Mg2+ and Cr3+ Co-Doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Derived from Ni/Mn Bimetal Oxide as High-Performance Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Material Synthesis
2.2. Material Characterization and Electrochemical Analysis
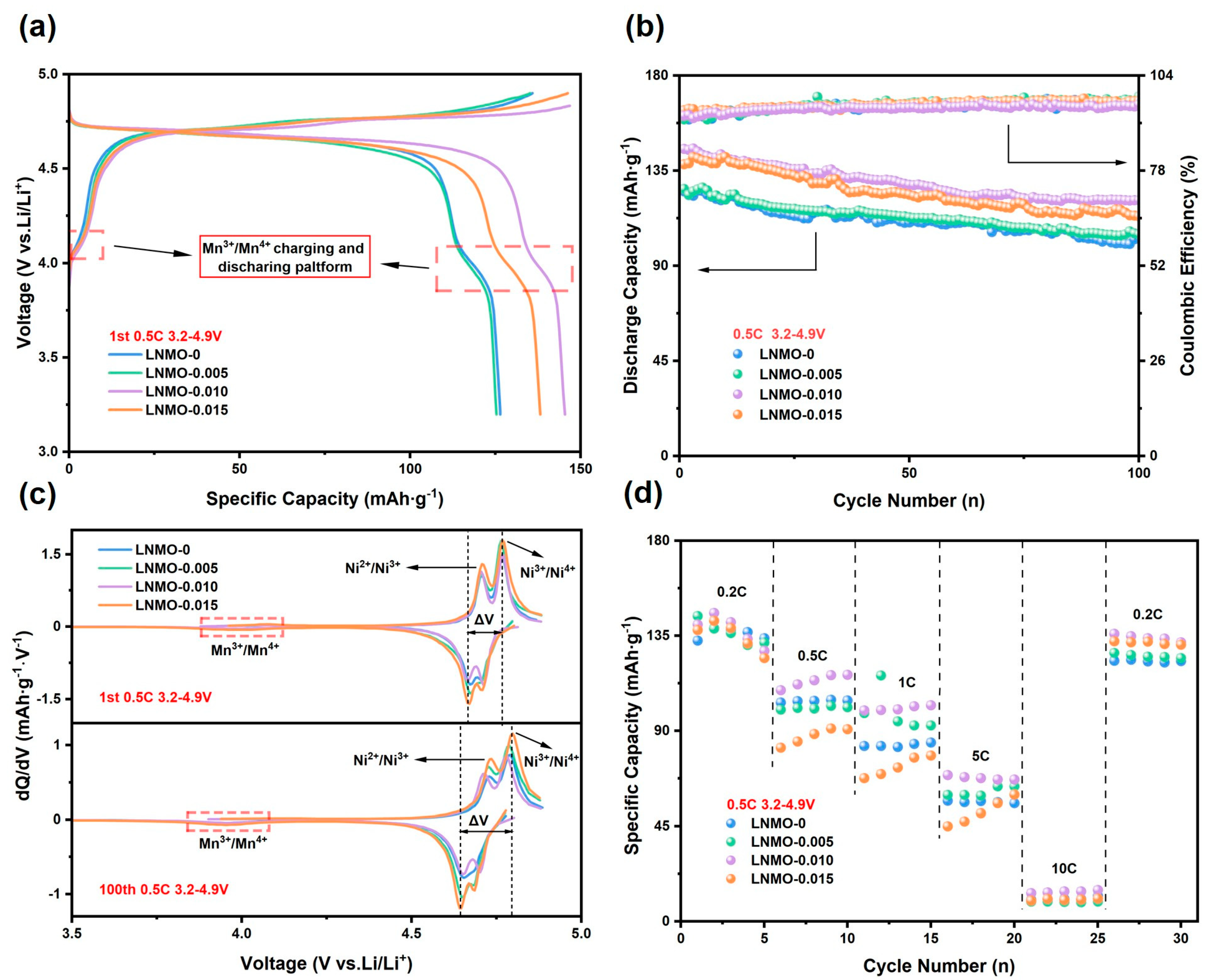
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, X.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.Z.; Liu, X.G.; Jin, X.; He, R.; Liu, Z.F.; Pan, J.Q. Clean Universal Solid-State Recovery Method of Waste Lithium-Ion Battery Ternary Positive Materials and Their Electrochemical Properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3673–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.J.; Yan, S.P.; Lang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S.X.; Guo, J.L.; Wang, L.; Liang, G.C. Effect of Cr3+ doping on morphology evolution and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 material for Li-ion battery. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B.; Kaliyappan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Banis, M.N.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. Nanoscale Manipulation of Spinel Lithium Nickel Manganese Oxide Surface by Multisite Ti Occupation as High-Performance Cathode. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Sun, X. Surface and subsurface reactions of lithium transition metal oxide cathode materials: An overview of the fundamental origins and remedying approaches. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Mei, T.; Li, J.; Pi, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Hierarchical LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 micro-rods with enhanced rate performance for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 9710–9720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakaran, A.M.; Minakshi, M.; Bahri, P.A.; Paul, S.; Kumari, P.; Divakaran, A.M.; Manjunatha, K.N. Rational design on materials for developing next generation lithium-ion secondary battery. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2021, 62, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, P.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Surface and interface issues in spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4: Insights into a potential cathode material for high energy density lithium ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3578–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-S.; Huang, J.-H.; Cheng, T.-H.; Hu, C.-W.; Wu, N.-J.; Yen, C.-Y.; Hsu, S.-C.; Weng, H.C.; Chen, C.-P. Cr-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 derived from bimetallic Ni/Mn metal-organic framework as high-performance cathode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Pieczonka, N.P.; Yang, L. Challenges and approaches for high-voltage spinel lithium-ion batteries. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1940–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Li, W.; Chang, Q.; Bai, X.; He, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Effect of Mg2+/F− co-doping on electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for 5 V lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 323, 134692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Xing, L.D.; Xu, M.Q.; Lin, H.B.; Li, W.S. New solution to instability of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as cathode for lithium ion battery at elevated temperature. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 34, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Christiansen, T.L.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Fei, H.; Mamakhel, A.; Iversen, B.B.; Watkins, J.J. High-power lithium-ion microbatteries from imprinted 3D electrodes of sub-10 nm LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 nanocrystals and a copolymer gel electrolyte. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Ben, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Gu, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhao, H.; Yu, R.; et al. Insight into the Atomic Structure of High-Voltage Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Material in the First Cycle. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, B.; Li, W.S.; Li, X.P.; Hu, S.J. Tris (pentafluorophenyl) phosphine: An electrolyte additive for high voltage Li-ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 18, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.J.; Bao, Z.Q.; Tan, H.; Zhou, H.M.; Li, J. Metal-organic framework-mediated synthesis of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4: Tuning the Mn3+ content and electrochemical performance by organic ligands. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Shilina, Y.; Ziv, B.; Ziegelbauer, J.M.; Luski, S.; Aurbach, D.; Halalay, I.C. On the Oxidation State of Manganese Ions in Li-Ion Battery Electrolyte Solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1738–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Liang, C.; Dudney, N.J. Unravelling the Impact of Reaction Paths on Mechanical Degradation of Intercalation Cathodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13732–13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, L.A.; Sergio Moreno, M.; Cuscueta, D.J. Improving the electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by ZnO nanocrystals coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 303, 117307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Ali, M.E.S.; Shakoor, R.A.; AlQaradawi, S.; Kahraman, R. Impact of synergistic interfacial modification on the electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 17818–17835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, C.; Zheng, J. Stabilizing the Mn4+/Mn3+ redox at 2.7 V plateau in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for high energy density and long cycle lifetime via Mo6+ doping. