A Hydrothermal-Assisted Ball Milling Approach for Scalable Production of High-Quality Functionalized MoS2 Nanosheets for Polymer Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanosheets Preparation
2.3. Polymer Nanocomposites Fabrication
2.4. Characterisations
3. Results and Discussion
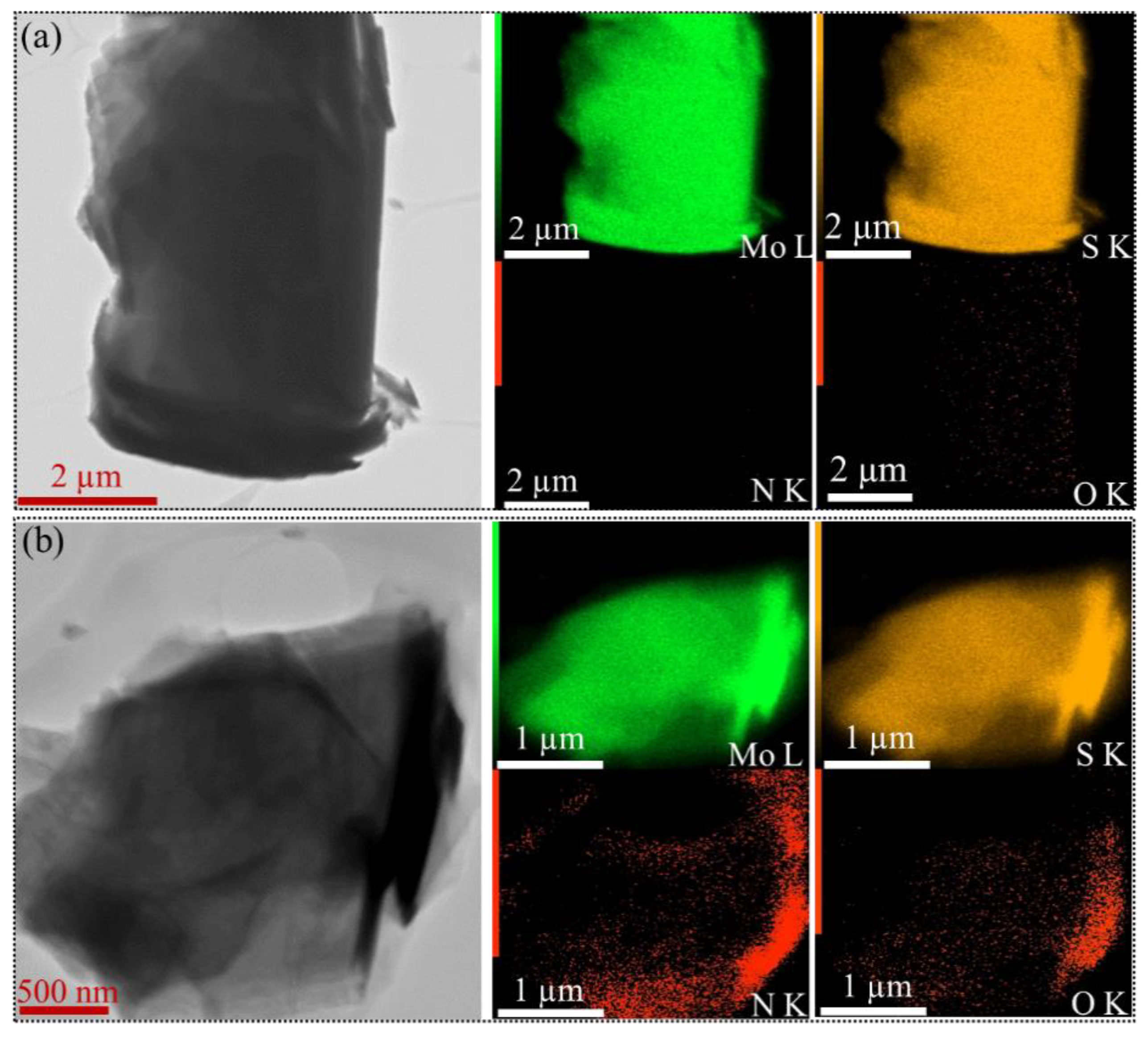
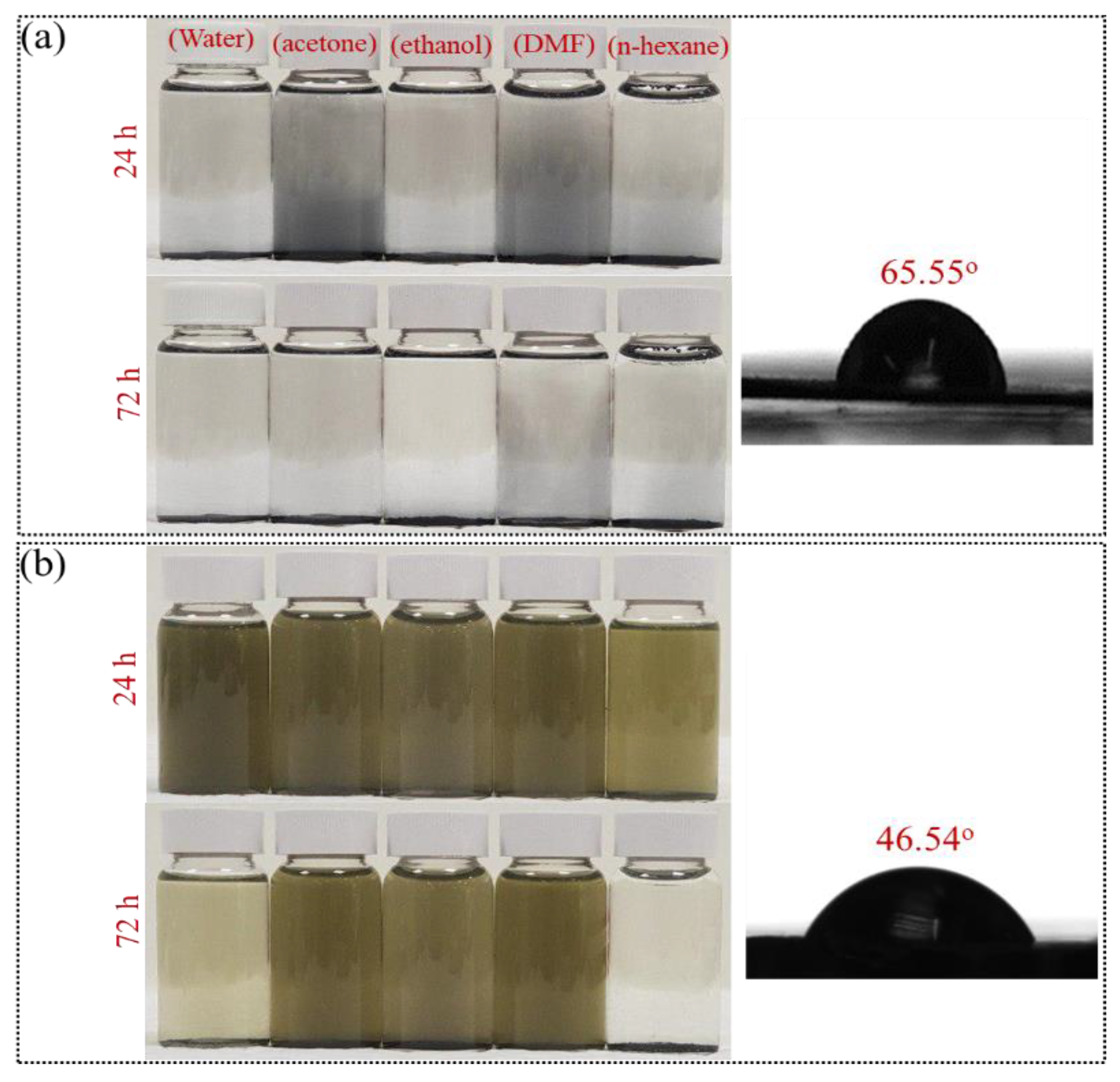
3.1. Morphological Characteristics
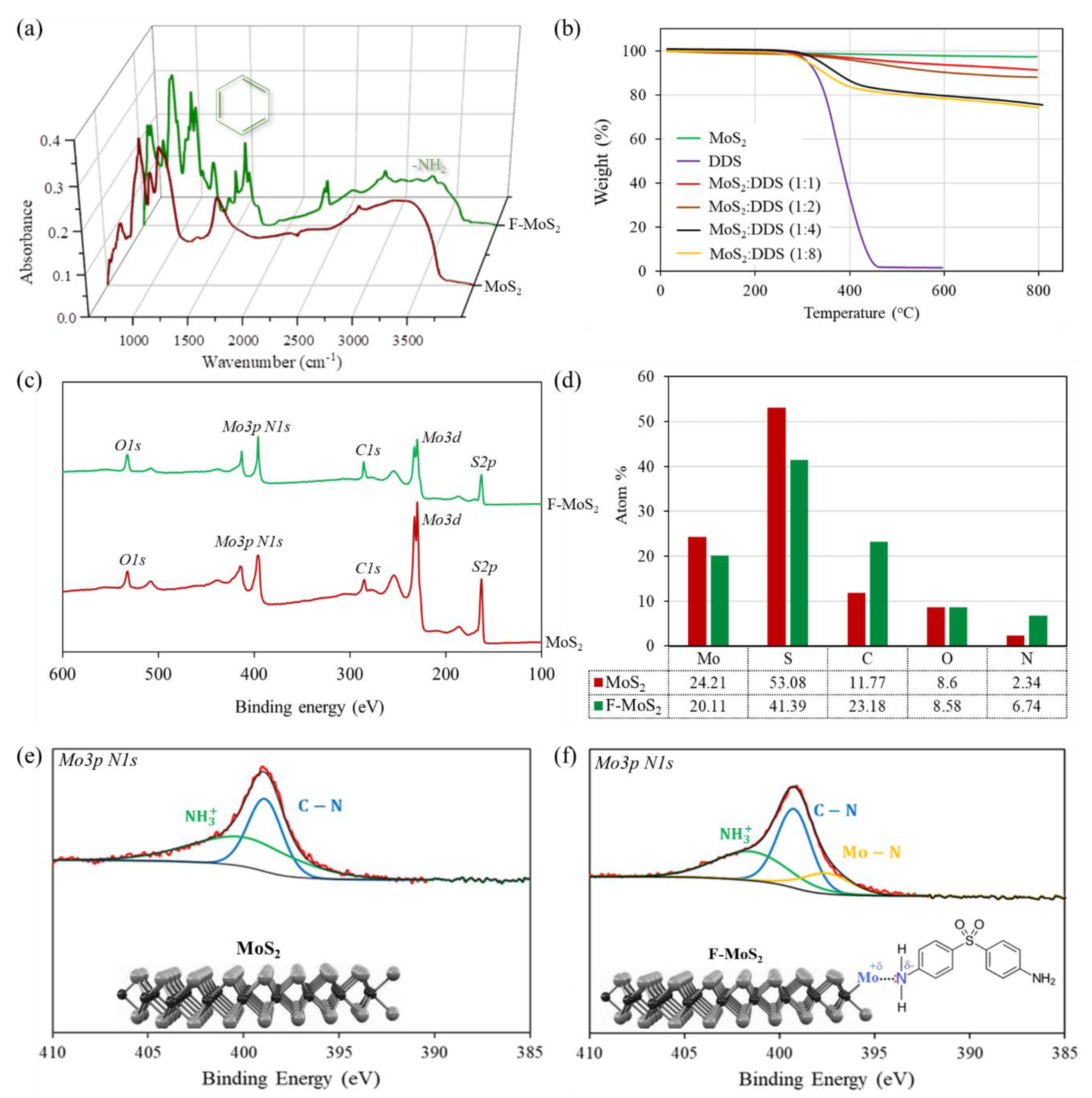
3.2. Chemical Structure of F-MoS2 Nanosheets
3.3. Structural Characteristics of F-MoS2 Nanosheets
3.4. MoS2 Application in Reinforcing Polymers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Sunarso, J.; Liu, S.; Zhi, L. Graphene nanostructures toward clean energy technology applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2012, 1, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Abbas, A.; Zhou, C. Two-Dimensional Semiconductors: From Materials Preparation to Electronic Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1700045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Xie, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Navarrete, J.; Moskovits, M.; Banerjee, K. Functionalization of Transition Metal Dichalcogenides with Metallic Nanoparticles: Implications for Doping and Gas-Sensing. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 2852–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissessur, R.; White, W. Novel alkyl substituted polyanilines/molybdenum disulfide nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 99, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.F.; Lee, C.; Hone, J.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T.F. Atomically thin MoS2: A new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 136805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanakata, P.Z.; Qi, Z.; Campbell, D.K.; Park, H.S. Highly stretchable MoS2 kirigami. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Q.; Weng, P.; Guo, B. Remarkably improving performance of carbon black-filled rubber composites by incorporating MoS2 nanoplatelets. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 132, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.-K.; Zhang, W.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, M.-T.; Su, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-S.; Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Growth of Large-Area and Highly Crystalline MoS2 Thin Layers on Insulating Substrates. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, J.O.; Agbo, P.; Sutherland, A.M.; Brar, V.W.; Rossman, G.R.; Gray, H.B.; Heath, J.R. The Influence of Water on the Optical Properties of Single-Layer Molybdenum Disulfide. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2734–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Lotya, M.; O’Neill, A.; Bergin, S.D.; King, P.J.; Khan, U.; Young, K.; Gaucher, A.; De, S.; Smith, R.J.; et al. Two-Dimensional Nanosheets Produced by Liquid Exfoliation of Layered Materials. Science 2011, 331, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyeonyeol, J.; Jae-Min, J.; Gyu, K.H.; Hyung-Jin, K.; Jeyoung, P.; Hyun, K.D.; Mee, J.Y.; Yeon, H.S.; Young-Kyu, H.; Gill, C.B. Scalable Water-Based Production of Highly Conductive 2D Nanosheets with Ultrahigh Volumetric Capacitance and Rate Capability. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800227. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos-Gomez, A.; Barkelid, M.; Goossens, A.M.; Calado, V.E.; van der Zant, H.S.J.; Steele, G.A. Laser-Thinning of MoS2: On Demand Generation of a Single-Layer Semiconductor. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3187–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Kim, P.; Kim, J.H.; Ye, J.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, C.J. Large-Area Atomically Thin MoS2 Nanosheets Prepared Using Electrochemical Exfoliation. Acs Nano 2014, 8, 6902–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Song, X.; Moon, K.-S.; Wong, C.-P. Large-scale production of two-dimensional nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13494–13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, W.; Chang, M.T.; Lin, C.T.; Chang, K.D.; Yu, Y.C.; Wang, J.T.; Chang, C.S.; Li, L.J.; et al. Synthesis of Large-Area MoS2 Atomic Layers with Chemical Vapor Deposition. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, A.-Y.; Fang, W.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hsu, A.L.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.K.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, L.-J.; et al. van der Waals Epitaxy of MoS2 Layers Using Graphene As Growth Templates. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhong, C.; Lu, J.; Yu, W.; Jia, Y.; Qian, Y. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Single-Molecular-Layer MoS2 and MoSe2. Chem. Lett. 2001, 30, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sakthivel, T.; Seal, S. Recent development in 2D materials beyond graphene. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 73, 44–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Ballesté, R.; Gómez-Navarro, C.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Zamora, F. 2D materials: To graphene and beyond. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, S.Z.; Hollen, S.M.; Cao, L.; Cui, Y.; Gupta, J.A.; Gutiérrez, H.R.; Heinz, T.F.; Hong, S.S.; Huang, J.; Ismach, A.F.; et al. Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Two-Dimensional Materials Beyond Graphene. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2898–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, C.; Berner, N.C.; Chen, X.; Lafargue, P.; LaPlace, P.; Freeley, M.; Duesberg, G.S.; Coleman, J.N.; McDonald, A.R. Functionalization of Liquid-Exfoliated Two-Dimensional 2H-MoS2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eda, G.; Yamaguchi, H.; Voiry, D.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.; Chhowalla, M. Photoluminescence from Chemically Exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5111–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voiry, D.; Goswami, A.; Kappera, R.; Silva, C.D.C.C.E.; Kaplan, D.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.; Asefa, T.; Chhowalla, M. Covalent functionalization of monolayered transition metal dichalcogenides by phase engineering. Nat. Chem. 2014, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kis, A.; Coleman, J.N.; Strano, M.S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, S.