Self-Assembly Fluorescent Cationic Cellulose Nanocomplex via Electrostatic Interaction for the Detection of Fe3+ Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of SPOTPE
2.3. Preparation of SPOTPE/QC Solutions
2.4. Fluorescence Detection of Fe3+ Ions
2.5. In Vitro Release of SPOTPE from SPOTPE/QC Complexes with/without Fe3+ Ions
2.6. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
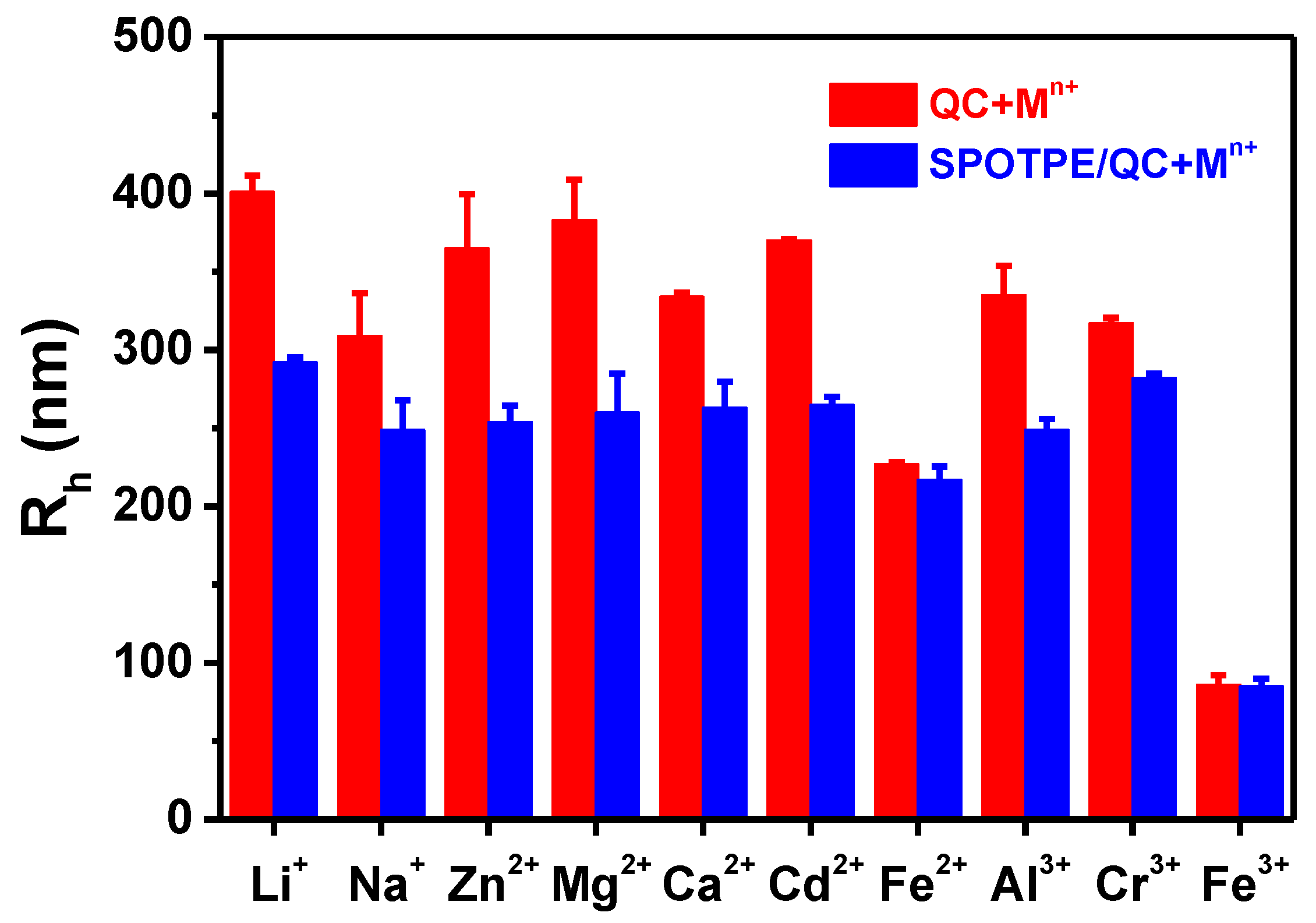
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of SPOTPE/QC Solutions
3.2. Fluorescence Properties of SPOTPE/QC Solutions
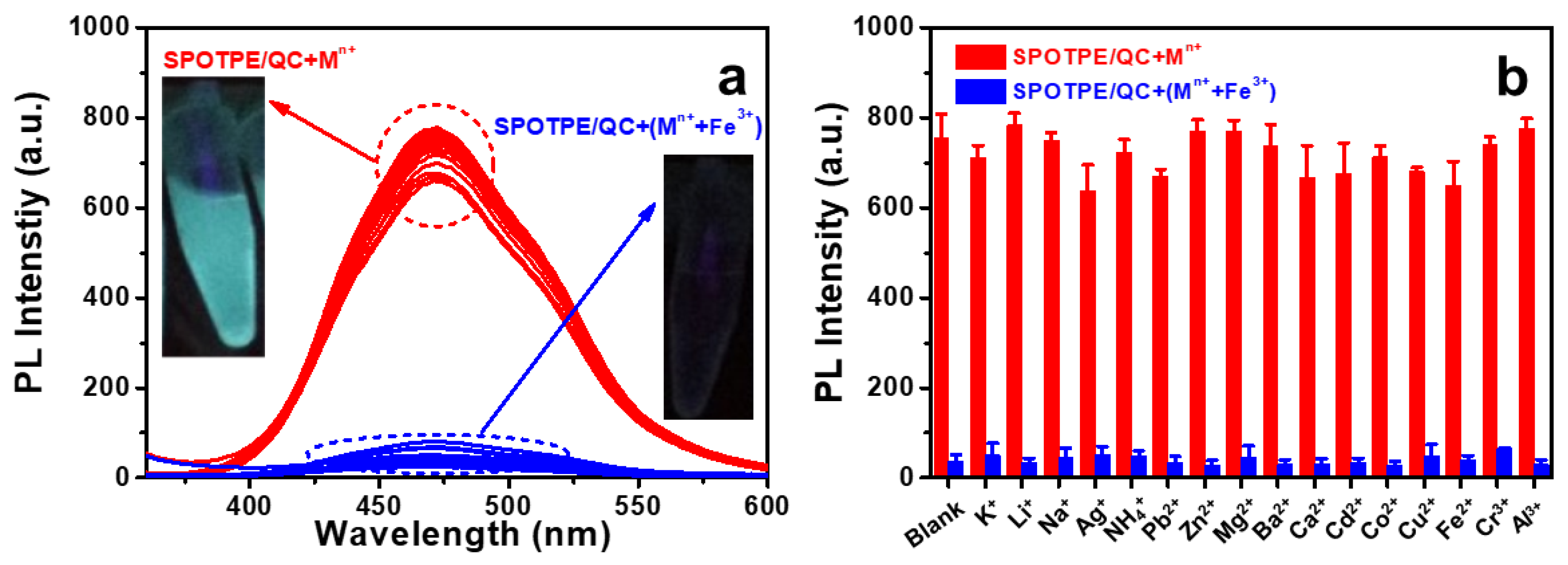
3.3. Selective Detection of Fe3+ Ions
3.4. Quenching Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahoo, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Bera, R.K.; Crisponi, G.; Callan, J.F. Iron(III) selective molecular and supramolecular fluorescent probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7195–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, E.C.; Goss, D.J. Living. with iron (and Oxygen): Questions and answers about iron homeostasis. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4568–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, C.D.; Kaplan, J. Iron acquisition and transcriptional regulation. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4536–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelles, A.S.; Garcia, V.A.; de Lima, M.N.; Vedana, G.; Alcalde, L.A.; Bogo, M.R.; Schroder, N. mRNA expression of proteins involved in iron homeostasis in brain regions is altered by age and by iron overloading in the neonatal period. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaeta, A.; Hider, R.C. The crucial role of metal ions in neurodegeneration: The basis for a promising therapeutic strategy. Br. J. Pharmacol 2005, 146, 1041–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Pan, D.; Lin, M.; Han, H.; Li, F. Graphene oxide-assisted synthesis of bismuth nanosheets for catalytic stripping voltammetric determination of iron in coastal waters. Microchim. Acta 2015, 183, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Caruso, U.; Concilio, S.; Piotto, S.; Tuzi, A.; Panunzi, B. A real-time tripodal colorimetric/fluorescence sensor for multiple target metal ions. Dyes Pigment. 2018, 155, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Lee, W.; Ko, G.; Yin, J.; Yoon, J. Recent progress in the development of organic dye based near-infrared fluorescence probes for metal ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 354, 74–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.-R.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. From ACQ to AIE: The suppression of the strong pi-pi interaction of naphthalene diimide derivatives through the adjustment of their flexible chains. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11496–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, N.; Cui, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Dong, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, G. AIE-doped poly(ionic liquid) photonic spheres: A single sphere-based customizable sensing platform for the discrimination of multi-analytes. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6281–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.N.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Phenomenon, mechanism and applications. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4332–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.D.; Xie, Z.L.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Qiu, C.F.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.W.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhu, D.B.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Together We Shine, United We Soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, R.T.K.; Geng, J.L.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Zhao, E.G.; Wang, G.; Zhan, R.Y.; Liu, B.; Tang, B. Water-soluble bioprobes with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for light-up sensing of heparin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4134–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.K.; Lee, J.; Min, I.; Vales, T.P.; Choi, K.H.; Park, B.J.; Cho, S.; Kim, H.J. Aggregation-induced emission of tetraphenylethene-conjugated phenanthrene derivatives and their bio-imaging applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 728. [Google Scholar]
- Duong Duc, L.; Bhosale, S.V.; Jones, L.A.; Bhosale, S.V. Tetraphenylethylene-based aie-active probes for sensing applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12189–12216. [Google Scholar]
- Khandare, D.G.; Joshi, H.; Banerjee, M.; Majik, M.S.; Chatterjee, A. Fluorescence turn-on chemosensor for the detection of dissolved CO2 based on ion-induced aggregation of tetraphenylethylene derivative. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10871–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanji, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kawamata, S.; Tanaka, M.; Itagaki, S.; Gunji, T. Fluorescence “turn-on” detection of melamine with aggregation-induced-emission-active tetraphenylethene. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15254–15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, D.