An Ultra-Low Power Surface EMG Sensor for Wearable Biometric and Medical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
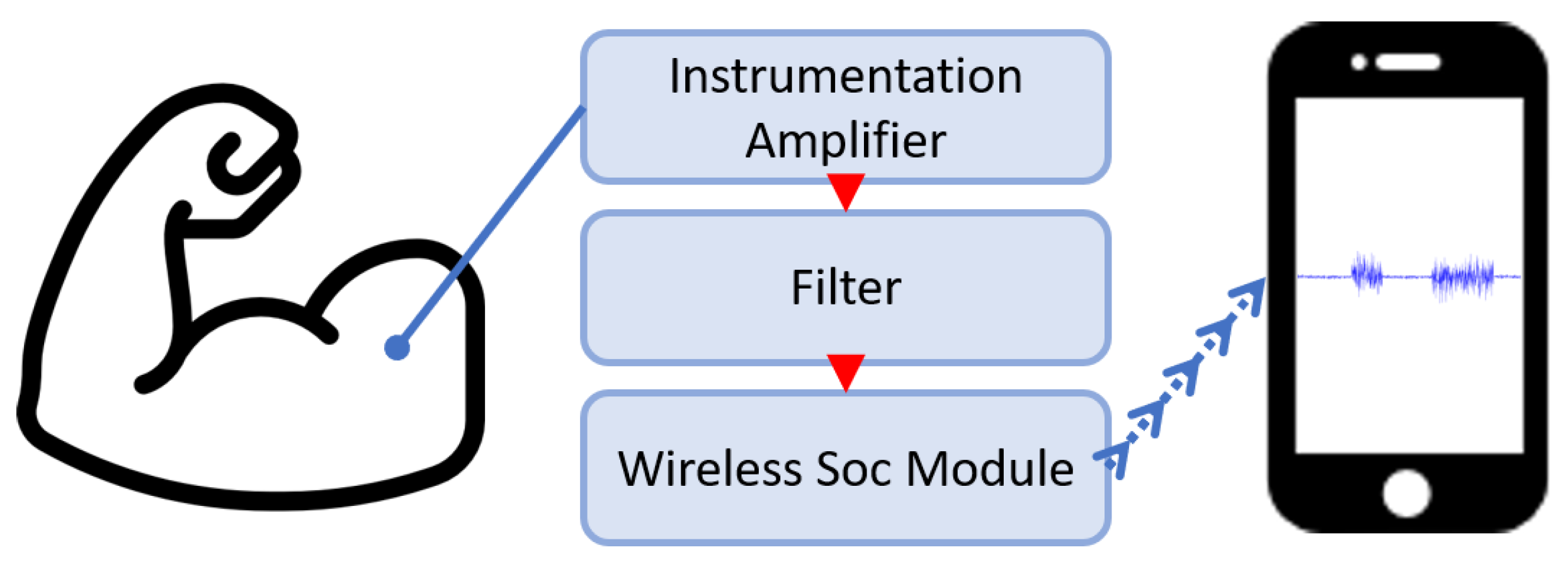
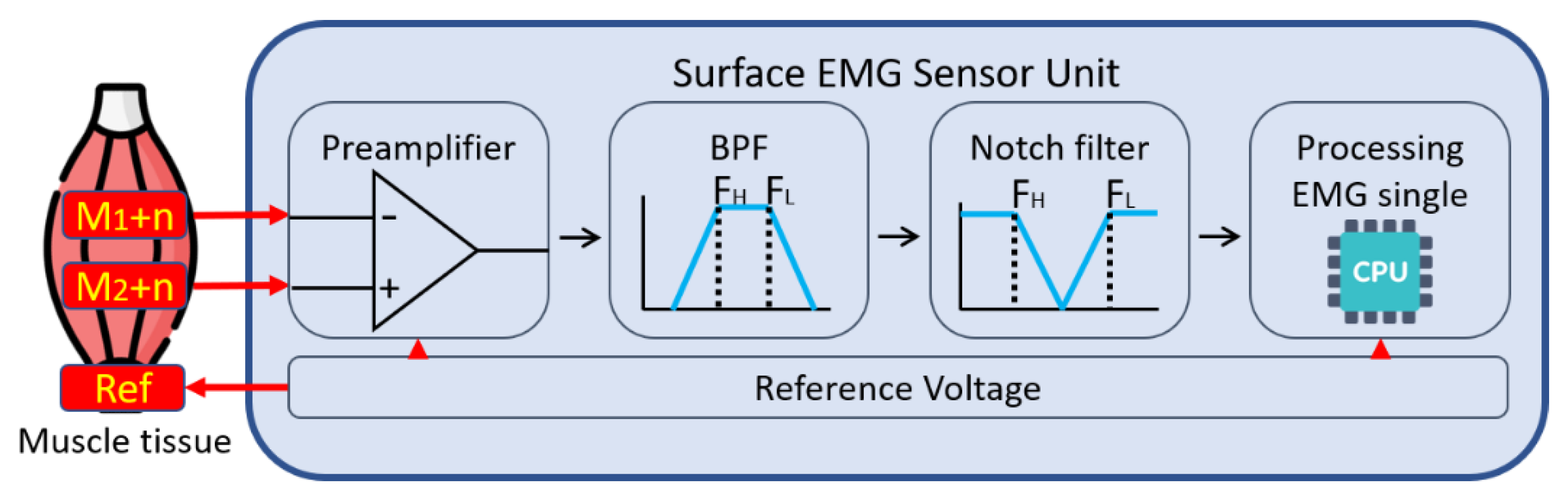
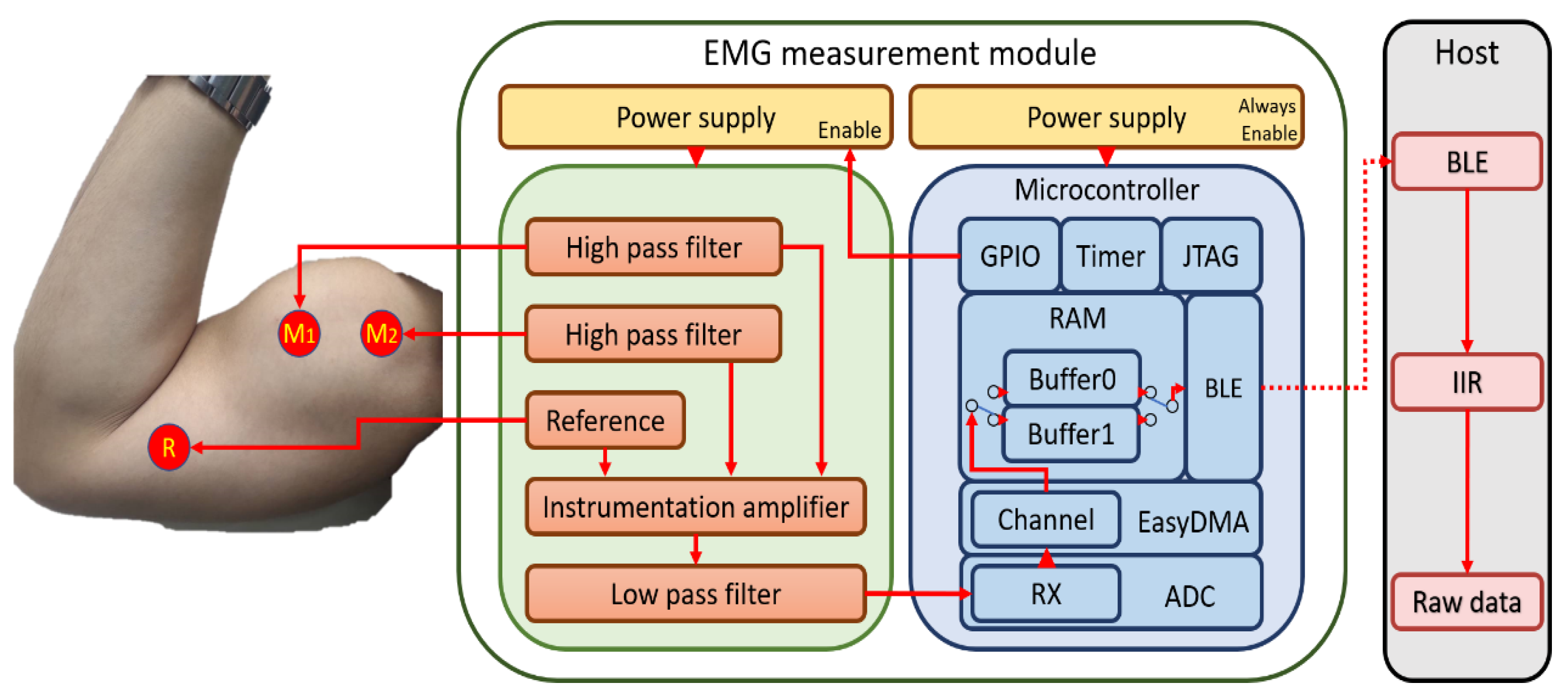
2. Surface EMG Architecture
2.1. Instrumentation Amplifier
2.2. Processing Surface EMG Noise of Filter
2.2.1. Active Filter
2.2.2. Notch Filter
- Power line noise
- Inherent instability of signal
2.3. Storage Method of Wireless Embedded System
2.3.1. The Use of Wireless Transmission Technology
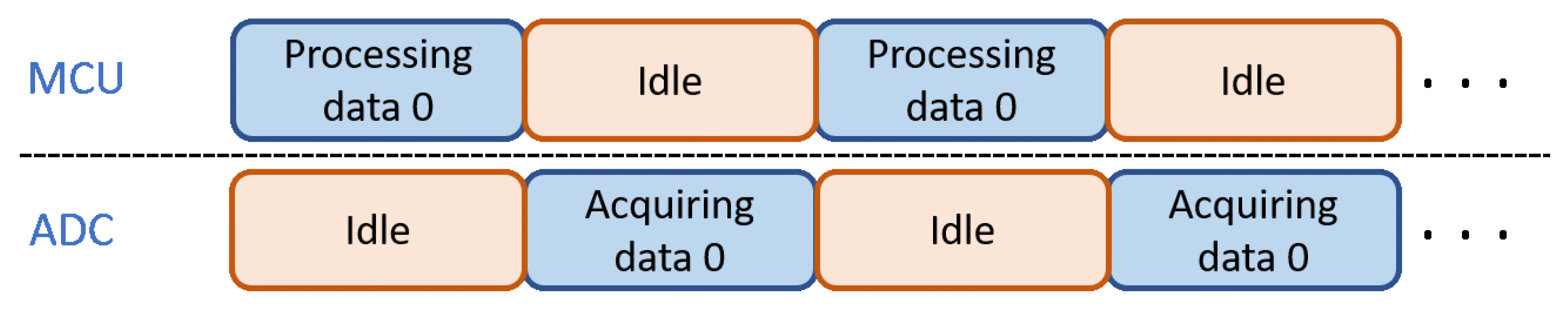
2.3.2. Improvement in Data Processing Efficiency Based on Ping-Pong Buffer
3. Implementation Method
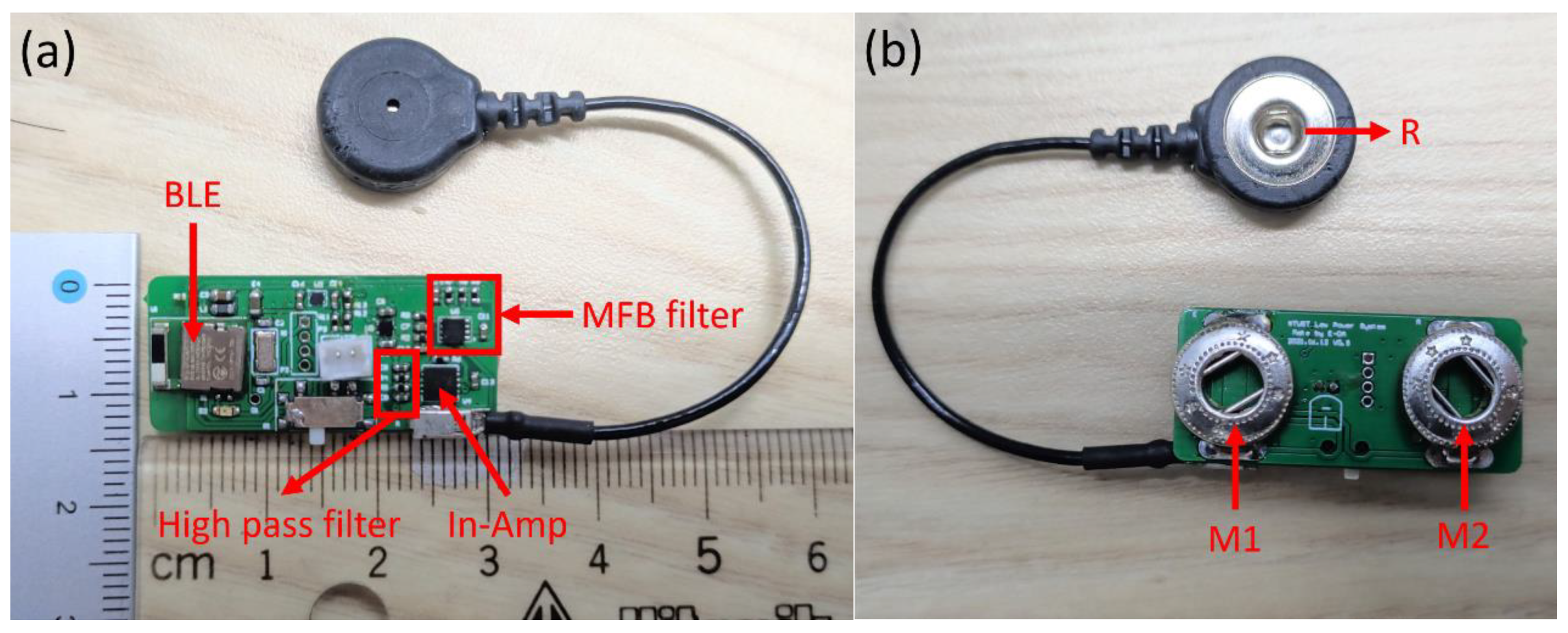
3.1. Measurement Module Design
3.1.1. Instrumentation Amplifier with Passive High-Pass Filter
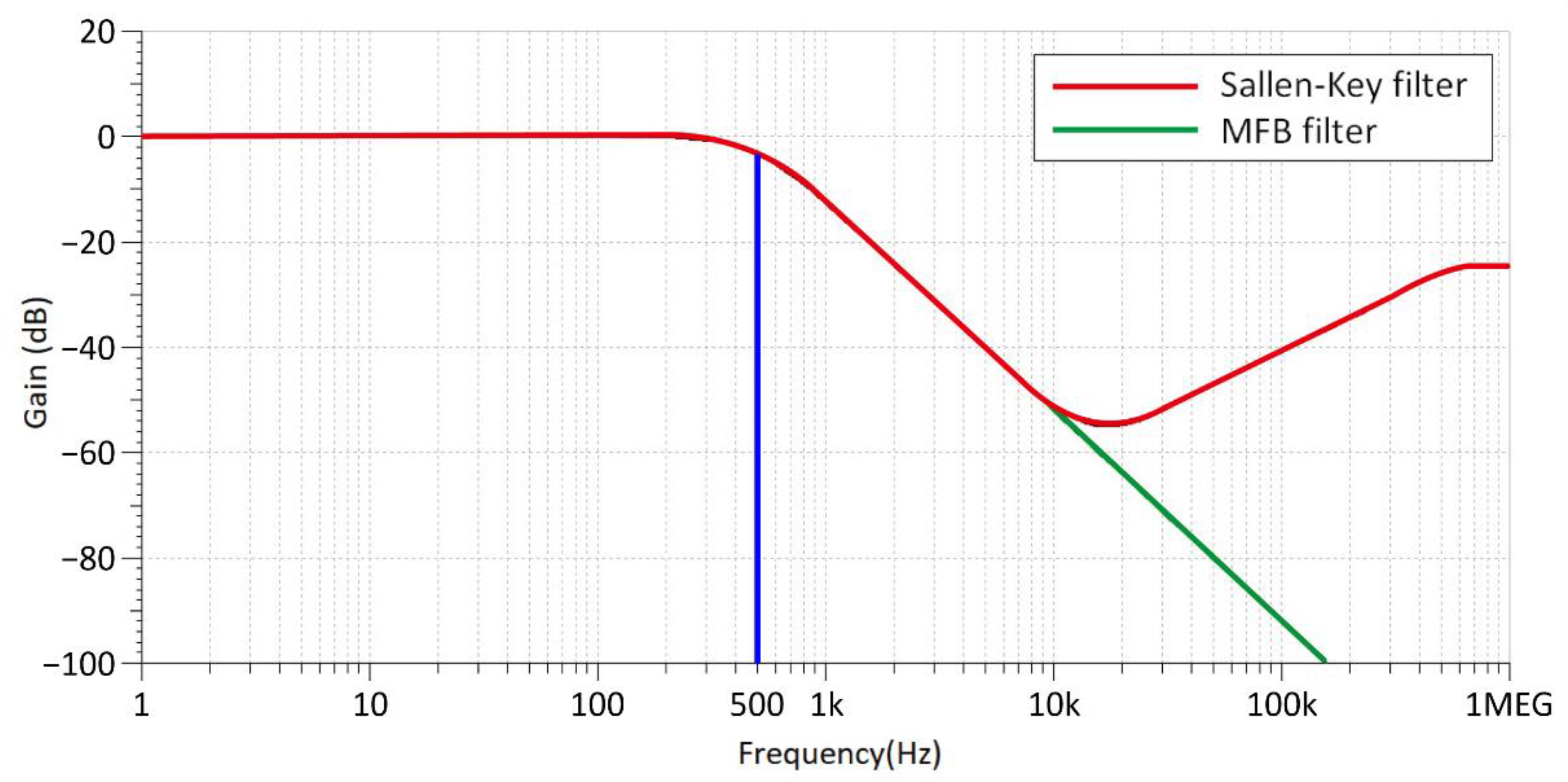
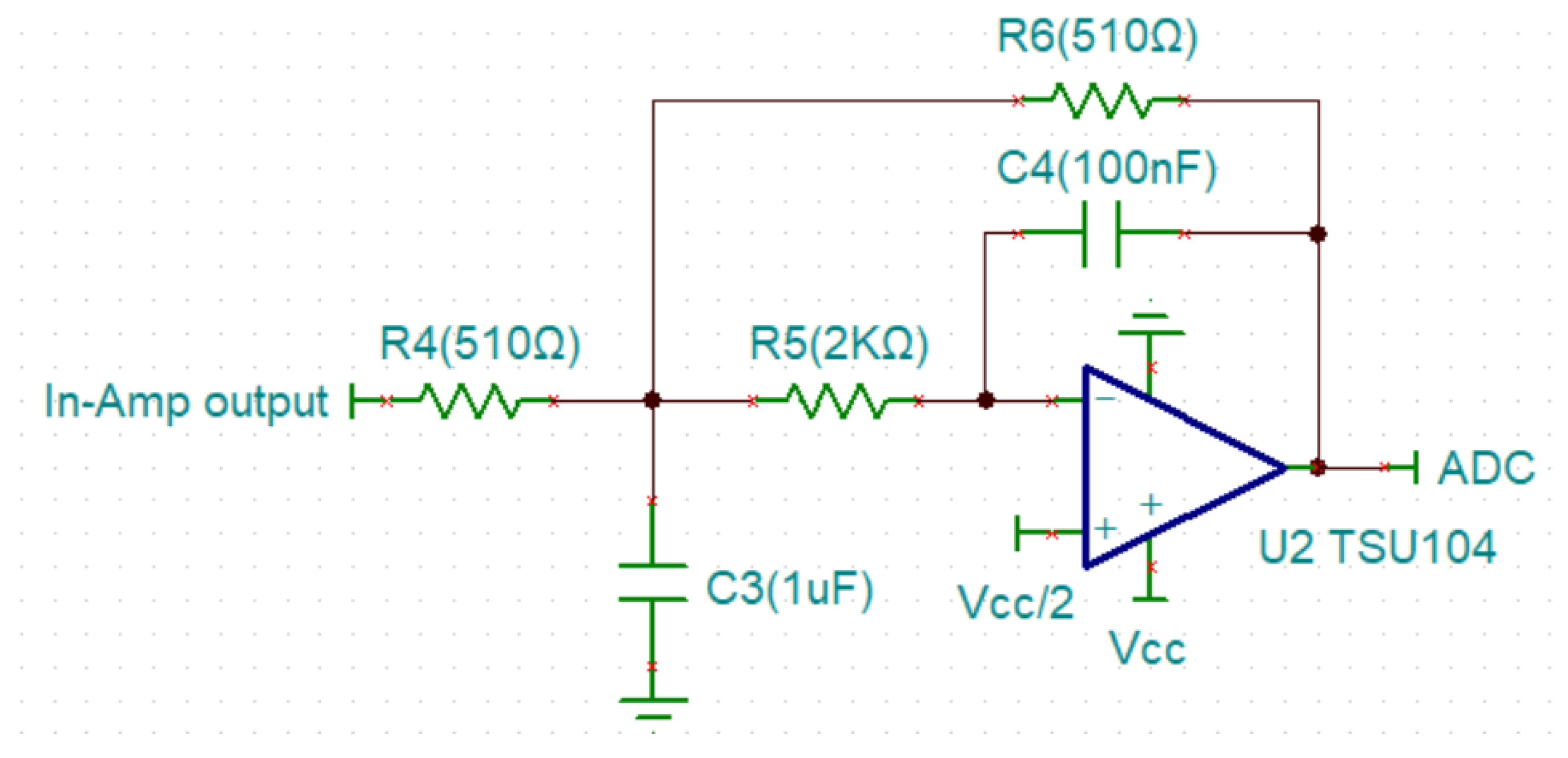
3.1.2. Design of the MFB Low-Pass Filter
3.1.3. Central Control Unit
Saving-Power Mechanism
Storing Surface EMG Data by the Ping-Pong Buffer Mechanism
3.2. The Host Processing with IIR
4. Results
4.1. SNR
4.2. Linear Correlation Coefficient
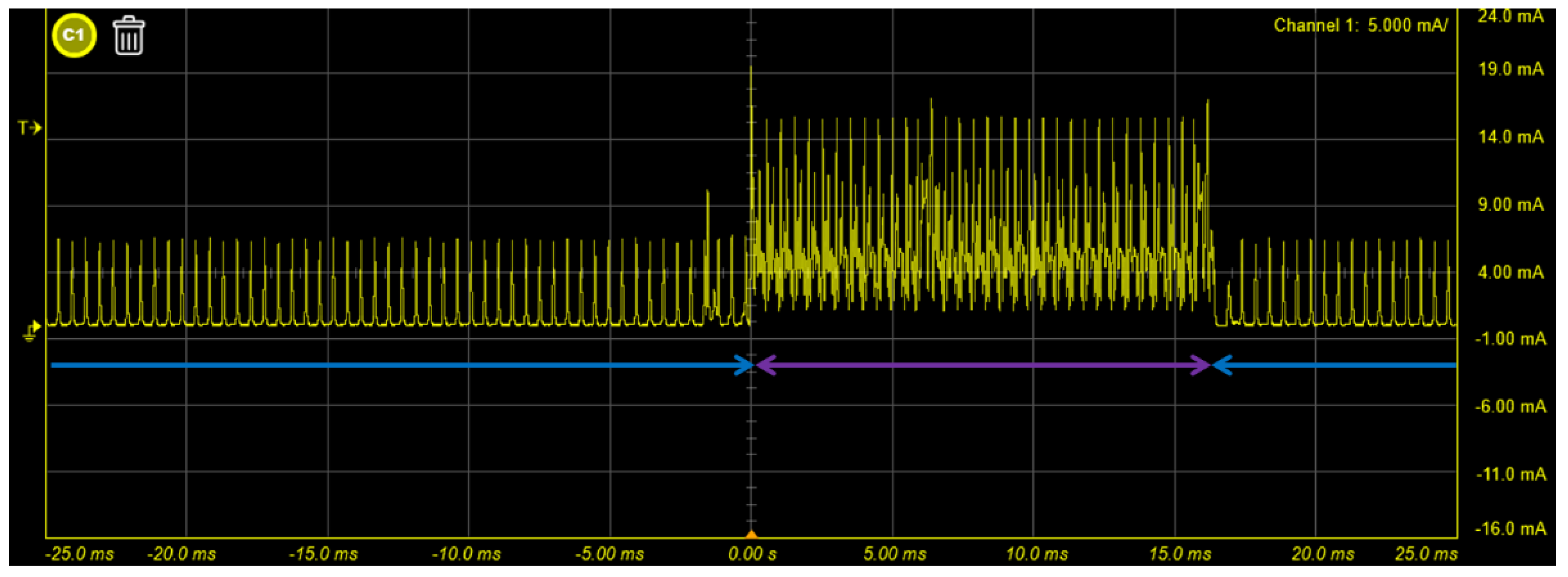
4.3. Power Consumption
4.4. Advantages
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H. Towards a high-stability EMG recognition system for prosthesis control: A one-class classification based non-target EMG pattern filtering scheme. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Antonio, TX, USA, 11–14 October 2009; pp. 4752–4757. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Samuel, O.W.; Yu, M.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Li, G. Identification of Upper-Limb Movements Based on Muscle Shape Change Signals for Human-Robot Interaction. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Fisher, M.H.; Wolczowski, A.; Bell, G.D.; Burn, D.; Gao, R. Towards an EMG Controlled Prosthetic Hand Using a 3D Electromagnetic Positioning System. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Instrumentationand Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–19 May 2005; pp. 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Brunelli, D.; Tadesse, A.M.; Vodermayer, B.; Nowak, M.; Castellini, C. Low-cost wearable multichannel surface EMG acquisition for prosthetic hand control. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th International Workshop on Advances in Sensors and Interfaces (IWASI), Gallipoli, Italy, 18–19 June 2015; pp. 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, K.; Meyers, J. Using surface electromyography in physiotherapy research. Aust. J. Physiother. 1983, 29, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulla, M.R.; Sepulveda, F.; Colley, M. A review of non-invasive techniques to detect and predict localised muscle fatigue. Sensors 2011, 11, 3545–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trignotm Wireless Biofeedback System User’s Guide Delsys Incorporated. 2021. Available online: https://www.delsys.com/downloads/USERSGUIDE/trigno/wireless-biofeedback-system.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Mini Wave Infinity. 2004. Available online: http://www.h-elmar-ms.pl/helmar-ms/plik/cometa-systems_wavetrack-inertial-system_nn4776.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Ultium EMG Brochure. 2019. Available online: https://www.noraxo-n.com/noraxon-download/ultium-emg-datasheet/ (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Shimmer User Manual Revision 3p. 2017. Available online: http://www.shimmersensing.com/images/uploads/docs/Shimmer_User_Manual_rev3p.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. Human activity monitoring system based on wearable sEMG and accelerometer wireless sensor nodes. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhandarkar, A. Design Considerations for a Robust EMG Amplifier. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) 2016, 5, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hung, W.-C.; Ho, K.-W.; Chen, M.-S. The Design of EMG Measurement System for Arm Strength Training Machine. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gargiulo, G.; Calvo, R.; Jin, C. Giga-ohm high-impedance FET input amplifiers for dry electrode biosensor circuits and systems. In Integrated Microsystems: Electronics, Photonics, and Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 165–194. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, W.M.; Baloch, M.U.; Mengal, M.A.; Shah, S.J. Performance analysis of analog butterworth low pass filter as compared to Chebyshev type-I filter, Chebyshev type-II filter and elliptical filter. Circuits Syst. 2014, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabanov, A.A.; Nikonova, G.V. Development of Analog Filtering Circuit for Electromyography Signals. In Proceedings of the 2019 Ural Symposium on Biomedical Engineering, Radioelectronics and Information Technology (USBEREIT), Yekaterinburg, Russia, 25–26 April 2019; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Elamvazuthi, I.; Zulkifli, Z.; Ali, Z.; Khan, M.K.A.A.; Parasuraman, S.; Balaji, M.; Chandrasekaran, M. Development of Electromyography Signal Signature for Forearm Muscle. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Tang, L.; Bronlund, J.E. Surface EMG signal amplification and filtering. Int. J. Comput. Appl. (IJCA) 2013, 82, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozaqi, L.; Nugroho, A.; Sanjaya, K.H.; Simbolon, A.I. Design of Analog and Digital Filter of Electromyography. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application (ICSEEA), Tangerang, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2019; pp. 