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Didier, C.; Guo, Z.; Pang, W.K.; Peterson, V.K. Understanding Rechargeable Battery Function Using in Operando Neutron Powder Diffraction. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, L.; Qu, Q.; Shen, M.; Zheng, H. Controllable synthesis of spinel lithium nickel manganese oxide cathode material with enhanced electrochemical performances through a modified oxalate co-precipitation method. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Kang, B. High electrochemical performance of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by decoupling the Ni/Mn disordering from the presence of Mn3+ ions. NPG Asia Mater. 2015, 7, e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Myung, S.-T.; Yoon, C.; Kang, S.; Sun, Y.-K. Comparative study of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4−δ and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes having two crystallographic structures: Fd 3m and P4332. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tsai, C.-J. Qualitative modeling of the electrolyte oxidation in long-term cycling of LiCoPO4 for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 368, 137585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.J.F.; Remédios, C.M.R.; Gratens, X.; Chitta, V.A. Effects of microstructure on the magnetic properties of polycrystalline NiMn2O4 spinel oxides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, H.S.C.; Navrotsky, A. Simple spinels; crystallographic parameters, cation radii, lattice energies, and cation distribution. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Watcharatharapong, T.; Minakshi Sundaram, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Li, D.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Aughterson, R.D.; Ahuja, R. Effect of Transition Metal Cations on Stability Enhancement for Molybdate-Based Hybrid Supercapacitor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17977–17991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabers, V.A.M.; van Setten, F.M.; Knapen, P.S.A. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the cation valencies in nickel manganite. J. Solid State Chem. 1983, 49, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Sanjana, N.; Biswas, A. On the structure of some anganites. Acta Crystallogr. 