ZIF-8-Derived Hollow Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Antibiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
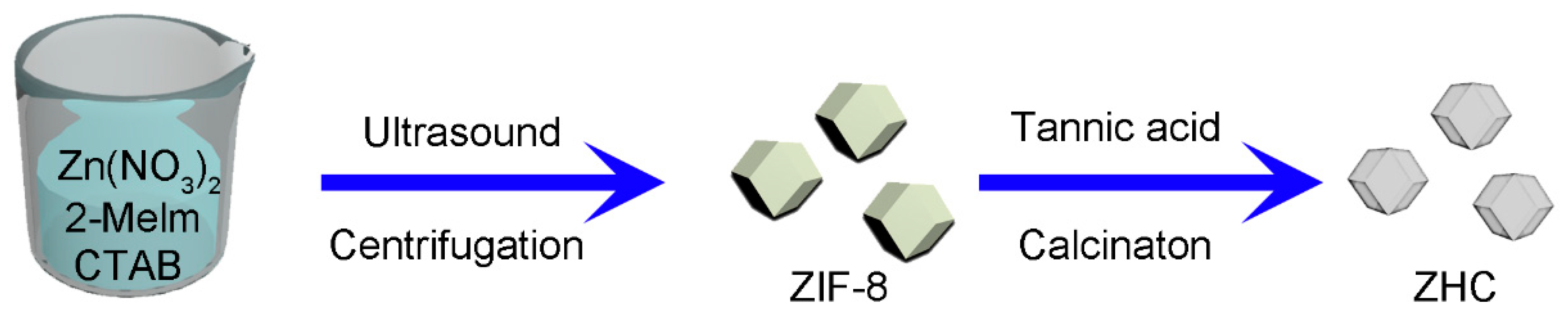
2.2. ZIF-8 Derived Hollow Carbon (ZHC) Preparation
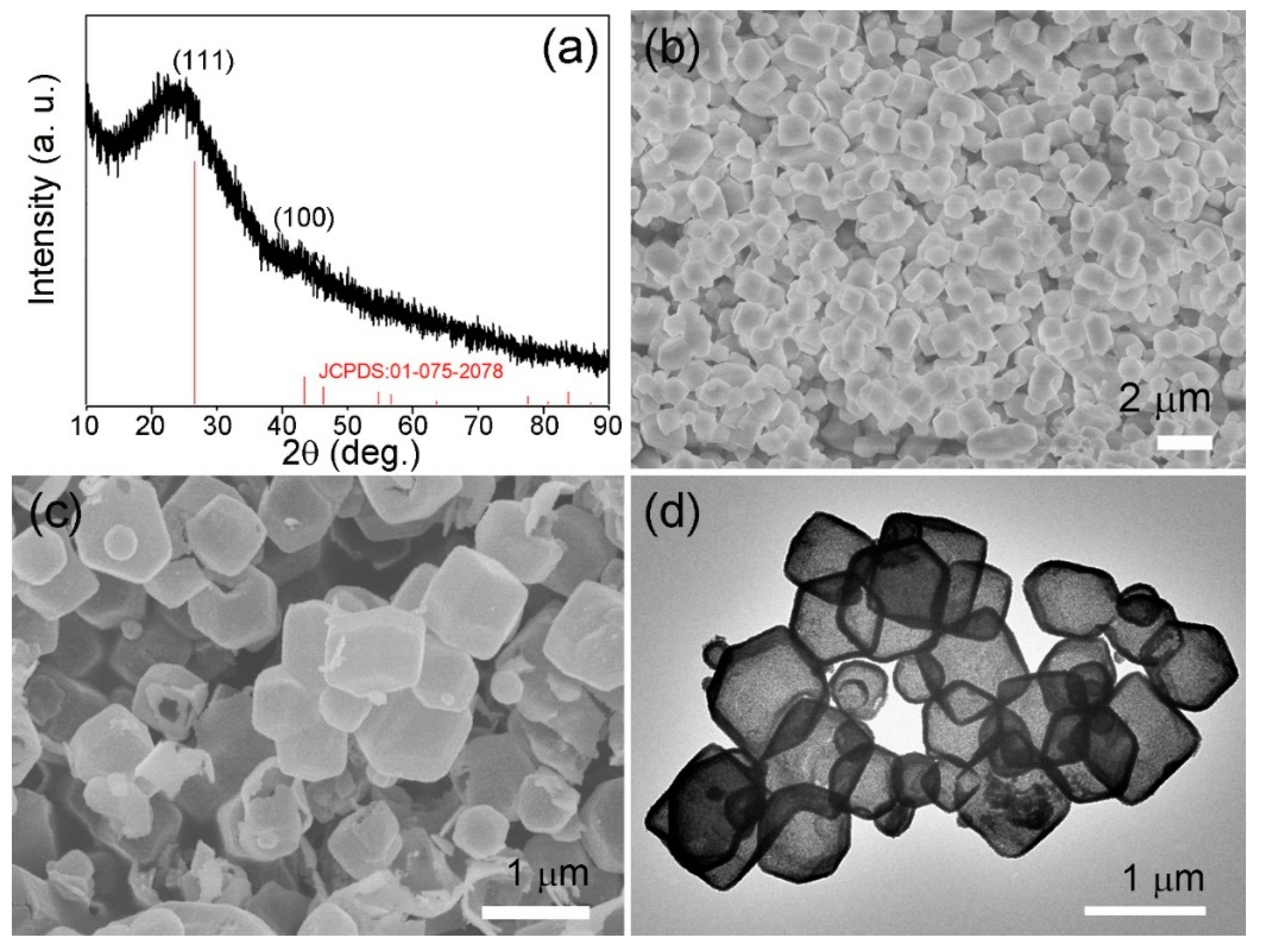
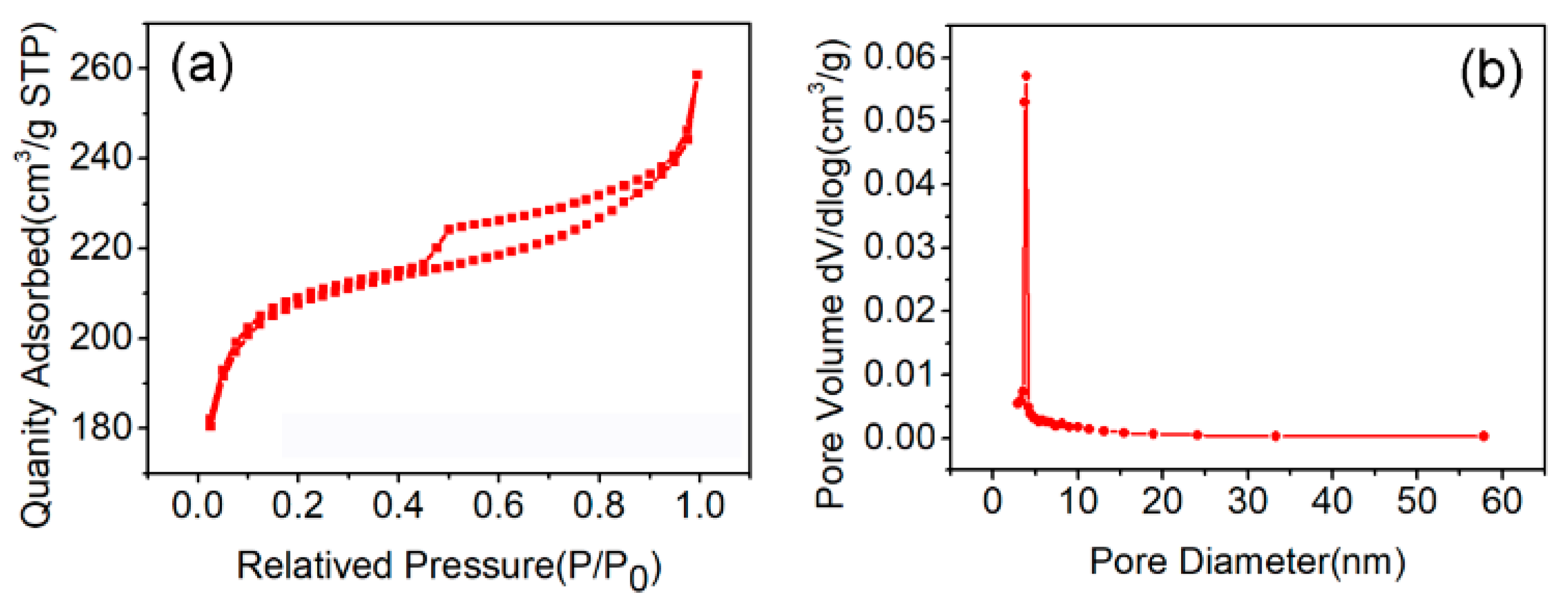
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Process
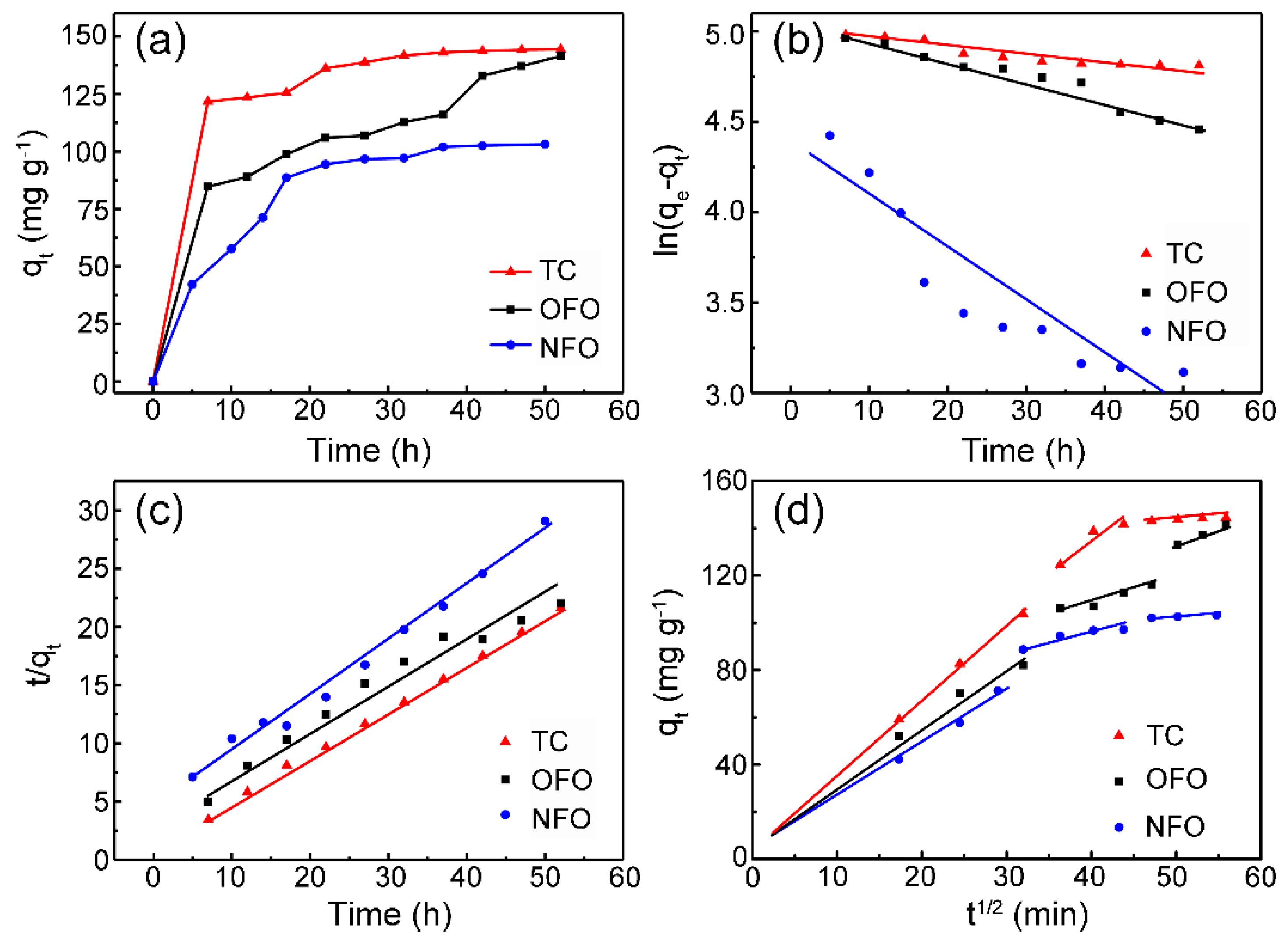
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michael, I.; Rizzo, L.; McArdell, C.S.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: A review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.K.; Liu, Y.Y.; Bao, D.D.; Zhu, G.; Yang, G.H.; Geng, J.F.; Li, H.T. Effective Removal of Tetracycline Antibiotics from Water using Hybrid Carbon Membranes. Sci. Rep. UK 2017, 7, 43717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.C.; Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Introduction to Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikittisilp, W.; Ariga, K.; Yamauchi, Y. A new family of carbon materials: Synthesis of MOF-derived nanoporous carbons and their promising applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, L.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Yuan, Q. Fabrication of a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot from MOF-derived porous carbon and its application for highly selective fluorescence detection of Fe3+. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachfule, P.; Shinde, D.; Majumder, M.; Xu, Q. Fabrication of carbon nanorods and graphene nanoribbons from a metal-organic framework. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Qiu, B.; Xia, D.; Zou, R. Facile preparation of hierarchically porous carbons from metal-organic gels and their application in energy storage. Sci. Rep. UK 2013, 3, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, J.S.; Katie, A.C.; Matthias, T. Characterization of Micro/Mesoporous Materials by Physisorption: Concepts and Case Studies. Acc. Mater. Surf. Res. 2018, 3, 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; He, G.; Yu, L.; Noor, N.; Sun, N.; Zhou, X.; Hu, J.; Parkin, I.P. Enhanced adsorption capacity of ultralong hydrogen titanate nanobelts for antibiotics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4352–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Xiao, X.; Duan, S.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Lei, J.; Wang, L. Synthesis of novel microporous nanocomposites of ZIF-8 on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for adsorptive removing benzoic acid from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Townsend, T.G.; Mazyck, D.; Boyer, T.H. Equilibrium and intra-particle diffusion of stabilized landfill leachate onto micro- and meso-porous activated carbon. Water Res. 2012, 46, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, Q.; Frear, C.; Zheng, Y. Synthesis of Fe3O4/Polyacrylonitrile Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Mat for Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14573–14583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Li, C.T.; Chien, H.T.; Salunkhe, R.R.; Suzuki, N.; Yamauchi, Y.; Ho, K.C.; Wu, K.C.W. Platinum-Free Counter Electrode Comprised of Metal-Organic-Framework (MOF)-Derived Cobalt Sulfide Nanoparticles for Efficient Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs). Sci. Rep. UK 2014, 4, 6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L. Magnetic Nanocomposites Derived from Hollow ZIF-67 and Core-Shell ZIF-67@ZIF-8: Synthesis, Properties, and Adsorption of Rhodamine B. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 35, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.U.; Yao, L.; Wang, J.; Gang, D.D.; Islam, F.; Lian, Q.; Zappi, M.E. Neodymium embedded ordered mesoporous carbon (OMC) for enhanced adsorption of sunset yellow: Characterizations, adsorption study and adsorption mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Chen, L.; Que, C.; Yang, K.; Deng, F.; Deng, X.; Shi, G.; Xu, G.; Wu, M. Adsorption of Antibiotics on Graphene and Biochar in Aqueous Solutions Induced by pi-pi Interactions. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 31920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, F. Efficient and synergistic removal of tetracycline and Cu(II) using novel magnetic multi-amine resins. Sci. Rep. UK 2018, 8, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Ma, J.; Han, S. Adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous solutions onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different oxygen contents. Sci. Rep. UK 2014, 4, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X. Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhuo, N.; Tian, Z.; Xu, P.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W. Interactions between Antibiotics and Graphene-Based Materials in Water: A Comparative Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24273–24280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Pan, B.; Xing, B. Norfloxacin Sorption and Its Thermodynamics on Surface-Modified Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, D.; Hua, X.; Guo, Z. Inhibitory effects of extracellular polymeric substances on ofloxacin sorption by natural biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Ge, C.; Feng, D. Effects of metal ions and pH on ofloxacin sorption to cassava residue-derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
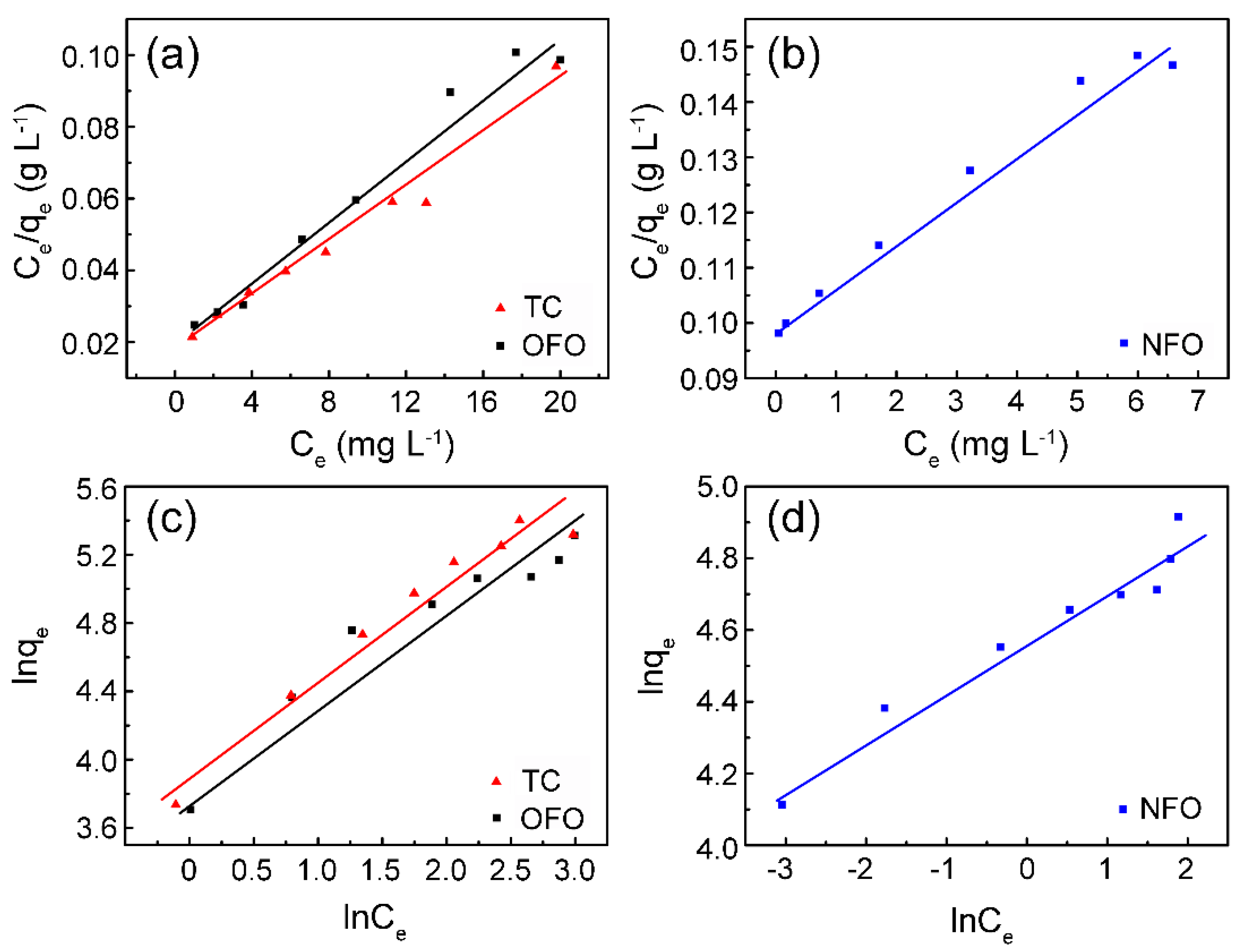
| Pollutants | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L mg−1) | qm (mg g−1) | R2 | Kf (mg g−1) (L mg−1)1/n | n | R2 | |
| TC | 0.212 | 267.3 | 0.972 | 70.80 | 1.8319 | 0.948 |
| NFO | 0.079 | 125.6 | 0.979 | 53.41 | 7.23 | 0.945 |
| OFO | 0.230 | 227.8 | 0.973 | 26.08 | 2.114 | 0.91 |
| Antibiotics | Adsorbents | qm (mg g−1) | Condition (pH) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetracycline | GN | 2 × 10−4 | 7 | [20] |
| E3D7 | 133.3 | 8 | [21] | |
| CNT-2%O | 217.8 | 4 | [22] | |
| Biochar | 102 | 6 | [23] | |
| ZIF-8 | 119.04 | 7 | This work | |
| ZHC | 267.3 | 7 | This work | |
| Norfloxacin | RGOS | 50 | 6 | [24] |
| H-CNTS | 76.3 | 7 | [25] | |
| ZIF-8 | 38.69 | 7 | This work | |
| ZHC | 125.6 | 7 | This work | |
| Ofloxacin | GN | 0.2 | 7 | [20] |
| BEPS-free biofilm-50 | 5.27 | 7 | [26] | |
| Cassava residue-derived biochar | 3.00 | 7 | [27] | |
| ZIF-8 | 111.48 | 7 | This work | |
| ZHC | 227.8 | 7 | This work |
| Model | C0 (mg L−1) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (L min−1) | qe, cal (mg g−1) | R2 | K2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe, cal (mg g−1) | R2 | ||
| TC | 40 | 0.00422 | 148.21 | 0.852 | 4.33 × 10−5 | 151.89 | 0.998 |
| NFO | 20 | 0.02963 | 76.77 | 0.87 | 6.25 × 10−5 | 126.17 | 0.987 |
| OFO | 40 | 0.01136 | 158.92 | 0.954 | 3.83 × 10−5 | 161.60 | 0.961 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Lin, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; He, G.; Shearing, P.R.; Brett, D.J.L. ZIF-8-Derived Hollow Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Antibiotics. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010117
Tang H, Li W, Jiang H, Lin R, Wang Z, Wu J, He G, Shearing PR, Brett DJL. ZIF-8-Derived Hollow Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Antibiotics. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(1):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010117
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hongmei, Wenyao Li, Haishun Jiang, Runjia Lin, Zhe Wang, Jianghong Wu, Guanjie He, Paul Robert Shearing, and Dan John Leslie Brett. 2019. "ZIF-8-Derived Hollow Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Antibiotics" Nanomaterials 9, no. 1: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010117
APA StyleTang, H., Li, W., Jiang, H., Lin, R., Wang, Z., Wu, J., He, G., Shearing, P. R., & Brett, D. J. L. (2019). ZIF-8-Derived Hollow Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Antibiotics. Nanomaterials, 9(1), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010117







