High-Quality GaP(111) Grown by Gas-Source MBE for Photonic Crystals and Advanced Nonlinear Optical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
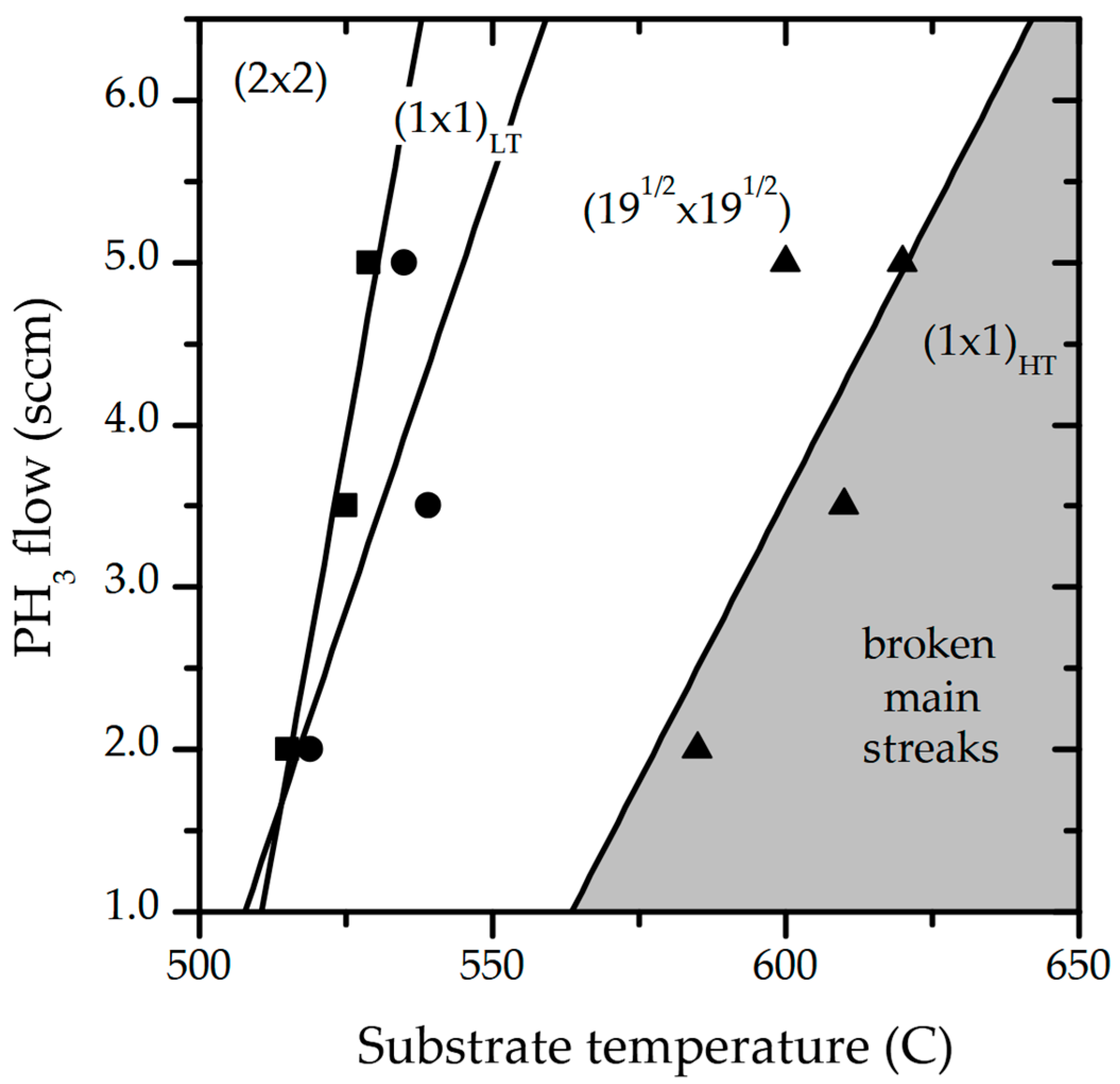
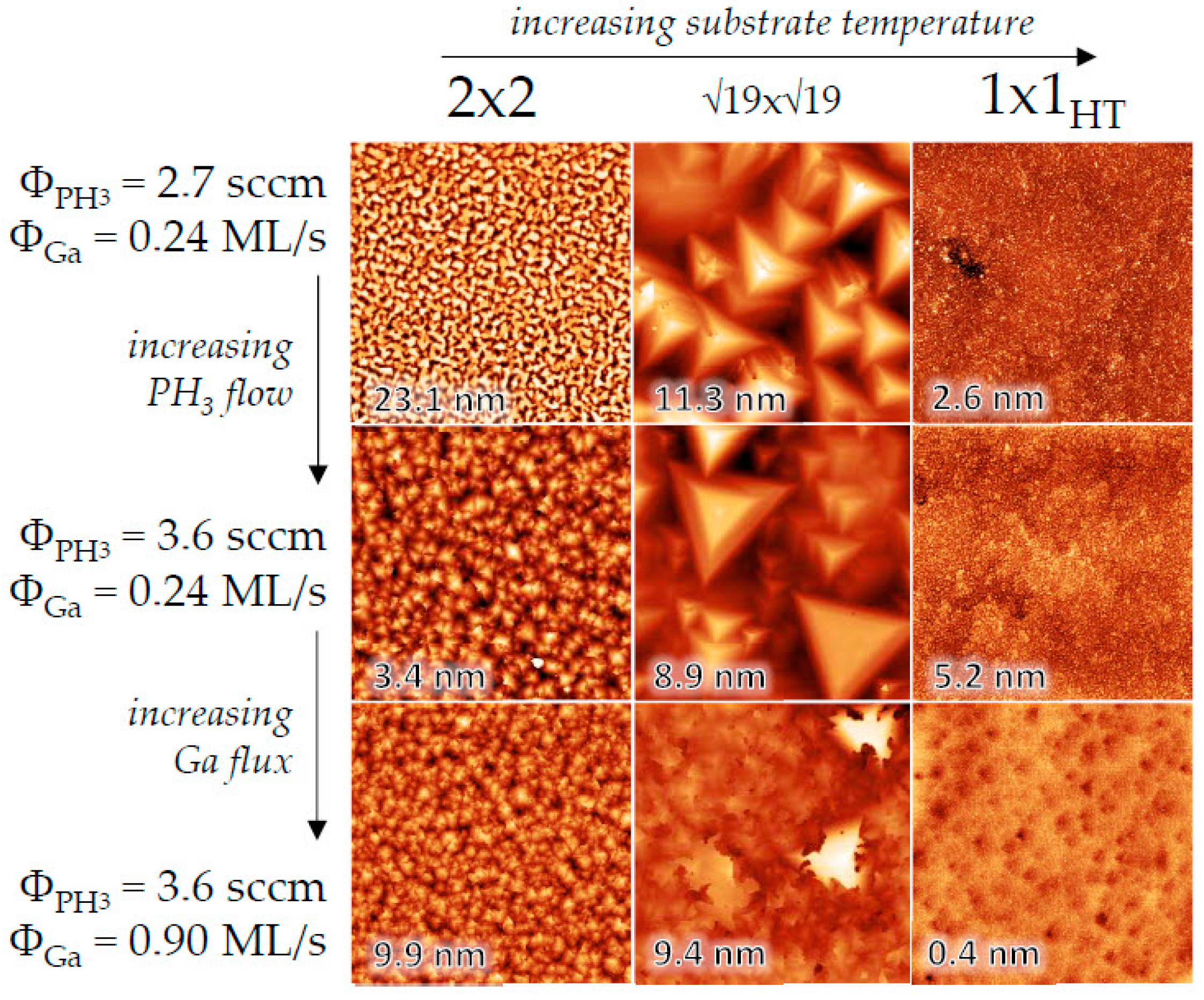
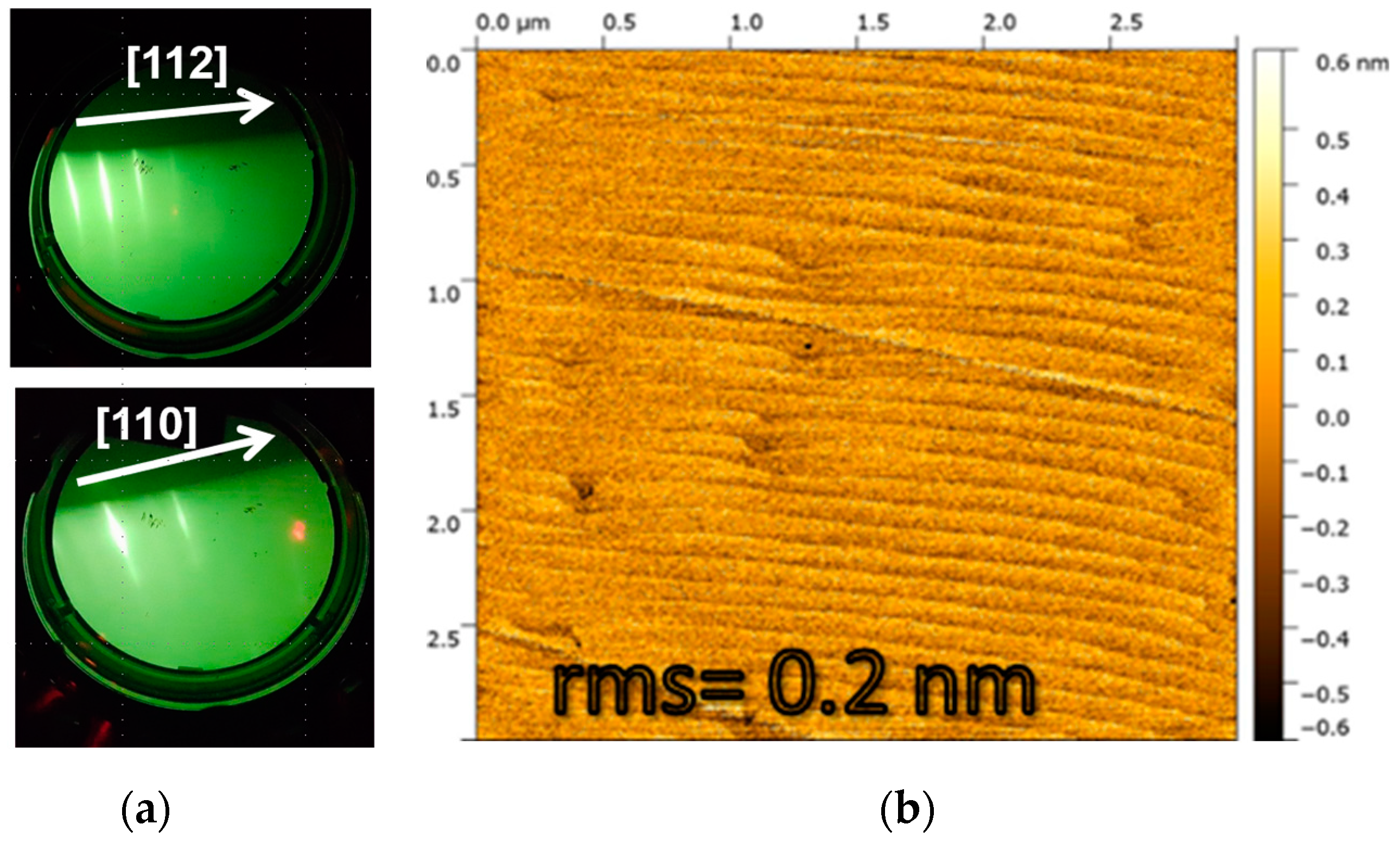
3.1. Gas-Source MBE of GaP(111)B and AlGaP(111)B
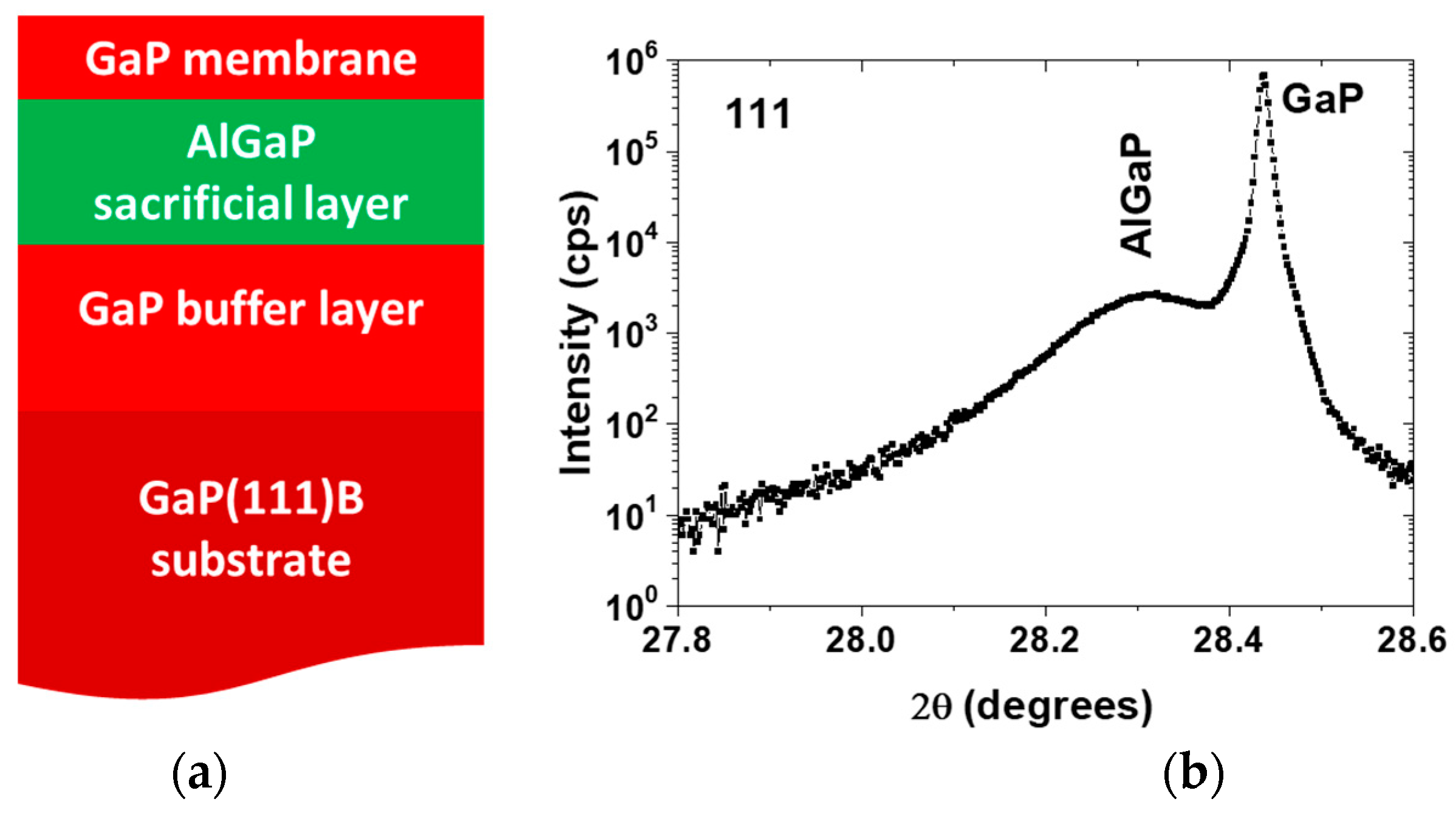
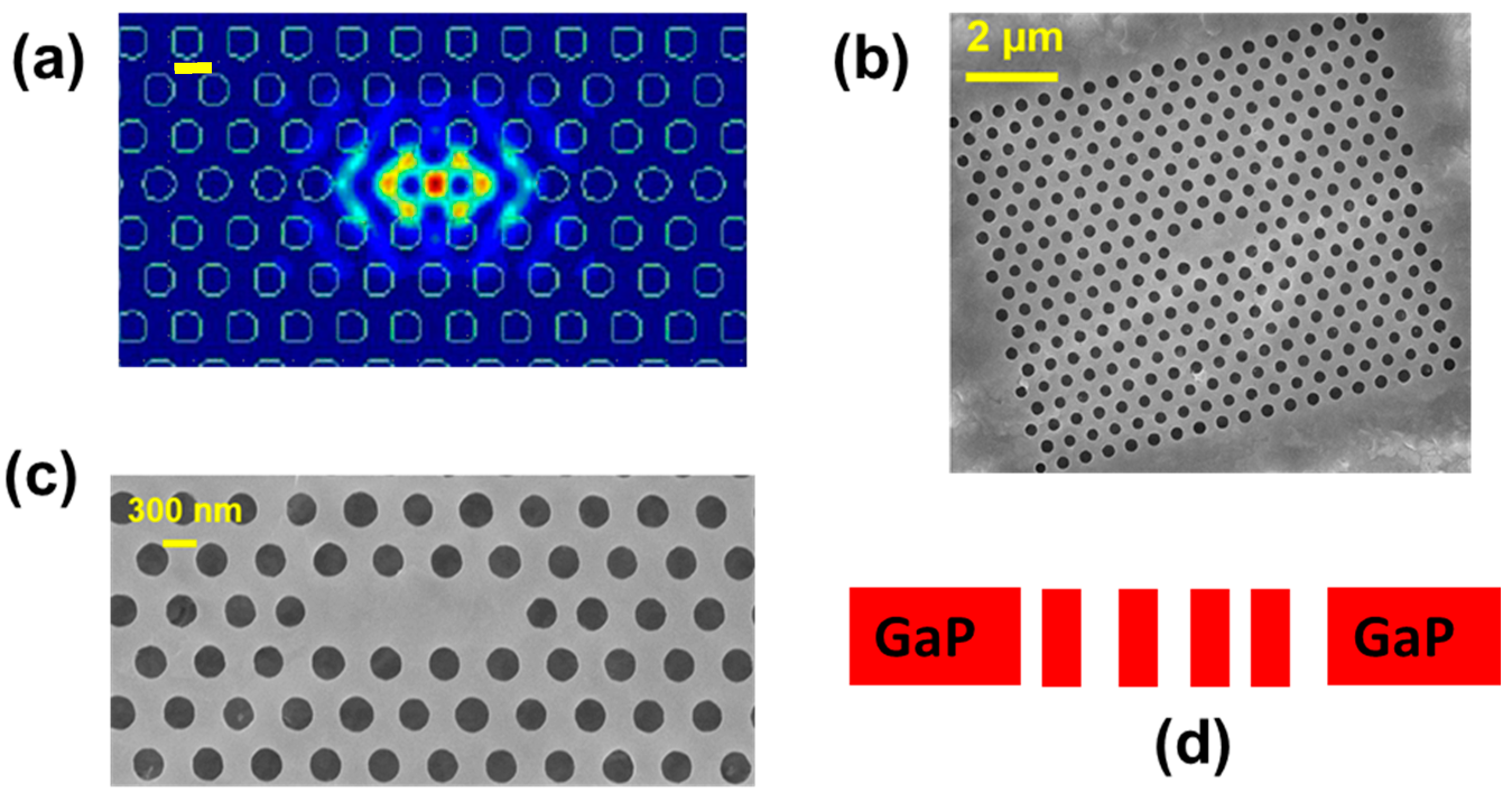
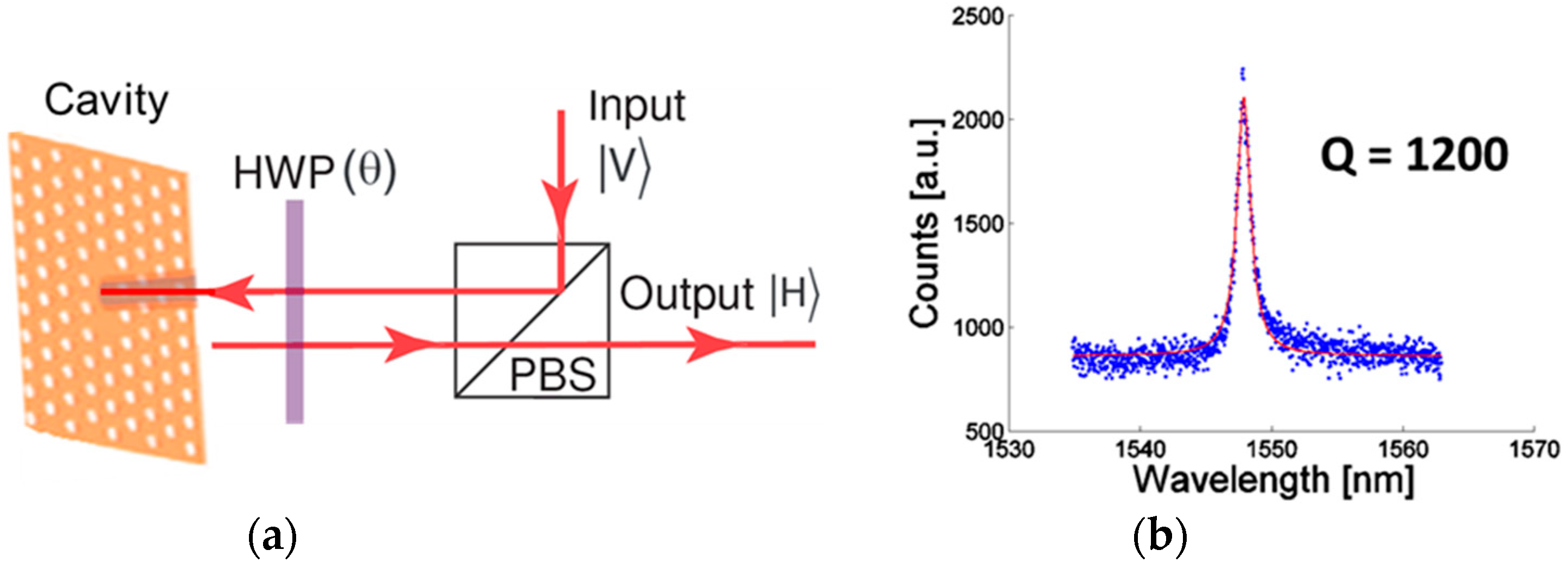
3.2. Fabrication and Examination of the Photonic Crystal Cavities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GS-MBE | Gas-Source Molecular-Beam Epitaxy |
| RHEED | Reflection High-Energy Electron Diffraction |
| UHV | Ultra-High Vacuum |
| SCCM | Standard Cubic Centimeters per Minute |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| LEED | Low-Energy Electron Diffraction |
| STM | Scanning Tunneling Microscopy |
| ML | Monolayer |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| L3 | Three-hole linear defect |
| RIE | Reactive Ion Etching |
| PBS | Polarizing Beam Splitter |
| HWP | half-wave plate |