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Zheng, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. A one-step approach to the large-scale synthesis of functionalized MoS2 nanosheets by ionic liquid assisted grinding. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10210–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Xu, P.; Zhou, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Terrones, M.; Mallouk, T.E. Fast and Efficient Preparation of Exfoliated 2H MoS2 Nanosheets by Sonication-Assisted Lithium Intercalation and Infrared Laser-Induced 1T to 2H Phase Reversion. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5956–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolosi, V.; Chhowalla, M.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Strano, M.S.; Coleman, J.N. Liquid Exfoliation of Layered Materials. Science 2013, 340, 1226419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wen, P.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Tai, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liew, K.M. Defect-free MoS2 nanosheets: Advanced nanofillers for polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 81, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Nafion-assisted exfoliation of MoS2 in water phase and the application in quick-response NIR light controllable multi-shape memory membrane. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zeng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Huang, Y. Facile scalable synthesis and superior lithium storage performance of ball-milled MoS2–graphite nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10466–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Ren, L.; Qi, X.; Yang, L.W.; Hao, G.L.; Li, J.; Wei, X.L.; Zhong, J.X. Preparation, characterization and photoelectrochemical property of ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets via hydrothermal intercalation and exfoliation route. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 571, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In-Yup, J.; Seo-Yoon, B.; Jeong-Min, S.; Jong-Beom, B. Scalable Production of Edge-Functionalized Graphene Nanoplatelets via Mechanochemical Ball-Milling. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6961–6975. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.E.D.; Stolle, A.; Stelter, M. Sustainable Synthesis of High-Surface-Area Graphite Oxide via Dry Ball Milling. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6358–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, G.S.; Nam, K.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, J.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, S.-Y. Effective Liquid-Phase Exfoliation and Sodium Ion Battery Application of MoS2 Nanosheets. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7084–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Chen, Y.; Yin, J.; Shen, S.; Cai, K. Preparation, characterization and properties of MoS2 nanosheets via a microwave-assisted wet-chemical route. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 5336–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, S.; Mohamed, A.; Tatariants, M. Mass production of graphene nanosheets by multi-roll milling technique. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, J.; Song, Q.; Hu, Q.; Fang, Y.; Tang, C. Scalable exfoliation and gradable separation of boric-acid-functionalized boron nitride nanosheets. 2D Mater. 2019, 6, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y. Facile synthesis of MoS2 nanosheet-silver nanoparticles composite for surface enhanced Raman scattering and electrochemical activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 559, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Si, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xue, D. Ferromagnetism in freestanding MoS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Zhang, X.; Song, S. AFM study on the adsorption of Hg2+ on natural molybdenum disulfide in aqueous solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 3837–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Muijsers, J.C.; van Wolput, J.H.M.C.; Verhagen, C.P.J.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W. Basic Reaction Steps in the Sulfidation of Crystalline MoO3 to MoS2, As Studied by X-ray Photoelectron and Infrared Emission Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 14144–14150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-A.; Li, C.-L. SO2 adsorption and thermal stability and reducibility of sulfates formed on the magnesium–aluminate spinel sulfur-transfer catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 161, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugé, F.; Lamotte, J.; Nesterenko, N.S.; Manoilova, O.; Tsyganenko, A.A. FT-IR study of surface properties of unsupported MoS2. Catal. Today 2001, 70, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, W. Effective reinforcement of amino-functionalized molybdenum disulfide on epoxy-based composites via strengthened interfacial interaction. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 8221–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Berner, N.C.; Backes, C.; Duesberg, G.S.; McDonald, A.R. Functionalization of Two-Dimensional MoS2: On the Reaction between MoS2 and Organic Thiols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5803–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, D.M.; Han, H.J.; Yim, S.; Choi, M.-J.; Jeon, J.; Jung, Y.S. Long-Term STable 2H-MoS2 Dispersion: Critical Role of Solvent for Simultaneous Phase Restoration and Surface Functionalization of Liquid-Exfoliated MoS2. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4678–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Song, X.; Lin, S.; Bi, K.; Hao, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Fan, D.; Wang, Y.; Lei, M. A facile route to graphite-tungsten nitride and graphite-molybdenum nitride nanocomposites and their ORR performances. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 16017–16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, P.; Sampath, A.; Waghmare, U.V.; Rao, C.N.R. Covalent Functionalization of Nanosheets of MoS2 and MoSe2 by Substituted Benzenes and Other Organic Molecules. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeshkumar, E.