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Çakar, H.I.; Kara, S.; Toker, O. Design of a Portable Electromyography Device for Back Herniated Patients. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices; SciTePress: Setúbal, Portugal, 2010; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Go, S.A.; Coleman-Wood, K.; Kaufman, K.R. Frequency analysis of lower extremity electromyography signals for the quantitative diagnosis of dystonia. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Boxtel, A. Optimal signal bandwidth for the recording of surface EMG activity of facial, jaw, oral, and neck muscles. Psychophysiology 2001, 38, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaz, M.B.I.; Hussain, M.S.; Mohd-Yasin, F. Techniques of EMG signal analysis: Detection, processing, classification and applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2006, 8, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Rymer, W.Z.; Li, G.; Zhou, P. The effects of notch filtering on electrically evoked myoelectric signals and associated motor unit index estimates. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2011, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladrova, M.; Martinek, R.; Nedoma, J.; Fajkus, M. Methods of Power Line Interference Elimination in EMG signal. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 40, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamata, K.; Aho, A.J.; Hagihira, S.; Yli-Hankala, A.; Jäntti, V. Frequency band of EMG in anaesthesia monitoring. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 107, 822–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tankisi, H.; Burke, D.; Cui, L.; de Carvalho, M.; Kuwabara, S.; Nandedkar, S.D.; Rutkove, S.; Stålberg, E.; van Putten, M.J.A.M.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A. Standards of instrumentation of EMG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soedirdjo, S.D.H.; Ullah, K.; Merletti, R. Power line interference attenuation in multi-channel sEMG signals: Algorithms and analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3823–3826. [Google Scholar]
