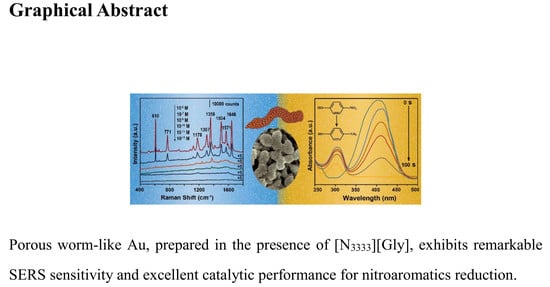
Ionic Liquid-Modulated Synthesis of Porous Worm-Like Gold with Strong SERS Response and Superior Catalytic Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization
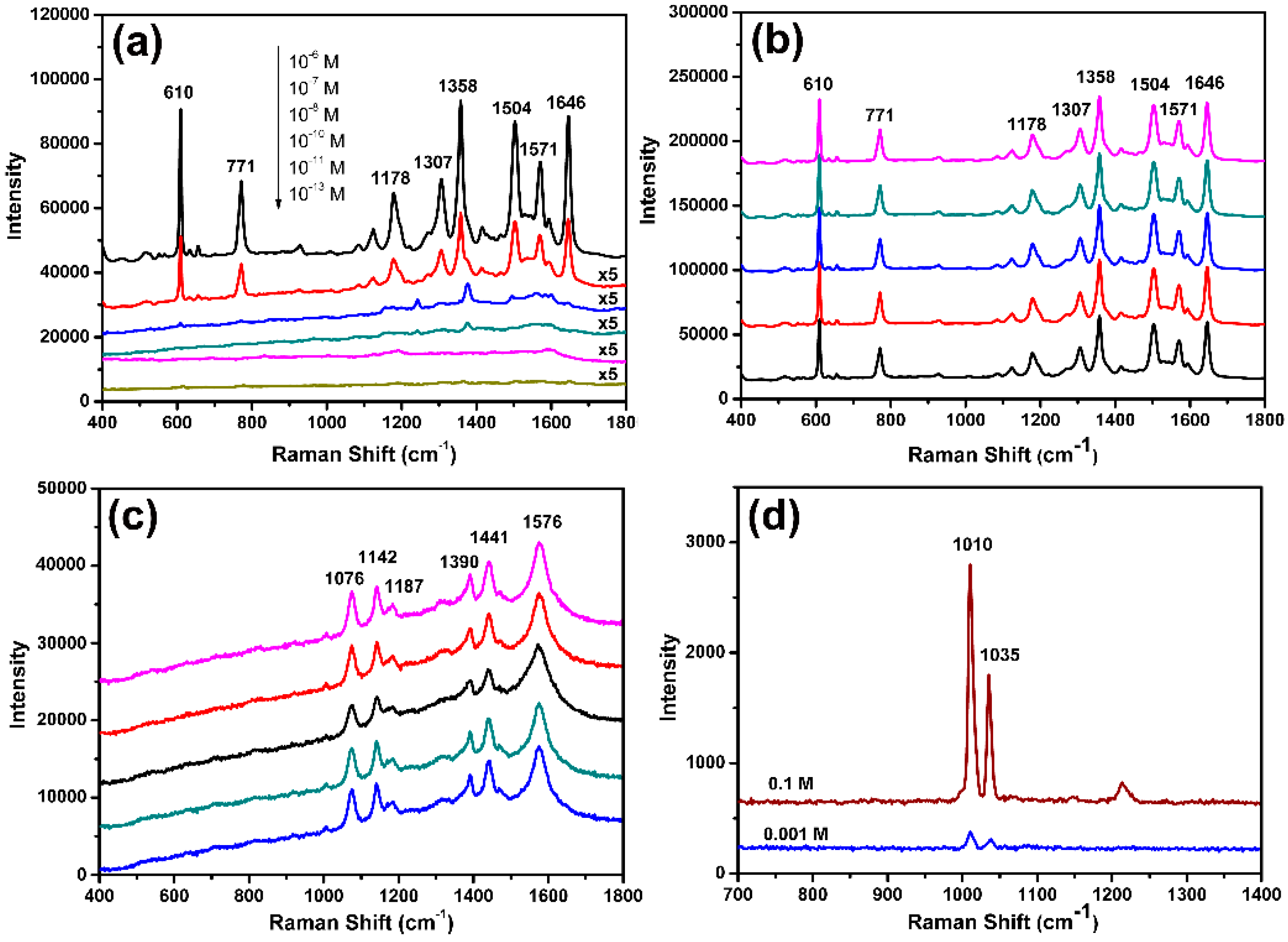
2.4. SERS Measurements
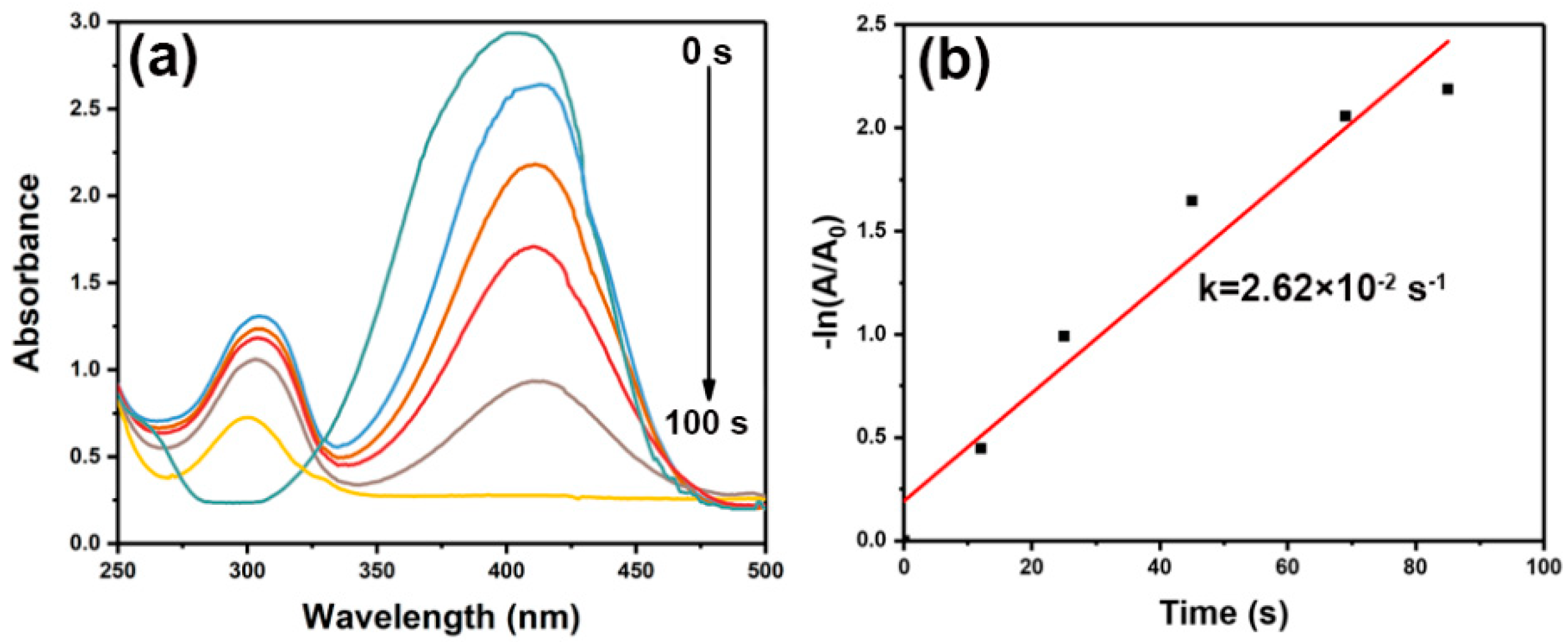
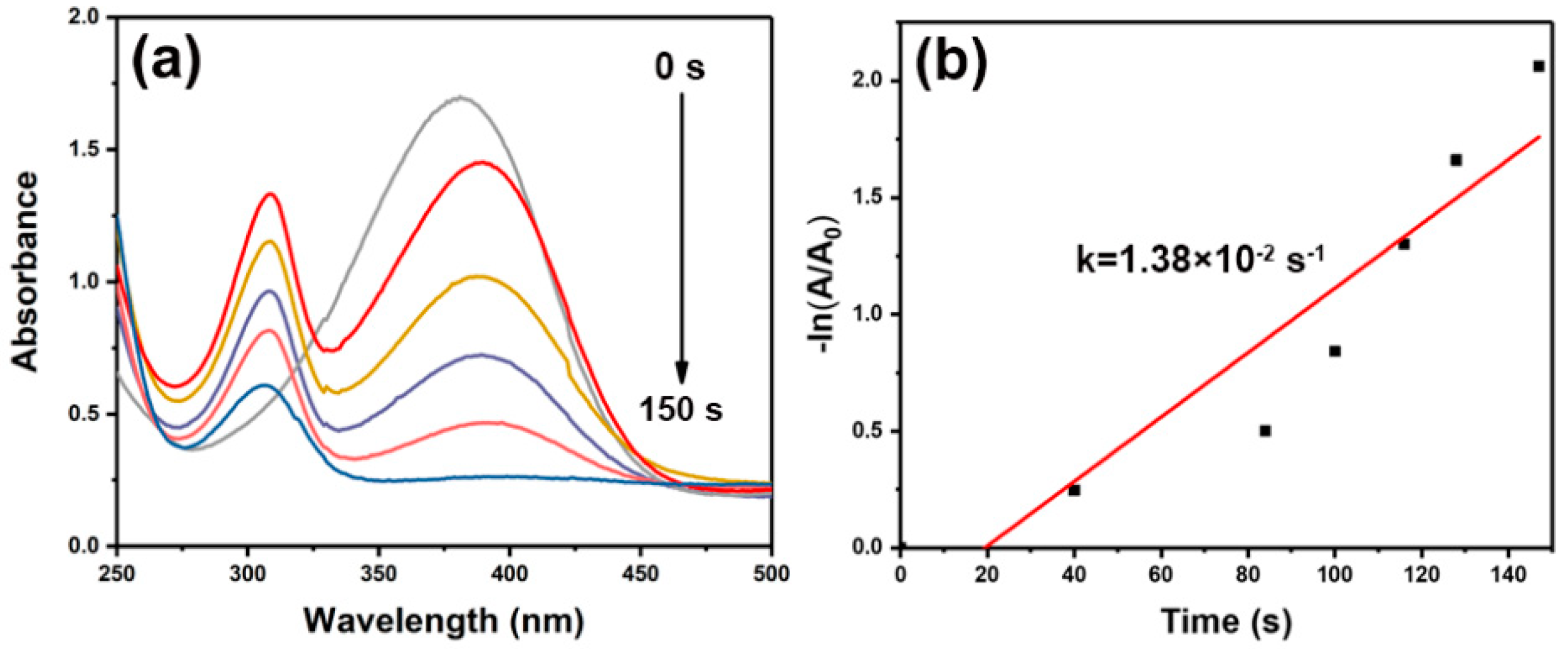
2.5. Catalytic Reduction of Nitaromatics
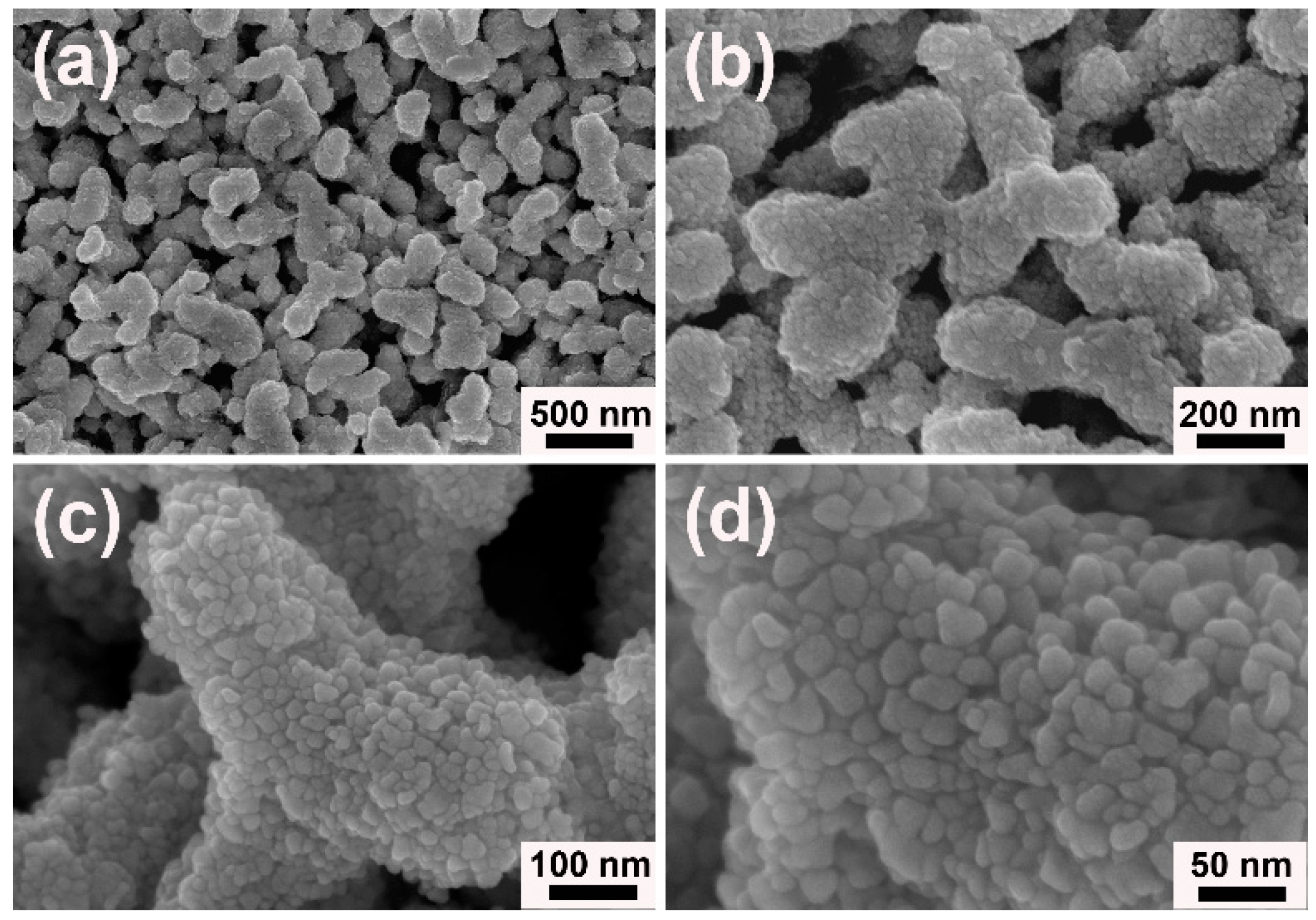
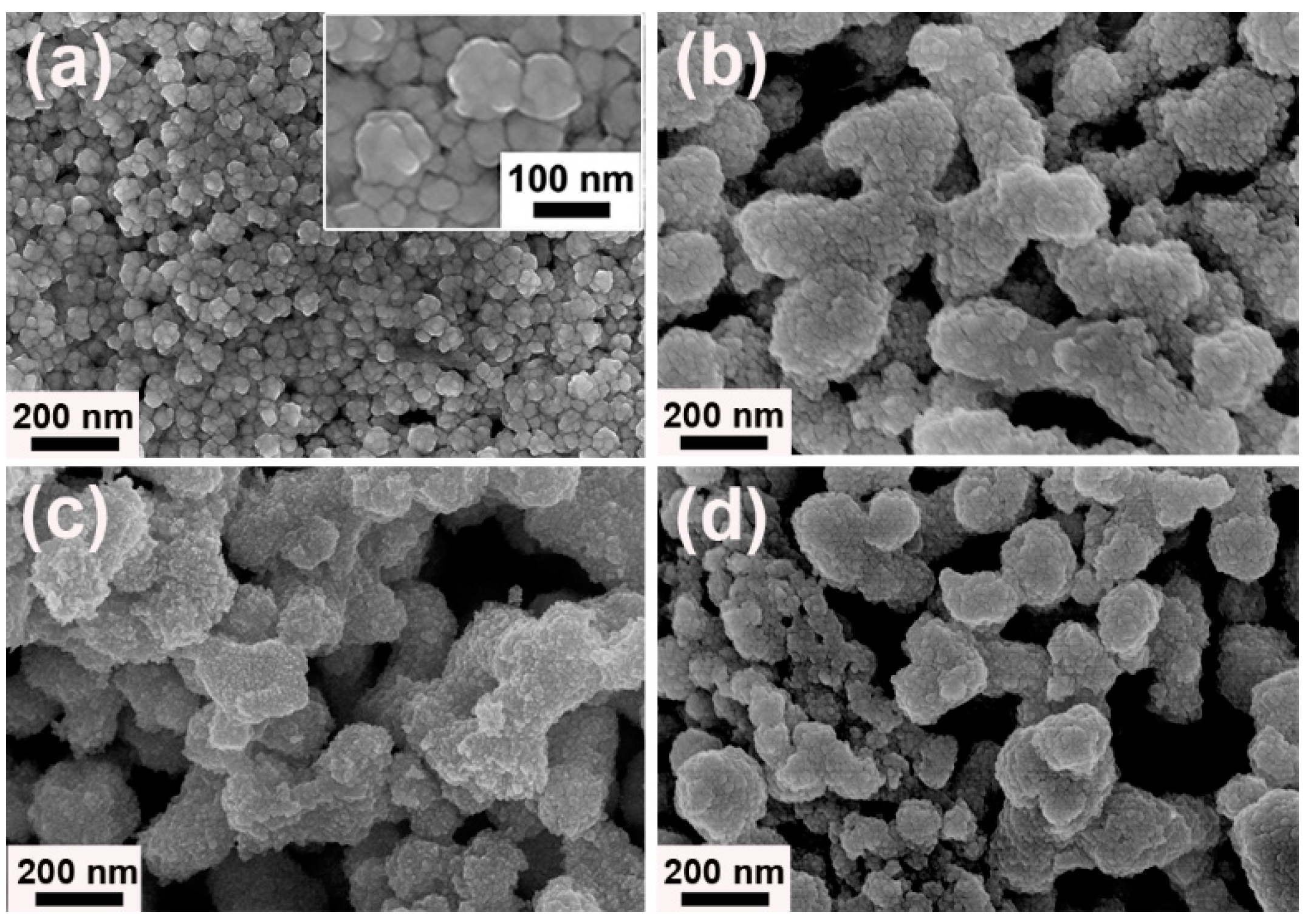
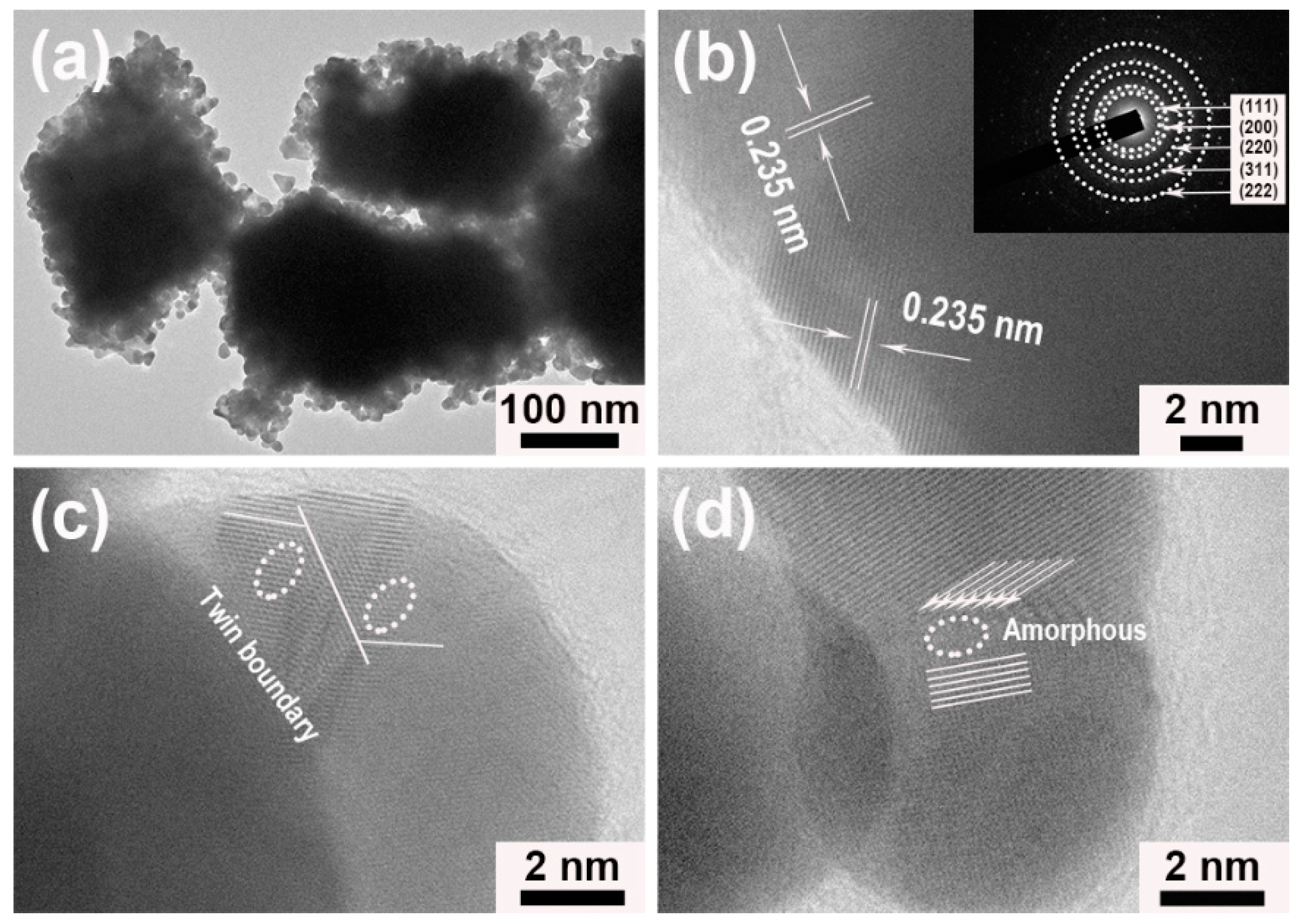
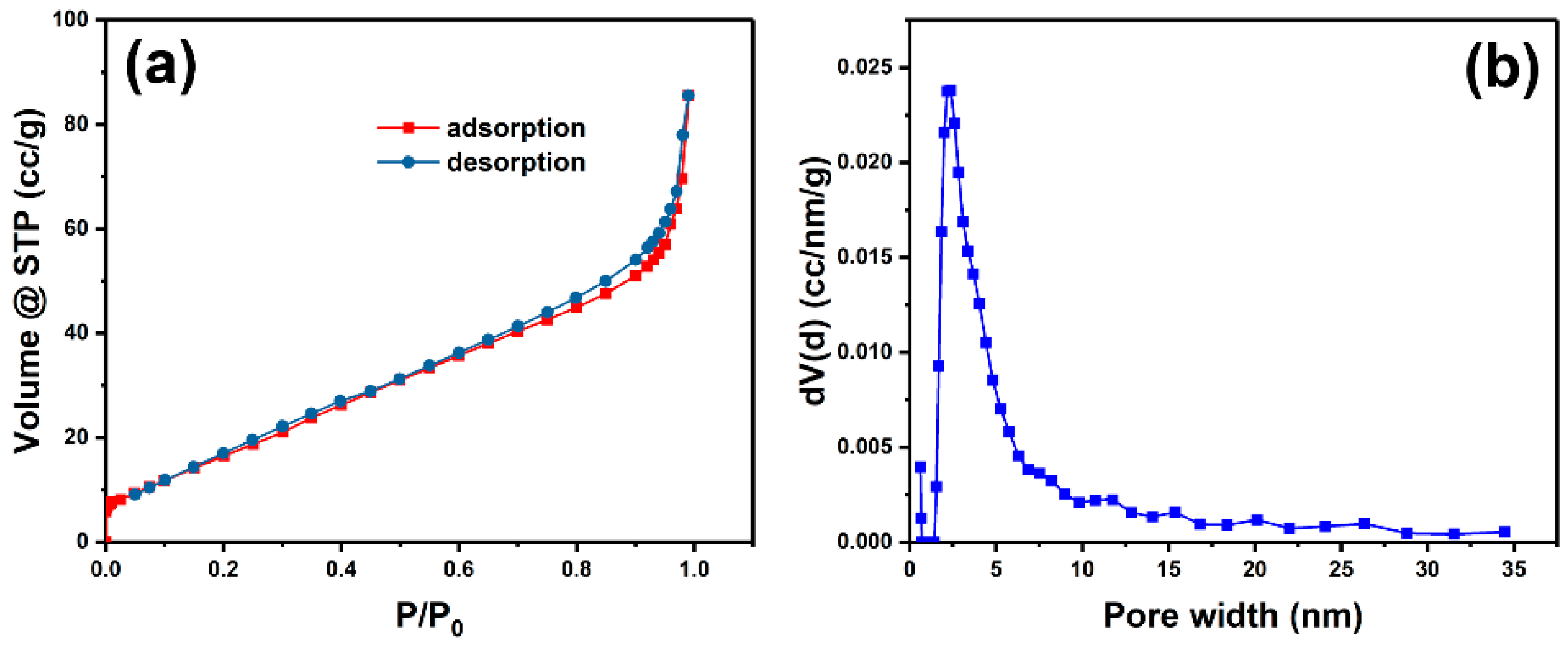
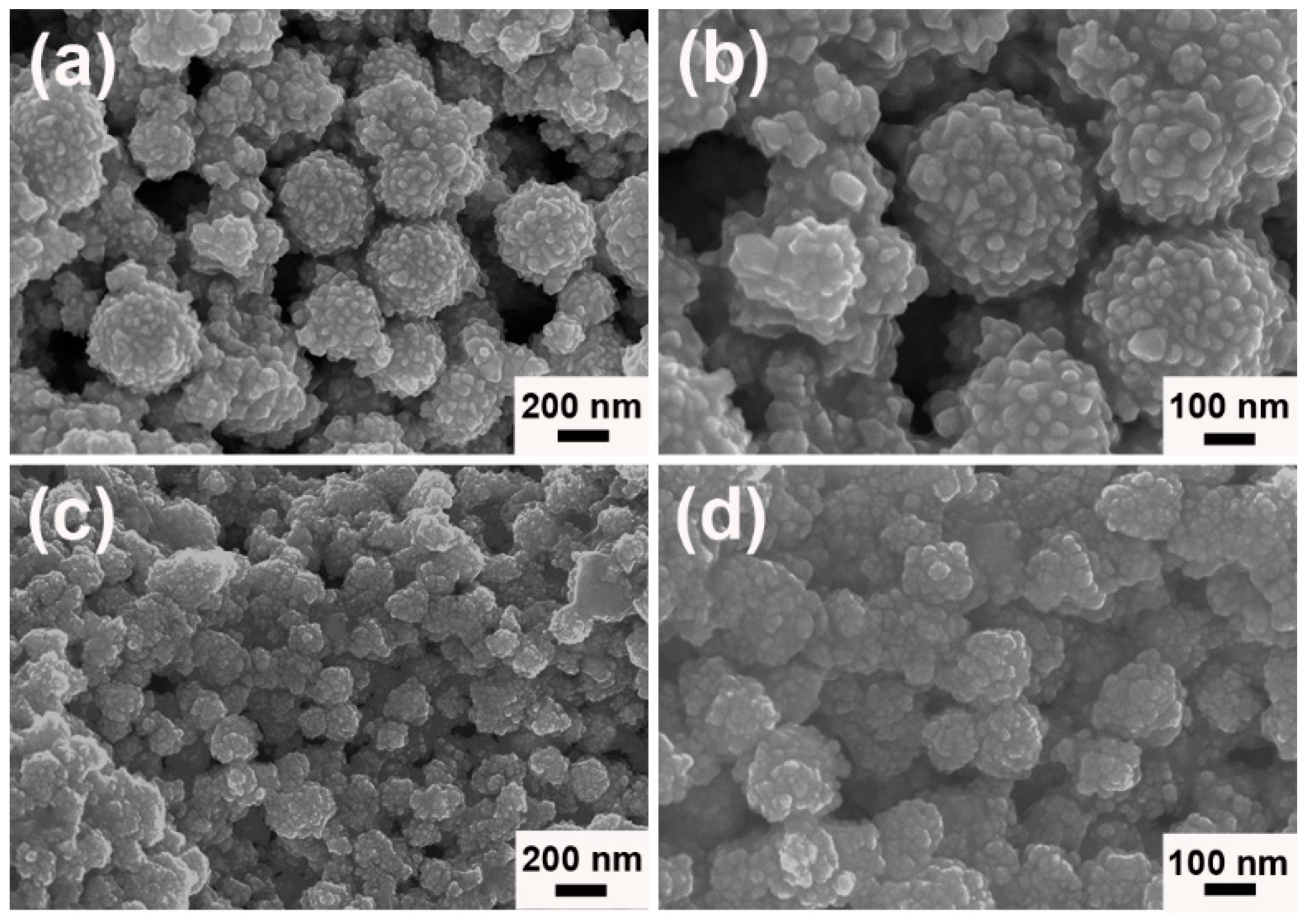
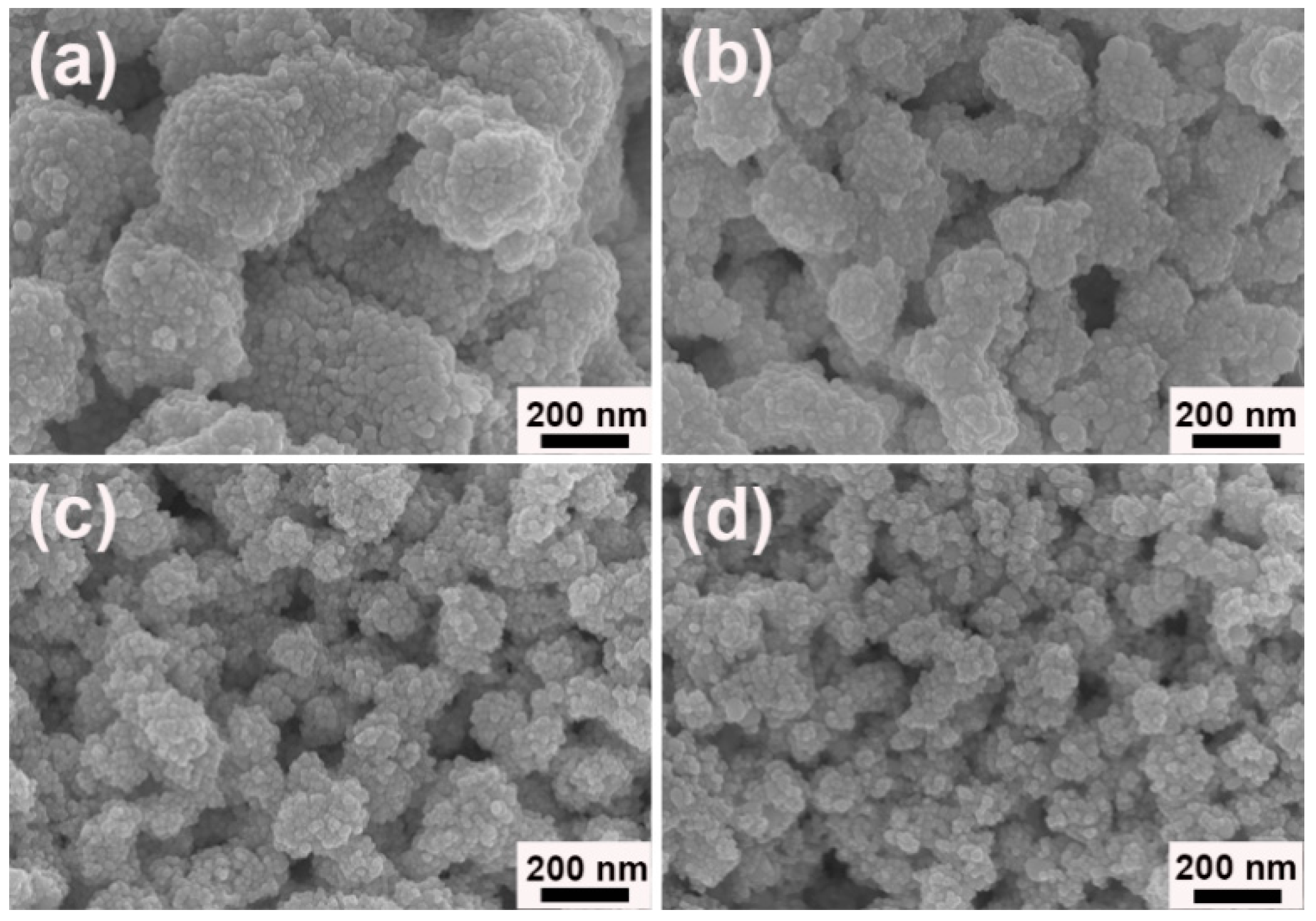
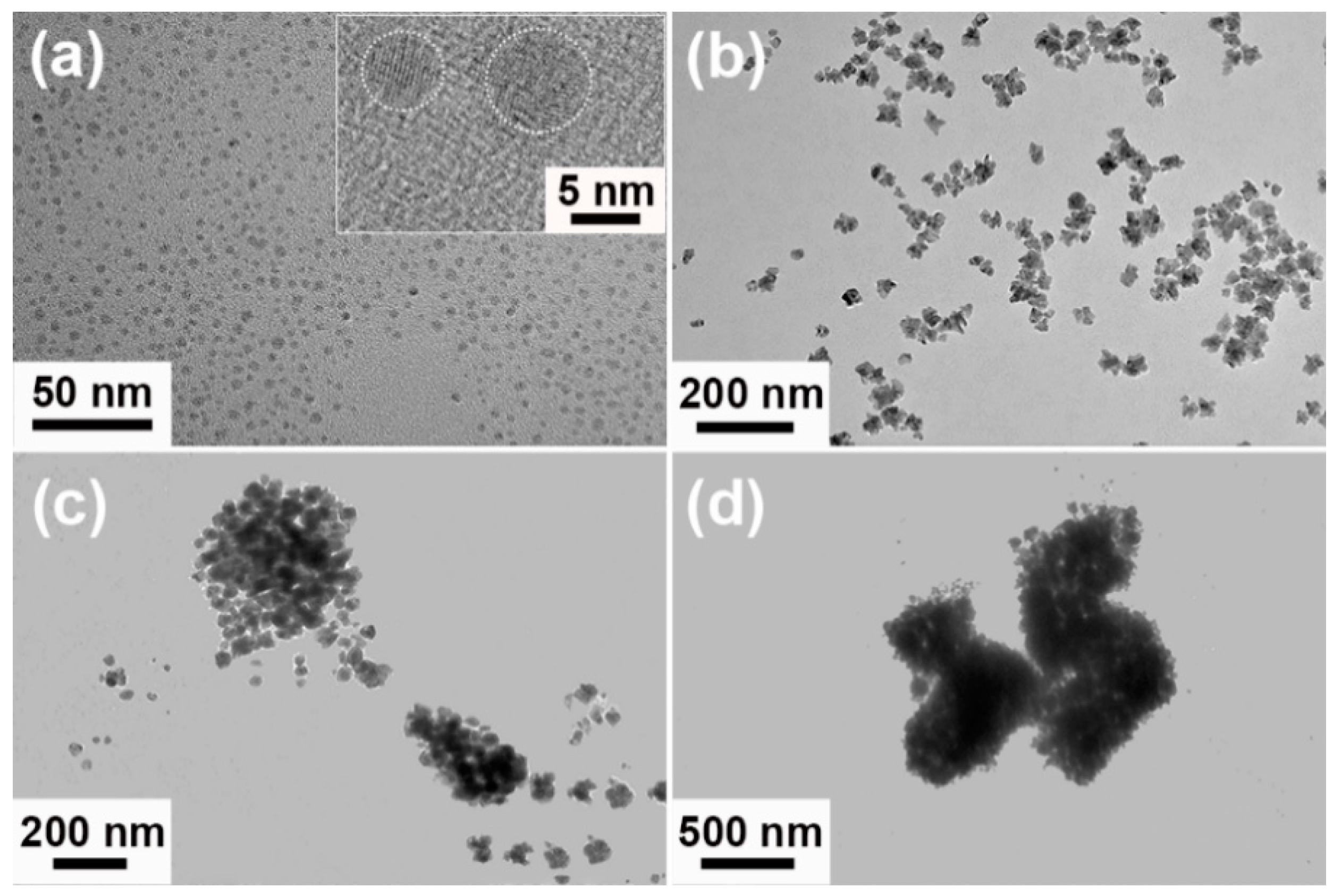
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wittstock, A.; Zielasek, V.; Biener, J.; Friend, C.; Bäumer, M. Nanoporous gold catalysts for selective gas-phase oxidative coupling of methanol at low temperature. Science 2010, 327, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graf, M.; Haensch, M.; Carstens, J.; Wittstock, G.; Weissmüller, J. Electrocatalytic methanol oxidation with nanoporous gold: Microstructure and selectivity. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17839–17848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villa, A.; Dimitratos, N.; Chan-Thaw, C.; Hammond, C.; Veith, G.; Wang, D.; Manzoli, M.; Prati, L.; Hutchings, G. Characterisation of gold catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4953–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anker, S.; Kitchens, C. Impact of gold nanoparticle stabilizing ligands on the colloidal catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5553–5560. [Google Scholar]
- Anker, J.N.; Hall, W.P.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N.C.; Zhao, J.; Duyne, R. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, J.; Langer, J.; de Abserasturi, D.J.; Liz-marzán, L.M. Anisotropic metal nanoparticles for surface enhanced reman scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3866–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, M.F.; Vander, E.E.; Hackler, R.A.; Mcanally, M.O.; Stair, P.C.; Schatz, G.C.; Duyne, R.P.V. Expanding applications of SERS through versatile nanomaterials engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3886–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeis, R.; Lei, T.; Sieradzki, K.; Snyder, J.; Erlebacher, J. Catalytic reduction of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide by nanoporous gold. J. Catal. 