Lyme Disease Biosensors: A Potential Solution to a Diagnostic Dilemma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Current Methods of Diagnosis
1.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Bacterial Cultures
2. Biosensors to the Rescue
2.1. Microfluidics
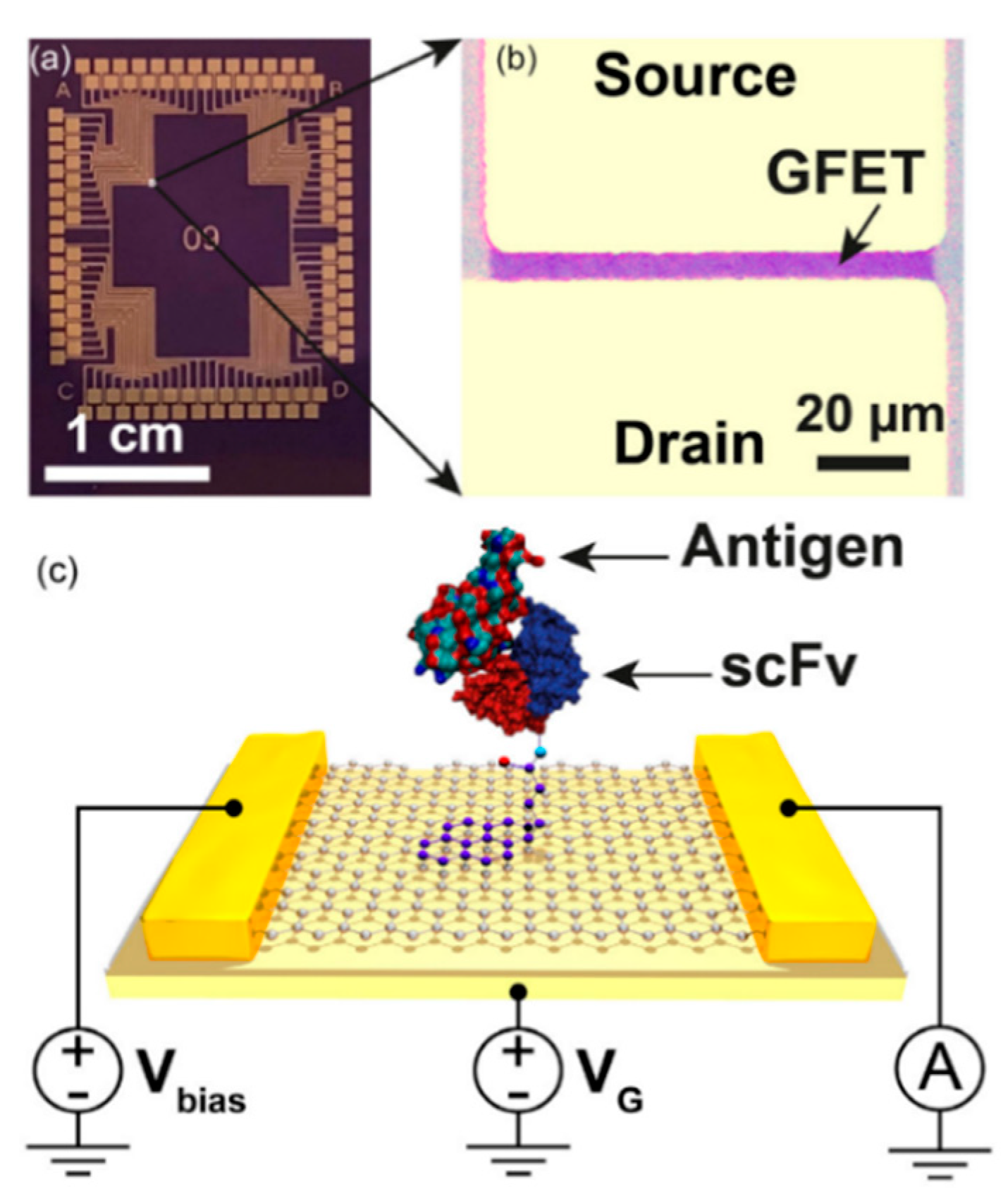
2.2. Field Effect Transistors (FETs)
2.3. Lateral Flow Assays (LFAs)
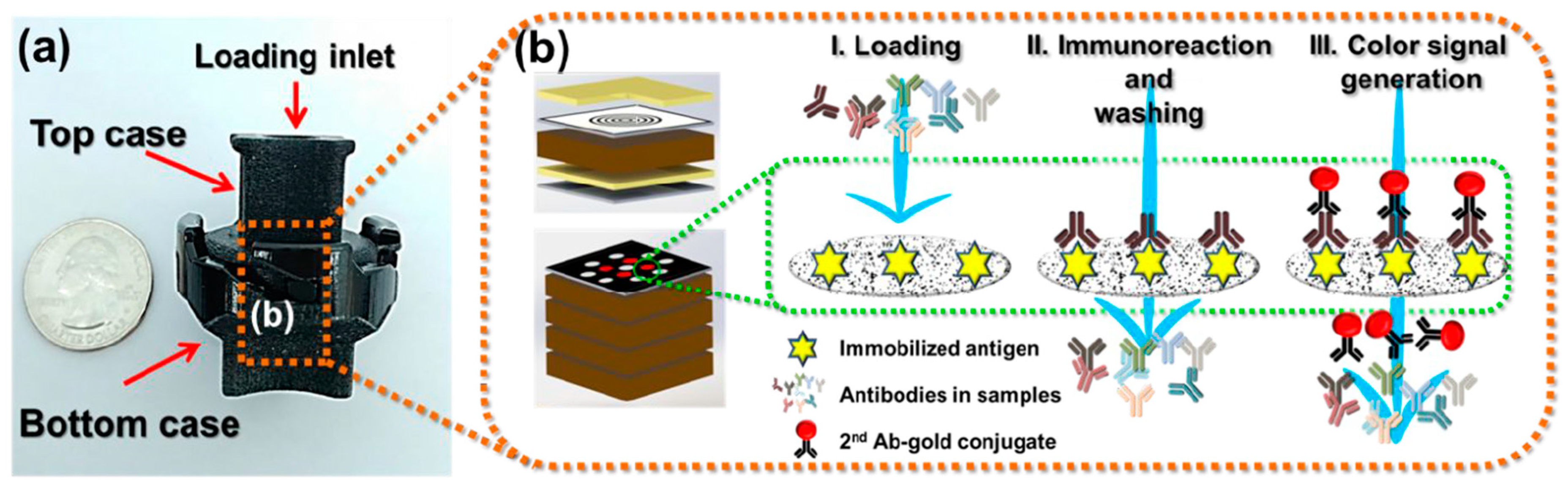
2.4. Vertical Flow Assays (VFAs)
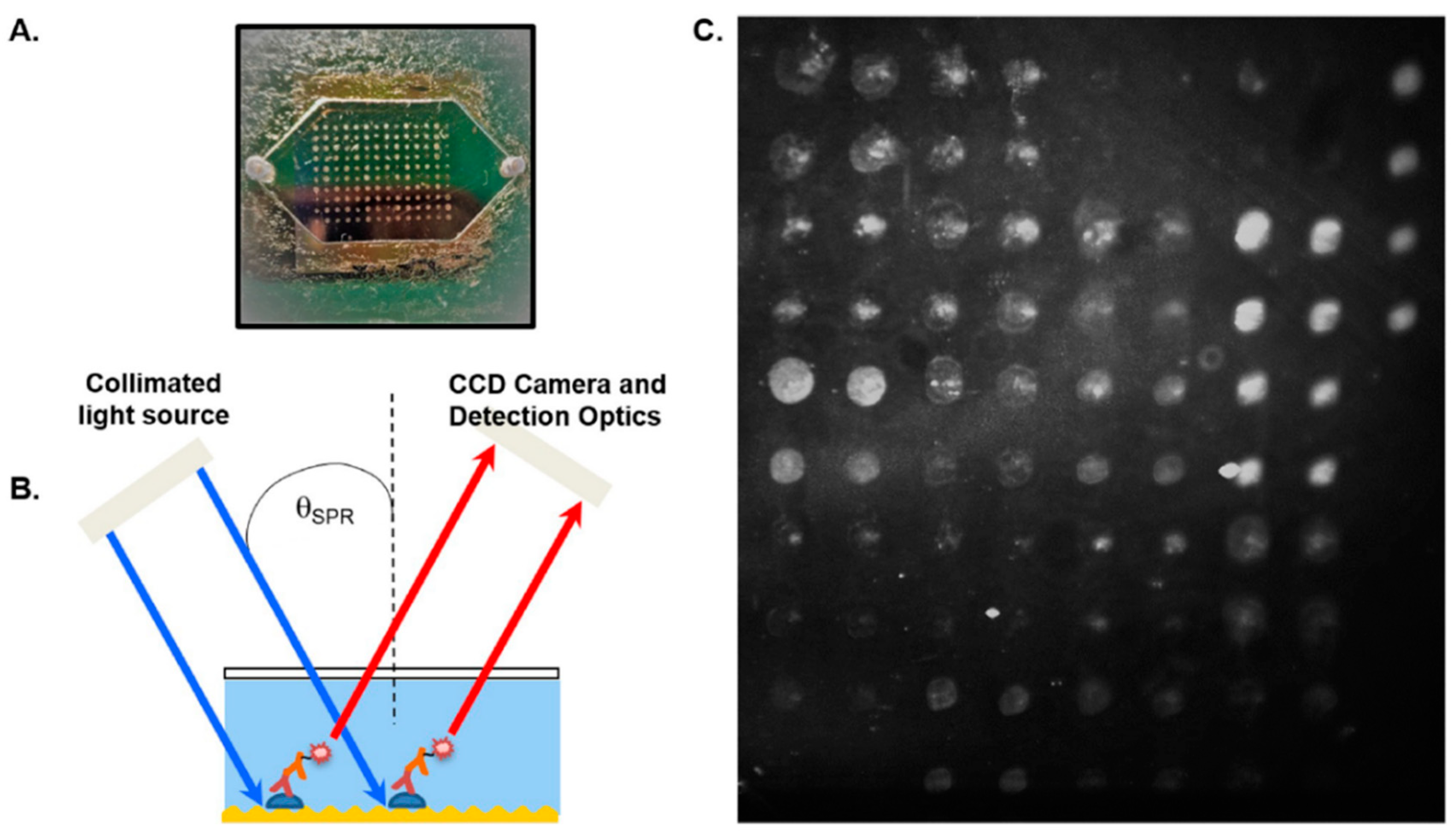
2.5. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
2.6. Biochips
3. Summary and Future Outlooks
3.1. Achievements & Challenges
3.2. Looking Ahead
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgdorfer, W.; Barbour, A.G.; Hayes, S.F.; Benach, J.L.; Grunwaldt, E.; Davis, J.P. Lyme disease–a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 1982, 216, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CDC Lyme Disease: Data and Surveillance. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance/index.html (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Shapiro, E.D. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr. Rev. 2014, 35, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, V.K.; Hawkins, R.G. Under-detection of Lyme disease in Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, J.A.; Marrotte, R.R.; Desrosiers, N.; Fiset, J.; Gaitan, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Koffi, J.K.; Lapointe, F.-J.; Leighton, P.A.; Lindsay, L.R.; et al. Climate change and habitat fragmentation drive the occurrence of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease, at the northeastern limit of its distribution. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelder, M.P.; Wijayasri, S.; Russell, C.B.; Johnson, K.O.; Marchand-Austin, A.; Cronin, K.; Johnson, S.; Badiani, T.; Patel, S.N.; Sider, D. The continued rise of Lyme disease in Ontario, Canada: 2017. Canada Commun. Dis. Rep. 2018, 44, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Morshed, M.; Sockett, P.N.; Artsob, H. The emergence of Lyme disease in Canada. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 180, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindgren, E.; Jaenson, T.G.T. Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: Influences of Climate and Climate Change, Epidemiology, Ecology and Adaptation Measures; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, B.L.; Tourand, Y.; Brissette, C.A. Brave new worlds: The expanding universe of Lyme disease. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.-Q.; Liu, K.; Li, X.-L.; Liang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yao, H.