1957, 10, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Ke, W.; Tang, J.; Xu, G.; Deng, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. Suppressed phase separation in high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode via Co-doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 993, 174587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Xu, S.; Huang, S.; Zhu, J. Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials with Cr3+ and F− Composite Doping for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, G.-H.; Myung, S.T.; Bang, H.J.; Prakash, J.; Sun, Y.-K. Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Li[Ni1/3Co1/3Mn(1/3-x)Mgx] O2-y Fy via Coprecipitation. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2004, 7, A477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, S.S.; Liu, Z.; Wen, W.; Xie, J.; Yan, L. Fluorine gradient-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel with improved high voltage stability for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 238, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, R.; Du, P.; Hu, H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H. Polyhedral LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with excellent electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 12835–12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kim, K.; Cho, W.; Shin, W.H.; Kanno, R.; Choi, J.W. A Truncated Manganese Spinel Cathode for Excellent Power and Lifetime in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6358–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, H.; Yang, X.-Y.; Goris, B.; Verbeeck, J.; Bals, S.; Colson, P.; Cloots, R.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Su, B.-L. Well Shaped Mn3O4 Nano-octahedra with Anomalous Magnetic Behavior and Enhanced Photodecomposition Properties. Small 2011, 7, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Qi, X.; Qiu, B.; Fang, J.; Kloepsch, R.; Schumacher, G.; Liu, Z.; et al. Morphological Evolution of High-Voltage Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Critical Effects of Surface Orientations and Particle Size. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4661–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yan, M.; Guo, J.; Deng, J.; Yang, J. Octahedral nano-particles constructed LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 microspheres as high-voltage cathode materials for long-life lithium-ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 20043–20048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qiu, S.; Cao, Y.; Ai, X.; Xie, K.; Hong, X.; Yang, H. Surface-oriented and nanoflake-stacked LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel for high-rate and long-cycle-life lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17768–17772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.Y.; Yoon, W.-S.; Lee, H.S.; Yang, X.-Q.; McBreen, J.; Deng, B.