Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer-Modified Graphene Oxide: Dispersion and Performance Enhancement in Cement Paste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
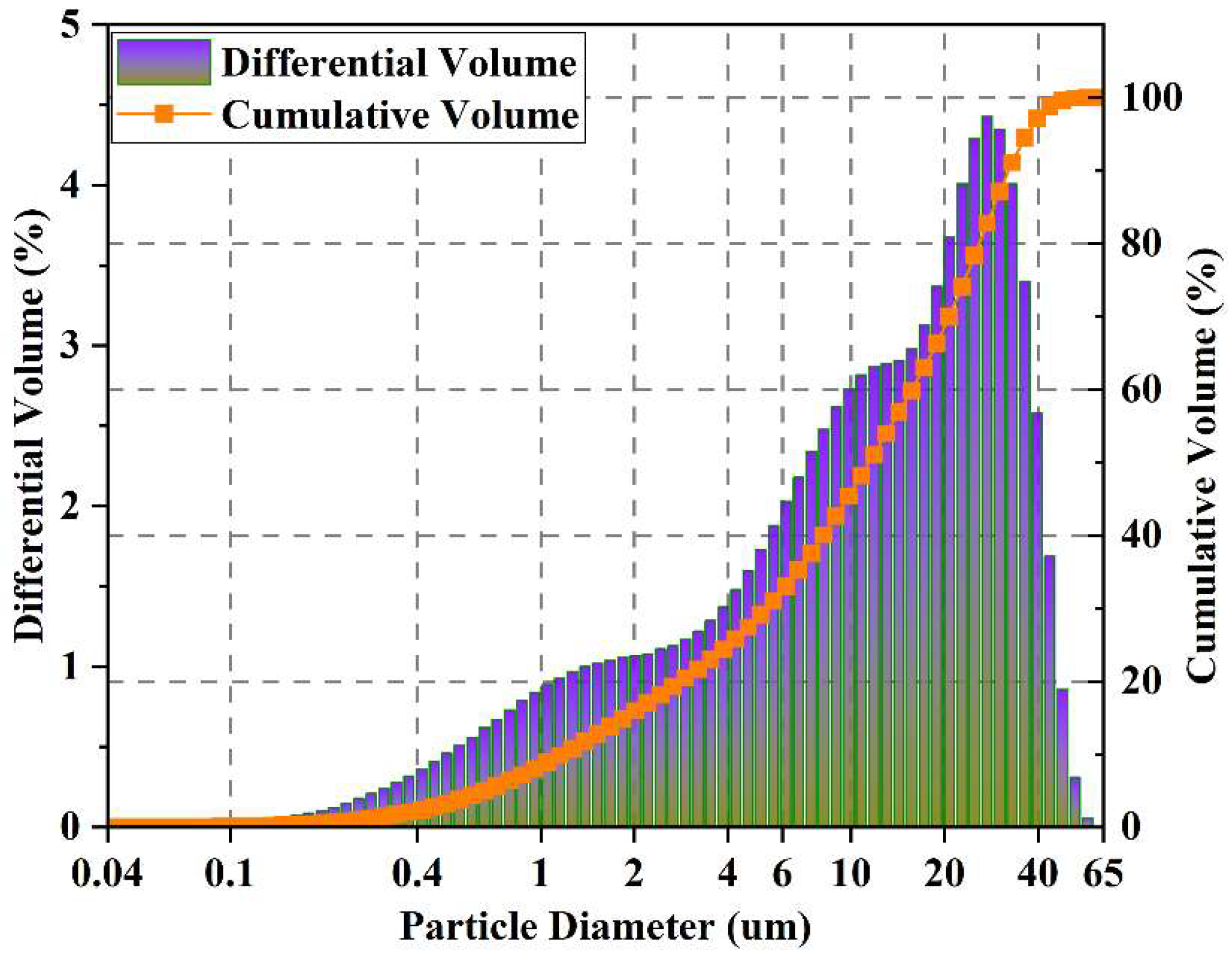
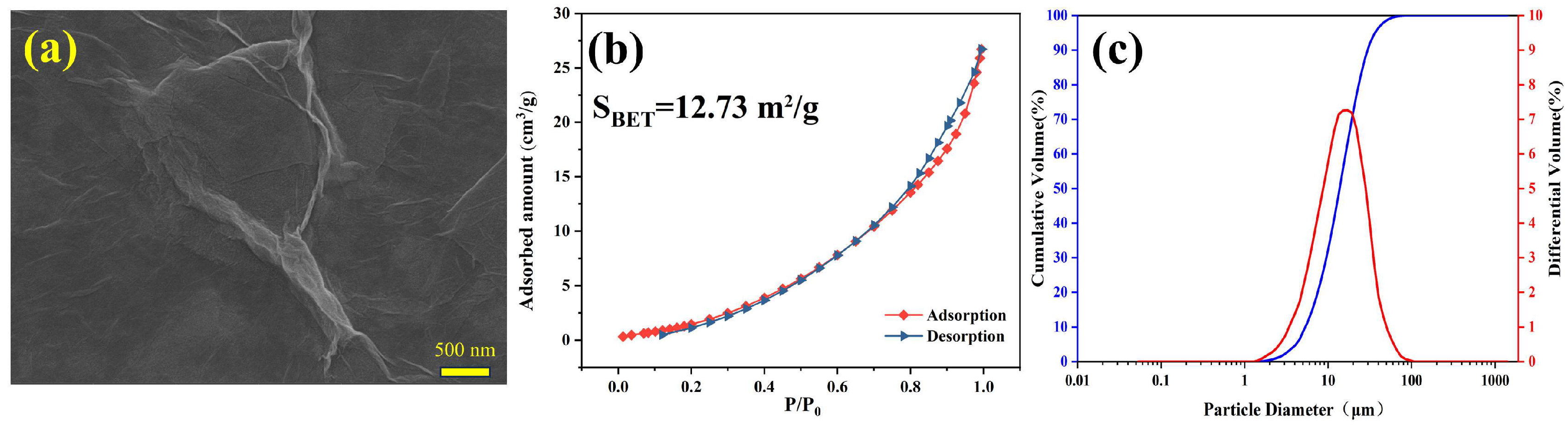
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of PC@GOs and Cement Paste
2.2.2. Preparation of Simulated Pore Solution
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Dispersion
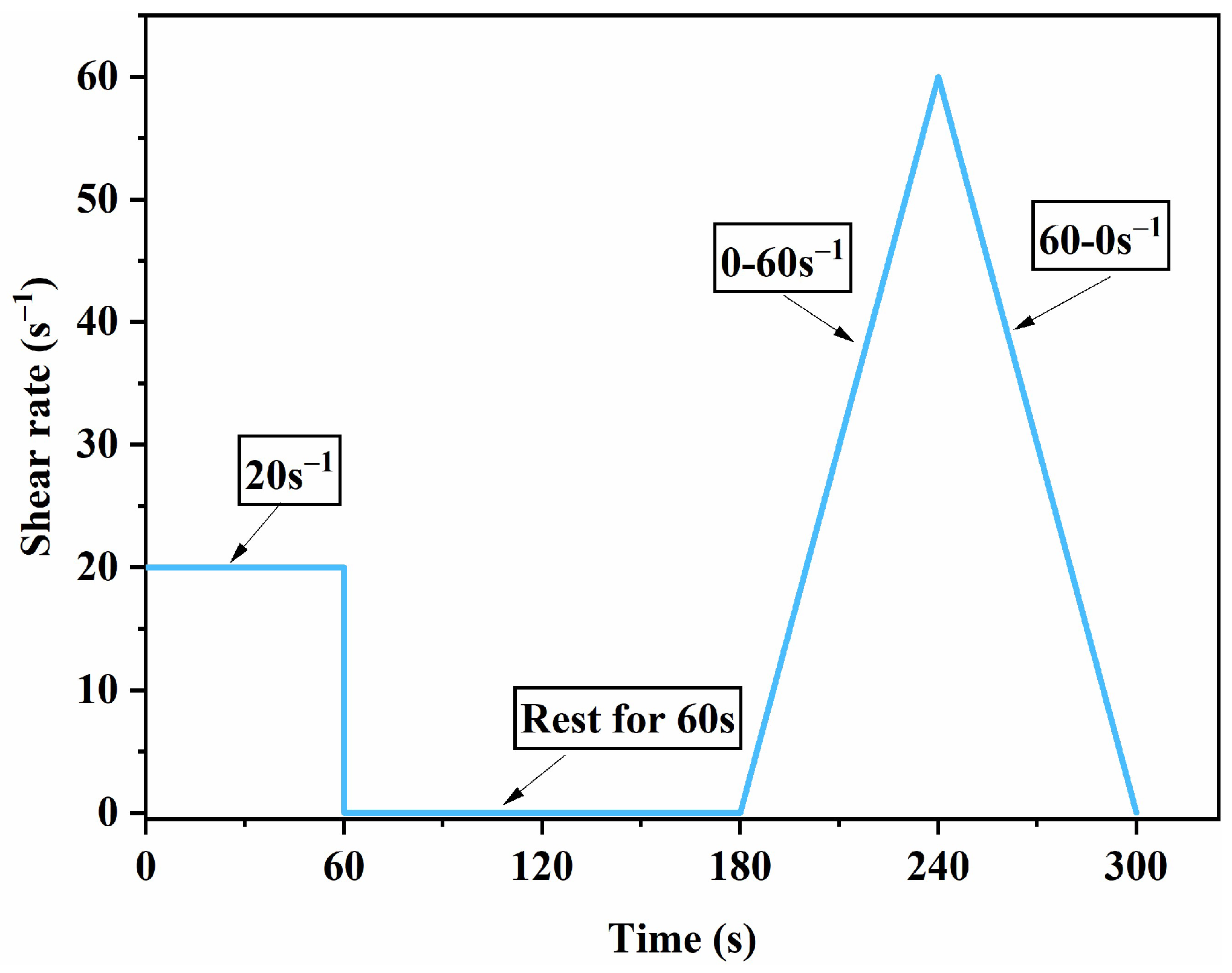
2.3.2. Rheological
2.3.3. Mechanical Properties
2.3.4. Carbon Emissions Evaluation
2.3.5. Pore Structure
2.3.6. Physical Characterization
2.3.7. Heat of Hydration
2.3.8. Hydration Products
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dispersion States and Absorbance of PC@GOs
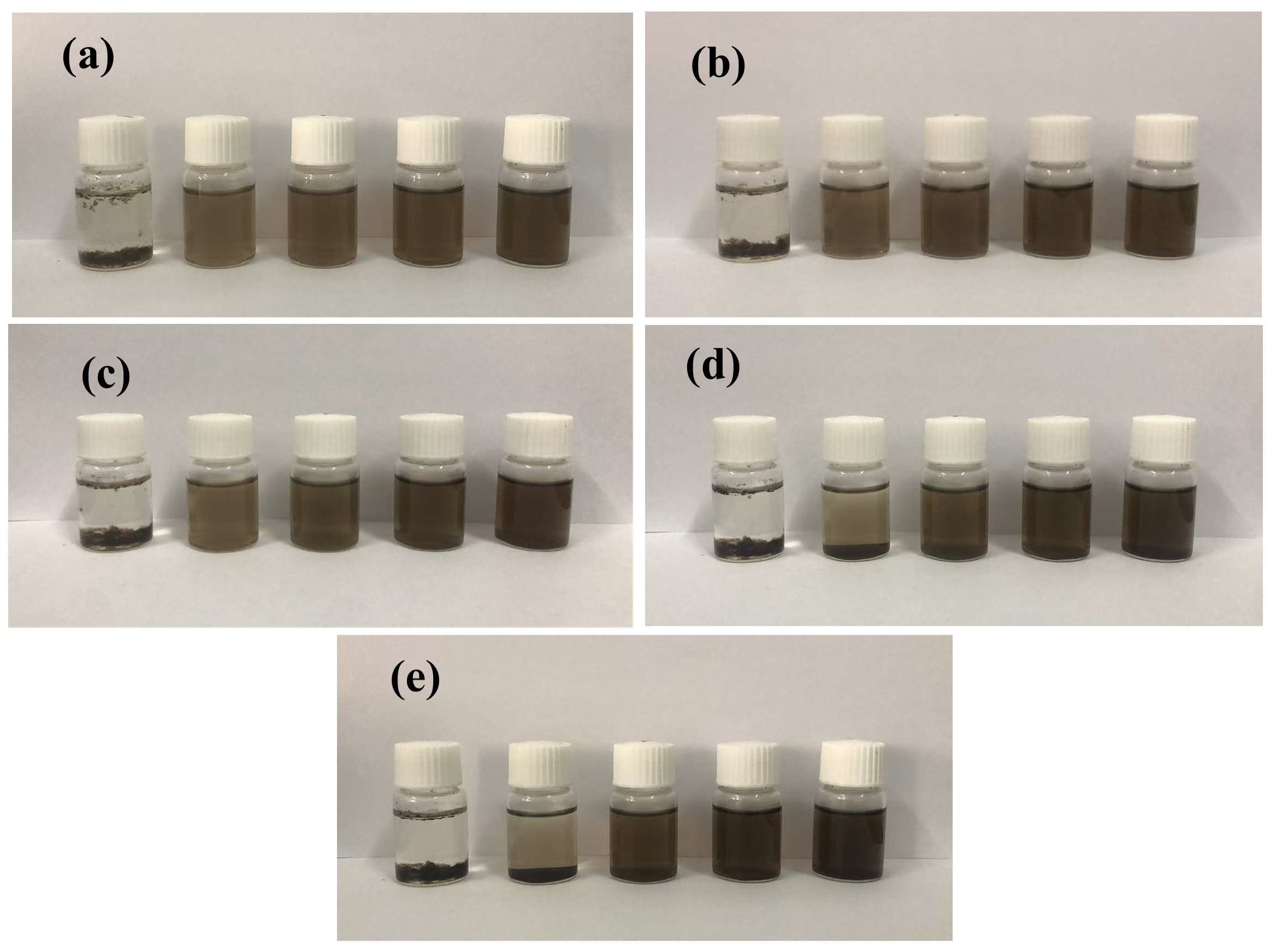
3.1.1. Dispersion States of PC@GOs
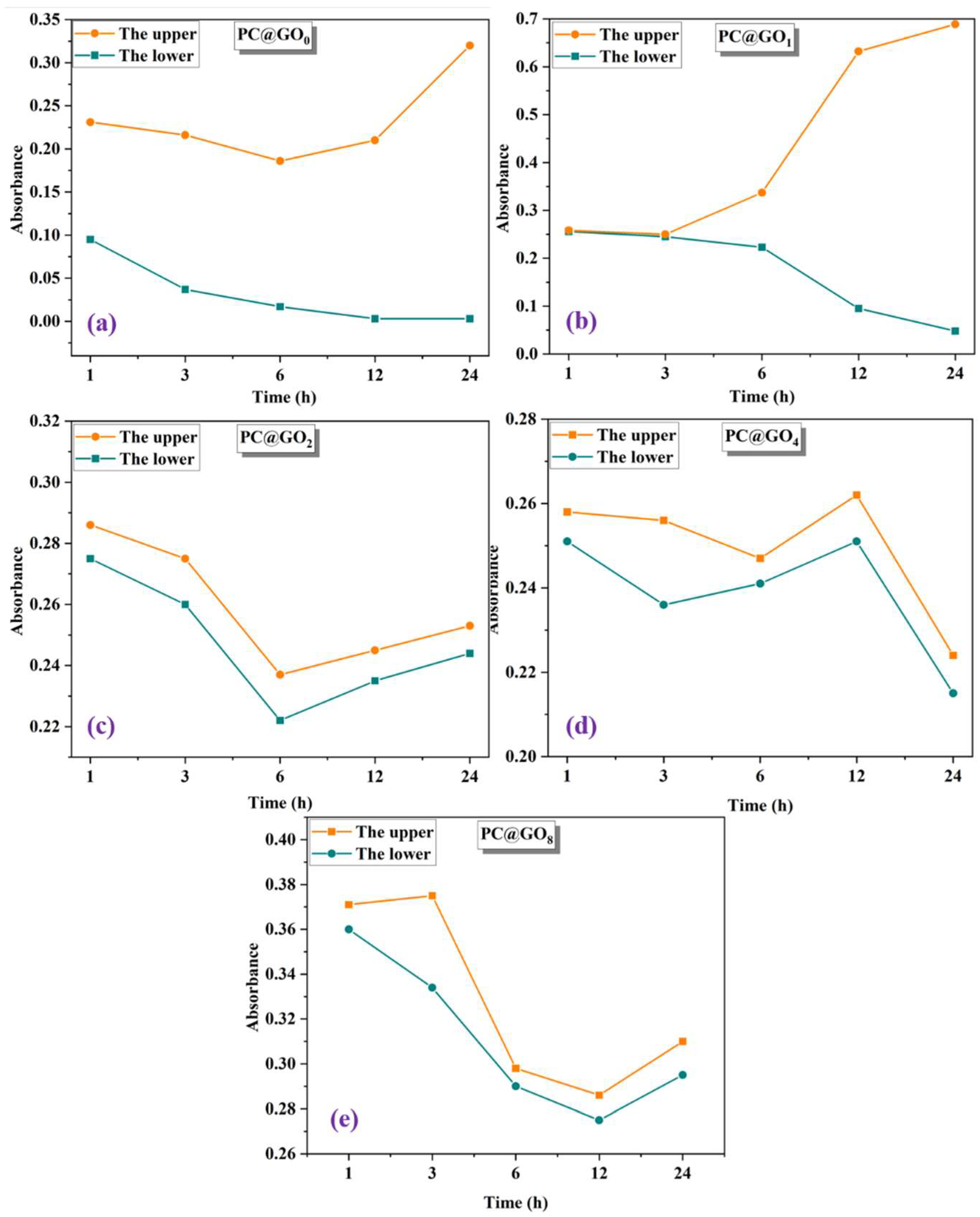
3.1.2. Absorbance of PC@GOs
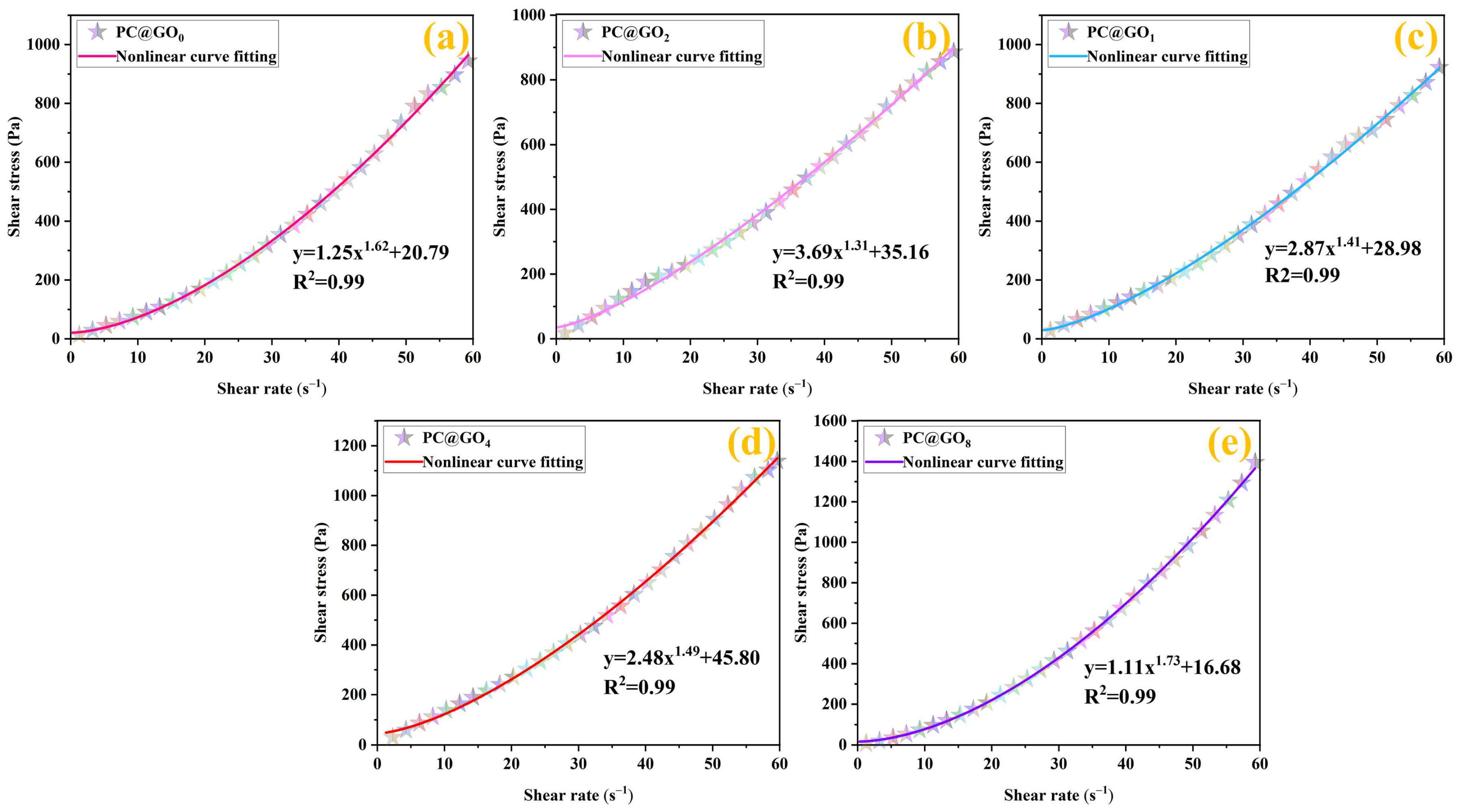
3.2. Rheological Properties
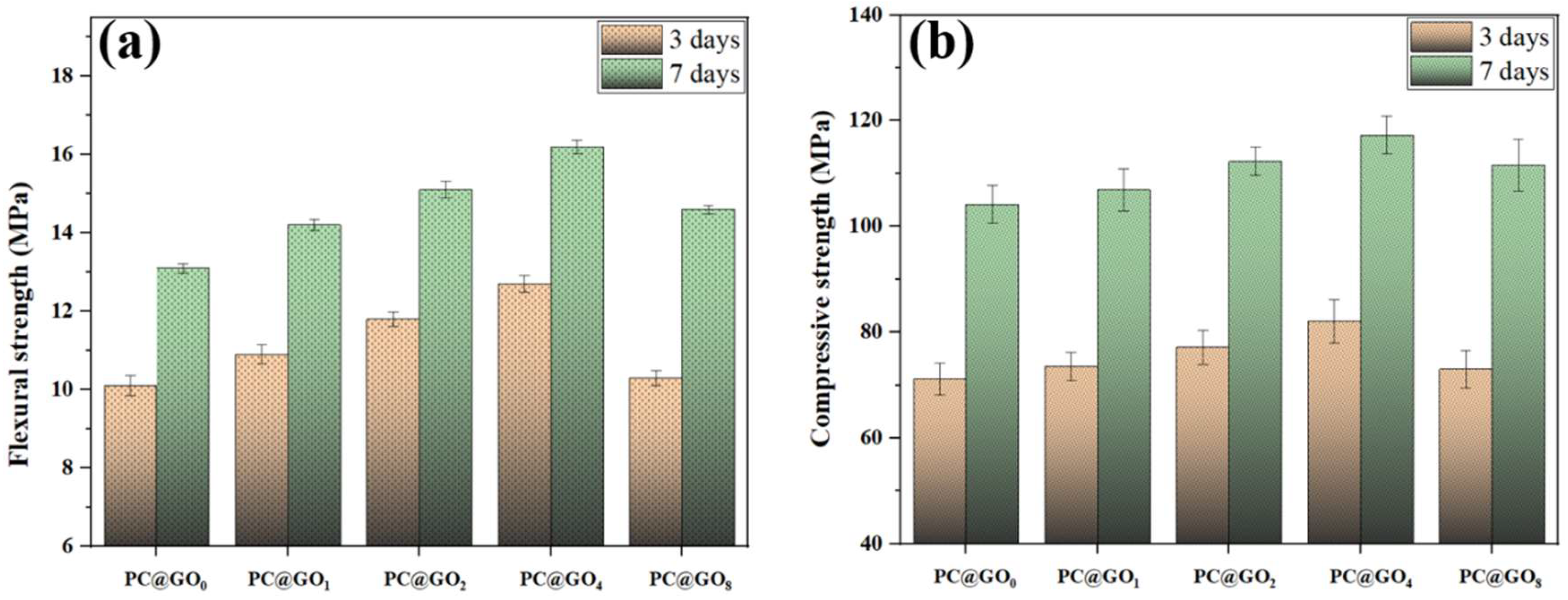
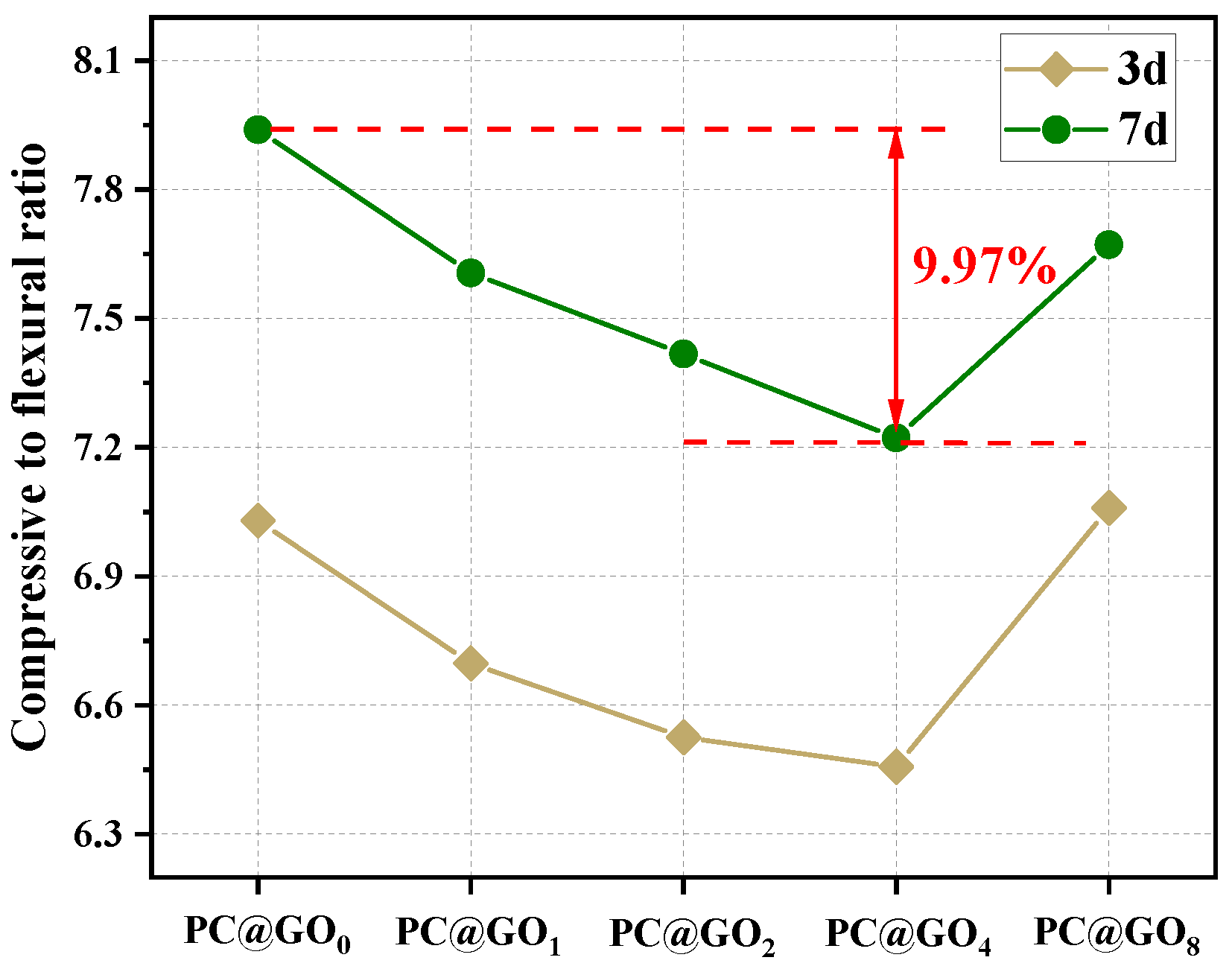
3.3. Mechanical Properties
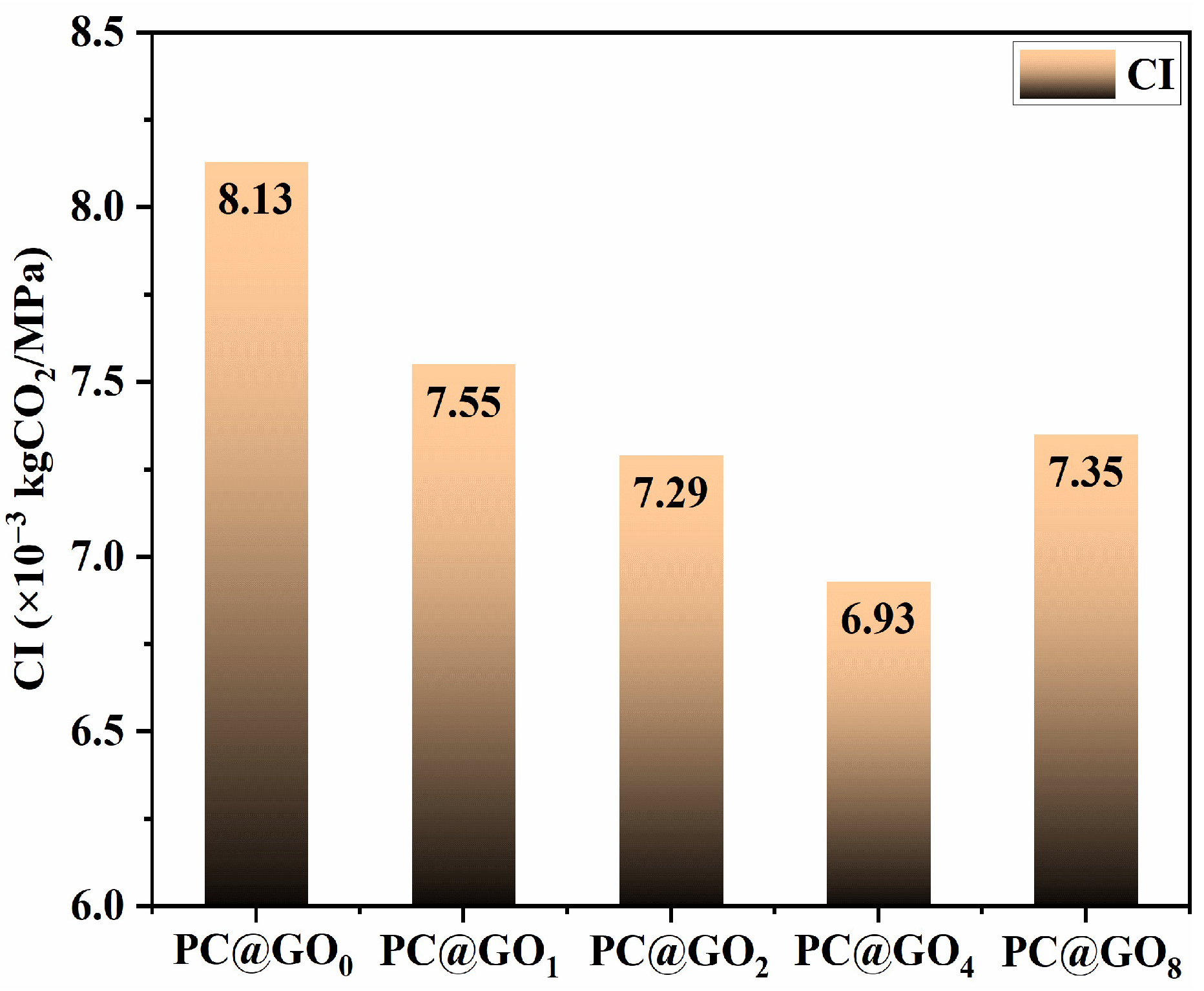
3.4. Carbon Emissions Evaluation
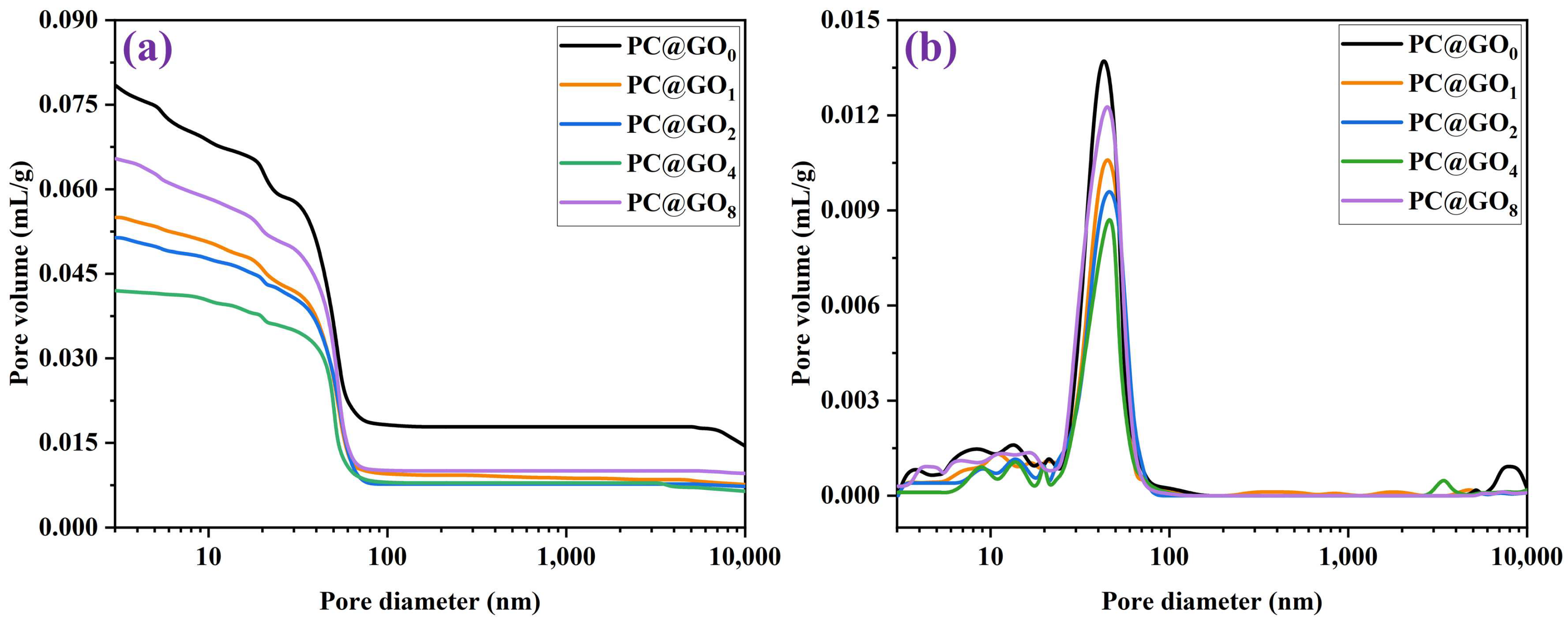
3.5. Pore Structure
3.6. Physical Characterization
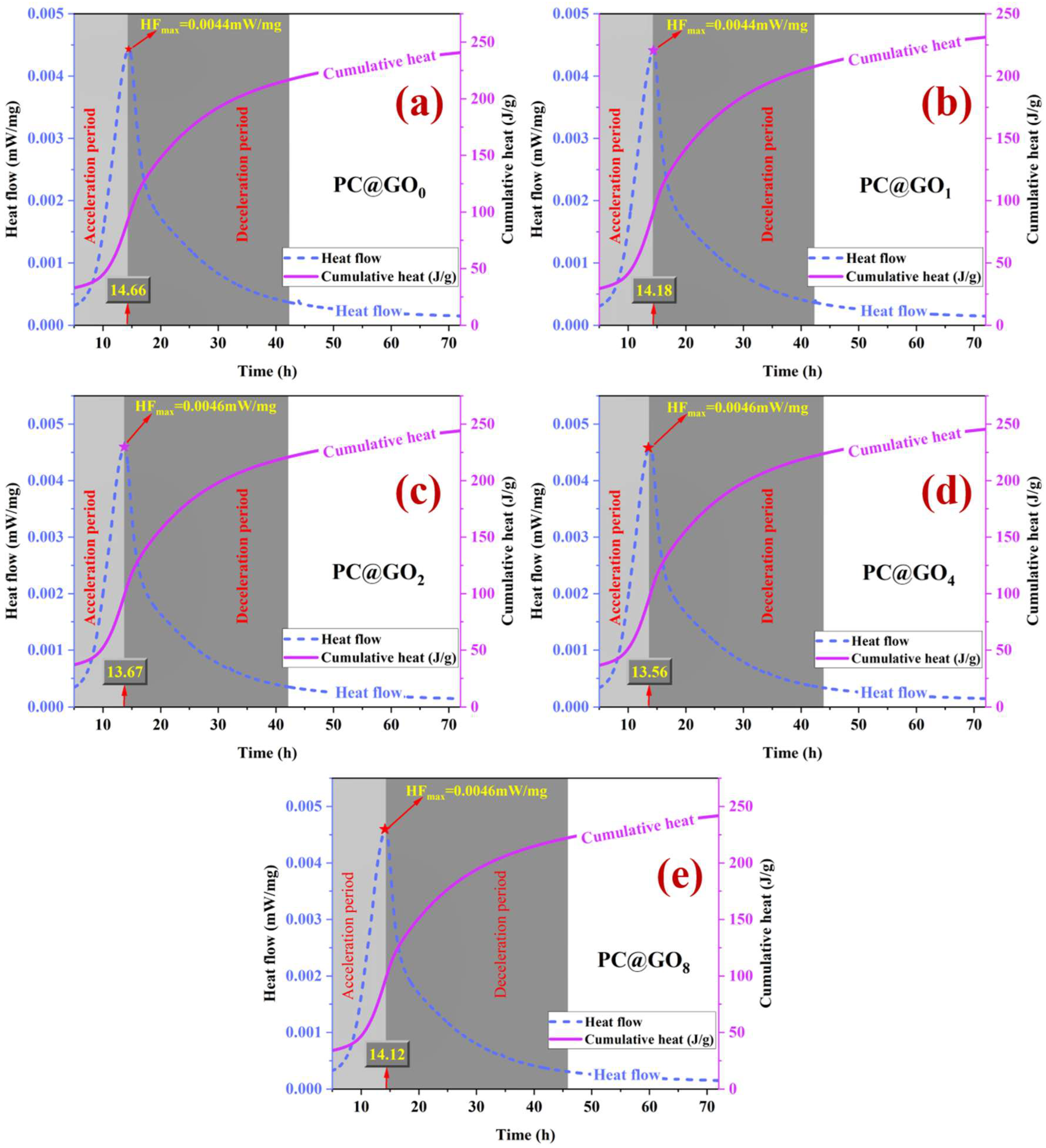
3.7. Hydration Evolution
3.8. Hydration Products
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- PC@GOs can be uniformly dispersed in the simulated alkaline pore solutions of cement paste.
- (2)
- PC@GOs can effectively shorten the acceleration period of cement hydration. Compared with the blank group, the hydration acceleration period of PC@GO4 cement paste was shortened by 7.50%, to as little as 13.56 h.
- (3)