-W.; Sun, R.-X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Zuo, S.-Q.; et al. Emerging tick-borne infections in mainland China: An increasing public health threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skar, G.L.; Simonsen, K.A. Lyme Disease. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, A.; Nelson, C.; Molins, C.; Mead, P.; Schriefer, M. Current guidelines, common clinical pitfalls, and future directions for laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatchette, T.F.; Davis, I.; Johnston, B.L. Lyme disease: Clinical diagnosis and treatment. Canada Commun. Dis. Rep. 2014, 40, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, C.; Raffetin, A.; Bouiller, K.; Hansmann, Y.; Roblot, F.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Review of European and American guidelines for the diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis. Méd. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, L.A.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Harding, S.; Lindsay, R.; Ogden, N. The accuracy of diagnostic tests for Lyme disease in humans, a systematic review and meta-analysis of North American research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mead, P.; Petersen, J.; Hinckley, A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pegalajar-Jurado, A.; Schriefer, M.E.; Welch, R.J.; Couturier, M.R.; MacKenzie, T.; Clark, R.J.; Ashton, L.V.; Delorey, M.J.; Molins, C.R. Evaluation of modified two-tiered testing algorithms for Lyme disease laboratory diagnosis using well-characterized serum samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01943-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, A.R. Revisiting the Lyme disease serodiagnostic algorithm: The momentum gathers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schutzer, S.E.; Body, B.A.; Boyle, J.; Branson, B.M.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Fikrig, E.; Gerald, N.J.; Gomes-Solecki, M.; Kintrup, M.; Ledizet, M.; et al. Direct diagnostic tests for Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priem, S.; Rittig, M.G.; Kamradt, T.; Burmester, G.R.; Krause, A. An optimized PCR leads to rapid and highly sensitive detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with Lyme borreliosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eldin, C.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Limitations of diagnostic tests for bacterial infections. Médecine Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donta, S.T. Issues in the diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease. Open Neurol. J. 2012, 6, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wills, M.K.B.; Kirby, A.M.; Lloyd, V.K. Detecting the lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, in ticks using nested PCR. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buss, M.; Case, L.; Kearney, B.; Coleman, C.; Henning, J.D. Detection of Lyme disease and anaplasmosis pathogens via PCR in Pennsylvania deer ked. J. Vector Ecol. 2016, 41, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Hammond-McKibben, D.; Guralski, D.; Lobo, S.; Fielder, P.N. Development of a sensitive molecular diagnostic assay for detecting Borrelia burgdorferi DNA from blood of Lyme disease patients by digital PCR. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, J.; Schwartz, I.; Liveris, D.; Wang, G.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Girao, G.; McKenna, D.; Nadelman, R.B.; Cavaliere, L.F.; Wormser, G.P.; et al. Laboratory diagnostic techniques for patients with early Lyme disease associated with erythema migrans: A comparison of different techniques. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, C.L.; Myszka, D.G. Current and emerging commercial optical biosensors. J. Mol. Recognit. 2001, 14, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Rechnitz, G. Biosensors based on plant and animal tissue. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1993, 8, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, B.; Tung, S. Development and applications of portable biosensors. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Santiago, G.T.; Alvarez, M.M.; Ribas, J.; Jonas, S.J.; Weiss, P.S.; Andrews, A.M.; Aizenberg, J.; Khademhosseini, A. Interplay between materials and microfluidics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics based point-of-care diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Sridhara, A.; Melo, R.; Richer, L.; Chee, N.H.; Kim, J.; Linder, V.; Steinmiller, D.; Sia, S.K.; Gomes-Solecki, M. Microfluidics-based point-of-care test for serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Nayak, S.; Williams, T.; di Santa Maria, F.S.; Guedes, M.S.; Chaves, R.C.; Linder, V.; Marques, A.R.; Horn, E.J.; Wong, S.J.; et al. A multiplexed serologic test for diagnosis of Lyme disease for point-of-care use. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-T.; Mulchandani, A. Carbon nanotubes and graphene nano field-effect transistor-based biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerner, M.B.; Dailey, J.; Goldsmith, B.R.; Brisson, D.; Johnson, A.T.C. Detecting Lyme disease using antibody-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.T., Jr.; Lerner, M.; Robinson, M.K.; Pazina, T.; Brisson, D.; Dailey, J. Carbon Nanotube Biosensors and Related Methods. US Patent US20150119263A1, 30 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Ducos, P.; Ye, H.; Zauberman, J.; Sriram, A.