Review of the Functions of Archimedes’ Spiral Metallic Nanostructures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Polarization-Sensitive Mechanism
3. Different Structural Constructions
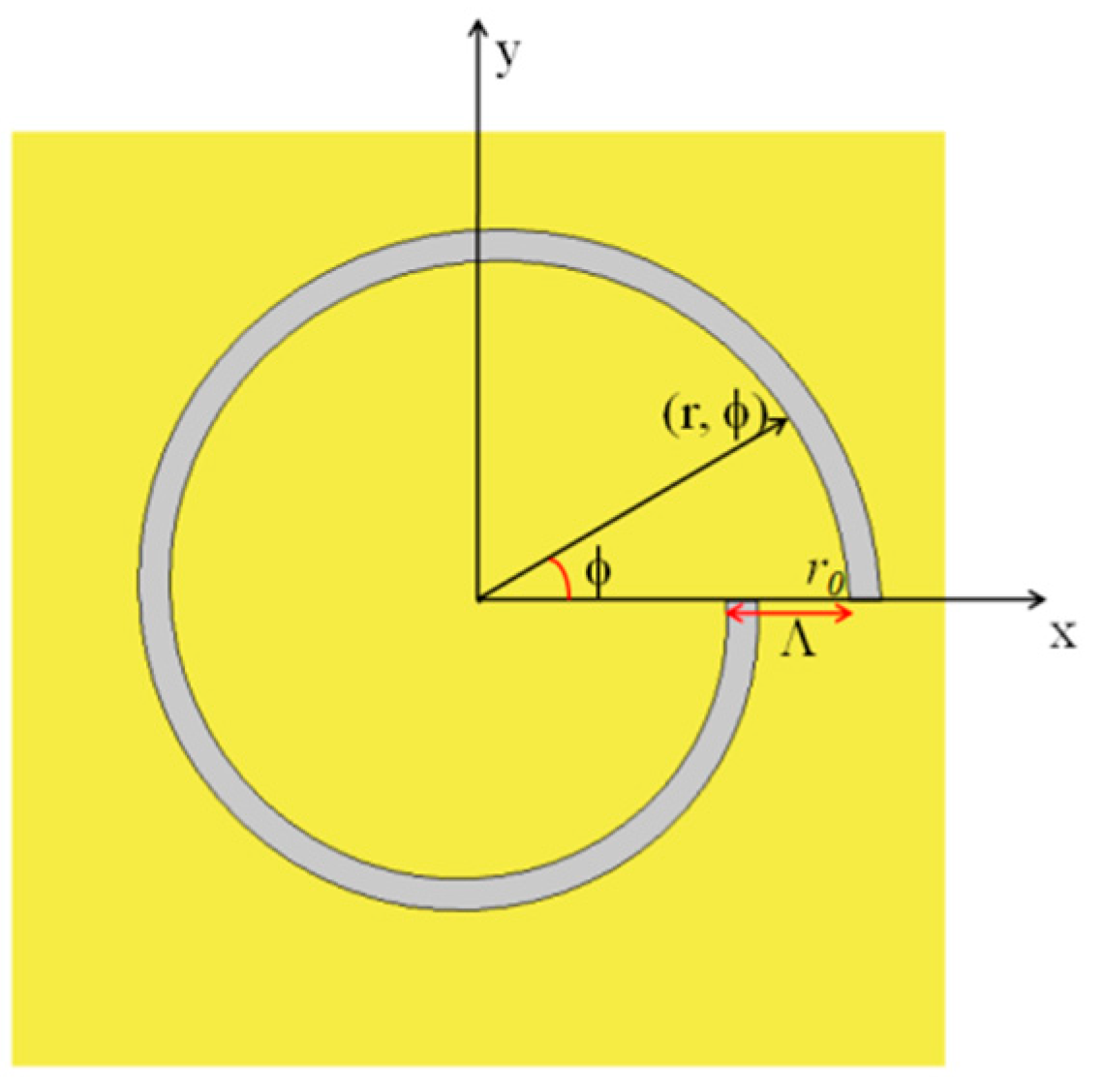
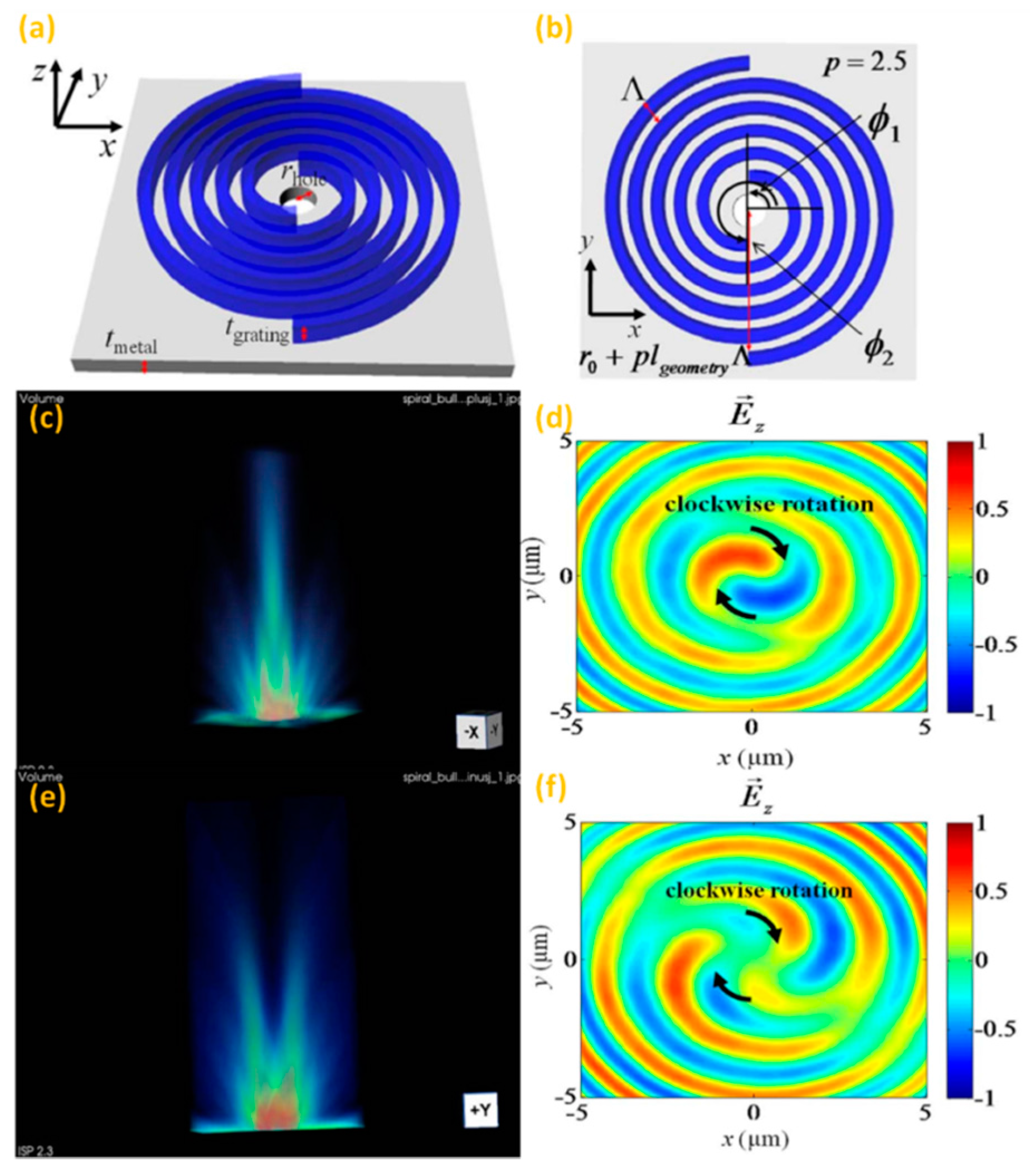
3.1. Pure Archimedes’ Spiral Plasmonic Lens
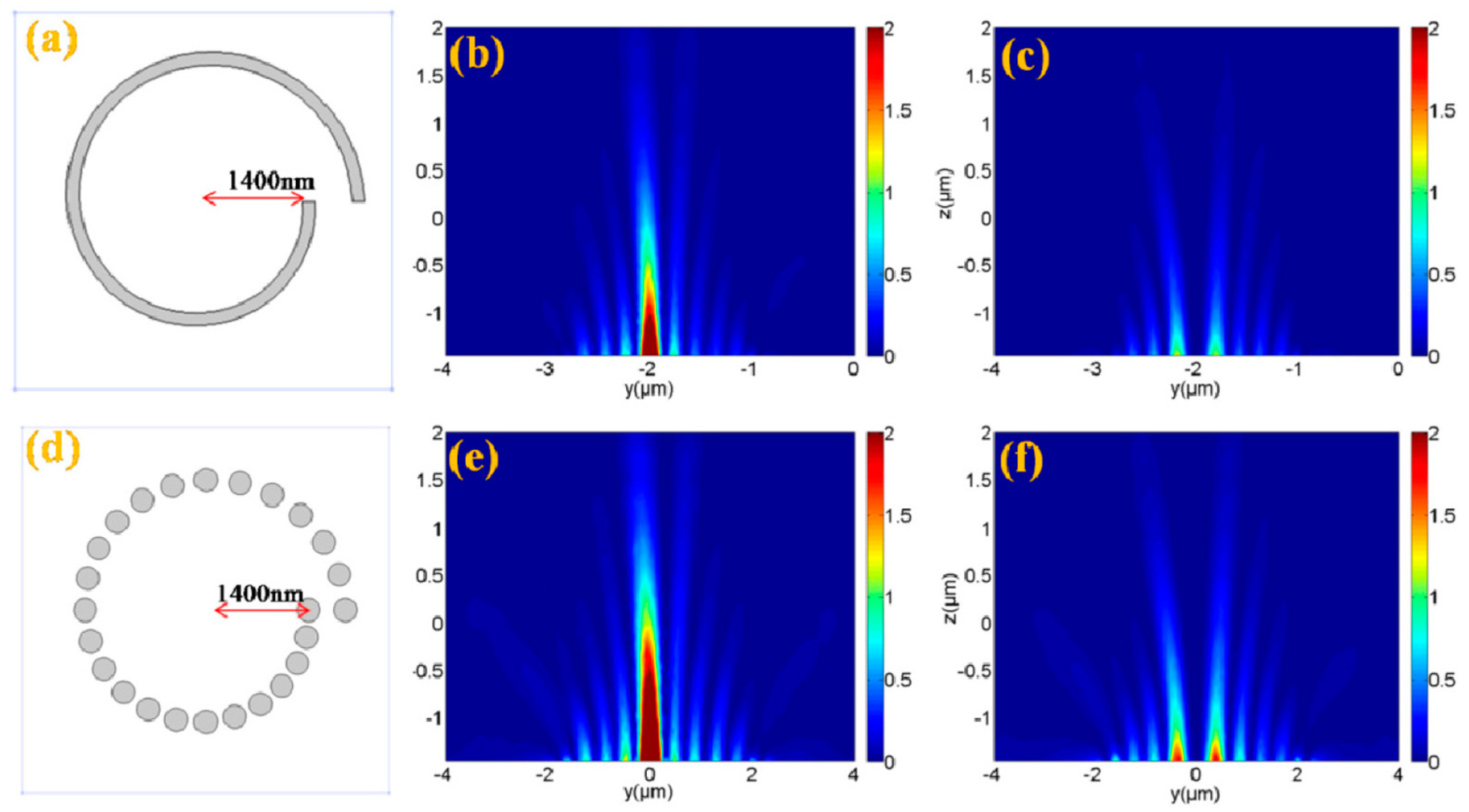
3.2. Multiple-Turn Spiral Slit
3.3. Hybrid Spiral Plasmonic Lens
3.4. ASS with a Concentric Annular Groove
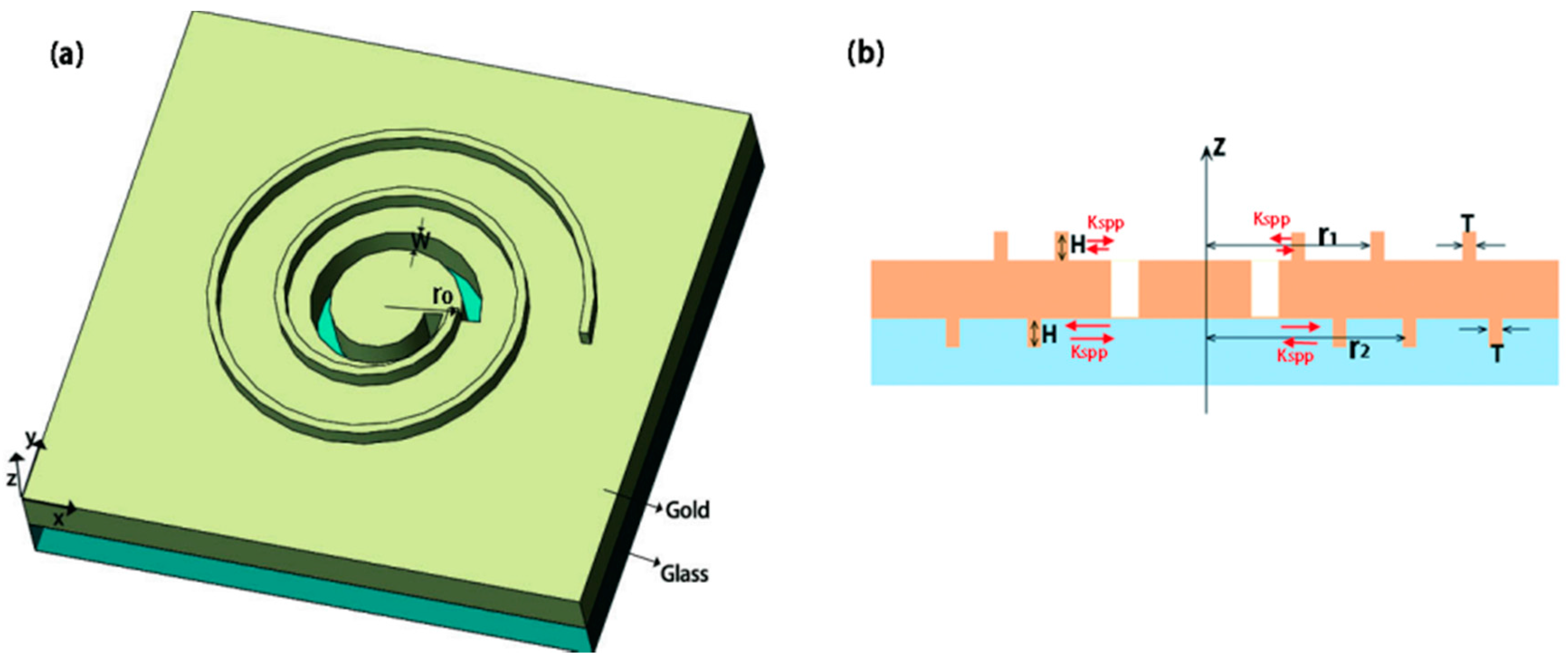
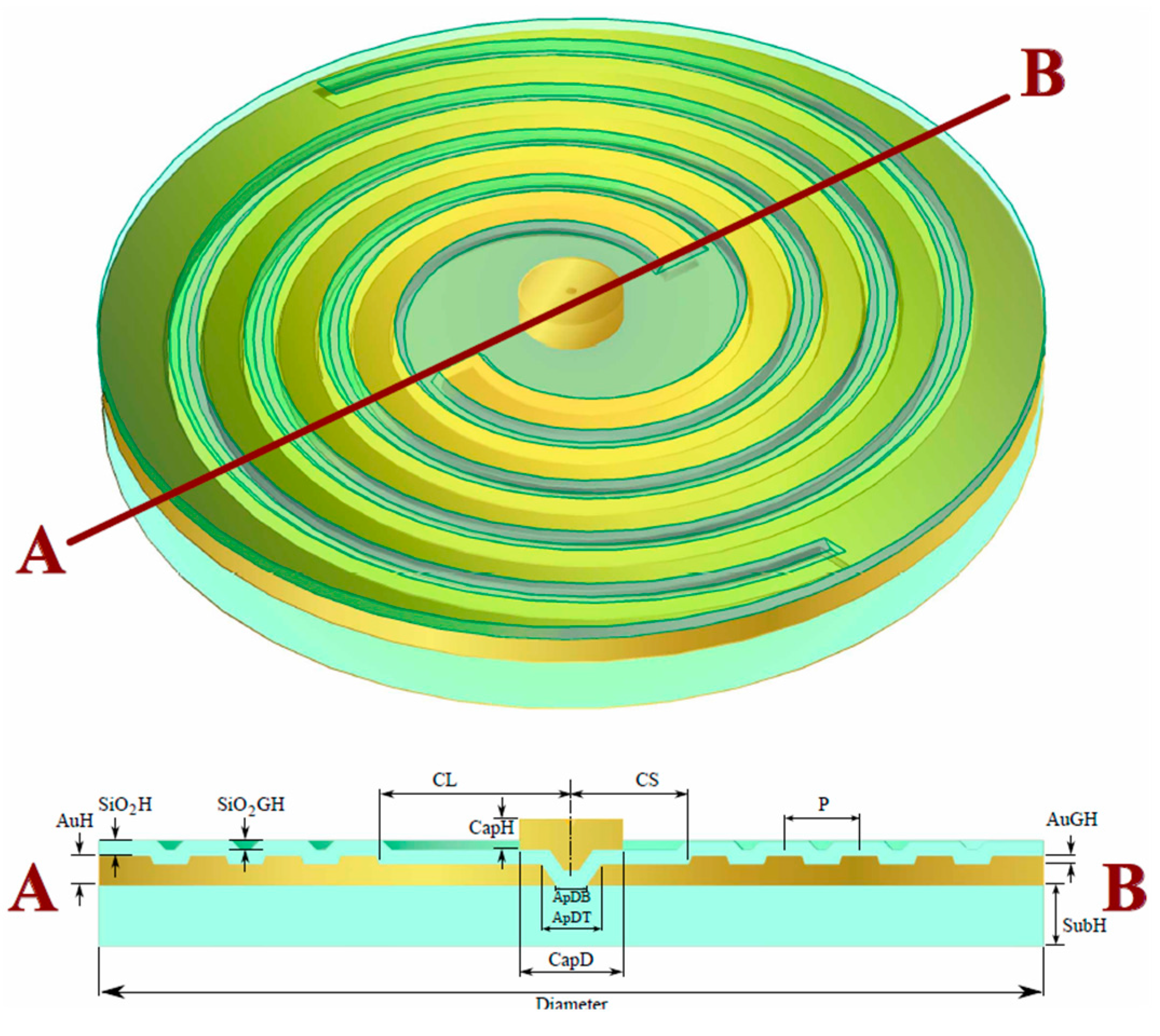
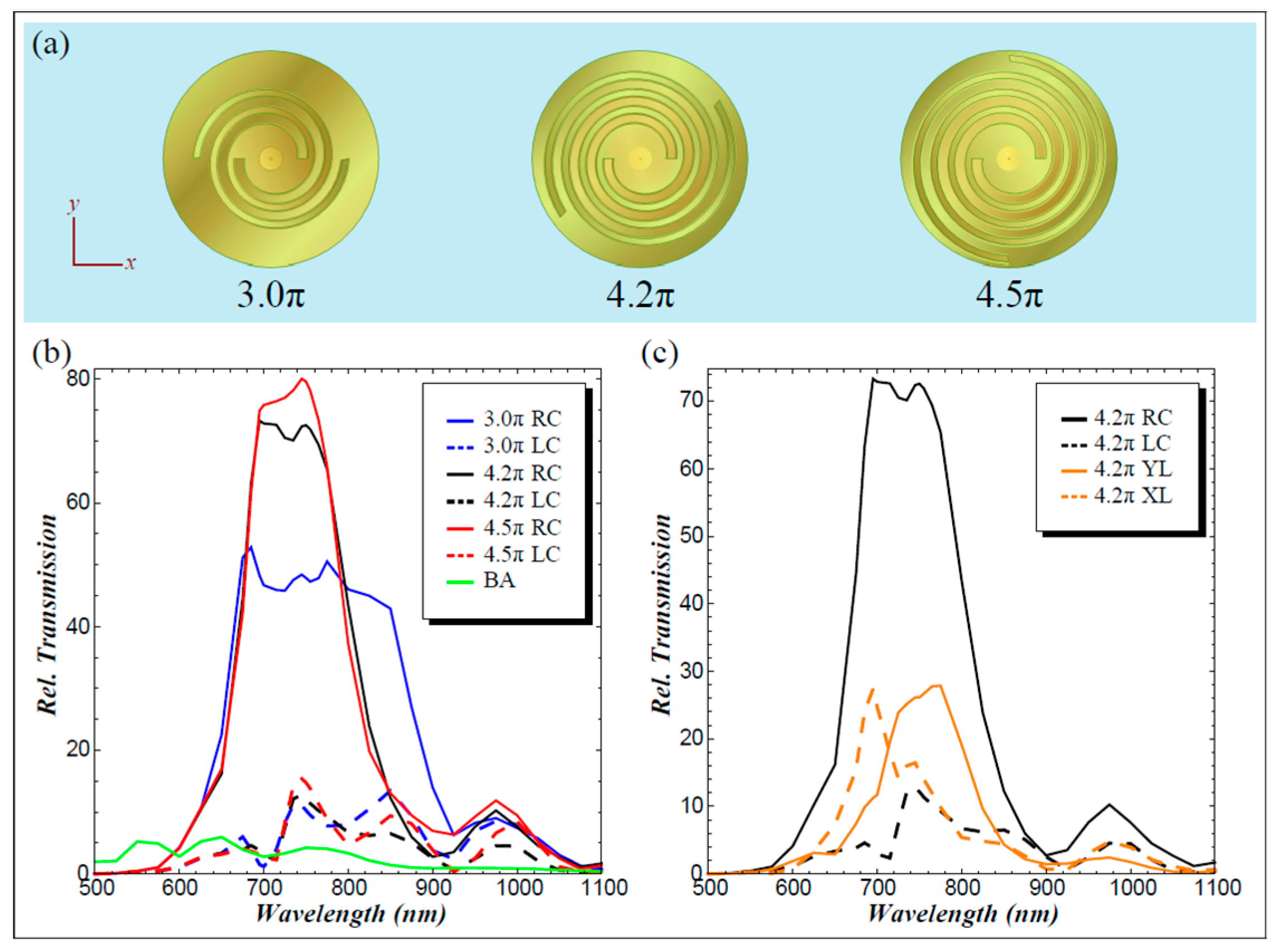
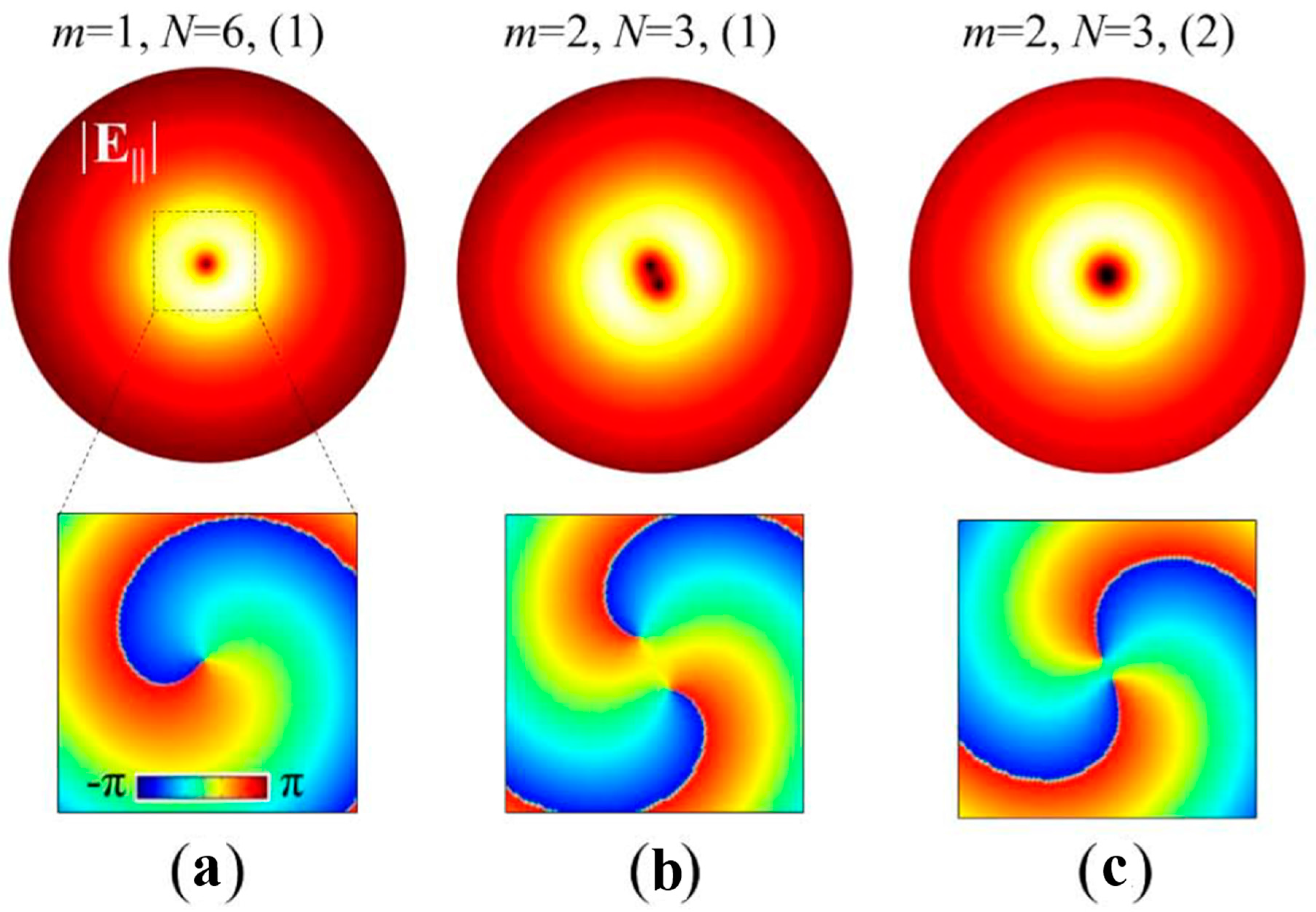
3.5. ASS Combined with Coaxial Archimedes’ Spiral Gratings
3.6. Combination of ASG and MIM Waveguide
3.7. The Derivative ASS Structure
3.8. Double Spiral Gratings with a Central Hole
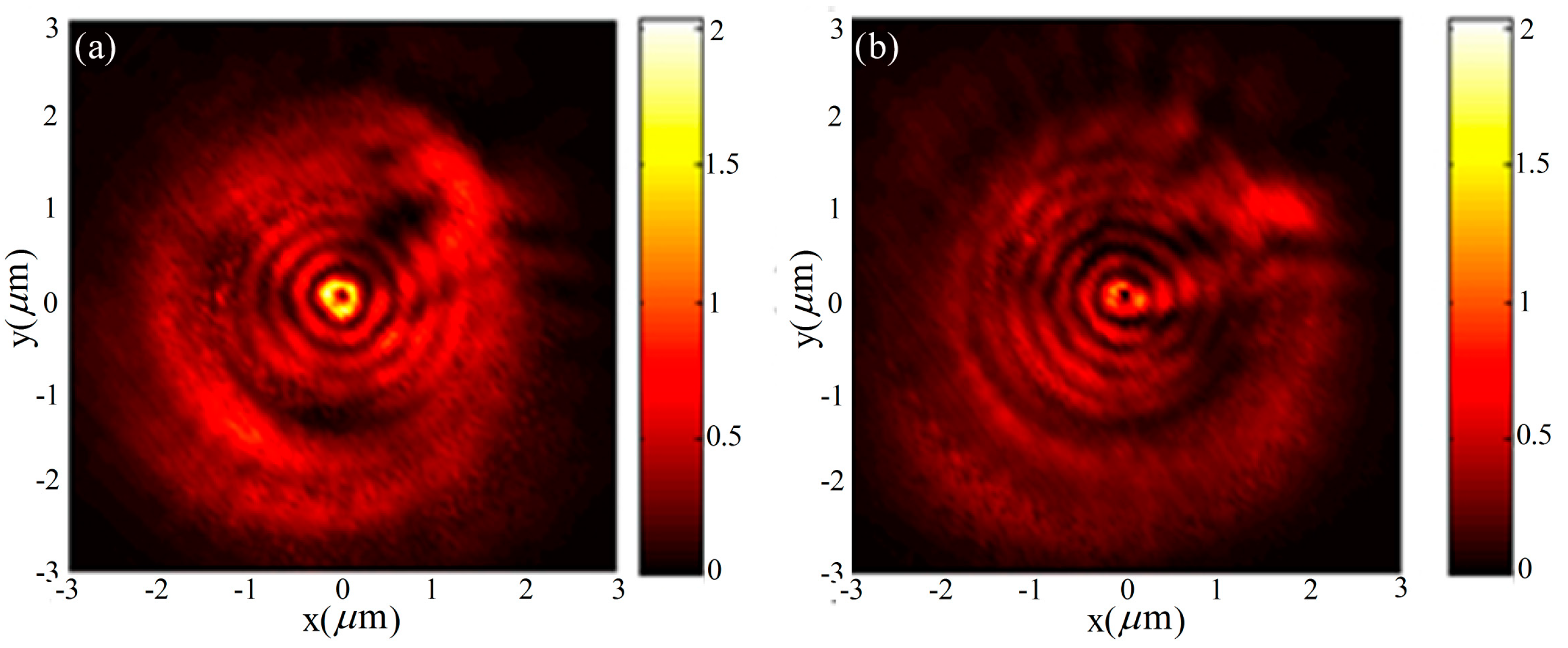
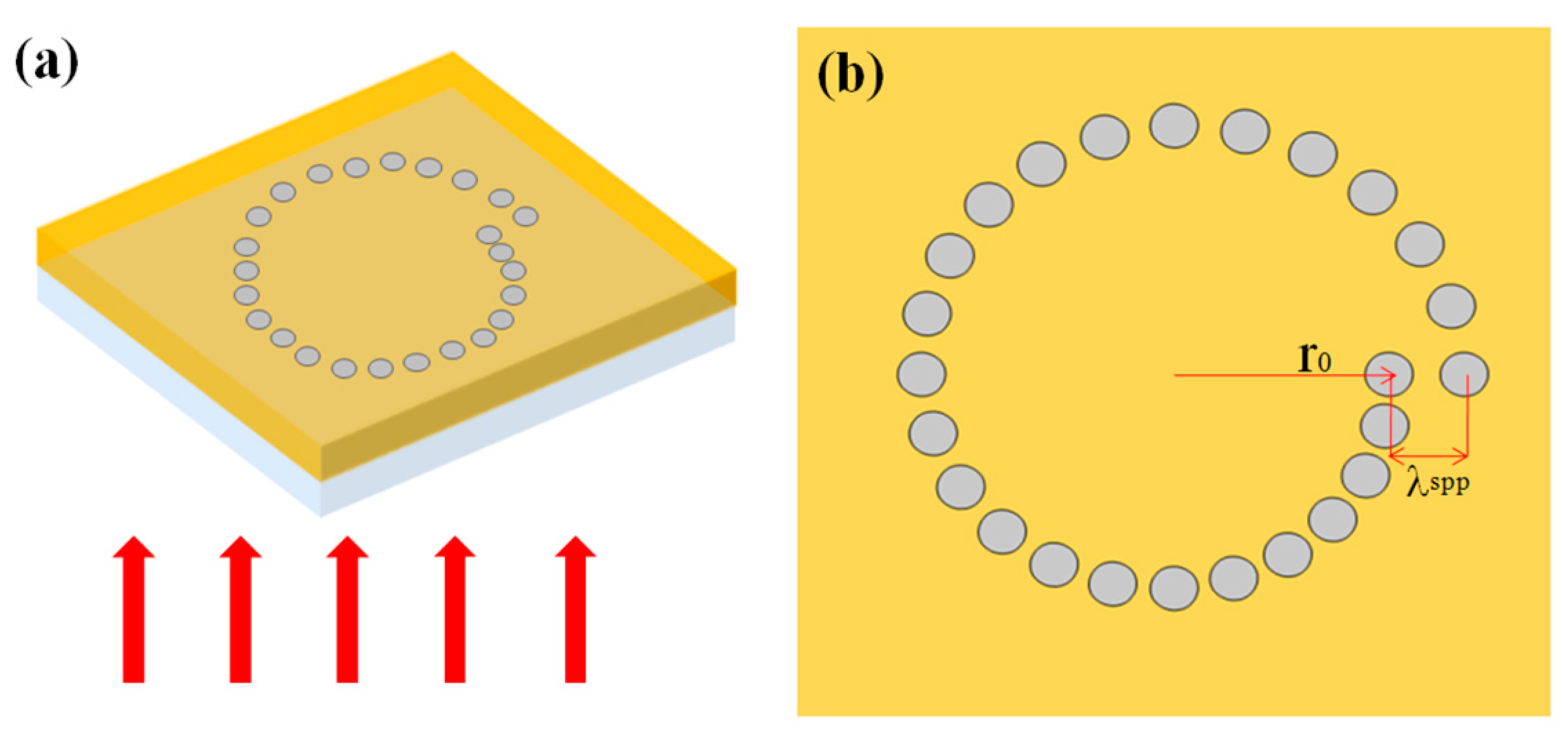
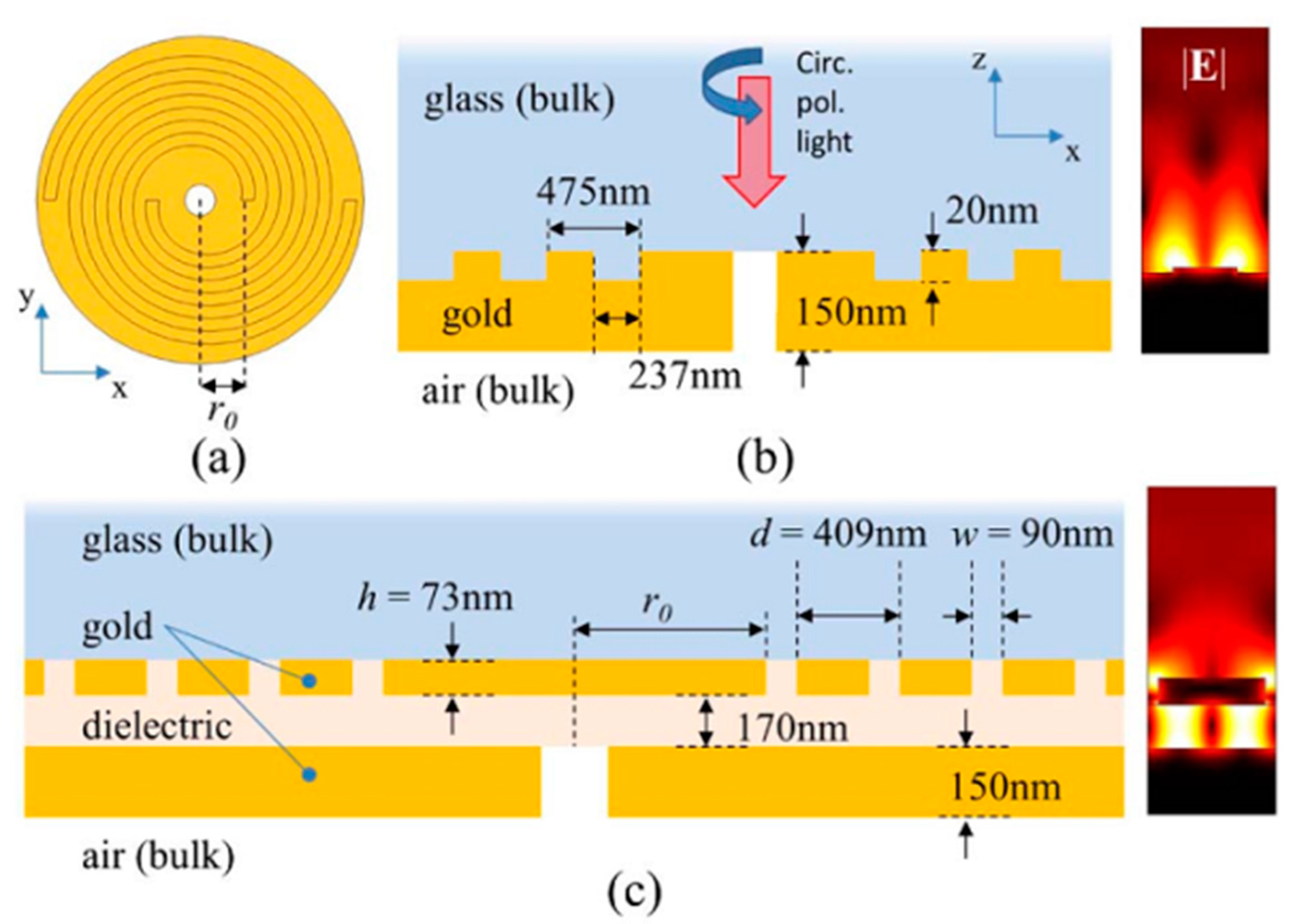
3.9. Spiral Structure Based on a Nano-Pinhole Array
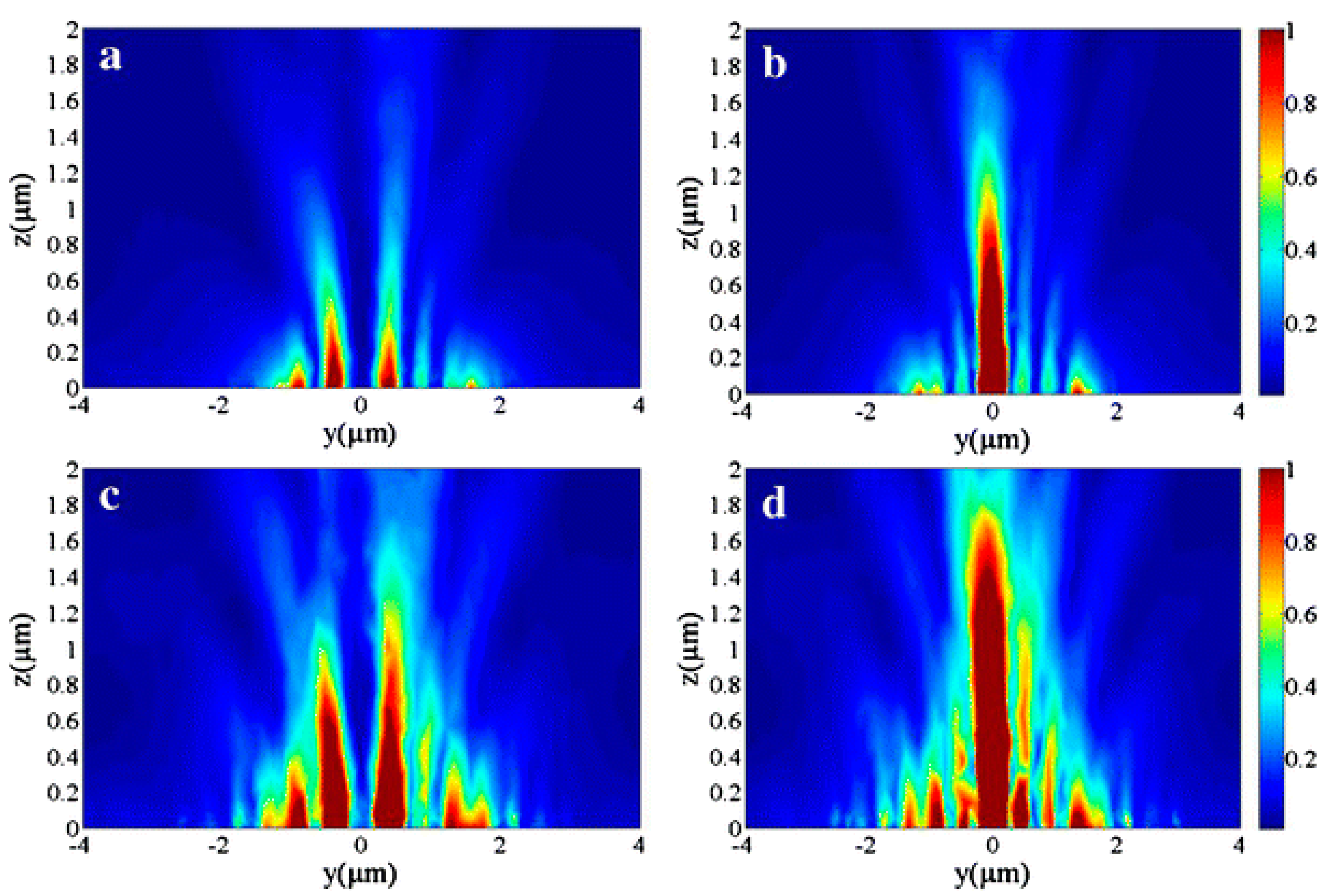
3.10. Bilayer Holey Spiral Plasmonic Lens
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caucheteur, C.; Shevchenko, Y.; Shao, L.Y.; Wuilpart, M.; Albert, J. High resolution interrogation of tilted fiber grating SPR sensors from polarization properties measurement. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, M.; Martinelli, P.; Pietralunga, S.M. Polarization stabilization in optical comminications systems. J. Lightw. Technol. 2006, 24, 4172–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyo, J.S.; Goldstein, D.L.; Chenault, D.B.; Shaw, J.A. Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 5453–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, J.; Bondar, A.; Timr, S.; Firestein, S.J. Two-photon polarization microscopy reveals protein structure and function. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruev, V.; Perkins, R.; York, T. CCD polarization imaging sensor with aluminum nanowire optical filters. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 19087–19094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruev, V.; Van der Spiegel, J.; Engheta, N. Dual-tier thin film polymer polarization imaging sensor. