Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Stabilized by Humic Acid in Sustainable Cement Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Process
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
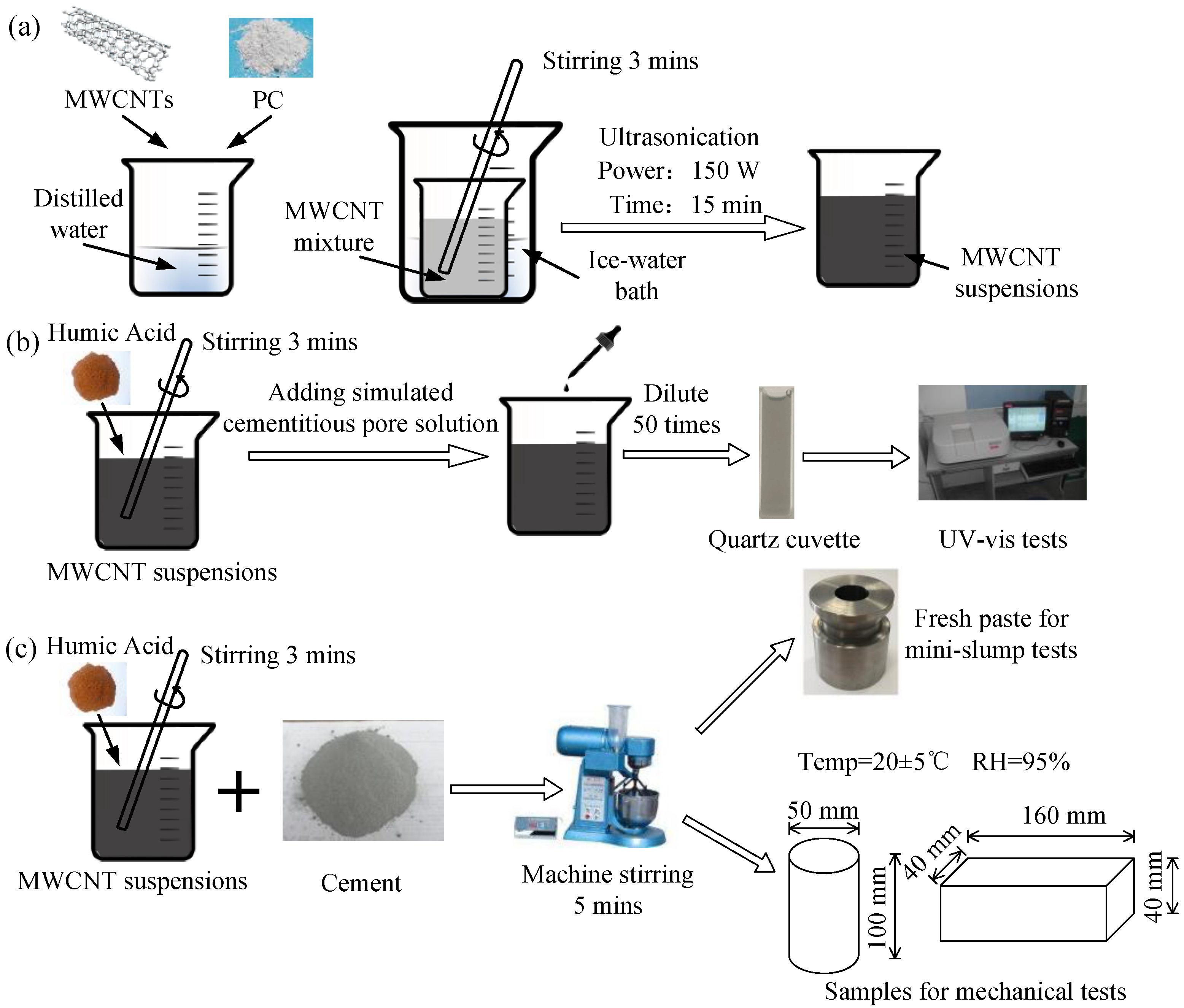
2.2. Preparation of MWCNT Suspensions
2.3. Preparation of Specimens
2.4. Characterization
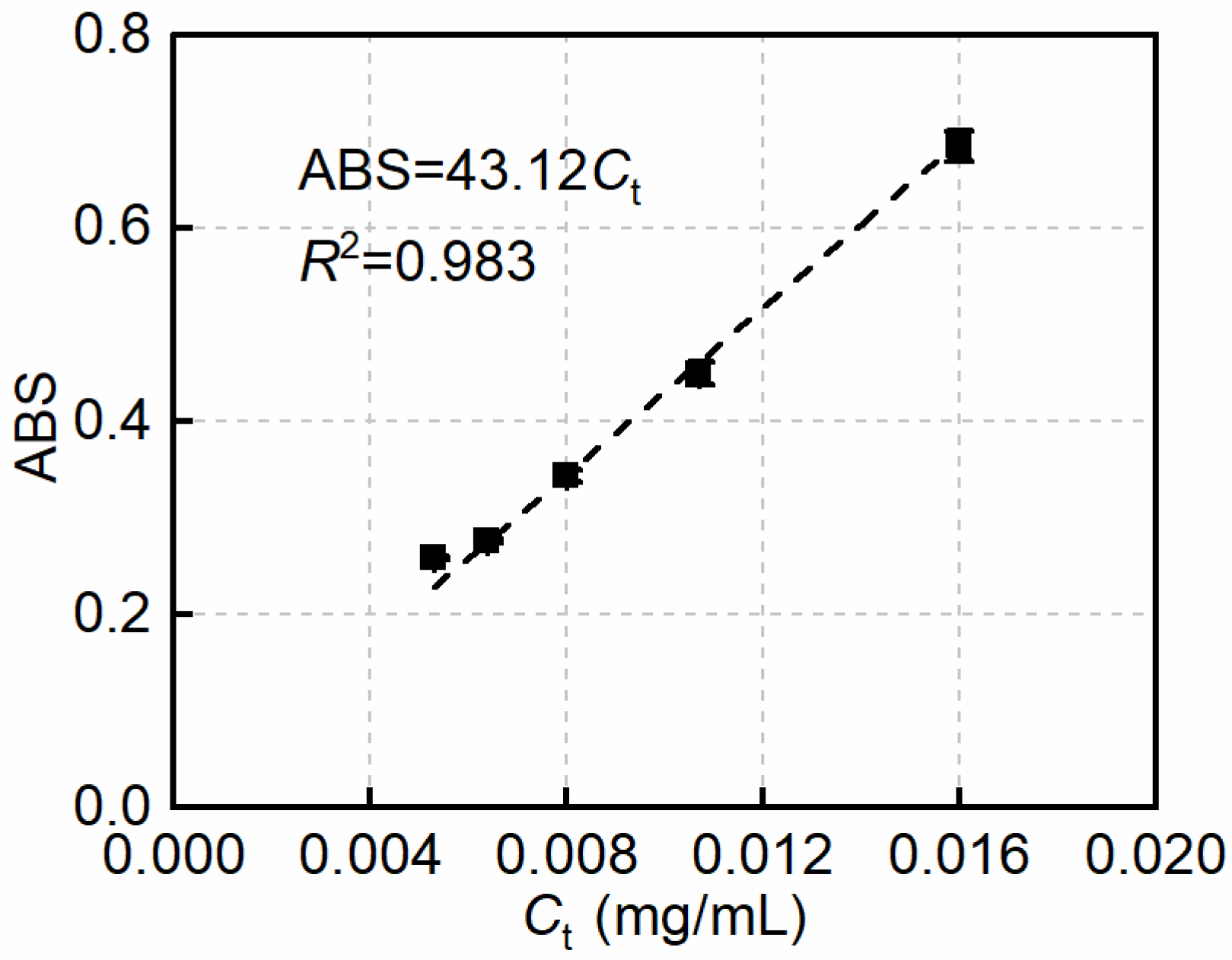
2.4.1. Dispersion Tests for MWCNT Suspensions
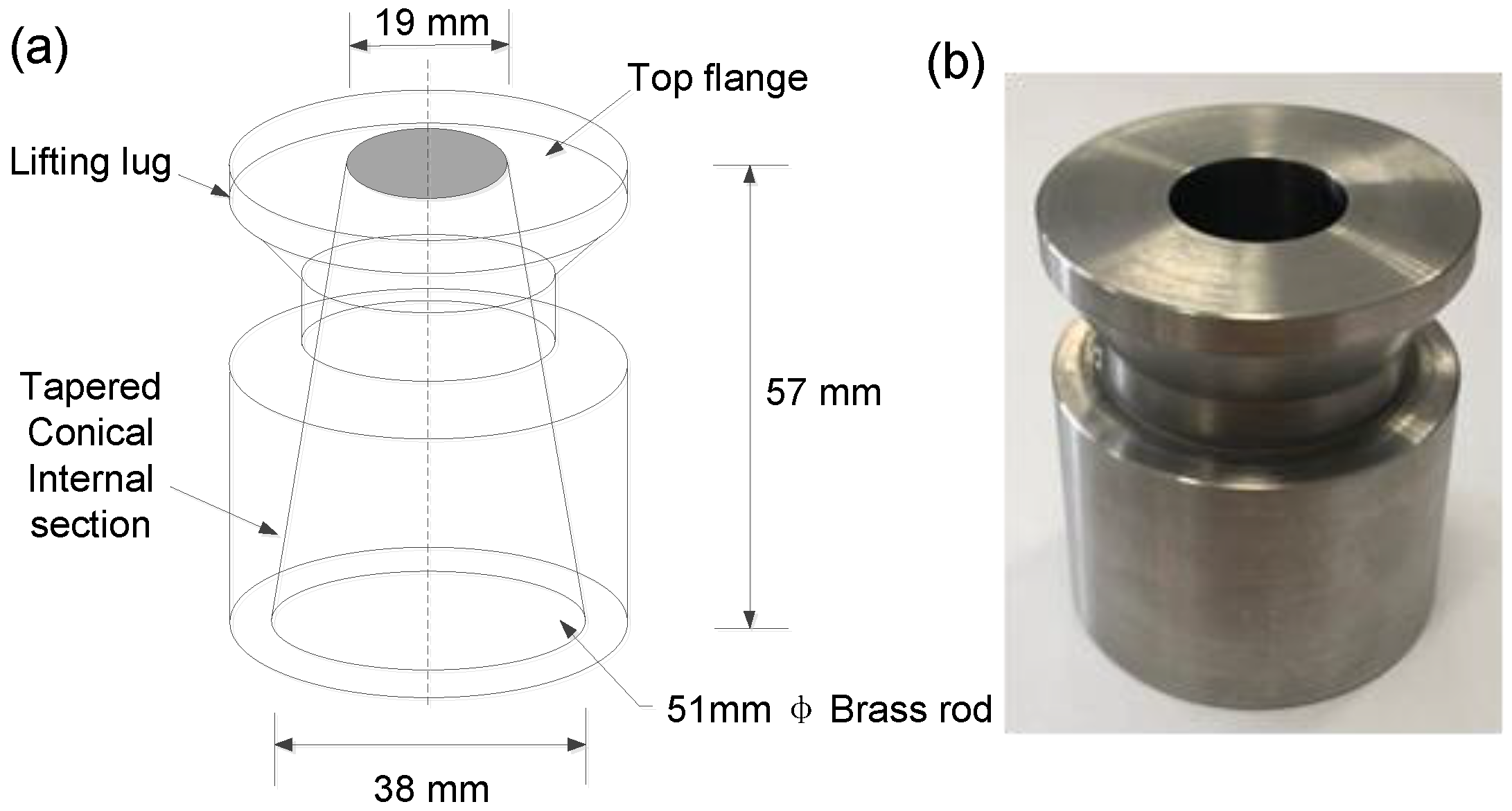
2.4.2. Characterization of Workability
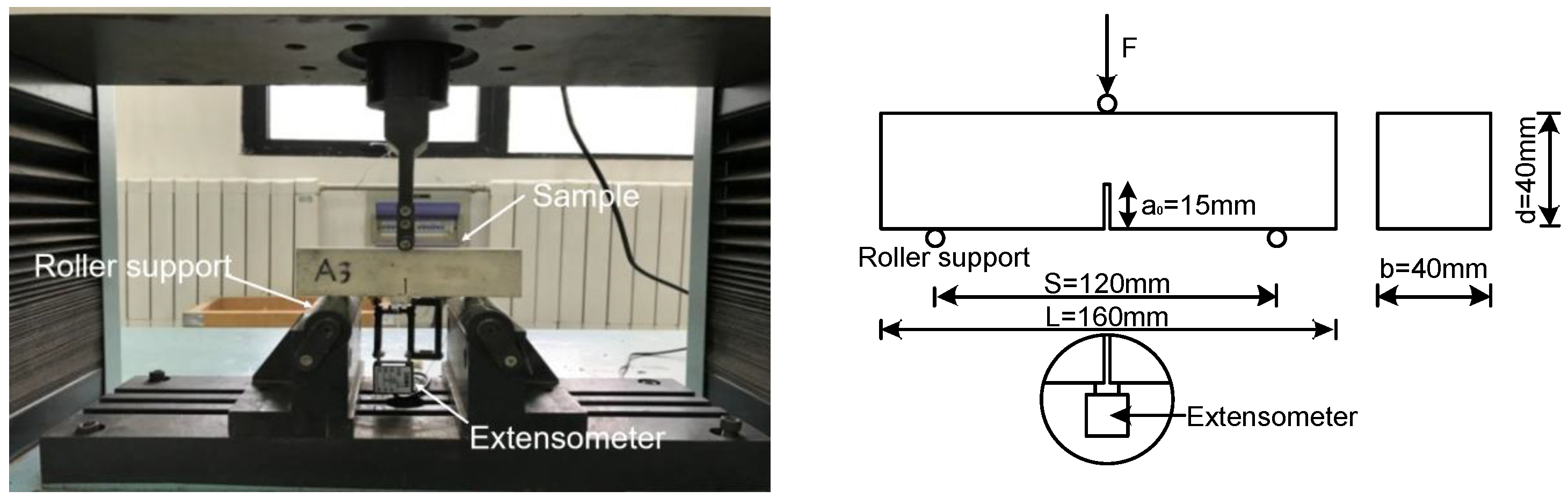
2.4.3. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Tests
3. Results and Discussion
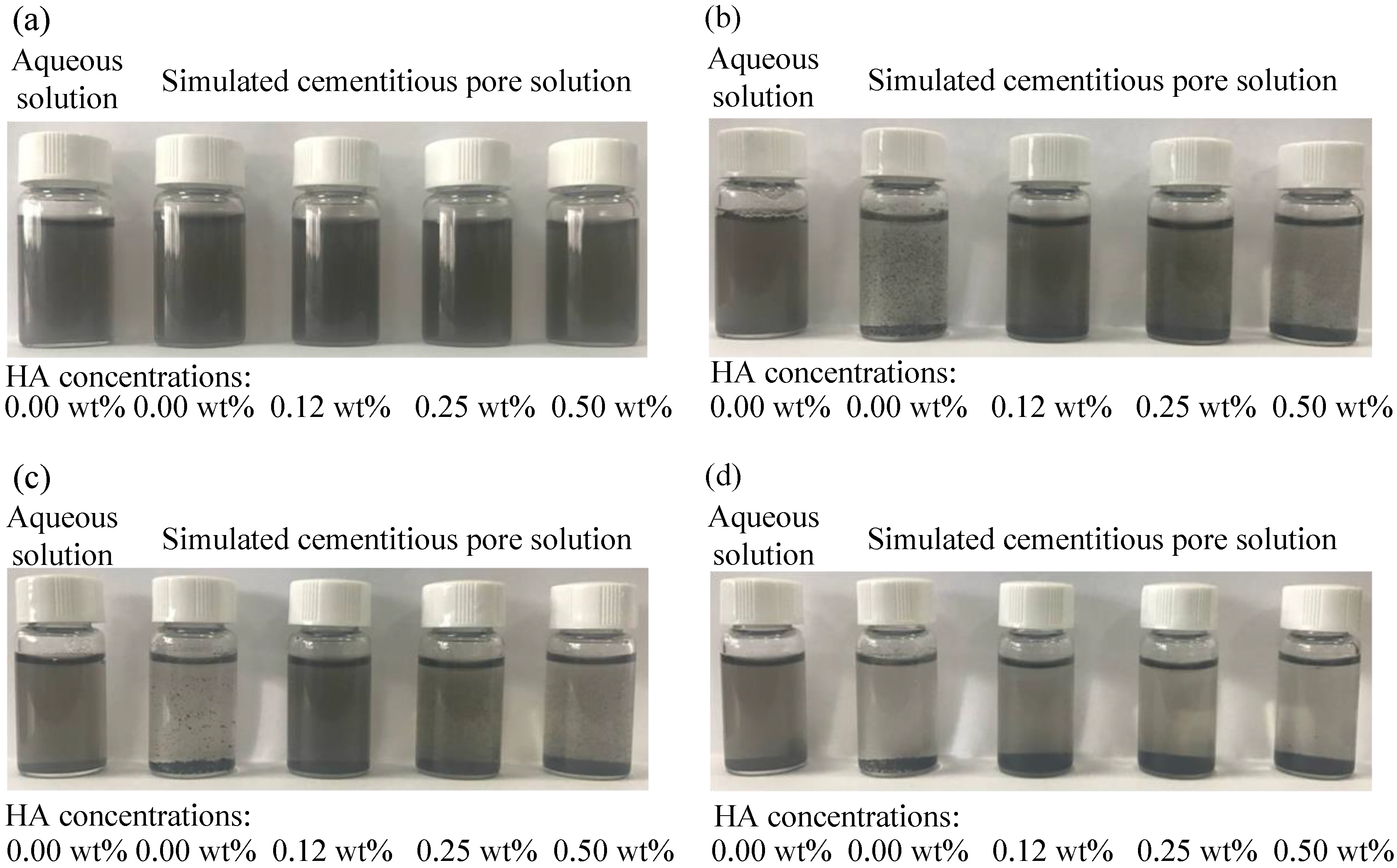
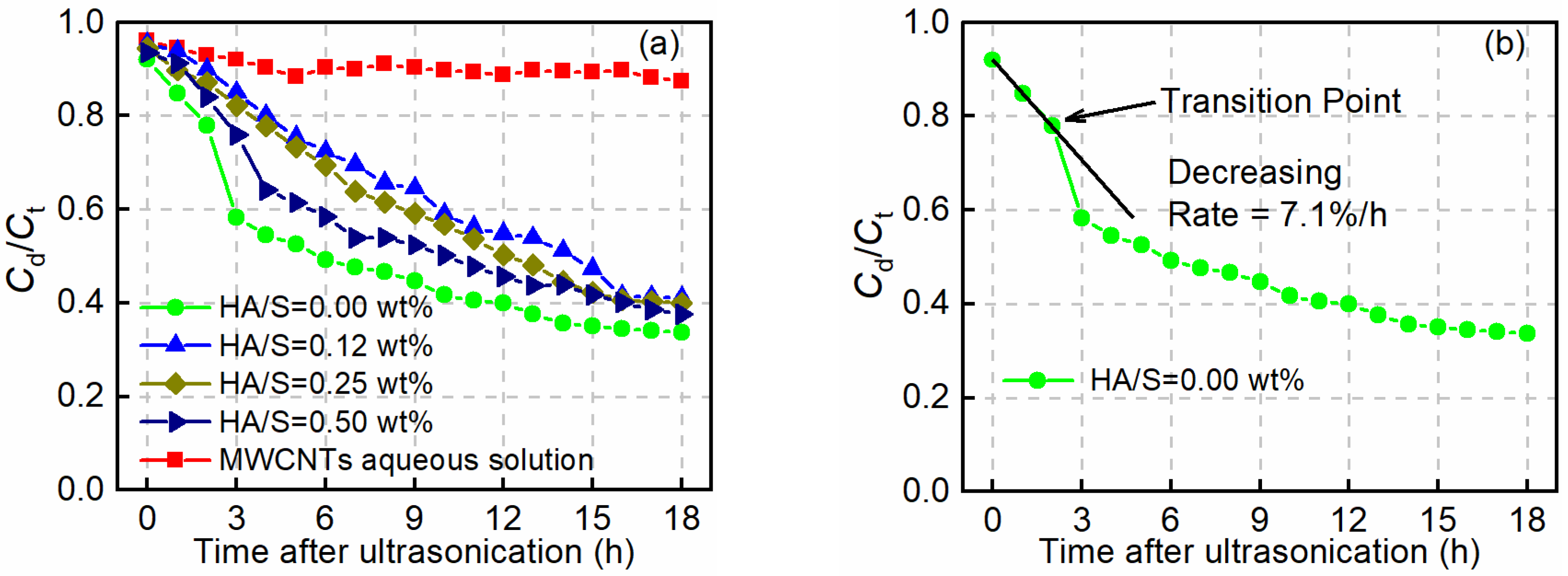
3.1. Stabilizing Effect of HA on the Dispersion of MWCNTs in an Alkaline Environment
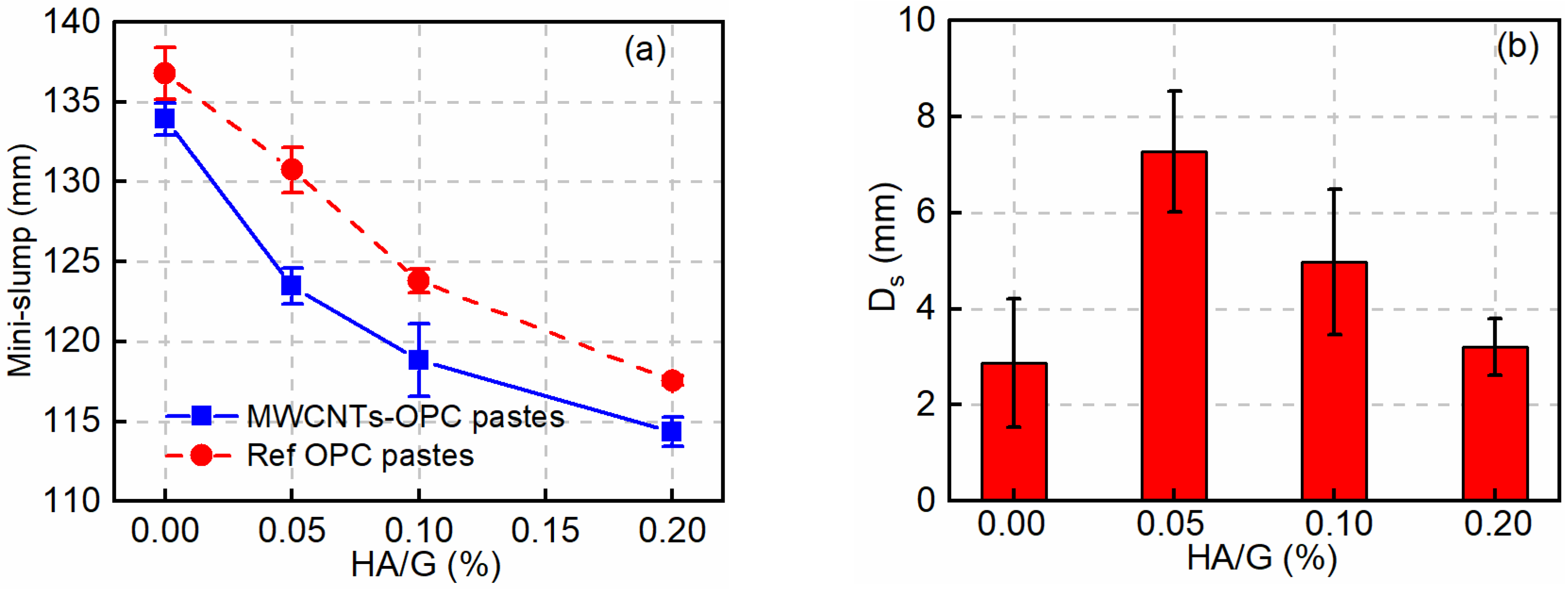
3.2. Effect of HA on the Workability of Fresh MWCNT-OPC Pastes
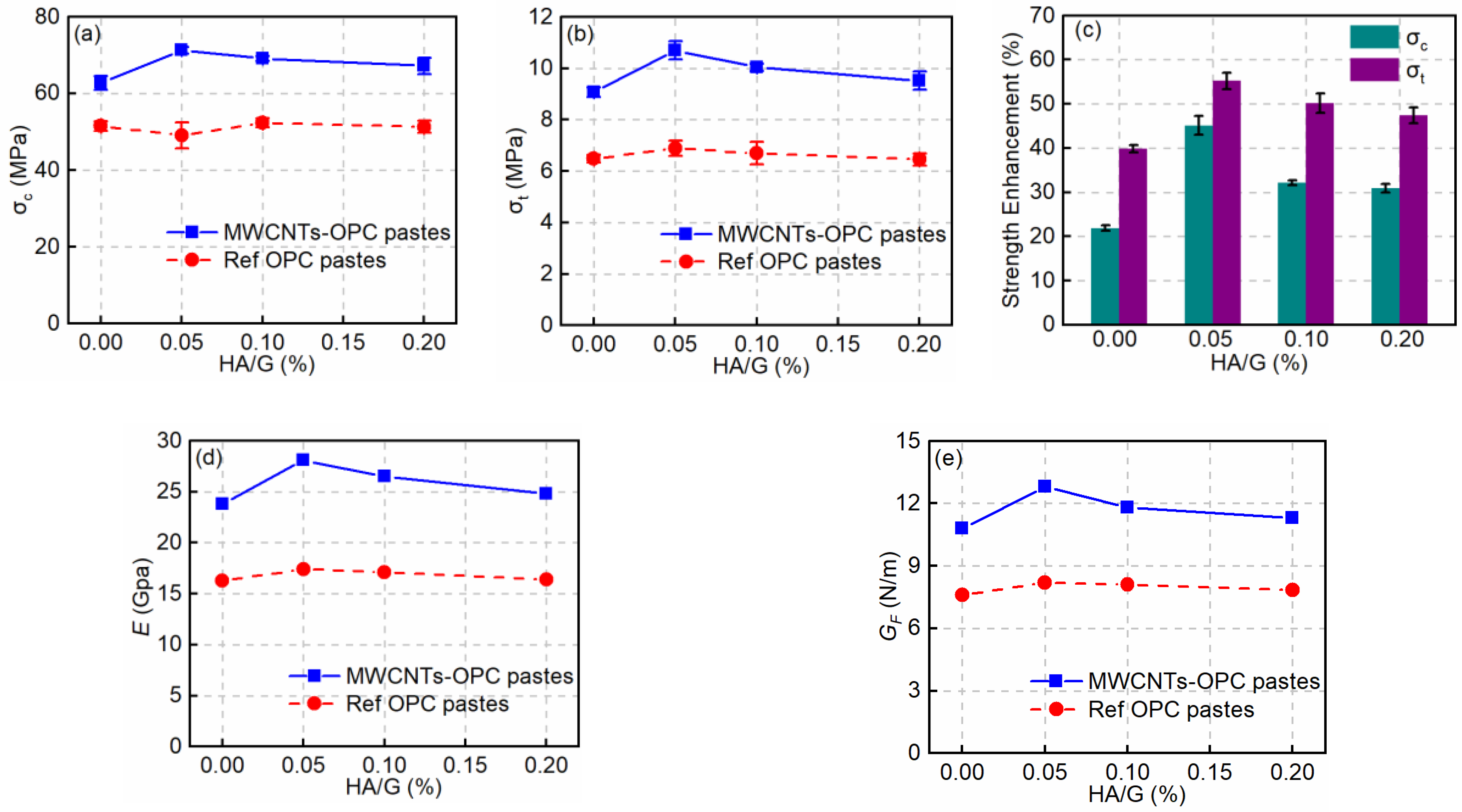