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Mitchell, M.W.; Lekkas, D.; Brisson, D.; et al. Graphene transistor arrays functionalized with genetically engineered antibody fragments for Lyme disease diagnosis. 2D Materials 2020, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quidel Sofia 2 Lyme FIA: Package Insert. Available online: https://www.quidel.com/immunoassays/rapid-lyme-tests/sofia-2-lyme-fia (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Jiang, N.; Ahmed, R.; Damayantharan, M.; Ünal, B.; Butt, H.; Yetisen, A.K. Lateral and vertical flow assays for point-of-care diagnostics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.-A.; Ballard, Z.S.; Ma, A.; Tseng, D.K.; Teshome, H.; Burakowski, S.; Garner, O.B.; Di Carlo, D.; Ozcan, A. Paper-based multiplexed vertical flow assay for point-of-care testing. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.-A.; Ballard, Z.S.; Wu, J.; Tseng, D.K.; Teshome, H.; Zhang, L.; Horn, E.J.; Arnaboldi, P.M.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Garner, O.B.; et al. Point-of-Care Serodiagnostic Test for Early-Stage Lyme Disease Using a Multiplexed Paper-Based Immunoassay and Machine Learning. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor technique: A review. J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, T.; Gajovic-Eichelmann, N.; Tobisch, S.; Schulte-Spechtel, U.; Bier, F.F. Serodiagnosis of Lyme borreliosis infection using surface plasmon resonance. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 394, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallioniemi, O.-P. Biochip technologies in cancer research. Ann. Med. 2001, 33, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.-L.; Ye, L.; Lv, H.; Du, Y.-X.; Schneider, M.; Fan, L.-B.; Du, W.-D. A biochip-based combined immunoassay for detection of serological status of Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme borreliosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 472, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, E.; Lasek-Nesselquist, E.; Taubner, B.; Pilar, A.; Guignon, E.; Page, W.; Lin, Y.-P.; Cady, N.C. A fluorescent plasmonic biochip assay for multiplex screening of diagnostic serum antibody targets in human Lyme disease. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CDC Notice to Readers Recommendations for Test Performance and Interpretation from the Second National Conference on Serologic Diagnosis of Lyme Disease. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1995, 44, 590–591.
