Transparent Sol-Gel Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramics with High Crystalline Fraction and Study of RE Incorporation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Characterization of Coatings and Self-supported Layers
3. Results and Discussion
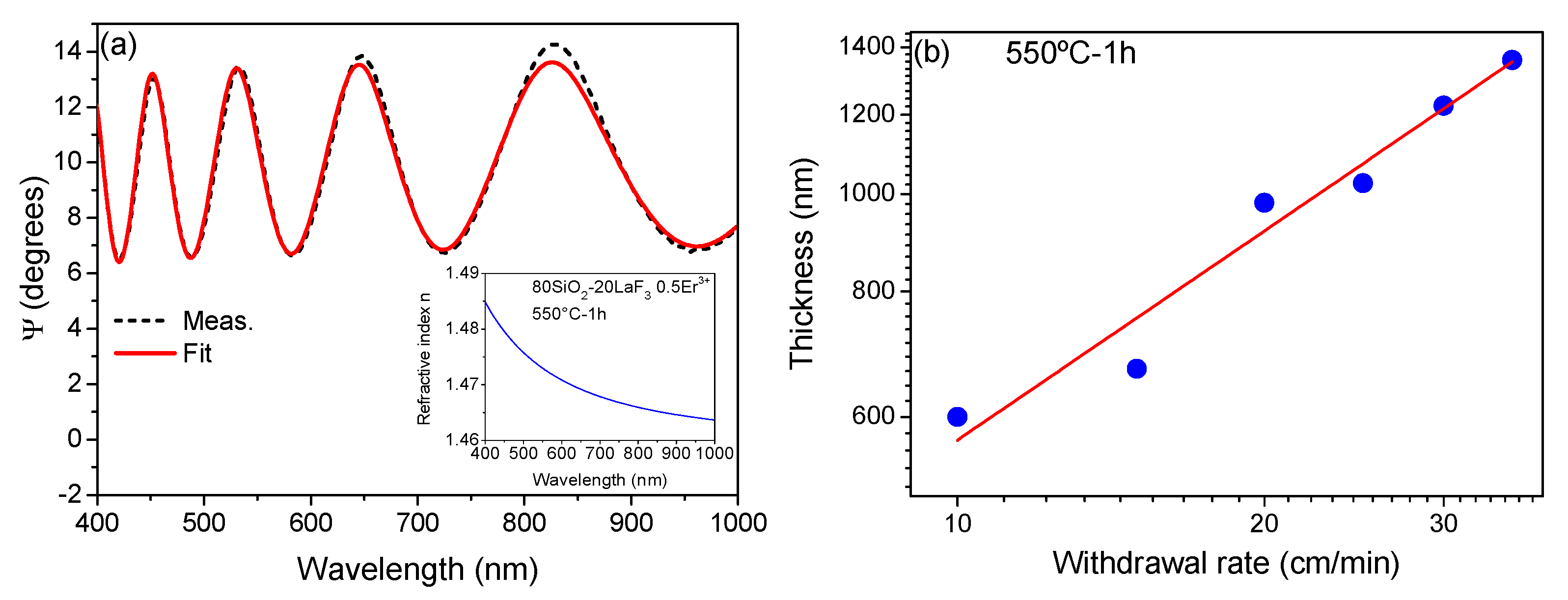
3.1. Self-supported Layers and Thin Films
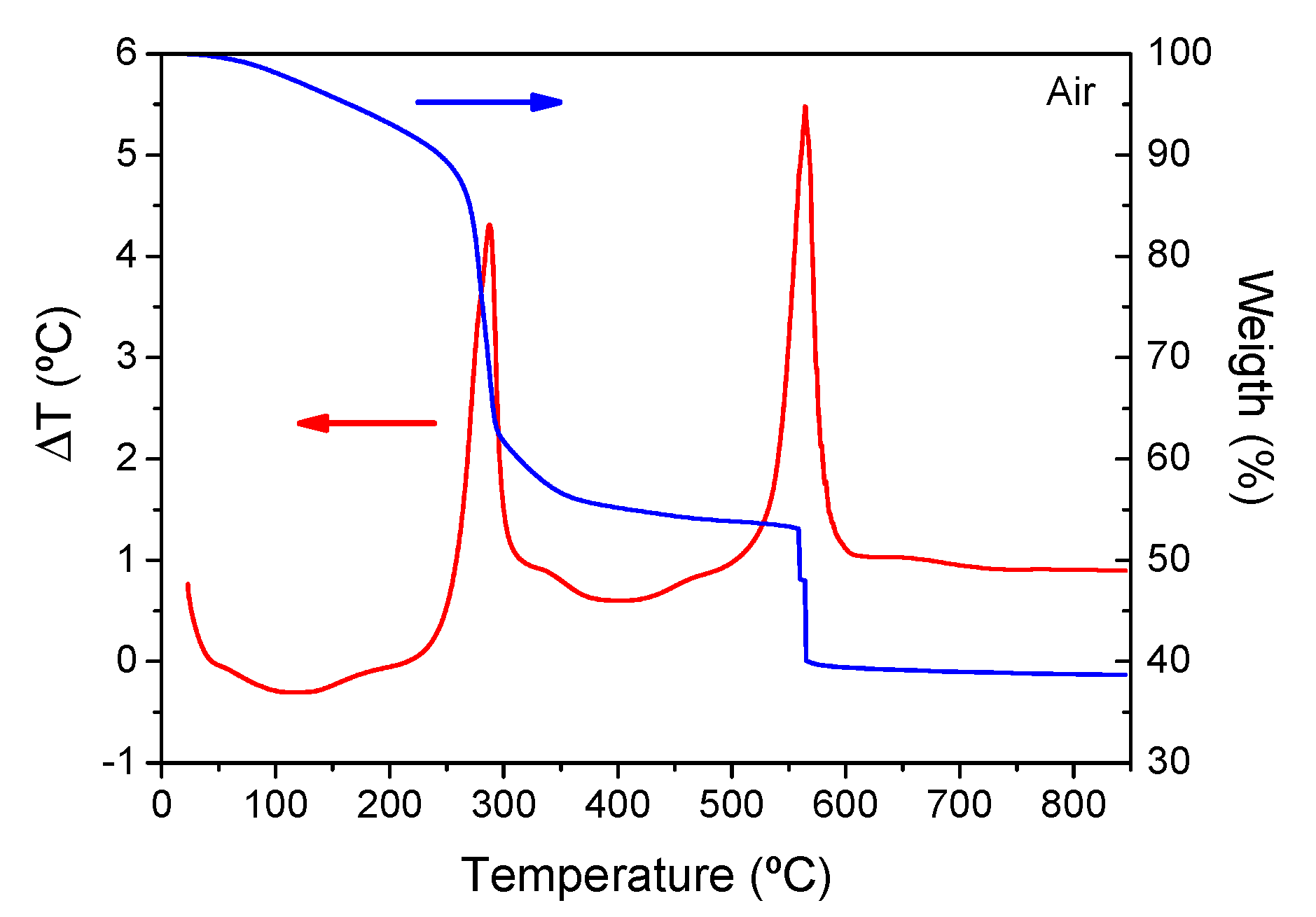
3.2. DTA and Crystallization
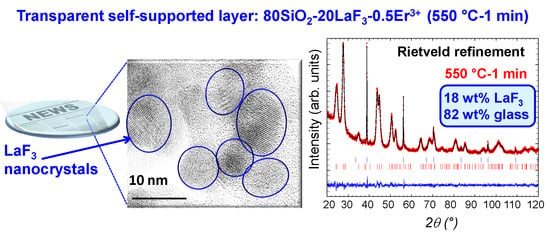
3.3. XRD, GI-XRD and Crystal Fraction
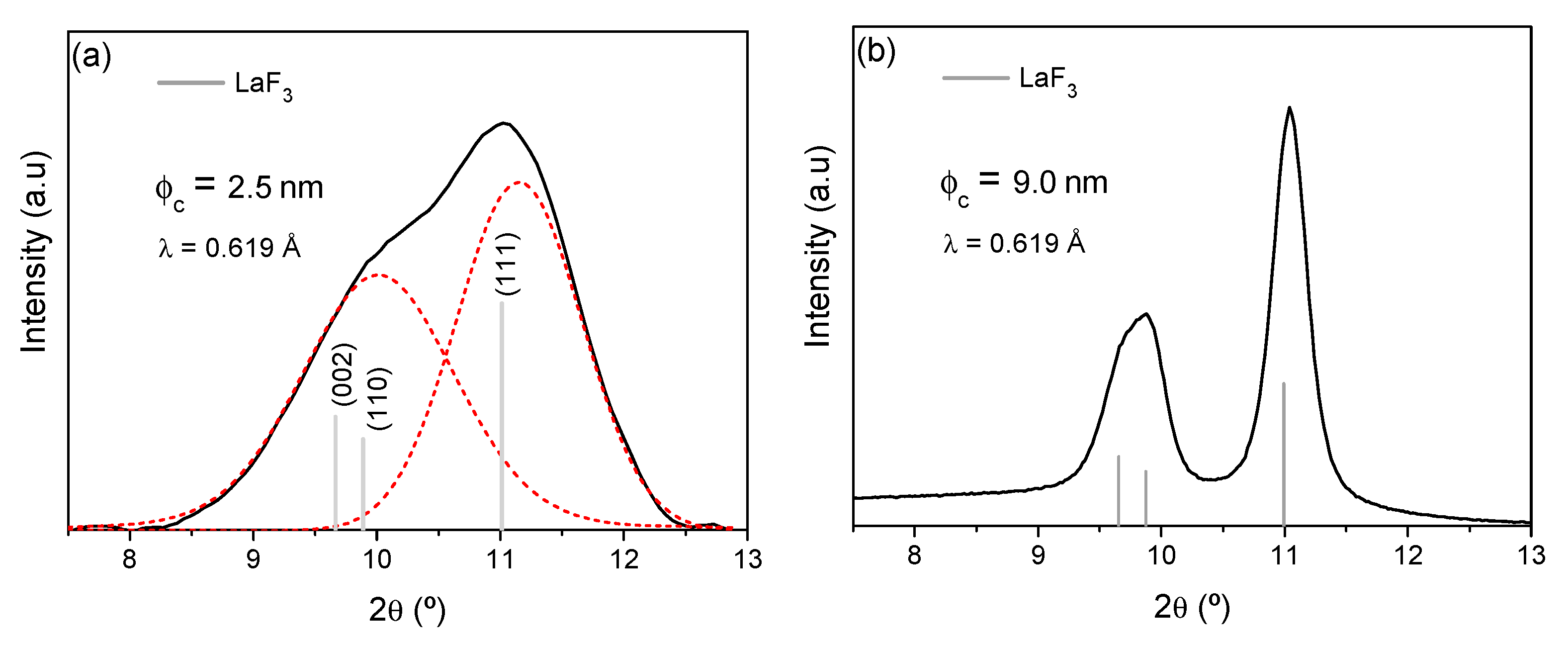
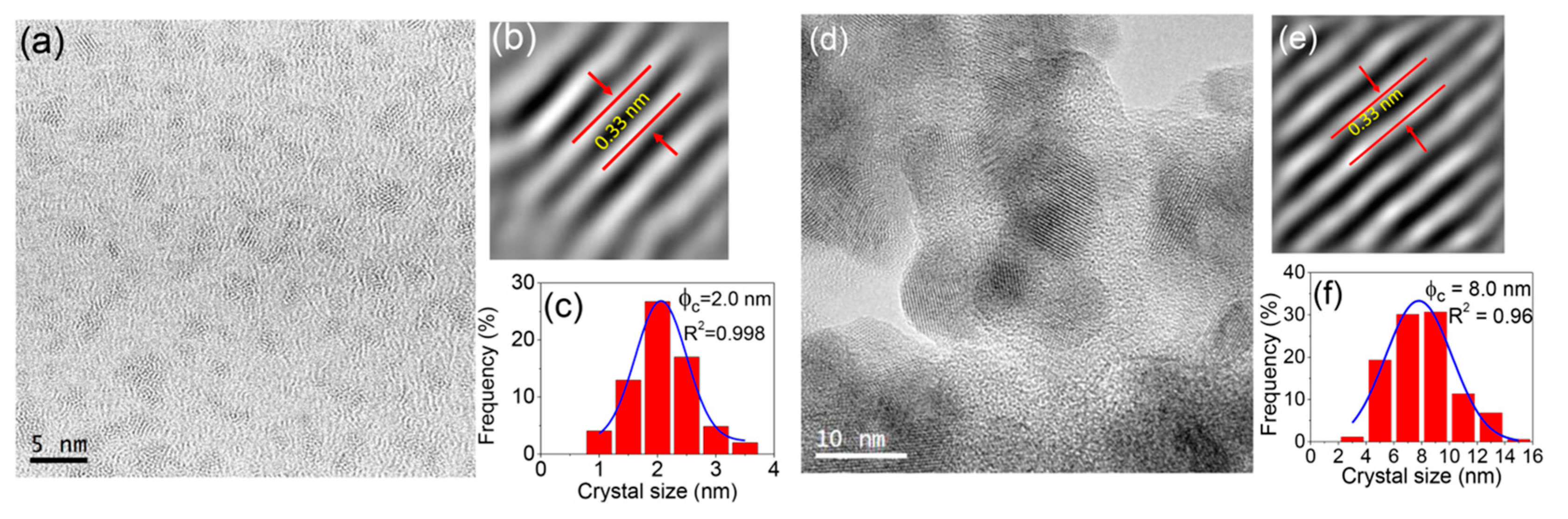
3.4. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) and Nanostructure Characterization
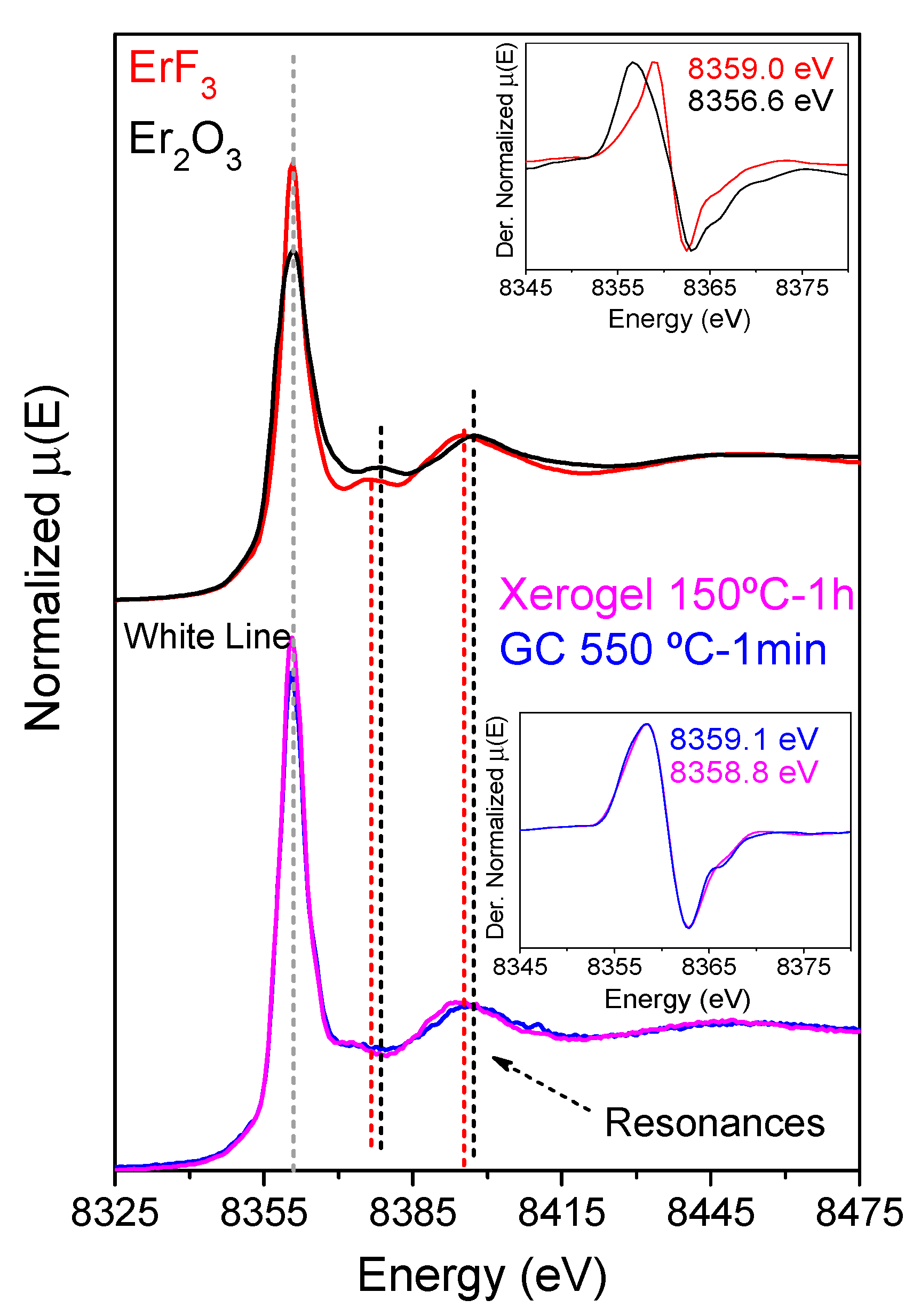
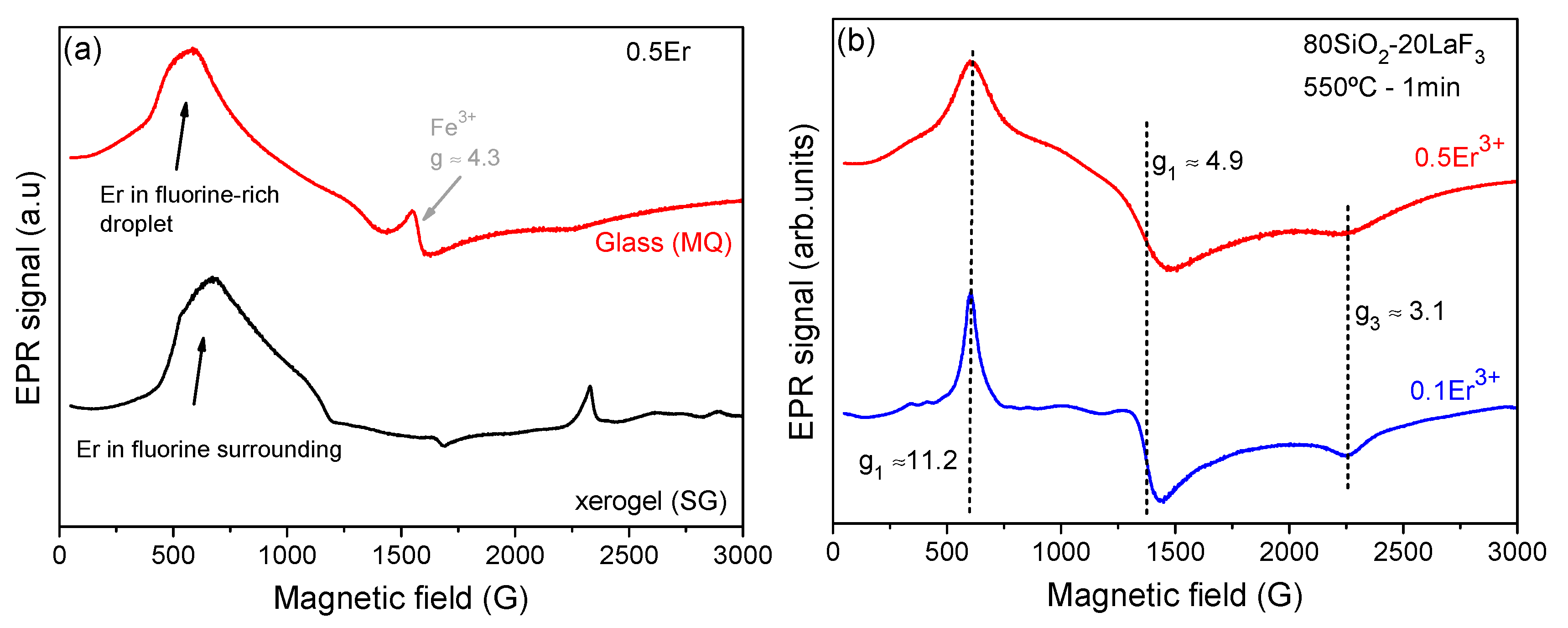
3.5. XAS, EPR and RE Environment
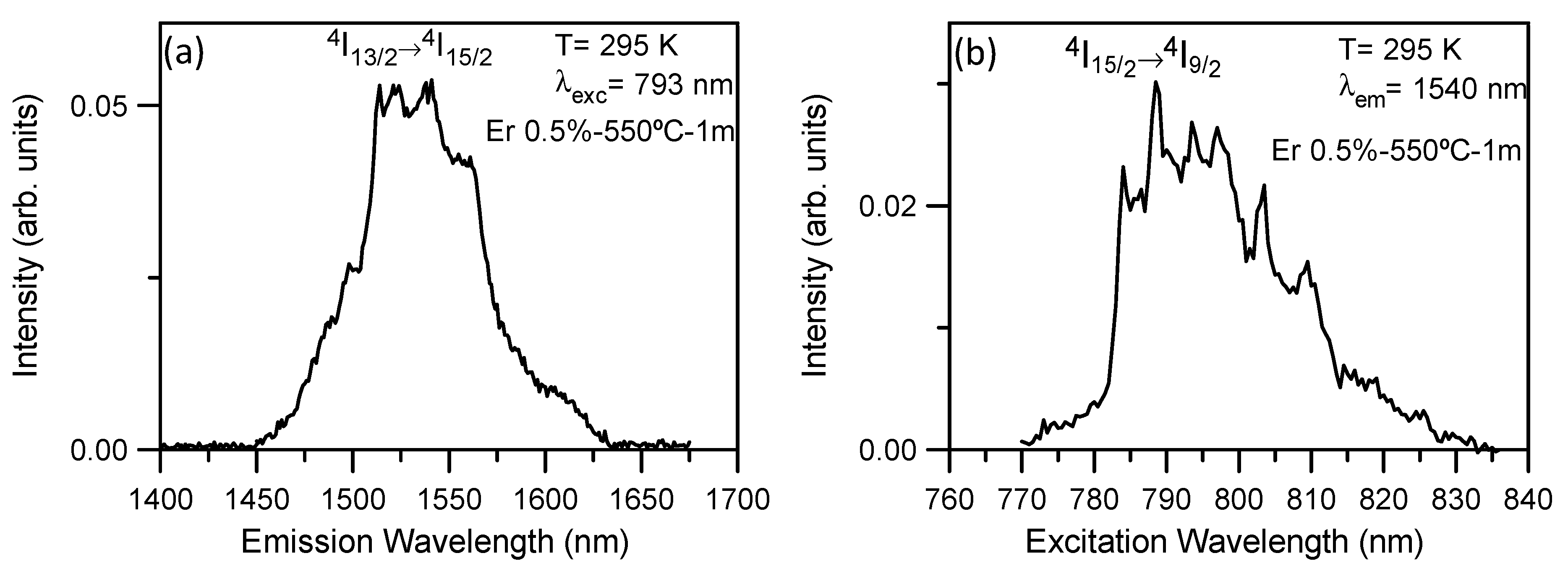
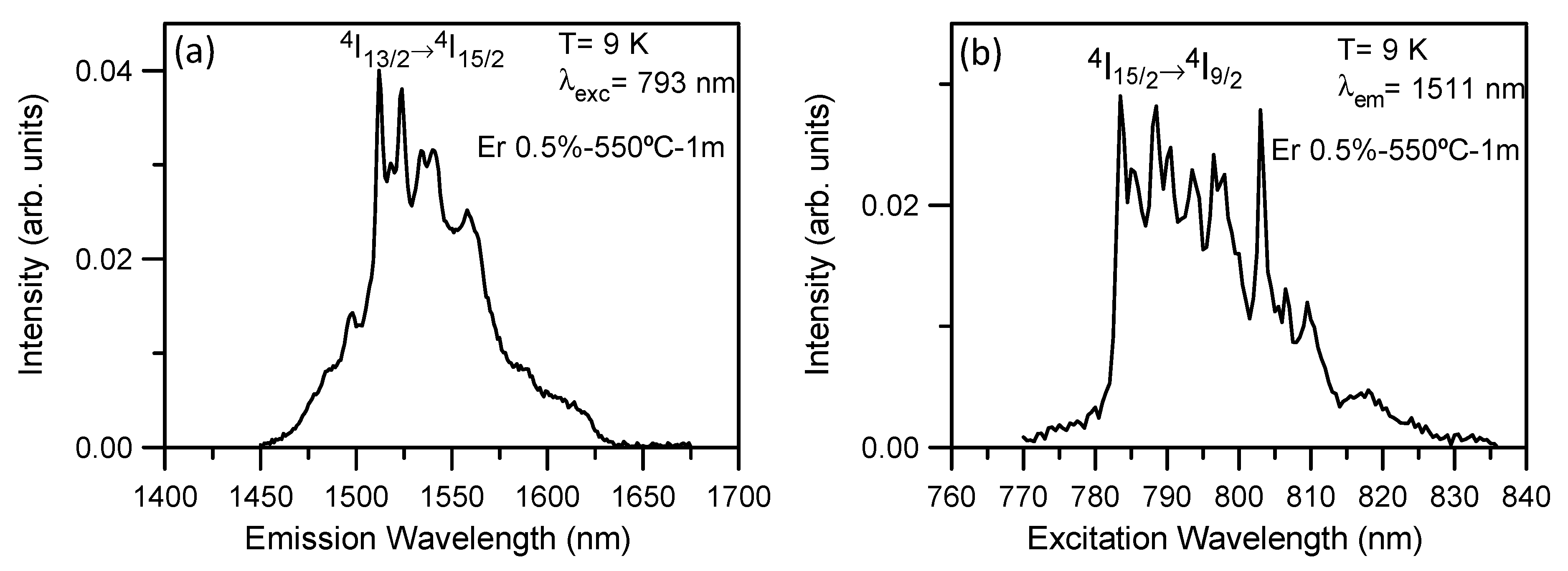
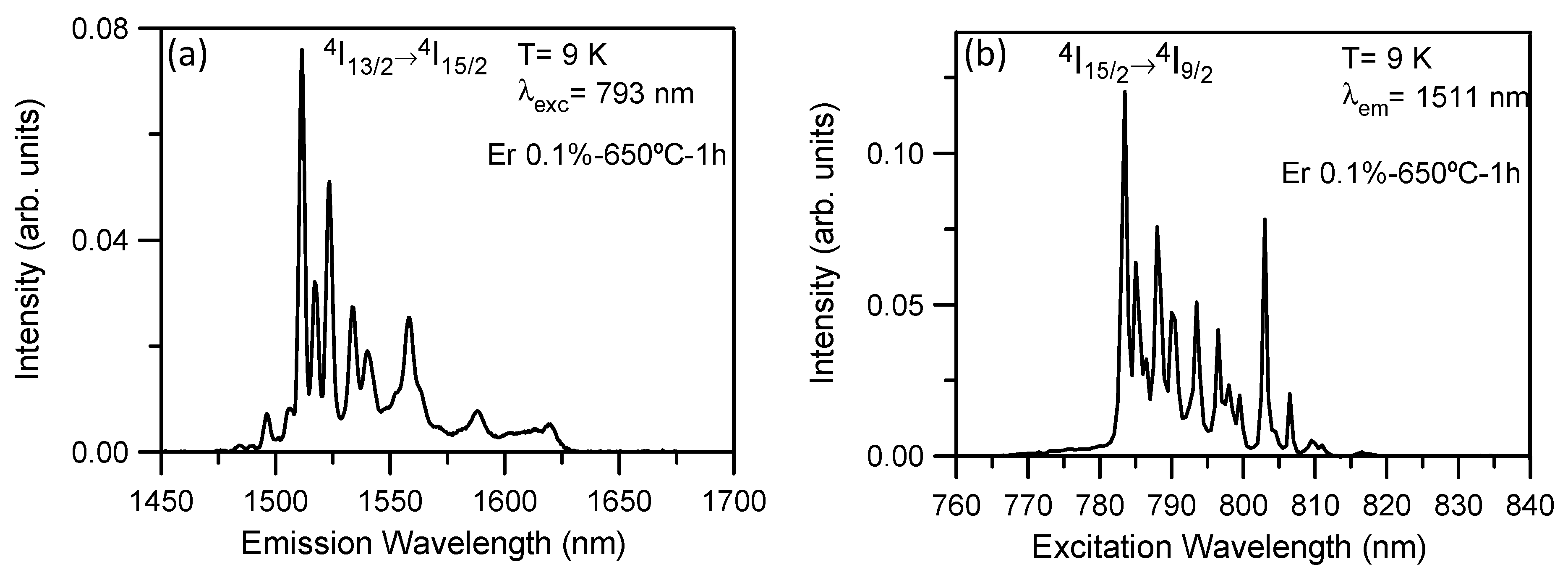
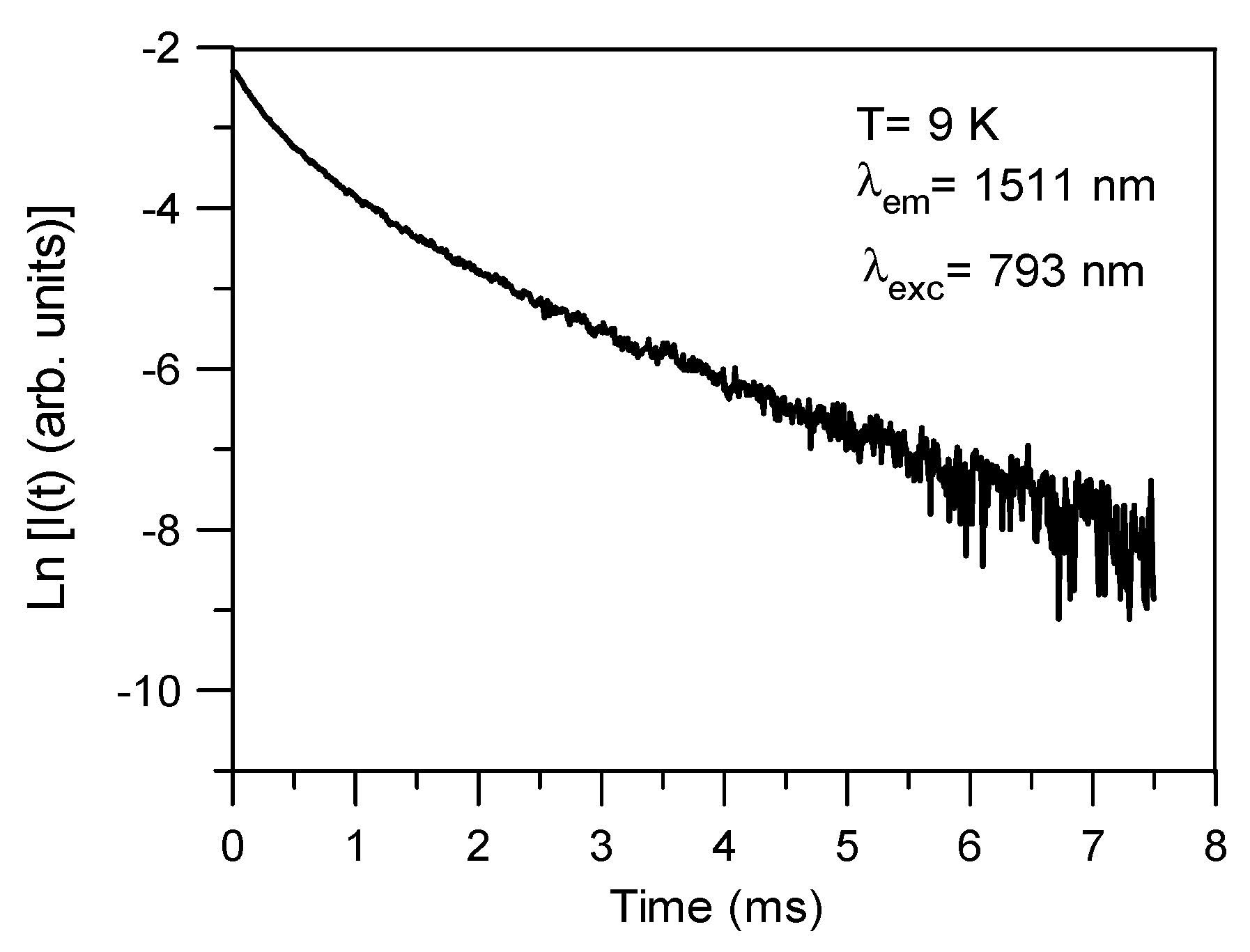
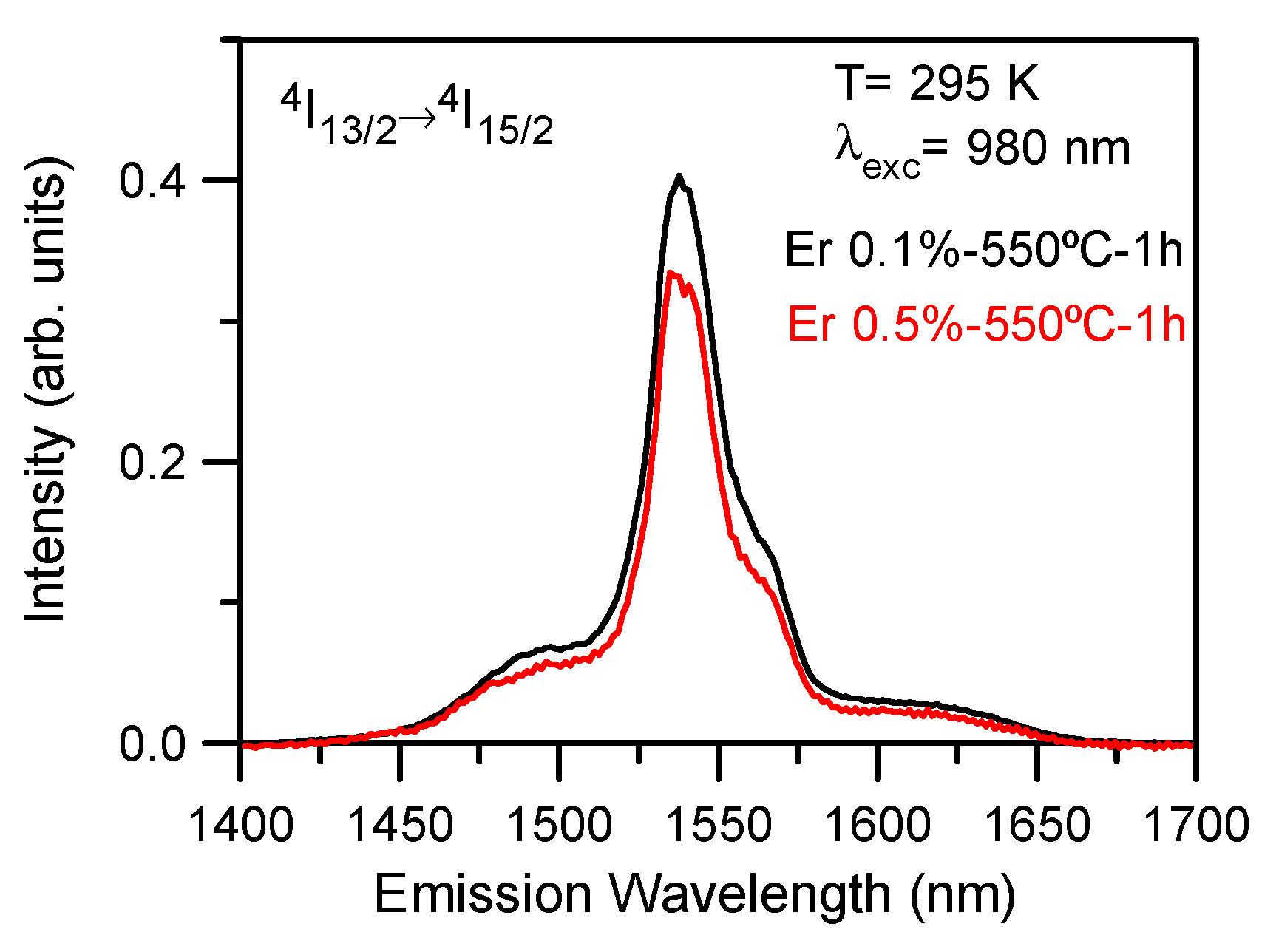
3.6. Photoluminescence (PL)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Ohwaki, J. New transparent vitroceramics codoped with Er3+ and Yb3+ for efficient frequency upconversion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 3268–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejneka, M.J. The luminescence and structure of novel transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 239, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Hayashi, H.; Hanada, T.; Onodera, N. Fluorescence properties of Er3+ ions in glass ceramics containing LaF3 nanocrystals. Opt. Mater. 2002, 19, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, V.; Iparraguirre, I.; Azkargorta, J.; Mendioroz, A.; González-Plata, J.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J. Stimulated and upconverted emissions of Nd3+ in a transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramic. Opt. Mater. (Amst.) 2004, 25, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattarelli, M.; Tikhomirov, V.K.; Seddon, A.B.; Montagna, M.; Moser, E. Tm3+-activated transparent oxy-fluoride glass–ceramics: Structural and spectroscopic properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 346, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, P.; Weng, F. Near-infrared quantum cutting in Ho3+/Yb3+ codoped nanostructured glass ceramic. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 876–878. [Google Scholar]
