Fe1-xNix Alloy Nanoparticles Encapsulated Inside Carbon Nanotubes: Controlled Synthesis, Structure and Magnetic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Binary Alloys Inside CNTs
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
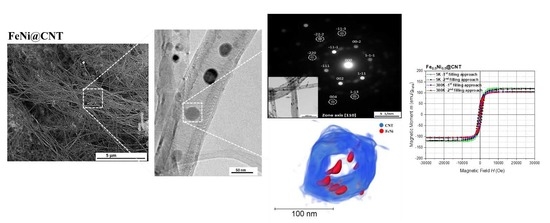
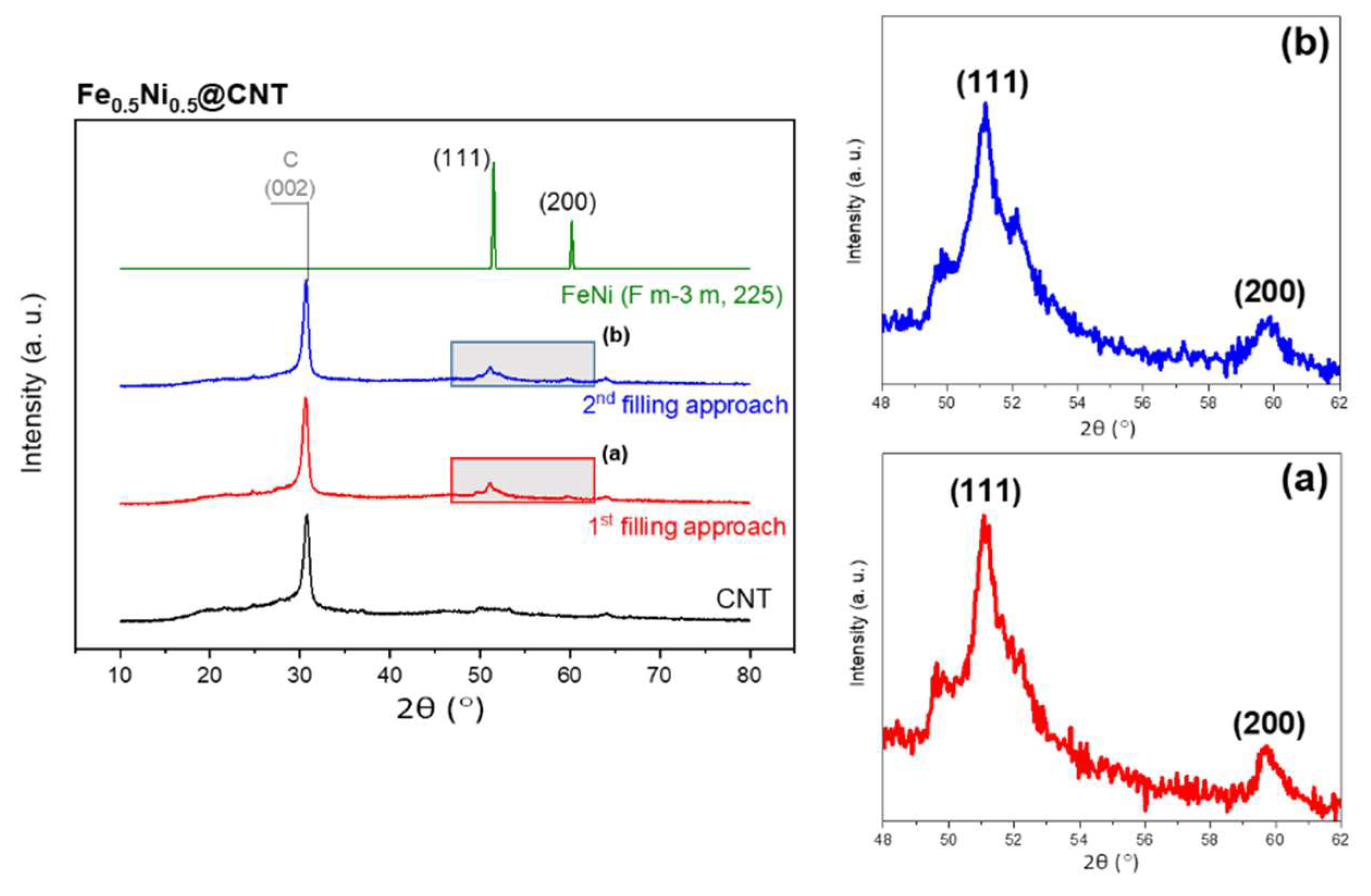
3.1. Fe50Ni50@CNT
3.1.1. Morphology and Structure
3.1.2. Magnetic Properties
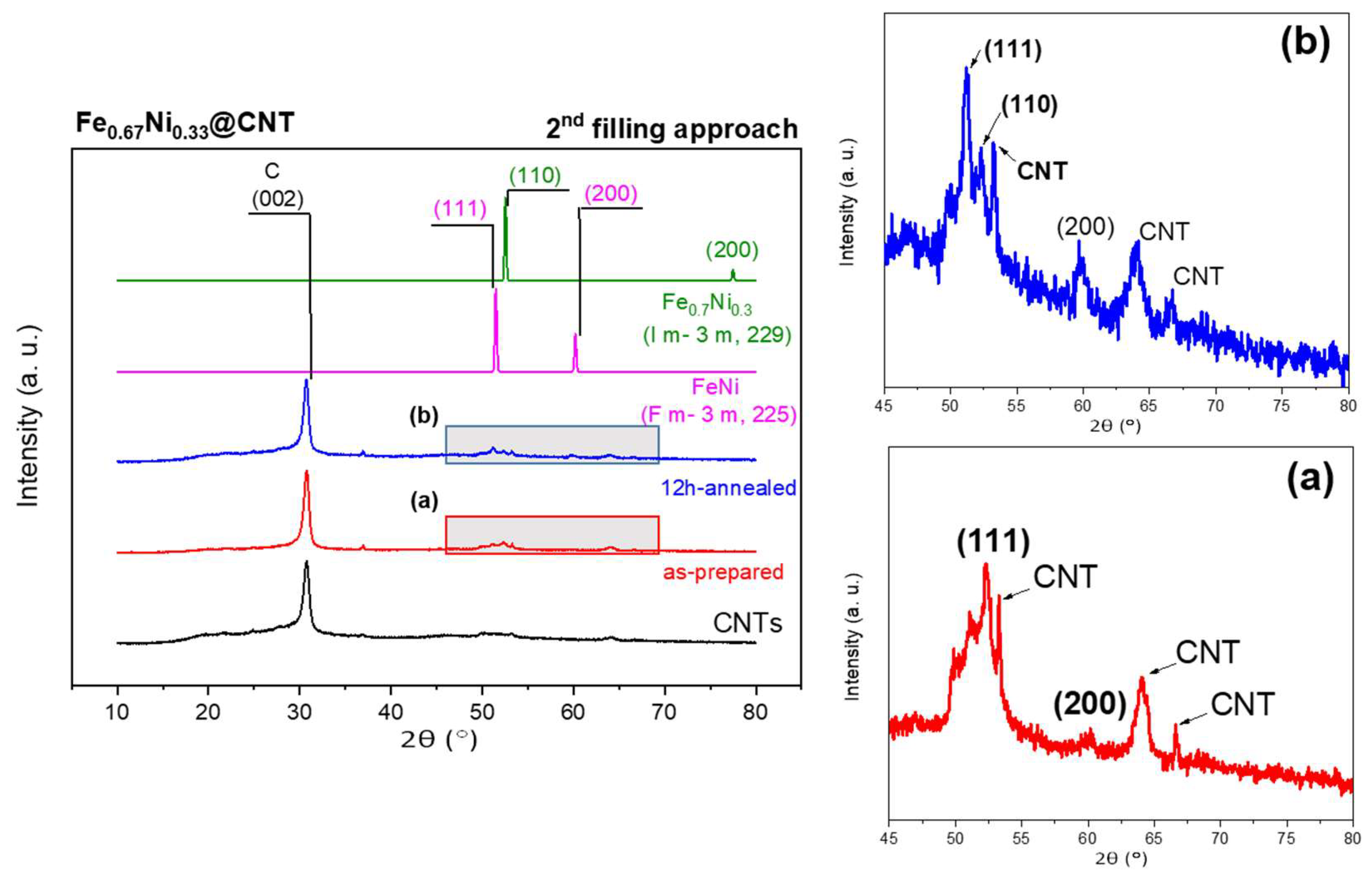
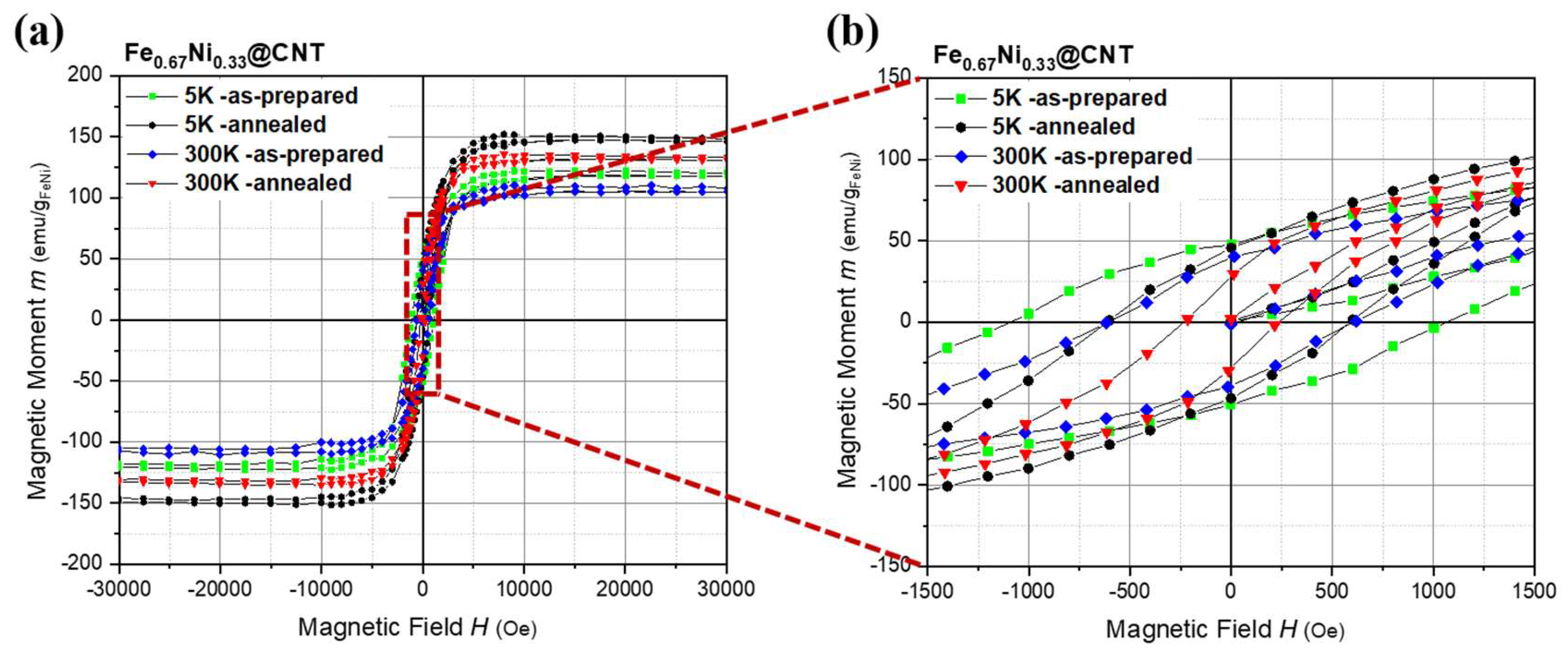
3.2. Fe67Ni33@CNT
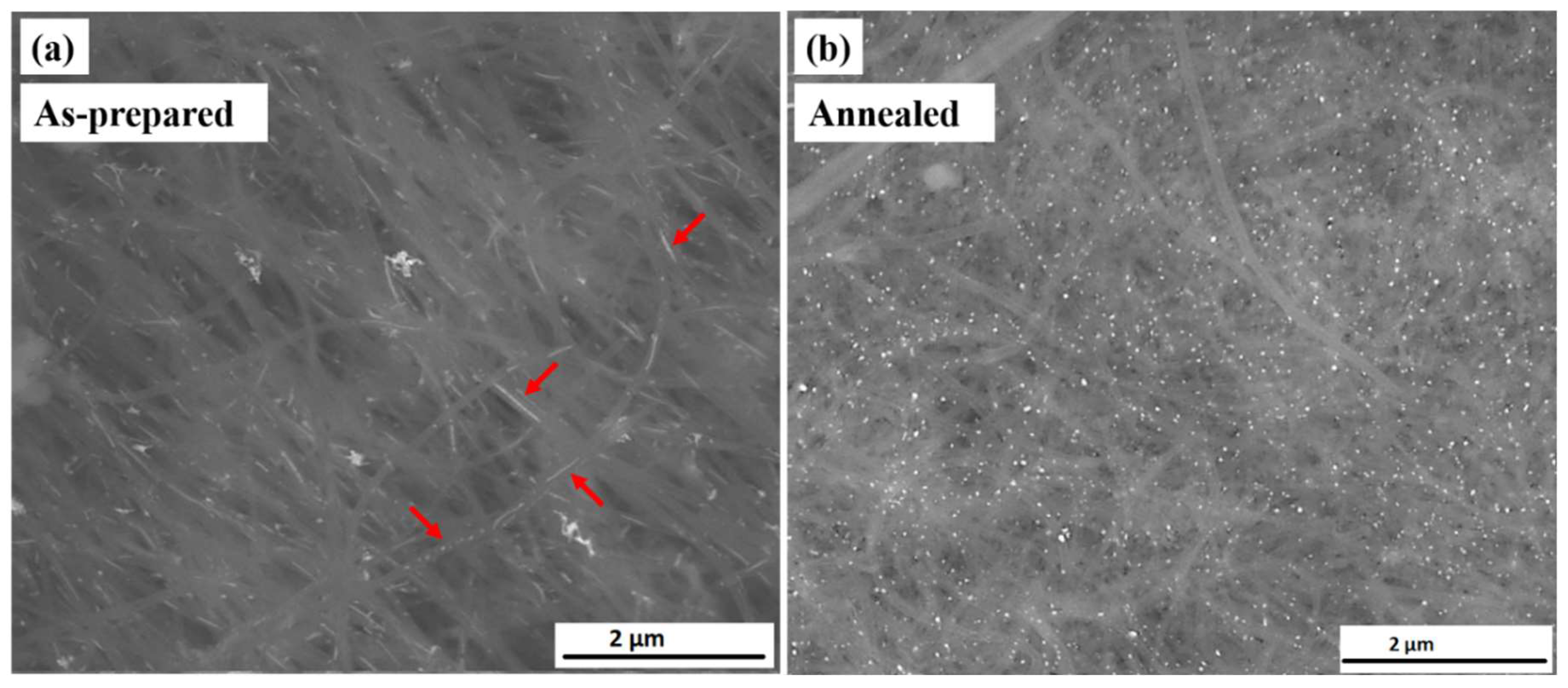
3.2.1. Morphology and Structure
3.2.2. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nalwa, H.S. Handbook of Nanostructured Materials and Nanotechnology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- McHenry, M.E.; Willard, M.A.; Laughlin, D.E. Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials for applications as soft magnets. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1999, 44, 291–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.-Q.; Cao, Y.-J.; Yuan, P.-S.; Xu, H.-Y.; Wei, X.-W. Controlled synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Fe1−xNix alloy nanoparticles attached on carbon nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 406, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigerwalt, E.S.; Deluga, G.A.; Lukehart, C. Pt-Ru/carbon fiber nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization, and performance as anode catalysts of direct methanol fuel cells. A search for exceptional performance. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, Q.-Z. Nanotube arrays of Zn/Co/Fe composite oxides assembled in porous anodic alumina and their magnetic properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 487, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Mühl, T.; Menzel, S.; Kozhuharova-Koseva, R.; Hampel, S.; Leonhardt, A.; Büchner, B. Magnetic force microscopy sensors using iron-filled carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 104905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mönch, I.; Meye, A.; Leonhardt, A.; Krämer, K.; Kozhuharova, R.; Gemming, T.; Wirth, M.P.; Büchner, B. Ferromagnetic filled carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles: Synthesis and lipid-mediated delivery into human tumor cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 290, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingeler, R.; Hampel, S.; Buchner, B. Carbon nanotube based biomedical agents for heating, temperature sensoring and drug delivery. Int. J. Hyperth. 2008, 24, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, E.; Jasen, P.; Gonzalez, G.; Moro, L.; Juan, A. Hydrogen and carbon interaction in a FeNi alloy with a vacancy. Phys. Status. Solidi. B 2009, 246, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisari, K.; Javadpour, S.; Oh, J.; Ghaffari, M. The effect of milling speed on the structural properties of mechanically alloyed Fe–45% Ni powders. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 472, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNerny, K.L.; Kim, Y.; Laughlin, D.E.; McHenry, M.E. Chemical synthesis of monodisperse γ-Fe–Ni magnetic nanoparticles with tunable Curie temperatures for self-regulated hyperthermia. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09A312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, N.; Deng, D.; Zhang, W.H.; Bao, X.; Li, C. Podlike N-doped carbon nanotubes encapsulating FeNi alloy nanoparticles: High-performance counter electrode materials for dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 7023–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, H.; Elmen, G. Permalloy, a new magnetic material of very high permeability. Bell. Labs. Tech. J. 1923, 2, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Kang, F.; Cai, D.; Wang, C.; Gu, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, D. Long continuous FeNi nanowires inside carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, property and application. J. Phys. Chem. Solid. 2008, 69, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, C.