Ionic Liquid Confined in Mesoporous Polymer Membrane with Improved Stability for CO2/N2 Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
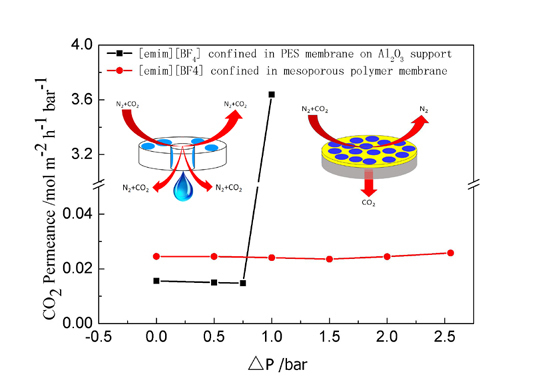
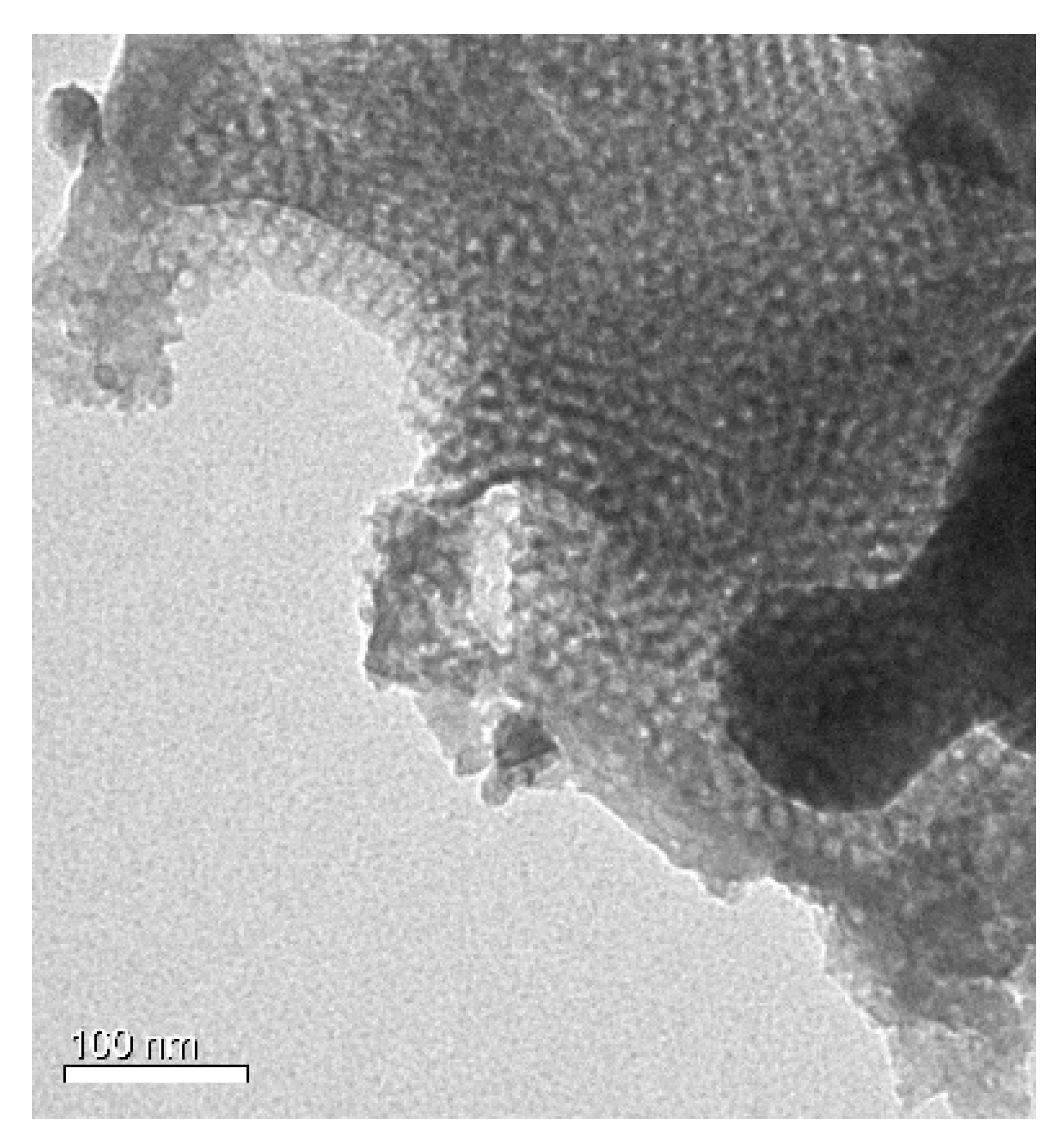
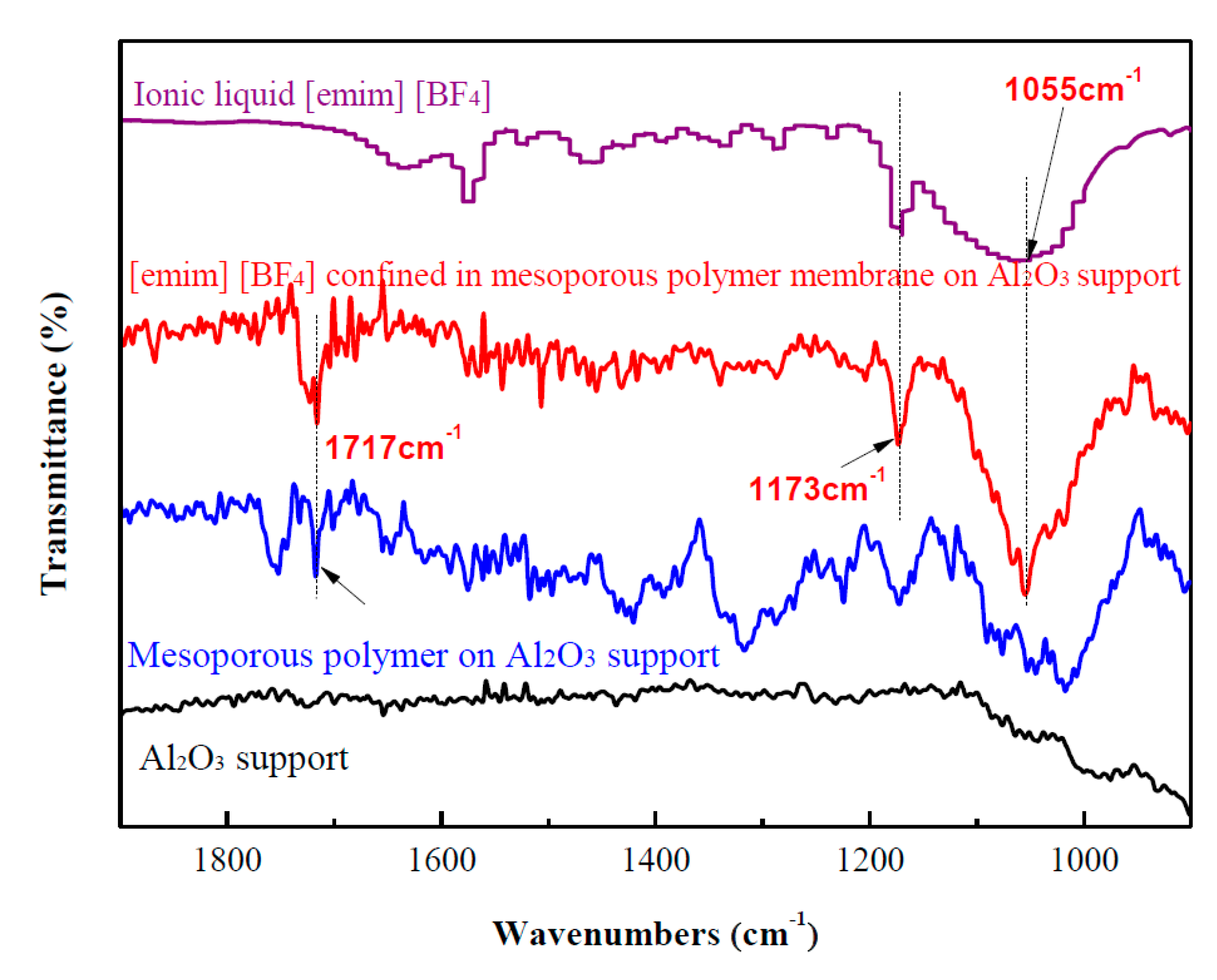
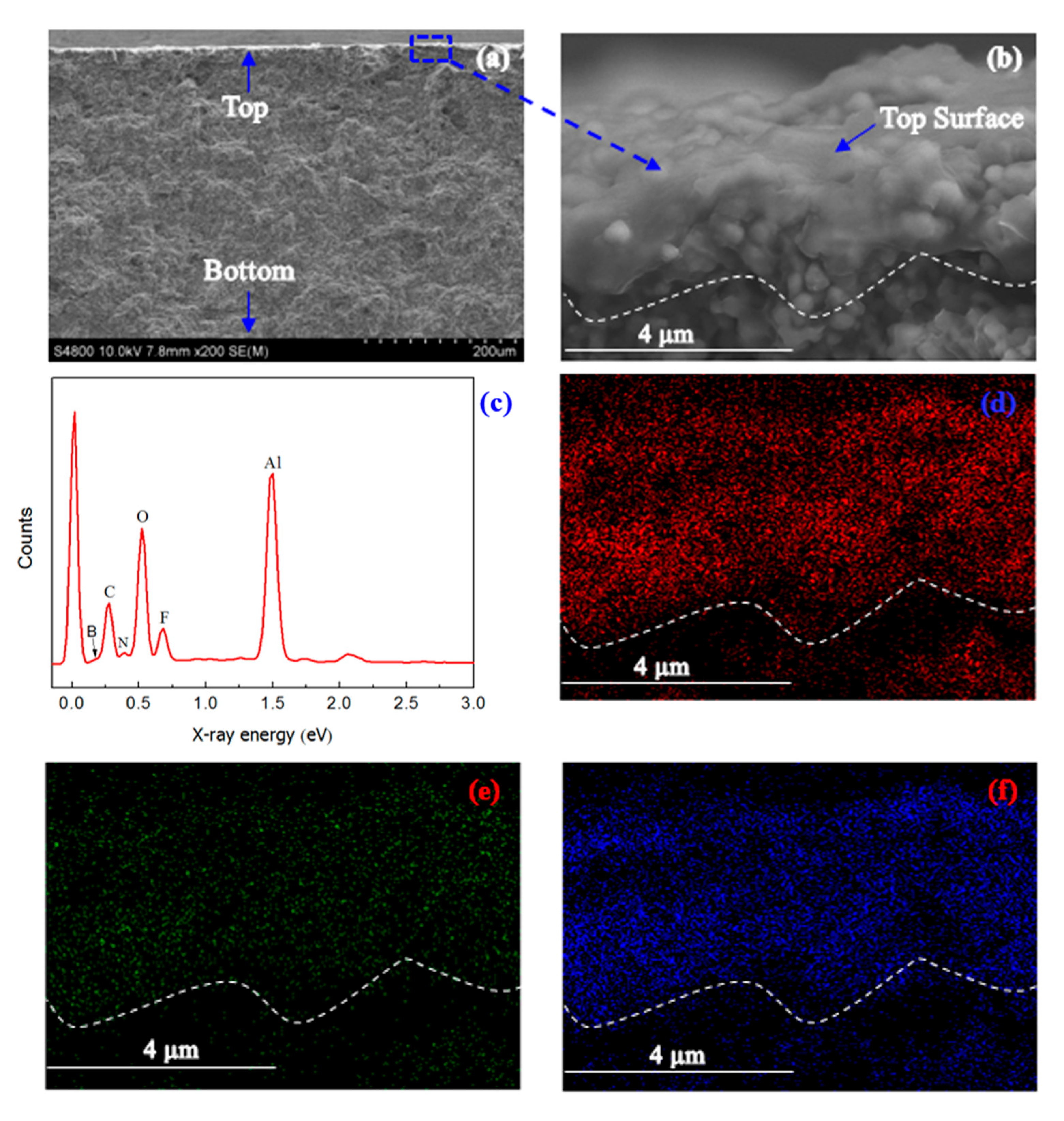
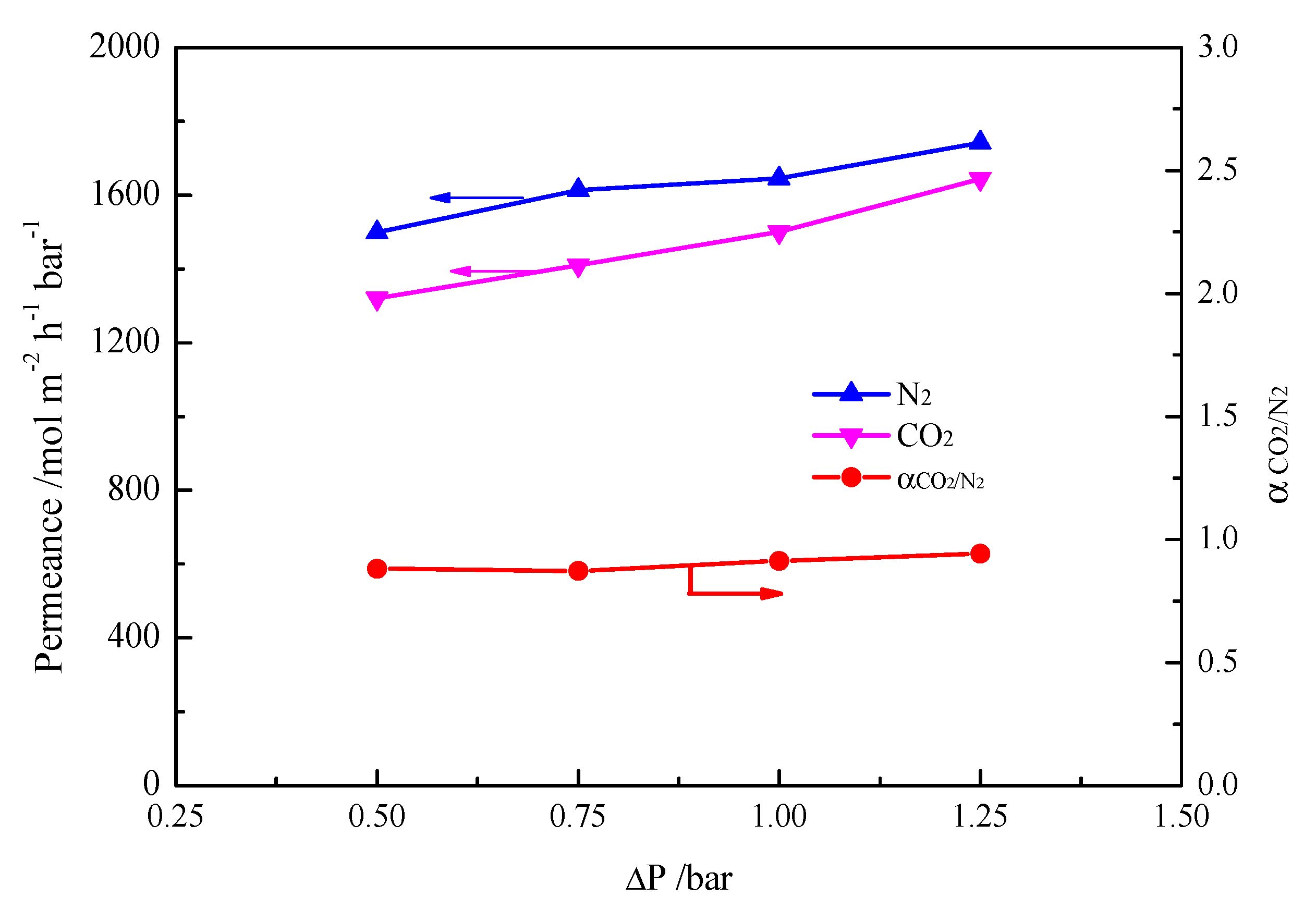
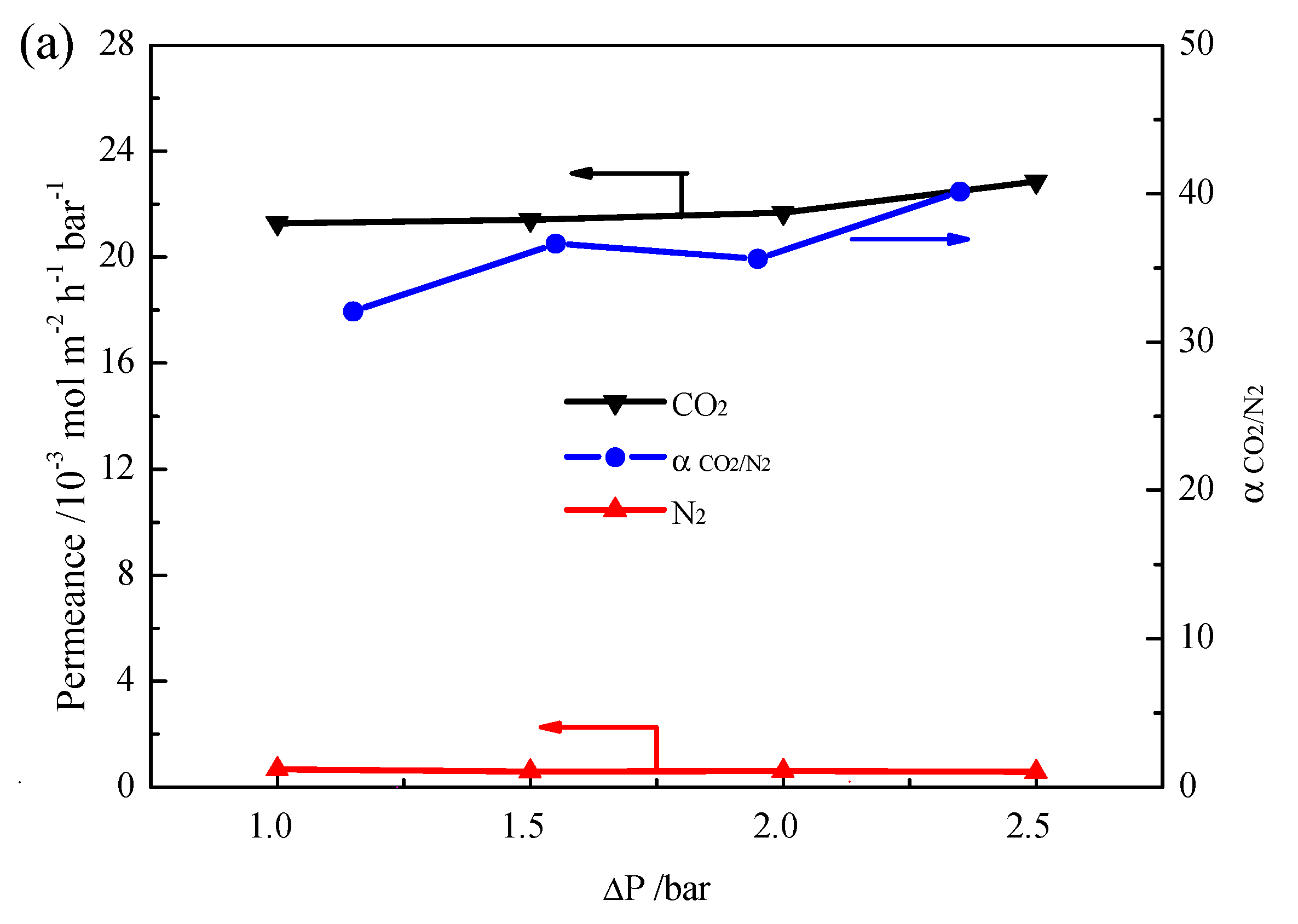
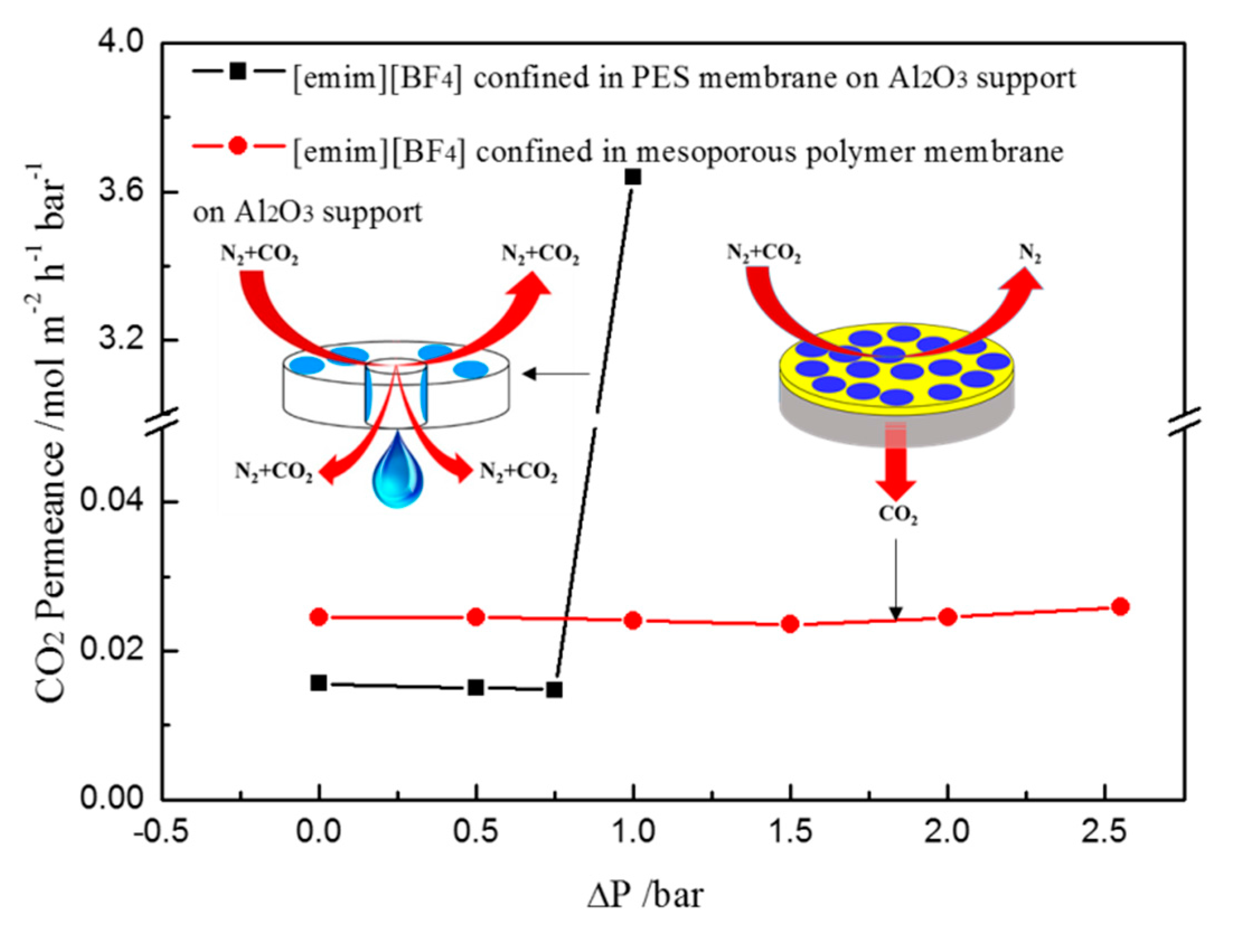
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
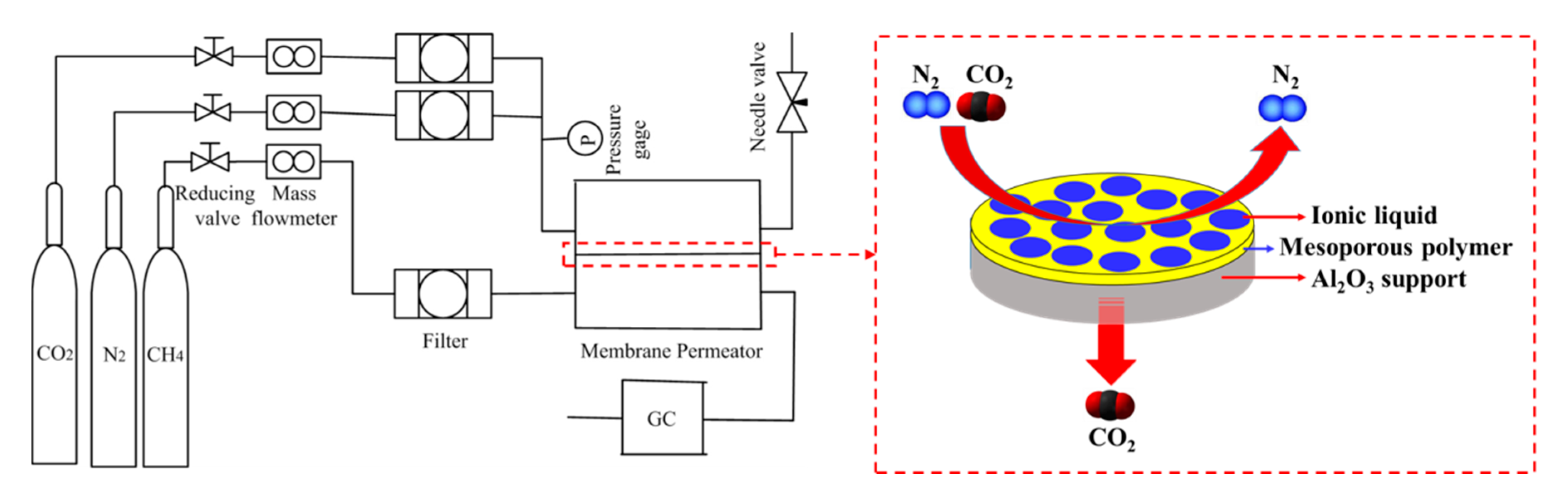
3.2. Preparation of Ionic Liquid Confined in Mesoporous Polymer Membrane
3.3. Gas Permeation Measurements
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilconich, J.; Myers, C.; Pennline, H.; Luebke, D. Experimental investigation of the permeability and selectivity of supported ionic liquid membranes for CO2/He separation at temperatures up to 125 °C. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 298, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanioka, S.; Maruyama, T.; Sotani, T.; Teramoto, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Nakashima, K.; Hanaki, M.; Kubota, F.; Goto, M. CO2 separation facilitated by task-specific ionic liquids using