3.3. Effect of HA on the Mechanical Properties of MWCNT-OPC Pastes
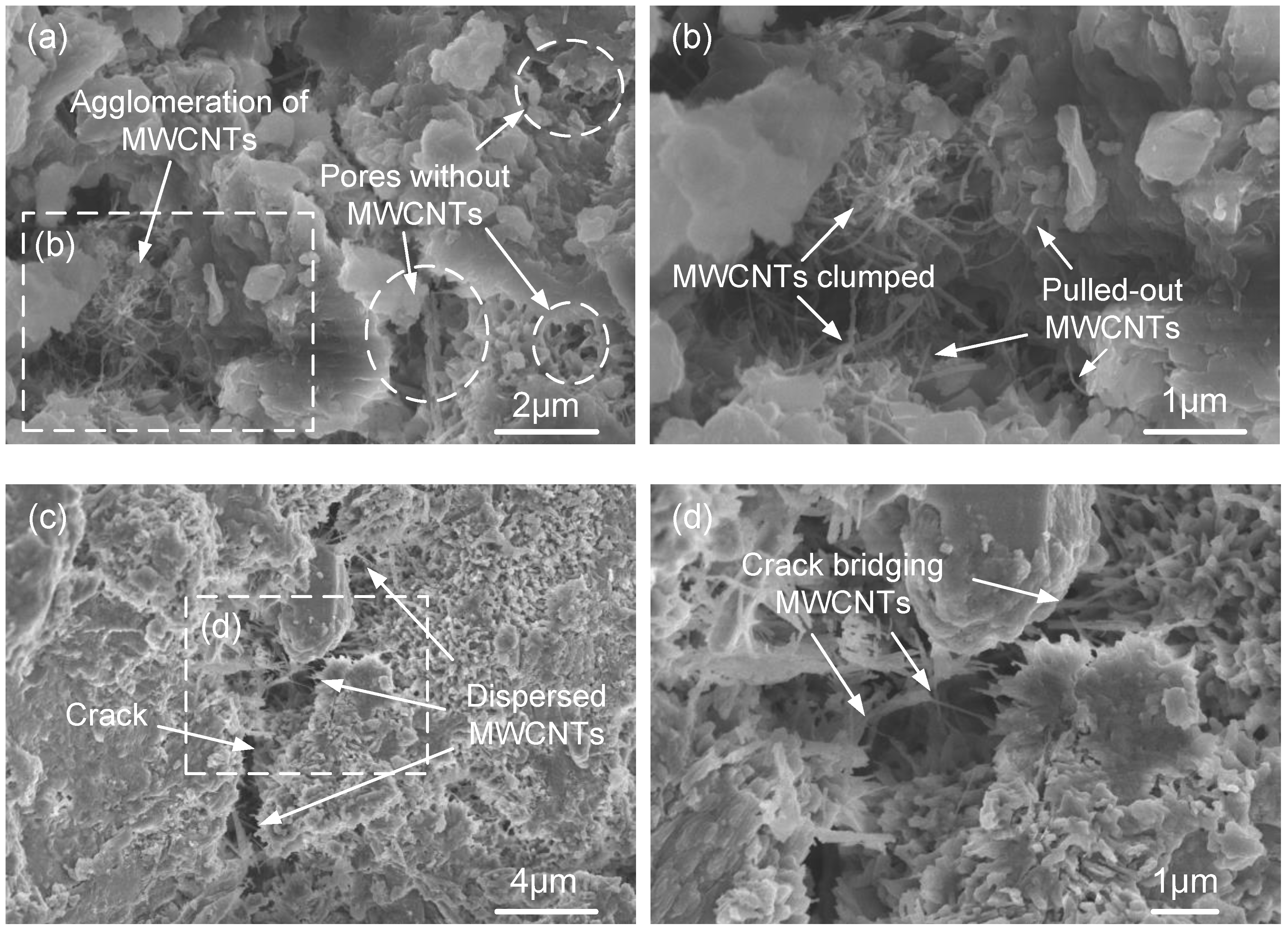
3.4. Distribution of MWCNTs in the OPC Matrix
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volder, M.F.L.D.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.F.; Lourie, O.; Dyer, M.J.; Moloni, K.; Kelly, T.F.; Ruoff, R.S. Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load. Science 2000, 287, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoff, R.S.; Lorents, D.C. Mechanical and thermal properties of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 1995, 33, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.W.; Lezec, H.J.; Hiura, H.; Bennett, J.W.; Ghaemi, H.F.; Thio, T. Electrical conductivity of individual carbon nanotubes. Nature 1996, 382, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojny, F.H.; Wichmann, M.H.G.; Fiedler, B.; Schulte, K. Influence of different carbon nanotubes on the