Rescaling Flow Curves of Protein-Stabilized Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of BSA Solutions
2.3. Emulsion Preparation
2.4. Droplet Size Determination
2.5. Rheological Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
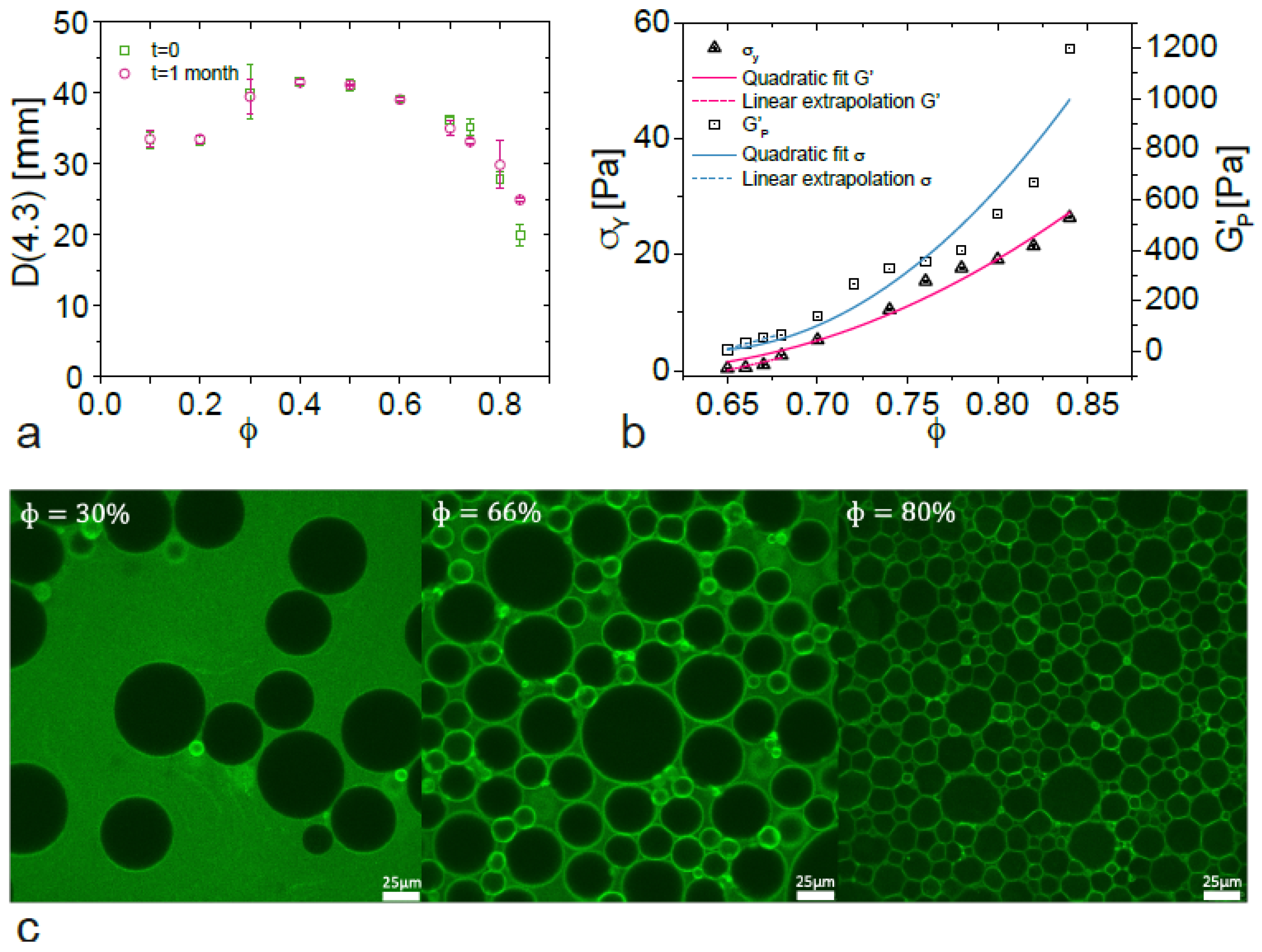
3.1. General Features of BSA-Stabilized Emulsions
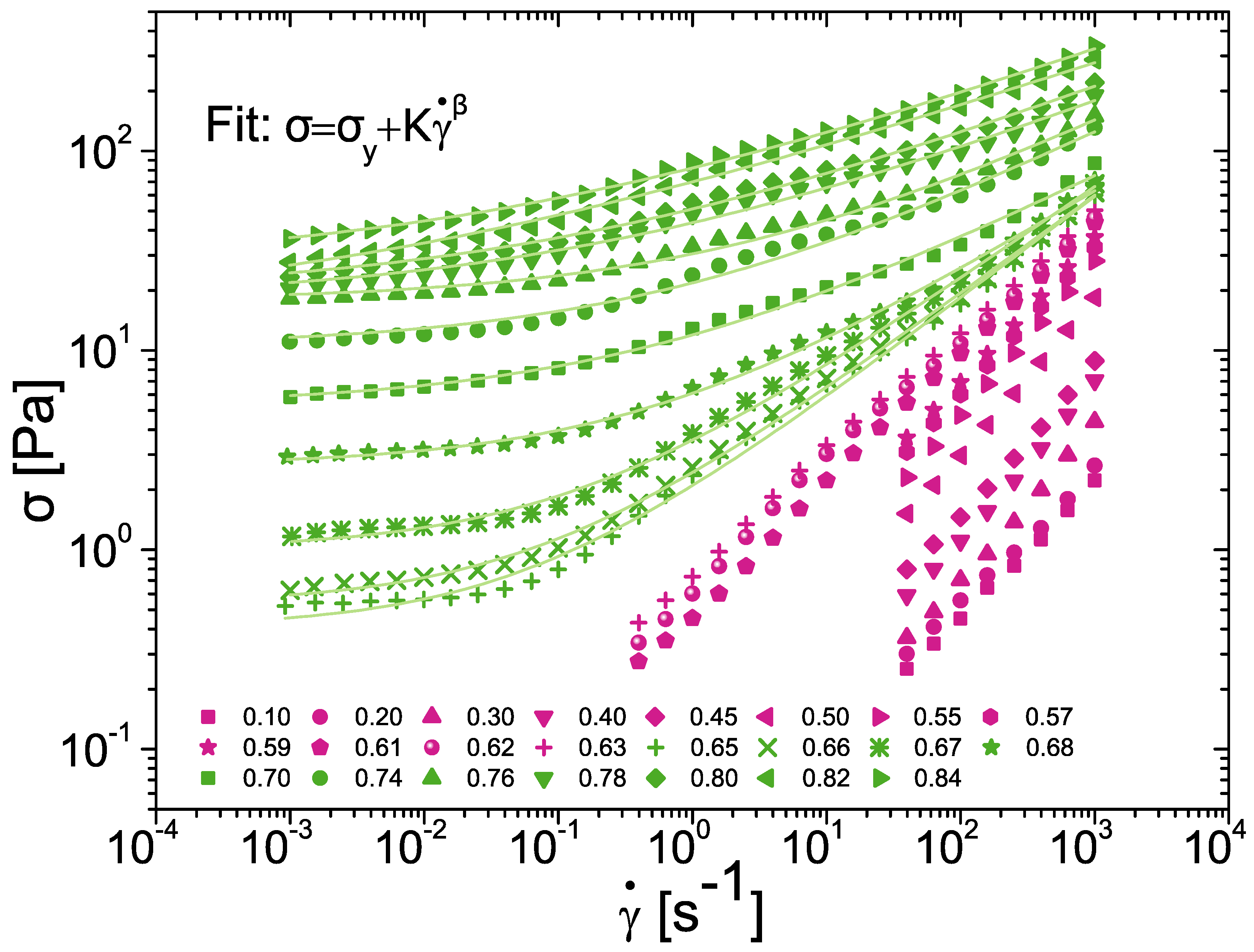
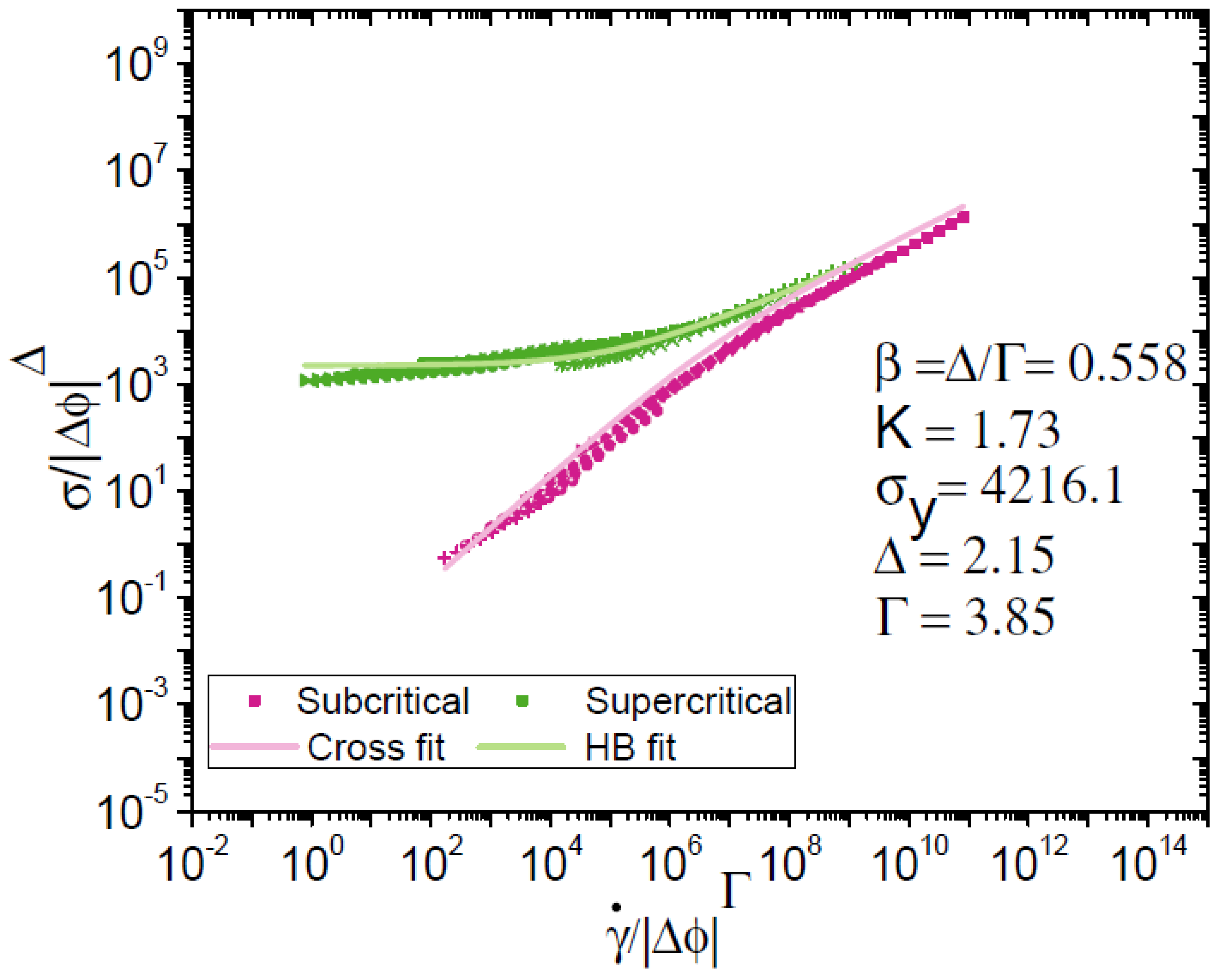
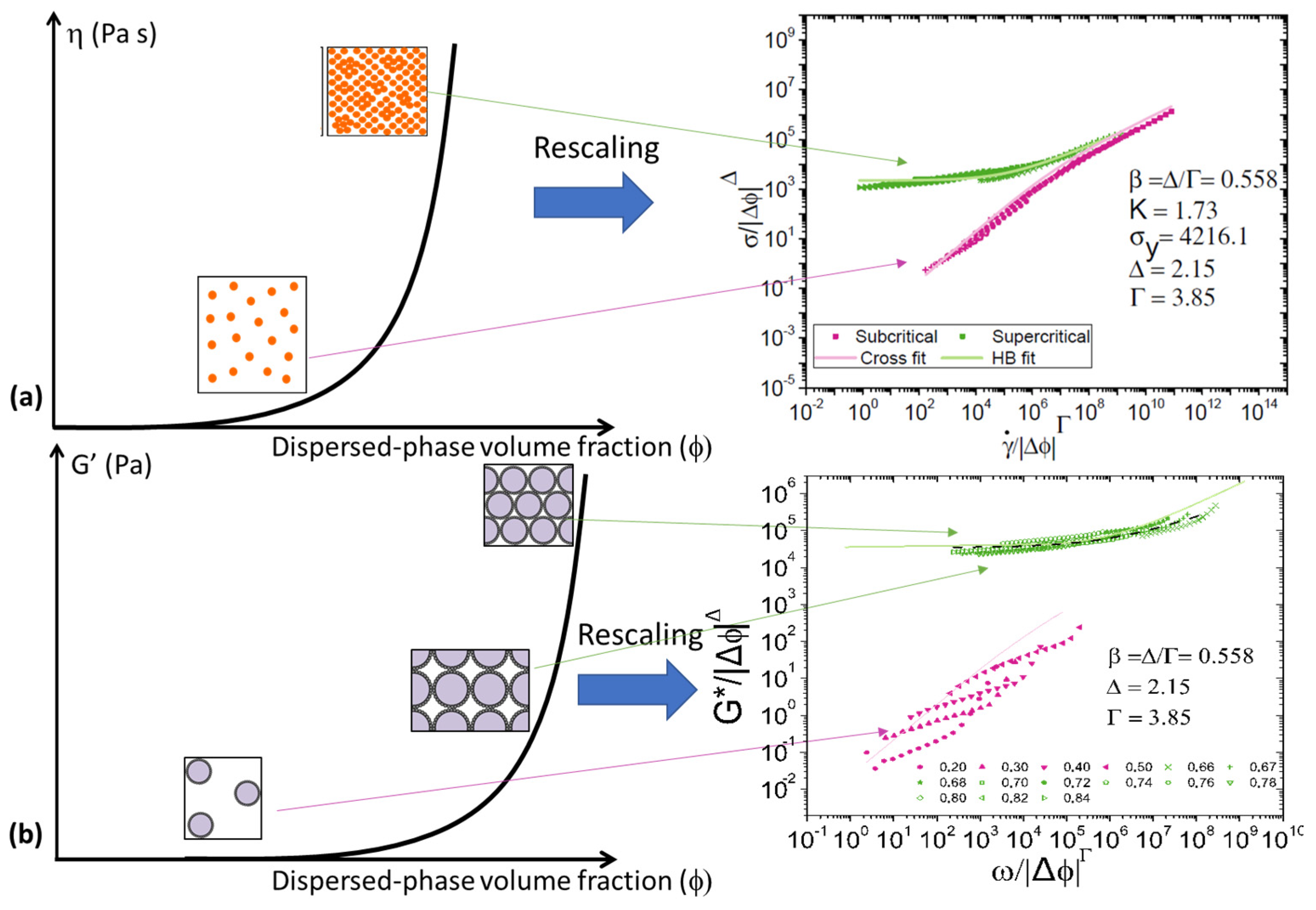
3.2. Scaling of Flow Behaviour
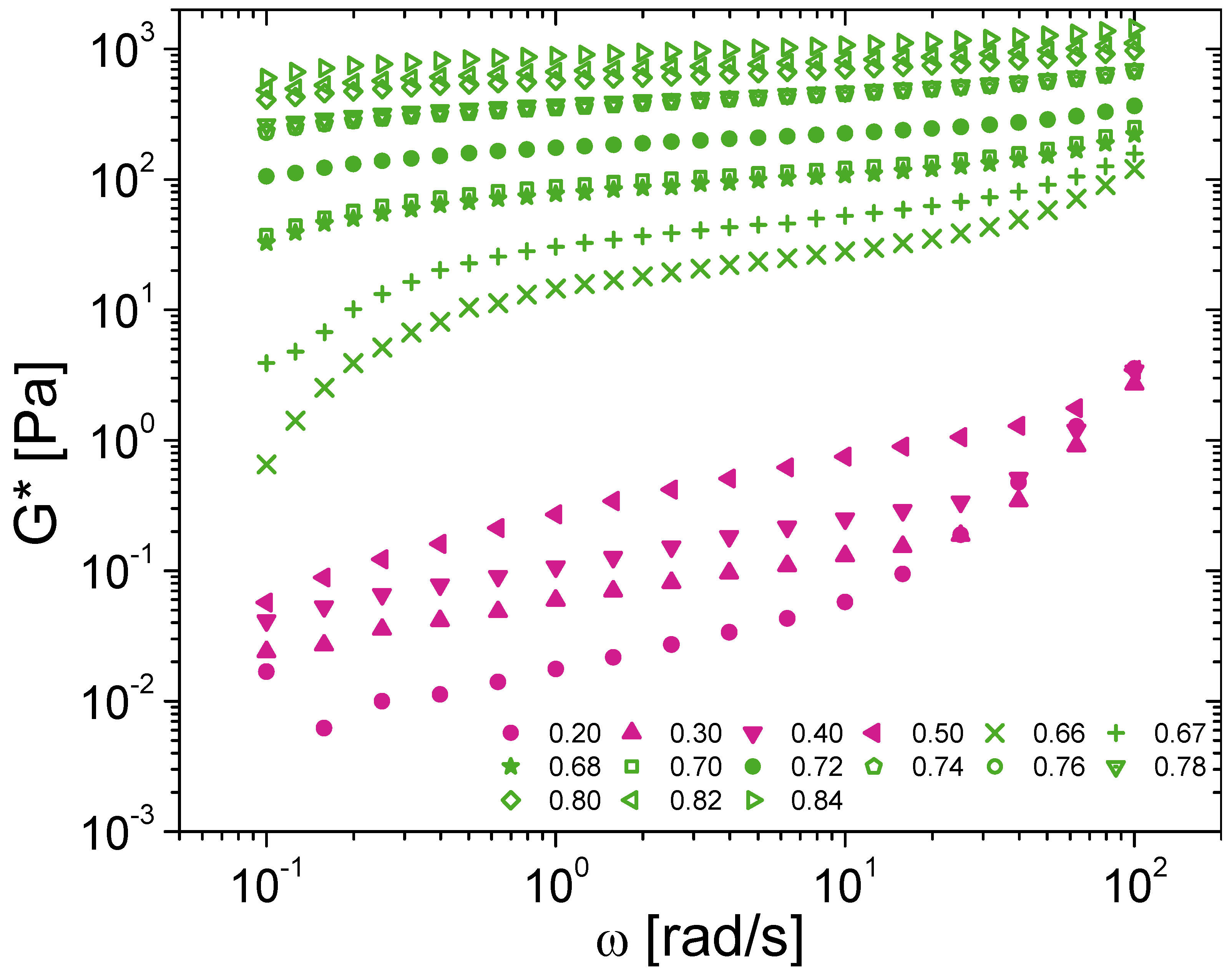
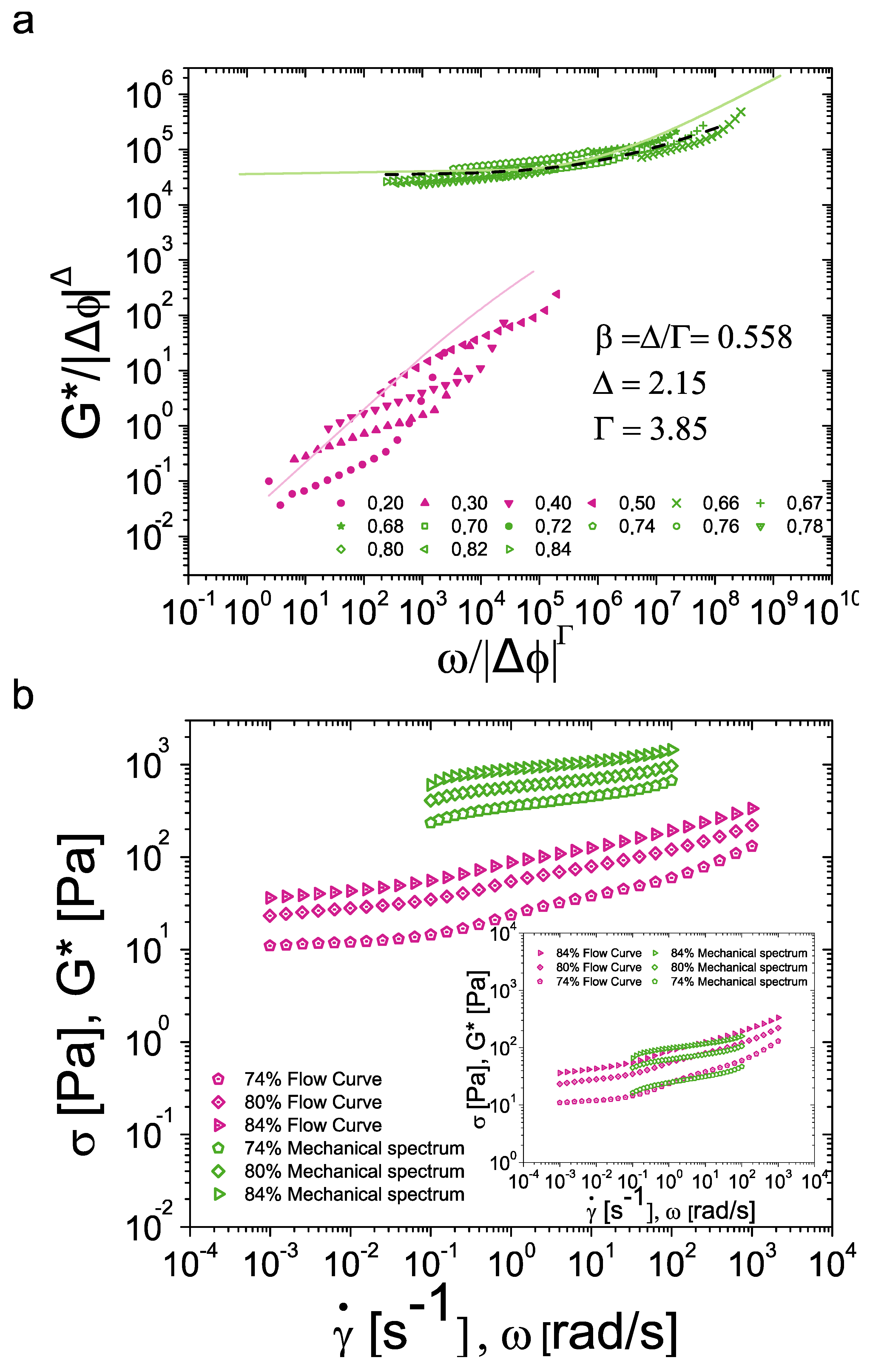
3.3. Extension to Oscillatory Rheology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, H.A. The yield stress—A review or ‘Παντα Pϵι’—Everything flows? J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1999, 81, 133–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Joyner, H.S. Effect of fish gelatin-gum arabic interactions on structural and functional properties of concentrated emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradilla, D.; Barrera, A.; Sætran, M.G.; Sørland, G.; Alvarez, O. Mechanisms of physical stabilization of concentrated water-in-oil emulsions probed by pulse field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance and rheology through a multiscale approach. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9489–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkgreve, M.; Michels, M.A.J.; Mason, T.G.; Bonn, D. Crossover between athermal jamming and the thermal glass transition of suspensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 228001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P. Particles as surfactants—Similarities and differences. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.-H. Soy protein nanoparticle aggregates as Pickering stabilizers for oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8888–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-S.; Luo, Z.-G.; Peng, X.-C. Fabrication and characterization of quinoa protein nanoparticle-stabilized food-grade Pickering emulsions with ultrasound treatment: Interfacial adsorption/arrangement properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4449–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkgreve, M.; Velikov, K.P.; Bonn, D. Stability of LAPONITE®-stabilized high internal phase Pickering emulsions under shear. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 22973–22977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-N.; Tang, C.-H. Pea protein exhibits a novel Pickering stabilization for oil in water emulsions at pH 3.0. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, M.; Wang, J.; Ngai, T. Pure protein scaffolds from Pickering high internal phase emulsion template. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H. Globular proteins as soft particles for stabilizing emulsions: Concepts and strategies. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-T.; Tang, C.-H.; Liu, T.-X.; Liu, R. Ovalbumin as an outstanding Pickering nanostabilizer for high internal phase emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8795–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-T.; Tang, C.-H.; Binks, B.P. High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by a globular protein glycated to form soft particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, V.; Destribats, M.; Backov, R. Colloidal particles as liquid dispersion stabilizer: Pickering emulsions and materials thereof. C. R. Phys. 2014, 15, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, S.F.; Marchal, P.; Lemaitre, C.; Sadtler, V.; Roques-Carmes, T. Evaluation of the repartition of the particles in Pickering emulsions in relation with their rheological properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, D.J.; Brown, A.T.; Schofield, A.B.; Fowler, J.; Taylor, P.; Clegg, P.S. The secret life of Pickering emulsions: Particle exchange revealed using two colours of particle. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destribats, M.; Gineste, S.; Laurichesse, E.; Tanner, H.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Héroguez, V.; Schmitt, V. Pickering emulsions: What are the main parameters determining the emulsion type and interfacial properties? Langmuir 2014, 30, 9313–9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, W.J.; van Duijneveld, J.S. Controlling the rheology of montmorillonite stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, L.; Röhl, S.; Stehl, D.; von Klitzing, R.; Kraume, M. Influence of nanoparticles and drop size distributions on the rheology of w/o Pickering emulsions. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2016, 88, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Theiler, S.; Knudsen, A.; Øye, G.; Sjöblom, J. Rheological properties of particle-stabilized emulsions. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Xiong, L.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Chang, R.; Liang, C.; Sun, Q. Characterizations of Pickering emulsions stabilized by starch nanoparticles: Influence of starch variety and particle size. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, S.; Meinders, M.B.J.; Bitter, J.H.; Nikiforidis, C.V. On the emulsifying properties of self-assembled pea protein particles. Langmuir 2020, 36, 12221–12229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadros, T.F. Fundamental principles of emulsion rheology and their applications. Colloids Surf. A 1994, 91, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hern, C.S.; Silbert, L.E.; Liu, A.J.; Nagel, S.R. Jamming at zero temperature and zero applied stress: The epitome of disorder. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 011306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herschel, W.H.; Bulkley, R. Konsistenzmessungen von Gummi-Benzollösungen. Kolloid-Zeitschrift 1926, 39, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Jan, B.M. Herschel-Bulkley rheological parameters of a novel environmentally friendly lightweight biopolymer drilling fluid from xanthan gum and starch. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.M. Rheology of non-Newtonian fluids: A new flow equation for pseudoplastic systems. J. Colloid Sci. 1965, 20, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullet, M.; Clegg, P.S.; Frith, W.J. Viscosity of protein-stabilized emulsions: Contributions of components and development of a semipredictive model. J. Rheo. 2019, 63, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.M.; Dougherty, T.J. A mechanism for non-Newtonian flow in suspensions of rigid spheres. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkgreve, M.; Paredes, M.J.; Michels, M.A.J.; Bonn, D. Universal rescaling of flow curves for yield-stress fluids close to jamming. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 012305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, P. Relaxations and rheology near Jamming. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 158303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkgreve, M.; Paredes, J.; Denn, M.M.; Bonn, D. On different ways of measuring “the” yield stress. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2016, 238, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princen, H.M. Rheology of foams and highly concentrated emulsions: I. Elastic properties and yield stress of a cylindrical model system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 91, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princen, H.M.; Kiss, A.D. Rheology of foams and highly concentrated emulsions: III. Static shear modulus. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 112, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princen, H.M.; Kiss, A.D. Rheology of foams and highly concentrated emulsions: IV. An experimental study of the shear viscosity and yield stress of concentrated emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 128, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.; Michels, M.A.J.; Bonn, D. Rheology across the zero-temperature jamming transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 015701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagois-Bohy, S.; Somfai, E.; Tighe, B.P.; van Hecke, M. Softening and yielding of soft glassy materials. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 9036–9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, R.I.; Dinkgreve, M.; de Cagny, H.; Koeze, D.; Tighe, B.P.; Bonn, D. Universal scaling of flow curves: Comparison between experiments and simulations. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2018, 261, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.R.S.; Ortore, M.G.; Spinozzi, F.; Mariani, P.; Bernstorff, S.; Itri, R. The Importance of protein-protein interactions on the pH-induced conformational changes of bovine serum albumin: A small-angle X-ray scattering study. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsarskaia, O.; Bühl, L.; Beck, C.; Grimaldo, M.; Schweins, R.; Zhang, F.; Seydel, T.; Schreiber, F.; Roosen-Runge, F. Evolution of the structure and dynamics of bovine serum albumin induced by thermal denaturation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 18507–18517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michnik, A.; Michalik, K.; Drzazga, Z. Stability of bovine serum albumin at different pH. J Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2005, 80, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Campbell, B. Coalescence stability of emulsions containing globular milk proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123–126, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. A simple model for the viscosity of Pickering emulsions. Fluids 2018, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R. Rheology of emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 151, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R. Rheology of high internal phase ratio emulsions and foams. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 339, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaganyuk, M.; Mohraz, A. Role of particles in the rheology of solid-stabilized high internal phase emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Mason, T.G. Advances and challenges in the rheology of concentrated emulsions and nanoemulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 247, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, W.P.; Merz, E.H. Correlation of dynamic and steady flow viscosities. J. Polym. Sci. 1958, 28, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.H. Three views of viscoelasticity for Cox–Merz materials. Rheol. Acta 2009, 48, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Nishinari, K. Intermolecular forces in bovine serum albumin solutions exhibiting solid like mechanical behaviors. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zaaboul, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Recent advances on protein-based Pickering high internal phase emulsions (Pickering HIPEs): Fabrication, characterization, and applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1934–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Holkar, A.; Srivastava, S. Protein–polyelectrolyte complexes and micellar assemblies. Polymers 2019, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruta-Tuarez, E.; Marchal, P. Association of percolation theory with Princen’s approach to model the storage modulus of highly concentrated emulsions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 11787–11791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougel, J.; Alvarez, O.; Baravian, C.; Caton, F.; Marchal, P.; Stébé, M.-J.; Choplin, L. Aging of an unstable w/o gel emulsion with a nonionic surfactant. Rheol. Acta 2006, 45, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruta-Tuarez, E.; Marchal, P.; Sadtler, V.; Choplin, L. Analysis of the Princen and Kiss equation to model the storage modulus of highly concentrated emulsions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10359–10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, S.F.; Ramos, D.; Lebrun, M.; Marchal, P.; Lemaitre, C.; Sadtler, V.; Roques-Carmes, T. Exploring the link between interfacial and bulk viscoelasticity in reverse Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 624, 126785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velandia, S.F.; Marchal, P.; Sadtler, V.; Lemaitre, C.; Bonn, D.; Roques-Carmes, T. Rescaling Flow Curves of Protein-Stabilized Emulsions. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090650
Velandia SF, Marchal P, Sadtler V, Lemaitre C, Bonn D, Roques-Carmes T. Rescaling Flow Curves of Protein-Stabilized Emulsions. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(9):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090650
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelandia, Santiago F., Philippe Marchal, Véronique Sadtler, Cécile Lemaitre, Daniel Bonn, and Thibault Roques-Carmes. 2025. "Rescaling Flow Curves of Protein-Stabilized Emulsions" Nanomaterials 15, no. 9: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090650
APA StyleVelandia, S. F., Marchal, P., Sadtler, V., Lemaitre, C., Bonn, D., & Roques-Carmes, T. (2025). Rescaling Flow Curves of Protein-Stabilized Emulsions. Nanomaterials, 15(9), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090650






