A Capillary-Perfused, Nanocalorimeter Platform for Thermometric Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Femtomole Sensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
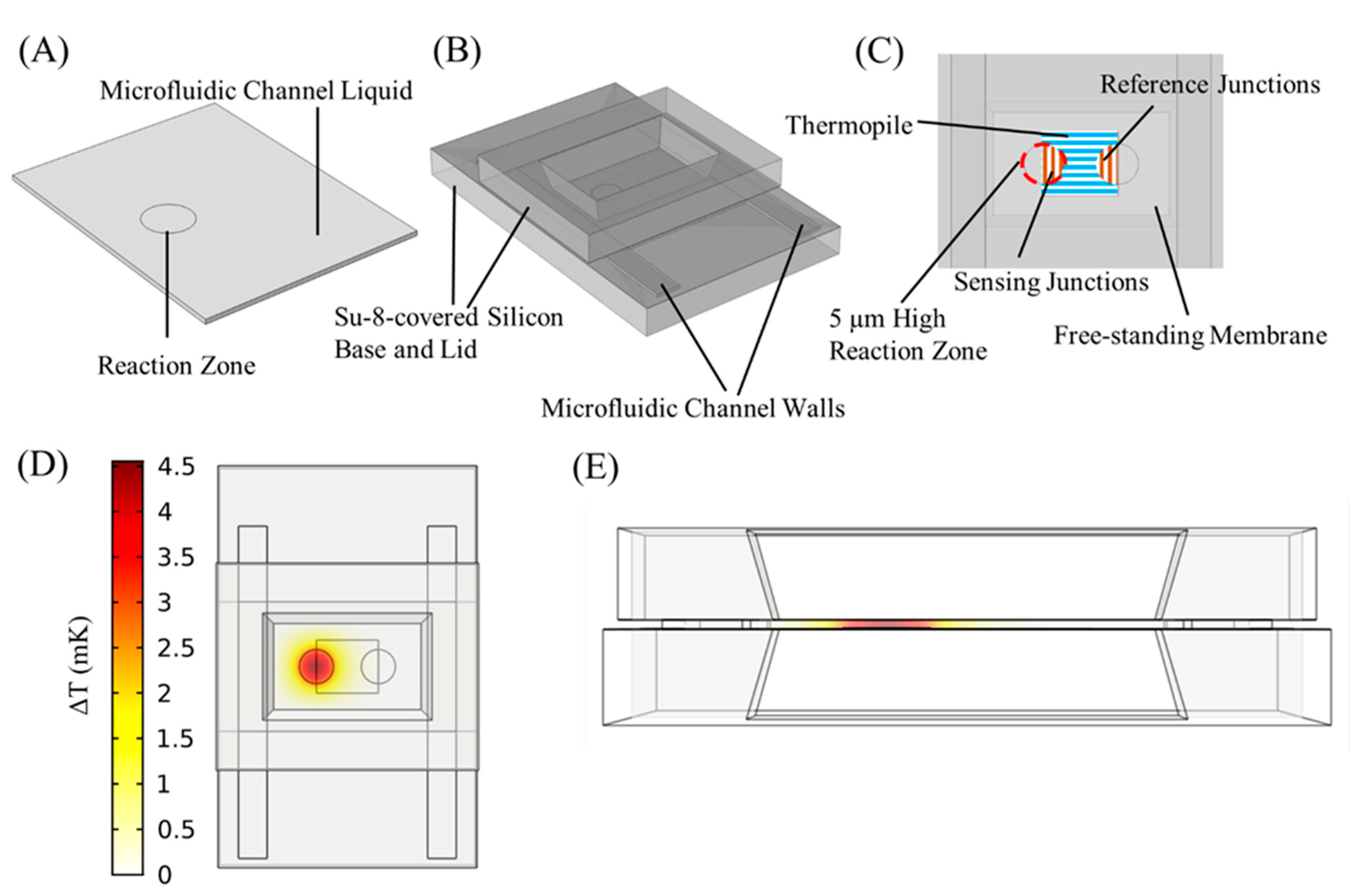
2.1. Nanocalorimeter Platform Layout
2.2. Model Construction
2.3. Model Operation and Data Processing
2.4. Catalase Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
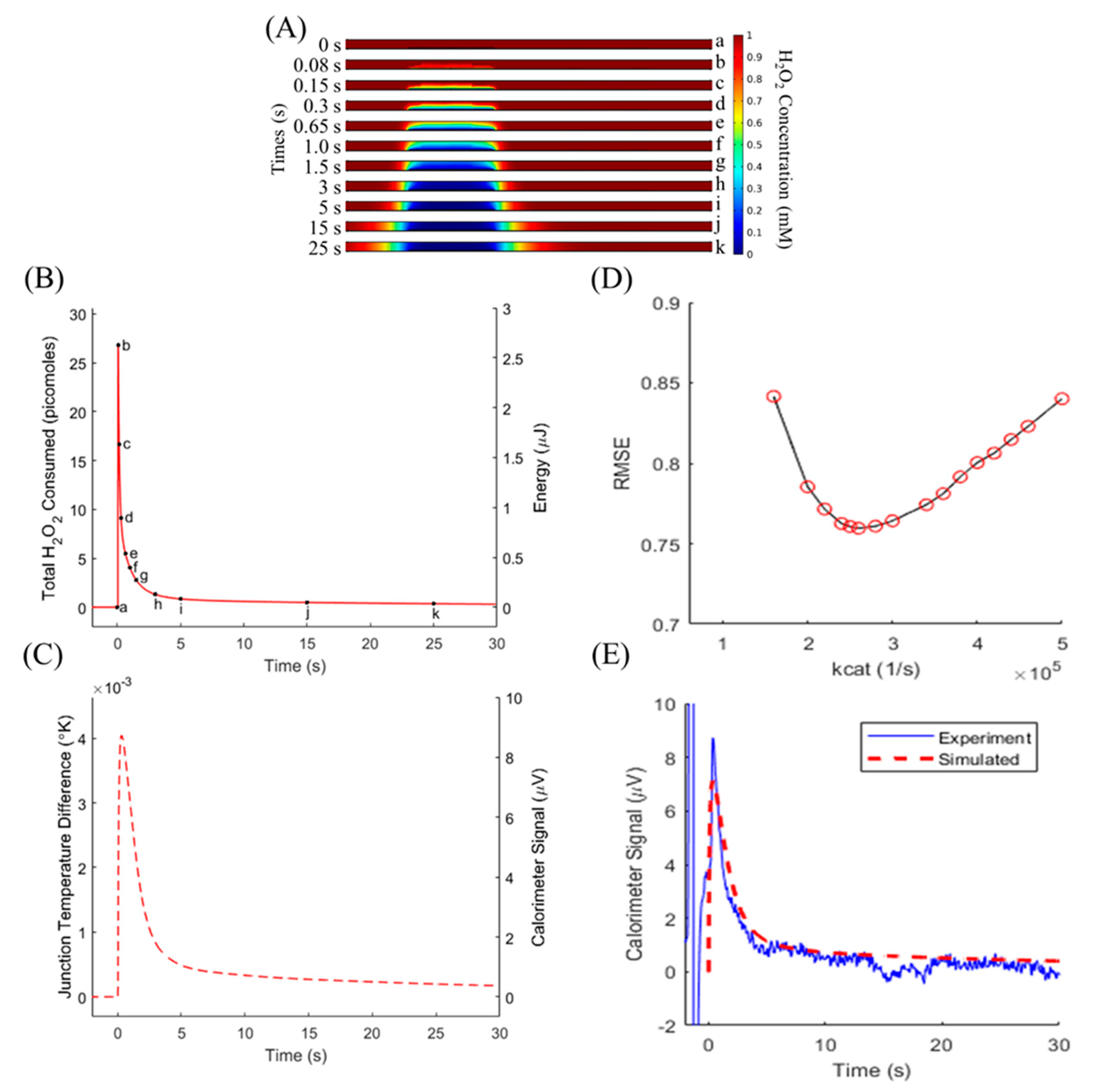
3.1. Enzyme-Based Model Operation
3.2. Validation of Numerical Model
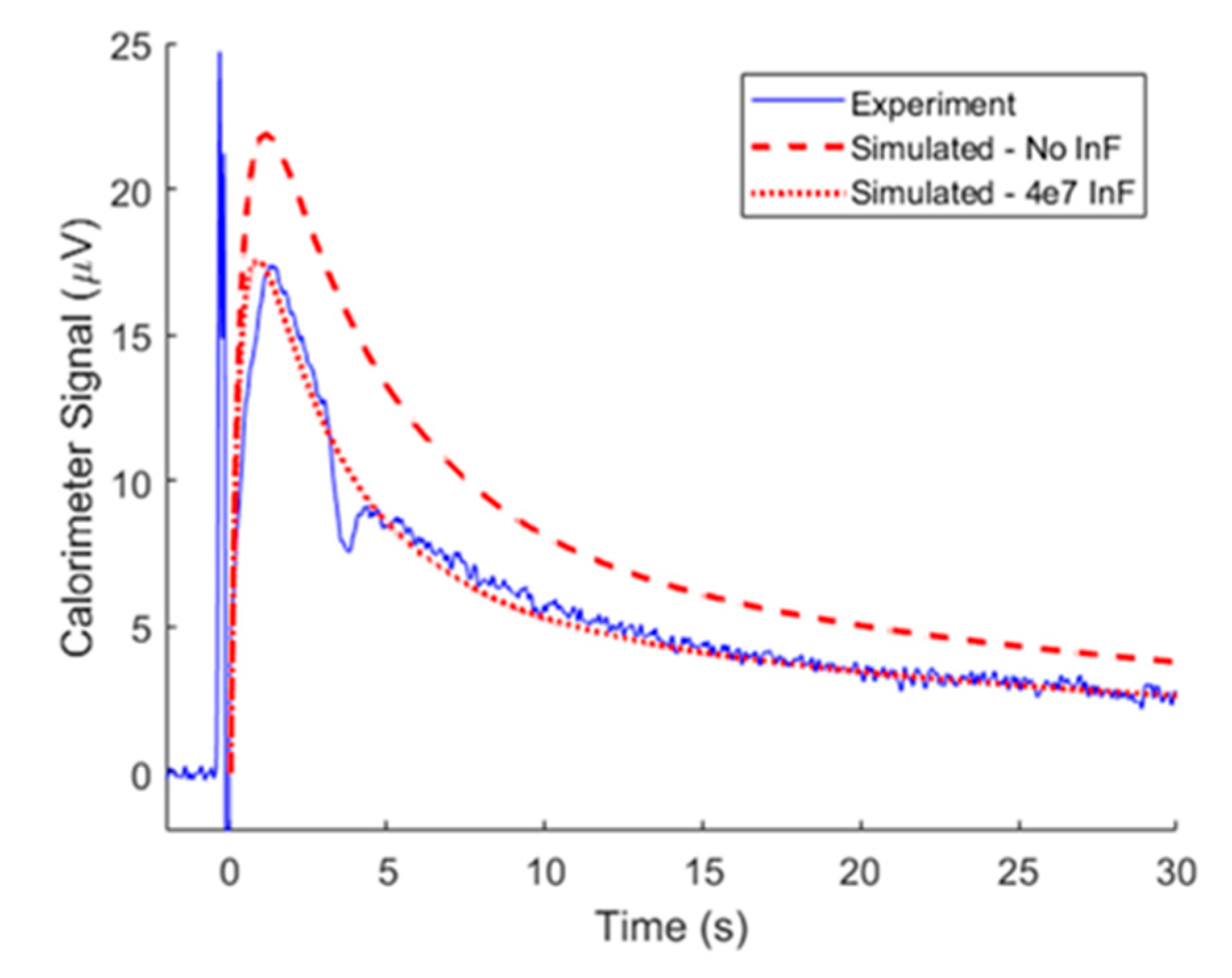
3.3. Model Adaptation at High Substrate Concentration
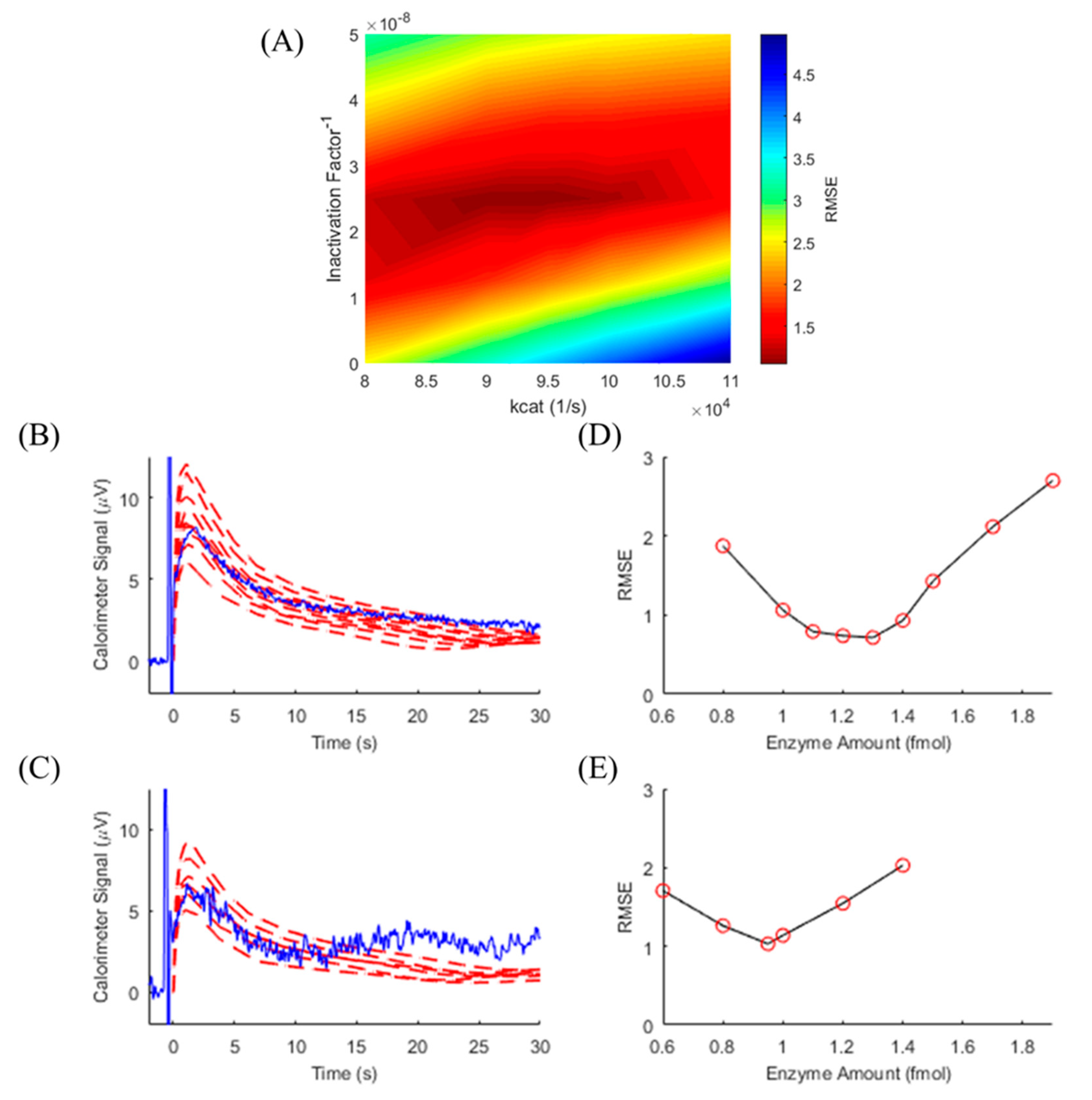
3.4. Model-Assisted TELISA
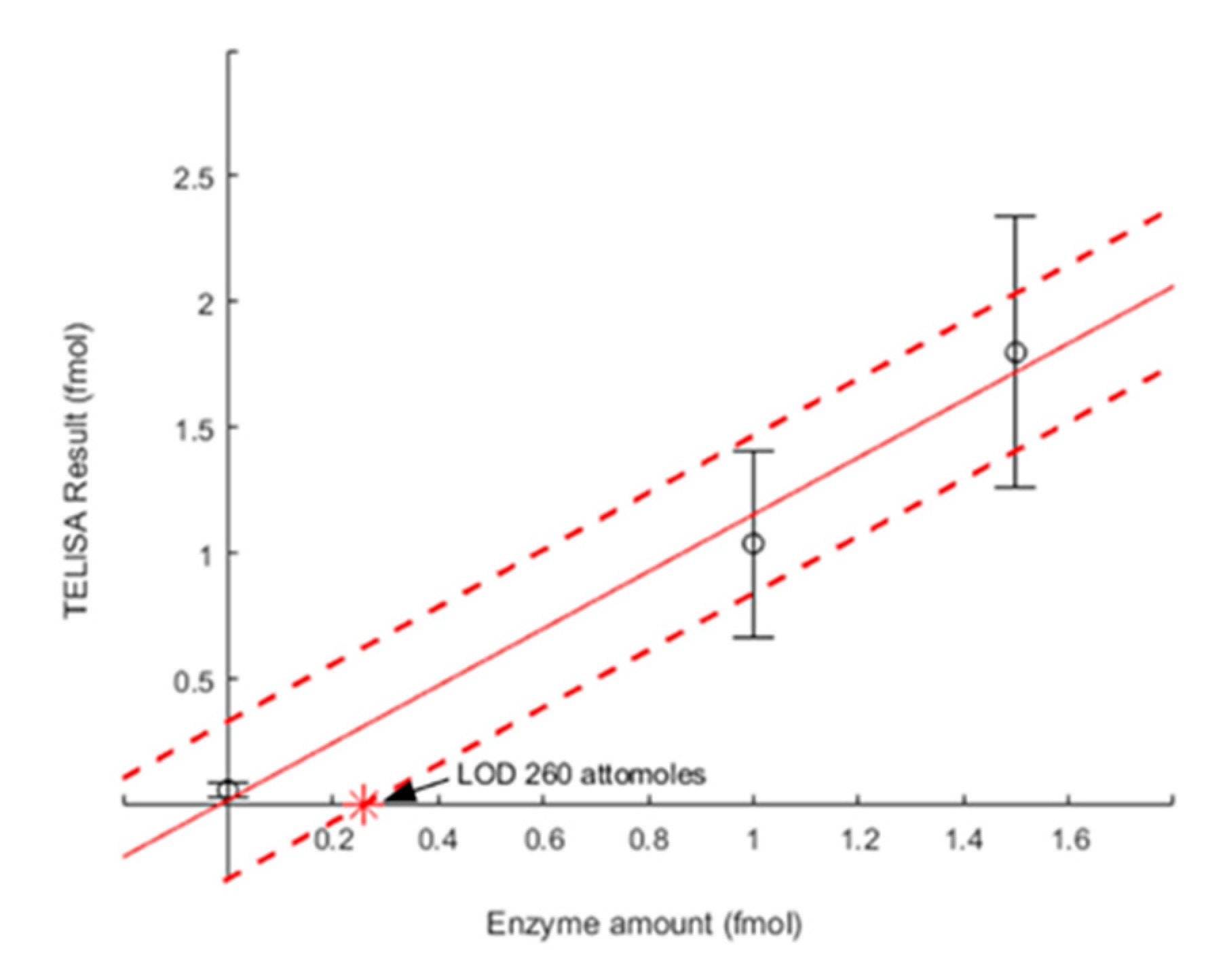
3.5. Determining TELISA Limit of Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Premjeet, S.; Deepika, G.; Sudeep, B.; Sonam, J.; Sahil, K.; Devashish, R.; Sunil, K. Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA), basics and it’s application: A comprehensive review. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 4, 4581–4583. [Google Scholar]
- Thiha, A.; Ibrahim, F. A colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection platform for a point-of-care dengue detection system on a lab-on-compact-disc. Sensors 2015, 15, 