- The mechanical properties of PC@GO4 cement paste were significantly improved. Compared with the blank group, after seven days, the flexural strength and compressive strength of the PC@GO4 sample increased by 23.7% and 12.6%, respectively.
- (4)
- PC@GO4 had the lowest water absorption rate and total porosity, which were 9.07% and 8.43%, respectively. Compared with the blank group, the water absorption rate and total porosity of PC@GO4 were decreased by 35.2% and 45.3%, respectively.
- (5)
- The incorporation of PC@GOs had a significant effect on the carbon emissions per unit strength of cement hardening paste. The CI of PC@GO4 was reduced by 14.8% compared with PC@GO0.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; He, C.; Zhou, H.; Xie, Z.; Li, D. Effects of polycarboxylate superplasticizer-modified graphene oxide on hydration characteristics and mechanical behavior of cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Shu, X.; Liu, J. Hydration kinetics, pore structure, 3D network calcium silicate hydrate, and mechanical behavior of graphene oxide reinforced cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Ge, C.; Li, Q.; Guo, L.; Shu, X.; Liu, J. Investigation of the effectiveness of PC@GO on the reinforcement for cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, J.; Thomas, B.S.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Nazar, S. Hybrid graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes reinforced cement paste: An investigation on hybrid ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Ye, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, X.; Strokova, V.; Nelyubova, V. Introducing reduced graphene oxide to enhance the thermal properties of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 109, 103559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Q.; Gao, R.; Tong, T. Experimental investigation on mechanical and piezoresistive properties of cementitious materials containing graphene and graphene oxide nanoplatelets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Korayem, A.H.