Antioxidant Activity of Graphene Quantum Dots Prepared in Different Electrolyte Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of GQDs
2.2. Free Radical Scavenging Assay
2.3. Characterization
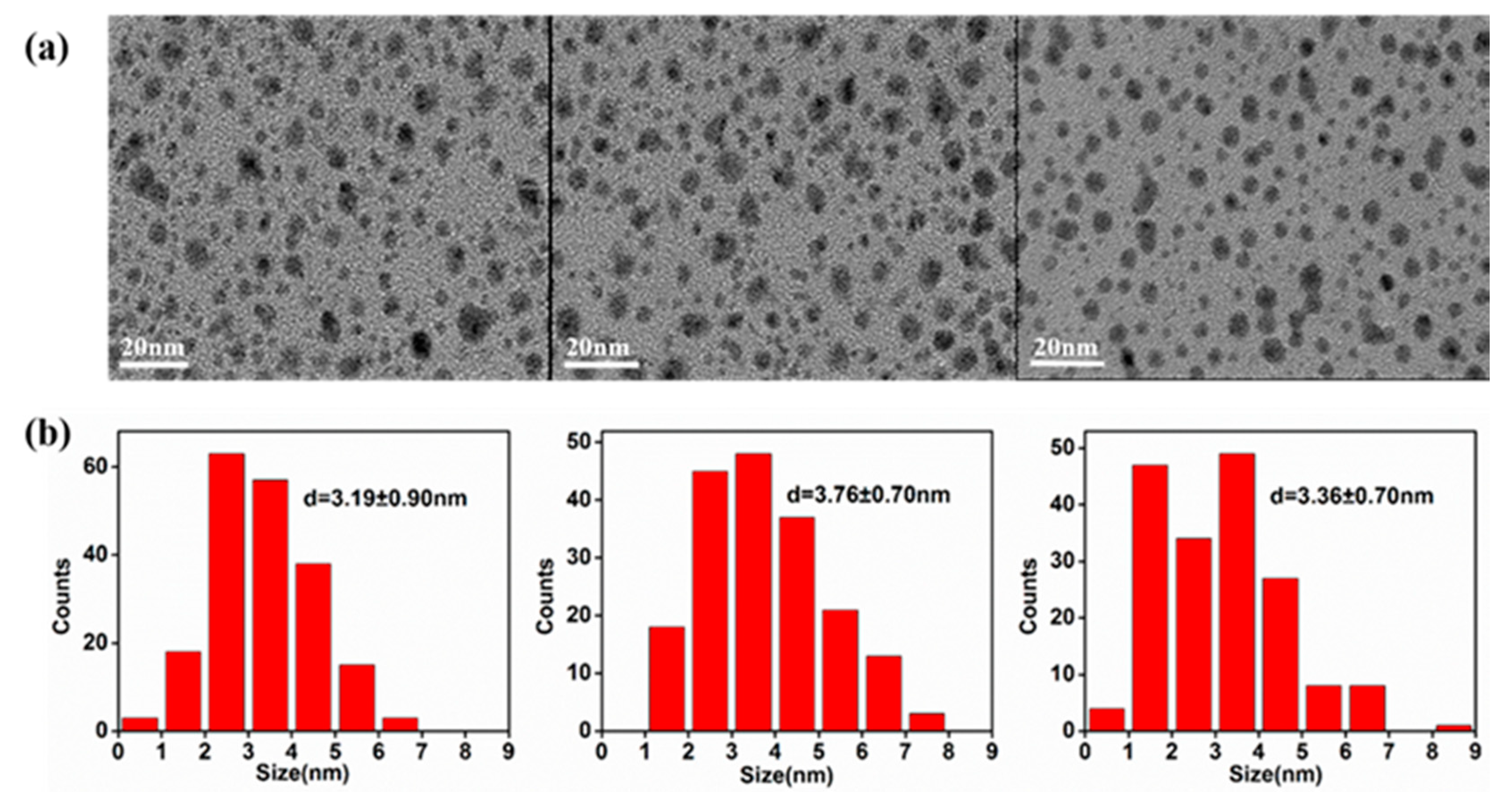
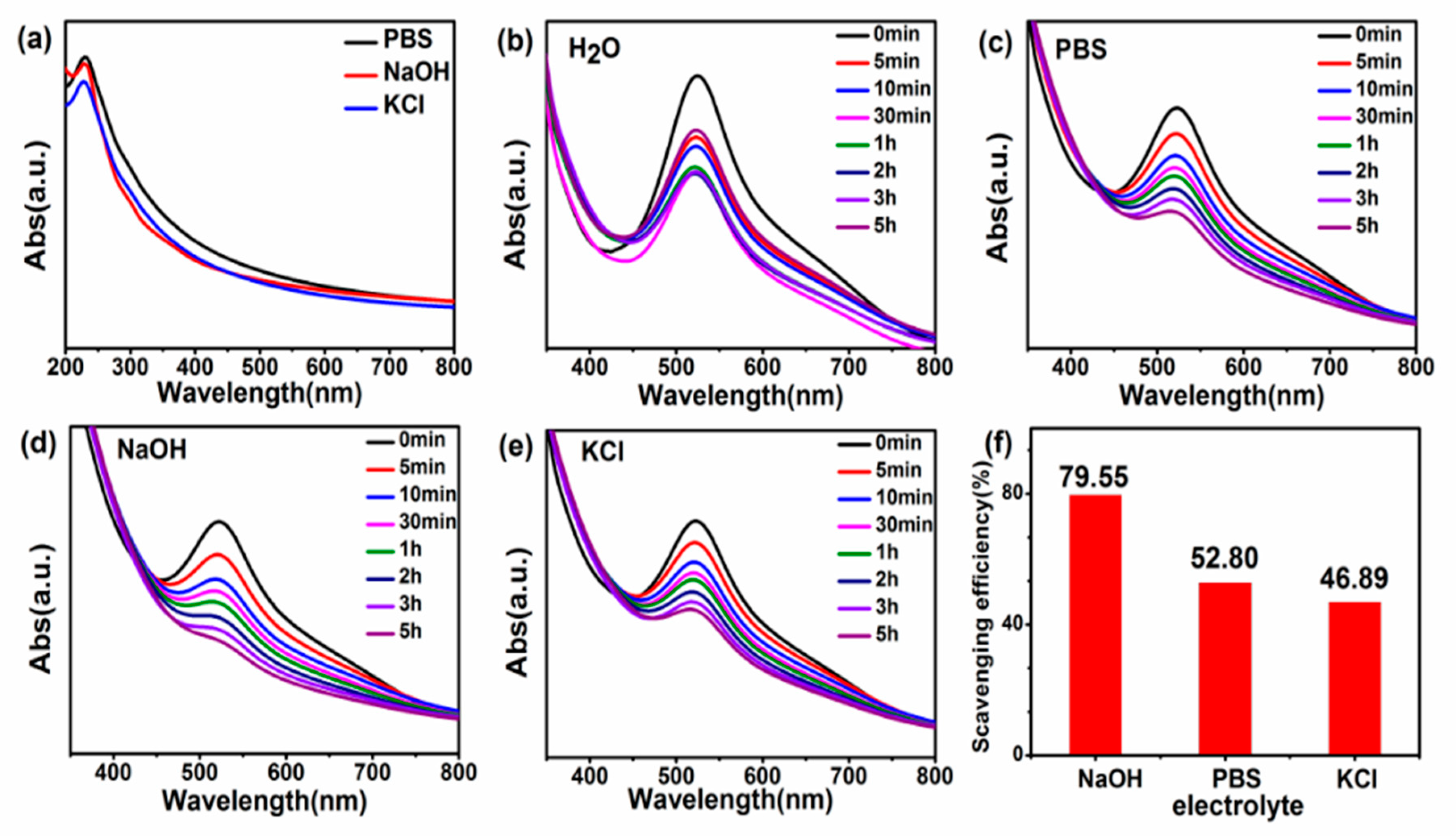
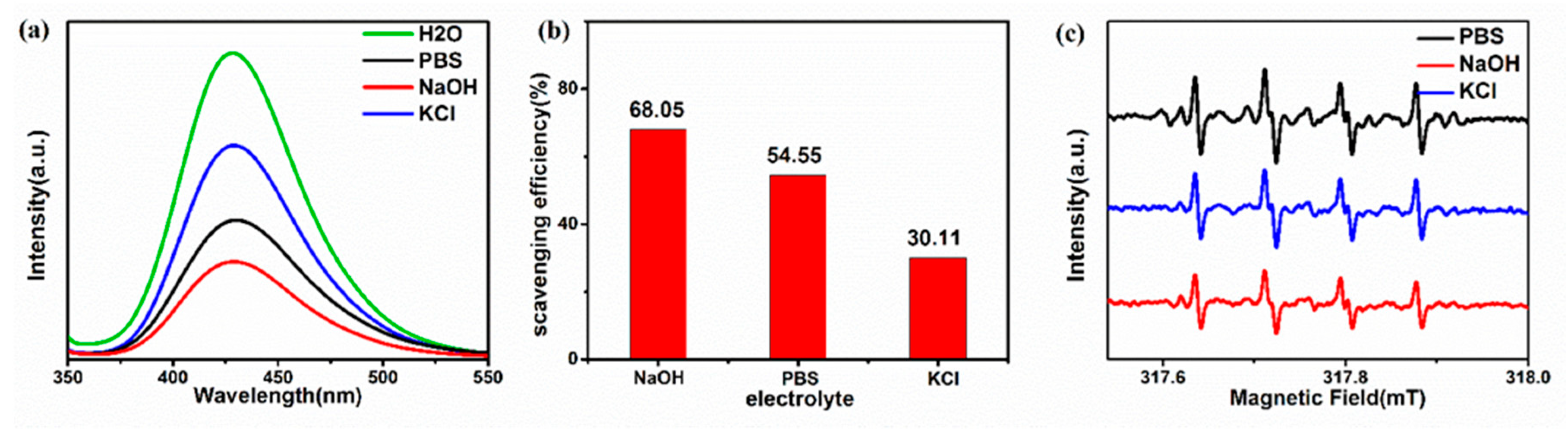
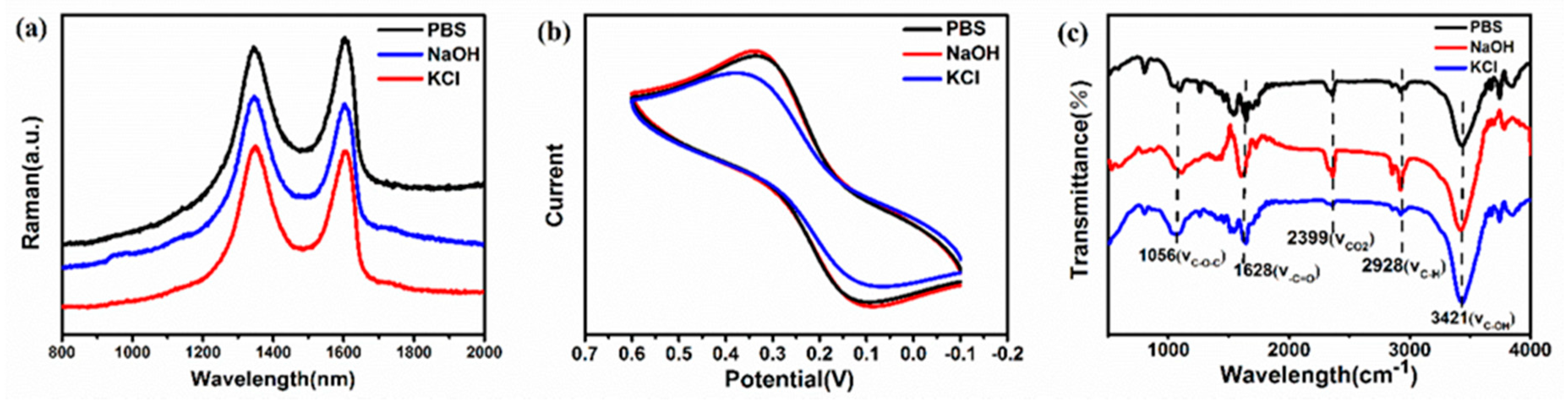
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chong, Y.; Ge, C.; Fang, G.; Tian, X.; Ma, X.; Wen, T.; Wamer, W.G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Yin, J. Crossover between anti-and pro-oxidant activities of graphene quantum dots in the absence or presence of light. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8690–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, C. A Graphene Quantum Dots-Hypochlorite Hybrid System for the Quantitative Fluorescent Determination of Total Antioxidant Capacity. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lan, M.; Zhu, X.; Xue, H.; Ng, T.W.; Meng, X.; Lee, C.S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Owens, A.C.; Kulaots, I.; Chen, Y.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R. Antioxidant chemistry of graphene-based materials and its role in oxidation protection technology. Carbon 2014, 6, 11744–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poprac, P.; Jomova, K.; Simunkova, M.; Kollar, V.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrini, C.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachootham, D.; Alexandre, J.; Huang, P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.Z.; Milenkovic, M.M.; Dakic, I.R.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Milosavljevic, M.S.; Budimir, M.D.; Paunovic, V.G.; Dramicanin, M.D.; Markovic, Z.M.; Trajkovic, V.S. Photodynamic antibacterial effect of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4428–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, B.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gong, J.R. Strong two-photon-induced fluorescence from photostable, biocompatible nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for cellular and deep-tissue imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Huang, G.; Xing, B.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C. Green preparation of high yield fluorescent graphene quantum dots from coal-tar-pitch by mild oxidation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zou, T.; Wang, Z.; Xing, X.; Peng, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. The Fluorescent Quenching Mechanism of N and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions and Their Application as a Novel Fluorescent Sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Geng, J.; Liu, B.J. Graphene quantum dots from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon for bioimaging and sensing of Fe3+ and hydrogen peroxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 30, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, P. Graphene-based nanomaterials for bioimaging. Part. Part. Syst. Char. 2016, 105, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, T.; Nie, Z.; Miao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticle modulated turn-on fluorescent probes for histidine detection and its imaging in living cells. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Ding, K.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J. Graphene quantum dots cut from graphene flakes: High electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction and low cytotoxicity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 23097–23106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, M.; Khatun, Z.; Huh, K.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y. In vivo biodistribution and toxicology of carboxylated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6858–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Electrochemical synthesis of small-sized red fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a bioimaging platform. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2544–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y. SnO2/graphene quantum dots composited photocatalyst for efficient nitric oxide oxidation under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Politano, A.; Drioli, E. The advent of graphene and other two-dimensional materials in membrane science and technology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2017, 16, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, F.; Su, B.; Hu, M.Z.; Gao, X.; Gao, C. Novel graphene quantum dots (GQDs)-incorporated thin film composite (TFC) membranes for forward osmosis (FO) desalination. Desalination 2019, 451, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Kebria, M.; Rahimpour, A.; Bakeri, G. Graphene quantum dots modified polyvinylidenefluride (PVDF) nanofibrous membranes with enhanced performance for air Gap membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 126, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, L.; Feng, C.; Zeng, G.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y. Construction of plasmonic Ag and nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots codecorated ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity: Full-spectrum response ability and mechanism insight. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 42816–42828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, A.; Chiarello, G. Plasmon modes in graphene: Status and prospect. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10927–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, T. Plasmonics in Dirac systems: From graphene to topological insulators. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuji, T.; Popov, V.; Ryzhii, V. Active graphene plasmonics for terahertz device applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, N.; Fen, Y.; Omar, N.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Ramdzan, N.S.M.; Saleviter, S. Development of Graphene Quantum Dots-Based Optical Sensor for Toxic Metal Ion Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, W.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Qu, L. Chlorine-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Enhanced Anti-and Pro-Oxidant Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21822–21829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Fu, A.; Junaid, M.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Fu, C.; Liu, L.; Su, D.-S.; Bian, W.-P.; Pei, D.-S. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) perturb redox-sensitive system via the selective inhibition of antioxidant enzyme activities in zebrafish. Biomaterials 2019, 206, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; White, J.C.; Xing, B. Graphene quantum dots in alveolar macrophage: Uptake-exocytosis, accumulation in nuclei, nuclear responses and DNA cleavage. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Genotoxic response and damage recovery of macrophages to graphene quantum dots. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lin, W.; Lin, B.; Wu, K.; Fan, H.; Yu, Y. Persistent DNA methylation changes in zebrafish following graphene quantum dots exposure in surface chemistry-dependent manner. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gu, M.M.; Tian, X.; Xiao, B.-B.; Lu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yu, L.; Shang, Z.-F. Hydroxylated-graphene quantum dots induce DNA damage and disrupt microtubule structure in human esophageal epithelial cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.; Okata, T.; Akita, T.; Kohyama, M.; Nakamura, J.; Honma, I. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of Pt subnanoclusters on graphene nanosheet surface. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2255–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, L.; Shang, W.; Xie, W.; Ma, H.; Fu, Y.; Fang, D.; Sun, H.; Fan, L.Z.; Han, M.; et al. Facile synthesis of water-soluble, highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a robust biological label for stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7461–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Liao, H.