Galvanic-Cell-Reaction-Driven Deposition of Large-Area Au Nanourchin Arrays for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. The Preparation of Salt-Bridge
2.3. The Synthesis of Ag Seeds Colloidal Solution
2.4. Coating Ag Seeds on ITO Substrate
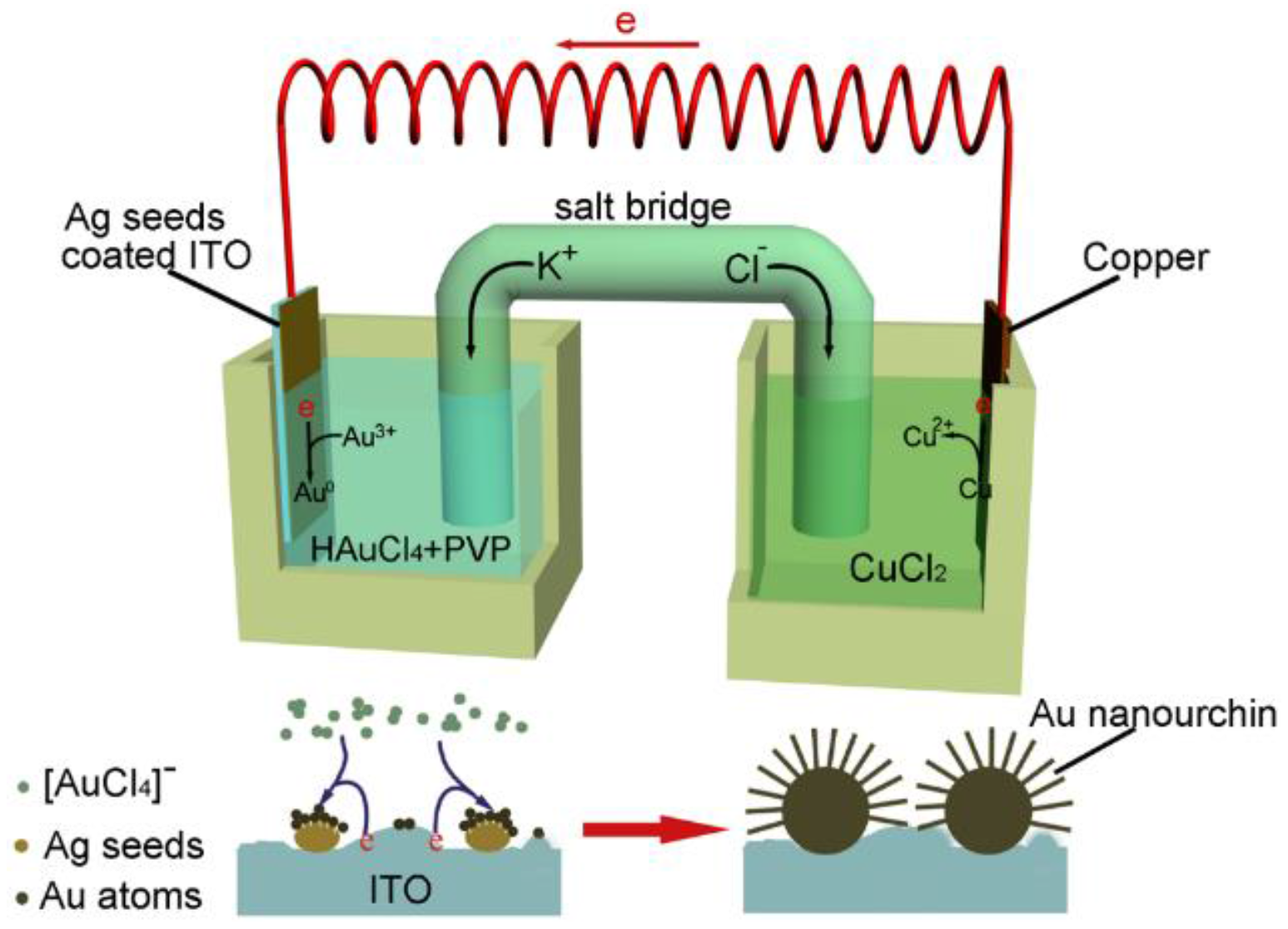
2.5. Synthesis of Au Nanourchin Arrays on Ag Seeds Spin-Coated ITO Substrates
2.6. Characterizations
2.7. Raman Measurements
2.8. FEM Calculations
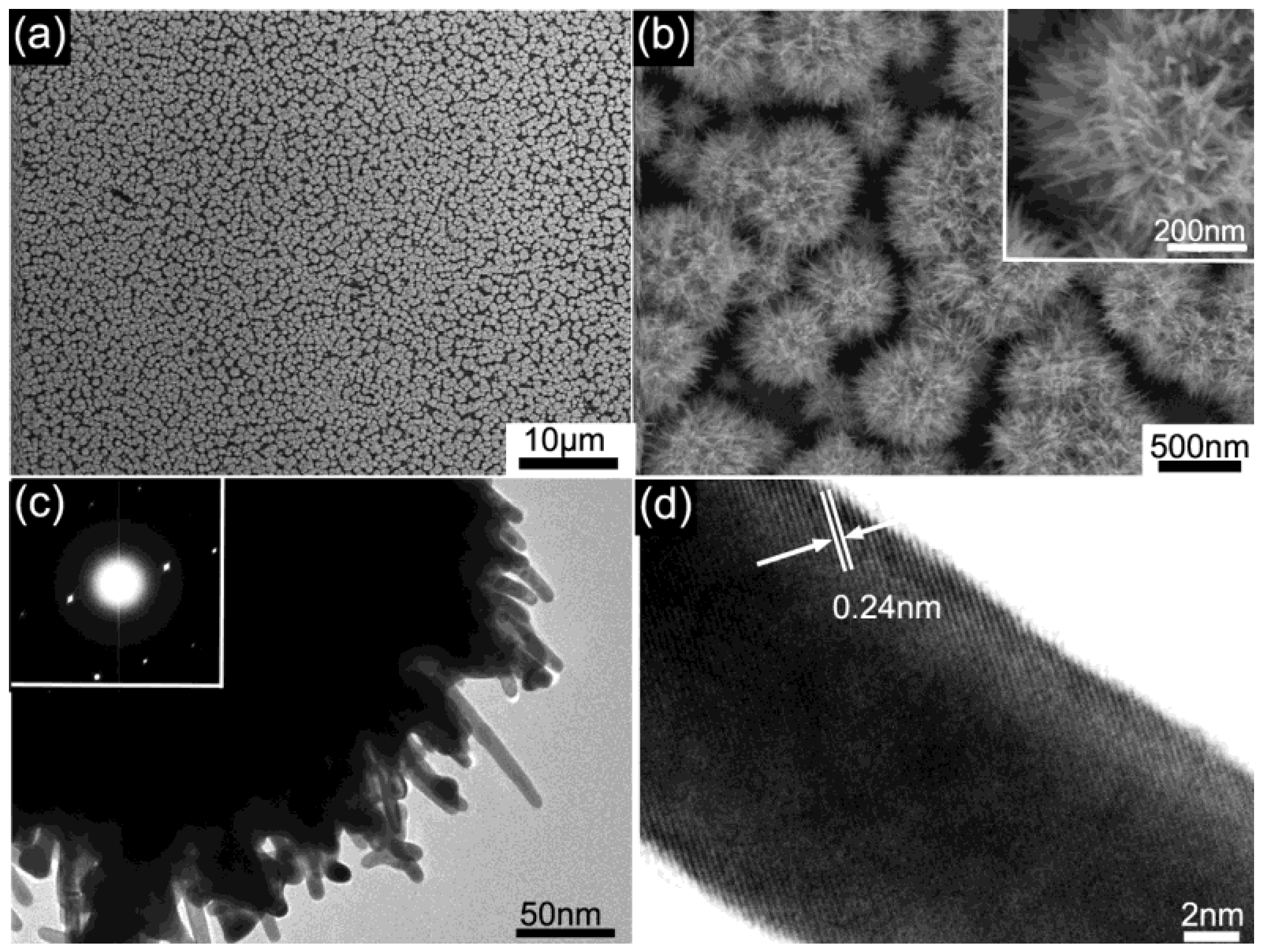
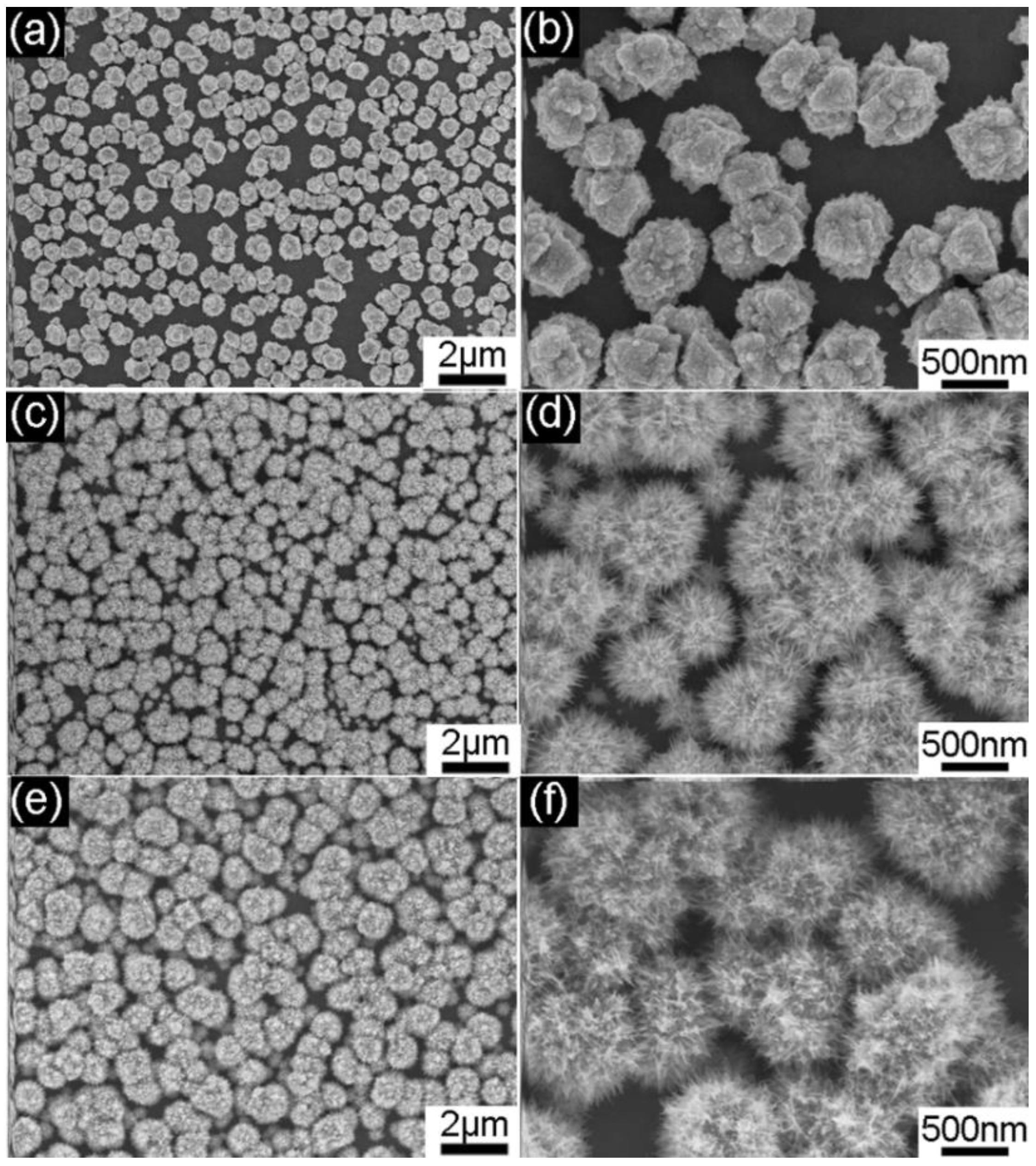
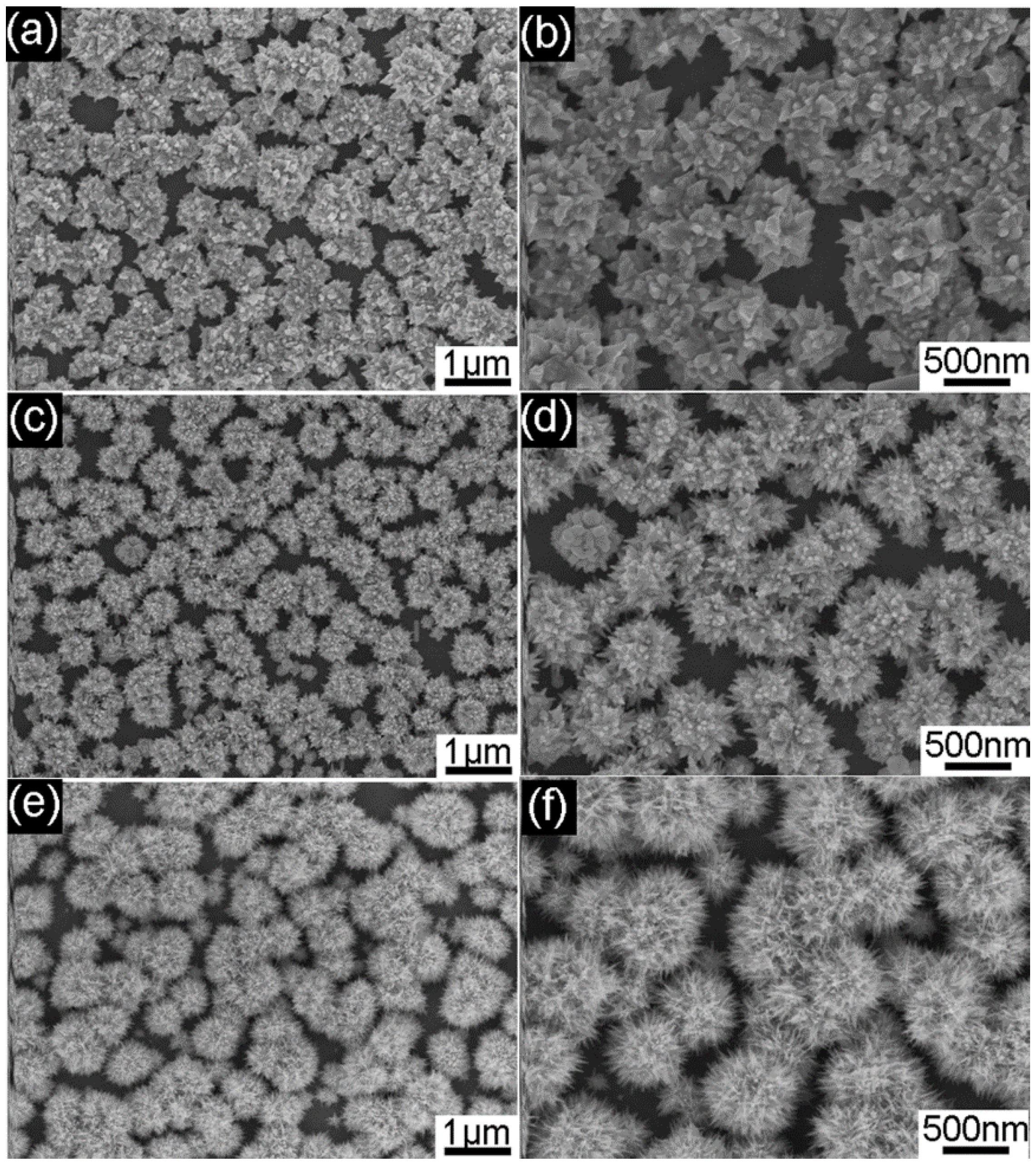
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, M.-C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zugic, B.; Wang, L.; Heine, C.; Zakharov, D.N.; Lechner, B.A.J.; Stach, E.A.; Biener, J.; Salmeron, M.; Madix, R.J.; Friend, C.M. Dynamic restructuring drives catalytic activity on nanoporous gold–silver alloy catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2016, 16, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: Applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Mulvaney, P. Gold nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1870–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, W.; Cui, S.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, B.; Cui, Z. Facile synthesis of Gd-functionalized gold nanoclusters as potential MRI/CT contrast agents. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Supported gold nanoparticles as catalysts for organic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2096–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, N.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Clausen, B.S.; Xu, Y.; Mavrikakis, M.; Bligaard, T.; Nørskov, J.K. On the origin of the catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles for low-temperature co oxidation. J. Catal. 