- Esp8266ex Datasheet. 2020. Available online: https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/0a-esp8266ex_datasheet_en.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- nRF52832 Datasheet. 2017. Available online: https://infocenter.nordicsemi.com/pdf/nRF52832_PS_v1.4.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Dieffenderfer, J.N.; Kalla, R.N. Ping-Pong Data Buffer for Transferring Data from One Data Bus to Another Data Bus. U.S. Patent US5224213A, 29 June 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, Y.-M.; McKeown, N. Doubling memory bandwidth for network buffers. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM ‘98, the Conference on Computer Communications. Seventeenth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. Gateway to the 21st Century (INFOCOM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 March–2 April 1998; Volume 2, pp. 808–815. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Sun, G.; Guan, Y.; Xiao, B.; Cong, J. Optimizing FPGA-Based Accelerator Design for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, USA, 22–14 February 2015; pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafin, M.; Turar, O.; Akhmed-Zaki, D. Testing of Vulkan Visualization for Geo-Models on Mobile Devices and Desktop Systems with Ray Tracing GPUs. In ECMOR XVII; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Houten, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.; Wakankar, A.; Khambete, N. Design and implementation of low power compact amplifier circuitry for wearable biosignal device. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 12–13 August 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- INA333 Datasheet. 2015. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/gpn/INA333 (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- AD620 Datasheet. 2011. Available online: https://datasheet.octopart.com/AD620ANZ-Analog-Devices-datasheet-9660204.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Salman, A.; Iqbal, J.; Izhar, U.; Khan, U.S.; Rashid, N. Optimized circuit for EMG signal processing. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 22–23 October 2012; pp. 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, G. Detection and Identification the Human Surface Electromyogra Signal. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 440, 022016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INA128 Datasheet. 2019. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/gpn/ina128 (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- AD8236 Datasheet. 2009. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD8236.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- 3-lead Muscle / Electromyography Sensor for Microcontroller Applications Datasheet. 2015. Available online: https://cdn.sparkfun.com/datasheets/Sensors/Biometric/MyowareUserManualAT-04-001.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Roland, T.; Wimberger, K.; Amsuess, S.; Russold, M.F.; Baumgartner, W. An Insulated Flexible Sensor for Stable Electromyography Detection: Applicationto Prosthesis Control. Sensors 2019, 19, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Importance of Input Bias Current Return Paths in Instrumentation Amplifier Applications. 2021. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/pdf/sboa503 (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Casas, O.; Pallas-Areny, R. Basics of analog differential filters. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1996, 45, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Designing Amplifier Circuits: How to Avoid Common Problems. 