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Duan, W.H. Incorporation of graphene oxide and silica fume into cement paste: A study of dispersion and compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Ge, C.; Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Shu, X.; Liu, J. Investigation of dispersion behavior of GO modified by different water reducing agents in cement pore solution. Carbon 2018, 127, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, J.; Silva, D. Impact of nanosilica deposited on cellulose pulp fibers surface on hydration and fiber-cement compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Thielemans, W.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J. PVA fiber reinforced cement composites with calcined cutter soil mixing residue as a partial cement replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yu, Z. Cement-based materials containing graphene oxide and polyvinyl alcohol fiber: Mechanical properties, durability, and microstructure. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajouguim, S.; Page, J.; Djelal, C.; Waqif, M.; Saâdi, L. Impact of Alfa fibers morphology on hydration kinetics and mechanical properties of cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Deng, H.; Guo, X.; Yin, J.; Zhao, Y. The investigating on mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites with high ductility and low cost. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Lee, J.C.; Qian, B. Mechanical properties and microstructure of high-strength lightweight concrete incorporating graphene oxide. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, T.; Li, P.; Im, S.; Liu, J.; Choi, H.; Bae, S. Impacts of graphene nanoribbon dispersion and stability on the mechanical and hydration properties of cement paste: Insights from surfactant-assisted ultrasonication. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, J. Interfacial heat transfer behavior of graphene-based filler and calcium-silicate-hydrate in cement composites. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 176, 121165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Muhammad, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J. A review on the development and application of graphene based materials for the fabrication of modified asphalt and cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagna, L.; Massella, D.; Priola, E.; Pavese, M. Relationship between oxygen content of graphene and mechanical properties of cement-based composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Gao, S.; Peng, S.; Shi, L.; Shah, S.P.; Li, W. Graphene reinforced cement-based triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient energy harvesting in civil infrastructure. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Shah, S.P. Physicochemical and Piezoresistive properties of smart cementitious composites with graphene nanoplates and graphite plates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Liu, S.; Ou, C.; Liu, Q.; Meng, G. Experimental investigation for the influence of graphene oxide on properties of the cement-waste concrete powder composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, D.; Wang, P.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. Experimental and molecular dynamics studies on the durability of sustainable cement-based composites: Reinforced by graphene. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.; Panesar, D. Nano reinforced cement paste composite with functionalized graphene and pristine graphene nanoplatelets. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2020, 197, 108063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Hu, H.; Hou, Y.; Lei, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Investigation of the effects of polymer dispersants on dispersion of GO nanosheets in cement composites and relative microstructures/performances. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Guo, Q.; Da, Z.; Yue, W.; Hai, Z. Influence of the molecular structure of a polycarboxylate superplasticiser on the dispersion of graphene oxide in cement pore solutions and cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Li, H.; Fang, C.; Xing, F. Uniformly dispersed and re-agglomerated graphene oxide-based cement pastes: A comparison of rheological properties, mechanical properties and microstructure. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbaniang, D.F.; Adak, D.; Kar, A.; Barbhuiya, S.; Chottemada, P.G.; Marthong, C. Enhancing mechanical strength and microstructural properties of alkali-activated systems through nano graphene oxide dispersion and polycarboxylate ether admixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 139004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, K.; Ghasemi, A.; Amiri, S.; Mirvalad, S.; Korayem, A.H. The synergic effects of metakaolin and polycarboxylate-ether on dispersion of graphene oxide in cementitious environments and macro-level properties of graphene oxide modified cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1346-2011; Test methods for water requirement of normal consistency, setting time and soundness of the Portland cement. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Preparation of a three-dimensional modified graphene oxide via RAFT polymerization for reinforcing cement composites. Colloid. Surface. A 2021, 610, 125925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, X. Coupling evaluation of carbon emissions and strength: Early carbonation curing of cement mortar containing incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 427, 136278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Xie, J.; Hu, X.; Shi, C. Trends toward lower-carbon ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC)–A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 420, 135602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkhonde, D.; Bezabih, T. On the computational evaluation of carbon dioxide emissions of concrete mixes incorporating waste materials: A strength-based approach. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024, 8, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 7019-2014; Test methods for fiber cement products. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB/T 12959-2008; Test methods for heat of hydration of cement. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Hou, D.; Wu, C.; Yin, B.; Hua, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xu, W.; et al. Investigation of composite silane emulsion modified by in-situ functionalized graphene oxide for cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, J.; Crentsil, K.; Duan, W. Dispersion of silane-functionalized GO and its reinforcing effects in cement composites. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 103228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, S.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Sanjayan, J.; Duan, W. Investigation on dispersion of graphene oxide in cement composite using different surfactant treatments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaka, M.; Walvekar, R.; Khalid, M.; Jagadish, P.; Mujawar, N.; Faik, A. Rheological behaviour of eutectic nanofluids containing a low fraction of GO/TiO2 hybrid nanoparticles. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 20, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, P.; Wang, S.; Lu, L.; Cheng, X. Yield stress and thixotropy control of 3D-printed calcium sulfoaluminate cement composites with metakaolin related to structural build-up. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, P.; Lu, L. Cheng, Rheological parameters and building time of 3D printing sulphoaluminate cement paste modified by retarder and diatomite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Huang, J.; Hu, H.; Huang, J.; Kuang, H.; Wang, T.; Yang, R.; Ma, B. Comparative study of phosphate ester grafted polycarboxylate superplasticizer graphene oxide assembly (HPCE@GO) on improvement of GO dispersion and mechanical properties of ordinary Portland cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Bhatrola, K.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, J.; Suhag, S.; Maurya, S.K.; Kothiyal, N.C. Durability of cementitious mortar: Incorporation of highly dispersed superplasticizer modified graphene oxide in fly ash blended mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 107888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Q.; Song, L.; Song, Y.; Guo, X. Deep research about the mechanisms of graphene oxide (GO) aggregation in alkaline cement pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Monasterio, M.; Cui, H.; Han, N. Experimental study of the effects of graphene oxide on microstructure and properties of cement paste composite. Compos. Part. A Appl. S. 2017, 102, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lei, J.; Guo, L.; Du, X.; Li, J. The application of thermal analysis, XRD and SEM to study the hydration behavior of tricalcium silicate in the presence of a polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 613, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compositions | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 67.70 | 16.29 | 5.31 | 3.58 | 2.78 | 2.56 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 0.99 |