2004, 223, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbillon, G.; Bijeon, J.L.; Lérondel, G.; Plain, J.; Royer, P. Detection of chemical molecules with integrated plasmonic glass nanotips. Surf. Sci. 2008, 602, L119–L122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Dinh, T.; Dhawan, A.; Norton, S.J.; Khoury, C.G.; Wang, H.-N.; Misra, V.; Gerhold, M.D. Plasmonic nanoparticles and nanowires: Design, fabrication and application in sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7480–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, C.-J.; Jeon, H.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, S.G.; Cho, S.; Choi, Y.; Yang, S.-M. Robust plasmonic sensors based on hybrid nanostructures with facile tunability. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13903–13907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.A.; Brongersma, M.L.; Kik, P.G.; Meltzer, S.; Requicha, A.A.G.; Atwater, H.A. Plasmonics—A route to nanoscale optical devices. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; WuDe, Y.; et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Dong, R.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Fabrication of Au nanorod-coated Fe3O4 microspheres as sers substrate for pesticide analysis by near-infrared excitation. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Dai, X.; Stogin, B.B.; Wong, T.-S. Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, D.; Langer, J.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Hybrid Au–SiO2 core–satellite colloids as switchable sers tags. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, A.; Sanchez-Iglesias, A.; Altantzis, T.; Bals, S.; Grzelczak, M.