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sreedhara, M.B.; Pati, S.K.; Rao, C.N.R.; Yoshimura, M. One-Step Simultaneous Exfoliation and Covalent Functionalization of MoS2 by Amino Acid Induced Solution Processes. ChemNanoMat 2017, 3, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, K.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, C.; Feng, Y.; Hu, P. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous carbon derived from bio-waste as a promising electrocatalyst for zinc-air battery. Energy 2018, 143, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar Vattikuti, S.V.; Byon, C.; Venkata Reddy, C.; Venkatesh, B.; Shim, J. Synthesis and structural characterization of MoS2 nanospheres and nanosheets using solvothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5024–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, B.; Sharu, B.K.; Gopika, M.S.; Praseetha, P.K.; Veluraja, K. Molybdenum disulfide nanoflakes through Li-AHA assisted exfoliation in an aqueous medium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22026–22033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Gong, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. High efficiency shear exfoliation for producing high-quality, few-layered MoS2 nanosheets in a green ethanol/water system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 82763–82773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Tang, G.; Gao, R.; Guo, H. Constructing hierarchical polymer@MoS2 core-shell structures for regulating thermal and fire safety properties of polystyrene nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 107, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, M.P.; Bhatt, S.V.; Sathe, V.; Soni, B.H.; Garg, N.; Chaki, S.H. Raman scattering in 2H-MoS2 single crystal. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1512, 808–809. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous Lattice Vibrations of Single- and Few-Layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Sandoval, S.J.; Divigalpitiya, W.; Irwin, J.; Frindt, R. Structure of single-molecular-layer MoS2. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 43, 12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Gaur, A.P.S.; Ahmadi, M.; Guinel, M.J.F.; Katiyar, R.S. Temperature-Dependent Raman Studies and Thermal Conductivity of Few-Layer MoS2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 9042–9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillo, N.A.; Birdwell, A.G.; Amani, M.; Crowne, F.J.; Shah, P.B.; Najmaei, S.; Liu, Z.; Ajayan, P.M.; Lou, J.; Dubey, M.; et al. Temperature-dependent phonon shifts in monolayer MoS2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 093102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C.C.R.; Tay, B.K.; Edwin, T.H.T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From Bulk to Monolayer MoS2: Evolution of Raman Scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.-J.; Fang, B. Swollen Ammoniated MoS2 with 1T/2H Hybrid Hybrid Phases for High-Rate Electrochemical Energy Storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.C.N.; Vasudeo, W.U. 2d Inorganic Materials beyond Graphene; World Scientific Publishing Europe: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Splendiani, A.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Kim, J.; Chim, C.