2007. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/application-notes/AN-937.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Tabassum, F.; Islam, M.I.; Amin, M.R. Comparison of FIR and IIR Filter Bank in Reconstruction of Speech Signal. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2016, 14, 864. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction to Filters: FIR Versus IIR. 2020. Available online: https://community.sw.siemens.com/s/artic-le/introduction-to-filters-fir-versus-iir (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Chang, J.; Phinyomark, A.; Scheme, E. Assessment of EMG Benchmark Data for Gesture Recognition Using the NinaPro Database. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 3339–3342. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, G.D.; Chan, A.D.C.; Green, J.R.; MacIsaac, D.T. Automated Biosignal Quality Analysis for Electromyography Using a One-Class Support Vector Machine. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, S.; Pua, Y.; McClelland, J.; Geigle, P.; Rahmann, A.; Bower, K.J.; Clark, R. Low-cost electromyography—Validation against a commercial system using both manual and automated activation timing thresholds. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 42, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, A.B.; Bagree, R.; Roy, A.K. Design of a low-power, low-cost ECG & EMG sensor for wearable biometric and medical application. IEEE Sens. 2017, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguna, C.; Buhagiar, S.; Scerri, J.; Scicluna, K. Development of a New EMG Wearable Sensor for Myoelectric Control. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Valletta, Malta, 24–26 February 2020; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.-C.; Ruan, S.-J.; Tu, Y.