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 19292–19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyo, J.S.; Ratliff, B.M.; Boger, J.K.; Black, W.T.; Bowers, D.L.; Fetrow, M.P. The effects of thermal equilibrium and contrast in LWIR polarimetric images. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15161–15167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R.M.; Bashara, N.M. Ellipsometry and Polarized Light; Sole Distributors for the USA and Canada: New York, NY, USA; Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, H.G.; Gabrielse, G.; Livingston, A.E. Measurement of the stokes parameters of light. Appl. Opt. 1977, 16, 3200–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J. The Archimedean two-wire spiral antenna. IRE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1960, 8, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, J. An Experimental Investigation of the Spiral Antenna; University of Illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, W. Spiral antennas. IRE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1960, 8, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawer, R.; Wolfe, J. The spiral antenna. In Proceedings of the 1958 IRE International Convention Record, New York, NY, USA, 21–25 March 1966; Volume 8, pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, W.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Huang, C.B. Selective trapping or rotation of isotropic dielectric microparticles by optical near field in a plasmonic archimedes spiral. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasavin, A.V.; Schwanecke, A.S.; Zheludev, N.I.; Reichelt, M.; Stroucken, T.; Koch, S.W.; Wright, E.M. Polarization conversion and “focusing” of light propagating through a small chiral hole in a metallic screen. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 201105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata-Gonokami, M.; Saito, N.; Ino, Y.; Kauranen, M.; Jefimovs, K.; Vallius, T.; Svirko, Y. Giant optical activity in quasi-two-dimensional planar nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 227401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasavin, A.V.; Schwanecke, A.S.; Zheludev, N.I. Extraordinary properties of light transmission through a small chiral hole in a metallic screen. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2006, 8, S98–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, V.A.; Schwanecke, A.S.; Zheludev, N.I.; Khardikov, V.V.; Prosvirnin, S.L. Asymmetric transmission of light and enantiomerically sensitive plasmon resonance in planar chiral nanostructures. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1996–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanecke, A.S.; Fedotov, V.A.; Khardikov, V.V.; Prosvirnin, S.L.; Chen, Y.; Zheludev, N.I. Nanostructured metal film with asymmetric optical transmission. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2940–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.; Lin, F.; Zhu, X. Plasmonic focusing in spiral nanostructures under linearly polarized illumination. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 16686–16693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, W.L.; Dereux, A.; Ebbesen, T.W. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 2003, 424, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, W.L. Surface plasmon–polariton length scales: A route to sub-wavelength optics. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2006, 8, S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodetski, Y.; Niv A Kleiner, V.; Hasman, E. Observation of the spin-based plasmonic effect in nanoscale structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 043903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliokh, K.Y.; Gorodetski, Y.; Kleiner, V.; Hasman, E. Coriolis effect in optics: Unified geometric phase and spin-Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 030404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, T.; Miyanishi, S. Study of surface plasmon chirality induced by Archimedes’ spiral grooves. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 6285–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodetski, Y.; Shitrit, N.; Bretner, I.; Kleiner, V.; Hasman, E. Observation of Optical Spin Symmetry Breaking in Nanoapertures. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3016–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.W.; Park, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, B. Coupling of spin and angular momentum of light in plasmonic vortex. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 10083–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.R.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, R.Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, A.J.; Liu, J.L.; Qu, S.L.; Gao, J. Circular polarization analyzer based on the combined coaxial Archimedes’ spiral structure. Plasmonics 2015, 10, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.Z.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhang, A.J.; Qu, S.L. Ultra-thin optical vortex phase plate based on the metasurface and the angular momentum transformation. J. Opt. 2015, 17, 045102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Shen, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.S.; Qu, S.L. Ultra-thin optical vortex phase plate based on the L-shaped nanoantenna for both linear and circular polarized incidences. Opt. Commun. 2015, 355, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Abeysinghe, D.C.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Experimental confirmation of miniature spiral plasmonic lens as a circular polarization analyzer. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Chen, W.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Miniature circular polarization analyzer with spiral plasmonic lens. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 3047–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhan, Q.W. Realization of an evanescent Bessel beam via surface plasmon interference excited by a radially polarized beam. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, G.M.; Yanai, A.; Levy, U. Demonstration of nanofocusing by the use of plasmonic lens illuminated with radially polarized light. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Abeysinghe, D.C.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Plasmonic lens made of multiple concentric metallic rings under radially polarized illumination. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4320–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.W. Cylindrical vector beams: From mathematical concepts to applications. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2009, 1, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, G.; Chen, W.; Zhan, Q.W. High efficiency plasmonic probe design for parallel near-field optics applications. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 5187–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzig, E.; Isaacson, M.; Lewis, A. Collection mode near-field scanning optical microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 51, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Peng, Q.; Song, W.; Hao, F.; Wang, J.; Nordlander, P.; Zhu, X. Plasmonic focusing in symmetry broken nanocorrals. Nano Lett. 2010, 11, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, W.; Abeysinghe, D.C.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Two-photon fluorescence characterization of spiral plasmonic lenses as circular polarization analyzers. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Okuda, S.; Inoue, T.; Aizawa, K. Focusing Characteristics of a Spiral Plasmonic Lens. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 09LG03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Inami, W.; Kawata, Y. Deep-ultraviolet light excites surface plasmon for the enhancement of photoelectron emission. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 023112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srituravanich, W.; Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Bogy, D.B.; Zhang, X. Flying plasmonic lens in the near field for high-speed nanolithography. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Tian, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Plasmonic lens with multiple-turn spiral nano-structures. Plasmonics 2011, 6, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Efficient miniature circular polarization analyzer design using hybrid spiral plasmonic lens. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Rui, G.; Abeysinghe, D.C.