a supported liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scovazzo, P.; Havard, D.; McShea, M.; Mixon, S.; Morgan, D. Long-term, continuous mixed-gas dry fed CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation performance and selectivities for room temperature ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z. Permeability and selectivity of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide in supported ionic liquid membranes. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 17, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurin, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Baker, G.A.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Performance of nitrile-containing anions in task-specific ionic liquids for improved CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, G.; Nie, F.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Liu, H. Membrane liquid loss mechanism of supported ionic liquid membrane for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 411, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowska-Kopczyńska, I.; Joskowska, M.; Dębski, B.; Łuczak, J.; Aranowski, R. Influence of ionic liquid structure on supported ionic liquid membranes effectiveness in carbon dioxide/methane separation. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 980689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Afonso, C.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Integrated CO2 capture and enzymatic bioconversion in supported ionic liquid membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindaratsamee, P.; Ito, A.; Komuro, S.; Shimoyama, Y. Separation of CO2 from the CO2/N2 mixed gas through ionic liquid membranes at the high feed concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarca, G.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Copper(I)-containing supported ionic liquid membranes for carbon monoxide/nitrogen separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 438, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Daniel, C.I.; Portugal, C.A.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Irabien, A. Permeability modulation of supported magnetic ionic liquid membranes (SMILMs) by an external magnetic field. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 430, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Appleby, J.B.; Pez, G.P. New facilitated transport membranes for the separation of carbon dioxide from hydrogen and methane. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 104, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, I.-N.; Yoo, S.; Park, S.-J.; Won, J. CO2 separation membranes using ion gels by self-assembly of a triblock copolymer in ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibi, M.; Barghi, S.H.; Rashtchian, D. Predictive models for permeability and diffusivity of CH4 through imidazolium-based supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarikov, D.D.; Hacarlioglu, P.; Oyama, S.T. Supported room temperature ionic liquid membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahkaramipour, N.; Adibi, M.; Seifkordi, A.A.; Fazli, Y. Separation of CO2/CH4 through alumina-supported geminal ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, D.; Zeh, M.; Luebke, D. The bubble point of supported ionic liquid membranes using flat sheet supports. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Crespo, J.G.; Coelhoso, I.M. Gas permeation studies in supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Santos, E.; Neves, L.A.; Simeonov, S.P.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Irabien, A. Separation performance of CO2 through supported magnetic ionic liquid membranes (SMILMs). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Porous AL2O3/TiO2 tubes in combination with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ionic liquid for CO2/N2 separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Tsuru, T. Thin ionic liquid membranes based on inorganic supports with different pore sizes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8045–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzialla, O.; Labropoulos, A.; Panou, A.; Sanopoulou, M.; Kouvelos, E.; Athanasekou, C.; Beltsios, K.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P.; Romanos, G. Phase behavior and permeability of alkyl-methyl-imidazolium tricyanomethanide ionic liquids supported in nanoporous membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Rooney, D.; Zou, Y. Supported ionic liquid membranes in nanopore structure for gas separation and transport studies. Desalination 2006, 199, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Ordered mesoporous polymers and homologous carbon frameworks: Amphiphilic surfactant templating and direct transformation. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 7215–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, L.; Feng, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wan, Y.; Stein, A.; et al. A family of highly ordered mesoporous polymer resin and carbon structures from organic–organic self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4447–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Meng, Y.; Gu, D.; Yan, Y.; Yu, C.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. A facile aqueous route to synthesize highly ordered mesoporous polymers and carbon frameworks with Ia3̄d bicontinuous cubic structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13508–13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanbu, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Kitamura, F. In situ FT-IR spectroscopic observation of a room-temperature molten salt|gold electrode interphase. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, N.; Park, H.B.; Robertson, G.P.; Dal-Cin, M.M.; Visser, T.; Scoles, L.; Guiver, M.D. Polymer nanosieve membranes for CO2-capture applications. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazarian, S.G.; Briscoe, B.J.; Welton, T. Combining ionic liquids and supercritical fluids: ATR-IR study of co dissolved in two ionic liquids at high pressures. Chem. Commun. 2000, 2047–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.-H.; Choe, W.-H.; Shim, J.-J.; Ra, C.S.; Tuma, D.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.S. High-pressure solubility of carbon dioxide in imidazolium-based ionic liquids with anions [PF6] and [BF4]. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 26, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.A.; Gu, Z.; Brennecke, J.F. High-pressure phase behavior of ionic liquid/CO2 systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Enschede, The Netherlands, 1997; p. 497. [Google Scholar]
- Hojniak, S.D.; Khan, A.L.; Holloczki, O.; Kirchner, B.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Separation of carbon dioxide from nitrogen or methane by supported ionic liquid membranes (SILMs): Influence of the cation charge of the ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 15131–15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D.; Ferguson, L.; Scovazzo, P. Diffusivities of gases in room-temperature ionic liquids: Data and correlations obtained using a lag-time technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 4815–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Besra, L.; Singh, B.P. Effect of additives on the microstructure of porous alumina. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H. Ionic Liquid Confined in Mesoporous Polymer Membrane with Improved Stability for CO2/N2 Separation. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7100299
Tan M, Lu J, Zhang Y, Jiang H. Ionic Liquid Confined in Mesoporous Polymer Membrane with Improved Stability for CO2/N2 Separation. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(10):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7100299
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Ming, Jingting Lu, Yang Zhang, and Heqing Jiang. 2017. "Ionic Liquid Confined in Mesoporous Polymer Membrane with Improved Stability for CO2/N2 Separation" Nanomaterials 7, no. 10: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7100299
APA StyleTan, M., Lu, J., Zhang, Y., & Jiang, H. (2017). Ionic Liquid Confined in Mesoporous Polymer Membrane with Improved Stability for CO2/N2 Separation. Nanomaterials, 7(10), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7100299