mechanical properties of epoxy matrix composites–a comparative study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2300–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.S.; Atala, A. Carbon nanotube applications for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Riester, L.; Curtin, W.A.; Li, H.; Sheldon, B.W.; Liang, J.; Chang, B.; Xu, J.M. Direct observation of toughening mechanisms in carbon nanotube ceramic matrix composites. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Khan, U.; Blau, W.J.; Gun Ko, Y.K. Small but strong: A review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube–polymer composites. Carbon 2006, 44, 1624–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, W.; Torabian, I.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Xing, F. Nano-silica sol-gel and carbon nanotube coupling effect on the performance of cement-based materials. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, S.; Cui, H.; Li, D. Effect of Nano-SiO2 on the hydration and microstructure of portland cement. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeląg, M. Mechano-physical properties and microstructure of carbon nanotube reinforced cement paste after thermal load. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, B.; Chen, S.J.; Korayem, A.H.; Collins, F.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Effect of ultrasonication energy on engineering properties of carbon nanotube reinforced cement pastes. Carbon 2015, 85, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Q. Mechanical properties and microstructure of multi-walled carbon nanotube-reinforced cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girifalco, L.A.; Hodak, M.; Lee, R.S. Carbon nanotubes, buckyballs, ropes, and a universal graphitic potential. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 13104–13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.F.; Rojas, E.; Bergey, D.M.; Johnson, A.T.; Yodh, A.G. High Weight-Fraction surfactant solubilization of Single-Wall carbon nanotubes in water. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.; Lambert, J.; Duan, W.H. The influences of admixtures on the dispersion, workability, and strength of carbon nanotube—OPC paste mixtures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Wang, W.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Collins, F.; Zhao, X.L.; Majumder, M.; Duan, W. Distribution of carbon nanotubes in fresh ordinary Portland cement pastes: Understanding from a two-phase perspective. RSC Adv 2016, 6, 5745–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabipour, F.; Sant, G.; Weiss, J. Interactions between shrinkage reducing admixtures (SRA) and cement paste’s pore solution. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; Mcrae, G.; Miller, T. The effect of concrete pore solution composition on the quality of passive oxide films on black steel reinforcement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.R.; Jing, H.W.; Duan, W.H.; Han, G.S.; Chen, S.J. Methylcellulose stabilized multi-walled carbon nanotubes dispersion for sustainable cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosquoët, F.; Alexis, A.; Khelidj, A.; Phelipot, A. Experimental study of cement grout: Rheological behavior and sedimentation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Harris, J.L.; Roddick, F.A.; Booker, N.A. Influence of the characteristics of natural organic matter on the fouling of microfiltration membranes. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4455–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, N.B.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Aggregation kinetics of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in aquatic systems: Measurements and environmental implications. Environ. Chem. 2015, 42, 7963–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Hwang, G.; Park, S.; Gomezflores, A.; Jo, E.; Eom, I.C.; Tong, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H. Stability of carboxyl-functionalized carbon black nanoparticles: The role of solution chemistry and humic acid. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xing, B. Adsorption of fulvic acid by carbon nanotubes from water. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyung, H.; Fortner, J.D.; Hughes, J.B.; Kim, J.H. Natural organic matter stabilizes carbon nanotubes in the aqueous phase. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, J. Impacts and mechanisms of natural organic matter and pH on the transport of nanobiochar. Geoscience 2018, 32, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Common Portland Cement; Chinese National Standard GB/T 175-2007; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 9 Novemeber 2007.