-Y.; Galli, G.; Wang, F. Emerging Photoluminescence in Monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adilla, S.J.; Nurfani, E.; Kurniawan, R.; Satrya, C.D.; Darma, Y. Structural and optical properties analysis of MoS2 nanoflakes on quartz substrate as prepared by mechanical exfoliation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 877, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Akhlaghi bagherjeri, M.; Naebe, M. One-pot synthesis of aminated multi-walled carbon nanotube using thiol-ene click chemistry for improvement of epoxy nanocomposites properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98692–98699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Zabihi, O.; Masoomi, M.; Naebe, M. Synergistic effect of MWCNTs functionalization on interfacial and mechanical properties of multi-scale UHMWPE fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 134, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Nikafshar, S.; Chandrakumar Preyeswary, K.; Naebe, M. A technical review on epoxy-clay nanocomposites: Structure, properties, and their applications in fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 135, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksik, O.; Gao, J.; Shojaee, S.A.; Thomas, A.; Chow, P.; Bartolucci, S.F.; Lucca, D.A.; Koratkar, N. Epoxy Nanocomposites with Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Additives. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5282–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Li, Q.; Fakhrhoseini, S.M.; Komeily Nia, Z.; Arjmand, M.; Parvez, K.; Naebe, M. Simultaneous electrochemical-assisted exfoliation and in situ surface functionalization towards large-scale production of few-layer graphene. FlatChem 2019, 18, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Abdollahi, T.; Nikafshar, S.; Naebe, M. Collision-induced activation: Towards industrially scalable approach to graphite nanoplatelets functionalization for superior polymer nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Naebe, M. Self-assembly of quaternized chitosan nanoparticles within nanoclay layers for enhancement of interfacial properties in toughened polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.; Narashimhan, L.; Prakash, O.; Raichur, A.M. Noncovalently Functionalized Tungsten Disulfide Nanosheets for Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14347–14357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Khayyam, H.; Naebe, M. Fish DNA-modified clays: Towards highly flame retardant polymer nanocomposite with improved interfacial and mechanical performance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhetri, S.; Adak, N.C.; Samanta, P.; Mandal, N.; Kuila, T.; Murmu, N.C. Investigation of mechanical and thermal properties of the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide functionalized molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)/epoxy composites. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xing, W.; Yang, H.; Yuan, B.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Liew, K.M. High-Performance Poly(ethylene oxide)/Molybdenum Disulfide Nanocomposite Films: Reinforcement of Properties Based on the Gradient Interface Effect. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13164–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Yoon, K.-B. Preparation of Isotactic Polypropylene/Exfoliated MoS2 Nanocomposites via In Situ Intercalative Polymerization. Polymers 2017, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Ko, E.-B.; Park, J.-H.; Moon, Y.-K.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Yoon, K.-B. Preparation and properties of PE/MoS2 nanocomposites with an exfoliated-MoS2/MgCl2-supported Ziegler-Natta catalyst via an in situ polymerization. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 93, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhamalai, P.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Manoharan, S.; Kim, S.J. High energy symmetric supercapacitor based on mechanically delaminated few-layered MoS2 sheets in organic electrolyte. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Komatsu, N. Readily Available “Stock Solid” of MoS2 and WS2 Nanosheets through Solid-Phase Exfoliation for Highly Concentrated Dispersions in Water. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, D.; Sun, A. Preparation of MoS2 nanoflakes by a novel mechanical activation method. J. Cryst. Growth 2010, 312, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fang, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, W.; Alfantazi, A.; Wang, D.; Wilkinson, D.P. MoS2 Nanosheets: A Designed Structure with High Active Site Density for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, B.; Simsek, E.J.P. Plasmonics Enhanced Average Broadband Absorption of Monolayer MoS2. Plasmonics 2016, 11, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, E.; Monaghan, S.; Gity, F.; Schmidt, M.; Connolly, J.; Lin, J.; Walsh, L.; Cherkaoui, K.; O’Neill, K.; McEvoy, N.; et al. Large Area Growth of MoS2 by Chemical Vapour Deposition. Meet. Abstr. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 16, 708. [Google Scholar]
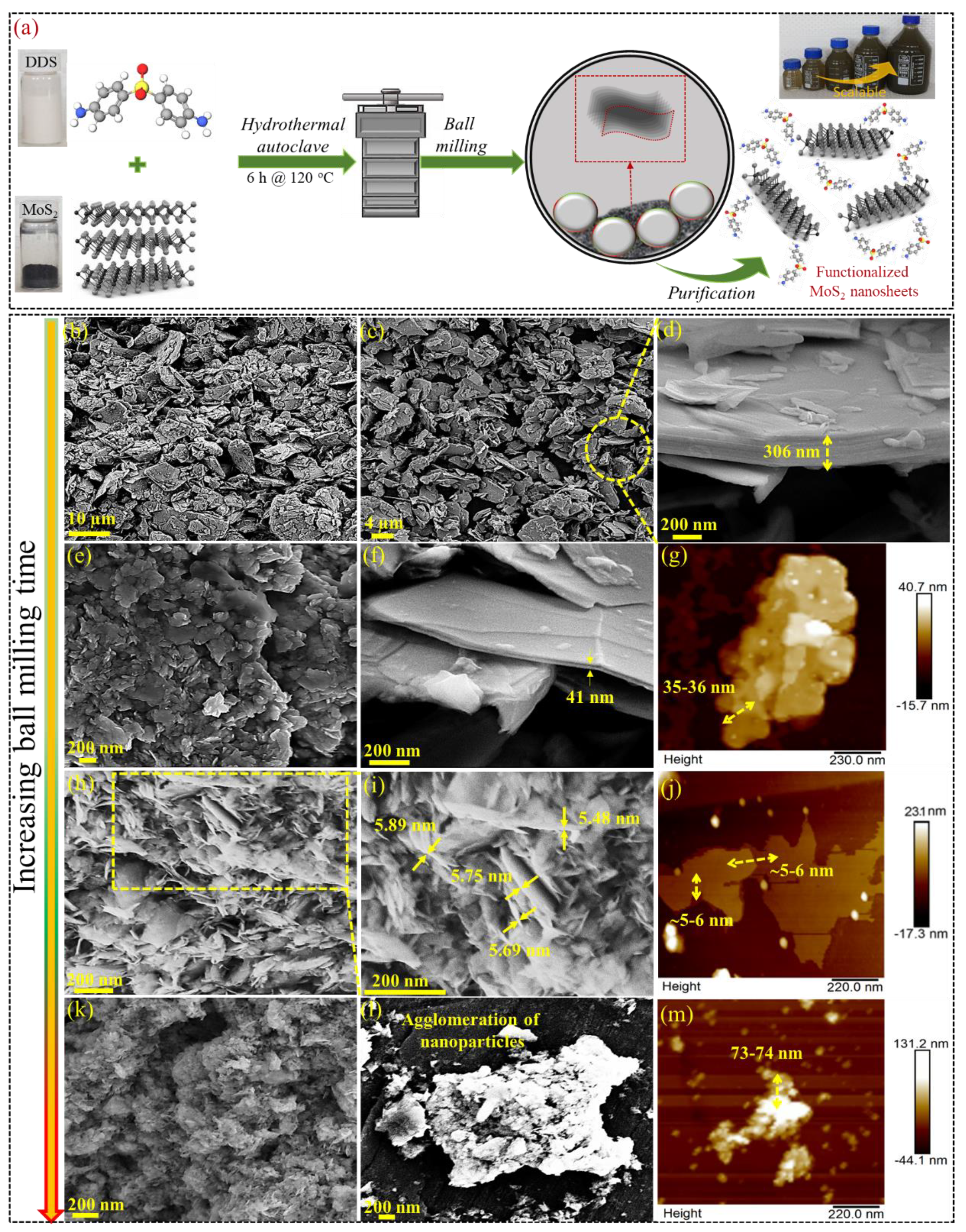
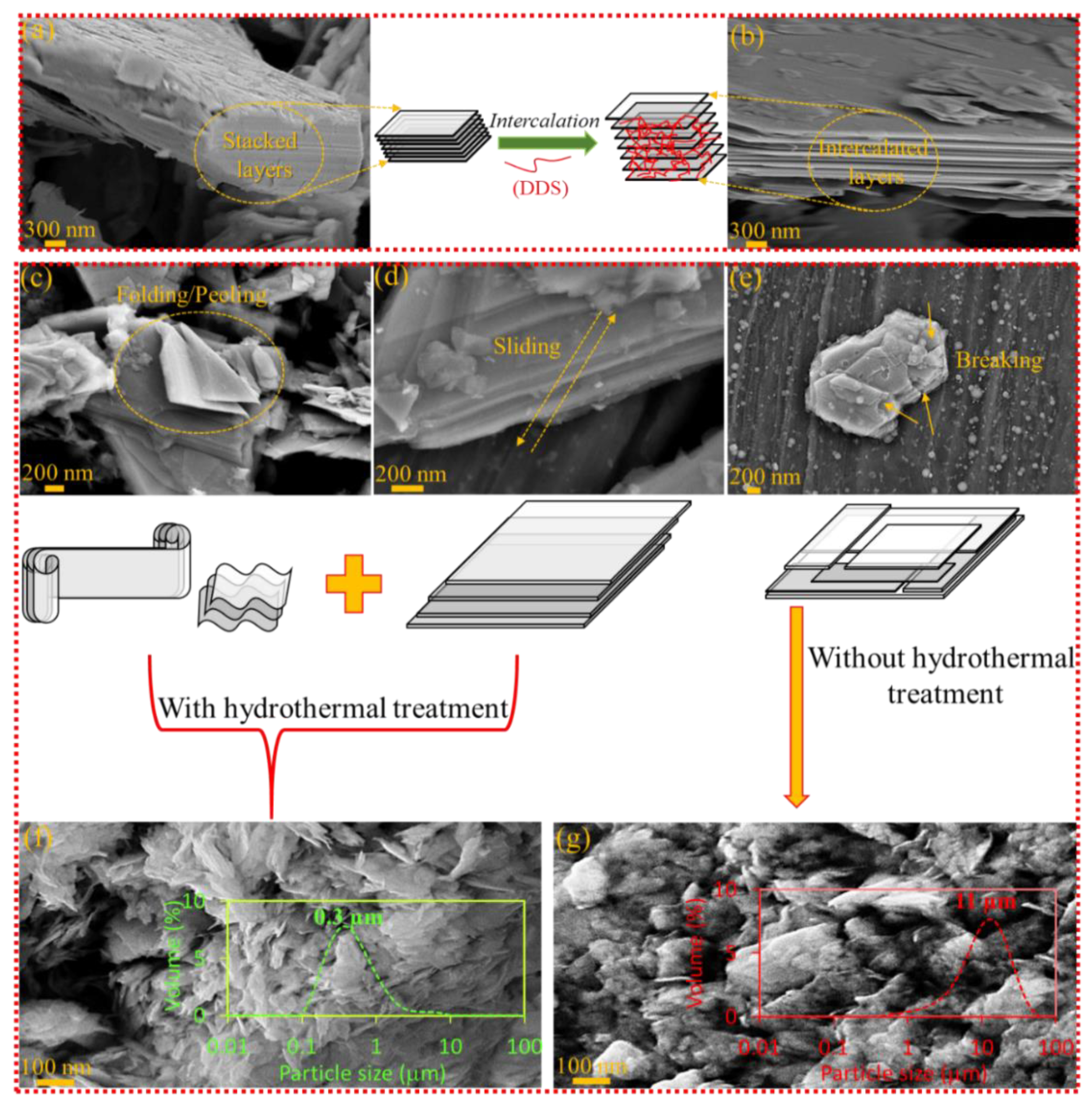
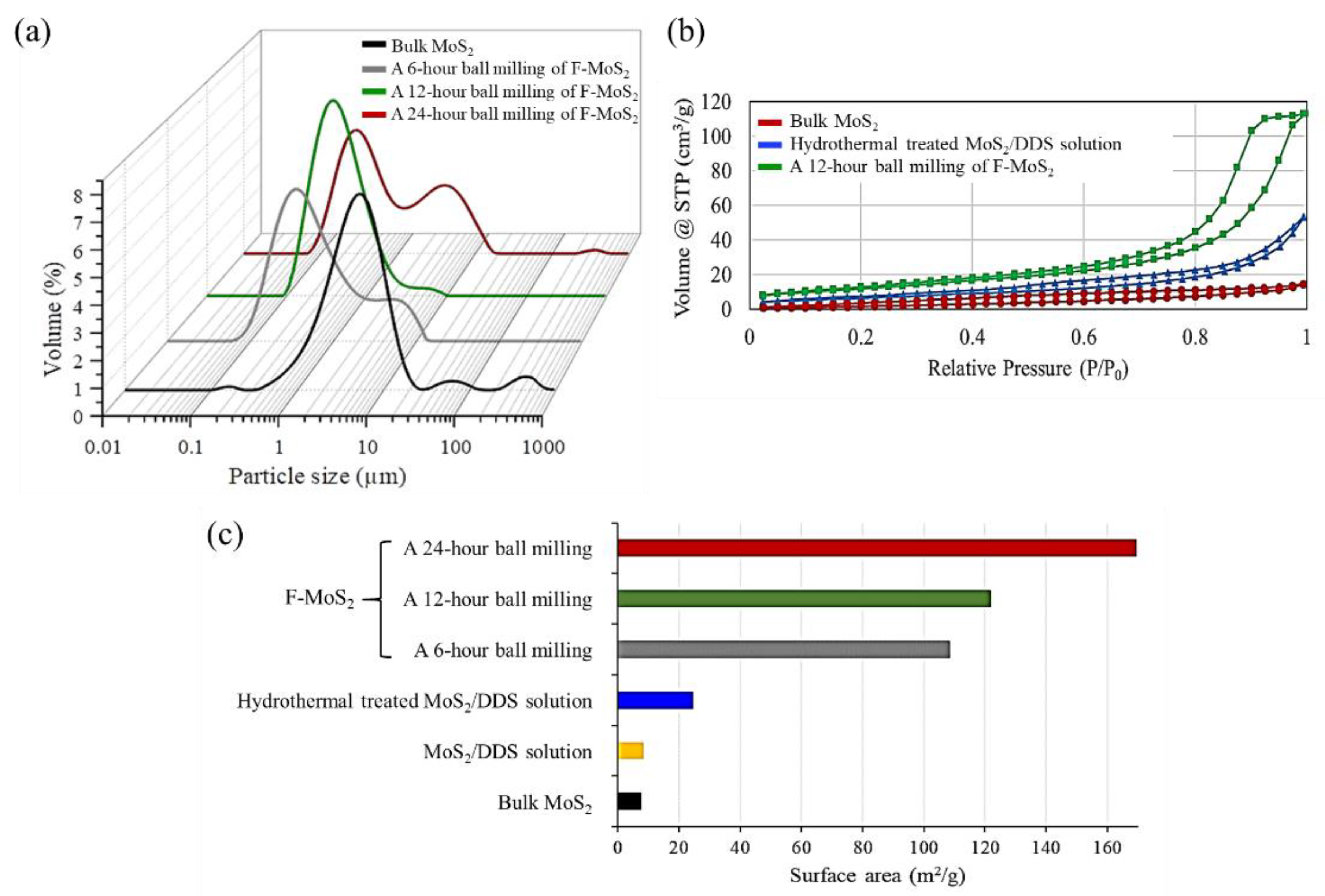
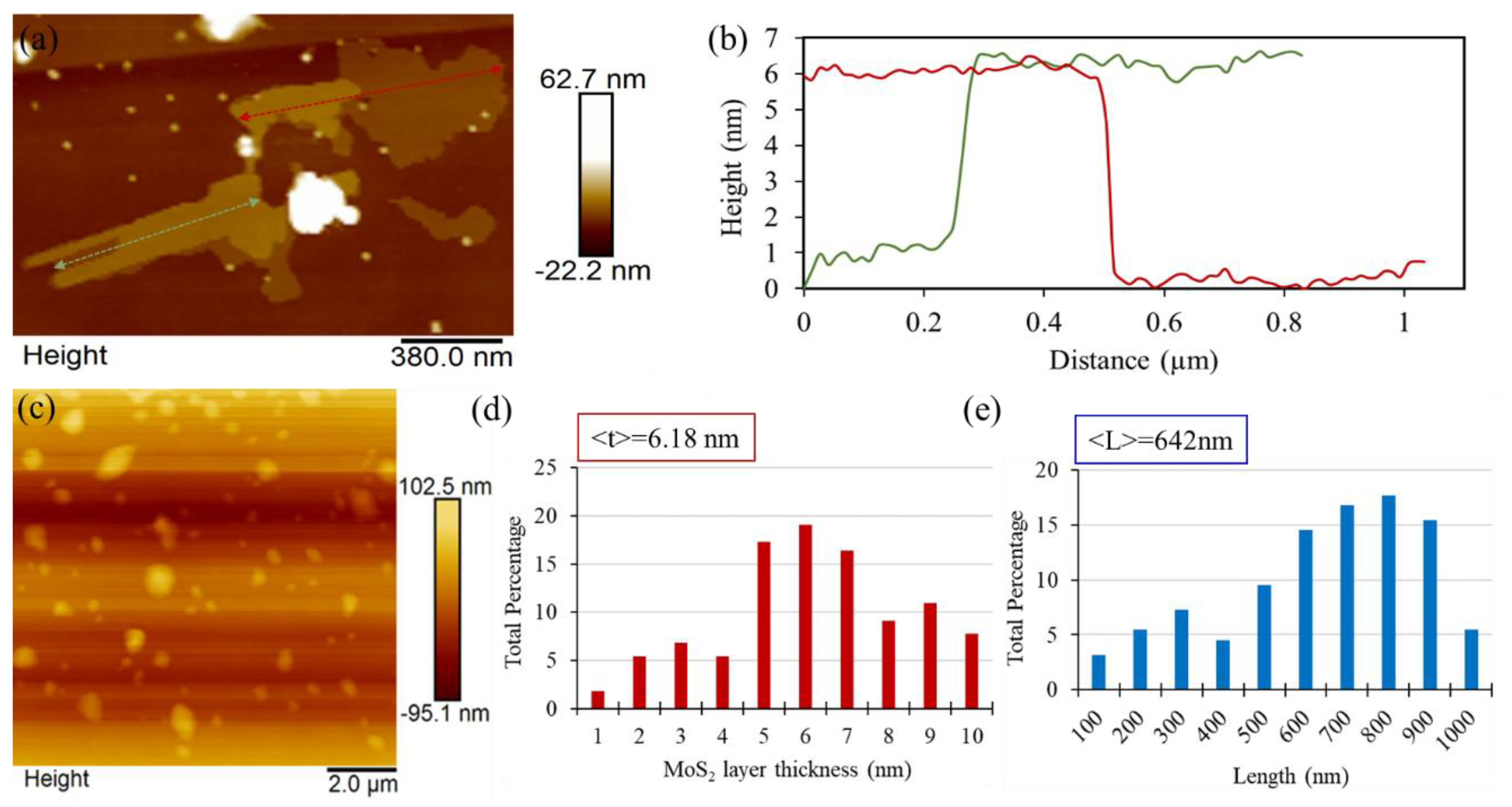

| Sample | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Strain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester (PS) | |||
| Neat PS | 27.81 ± 1.6 | 3.75 ± 0.05 | 0.782 ± 0.021 |
| PS-Bulk-MoS2 | 26.78 ± 2.1 | 3.53 ± 0.08 | 0.698 ± 0.042 |
| PS-Ball milled-MoS2 | 31.17 ± 1.5 | 3.92 ± 0.04 | 0.865 ± 0.043 |
| PS-F-MoS2 | 36.27 ± 1.8 | 3.98 ± 0.03 | 0.891 ± 0.036 |
| Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) | |||
| Neat PVA | 24.26 ± 2.2 | 1.81 ± 0.03 | 83.5 ± 6.9 |
| PVA-Bulk-MoS2 | 22.88 ± 2.8 | 1.86 ± 0.02 | 62.3 ± 5.8 |
| PVA-Ball milled-MoS2 | 25.52 ± 2.3 | 1.91 ± 0.01 | 85.4 ± 4.3 |
| PVA-F-MoS2 | 27.98 ± 1.8 | 1.97 ± 0.03 | 81.9 ± 4.7 |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | |||
| Neat TPU | 33.16 ± 3.5 | 0.051 ± 0.004 | 551 ± 8.2 |
| TPU-Bulk-MoS2 | 29.18 ± 2.8 | 0.054 ± 0.003 | 402 ± 5.4 |
| TPU-Ball milled-MoS2 | 32.25 ± 3.1 | 0.057 ± 0.003 | 545 ± 7.7 |
| TPU-F-MoS2 | 36.69 ± 1.9 | 0.060 ± 0.002 | 536 ± 3.9 |