-W. Power-Management Strategies in sEMG Wireless Body Sensor Networks Based on Computation Allocations: A Case Study for Fatigue Assessments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 181366–181374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Chip | BW (kHz) | CMRR (dB) | (GΩ) | Noise | (μV) | (μA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INA333 | 3.5 | 115 | 100 | 50 | 1 | 50 |
| AD8236 | 0.8 | 110 | 110 | 76 | 2.5 | 40 |
| AD620 | 120 | 130 | 10 | 28 | 50 | 900 |
| INA128 | 200 | 120 | 10 | 8 | 50 | 700 |
| Architecture | This Work | [54] | [7] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wireless Technology | BLE | BLE | BLE |
| PCB Size () | 1.4 × 3.1 | 3.8 × 4.45 | 2.7 × 3.7 |
| Battery (mAH) | 300 | 300 | N/A |
| Total Power Consumption | 4.735 mW | 62.7 mW | 65 mW |
| Sampling Rate (Hz) | 2k | 1k | 2.148k |
| SNR (dB) | 23.1 | N/A | 65 |
| Battery Life (hours) | 63.4 | 11.2 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.-D.; Ruan, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-H. An Ultra-Low Power Surface EMG Sensor for Wearable Biometric and Medical Applications. Biosensors 2021, 11, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110411
Wu Y-D, Ruan S-J, Lee Y-H. An Ultra-Low Power Surface EMG Sensor for Wearable Biometric and Medical Applications. Biosensors. 2021; 11(11):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110411
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yi-Da, Shanq-Jang Ruan, and Yu-Hao Lee. 2021. "An Ultra-Low Power Surface EMG Sensor for Wearable Biometric and Medical Applications" Biosensors 11, no. 11: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110411
APA StyleWu, Y.-D., Ruan, S.-J., & Lee, Y.-H. (2021). An Ultra-Low Power Surface EMG Sensor for Wearable Biometric and Medical Applications. Biosensors, 11(11), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110411