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Hybrid spiral plasmonic lens: Towards an efficient miniature circular polarization analyzer. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 26299–26307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Nelson, R.L.; Zhan, Q.W. Geometrical phase and surface plasmon focusing with azimuthal polarization. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Misawa, H. Far-Field Focusing of Spiral Plasmonic Lens. Plasmonics 2012, 7, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, A.; Levy, U. Plasmonic focusing with a coaxial structure illuminated by radially polarized light. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, K.A.; Peltzer, J.J.; Flammer, P.D.; Furtak, T.E.; Collins, R.T.; Hollingsworth, R.E. Spiral plasmonic nanoantennas as circular polarization transmission filters. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, G.; Zhan, Q.W. Highly sensitive beam steering with plasmonic antenna. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, J.A.; Lezec, H.J.; Atwater, H.A. Highly Confined photon transport in subwavelength metallic slot waveguides. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, E.; Dionne, J.A.; Kuipers, L.; Atwater, H.A.; Polman, A. Near-field visualization of strongly confined surface plasmon polaritons in–metal–insulator waveguides. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2925–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Zhong, K.; Sui, C.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. 2014 Study of spiral-ring plasmonic structures for optical manipulation. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9285, 7th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies (AOMATT), Harbin, China, 26–29 April 2014; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; p. 92850. [Google Scholar]
- Ebbesen, T.W.; Lezec, H.J.; Ghaemi, H.F.; Thio, T.; Wolff, P.A. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 1998, 391, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications; Search PubMed: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Shitrit, N.; Bretner, I.; Gorodetski, Y.; Kleiner, V.; Hasman, E. Optical spin Hall effects in plasmonic chains. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2038–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, I.M.; Park, J.; Hwang, C.Y.; Lee, B. Dynamic switching of the chiral beam on the spiral plasmonic bull’s eye structure. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, G104–G112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Lim, Y.; Lee, B. Off-axis directional beaming of optical field diffracted by a single subwavelength metal slit with asymmetric dielectric surface gratings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 051113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, J.; Cho, S.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, M.; Lee, B. Synthesis and dynamic switching of surface plasmon vortices with plasmonic vortex lens. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezec, H.J.; Degiron, A.; Devaux, E.; Linke, R.A.; Martin-Moreno, L.; Garcia-Vidal, F.J.; Ebbesen, T.W. Beaming light from a subwavelength aperture. Science 2002, 297, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curto, A.G.; Volpe, G.; Taminiau, T.H.; Kreuzer, M.P.; Quidant, R.; Van Hulst, N.F. Unidirectional emission of a quantum dot coupled to a nanoantenna. Science 2010, 329, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, K.; Ran, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Shen, F.; Gao, J.; Liu, S. Circular polarization analyzer based on an Archimedean nano-pinholes array. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 30523–30531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilio, P.; Parisi, G.; Garoli, D.; Carli, M.; Romanato, F. Bilayer holey plasmonic vortex lenses for the far-field transmission of pure orbital angular momentum light states. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4899–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilio, P.; Mari, E.; Parisi, G.; Tamburini, F.; Romanato, F. Angular momentum properties of electromagnetic field transmitted through holey plasmonic vortex lenses. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3234–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Ran, L.; Guo, K.; Lu, Z.; Liu, S. Focusing surface plasmon and constructing central symmetry of focal field with linearly polarized light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 013116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, P.; Liu, W.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, F.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, X. Plasmonic circular polarization analyzer formed by unidirectionally controlling surface plasmon propagation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 161106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ren, G.; Gao, Y.; Wu, B.; Wan, C.; Jian, S. Graphene circular polarization analyzer based on unidirectional excitation of plasmons. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32420–32428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Ren, G.; Cryan, M.J.; Wan, C.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jian, S. Tunable graphene-coated spiral dielectric lens as a circular polarization analyzer. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 8348–8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, C.; Hu, X. A spiral plasmonic lens with directional excitation of surface plasmons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, K.; Shen, F.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, H. Review of the Functions of Archimedes’ Spiral Metallic Nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110405
Guo Z, Li Z, Zhang J, Guo K, Shen F, Zhou Q, Zhou H. Review of the Functions of Archimedes’ Spiral Metallic Nanostructures. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(11):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110405
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhongyi, Zixiang Li, Jingran Zhang, Kai Guo, Fei Shen, Qingfeng Zhou, and Hongping Zhou. 2017. "Review of the Functions of Archimedes’ Spiral Metallic Nanostructures" Nanomaterials 7, no. 11: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110405
APA StyleGuo, Z., Li, Z., Zhang, J., Guo, K., Shen, F., Zhou, Q., & Zhou, H. (2017). Review of the Functions of Archimedes’ Spiral Metallic Nanostructures. Nanomaterials, 7(11), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110405