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Multifunctional self-assembled composite colloids and their application to SERS detection. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10377–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Guan, P.; Qin, D.; Golden, G.; Wallace, P.M. Inverted size-dependence of surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold nanohole and nanodisk arrays. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbillon, G.; Sandana, V.E.; Humbert, C.; Belier, B.; Rogers, D.J.; Teherani, F.H.; Bove, P.; McClintock, R.; Razeghi, M. Study of Au coated ZnO nanoarrays for surface enhanced Raman scattering chemical sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 3528–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryche, J.-F.; Bélier, B.; Bartenlian, B.; Barbillon, G. Low-cost SERS substrates composed of hybrid nanoskittles for a highly sensitive sensing of chemical molecules. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 239, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Mayen, L.; Oliva, J.; Torres-Castro, A.; De la Rosa, E. SERS substrates fabricated with star-like gold nanoparticles for zeptomole detection of analytes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10249–10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, C.; Pengyu, X.; Yue, L.; Junfei, X.; Song, H.; Weihui, O.; Yaping, D.; Weihai, N. Rapid seedless synthesis of gold nanoplates with micro-scaled edge length in a high yield and their application in SERS. Nano-Micro Lett. 2016, 8, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.-W.; Tsao, Y.-C.; Yang, M.-Y.; Huang, M.H. Seed-mediated growth of silver nanocubes in aqueous solution with tunable size and their conversion to au nanocages with efficient photothermal property. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 2326–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wiley, B.; Li, Z.Y.; Campbell, D.; Saeki, F.; Cang, H.; Au, L.; Lee, J.; Li, X.; Xia, Y. Gold nanocages: Engineering their structure for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, F.; Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L. Facile synthesis of gold and gold-based alloy nanowire networks using wormlike micelles as soft templates. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Levin, C.S.; Halas, N.J. Nanosphere arrays with controlled sub-10-nm gaps as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14992–14993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, W.; McKiernan, M.; Xie, Z.; Xia, Y. Seed-mediated synthesis of truncated gold decahedrons with a AuCl/oleylamine complex as precursor. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Camargo, P.H.C.; Xia, Y. Facile synthesis of branched Au nanostructures by templating against a self-destructive lattice of magnetic fe nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9653–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiohara, A.; Langer, J.; Polavarapu, L.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Solution processed polydimethylsiloxane/gold nanostar flexible substrates for plasmonic sensing. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9817–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L.; Jing, C.; Shi, X.; Yang, Z.; Long, Y.; Fang, J. Large-area fabrication of highly reproducible surface enhanced Raman substrate via a facile double sided tape-assisted transfer approach using hollow Au-Ag alloy nanourchins. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Peng, B.; Cao, C.; Zhang, C.; You, H.; Xiong, Q.; Li, Z.; Fang, J. Highly sensitive, uniform, and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy from hollow Au-Ag alloy nanourchins. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, Y.M.; Kandjani, A.E.; Ippolito, S.J.; Bhargava, S.K. Ordered monolayer gold nano-urchin structures and their size induced control for high gas sensing performance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, P.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, B.; Du, Y.; Han, X.; Mack, N.H.; Wang, H.-L. Fabrication of thorny Au nanostructures on polyaniline surfaces for sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Du, S.; Lebedkin, S.; Li, Z.; Kruk, R.; Kappes, M.; Hahn, H. Gold mesostructures with tailored surface topography and their self-assembly arrays for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 5006–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, D.-P.; Huang, P.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Chen, D.; Cui, D. Hierarchically assembled Au microspheres and sea urchin-like architectures: Formation mechanism and SERS study. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7766–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Cui, K.; Sun, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z. Facile synthesis of urchin-like gold submicrostructures for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Talanta 2010, 82, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Xing, T.T.; Ge, L.; Yang, T.; Chen, B.; Huang, C.Z. A portable multi-channel sensing device using Au nano-urchins as probes for melamine detection in milk. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7806–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Meng, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Urchin-like Au-nanoparticles@Ag-nanohemisphere arrays as active SERS-substrates for recognition of pcbs. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 19654–19657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, B.; Ippolito, S.J.; Bansal, V.; Sabri, Y.M.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Bhargava, S.K. Gold nanospikes formed through a simple electrochemical route with high electrocatalytic and surface enhanced Raman scattering activity. Chem. Commun. 2009, 5039–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, E. Templateless, surfactantless, simple electrochemical route to rapid synthesis of diameter-controlled 3D flowerlike gold microstructure with “clean surface”. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3163–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, K.D.; Skinner, K.; Zhang, S.; Wei, H.; Lopez, R. Tunable SERS in gold nanorod dimers through strain control on an elastomeric substrate. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4488–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Meng, G.; Chen, B.; Zhu, C.; Han, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from Au-nanorod arrays with sub-5-nm gaps stuck out of an AAO template. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cai, W. Gold quasi rod-shaped nanoparticle-built hierarchically micro/nanostructured pore array via clean electrodeposition on a colloidal monolayer and its structurally enhanced sers performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 8816–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polavarapu, L.; Zanaga, D.; Altantzis, T.; Rodal-Cedeira, S.