- de Pablos-Martín, A.; Durán, A.; Pascual, M.J. Nanocrystallization in oxyfluoride systems: Mechanisms of crystallization and photonic properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Chi, X.; Guo, H. Enhanced green upconversion in Tb3+-Yb3+ co-doped oxyfluoride glass ceramics containing LaF3 nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 2013, 137, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablos-Martín, A.; Ferrari, M.; Pascual, M.J.; Righini, G.C. Glass-ceramics: A class of nanostructured materials for photonics. Riv. Nuovo Cimento 2015, 38, 311–369. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, P.P.; Luginina, A.A.; Popov, A.I. Transparent oxyfluoride glass ceramics. J. Fluor. Chem. 2015, 172, 22–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.J.; Garrido, C.; Durán, A.; Pascual, L.; de Pablos-Martín, A.; Fernández, J.; Balda, R. Optical Properties of Transparent Glass–Ceramics Containing Er3+-Doped Sodium Lutetium Fluoride Nanocrystals. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2016, 40, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Velázquez, J.J.; Mather, G.C.; Durán, A.; Chen, G.; Sundararajan, M.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Pascual, M.J. Selective excitation in transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics doped with Nd3+. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Pascual, L.; Durán, A.; Pascual, M.J. Effect of the heat treatment on the spectroscopic properties of Er3+-Yb3+- doped transparent oxyfluoride nano-glass-ceramics. J. Lumin. 2018, 193, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.J.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Gorni, G.; Pascual, L.; Chen, G.; Sundararajan, M.; Durán, A.; Pascual, M.J. Transparent oxy fl uoride glass-ceramics with NaGdF4 nanocrystals doped with Pr3+ and Pr3+-Yb3+. J. Lumin. 