| V | vertically polarized mode |
| H | horizontally polarized mode |
| Q | Quality Factor |
References
- Wilson, D.J.; Schneider, K.; Hönl, S.; Anderson, M.; Baumgartner, Y.; Czornomaz, L.; Kippenberg, T.J.; Seidler, P. Integrated gallium phosphide nonlinear photonics. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoire, K.; Buckley, S.; Hatami, F.; Vučković, J. Second harmonic generation in GaP photonic crystal waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 263113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoire, K.; Lin, Z.; Hatami, F.; Vučković, J. Sum-frequency generation in doubly resonant GaP photonic crystal nanocavities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 043103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamori, T.; Schunemann, P.G.; Gruzdev, V.; Vodopyanov, K.L. High-order (N = 4–6) multiphoton absorption and mid-infrared Kerr nonlinearity in GaP, ZnSe, GaSe, and ZGP crystals. APL Photonics 2022, 7, 086101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, K.; Beyer, A.; Witte, W.; Ohlmann, J.; Németh, I.; Kunert, B.; Stolz, W. GaP-nucleation on exact Si (0 0 1) substrates for III/V device integration. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 315, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, S.M.; Irvine, W.T.M.; Kleckner, D.; Bouwmeester, D. Polychromatic photonic quasicrystal cavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 243901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahane, Y.; Asano, T.; Song, B.; Noda, S. High-Q photonic nanocavity in a two-dimensional photonic crystal. Nature 2003, 425, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoire, K.; Faraon, A.; Vučković, J. Gallium phosphide photonic crystal nanocavities in the visible. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 063103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.Y. Morphology of epitaxial growth of GaAs by a molecular beam method: The observation of surface structures. J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Ishihara, K.; Miyatake, Y.; Matsui, F.; Takeda, S.; Daimon, H.; Komori, F. GaP(-1-1-1) reconstructed surface studied with STM