Conformational Changes of Calmodulin on Calcium and Peptide Binding Monitored by Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. FBAR and Read-Out
2.2. Reagents and Materials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Immobilisation of Neutravidin and Biotinylated Calmodulin
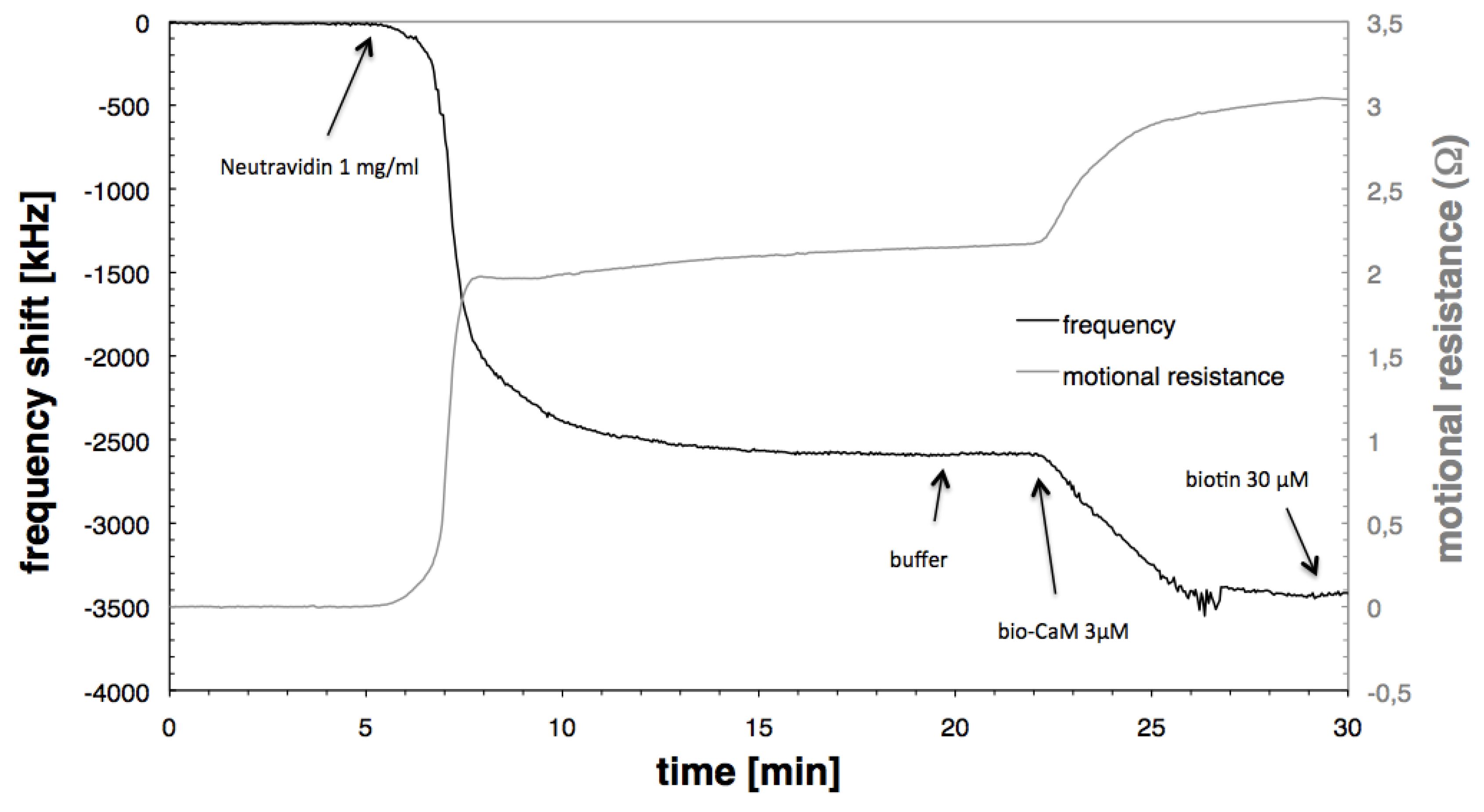
| Measured on | Concentration bio-CaM [nM] | Bio-CaM bound to surface [ng/cm2] | Binding efficiency of bio-CaM to Neutravidin | Mass change on addition of 1 mM CaCl2 [ng/cm2] | Ratio surface mass CaCl2/bio-CaM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBAR | 30 | 79 | 0.45 | 10 | 12.7% |
| FBAR | 300 | 100 | 0.69 | 6 | 6.0% |
| FBAR | 3,000 | 190 | 1.17 | −36 | −19.1% |
| QCM (Data from [15]) | 30 | 111 | 0.7 | 6 | 5.5% |
| QCM (Data from [16]) | 3,000 | 42 | n.a. | 10 | 23.1% |