É. Recherches sur les aciers au nickel. Dilatations aux temperatures elevees; resistance electrique. CR Acad. Sci. 1897, 125, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Grobert, N.; Mayne, M.; Walton, D.R.M.; Kroto, H.W.; Terrones, M.; Kamalakaran, R.; Seeger, T.; Rühle, M.; Terrones, H.; Sloan, J.; et al. Alloy nanowires: Invar inside carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2001, 5, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantz, C.; Koshkina, O.; Lang, T.; Galla, H.-J.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Stauber, R.H.; Maskos, M. The surface properties of nanoparticles determine the agglomeration state and the size of the particles under physiological conditions. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.H.; Zhong, W.; Qi, X.S.; Au, C.T.; Deng, Y.; Du, Y.W. Highly stable Fe–Ni alloy nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 495, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghunaim, R.; Eckert, V.; Scholz, M.; Gellesch, M.; Wurmehl, S.; Damm, C.; Buechner, B.; Mertig, M.; Hampel, S. Carbon nanotube-assisted synthesis of ferromagnetic Heusler nanoparticles of Fe3Ga (Nano-Galfenol). J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Gautam, U.K.; Bando, Y.; Golberg, D. Comparative study of the stability of sulfide materials encapsulated in and expelled from multi-walled carbon nanotube capsules. Carbon 2011, 49, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipert, K.; Bahr, S.; Wolny, F.; Atkinson, P.; Weißker, U.; Mühl, T.; Schmidt, O.; Büchner, B.; Klingeler, R. An individual iron nanowire-filled carbon nanotube probed by micro-Hall magnetometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 212503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.M.M.; Hampel, S.; Wolter, A.U.B.; Kath, M.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Klingeler, R.; Täschner, C.; Khavrus, V.O.; Gemming, T.; Leonhardt, A.; et al. Superparamagnetic FeCo and FeNi Nanocomposites Dispersed in Submicrometer-Sized C. Spheres. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22509–22517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, J.; Wright, D.M.; Woo, H.G.; Bailey, S.; Brown, G.; York, A.P.E.; Coleman, K.S.; Hutchison, J.L.; Green, M.L.H. Capillarity and silver nanowire formation observed in single walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 1999, 8, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, E.; Ebbesen, T.; Hiura, H.; Tanigaki, K. Capillarity and wetting of carbon nanotubes. Science 1994, 265, 1850–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayan, P.M. Capillarity-induced filling of carbon nanotubes. Nature 1993, 361, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-Q.; Wei, X.-W.; Shao, M.-W.; Gu, J.-S.; Qu, M.-Z. Preparation of Fe–Ni alloy nanoparticles inside carbon nanotubes via wet chemistry. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1919–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrograf Products. Available online: www.pyrografproducts.com (accessed on 5 July 2018).