2008, 253, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Ding, Y. Xylanase immobilized nanoporous gold as a highly active and stable biocatalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 161, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Vainio, U.; Kornowski, A.; Ritter, M.; Weller, H.; Jin, H.; Weissmüller, J. Porous gold with a nested network architecture and ultrafine structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Ning, S.; Liu, P.; Ding, Y.; Hirata, A.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M. Tuning surface structure of 3D nanoporous gold by surfactant-free electrochemical potential cycling. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Cai, W.; Lin, Y.; Chen, B. Au nanochain-built 3D netlike porous films based on laser ablation in water and electrophoretic deposition. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7223–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, B. Synergism of interparticle electrostatic repulsion modulation and heat-induced fusion: A generalized one-step approach to porous network-like noble metals and their alloy nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 22, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J. Effect of pH on anodic formation of nanoporous gold films in chloride solutions: Optimization of anodization for ultrahigh porous structures. Langmuir 2014, 30, 4844–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, K.; Masuda, H. Anodization of gold in oxalate solution to form a nanoporous black film. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 123, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedireddy, S.; Lee, H.K.; Koh, C.S.; Tan, J.M.; Tjiu, W.W.; Ling, X.Y. Nanoporous gold bowls: A kinetic approach to control open shell structures and size-tunable lattice strain for electrocatalytic applications. Small 2016, 12, 4531–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimasaki, Y.; Kitahara, M.; Shoji, M.; Shimojima, A.; Wada, H.; Kuroda, K. Preparation of ordered mesoporous Au using double gyroid mesoporous silica KIT-6 via a seed-mediated growth process. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 3935–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Liu, L.; Feng, J.J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, A.J.; Xu, Q.Q. Poly (ionic liquid) assisted synthesis of hierarchical gold-platinum alloy nanodendrites with high electrocatalytic properties for ethylene glycol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 2016, 41, 14058–14067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, S.; Otaki, H.; Kitagawa, A.; Kitamura, K.; Morii, Y.; Ishihara, J.; Nishi, K.; Hashimoto, R.; Usui, T.; Chiba, K. Ionic liquid-mediated hydrofluorination of o-azaxylylenes derived from 3-bromooxindoles. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2572–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.; Fa, E.S.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: Past, present, and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ettelaie, R.; Yan, T.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, F.; Binks, B.P.; Yang, H. Ionic liquid droplet micro-reactor for catalysis reactions not at equilibrium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17387–17396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Sun, X.; Han, B. Synthesis of functional nanomaterials in ionic liquids. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Sun, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Han, B. Synthesis of hierarchical porous metals using ionic liquid-based media as solvent and template. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12683–12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Zhao, C.; Li, T.; Wang, N.; Lu, W.; Wang, J. An aqueous synthesis of porous PtPd nanoparticles with reversed bimetallic structures for highly efficient hydrogen generation from ammonia borane hydrolysis. Nanoscale 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Xu, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Tunable synthesis of Ag films at the interface of ionic liquids and water by changing cationic structures of ionic liquids. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zhao, C.; Wang, N.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of 3D nanoporous gold and its superior catalytic properties. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 6328–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Lu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Tailoring the properties of aqueous-ionic liquid interfaces for tunable synthesis and self-assembly of ZnS nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5140–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, R.; Mu, T.; Luan, Y. Ionic liquid assisted synthesis of Au-Pd bimetallic particles with enhanced electrocatalytic activity. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6005–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, W.; Qin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cen, J.; Jing, H.; Jing, Z.; Zheng, W. Ionic liquid-bifunctional modulated aggregate-coalescence mechanism to synthesize SnSe single-crystalline nanorod/nanoparticles core shell nanostructures and single-crystalline nanorods for optoelectronics. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Xu, Q. Bimetallic AuPt alloy nanodendrites/reduced graphene oxide: One-pot ionic liquid-assisted synthesis and excellent electrocatalysis towards hydrogen evolution and methanol oxidation reactions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Lee, J.M. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of platinum nanocubes and their improved electrocatalytic activity for the ammonia oxidation reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Yao, K.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Synthesis of various gold hierarchical architectures assisted by functionalized ionic liquids in aqueous solutions and their efficient SERS responses. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 531, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Vongehr, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Versatile synthesis of high surface area multimetallic nanosponges allowing control over nanostructure and alloying for catalysis and SERS detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3648–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Ray, C.; Roy, A.; Sahoo, R.; Pal, T. Mesoporous