Glancing-Angle Deposition of Nanostructures on an Implant Material Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Fabrication
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Osteogenic Differentiation
2.4. Bacterial Adherence
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
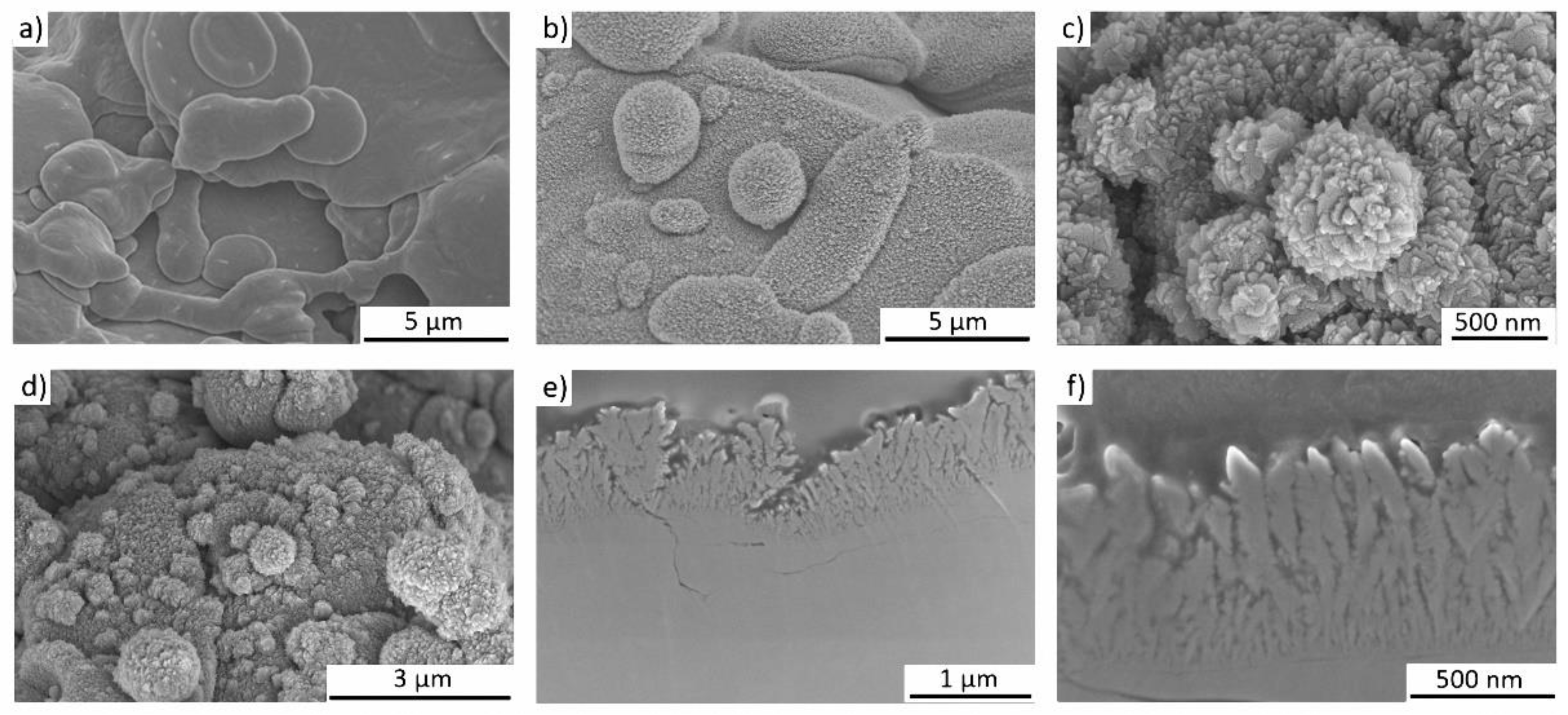
3.1. Formation of Nano-Spikes on the TPS Surface
3.2. Biological Properties of the TPS+ Surface
3.2.1. Cell-Compatibility
3.2.2. Antibacterial Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Fonseca, C.; Boudin, S.; Da Cunha Belo, M. Characterisation of titanium passivation films by in situ ac impedance measurements and XPS analysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 379, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, Y.; Johansson, C.B.; Petronis, S.; Krozer, A.; Jeong, Y.; Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Characteristics of the surface oxides on turned and electrochemically oxidized pure titanium implants up to dielectric breakdown: The oxide thickness, micropore configurations, surface roughness, crystal structure and chemical composition. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausmaa, J.; Kasemo, B. Surface Spectroscopic characterization of titanium implant materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1990, 44, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, D.; Naujoks, D.; De los Arcos, T.; Grosse-Kreul, S.; Ludwig, A. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Investigations of the Surface Reaction Layer and its Effects on the Transformation Properties of Nanoscale Ti51Ni38Cu 11 Shape Memory Thin Films. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidambe, A.T. Biocompatibility of advanced manufactured titanium implants-A review. Materials 2014, 7, 8168–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsari, V.; Giavaresi, G.; Fini, M.; Torricelli, P.; Tschon, M.; Chiesa, R.; Chiusoli, L.; Salito, A.; Volpert, A.; Giardino, R. Comparative in vitro study on a ultra-high roughness and dense titanium coating. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4948–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, C.; Buzzi, M.P.; Bozzini, S.; Boiocchi, C.; D’Angelo, A.; Schirinzi, S.; Esposito, C.; Torreggiani, M.; Choi, J.; Ochan Kilama, M.; et al. Microalbuminuria and sRAGE in High-Risk Hypertensive Patients Treated with Nifedipine/Telmisartan Combination Treatment: A Substudy of TALENT. Mediators Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fousova, M.; Vojtech, D.; Jablonska, E.; Fojt, J.; Lipov, J. Novel approach in the use of plasma spray: Preparation of bulk titanium for bone augmentations. Materials 2017, 10, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Dimitriou, R.; Parvizi, J.; Babis, G.C. Biology of implant osseointegration. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2009, 9, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Coelho, P.G.; Kang, B.S.; Sul, Y.T.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of osseointegrated implant surfaces: Materials, chemistry and topography. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cao, H.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Yang, G.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Enhanced Osseointegration of Hierarchical Micro/Nanotopographic Titanium Fabricated by Microarc Oxidation and Electrochemical Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3840–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhatanadgit, W. Biological Responses to New Advanced Surface Modifications of Endosseous Medical Implants. Bone Tissue Regen. Insights 2009, 2, BTRI.S3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motemani, Y.; Greulich, C.; Khare, C.; Lopian, M.; Buenconsejo, P.J.S.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Ludwig, A.; Köller, M. Adherence of human mesenchymal stem cells on Ti and TiO2 nano-columnar surfaces fabricated by glancing angle sputter deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Hasan, J.; Webb, H.K.; Truong, V.K.; Watson, G.S.; Watson, J.A.; Baulin, V.A.; Pogodin, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Tobin, M.J.; et al. Natural bactericidal surfaces: Mechanical rupture of pseudomonas aeruginosa cells by cicada wings. Small 2012, 8, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengstock, C.; Lopian, M.; Motemani, Y.; Borgmann, A.; Khare, C.; Buenconsejo, P.J.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Ludwig, A.; Koller, M. Structure-related antibacterial activity of a titanium nanostructured surface fabricated by glancing angle sputter deposition. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; García-Martín, J.M.; Álvarez, R.; Palmero, A.; Esteban, J.; Pérez-Jorge, C.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanocolumnar coatings with selective behavior towards osteoblast and Staphylococcus aureus proliferation. Acta Biomater. 2015, 15, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, A.; Pickford, M.; Shawcross, J. The History, Technical Specifications and Efficacy of Plasma Spray Coatings Applied to Joint Replacement Prostheses. Reconstr. Rev. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkeye, M.M.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Glacing Angle Deposition of Thin Films: Engineering the Nanoscale; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco, A.; Borras, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: From fundamentals to devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 59–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A. The microstructure of sputter-deposited coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vacuum Surfaces Films 1986, 4, 3059–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Gall, D. Structure zone model for extreme shadowing conditions. Thin Solid Films 2013, 527, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, G.; Mendonça, D.B.S.; Simões, L.G.P.; Araújo, A.L.; Leite, E.R.; Duarte, W.R.; Aragão, F.J.L.; Cooper, L.F. The effects of implant surface nanoscale features on osteoblast-specific gene expression. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4053–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittens, R.A.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. Implant osseointegration and the role of microroughness and nanostructures: Lessons for spine implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbourne, A.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Nano-structured antimicrobial surfaces: From nature to synthetic analogues. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, S.M.; Habimana, O.; Lawler, J.; Reilly, B.O.; Daniels, S.; Casey, E.; Cowley, A. Cicada Wing Surface Topography: An Investigation into the Bactericidal Properties of Nanostructural Features. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14966–14974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diu, T.; Faruqui, N.; Sjöström, T.; Lamarre, B.; Jenkinson, H.F.; Su, B.; Ryadnov, M.G. Cicada-inspired cell-instructive nanopatterned arrays. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Peppo, G.M.; Agheli, H.; Karlsson, C.; Ekström, K.; Brisby, H.; Lennerås, M.; Gustafsson, S.; Sjövall, P.; Johansson, A.; Olsson, E.; et al. Osteogenic response of human mesenchymal stem cells to well-defined nanoscale topography in vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2499–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchison, T.J.; Cramer, L.P. Actin-based cell motility and cell locomotion. Cell 1996, 84, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, M.J.; Gadegaard, N.; Tare, R.; Andar, A.; Riehle, M.O.; Herzyk, P.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Oreffo, R.O.C. The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyan, B.D.; Cheng, A.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Schwartz, Z. Implant Surface Design Regulates Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation and Maturation. Adv. Dent. Res. 2016, 28, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köller, M.; Ziegler, N.; Sengstock, C.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Ludwig, A. Bacterial cell division is involved in the damage of gram-negative bacteria on a nano-pillar titanium surface. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziegler, N.; Sengstock, C.; Mai, V.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Köller, M.; Ludwig, A. Glancing-Angle Deposition of Nanostructures on an Implant Material Surface. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010060
Ziegler N, Sengstock C, Mai V, Schildhauer TA, Köller M, Ludwig A. Glancing-Angle Deposition of Nanostructures on an Implant Material Surface. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiegler, Nadine, Christina Sengstock, Viola Mai, Thomas A. Schildhauer, Manfred Köller, and Alfred Ludwig. 2019. "Glancing-Angle Deposition of Nanostructures on an Implant Material Surface" Nanomaterials 9, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010060
APA StyleZiegler, N., Sengstock, C., Mai, V., Schildhauer, T. A., Köller, M., & Ludwig, A. (2019). Glancing-Angle Deposition of Nanostructures on an Implant Material Surface. Nanomaterials, 9(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010060





