Green Synthesis of Hydrophobic Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Plant Extract and Their Application as Petroleum Oil Spill Collectors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.3. Synthesis of MNPs
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Application of APH-MNPs and APC-MNPs as Oil Spill Collectors
3. Results
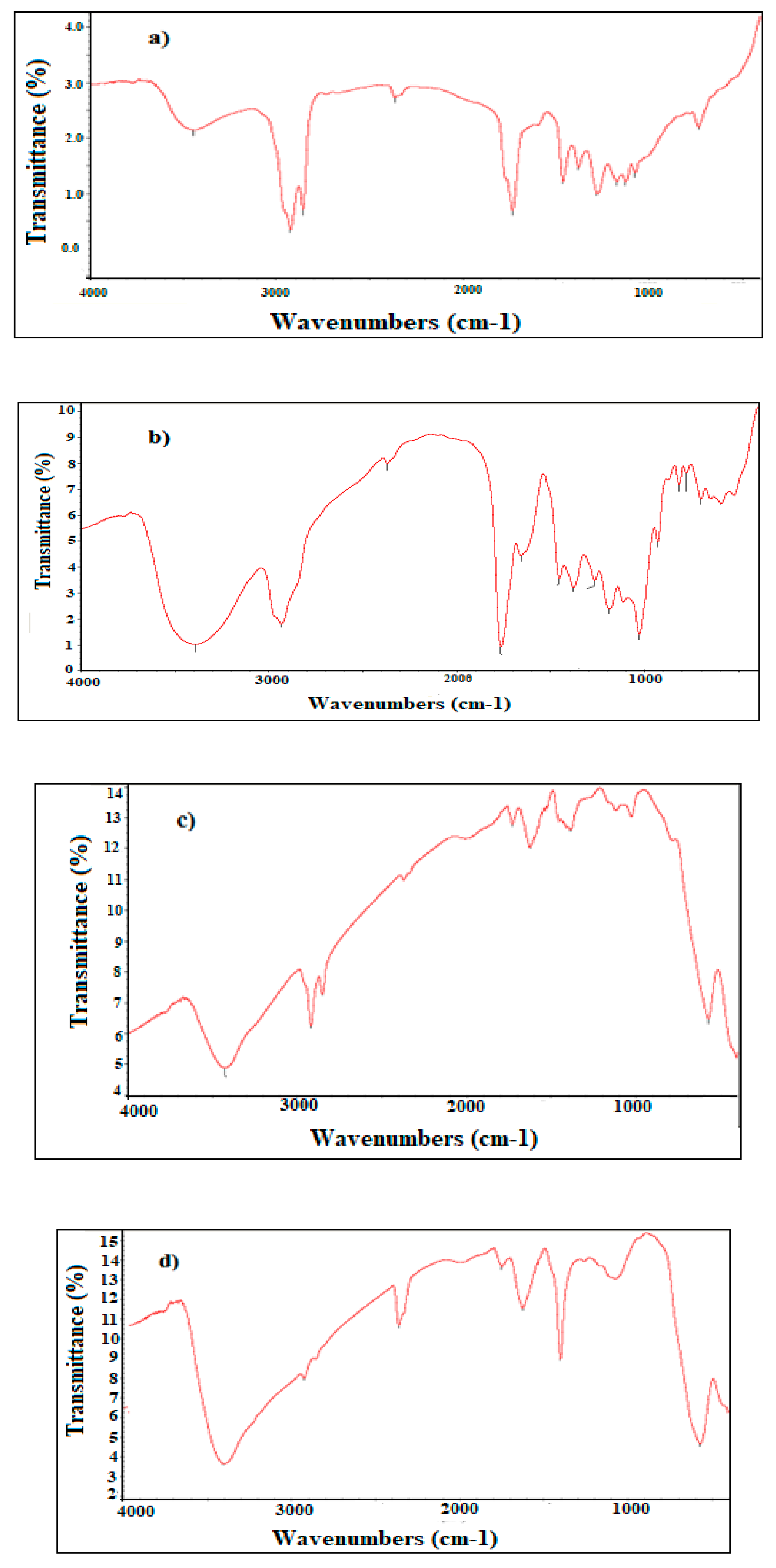
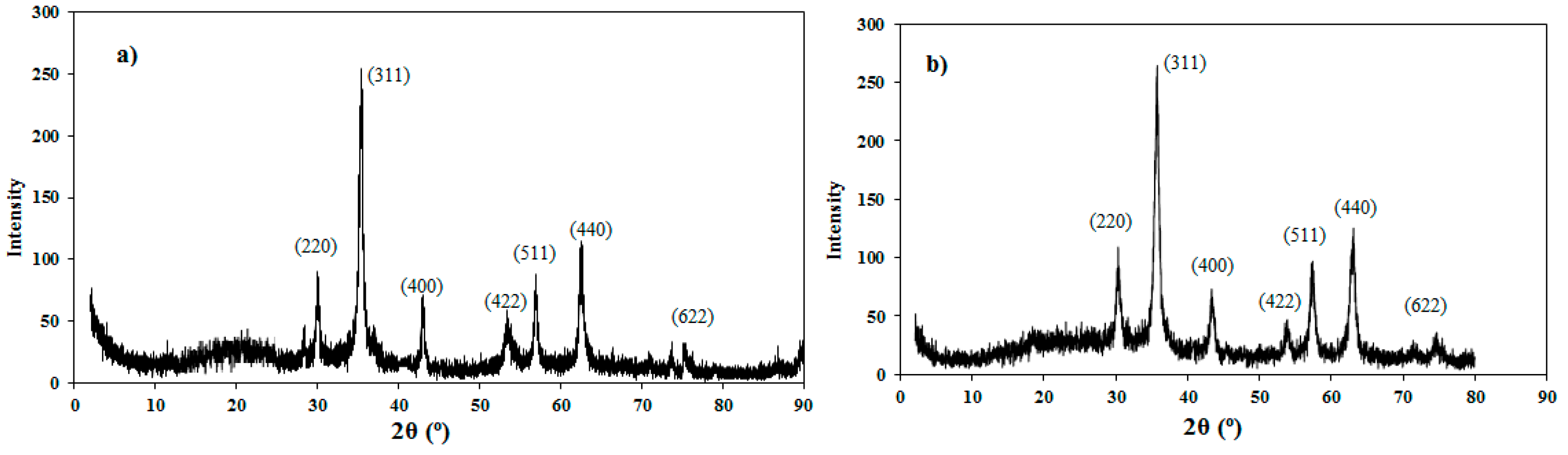
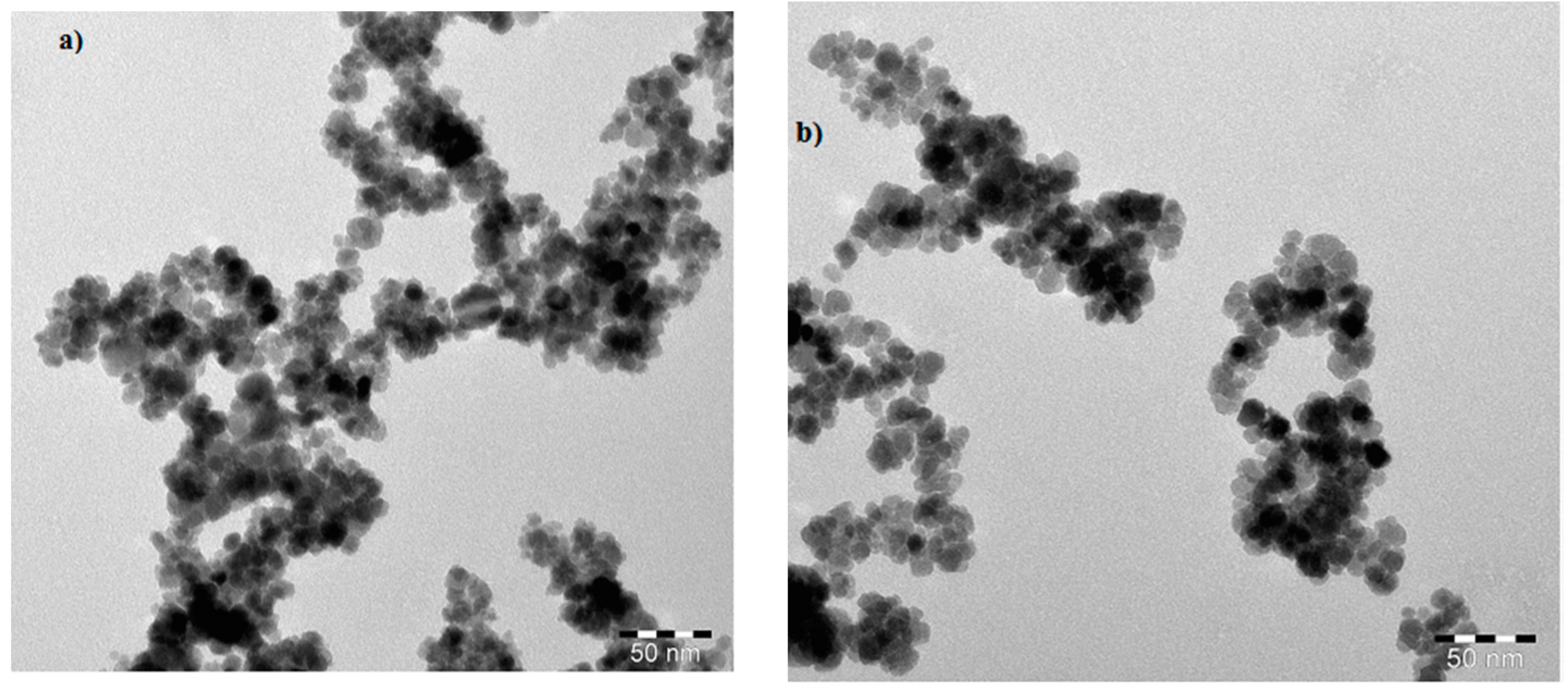
3.1. Chemical Structure of MNPs
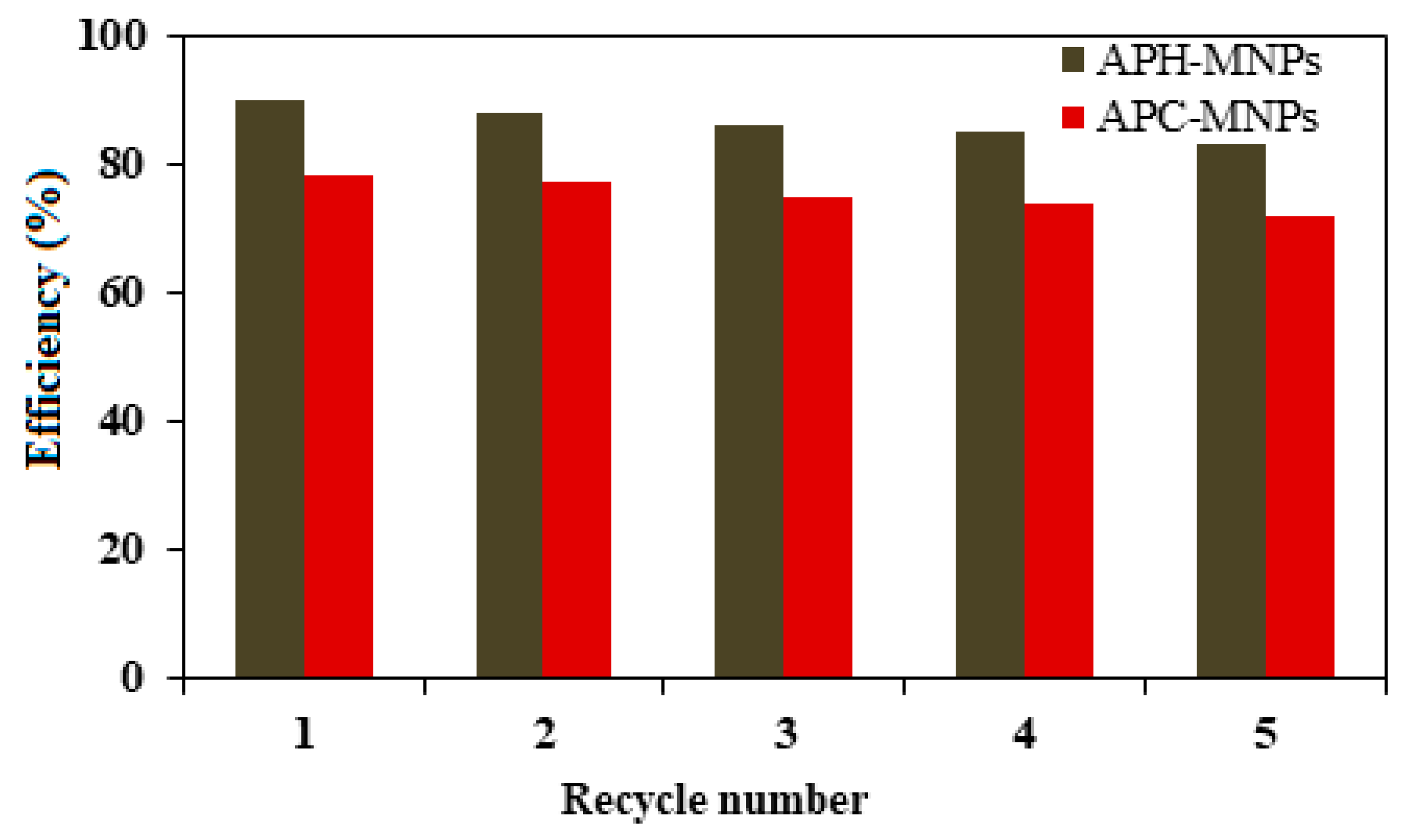
3.2. Efficiency of APH-MNPs and APC-MNPs in the Collection of Oil Spills
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, H.; Purnell, K.; Law, R.J.; Kirby, M.F. The use of chemical dispersants to combat oil spills at sea: A review of practice and research needs in Europe. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etkin, D.S. Estimating cleanup costs for oil spills. Proceedings of International oil spill conference, Arlington, MA, USA, 8–11 March 1999; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fingas, M. Oil Spill Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Gulf professional publishing: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Balba, M.; Al-Awadhi, N.; Al-Daher, R. Bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil: Microbiological methods for feasibility assessment and field evaluation. J. Microbiol. Meth. 1998, 32, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Modification of formaldehyde-melamine-sodium bisulfite copolymer foam and its application as effective sorbents for clean up of oil spills. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 160, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Pricop, L.; Samoila, P.; Rotaru, R.; Harabagiu, V. Surface hydrophobization of polyester fibers with poly(methylhydro-dimethyl) siloxane copolymers: Experimental design for testing of modified nonwoven materials as oil spill sorbents. Polym. Test. 2017, 59, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Dorneanu, P.P.; Airinei, A.; Olaru, N.; Samoila, P.; Rotaru, A. Design and evaluation of electrospun polysulfone fibers and polysulfone/NiFe2O4 nanostructured composite as sorbents for oil spill cleanup. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongsayamanont, W.; Soonglerdsongpha, S.; Khondee, N.; Pinyakong, O.; Tongcumpou, C.; Sabatini, D.A.; Luepromchai, E. Formulation of crude oil spill dispersants based on the HLD concept and using a lipopeptide biosurfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 334, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, A.M.; Ezzat, A.O.; Hashem, A.I. Synthesis and application of monodisperse hydrophobic magnetite nanoparticles as an oil spill collector using an ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16524–16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Abdullah, M.M.; ElSaeed, S.M. Application of new amphiphilic ionic liquid based on ethoxylated octadecylammonium tosylate as demulsifier and petroleum crude oil spill dispersant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abullah, M.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Attah, A.M. Synthesis and application of amphiphilic ionic liquid based on acrylate copolymers as demulsifier and oil spill dispersant. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Atta, A.M. Novel magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with sulfonated asphaltene as crude oil spill collectors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59242–59249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Al-Hussain, S.A. Functionalization of magnetite nanoparticles as oil spill collector. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6911–6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.H.; Budarin, V.; Deswarte, F.E.; Hardy, J.J.; Kerton, F.M.; Hunt, A.J.; Luque, R.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Milkowski, K.; Rodriguez, A. Green chemistry and the biorefinery: a partnership for a sustainable future. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, S.; Jaiswal, L.; Aparna, R.; Prasad, R. Synthesis, characterization, in vitro biocompatibility, and antimicrobial activity of gold, silver and gold silver alloy nanoparticles prepared from Lansium domesticum fruit peel extract. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, V.; Love, A.; Sinitsyna, O.; Makarova, S.; Yaminsky, I.; Taliansky, M.; Kalinina, N. “Green” nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 2014, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications—An updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.-M.; Park, I.; Seung-Hyun, K.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankamwar, B.; Chaudhary, M.; Sastry, M. Gold nanotriangles biologically synthesized using tamarind leaf extract and potential application in vapor sensing. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. 2005, 35, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. NBM 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, M.; Kesharwani, J.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against pathogenic fungi in combination with fluconazole. Nanomed. NBM 2009, 5, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhainsa, K.C.; D’souza, S. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 47, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 28, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polavarapu, L.; Xu, Q.-H. A single-step synthesis of gold nanochains using an amino acid as a capping agent and characterization of their optical properties. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 075601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Pandoli, O.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Lin, J.; Cui, D.; Chen, X. Chiral guanosine 5′-monophosphate-capped gold nanoflowers: Controllable synthesis, characterization, surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity, cellular imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler, N.; Fadeev, L.; Mentovich, E.D.; Belgorodsky, B.; Gozin, M.; Richter, S. Bio-inspired synthesis of chiral silver nanoparticles in mucin glycoprotein—the natural choice. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7419–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhumkar, D.R.; Joshi, H.M.; Sastry, M.; Pokharkar, V.B. Chitosan reduced gold nanoparticles as novel carriers for transmucosal delivery of insulin. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Khairudin, N.B.B.A.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Lee, K.X. Green synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Rao, Y.S.; Balaji, T.; Prathima, B.; Jyothi, N. Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using plantain peel extract. Mater. Lett. 2013, 100, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Sathy, B.N.; Mony, U.; Koyakutty, M.; Nair, S.V.; Menon, D. Biocompatible magnetite/gold nanohybrid contrast agents via green chemistry for MRI and CT bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 4, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latha, N.; Gowri, M. Biosynthesis and characterisation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Caricaya papaya leaves extract. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Basavegowda, N.; Mishra, K.; Lee, Y.R. Sonochemically synthesized ferromagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a recyclable catalyst for the preparation of pyrrolo[3,4-c]quinoline-1,3-dione derivatives. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61660–61666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collenette, S. Illustrated Guide to the Flowers of Saudi Arabia; Scorpion: FLINT, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Aliyu, A.B.; Abdullahi, M.S.; Tajuddeen, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Oyewale, A.O. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of hexane leaf extract of Anisopus mannii (Asclepiadaceae). J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Al-Toubi, W.A.; Weli, A.M.; Al-Riyami, Q.A.; Al-Sabahi, J.N. Identification and characterization of chemical compounds in different crude extracts from leaves of Omani neem. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2013, 7, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwanida, N. A review on the extraction methods use in medicinal plants, principle, strength and limitation. Med. Aromat. Plants 2015, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, J.R.; Ford, M.J.; Marcuccio, S.M.; Ulstrup, J.; Hush, N.S. Competition of van der Waals and chemical forces on gold–sulfur surfaces and nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Vinoth, M.; Srither, S.R.; Manivasakan, P.; Rajendran, V.; Valiyaveettil, S. Larvicidal, super hydrophobic and antibacterial properties of herbal nanoparticles from Acalypha indica for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41763–41770. [Google Scholar]
- Attard, P. Long-range attraction between hydrophobic surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 6441–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phumying, S.; Labuayai, S.; Thomas, C.; Amornkitbamrung, V.; Swatsitang, E.; Maensiri, S. Aloe vera plant-extracted solution hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 111, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, M.; Sabry, S.; Ghozlan, H.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Carpenter, E.E. Microbial-physical synthesis of Fe and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using Aspergillus niger YESM1 and supercritical condition of ethanol. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 9174891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
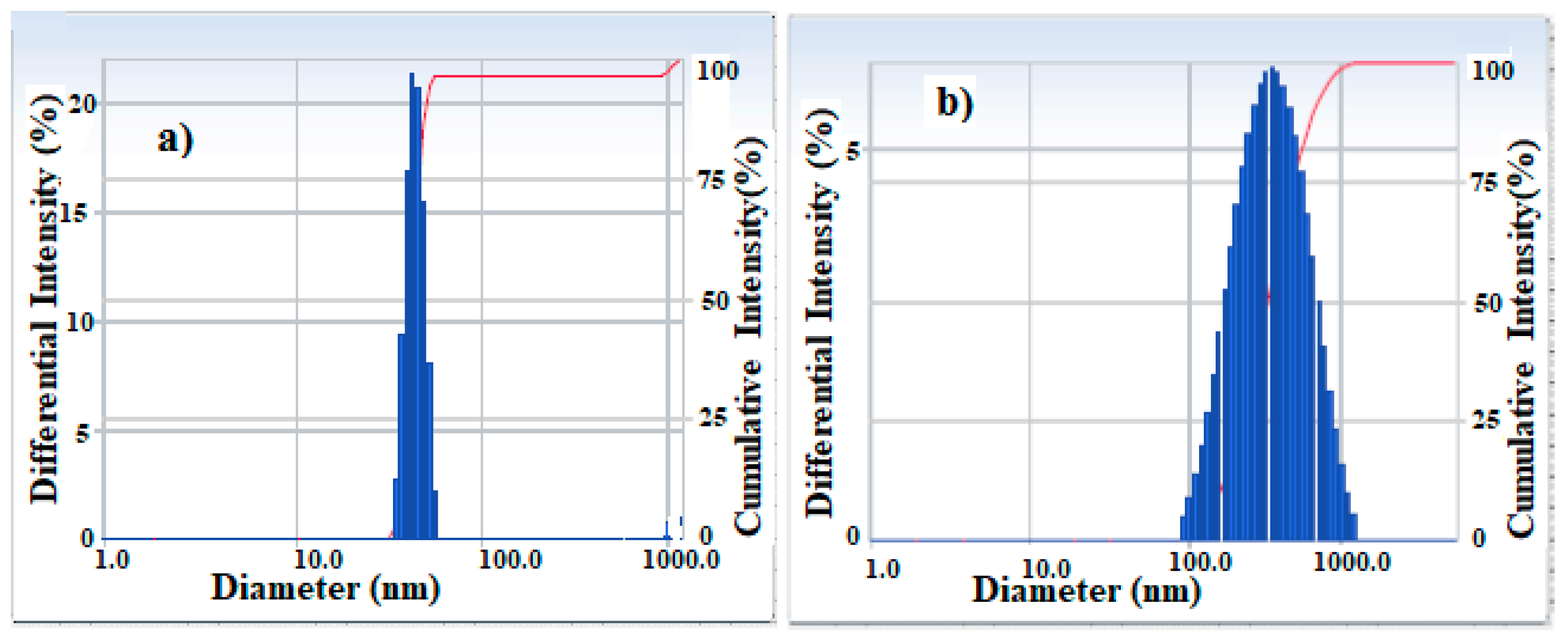
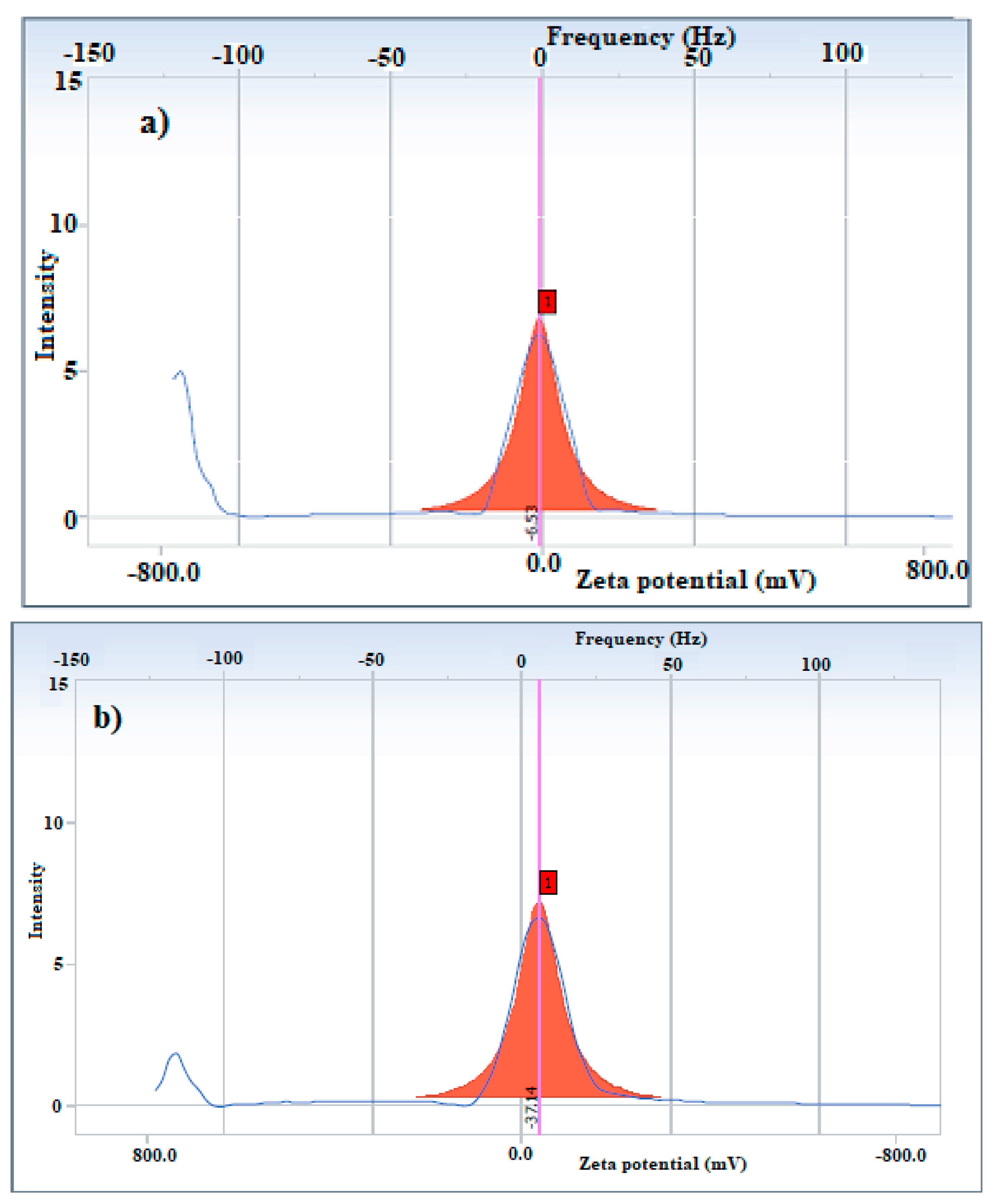
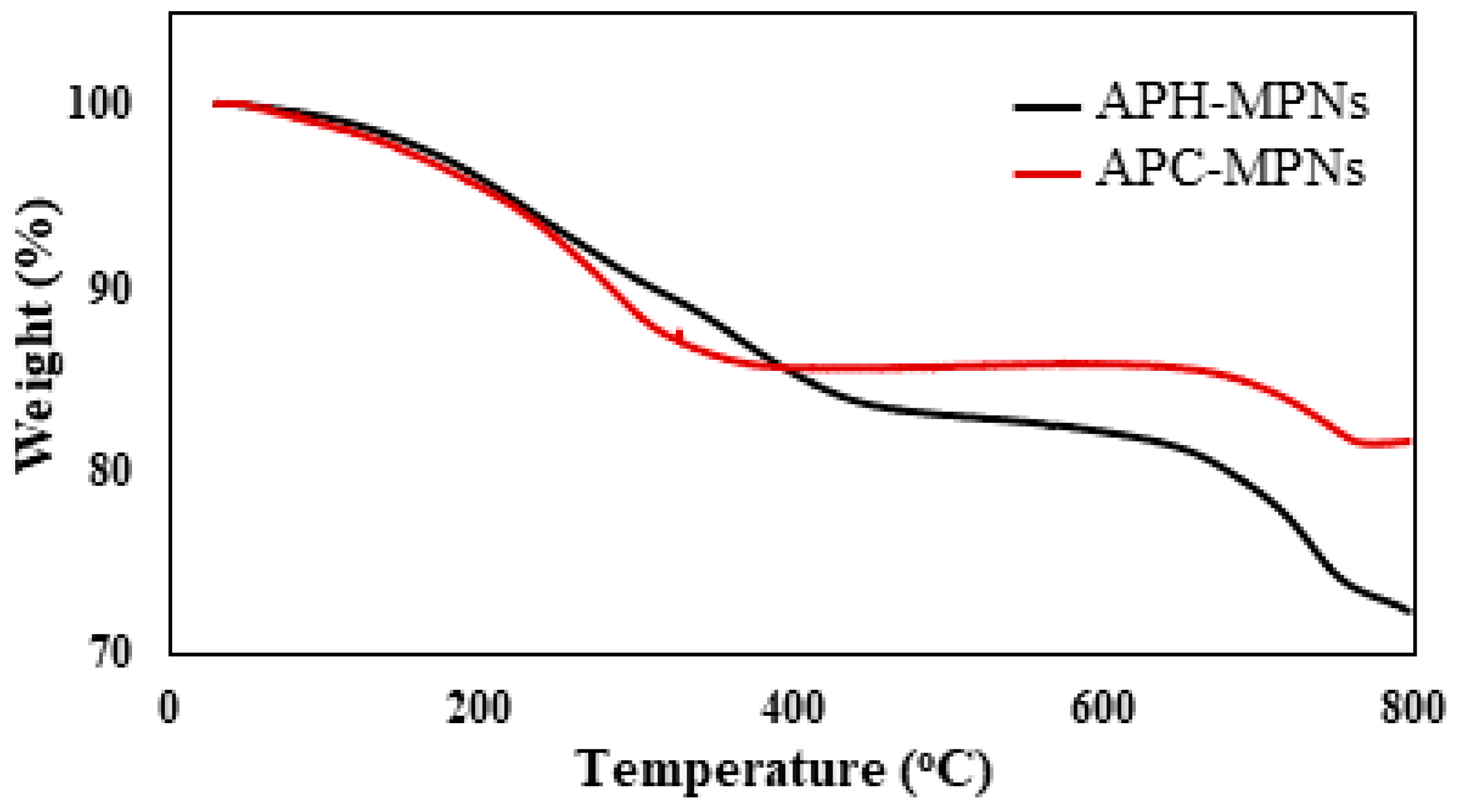
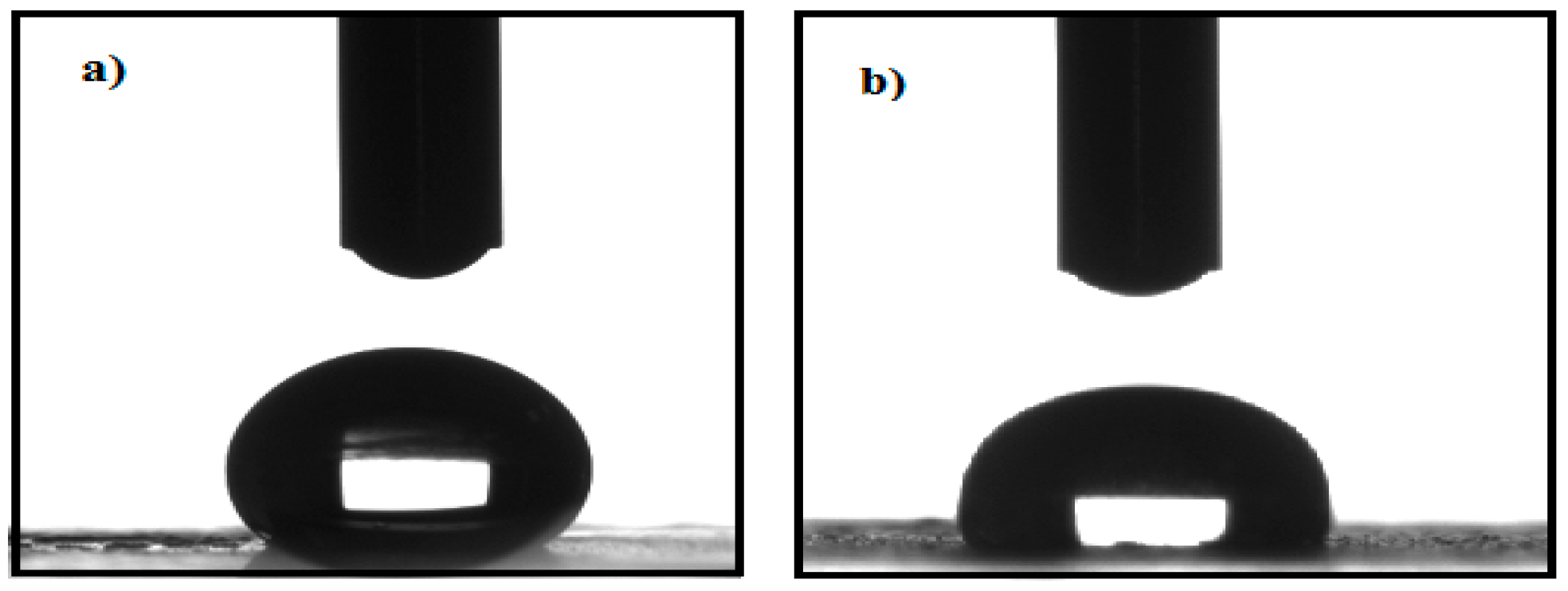
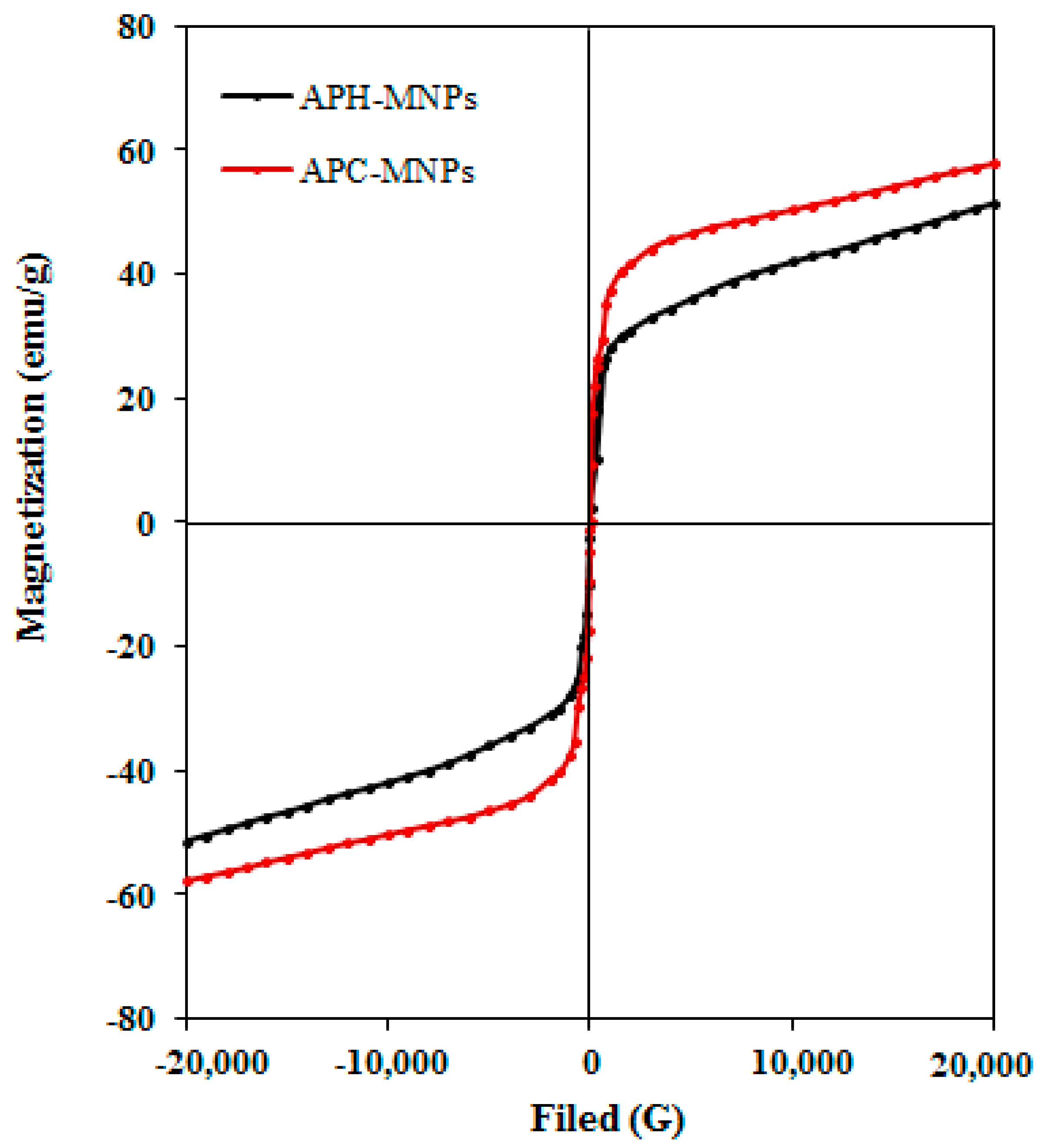
| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| APH-MNPs | 565.1 | 0.338 | −6.53 |
| APC-MNPs | 308.8 | 0.229 | −37.14 |
| Sample | Ms (emu/g) | Mr (emu/g) | Hc (Oe) |
|---|---|---|---|
| APH-MNPs | 51.42 | 0.153 | 6.4 |
| APC-MNPs | 57.83 | 0.098 | 5.1 |
| Ratio | 1:1 | 1:10 | 1:25 | 1:50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||||
| APH-MNPs | 92 | 90 | 88 | 83 | |
| APC-MNPs | 81 | 78 | 74 | 70 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, M.M.S.; Atta, A.M.; Allohedan, H.A.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Khan, M.; Ezzat, A.O. Green Synthesis of Hydrophobic Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Plant Extract and Their Application as Petroleum Oil Spill Collectors. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100855
Abdullah MMS, Atta AM, Allohedan HA, Alkhathlan HZ, Khan M, Ezzat AO. Green Synthesis of Hydrophobic Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Plant Extract and Their Application as Petroleum Oil Spill Collectors. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(10):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100855
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Mahmood M. S., Ayman M. Atta, Hamad A. Allohedan, Hamad Z. Alkhathlan, M. Khan, and Abdelrahman O. Ezzat. 2018. "Green Synthesis of Hydrophobic Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Plant Extract and Their Application as Petroleum Oil Spill Collectors" Nanomaterials 8, no. 10: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100855
APA StyleAbdullah, M. M. S., Atta, A. M., Allohedan, H. A., Alkhathlan, H. Z., Khan, M., & Ezzat, A. O. (2018). Green Synthesis of Hydrophobic Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Plant Extract and Their Application as Petroleum Oil Spill Collectors. Nanomaterials, 8(10), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100855