3.2. Calcium Induced Conformational Changes of Calmodulin
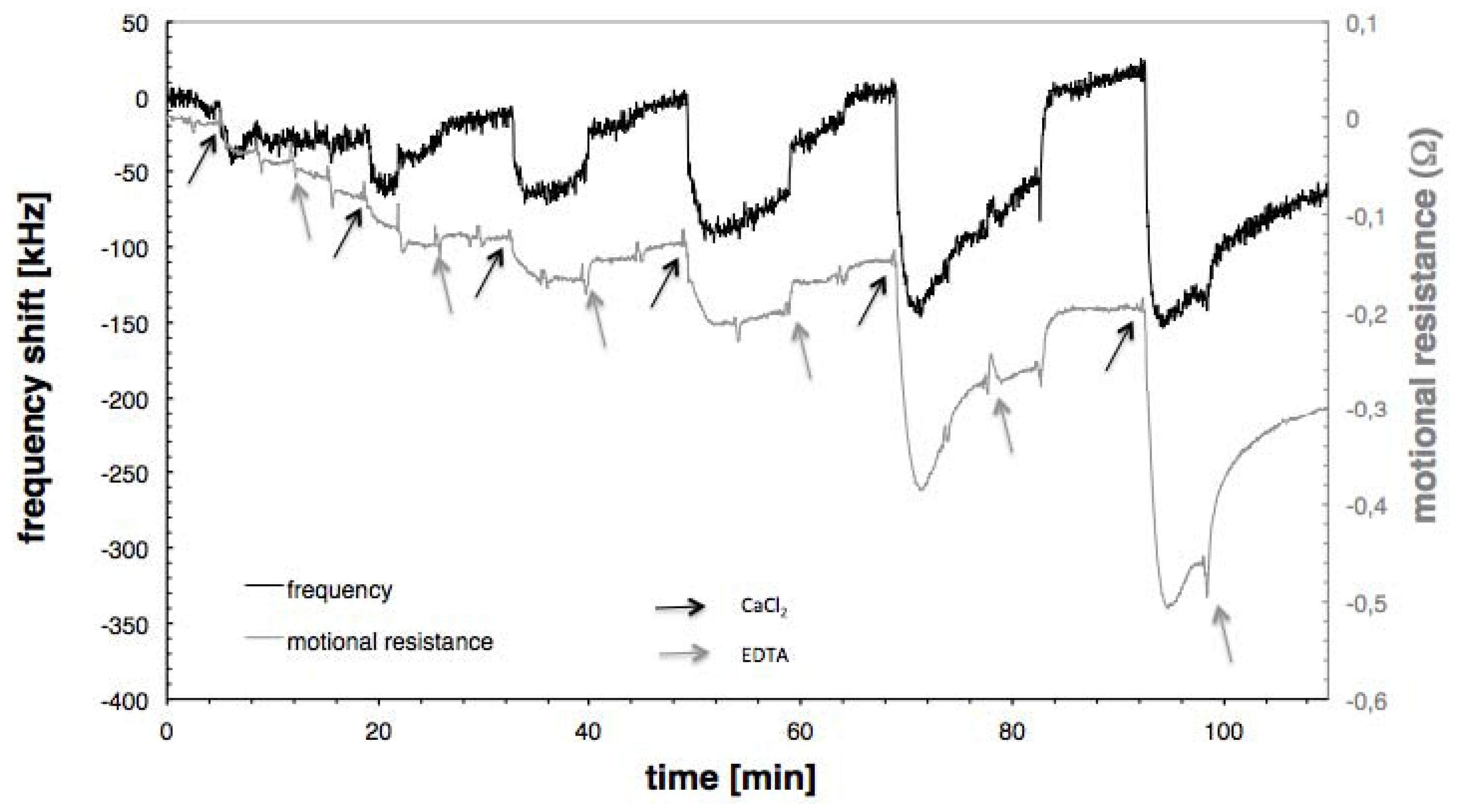

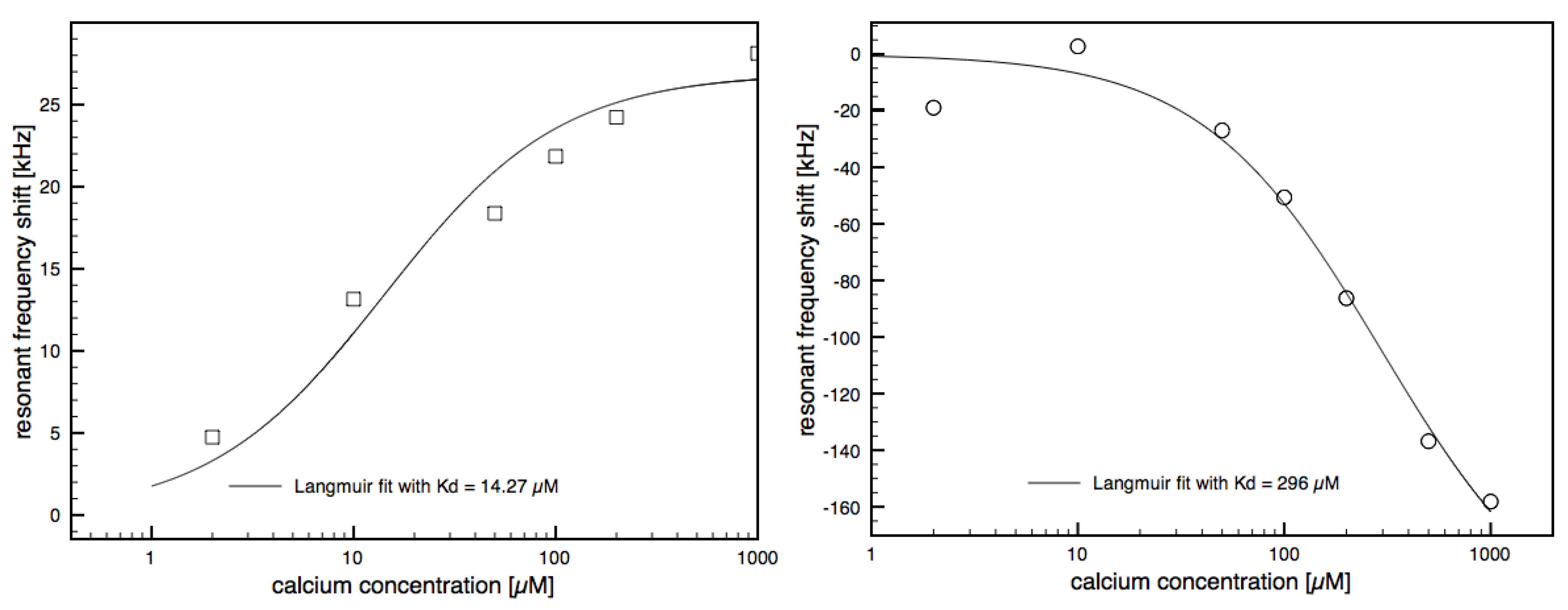
3.3. CaMKII Binding
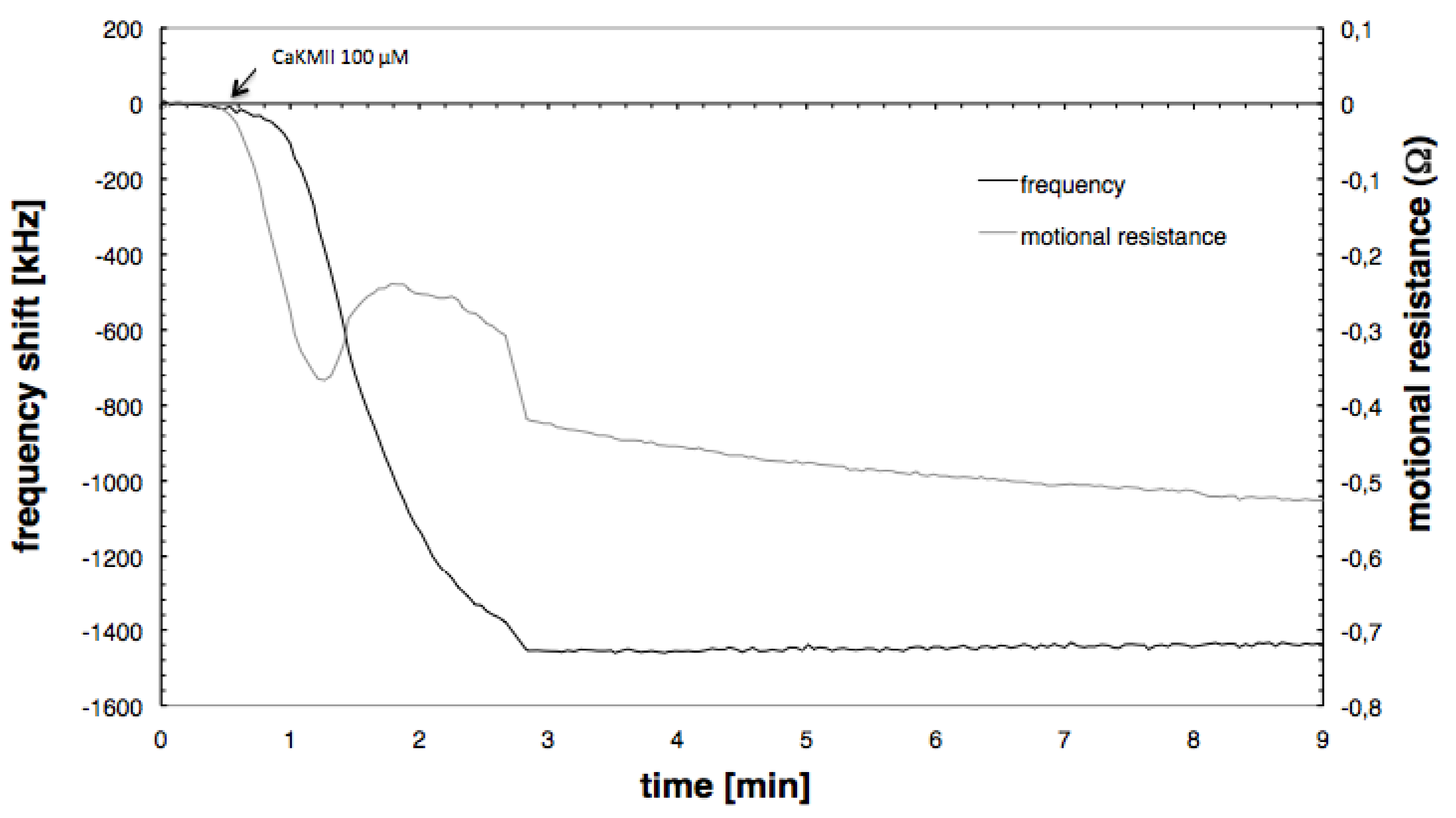
3.4. Conductance versus Frequency Shift Plots
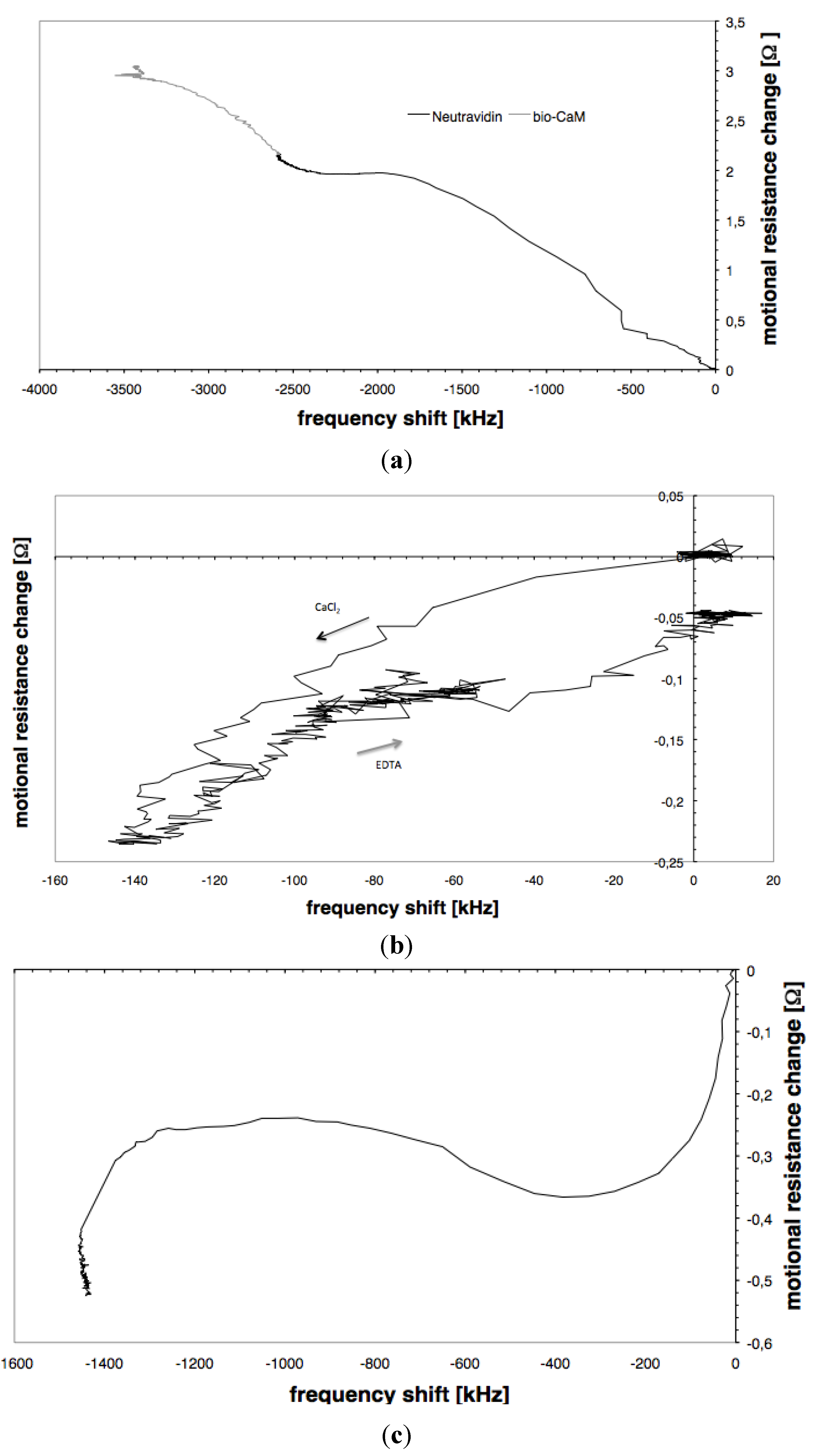
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Rabiller, M.; Getlik, M.; Klüter, S.; Richters, A.; Tückmantel, S.; Simard, J.; Rauh, D. Proteus in the world of proteins: Conformational changes in protein kinases. Arch. Pharm. 2010, 343, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.L.; Ames, J.B.; Swindells, M.B.; Ikura, M. Diversity of conformational states and changes within the EF-hand protein superfamily. Proteins 1999, 37, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirovskiy, O.; Giblin, D.; Gross, M. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and hydrogen/deuterium exchange for probing the interaction of calmodulin with calcium. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 10, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porumb, T.; Crivici, A.; Blackshear, P.; Ikura, M. Calcium binding and conformational properties of calmodulin complexed with peptides derived from myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) and MARCKS-related protein (MRP). Eur. Biophys. J. 1997, 25, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, D.; Creighton, T. Gel electrophoresis in studies of protein conformation and folding. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 138, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajihara, D.; Abe, R.; Iijima, I.; Komiyama, C.; Sisido, M.; Hohsaka, T. FRET analysis of protein conformational change through position-specific incorporation of fluorescent amino acids. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, B.; Head, J.; Engelman, D.; Richards, F. Calcium-induced increase in the radius of gyration and maximum dimension of calmodulin measured by small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 6740–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulet, Y.; Cox, J. Structural changes in melittin and calmodulin upon complex formation and their modulation by calcium. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 5680–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, D.; Tsvetkov, P.; Devred, F.; Toci, R.; Barras, F.; Briand, C.; Makarov, A.; Haiech, J. Cation binding mode of fully oxidised calmodulin explained by the unfolding of the apostate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteomics 2002, 1600, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhop, D.J.; Latham, J.C.; Kussrow, A.; Markov, D.A.; Jones, R.D.; Sorensen, H.S. Free-solution, label-free molecular interactions studied by back-scattering interferometry. Science 2007, 317, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, G.; Freeman, N.; Swann, M. Dual polarization interferometry: A real time optical technique for measuring (bio) molecular orientation, structure and function at the solid/liquid interface. In Handbook of Biosensors and Biochips; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Salafsky, J. Detection of protein conformational change by optical second-harmonic generation. J. Chem. Phys. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conformational changes detected on surface attached calmodulin. Available online: http://www.saw-instruments.de/pdf/apps/Sam5_App_Note16_110311.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2011).
- Länge, K.; Rapp, B.; Rapp, M. Surface acoustic wave biosensors: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, H.; Komatsu, M.; Okahata, Y. In situ monitoring of conformational changes of and peptide bindings to calmodulin on a 27 MHz quartz-crystal microbalance. Anal. Chem 2009, 81, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ellis, J.; Lyle, E.; Sundaram, P.; Thompson, M. Conformational chemistry of surface-attached calmodulin detected by acoustic shear wave propagation. Mol. BioSyst. 2006, 2, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakin, K.M. Thin film resonators and filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Caesars Tahoe, NV, USA, 17–21 October 1999; Volume 2, pp. 895–906.