gold and palladium nanoleaves from liquid-liquid interface: Enhanced catalytic activity of the palladium analogue toward hydrazine-assisted room-temperature 4-nitrophenol reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9134–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.W.; Liu, J.; Balaji, T.; Xu, X.; Matsunaga, H.; Hakuta, Y.; Zuo, L.; Raveendran, P. A facile and template-free method to prepare mesoporous gold sponge and its pore size control. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10352–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielasek, V.; Jürgens, B.; Schulz, C.; Biener, J.; Biener, M.M.; Hamza, A.V.; Bäumer, M. Gold catalysts: Nanoporous gold foams. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 8241–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Qian, L.H.; Inoke, K.; Erlebacher, J.; Chen, M.W. Three-dimensional morphology of nanoporous gold. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, E.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Duan, X.; Huang, Y. Palladium-based nanostructures with highly porous features and perpendicular pore channels as enhanced organic catalysts. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Xu, D.; Henzie, J.; Feng, J.; Lopes, A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Liu, B. Mesoporous gold nanospheres via thiolate-Au(I) intermediates. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6423–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, H.; Sun, L.; Lopes, A.; Xu, D.; Liu, B. Insights into compositional and structural effects of bimetallic hollow mesoporous nanospheres toward ethanol oxidation electrocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5490–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Qi, L. Surfactant-assisted, shape-controlled synthesis of gold nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plascencia-Villa, G.; Torrente, D.; Marucho, M.; José-Yacamán, M. Biodirected synthesis and nanostructural characterization of anisotropic gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3527–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, H.M.; Shah, A.; Konieczny, M.