11431–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Michelini, E.; Di Fusco, M.; Zangheri, M.; Cevenini, L.; Roda, B.; Simoni, P. Progress in chemical luminescence-based biosensors: A critical review. Biosens. Bioelect. 2016, 76, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, S.K.; Girigoswami, K. Diagnostic biosensors in medicine: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotech. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh-Panahi, P.; Mahmoudi, T.; Chenab, K.K.; Baradaran, B.; Hashemzaei, M.; Radinekiyan, F.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Maleki, A. Dengue virus: A review on advances in detection and trends—from conventional methods to novel biosensors. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, D.F.; Hew, B.E.; Holdaway, C.; Jen, M.; Peckham, G.D. Rapid detection of Bacillus anthracis spores using immunomagnetic separation and amperometry. Biosensors 2016, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, B. Disease-related detection with electrochemical biosensors: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byzova, N.A.; Vinogradova, S.V.; Porotikova, E.V.; Terekhova, U.D.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Lateral flow immunoassay for rapid detection of grapevine leafroll-associated virus. Biosensors 2018, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, X.; Gaur, G.; Neethirajan, S. Rapid detection of food allergens by microfluidics ELISA-based optical sensor. Biosensors 2016, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiasson, B.; Borrebaeck, C.; Sanfridson, B.; Mosbach, K. Thermometric enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: TELISA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Enzymol. 1977, 483, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecklenburg, M.; Lindbladh, C.; Li, H.; Mosbach, K.; Danielsson, B. Enzymatic amplification of a flow-injected thermometric enzyme-linked immunoassay for human insulin. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 212, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.H.C.; Uddayasankar, U.; Wheeler, A.R. Immunoassays in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, B. The enzyme thermistor. App. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1982, 7, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangutooru, S.M.; Kopparthy, V.L.; Nestorova, G.G.; Guilbeau, E.J. Dynamic thermoelectric glucose sensing with layer-by-layer glucose oxidase immobilization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, B.; Baudenbacher, F. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry in Nanoliter Droplets with Subsecond Time Constants. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7955–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestorova, G.G.; Kopparthy, V.L.; Crews, N.D.; Guilbeau, E.J. Thermoelectric lab-on-a-chip ELISA. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Bai, J.; Peng, Y.; Qie, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Ning, B. Pretreatment-free detection of diazepam in beverages based on a thermometric biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadermarzi, M.; & Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. Determination of the kinetic parameters for the “suicide substrate” inactivation of bovine liver catalase by hydrogen peroxide. J. Enzym Inhib. 1996, 10, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazura, E.; Lubbers, B.R.; Dawson, E.; Phillips, J.A.; Baudenbacher, F. Nano-Calorimetry based point of care biosensor for metabolic disease management. Biomed. Microdev. 2017, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, B.R.; Kazura, E.; Dawson, E.; Mernaugh, R.; Baudenbacher, F. Microfabricated calorimeters for thermometric enzyme linked immunosorbent assay in one-nanoliter droplets. Biomed. Microdev. 2019, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, B.R. Nano-Calorimetry for Point of Care Diagnostics. Ph.D. Thesis, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA, March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Switala, J.; Loewen, P.C. Diversity of properties among catalases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 401, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Packer, L., Ed.; Elsvier, Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hertwig, B.; Streb, P.; Feierabend, J. Light dependence of catalase synthesis and degradation in leaves and the influence of interfering stress conditions. Plant. Physiol. 1992, 100, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, P.A.; Yogeswaran, U.; Chen, S. A review on direct electrochemistry of catalase for electrochemical sensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 1821–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoras, A. Catalase immobilization—A review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | TELISA Quantification | LOD (Femtomole) |
|---|---|---|
| Flow-injected immunosorbent column (Mecklenburg et al. [11]) | Baseline shift | 86,000 |
| Flow-injection nanocalorimeter (Xu et al. [17]) | Baseline shift | 43,800 |
| Capillary nanocalorimeter (Kazura et al. [19]) | Phenomenological | 25 |
| Model-assisted capillary nanocalorimeter | Model-assisted signal interpretation | 0.260 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazura, E.; Mernaugh, R.; Baudenbacher, F. A Capillary-Perfused, Nanocalorimeter Platform for Thermometric Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Femtomole Sensitivity. Biosensors 2020, 10, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10060071
Kazura E, Mernaugh R, Baudenbacher F. A Capillary-Perfused, Nanocalorimeter Platform for Thermometric Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Femtomole Sensitivity. Biosensors. 2020; 10(6):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10060071
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazura, Evan, Ray Mernaugh, and Franz Baudenbacher. 2020. "A Capillary-Perfused, Nanocalorimeter Platform for Thermometric Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Femtomole Sensitivity" Biosensors 10, no. 6: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10060071
APA StyleKazura, E., Mernaugh, R., & Baudenbacher, F. (2020). A Capillary-Perfused, Nanocalorimeter Platform for Thermometric Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Femtomole Sensitivity. Biosensors, 10(6), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10060071