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Sun, L.; et al. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: Properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Yadav, R.M.; Narayanan, T.; Shelke, M.V.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Pillai, V.K. Synthesis of N, F and S co-doped graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11515–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Guan, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, F. Hydrothermal synthesis of graphene quantum dots supported on three-dimensional graphene for supercapacitors. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Xue, W.; Ma, N. Electrochemical synthesis of phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dots for free radical scavenging. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11631–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, V.; Yate, L.; García, I.; Cabanero, G.; Grande, H. Tuning the antioxidant activity of graphene quantum dots: Protective nanomaterials against dye decoloration. Carbon 2017, 116, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Optimizing oxygen functional groups in graphene quantum dots for improved antioxidant mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.T.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Ryan, C.; Faerber, N.; Coffer, J.L.; Naumov, A.V. Photo-and Electroluminescence from Nitrogen-Doped and Nitrogen-Sulfur Codoped Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Func. Mater. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, M.; Bradley, S.J.; Nann, T. Graphene quantum dots. Part. Part. Syst. Chara. 2014, 31, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; You, X.; Mao, B.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; He, P.; et al. Electrochemical Cutting in Weak Aqueous Electrolytes: The Strategy for Efficient and Controllable Preparation of Graphene Quantum Dots. Langmuir 2017, 34, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, J. Electrochemical Study of DPPH Radical Scavenging for Evaluating the Antioxidant Capacity of Carbon Nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 18635–18642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, X.; Guo, Z.; Lin, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Fluorescent TPA@GQDs Probe for Sensitive Assay and Quantitative Imaging of Hydroxyl Radicals in Living Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5853–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ležaić, A.J.; Pašti, I.; Vukomanović, M.; Ćirić-Marjanović, G. Polyaniline tannate-Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical assessment of superoxide anion radical scavenging activity. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 142, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yue, H.; Yang, Z.; Gaoquan, S.; Lier, D.; Yanbing, H.; Liangti, Q. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, G.; An, X.; Zhuo, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, C. A reformative oxidation strategy using high concentration nitric acid for enhancing the emission performance of graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 47977–47981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, P.; Deming, C.P.; Wang, N.; Lu, J.E.; Chen, S. Intervalence Charge Transfer of Ruthenium–Nitrogen Moieties Embedded within Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13303–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Sarkar, S.; Ghosh, T.; Basak, D. ZnO/Graphene Quantum Dot Solid-State Solar Cell. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 20127–20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Hou, Y.; Wan, W.; Xue, W.; Ma, N.; Zhang, J. Chemical nature of redox-controlled photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots by post-synthesis treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 26004–26011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, F.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. How functional groups influence the ROS generation and cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 10588–10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Antioxidant Activity of Graphene Quantum Dots Prepared in Different Electrolyte Environments. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121708
Zhao L, Wang Y, Li Y. Antioxidant Activity of Graphene Quantum Dots Prepared in Different Electrolyte Environments. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(12):1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121708
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lin, Yingmin Wang, and Yan Li. 2019. "Antioxidant Activity of Graphene Quantum Dots Prepared in Different Electrolyte Environments" Nanomaterials 9, no. 12: 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121708
APA StyleZhao, L., Wang, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Antioxidant Activity of Graphene Quantum Dots Prepared in Different Electrolyte Environments. Nanomaterials, 9(12), 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121708