- Arlt, M.; Haase, D.; Hampel, S.; Oswald, S.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Klingeler, R.; Schulze, R.; Ritschel, M.; Leonhardt, A.; Fuessel, S.; et al. Delivery of carboplatin by carbon-based nanocontainers mediates increased cancer cell death. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 335101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessonnier, J.-P.; Rosenthal, D.; Hansen, T.W.; Hess, C.; Schuster, M.E.; Blume, R.; Girgsdies, F.; Pfänder, N.; Timpe, O.; Su, D.S. Analysis of the structure and chemical properties of some commercial carbon nanostructures. Carbon 2009, 47, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghunaim, R.; Scholz, M.; Damm, C.; Rellinghaus, B.; Klingeler, R.; Büchner, B.; Mertig, M.; Hampel, S. Single-crystalline FeCo nanoparticle-filled carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, structural characterization and magnetic properties. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, S.; Chen, Y.; Harris, P.; Green, M. A simple chemical method of opening and filling carbon nanotubes. Nature 1994, 372, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellesch, M. Statistical study of the effect of annealing treatments on assemblies of intermetallic magnetic nanoparticles related to the Heusler compound Co2FeGa. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.M.; Sloan, J.; Rutherford, T.; Green, M.L. Encapsulation of RexOy clusters within single-walled carbon nanotubes and their in tubulo reduction and sintering to Re metal. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6579–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A. The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haft, M.; Grönke, M.; Gellesch, M.; Wurmehl, S.; Büchner, B.; Mertig, M.; Hampel, S. Tailored nanoparticles and wires of Sn, Ge and Pb inside carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2016, 101, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellesch, M.; Dimitrakopoulou, M.; Scholz, M.; Blum, C.G.F.; Schulze, M.; van den Brink, J.; Hampel, S.; Wurmehl, S.; Büchner, B. Facile Nanotube-Assisted Synthesis of Ternary Intermetallic Nanocrystals of the Ferromagnetic Heusler Phase Co2FeGa. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2013, 13, 2707–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorth, R.M. Ferromagnetism. Wiley-VCH 1993, 1, 992. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Davaran, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Cha, J.M.; Yoon, H.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, Y.K. Magnetic multi-granule nanoclusters: A model system that exhibits universal size effect of magnetic coercivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kneller, E.F.; Luborsky, F.E. Particle Size Dependence of Coercivity and Remanence of Single-Domain Particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués, J.; Schuller, I.K. Exchange bias. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 192, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyama, K.; Kadono, M.; Nakamura, Y. Metastable bcc phase in sputtered Fe–Ni alloys. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1983, 24, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Elshafaie, A.; Hamdan, S.K.; Ahmed, A. Electric, thermoelectric and magnetic characterization of γ-Fe2O3 and Co3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by facile thermal decomposition of metal-Schiff base complexes. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 99, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Filling Approach | |
|---|---|---|
| First Approach | Second Approach | |
| dTEM (nm) | 19 ± 10 | 17 ± 4 |
| dXRD (nm) | 8.9 ± 0.2 | 9.8 ± 0.2 |
| TGA (wt. %) | 5.0 ± 1 | 5.6 ± 1 |
| Ms (emu/gFeNi) (300K) | 108 ± 22 | 104 ± 19 |
| Ms (emu/gFeNi) (5K) | 123 ± 25 | 118 ± 21 |
| Hc (Oe) (300K) | 143 ± 2 | 492 ± 3 |
| Hc (Oe) (5K) | 548 ± 7 | 967 ± 12 |
| Parameter | Second Approach | |
|---|---|---|
| As-Prepared | Annealed | |
| dTEM (nm) | 19 ± 8 | 28 ± 9 |
| dXRD (nm) | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 9.0 ± 0.4 |
| TGA (wt. %) | 2.7 ± 1 | |
| Ms (emu/gFeNi) (300K) | 110 ± 40 | 136 ± 50 |
| Ms (emu/gFeNi) (5K) | 123 ± 47 | 152 ± 56 |
| Hc (Oe) (300K) | 608 ± 1 | 234 ± 1 |
| Hc (Oe) (5K) | 1080 ± 16 | 601 ± 17 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghunaim, R.; Damm, C.; Wolf, D.; Lubk, A.; Büchner, B.; Mertig, M.; Hampel, S. Fe1-xNix Alloy Nanoparticles Encapsulated Inside Carbon Nanotubes: Controlled Synthesis, Structure and Magnetic Properties. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080576
Ghunaim R, Damm C, Wolf D, Lubk A, Büchner B, Mertig M, Hampel S. Fe1-xNix Alloy Nanoparticles Encapsulated Inside Carbon Nanotubes: Controlled Synthesis, Structure and Magnetic Properties. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(8):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080576
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhunaim, Rasha, Christine Damm, Daniel Wolf, Axel Lubk, Bernd Büchner, Michael Mertig, and Silke Hampel. 2018. "Fe1-xNix Alloy Nanoparticles Encapsulated Inside Carbon Nanotubes: Controlled Synthesis, Structure and Magnetic Properties" Nanomaterials 8, no. 8: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080576
APA StyleGhunaim, R., Damm, C., Wolf, D., Lubk, A., Büchner, B., Mertig, M., & Hampel, S. (2018). Fe1-xNix Alloy Nanoparticles Encapsulated Inside Carbon Nanotubes: Controlled Synthesis, Structure and Magnetic Properties. Nanomaterials, 8(8), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080576