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Yoshio, M.; Wang, R.; Gui, J.; et al. Comparative studies between oxygen-deficient LiMn2O4 and Al-doped LiMn2O4. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-R.; Lin, C.-W.; Lu, H.-Y. Crystallographic facetting in solid-state reacted LiMn2O4 spinel powder. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 177, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-K.; Lee, K.-H.; Moon, S.-I.; Oh, I.-H. Effect of crystallinity on the electrochemical behaviour of spinel Li1.03Mn2O4 cathode materials. Solid State Ion. 1998, 112, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, M.M. Structural Considerations of Layered and Spinel Lithiated Oxides for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafta, C.; Mathe, M.; Manyala, N.; Roos, W.; Ozoemena, K. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of High-Voltage Nanostructured LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 Spinel: Tuning the Mn3+ Content and Electrochemical Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7592–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Huq, A.; Chi, M.; Pieczonka, N.P.W.; Lee, E.; Bridges, C.A.; Tessema, M.M.; Manthiram, A.; Persson, K.A.; Powell, B.R. Integrated Nano-Domains of Disordered and Ordered Spinel Phases in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for Li-Ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4377–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shin, D.W.; Lu, Y.; Amos, C.D.; Manthiram, A.; Goodenough, J.B. Role of Oxygen Vacancies on the Performance of Li[Ni0.5–xMn1.5+x]O4 (x = 0, 0.05, and 0.08) Spinel Cathodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Zhong, B.; Chen, M.; Yin, K.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Guo, X. Synthesis of LiCr0.2Ni0.4Mn1.4O4 with superior electrochemical performance via a two-step thermo polymerization technique. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.-J.; Li, C.-M.; Li, H.-L.; Luong, J.H.T. Morphology and electrochemistry of LiMn2O4 optimized by using different Mn-sources. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Huang, Z.; Guo, C.; Chernova, N.A.; Upreti, S.; Whittingham, M.S. An Organic Coprecipitation Route to Synthesize High Voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10227–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, W.; Wu, B.; Zhao, J. Syntheses and electrochemical properties of the Na-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 145, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduraci, M.; Al-Sharab, J.F.; Amatucci, G.G. High-Power Nanostructured LiMn2-xNixO4 High-Voltage Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode Materials: Electrochemical Impact of Electronic Conductivity and Morphology. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3585–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Mu, J.; He, R.; Bai, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Enhancing electrochemical performance and structural stability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries by boron doping. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B.; Banis, M.N.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Cui, X.; Sham, T.-K.; et al. Unravelling the Role of Electrochemically Active FePO4 Coating by Atomic Layer Deposition for Increased High-Voltage Stability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Material. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xiao, J.; Yu, X.; Kovarik, L.; Gu, M.; Omenya, F.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.-Q.; Liu, J.; Graff, G.L.; et al. Enhanced Li+ ion transport in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 through control of site disorder. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 13515–13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Baudrin, E. A comparative study of Fd-3m and P4332 “LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4”. Solid State Ion. 2011, 193, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppeler, M.; Nageswaran, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Srinivasan, M. Silicon Doping of High Voltage Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 towards Superior Electrochemical Performance of Lithium Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, W.; Wu, B.; Zhao, J. Porous LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 sphere as 5 V cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16434–16442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Austin, M.H.; Bartlett, B.M. Two-step hydrothermal synthesis of submicron Li1+xNi0.5Mn1.5O4−δ for lithium-ion battery cathodes (x = 0.02, δ = 0.12). Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 8067–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Munnangi, A.R.; Barlow, A.J.; Fichtner, M. New insights into the electrochemistry of magnesium molybdate hierarchical architectures for high performance sodium devices. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13277–13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-D.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.-G.; Xu, C.-L.; Li, Y.-C.; Xiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.-J.; Guo, X.-D.; Chen, H. Stabilizing the Structure of Nickel-Rich Lithiated Oxides via Cr Doping as Cathode with Boosted High-Voltage/Temperature Cycling Performance for Li-Ion Battery. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 1900498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-F.; Zhao, S.-X.; Xu, Y.-H.; Gao, K.; Nan, C.