and LEED. Surf. Sci. 2003, 525, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, A.U. Low energy electron diffraction study of the polar {111} surfaces of GaAs and GaSb. Surf. Sci. 1966, 4, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bommel, A.J.; Crombeen, J.E. The adsorption and desorption of Cs on GaP and GaSb (001), (110), (111), and (-1-1-1) surfaces, studied by LEED, AES, and Photoemission. Surf. Sci. 1980, 93, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, P.; Mutombo, P.; Berthold, T.; Paszuk, A.; Steidl, M.; Ecke, G.; Nägelein, A.; Koppka, C.; Supplie, O.; Krischok, S.; et al. Atomic surface structure of MOVPE-prepared GaP(111)B. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 534, 147346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, J.B.; Dadgostar, S.; Hestroffer, K.; Bierwagen, O.; Trampert, A.; Hatami, F. Growth of GaP and AlGaP on GaP(111)B using gas-source molecular-beam-epitaxy. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 477, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Schowalter, L.J. Surface reconstruction phase diagram and growth on GaAs(111)B substrates by molecular beam epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1992, 60, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.M.C.; Woolf, D.A.; Weightman, P. Reconstructions of the GaAs(111)B surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 123, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, D.A.; Westwood, D.L.; Williams, R.H. Surface reconstructions of GaAs(111)A and (111)B: A static surface phase study by reflection high-energy electron diffraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 62, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Rajkumar, K.; Madhukar, A. Growth control of GaAs epilayers with specular surface free of pyramids and twins on nonmisoriented (111)B substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 58, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilner, E.; Zakharov, A.A.; Schulte, K.; Andersen, J.N.; Lundgren, E.; Mikkelsen, A. Faceting and surface reconstruction of the GaP(111)B surface. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, A.U. The location of atoms at surfaces. Surf. Sci. 1965, 4, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilner, E.; Zakharov, A.A.; Schulte, K.; Kratzer, P.; Andersen, J.N.; Lundgren, E.; Mikkelsen, A. Growth mechanism of self-catalyzed group III-V nanowires. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivoire, K.; Lin, Z.; Hatami, F.; Masselink, W.T.; Vučković, J. Second harmonic generation in gallium phosphide photonic crystal nanocavities with ultralow continuous wave pump power. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 22609–22615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.G.; Povinelli, M.L.; Soljačić, M.; Karalis, A.; Jacobs, S.; Joannopoulos, J.D. Roughness losses and volume-current methods in photonic-crystal waveguides. Appl. Phys. B. 2005, 81, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkov, M.; Dharanipathy, U.P.; Houdré, R.; Savona, V. Statistics of the disorder-induced losses of high-Q photonic crystal cavities. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 28233–28245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hestroffer, K.; Rivoire, K.; Vučković, J.; Hatami, F. High-Quality GaP(111) Grown by Gas-Source MBE for Photonic Crystals and Advanced Nonlinear Optical Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080619
Hestroffer K, Rivoire K, Vučković J, Hatami F. High-Quality GaP(111) Grown by Gas-Source MBE for Photonic Crystals and Advanced Nonlinear Optical Applications. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(8):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080619
Chicago/Turabian StyleHestroffer, Karine, Kelley Rivoire, Jelena Vučković, and Fariba Hatami. 2025. "High-Quality GaP(111) Grown by Gas-Source MBE for Photonic Crystals and Advanced Nonlinear Optical Applications" Nanomaterials 15, no. 8: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080619
APA StyleHestroffer, K., Rivoire, K., Vučković, J., & Hatami, F. (2025). High-Quality GaP(111) Grown by Gas-Source MBE for Photonic Crystals and Advanced Nonlinear Optical Applications. Nanomaterials, 15(8), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080619