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X. Fluorescence turn-on detection of DNA based on the aggregation-induced emission of conjugated poly(pyridinium salt)s. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 4045–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.R.; Saha, S.K.; Wang, Z.Y. Ultra-sensitive detection of explosives in solution and film as well as the development of thicker film effectiveness by tetraphenylethene moiety in AIE active fluorescent conjugated polymer. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5638–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.T.; Xue, W.X.; Cai, Z.X.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, D.Q. A facile and convenient fluorescence detection of gamma-ray radiation based on the aggregation-induced emission. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 14487–14491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.B.; Chen, J.L.; Xu, B.; Fu, X.Q.; Tian, W.J. Folic acid-functionalized AIE Pdots based on amphiphilic PCL-b-PEG for targeted cell imaging. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3824–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.S.; Chen, X.T.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Z.J.; Wei, R.R.; Tong, A.J. A ratiometric fluorescent pH probe based on aggregation-induced emission enhancement and its application in live-cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13470–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, J.S.; Chua, M.H.; Yan, H.; Tang, B.Z.; Xu, J.W. Poly(acrylate) with a tetraphenylethene pendant with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics: Highly stable AIE-active polymer nanoparticles for effective detection of nitro compounds. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5628–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, S.; Qu, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, A.; Hu, R.; Tang, B.Z. Thermoresponsive AIE polymers with fine-tuned response temperature. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 2964–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Lam, J.W.; Qin, W.; Kwok, R.T.; Xie, N.; Hu, Q.; Tang, B.Z. Long-term fluorescent cellular tracing by the aggregates of AIE bioconjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8238–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.Q.; He, T.; Song, J.; Chen, S.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Yu, Y.J.; Chen, S.G. A new AIE multi-block polyurethane copolymer material for subcellular microfilament imaging in living cells. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7541–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, T.; Hong, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S. A general strategy to construct fluorogenic probes from charge-generation polymers (CGPs) and AIE-active fluorogens through triggered complexation. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Liu, M.; Chen, T.; Huang, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, J.; Wen, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Facile construction and biological imaging of cross-linked fluorescent organic nanoparticles with aggregation-induced emission feature through a catalyst-free azide-alkyne click reaction. Dyes Pigment. 2018, 148, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Tong, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Ji, J.; Jin, Q. Zwitterionic phosphorylcholine-tpe conjugate for ph-responsive drug delivery and aie active imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21185–21192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; He, S.; Huang, Y.; Cui, D. Synthesis and AIE properties of PEG-PLA-PMPC based triblock amphiphilic biodegradable polymers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Pan, Y.; Manghnani, P.N.; Liu, B. AIE polymers: Synthesis, properties, and biological applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Tao, L.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y. Polymeric AIE-based nanoprobes for biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11486–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Homogeneous quaternization of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solutions as gene carriers. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, M.; Zheng, Z.; Chi, Z.; Tian, W.; Jin, C.; et al. High-performance two-photon absorption luminophores: Large action cross sections, free from fluorescence quenching and tunable emission of efficient non-doped organic light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3416–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.N.; Meng, L.M.; Chen, S.J.; Leung, C.W.T.; Da, L.T.; Faisal, M.; Silva, D.A.; Liu, J.Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Huang, X.H.; et al. Monitoring and inhibition of insulin fibrillation by a small organic fluorogen with aggregation-induced emission characteristics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, F.; Fukui, N. The behavior of cellulose molecules in aqueous environments. Cellulose 2004, 11, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, A.; Butchosa, N.; Berglund, L.A.; Zhou, Q. Surface quaternized cellulose nanofibrils with high water absorbency and adsorption capacity for anionic dyes. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACS. Guidelines for data acquisition and data quality evaluation in environmental chemistry. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Yu, M.; Liu, J. Fluoranthene-based pyridine as fluorescent chemosensor for Fe3+. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 1656–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Synthesis and photophysical behavior of pyrene-bearing cellulose nanocrystals for Fe3+ sensing. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

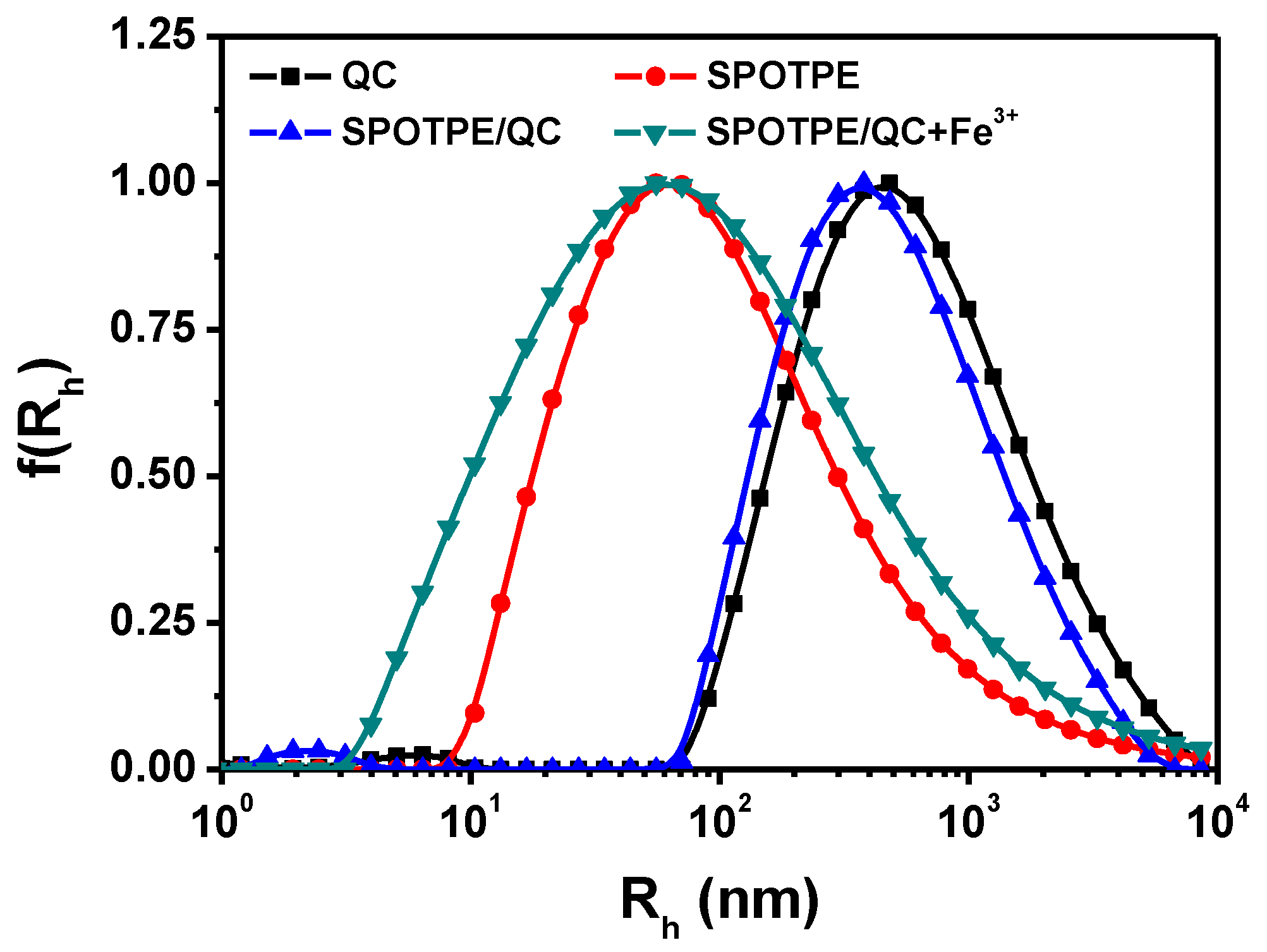

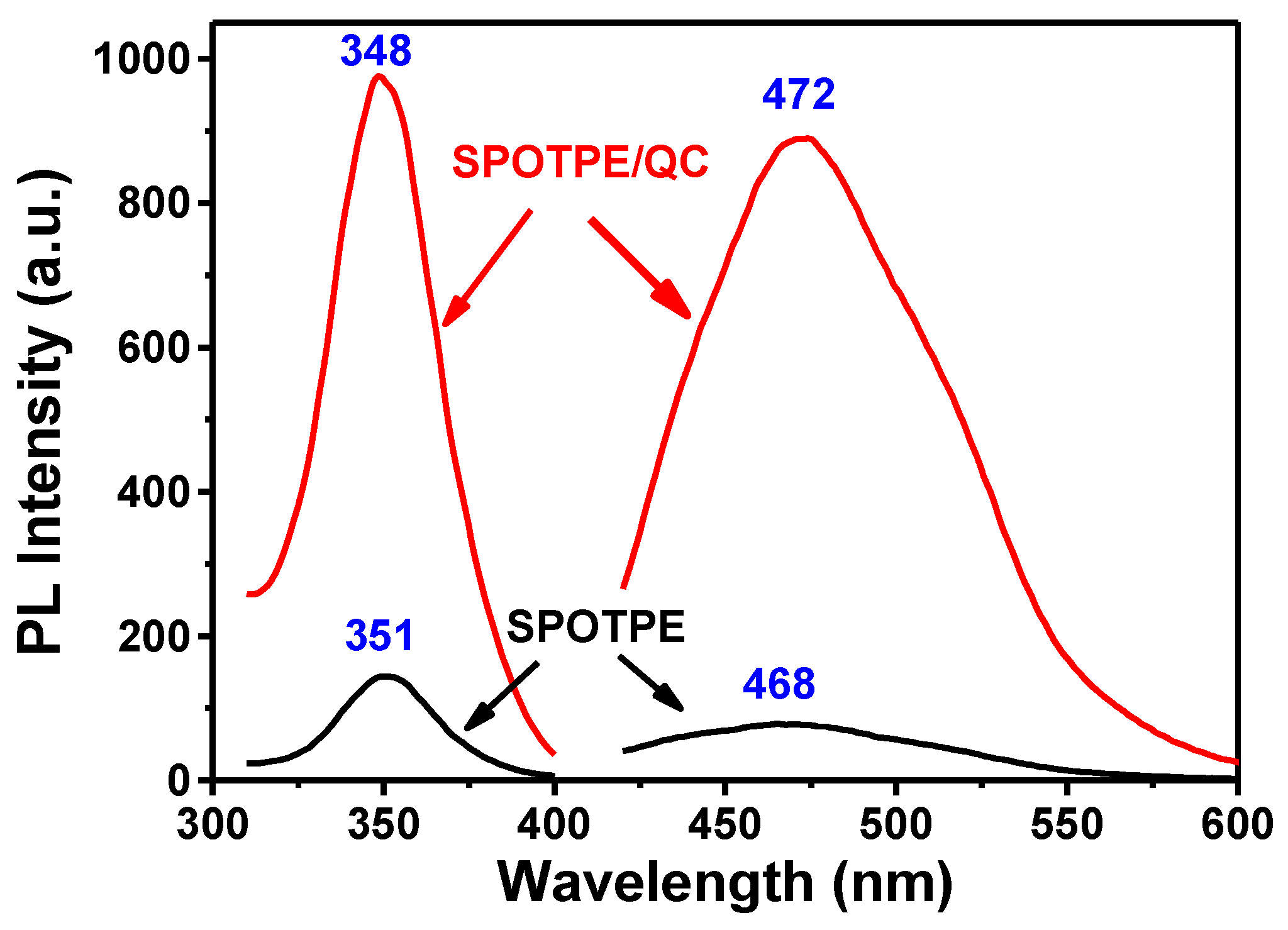

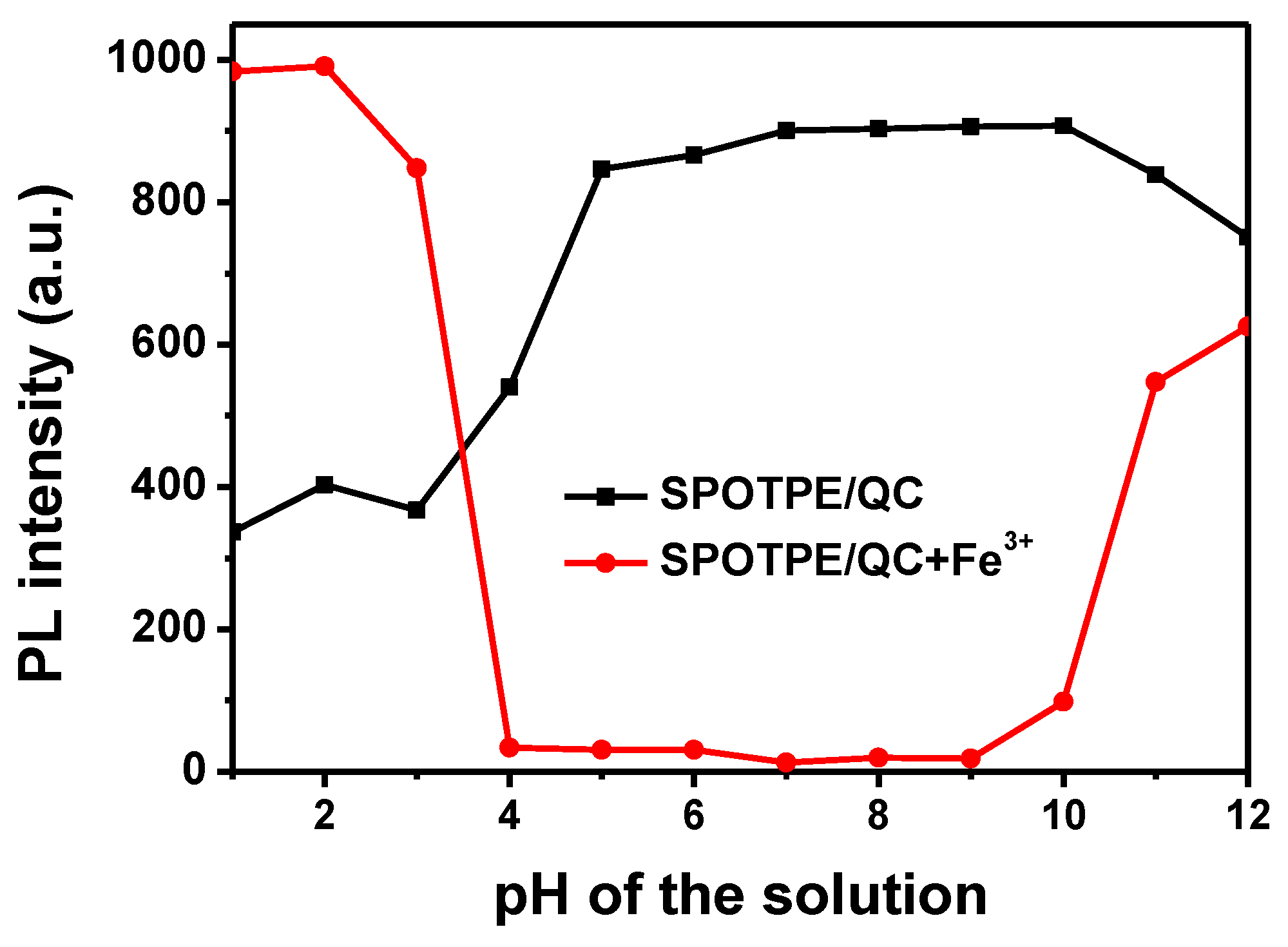
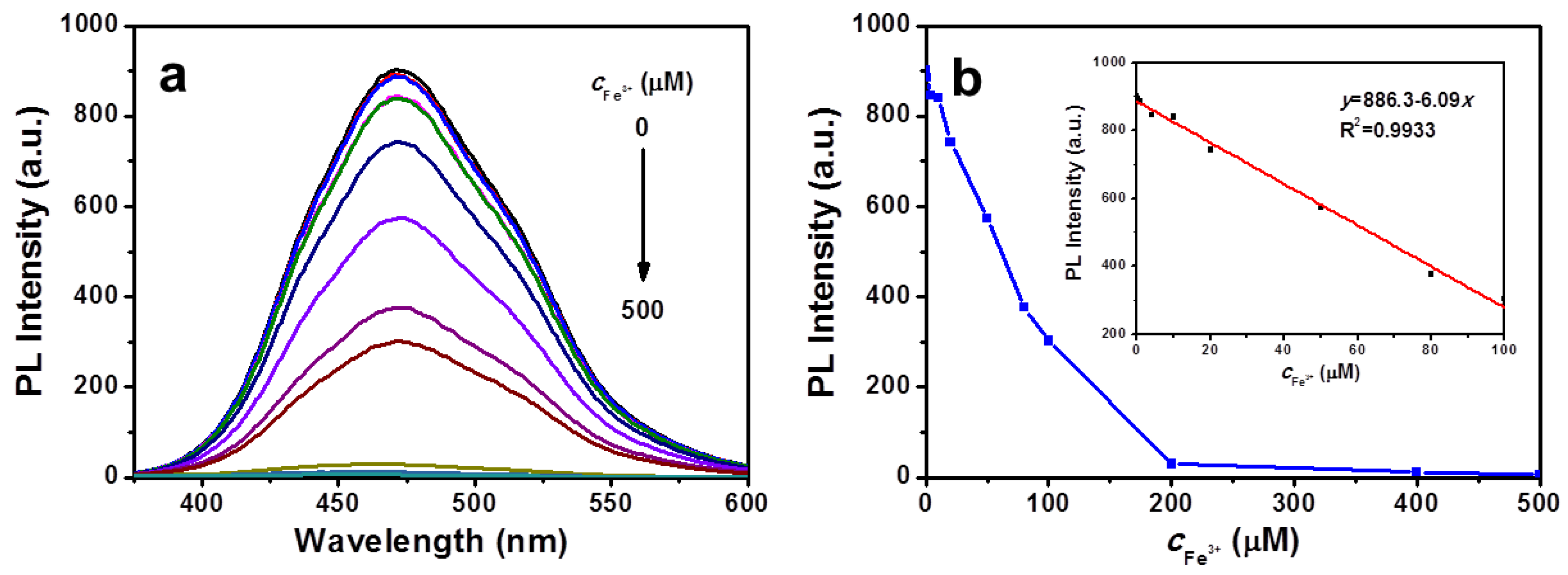
| Code | QC | SPOTPE | SPOTPE/QC | SPOTPE/QC+Fe3+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ζ (mV) | 48.3 | −14.6 | 46.4 | 42.7 |
| Rh (nm) | 571 | 82 | 467 | 85 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhou, J. Self-Assembly Fluorescent Cationic Cellulose Nanocomplex via Electrostatic Interaction for the Detection of Fe3+ Ions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020279
Wang H, Ye X, Zhou J. Self-Assembly Fluorescent Cationic Cellulose Nanocomplex via Electrostatic Interaction for the Detection of Fe3+ Ions. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020279
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haoying, Xiu Ye, and Jinping Zhou. 2019. "Self-Assembly Fluorescent Cationic Cellulose Nanocomplex via Electrostatic Interaction for the Detection of Fe3+ Ions" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020279
APA StyleWang, H., Ye, X., & Zhou, J. (2019). Self-Assembly Fluorescent Cationic Cellulose Nanocomplex via Electrostatic Interaction for the Detection of Fe3+ Ions. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020279