-W. Impact of P-Doped in Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 on Degree of Disorder, Grain Morphology, and Electrochemical Performance. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7734–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, O.; Tang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yuan, W.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Ma, L. The multi-substituted LiNi0.475Al0.01Cr0.04Mn1.475O3.95F0.05 cathode material with excellent rate capability and cycle life. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 77, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.Q.; Chen, C.H. Electrochemical investigations of the LiNi0.45M0.10Mn1.45O4 (M=Fe, Co, Cr) 5V cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 205, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Kong, X.; Wang, B.S.; Luo, T.B.; Liu, G.Y. Cu doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5-xCuxO4 (x = 0, 0.03, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15) with significant improved electrochemical performance prepared by a modified low temperature solution combustion synthesis method. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4603–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-T.; Mondal, A.; Kosova, N.V.; Lin, J.-Y. Improved high-temperature cyclability of AlF3 modified spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Sushko, P.V.; Sushko, M.L.; Kovarik, L.; Feng, J.; Deng, Z.; Zheng, J.; Graff, G.L.; Nie, Z.; et al. High-Performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Spinel Controlled by Mn3+ Concentration and Site Disorder. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiram, A.; Chemelewski, K.; Lee, E.-S. A perspective on the high-voltage LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinel cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Pieczonka, N.P.W.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Harris, S.; Powell, B.R. Understanding the capacity fading mechanism in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Matsuda, T.; Imamura, D. Degradation diagnosis of lithium-ion batteries with a LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 and LiMn2O4 blended cathode using dV/dQ curve analysis. J. Power Sources 2018, 390, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ma, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Yang, G. Exploring the origin of electrochemical performance of Cr-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 3831–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

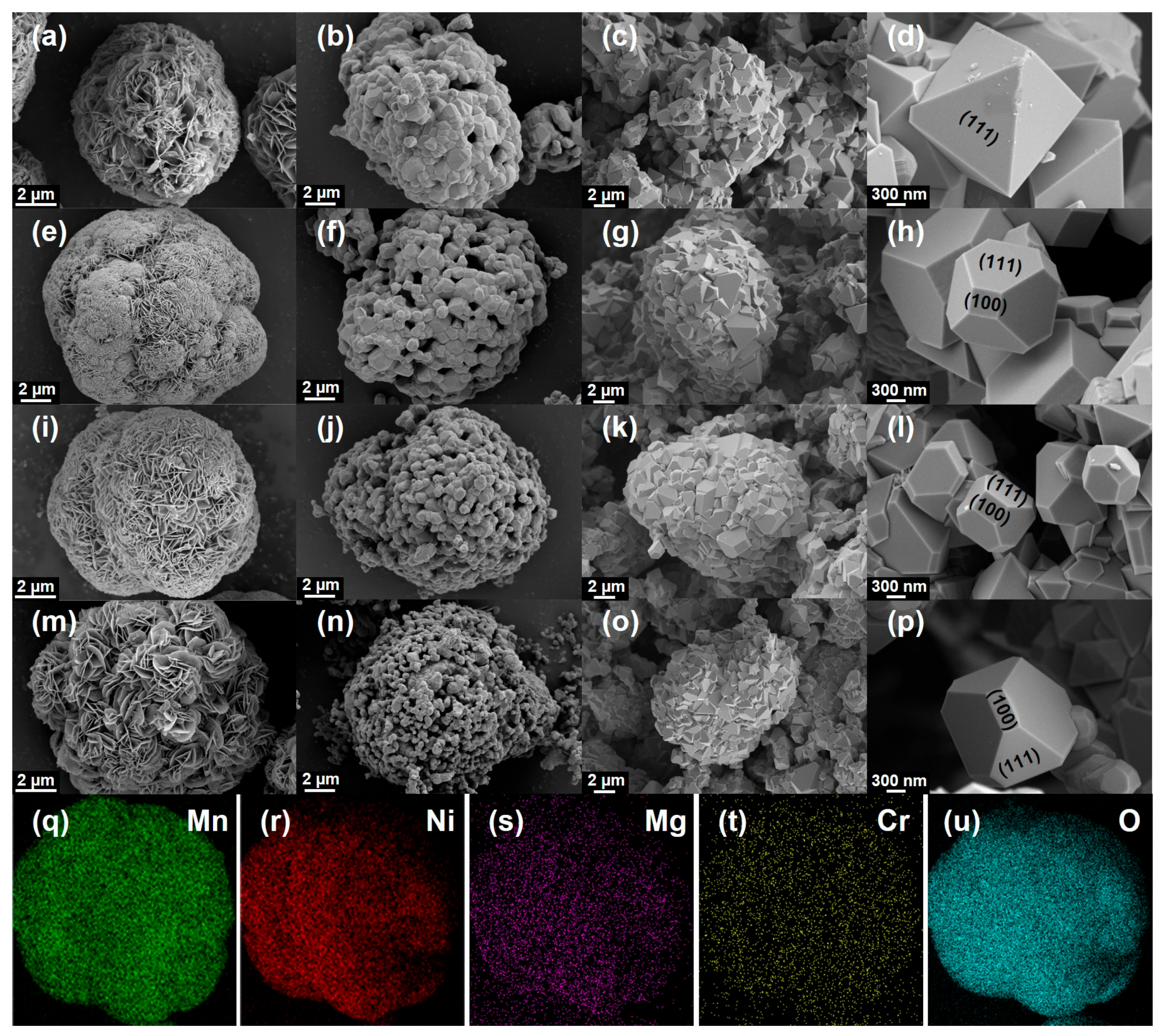
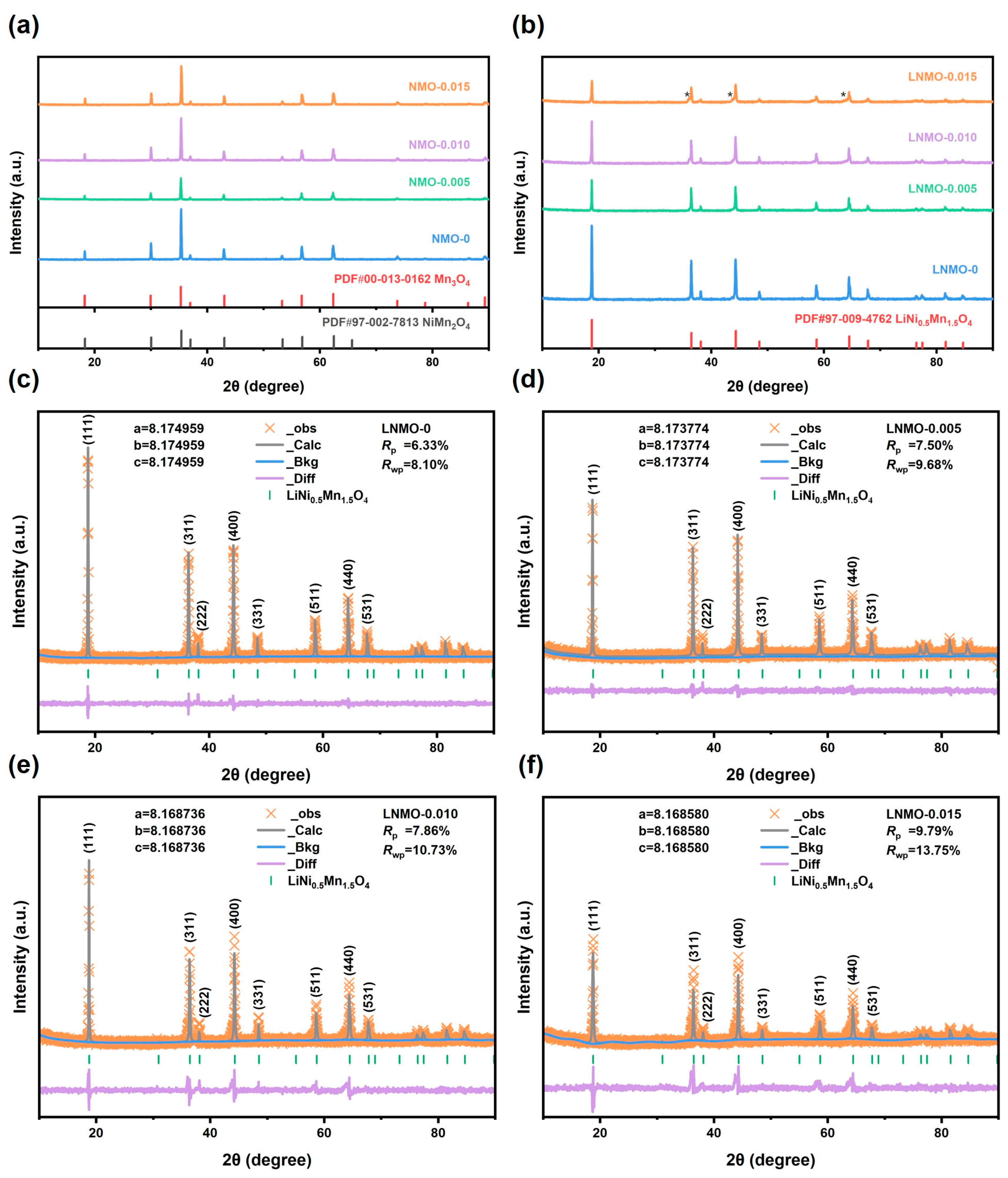


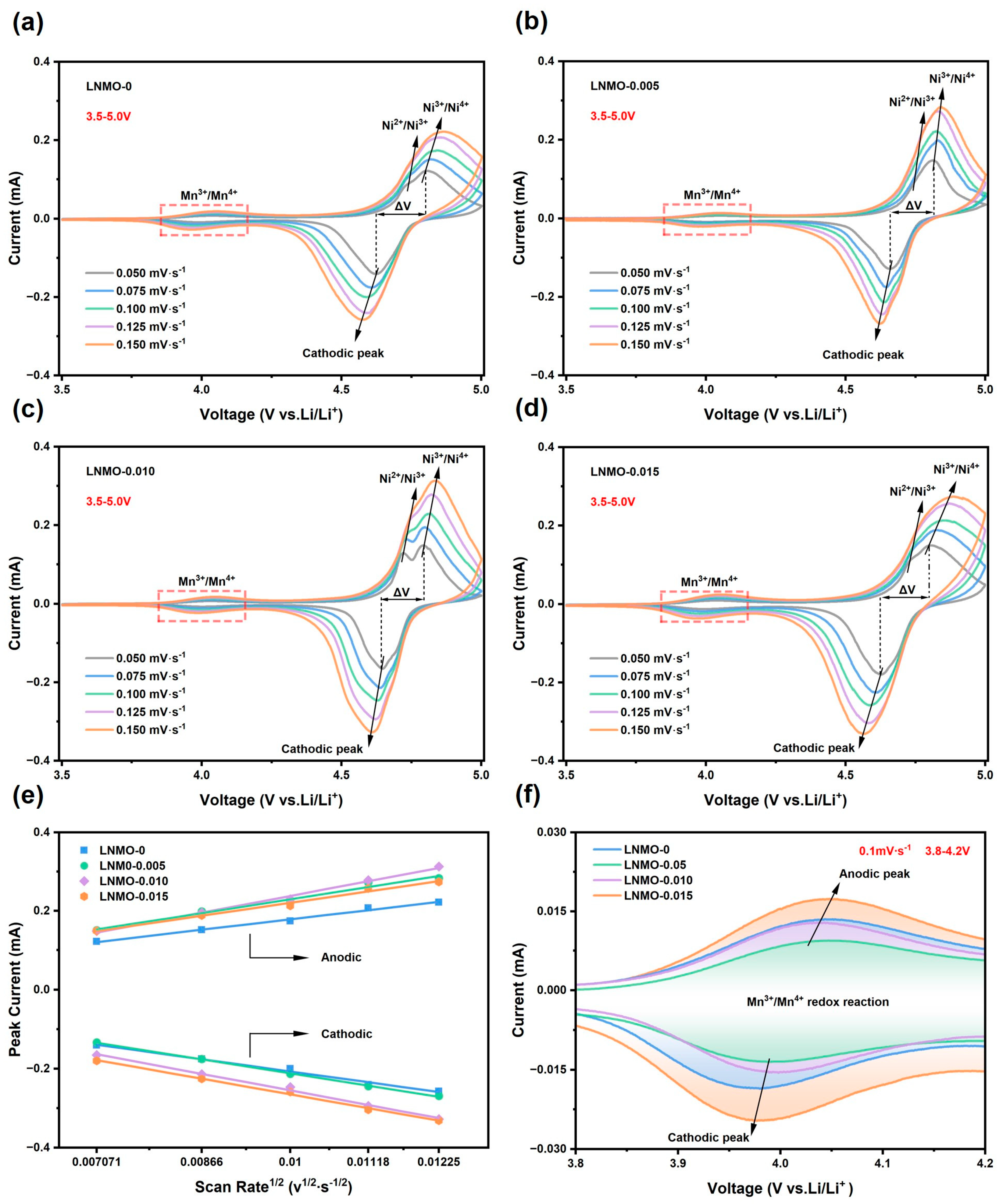
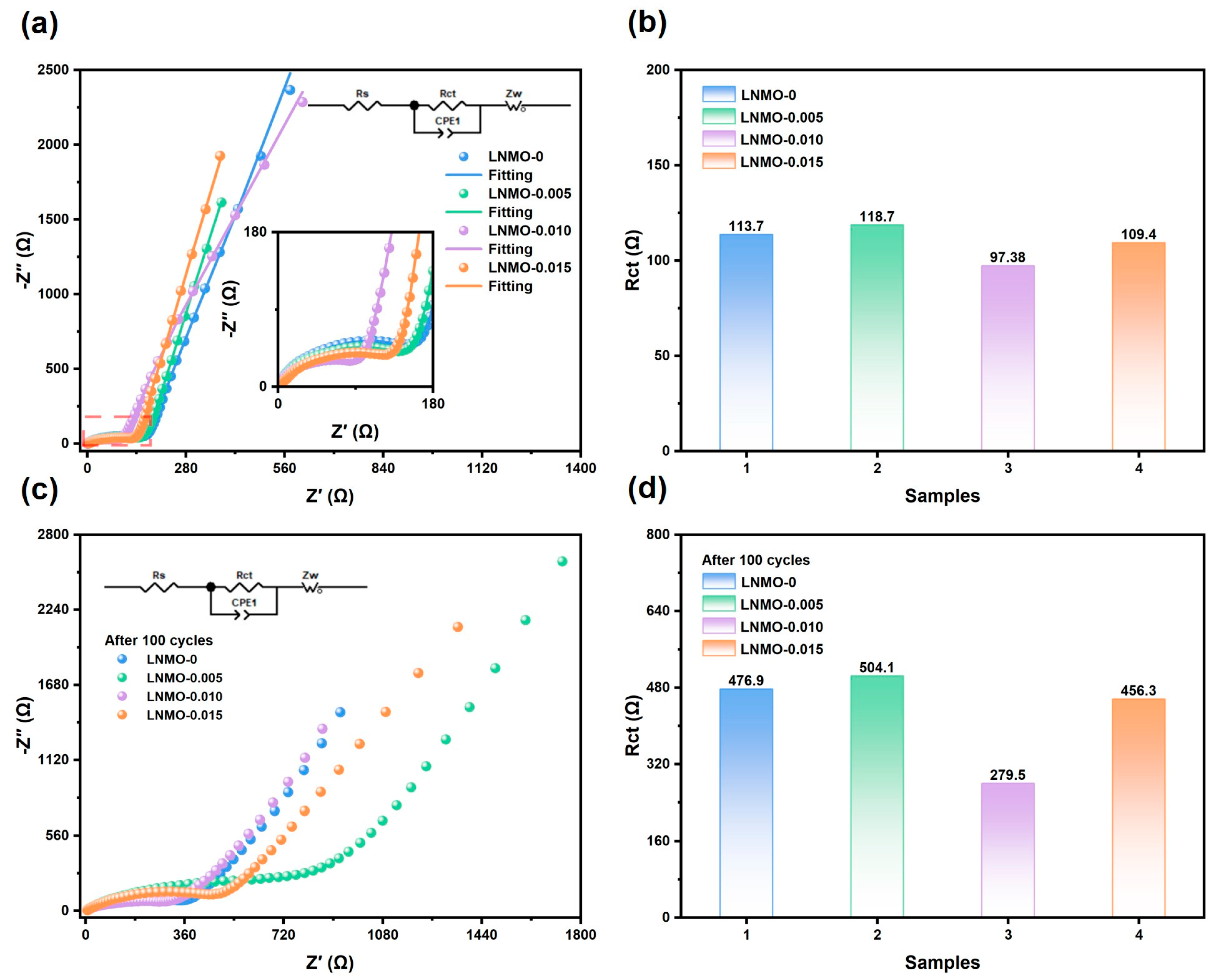
| Samples | a (Å) | V (Å3) | I311/I400 | Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LNMO-0 | 8.174959 | 546.33 | 0.97 | 8.10 |