| Sample | PC-1: GO Mass Ratio | PC-1 (g) | PC-2 (g) | GO (g) | Cement (g) | Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC@GO0 | 0:1 | 0 | 1.44 | 0.18 | 600 | 156 |
| PC@GO1 | 1:1 | 0.18 | 1.26 | 0.18 | 600 | 156 |
| PC@GO2 | 2:1 | 0.36 | 1.08 | 0.18 | 600 | 156 |
| PC@GO4 | 4:1 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.18 | 600 | 156 |
| PC@GO8 | 8:1 | 1.44 | 0 | 0.18 | 600 | 156 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Gan, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.; Lu, L. Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer-Modified Graphene Oxide: Dispersion and Performance Enhancement in Cement Paste. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060419
Zhang H, Gan X, Lu Z, Li L, Lu L. Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer-Modified Graphene Oxide: Dispersion and Performance Enhancement in Cement Paste. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(6):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060419
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haiming, Xingyu Gan, Zeyu Lu, Laibo Li, and Lingchao Lu. 2025. "Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer-Modified Graphene Oxide: Dispersion and Performance Enhancement in Cement Paste" Nanomaterials 15, no. 6: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060419
APA StyleZhang, H., Gan, X., Lu, Z., Li, L., & Lu, L. (2025). Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer-Modified Graphene Oxide: Dispersion and Performance Enhancement in Cement Paste. Nanomaterials, 15(6), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060419