2018, 193, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, B.N.; Tick, P.A.; Borrelli, N.F. Efficient neodymium-doped glass-ceramic fiber laser and amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reben, M.; Jaglarz, J. Nd3+-Doped Oxyfluoride Glass Ceramics Optical Fibre with SrF2 Nanocrystals. Opt. Appl. 2012, 42, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Lisiecki, R.; Augustyn, E.; Ryba-romanowski, W.; Zelechower, M. Er-doped and Er, Yb co-doped oxyfluoride glasses and glass–ceramics, structural and optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2011, 33, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Fang, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, D.; Xiao, X.; Qiu, J.; Dong, G. Precisely controllable fabrication of Er3+-doped glass ceramic fibers: Novel mid-infrared fiber laser materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Iparraguirre, I.; Velázquez, J.J.; Castro, Y.; Pascual, L.; Chen, G.; Sundararajan, M.; Pascual, M.J.; et al. Oxyfluoride glass–ceramic fibers doped with Nd3+: Structural and optical characterization. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6620–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Yu, H.; Ouyang, T.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, J.; Dong, G. Novel Er3+/Ho3+-codoped glass-ceramic fibers for broadband tunable mid-infrared fiber lasers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 3956–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, S.; Mochizuki, C.; Kimura, T. Formation of LaF3 microcrystals in sol-gel silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 244, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Maciel, G.S.; Friend, C.S.; Prasad, P.N. Upconversion properties of a transparent Er3+-Yb3+ co-doped LaF3-SiO2 glass-ceramics prepared by sol-gel method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 316, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, S.; Koji, S.; Kimura, T. Structure and optical properties of (Gd,Eu)F3-nanocrystallized sol–gel silica films. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Araújo, C.C.; Bueno, L.A.; Gonçalves, R.R.; Messaddeq, Y. Sol-gel Eu3+/Tm3+ doped transparent glass-ceramic waveguides. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 348, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Bao, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X. Crystallization behavior of PbF2-SiO2based bulk xerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 347, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, D.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, F. Transparent glass ceramic containing Er3+: CaF2 nano-crystals prepared by sol–gel method. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3988–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.J.; Yanes, A.C.; Del-Castillo, J.; Méndez-Ramos, J.; Rodríguez, V.D. Optical properties of Ho3+-Yb3+ co-doped nanostructured SiO2-LaF3 glass-ceramics prepared by sol-gel method. Phys. Status Solidi 2007, 204, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del-Castillo, J.; Yanes, A.C. Bright luminescence of Gd3+ sensitized RE3+-doped SiO2-BaGdF5 glass-ceramics for UV-LEDs colour conversion. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 3736–3743. [Google Scholar]
- Szpikowska-Sroka, B.; Pawlik, N.; Goryczka, T.; Pietrasik, E.; Bańczyk, M.; Pisarski, W.A. Lead fluoride β-PbF2 nanocrystals containing Eu3+ and Tb3+ ions embedded in sol-gel materials: Thermal, structural and optical investigations. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 8424–8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpikowska-Sroka, B.; Pawlik, N.; Goryczka, T.; Pisarski, W.A. Influence of silicate sol-gel host matrices and catalyst agents on the luminescent properties of Eu3+/Gd3+ under different excitation wavelengths. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98773–98782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secu, C.E.; Bartha, C.; Polosan, S.; Secu, M. Thermally activated conversion of a silicate gel to an oxyfluoride glass ceramic: Optical study using Eu3+ probe ion. J. Lumin. 2014, 146, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secu, C.E.; Negrea, R.F.; Secu, M. Eu3+ probe ion for rare-earth dopant site structure in sol–gel derived LiYF4 oxyfluoride glass–ceramic. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 2456–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Alonso, A.; Méndez-Ramos, J.; Yanes, A.C.; Del-Castillo, J.; Rodríguez, V.D. Up-conversion in sol-gel derived nano-glass-ceramics comprising NaYF4 nano-crystals doped with Yb3+, Ho3+ and Tm3+. Opt. Mater. 2010, 32, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpikowska-Sroka, B.; Zur, L.; Czoik, R.; Goryczka, T.; Swinarew, A.S.; Zadlo, M.; Pisarski, W.A. Long-lived emission from Eu3+:PbF2 nanocrystals distributed into sol–gel silica glass. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballato, J.; Riman, R.E.; Snitzer, E. Sol–gel synthesis of fluoride optical materials for planar integrated photonic applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1997, 213–214, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.A.; Riman, R.; Snitzer, E. Solution synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of high Er3+ content LaF3 for broadband 1.5 μm amplification. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L.; West, J.K. The sol-gel process. Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 33–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Durán, A.; Castro, Y. Transparent Glass-Ceramics Produced by Sol-Gel: A Suitable Alternative for Photonic Materials. Materials 2018, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Zuazo, J.; Ferrer, P.; López, A.; Gutiérrez-León, A.; Silva, I.; Castro, G.R. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A The multipurpose X-ray diffraction end-station of the BM25B-SpLine synchrotron beamline at the ESRF. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2013, 716, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenzi, P.; Abdirashid, M.O.; Guglielmi, M. Structure and properties of sol-gel coatings from methyltriethoxysilane and tetraethoxysilane. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1994, 3, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lee, H.R.; Tsuru, T. Study on Preparation and Hydrophobicity of MTES Derived Silica Sol and Gel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 535–537, 2563–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Pascual, M.J.; Caballero, A.; Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Castro, Y.; Durán, A. Crystallization