| LNMO-0.005 | 8.173774 | 546.09 | 0.95 | 9.68 |
| LNMO-0.010 | 8.168736 | 545.09 | 0.87 | 10.73 |
| LNMO-0.015 | 8.168580 | 545.05 | 0.86 | 13.75 |
| ν (mV∙s−1) | LNMO-0 | LNMO-0.005 | LNMO-0.010 | LNMO-0.015 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| φpa | φpc | ΔV | φpa | φpc | ΔV | φpa | φpc | ΔV | φpa | φpc | ΔV | |
| 0.05 | 4.806 | 4.622 | 0.184 | 4.816 | 4.654 | 0.162 | 4.791 | 4.645 | 0.146 | 4.806 | 4.627 | 0.179 |
| 0.075 | 4.816 | 4.608 | 0.208 | 4.790 | 4.683 | 0.107 | 4.798 | 4.640 | 0.158 | 4.828 | 4.607 | 0.221 |
| 0.1 | 4.839 | 4.586 | 0.253 | 4.825 | 4.642 | 0.183 | 4.819 | 4.628 | 0.191 | 4.853 | 4.584 | 0.269 |
| 0.125 | 4.852 | 4.595 | 0.257 | 4.833 | 4.630 | 0.203 | 4.820 | 4.621 | 0.199 | 4.867 | 4.58 | 0.287 |
| 0.150 | 4.868 | 4.577 | 0.291 | 4.838 | 4.621 | 0.217 | 4.834 | 4.609 | 0.225 | 4.886 | 4.569 | 0.317 |
| Samples | Slopepa | Slopepc | Li-Deintercalation DLi (cm2∙s−1) | Li-Intercalation DLi (cm2∙s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LNMO-0 | 1.976 × 10−2 | −2.308 × 10−2 | 7.468 × 10−12 | 1.019 × 10−11 |
| LNMO-0.005 | 2.636 × 10−2 | −2.641 × 10−2 | 1.329 × 10−11 | 1.333 × 10−11 |
| LNMO-0.010 | 3.180 × 10−2 | −3.122 × 10−2 | 1.934 × 10−11 | 1.864 × 10−11 |
| LNMO-0.015 | 2.458 × 10−2 | −2.956 × 10−2 | 1.156 × 10−11 | 1.671 × 10−11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Qian, G.; Zhou, X.; Pei, Z.; Zheng, K.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J. Mg2+ and Cr3+ Co-Doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Derived from Ni/Mn Bimetal Oxide as High-Performance Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060429
Ma D, Wang J, Wang H, Qian G, Zhou X, Pei Z, Zheng K, Wang Q, Lu J. Mg2+ and Cr3+ Co-Doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Derived from Ni/Mn Bimetal Oxide as High-Performance Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(6):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060429
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Dehua, Jiawei Wang, Haifeng Wang, Guibao Qian, Xingjie Zhou, Zhengqing Pei, Kexin Zheng, Qian Wang, and Ju Lu. 2025. "Mg2+ and Cr3+ Co-Doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Derived from Ni/Mn Bimetal Oxide as High-Performance Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Nanomaterials 15, no. 6: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060429
APA StyleMa, D., Wang, J., Wang, H., Qian, G., Zhou, X., Pei, Z., Zheng, K., Wang, Q., & Lu, J. (2025). Mg2+ and Cr3+ Co-Doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Derived from Ni/Mn Bimetal Oxide as High-Performance Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials, 15(6), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060429