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Nijdam, A.J.; Reeves, M.E. Small molecule- and amino acid-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7661–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangoo, N.; Bhasin, K.K.; Mehta, S.K.; Suri, C.R. Synthesis and capping of water-dispersed gold nanoparticles by an amino acid: Bioconjugation and binding studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakiari, A.H.; Jamshidi, Z. Interaction of amino acids with gold and silver clusters. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 4391–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, C.Y. Controlled growth of concave gold nanobars with high surface-enhanced Raman-scattering and excellent catalytic activities. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5794–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banholzer, M.J.; Millstone, J.E.; Lidong, Q.; Mirkin, C.A. Rationally designed nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.M.; Nie, S.M. Single-molecule and single-nanoparticle SERS: From fundamental mechanisms to biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Low, M.; Liu, S.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Geng, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Bharathi, M.S. Destabilization of thiolated gold clusters for the growth of single-crystalline gold nanoparticles and their self-assembly for SERS detection. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, C.; Yu, S.M. Nanostructured materials for applications in surface enhanced Raman scattering. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 9959–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Yuan, J. Facile interfacial synthesis of large sized 3D gold spherical architectures with strong individual particle SERS response and high reproducibility. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10154–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Han, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y. Facile synthesis of two-dimensional highly branched gold nanostructures in aqueous solutions of cationic gemini surfactant. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 2648–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, Z.