mechanism in sol-gel oxyfluoride glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 501, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Bao, F. Investigation on crystallization and influence of Nd3+ doping of transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Bocker, C.; Heil, T.; Jinschek, R.; Höche, T.; Rüssel, C.; Kohl, H. Experimental Evidence of Self-Limited Growth of Nanocrystals in Glass Experimental Evidence of Self-Limited Growth of Nanocrystals in Glass. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2493–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Höche, T.; Hemono, N.; Pascual, M.J.; van Aken, P.A. Nano-crystallization in LaF3-Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2 glass. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 4350–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablos-Martín, A.; Muñoz, F.; Mather, G.C.; Patzig, C.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Jinschek, J.R.; Höche, T.; Durán, A.; Pascual, M.J. KLaF4 nanocrystallization in oxyfluoride glass-ceramics. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 10323–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablos-Martín, A.; Hémono, N.; Mather, G.C.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Höche, T.; Bornhöft, H.; Deubener, J.; Muñoz, F.; Durán, A.; Pascual, M.J. Crystallization kinetics of LaF3 nanocrystals in an oxyfluoride glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 2420–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Gorni, G.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Pascual, L.; Durán, A.; Castro, Y. Transparent SiO2-GdF3 sol–gel nano-glass ceramics for optical applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.Q. Crystal radii and effective ionic radii of the rare earth ions. J. Solid State Chem. 1991, 95, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Velázquez, J.J.; Pascual, L.; Mosa, J.; Durán, A.; Castro, Y. 80SiO2-20LaF3 oxyfluoride glass ceramic coatings doped with Nd3+ for optical applications. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2018, 9, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Bai, T.; Dong, W.