- Goodman, J.L.; Bradley, J.F.; Ross, A.E.; Goellner, P.; Lagus, A.; Vitale, B.; Berger, B.W.; Luger, S.; Johnson, R.C. Bloodstream invasion in early Lyme disease: Results from a prospective, controlled, blinded study using the polymerase chain reaction. Am. J. Med. 1995, 99, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.L.; Jurkovich, P.; Kramber, J.M.; Johnson, R.C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwaiger, M.; Péter, O.; Cassinotti, P. Routine diagnosis of Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu lato) infections using a real-time PCR assay. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liveris, D.; Wang, G.; Girao, G.; Byrne, D.W.; Nowakowski, J.; McKenna, D.; Nadelman, R.; Wormser, G.P.; Schwartz, I. Quantitative detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in 2-millimeter skin samples of erythema migrans lesions: Correlation of results with clinical and laboratory findings. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, M.M.; Hackl, W.; Griesmacher, A. Point-of-care-testing—das intensivlaboratorium. Anaesthesist 1999, 48, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, C.R. A point-of-care device for acute kidney injury: A fantastic, futuristic, or frivolous “measure”? Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sin, M.L.Y.; Mach, K.E.; Wong, P.K.; Liao, J.C. Advances and challenges in biosensor-based diagnosis of infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Applications of commercial biosensors in clinical, food, environmental, and biothreat/biowarfare analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damborský, P.; Švitel, J.; Katrlík, J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammond, J.L.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P.; Carrara, S.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical biosensors and nanobiosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pohanka, M. Overview of piezoelectric biosensors, immunosensors and DNA sensors and their applications. Materials 2018, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Method | Sample | Target | Sensitivity or LOD | Specificity | Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microfluidics | Serum | Antibodies | 84% | 92% | 15 min | [32] |
| Serum | Antibodies | 80%/85% | 95% | - | [33] | |
| FET | Spiked Buffer | Antigen | 1 ng/mL | High | Minutes | [35] |
| Spiked Buffer | Antigen | 2–500 pg/mL | High | - | [37] | |
| LFA | Serum | Antibodies | 64.2%/80% | 89.5%/96.5% | 3–15 min | [39] |
| VFA | Serum | Antibodies | 162.2–1046 ng/mL | - | 20 min | [41] |
| Serum | Antibodies | 85.7% | 96.3% | 15 min | [42] | |
| SPR | Serum | Antibodies | 81%/92% | 86%/82% | A few min | [44] |
| Biochip | Serum | Antibodies | 0.39–0.78 µg/mL | - | - | [46] |
| Serum | Antibodies | 90% | 100% | - | [47] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flynn, C.; Ignaszak, A. Lyme Disease Biosensors: A Potential Solution to a Diagnostic Dilemma. Biosensors 2020, 10, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100137
Flynn C, Ignaszak A. Lyme Disease Biosensors: A Potential Solution to a Diagnostic Dilemma. Biosensors. 2020; 10(10):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100137
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlynn, Connor, and Anna Ignaszak. 2020. "Lyme Disease Biosensors: A Potential Solution to a Diagnostic Dilemma" Biosensors 10, no. 10: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100137
APA StyleFlynn, C., & Ignaszak, A. (2020). Lyme Disease Biosensors: A Potential Solution to a Diagnostic Dilemma. Biosensors, 10(10), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100137