- Li, X.; Korayem, A.H.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Wen, H.D. Incorporation of graphene oxide and silica fume into cement paste: A study of dispersion and compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 123, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, N.; Regev, O.; Loos, J.; Meuldijk, J.; Koning, C.E. Time-dependent study of the exfoliation process of carbon nanotubes in aqueous dispersions by using UV-visible spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5135–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Grossiord, N.; Koning, C.E.; Loos, J. Controlling the dispersion of multi-wall carbon nanotubes in aqueous surfactant solution. Carbon 2007, 45, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, F.; Masselink, W.T.; Harris, J.S. The quantitative characterization of the concentration and dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in suspension by spectrophotometry. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.D.; Jespersen, M.L.; Patel, R.J.; Leever, B.J. Predicting vertical phase segregation in polymer-fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells by free energy analysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4799–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, D.; Mays, J.W.; Bratcher, M.S. Noncovalent and nonspecific molecular interactions of polymers with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3389–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recommendation, R.D. Determination of the fracture energy of mortar and concrete by means of three-point bend tests on notched beams. Mater. Struct. 1985, 18, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillerborg, A. The theoretical basis of a method to determine the fracture energy GF of concrete. Mater. Struct. 1985, 18, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S. Determination of fracture parameters (KIcs and CTODc) of plain concrete using three-point bend test. Mater. Struct. 1900, 23, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Elimelech, M. Influence of humic acid on the aggregation kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, S.W.; Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Grassian, V.H. Aggregation and dissolution of 4 nm ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous environments: Influence of pH, ionic strength, size, and adsorption of humic acid. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Kim, D.; Hwang, G.; Lee, B.; Eom, I.; Kim, P.J.; Tong, M.; Kim, H. Aggregation and dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by different methods: Influence of ionic strength and humic acid. Colloid Surface. A 2014, 451, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Z.; Han, B.; Zhao, D. Aggregation and stabilization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in aqueous suspensions: Influences of carboxymethyl cellulose, starch and humic acid. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Keller, A.A. Role of morphology in the aggregation kinetics of ZnO nanoparticles. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2948–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Lenihan, H.S.; Cherr, G.; Cardinale, B.J.; Miller, R.; Ji, Z. Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Z.; Feng, N.Q.; Li, Y.D.; Chen, R.J. Effects of polyethlene oxide chains on the performance of polycarboxylate-type water-reducers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawa, T. Effect of chemical structure on steric stabilization of polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer. J. Struct. Constr. Eng. 2006, 66, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Feng, Y. Degradation of aqueous and soil-sorbed estradiol using a new class of stabilized manganese oxide nanoparticles. Water Res. 2015, 70, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makar, J.M.; Chan, G.W. Growth of cement hydration products on single walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 92, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Ge, C.; Li, Q.; Guo, L.; Shu, X. Mechanical behavior and toughening mechanism of polycarboxylate superplasticizer modified graphene oxide reinforced cement composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2017, 113, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K. Chloride penetration monitoring in reinforced concrete structure using carbon nanotube/cement composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Wang, P.M.; Zhao, X. Mechanical behavior and microstructure of cement composites incorporating surface-treated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2005, 43, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Multifunctional and Smart Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Cement-Based Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]

| Mix | C/S (wt.%) | P/S (wt.%) | HA/S (wt.%) | C/G (wt.%) | P/G (wt.%) | HA/G (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0 | 0.032 | 0.256 | 0 |
| MWCNTs-1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| MWCNTs-2 | 0.12 | 0.05 | ||||
| MWCNTs-3 | 0.25 | 0.10 | ||||
| MWCNTs-4 | 0.50 | 0.20 |
| Compounds | NaOH | KOH | CaSO4·2H2O | Ca(OH)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (g/L) | 8 | 22.4 | 27.6 | Saturated |
| HA Concentration (wt.%) | Transition Point (h) | Rate of Decrease of Cd/Ct (% per h) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 2 | 7.1 |
| 0.12 | 9 | 3.4 |
| 0.25 | 6 | 4.2 |
| 0.50 | 3 | 5.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Jing, H.; Du, M.; Chen, W. Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Stabilized by Humic Acid in Sustainable Cement Composites. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100858
Gao Y, Jing H, Du M, Chen W. Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Stabilized by Humic Acid in Sustainable Cement Composites. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(10):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100858
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuan, Hongwen Jing, Mingrui Du, and Weiqiang Chen. 2018. "Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Stabilized by Humic Acid in Sustainable Cement Composites" Nanomaterials 8, no. 10: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100858
APA StyleGao, Y., Jing, H., Du, M., & Chen, W. (2018). Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Stabilized by Humic Acid in Sustainable Cement Composites. Nanomaterials, 8(10), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100858