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Feng, S. Microwave-assisted synthesis and up–down conversion luminescent properties of multicolor hydrophilic LaF3:Ln3+ nanocrystals. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, B.K.; Verma, L.P. A rule for chemical shifts of X-ray absorption edges. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1970, 3, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.G. Covalence of chemical bonds and white-line intensity of an L3-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure of rare earth elements embedded in glass. Met. Mater. Int. 2009, 15, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.I.; van der Laan, G.; Harrison, S.E.; Cibin, G.; Hesjedal, T. Oxidation Effects in Rare Earth Doped Topological Insulator Thin Films. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pablos-Martín, A.; García, M.A.; Muñoz-Noval, A.; Castro, G.R.; Pascual, M.J.; Durán, A. Analysis of the distribution of Tm3+ ions in LaF3 containing transparent glass-ceramics through X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 384, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantelle, G.; Mortier, M.; Vivien, D. EPR and optical studies of erbium-doped β-PbF2 single-crystals and nanocrystals in transparent glass–ceramics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 5591–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; Rubins, R.S. Electron Spin Resonance in Two Groups of Lanthanon Salts. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1961, 78, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.B.; Jefries, C.D. Spin-Lattice Relaxation of Rare-Earth Ions in LaF3. Phys. Rev. 1966, 149, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budoyo, R.P.; Kakuyanagi, K.; Toida, H.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Munro, W.J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Saito, S. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of Er3+:Y2SiO5 using a Josephson bifurcation amplifier: Observation of hyperfine and quadrupole structures. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2018, 2, 11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Evans, S.M.; Halliburton, L.E.; Slack, G.A.; Schujman, S.B.; Morgan, K.E.; Bondokov, R.T.; Mueller, G.; Yang, S.; Evans, S.M.; et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance of ions in aluminum nitride Electron paramagnetic resonance of Er3+ ions in aluminum nitride. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 23714–23715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | a (Å) | c (Å) | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Undoped LaF3 [JCPDS]1 | 7.187 | 7.350 | 328 |
| Er3+ doped GCs 550°C 1 m | 7.16 ± 0.01 | 7.32 ± 0.01 | 325 ± 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorni, G.; Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Mather, G.C.; Serrano, A.; Vila, M.; Castro, G.R.; Bravo, D.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; et al. Transparent Sol-Gel Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramics with High Crystalline Fraction and Study of RE Incorporation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040530
Gorni G, Velázquez JJ, Mosa J, Mather GC, Serrano A, Vila M, Castro GR, Bravo D, Balda R, Fernández J, et al. Transparent Sol-Gel Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramics with High Crystalline Fraction and Study of RE Incorporation. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(4):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040530
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorni, Giulio, Jose J. Velázquez, Jadra Mosa, Glenn C. Mather, Aida Serrano, María Vila, Germán R. Castro, David Bravo, Rolindes Balda, Joaquín Fernández, and et al. 2019. "Transparent Sol-Gel Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramics with High Crystalline Fraction and Study of RE Incorporation" Nanomaterials 9, no. 4: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040530
APA StyleGorni, G., Velázquez, J. J., Mosa, J., Mather, G. C., Serrano, A., Vila, M., Castro, G. R., Bravo, D., Balda, R., Fernández, J., Durán, A., & Castro, Y. (2019). Transparent Sol-Gel Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramics with High Crystalline Fraction and Study of RE Incorporation. Nanomaterials, 9(4), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040530