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Tang, C.; Jia, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Island-like nanoporous gold: Smaller island generates stronger surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28902–28910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Dui, J.; Li, G.; Lou, S.; Zhou, S. Controlled synthesis of homogeneous Ag nanosheet-assembled film for effective SERS substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7308–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.-S.; Zhao, H.-L.; Wang, N.; Li, T.-J.; Zhao, S.; Lu, W.-W. Facile synthesis of ultra-large, single-crystal Ag nanosheet-assembled films at chloroform-water interface. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 278, 120912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, T.; Qi, L. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of thorned gold plates comprising three-branched nanotip arrays. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2985–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangapuram, B.R.; Bandi, R.; Madhusudhan, A.; Dadigala, R.; Kotu, G.M.; Guttena, V. Microwave assisted rapid green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using annona squamosa L peel extract for the efficient catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1167, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Roy, S.; Jaiswal, A. Cubic gold nanorattles with a solid octahedral core and porous shell as efficient catalyst: Immobilization and kinetic analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 22914–22925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugadoss, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Surface area controlled differential catalytic activities of one-dimensional chain-like arrays of gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11265–11271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, C.; Zou, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Mu, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. In situ assembly of well-dispersed gold nanoparticles on electrospun silica nanotubes for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3906–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jo, J.K.; Zhang, L.; Ha, C.S.; Suh, H.; Kim, I. A general and efficient route to fabricate carbon nanotube-metal nanoparticles and carbon nanotube-inorganic oxides hybrids. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3864–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ko, S.M.; Nam, J.M. Dealloying-based facile synthesis and highly catalytic properties of au core/porous shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11707–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, F.D.; Nascimento, L.; Calado, C.; Meneghetti, M.; Silva, M.D. Aqueous-phase catalytic chemical reduction of p-nitrophenol employing soluble gold nanoparticles with different shapes. Catalysts 2016, 6, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Q. Facile fabrication of nanoporous Au-Pd bimetallic foams with high catalytic activity for 2-nitrophenol reduction and SERS property. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11961–11967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xia, Y. A comparison study of the catalytic properties of Au-based nanocages, nanoboxes, and nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, K.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, J. Ionic Liquid-Modulated Synthesis of Porous Worm-Like Gold with Strong SERS Response and Superior Catalytic Activities. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121772
Yao K, Wang N, Li Z, Lu W, Wang J. Ionic Liquid-Modulated Synthesis of Porous Worm-Like Gold with Strong SERS Response and Superior Catalytic Activities. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(12):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121772
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Kaisheng, Nan Wang, Zhiyong Li, Weiwei Lu, and Jianji Wang. 2019. "Ionic Liquid-Modulated Synthesis of Porous Worm-Like Gold with Strong SERS Response and Superior Catalytic Activities" Nanomaterials 9, no. 12: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121772
APA StyleYao, K., Wang, N., Li, Z., Lu, W., & Wang, J. (2019). Ionic Liquid-Modulated Synthesis of Porous Worm-Like Gold with Strong SERS Response and Superior Catalytic Activities. Nanomaterials, 9(12), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121772