- Gabl, R.; Feucht, H.-D.; Zeininger, H.; Eckstein, G.; Schreiter, M.; Primig, R.; Pitzer, D.; Wersing, W. First results on label-free detection of DNA and protein molecules using a novel integrated sensor technology based on gravimetric detection principles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirschl, M.; Blüher, A.; Erler, C.; Katzschner, B.; Vikholm-Lundin, I.; Auer, S.; Vörös, J.; Pompe, W.; Schreiter, M.; Mertig, M. Film bulk acoustic resonators for DNA and protein detection and investigation of in vitro bacterial S-layer formation. Sens. Actuat. A 2009, 156, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirschl, M.; Rantala, A.; Tukkiniemi, K.; Auer, S.; Hellgren, A.-C.; Pitzer, D.; Schreiter, M.; Vikholm-Lundin, I. CMOS-integrated film bulk acoustic resonators for label-free biosensing. Sensors 2010, 10, 4180–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirschl, M.; Schreiter, M.; Voros, J. Comparison of FBAR and QCM-D sensitivity dependence on adlayer thickness and viscosity. Sens. Actuat. A 2010, 165, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, M.; Schreiter, M.; Weber, J.; Primig, R.; Pitzer, D.; Gabl, R. Solidly mounted ZnO shear mode film bulk acoustic resonators for sensing applications in liquids. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2006, 53, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Albers, W.M.; Tuppurainen, J.; Link, M.; Gabl, R.; Wersing, W.; Schreiter, M. Shear mode FBARs as highly sensitive liquid biosensors. Sens. Actuat. A 2006, 128, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyle, E.; Hayward, G.; Thompson, M. Acoustic coupling of transverse waves as a mechanism for the label-free detection of proteinñsmall molecule interactions. Analyst 2002, 127, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeiji, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Uebayasi, M. Molecular dynamics simulations revealed Ca2+-dependent conformational change of calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 2002, 521, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, F.; Furlong, D.; Kingshott, P. Characterization of ferritin adsorption onto gold. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 186, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höök, F.; Vörös, J.; Rodahl, M.; Kurrat, R.; Böni, P.; Ramsden, J.; Textor, M.; Spencer, N.; Tengvall, P.; Gold, J. A comparative study of protein adsorption on titanium oxide surfaces using in situ ellipsometry, optical waveguide lightmode spectroscopy, and quartz crystal microbalance/dissipation. Colloids Surf. B 2002, 24, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höök, F.; Rodahl, M.; Brzezinski, P.; Kasemo, B. Energy dissipation kinetics for protein and antibody-antigen adsorption under shear oscillation on a quartz crystal microbalance. Langmuir 1998, 14, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörös, J. The density and refractive index of adsorbing protein layers. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höök, F.; Kasemo, B. The QCM-D technique for probing biomacromolecular recognition reactions. Piezoelectric Sens. 2007, 5, 425–447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yuan, T. Molecular mechanisms of calmodulin’s functional versatility. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 76, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.-Y.; Mabuchi, Y.; Grabarek, Z. Blocking the Ca-induced conformational transitions in calmodulin with disulfide bonds. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7479–7483. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, W.P. Piezoelectric Crystals and Their Application to Ultrasonics; D. Van Nostrand Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum, J.F. Bulk Acoustic Wave Theory and Devices; Artech House, Inc.: Norwood, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Crouch, T.H.; Klee, C.B. Positive cooperative binding of calcium to bovine brain calmodulin. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 3692–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbrey, G. Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z. Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinova, M.V.; Jonson, M.; Kasemo, B. Missing mass effect in biosensor’s QCM applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, K.K.; Gordon, J.G. Frequency of a quartz microbalance in contact with liquid. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 1770–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nirschl, M.; Ottl, J.; Vörös, J. Conformational Changes of Calmodulin on Calcium and Peptide Binding Monitored by Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators. Biosensors 2011, 1, 164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1040164
Nirschl M, Ottl J, Vörös J. Conformational Changes of Calmodulin on Calcium and Peptide Binding Monitored by Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators. Biosensors. 2011; 1(4):164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1040164
Chicago/Turabian StyleNirschl, Martin, Johannes Ottl, and Janos Vörös. 2011. "Conformational Changes of Calmodulin on Calcium and Peptide Binding Monitored by Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators" Biosensors 1, no. 4: 164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1040164
APA StyleNirschl, M., Ottl, J., & Vörös, J. (2011). Conformational Changes of Calmodulin on Calcium and Peptide Binding Monitored by Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators. Biosensors, 1(4), 164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1040164