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Bals, S.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Galvanic replacement coupled to seeded growth as a route for shape-controlled synthesis of plasmonic nanorattles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11453–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polavarapu, L.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Growth and galvanic replacement of silver nanocubes in organic media. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Lu, S.; Liao, F.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Shao, M. Catalytic degradation of dye molecules and in situ SERS monitoring by peroxidase-like Au/CuS composite. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8117–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, D.; Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Mahata, C.; Lee, H.-S.; Min, B.-W.; Lee, T. Capillary force-induced glue-free printing of Ag nanoparticle arrays for highly sensitive sers substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9053–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Meng, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Galvanic-cell-induced growth of Ag nanosheet-assembled structures as sensitive and reproducible SERS substrates. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14948–14953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Meng, G.; Huang, Q.; Hu, X.; He, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, F. Ag nanoparticle-grafted pan-nanohump array films with 3D high-density hot spots as flexible and reliable SERS substrates. Small 2015, 11, 5452–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindzevicius, T.; Barten, J.; Vorobiev, M.; Schmidt, M.S.; Castillo, J.J.; Boisen, A. Detection of surface-linked polychlorinated biphenyls using surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2017, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Meng, G.; Huang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z. Large-area Ag nanorod array substrates for SERS: AAO template-assisted fabrication, functionalization, and application in detection PCBS. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
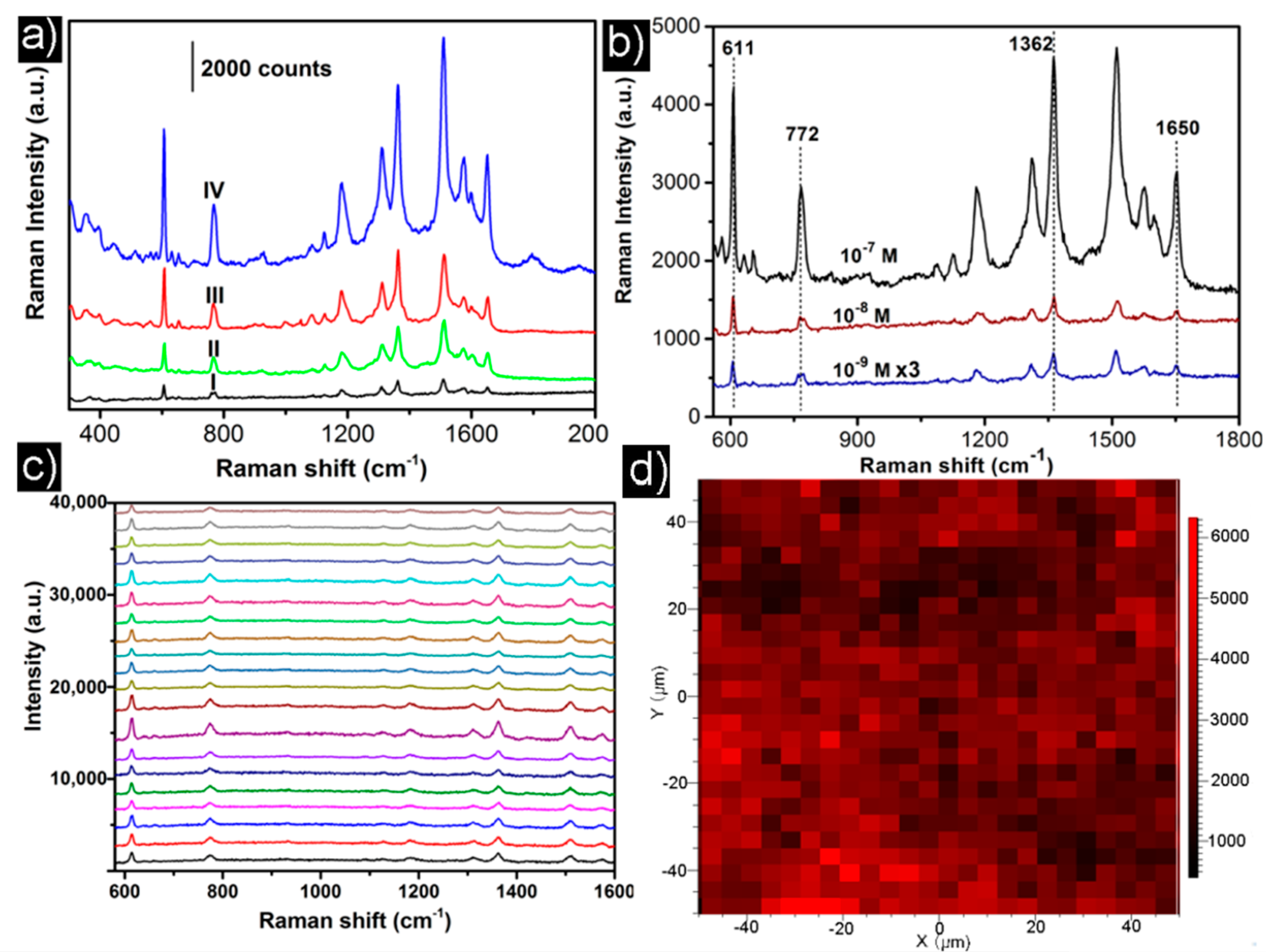
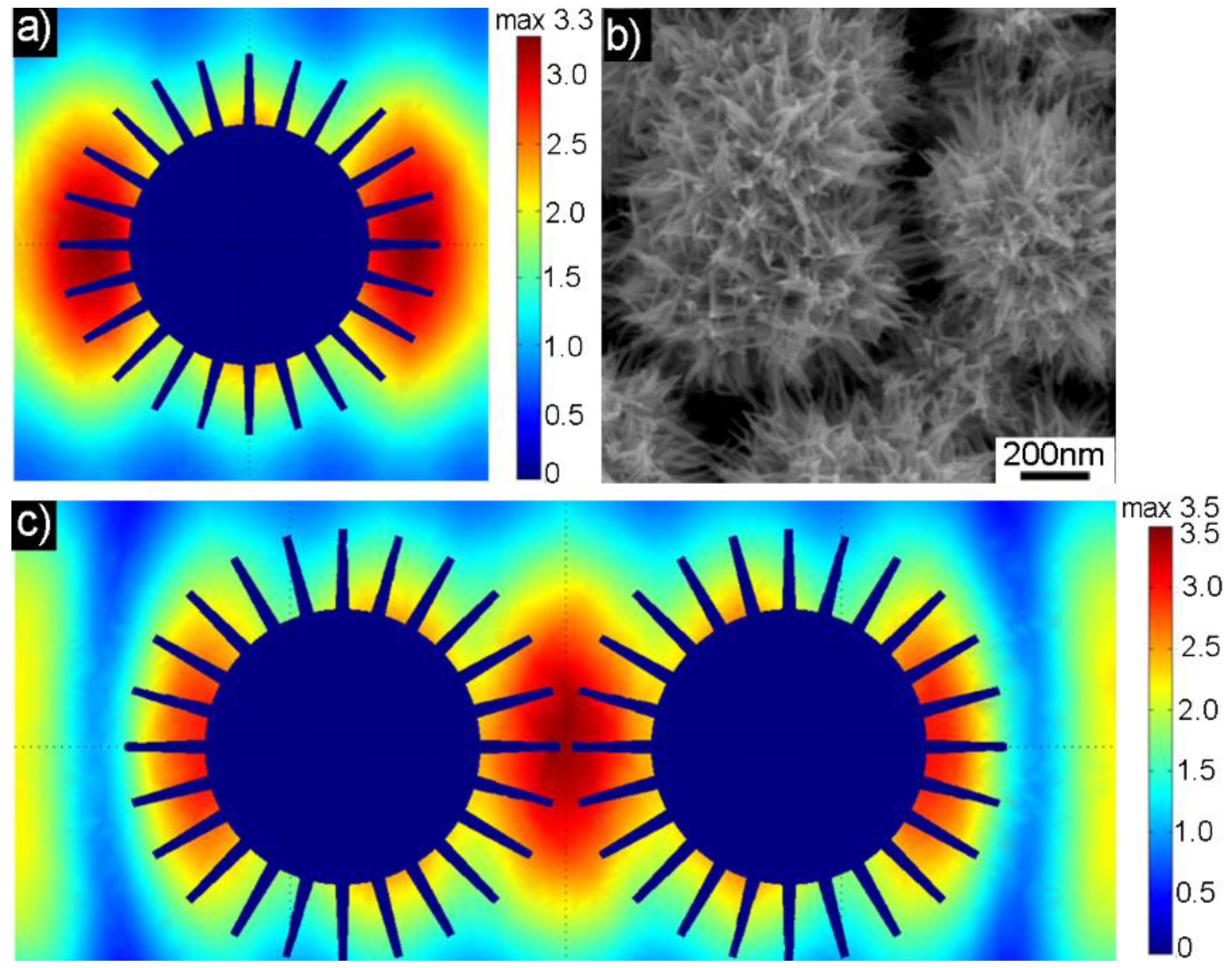
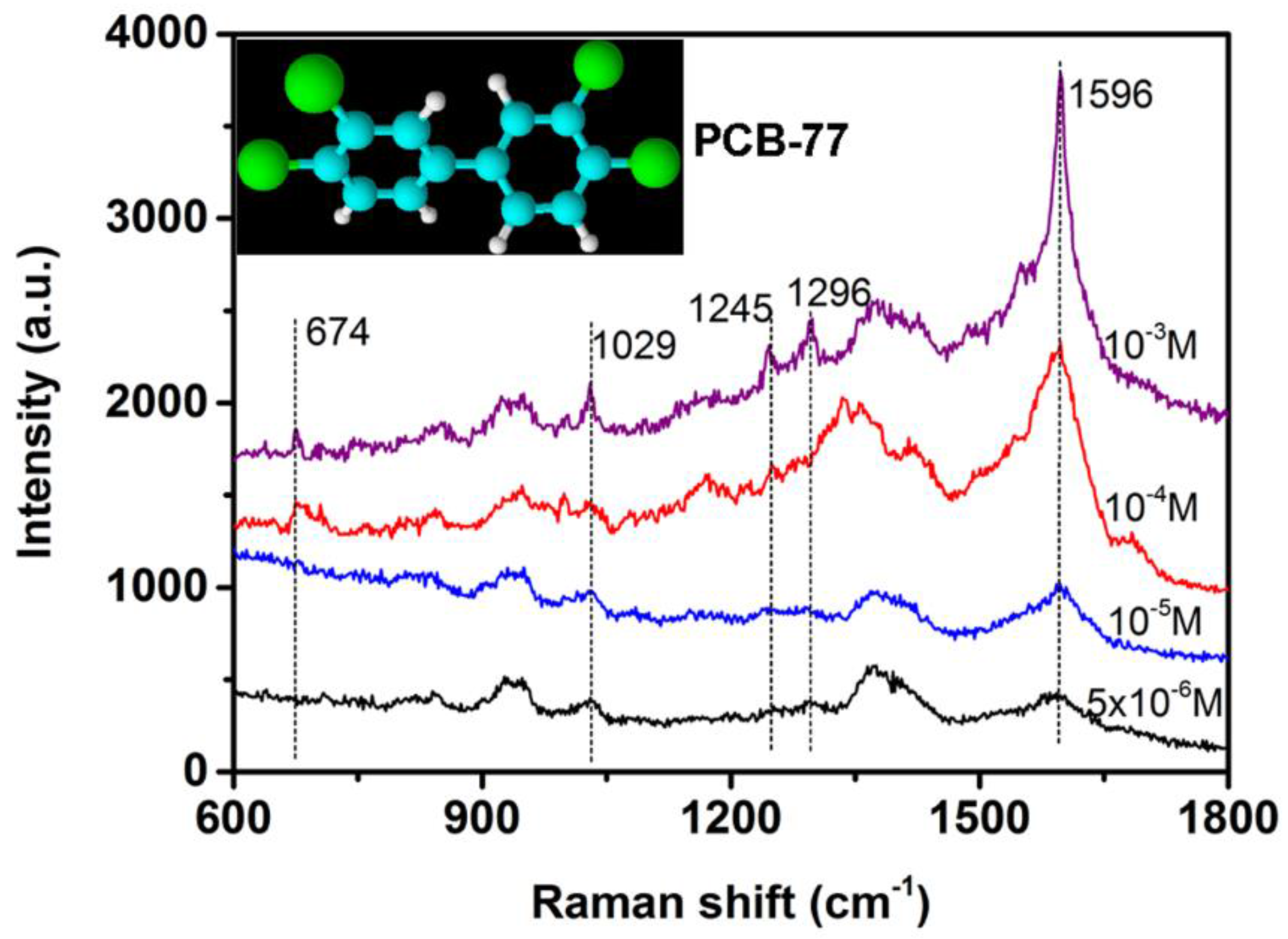
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Sun, K.; Du, Z.; Chen, B.; He, X. Galvanic-Cell-Reaction-Driven Deposition of Large-Area Au Nanourchin Arrays for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040265
Li Z, Sun K, Du Z, Chen B, He X. Galvanic-Cell-Reaction-Driven Deposition of Large-Area Au Nanourchin Arrays for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(4):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040265
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhongbo, Kexi Sun, Zhaofang Du, Bensong Chen, and Xuan He. 2018. "Galvanic-Cell-Reaction-Driven Deposition of Large-Area Au Nanourchin Arrays for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering" Nanomaterials 8, no. 4: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040265
APA StyleLi, Z., Sun, K., Du, Z., Chen, B., & He, X. (2018). Galvanic-Cell-Reaction-Driven Deposition of Large-Area Au Nanourchin Arrays for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials, 8(4), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040265