| Synthesising Method | Further Processing Step | Lateral Dimension (nm) | Thickness (nm) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball milling | Hydrothermal assisted + DDS | 642 | 6.18 | 121.8 | No need for any solvents during ball milling. Short ball milling time. The existence of reactive groups on edges. Excellent dispersion and high stability. 2H polytype formation. | This study |
| Ball milling | The use of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone | 100–150 | - | 20.25 | Toxic solvent. 72 h ball milling. 1T polytype formation. | [78] |
| Ball milling | Sodium cholate | 150 | 2.5–5.3 | - | 93% Yield. High dispersibility in water without the need for sonication. 2H crystal structure. 6 h ball milling. | [79] |
| Ball milling | Use of MoO3 and sulfur as precursors, followed by calcination at 600 °C for 2 h in argon | <100 | <2 | - | 24 h ball milling. The high density of coordinatively unsaturated surface atoms. | [80] |
| Ball milling | Use of MoO3 and sulfur as precursors, followed by thermal annealing at 350 °C | <100 | 5.6 | 61.4 | 24 h ball milling in argon. Rich exposed edge sites. | [81] |
| Micromechanical exfoliation using scotch tape | Functionalization with Spherical Gold nanoparticles | - | 0.8 | - | Differences in the dimension of the nanosheets. Low yield (limitations for scale-up) | [82] |
| High shear-induced liquid exfoliation | Lithium intercalation by ultrasonication in water | 300–800 | 1–1.2 | - | Difficulties in separation, vulnerable to defects, the change of polytype to 1T, and the need for high annealing temperature | [22] |
| Thermal ablation by lasers | The use of tape followed by laser-thinned | 200 | 0.9 | - | The need for the substrate. The limitation of scalable production. Low production rate. Harsh conditions, such as high temperature. Costly procedure. | [12] |
| Chemical vapour deposition | Using Mo(CO)6 and H2S precursors on several different substrates, including SiO2, sapphire, and amorphous alumina | 100 | 5–20 | - | The use of precursors, mostly expensive catalyst, the need for substrate, low yield, and high temperature | [83] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmadi, M.; Zabihi, O.; Li, Q.; Fakhrhoseini, S.M.; Naebe, M. A Hydrothermal-Assisted Ball Milling Approach for Scalable Production of High-Quality Functionalized MoS2 Nanosheets for Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101400
Ahmadi M, Zabihi O, Li Q, Fakhrhoseini SM, Naebe M. A Hydrothermal-Assisted Ball Milling Approach for Scalable Production of High-Quality Functionalized MoS2 Nanosheets for Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(10):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101400
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmadi, Mojtaba, Omid Zabihi, Quanxiang Li, Seyed Mousa Fakhrhoseini, and Minoo Naebe. 2019. "A Hydrothermal-Assisted Ball Milling Approach for Scalable Production of High-Quality Functionalized MoS2 Nanosheets for Polymer Nanocomposites" Nanomaterials 9, no. 10: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101400
APA StyleAhmadi, M., Zabihi, O., Li, Q., Fakhrhoseini, S. M., & Naebe, M. (2019). A Hydrothermal-Assisted Ball Milling Approach for Scalable Production of High-Quality Functionalized MoS2 Nanosheets for Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials, 9(10), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101400







