated microneedles. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Li, H.; Wong, A.H.H.; Dong, C.; Yi, S.; Jia, Y.; Mak, P.I.; Deng, C.X.; Martins, R.P. A digital microfluidic system with 3D microstructures for single-cell culture. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Li, X.; Jiang, A.; Lee, A.P. An integrated microfluidic platform for size-selective single-cell trapping of monocytes from blood. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Li, X.; Ma, N.; Digman, M.A.; Lee, A.P. Rapid and label-free identification of single leukemia cells from blood in a high-density microfluidic trapping array by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, M.K.; Jang, L.S.; Wang, M.H. Single-cell trapping and impedance measurement utilizing dielectrophoresis in a parallel-plate microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Chen, X.; Ge, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, J. Single-cell impedance analysis of osteogenic differentiation by droplet-based microfluidics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qiang, Y.; Alvarez, O.; Du, E. Electrical impedance microflow cytometry with oxygen control for detection of sickle cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, K.; Varma, M.; Sen, P. Double-peak signal features in microfluidic impedance flow cytometry enable sensitive measurement of cell membrane capacitance. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 4296–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Tang, D.; Ni, Z.; Xiang, N.; Yi, H. Microfluidic impedance cytometer with inertial focusing and liquid electrodes for high-throughput cell counting and discrimination. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3154–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchakup, C.; Hutchinson, P.E.; Tay, H.M.; Leong, S.Y.; Li, K.H.H.; Hou, H.W. Label-free quantitative lymphocyte activation profiling using microfluidic impedance cytometry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Song, H.; Ahn, H.; Kim, T.; Jung, J.; Cho, S.K.; Shin, D.-M.; Choi, J.-r.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, K. A Review of Advanced Impedance Biosensors with Microfluidic Chips for Single-Cell Analysis. Biosensors 2021, 11, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110412
Kim S, Song H, Ahn H, Kim T, Jung J, Cho SK, Shin D-M, Choi J-r, Hwang Y-H, Kim K. A Review of Advanced Impedance Biosensors with Microfluidic Chips for Single-Cell Analysis. Biosensors. 2021; 11(11):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110412
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Soojung, Hyerin Song, Heesang Ahn, Taeyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Soo Kyung Cho, Dong-Myeong Shin, Jong-ryul Choi, Yoon-Hwae Hwang, and Kyujung Kim. 2021. "A Review of Advanced Impedance Biosensors with Microfluidic Chips for Single-Cell Analysis" Biosensors 11, no. 11: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110412
APA StyleKim, S., Song, H., Ahn, H., Kim, T., Jung, J., Cho, S. K., Shin, D.-M., Choi, J.-r., Hwang, Y.-H., & Kim, K. (2021). A Review of Advanced Impedance Biosensors with Microfluidic Chips for Single-Cell Analysis. Biosensors, 11(11), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110412




