Calcium-Enriched Magnetic Core–Shell Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Potential Application in Bone Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 (Core)
2.3. Synthesis of mSiO2 (Shell Composition)
2.3.1. Experimental Procedure 1
Sample Fe3O4/mSi_1 (Modified Stöber)
Sample Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1A (Ca-Doped Variant 60:40 of the Modified Stöber)
Sample Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1B (Ca-Doped Variant 90:10 of the Modified Stöber)
Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1C (Wet Impregnation for Calcium Enrichment)
2.3.2. Experimental Procedure 2
Sample Fe3O4/mSi_2 (Surfactant-Templated Sol–Gel Synthesis)
Sample Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_2 (Ca-Doped Variant of the Surfactant-Templated Sol–Gel Synthesis)
2.4. Materials Characterization
2.5. Biological Characterization
2.5.1. Cytotoxicity
2.5.2. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Levels
2.5.3. Osteogenic Differentiation
- (1)
- hPDLCs cultured with each MNP type in OM;
- (2)
- hPDLCs cultured in OM without NPs (positive control).
2.5.4. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
2.5.5. Alizarine Red Staining
3. Results
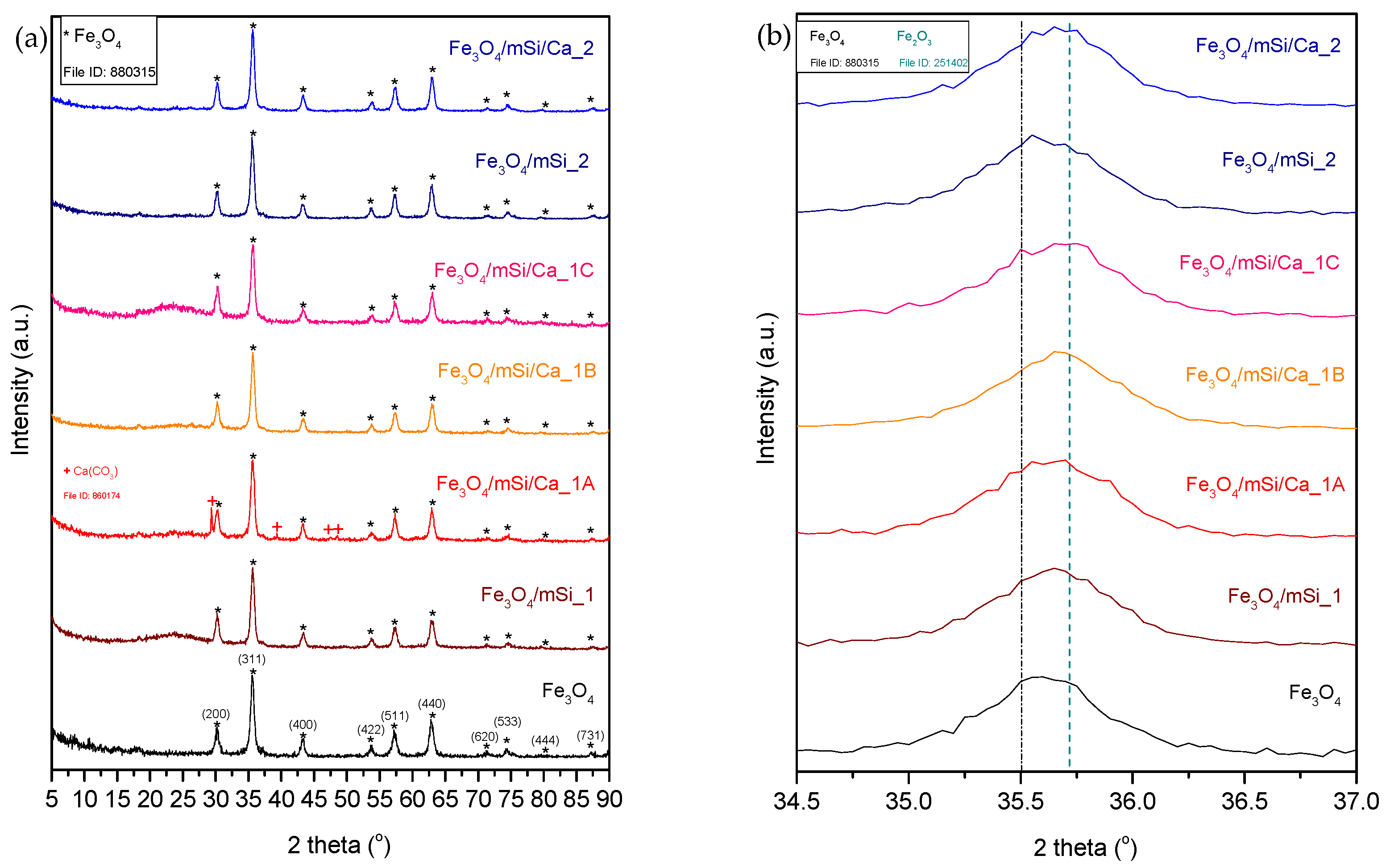
3.1. XRD
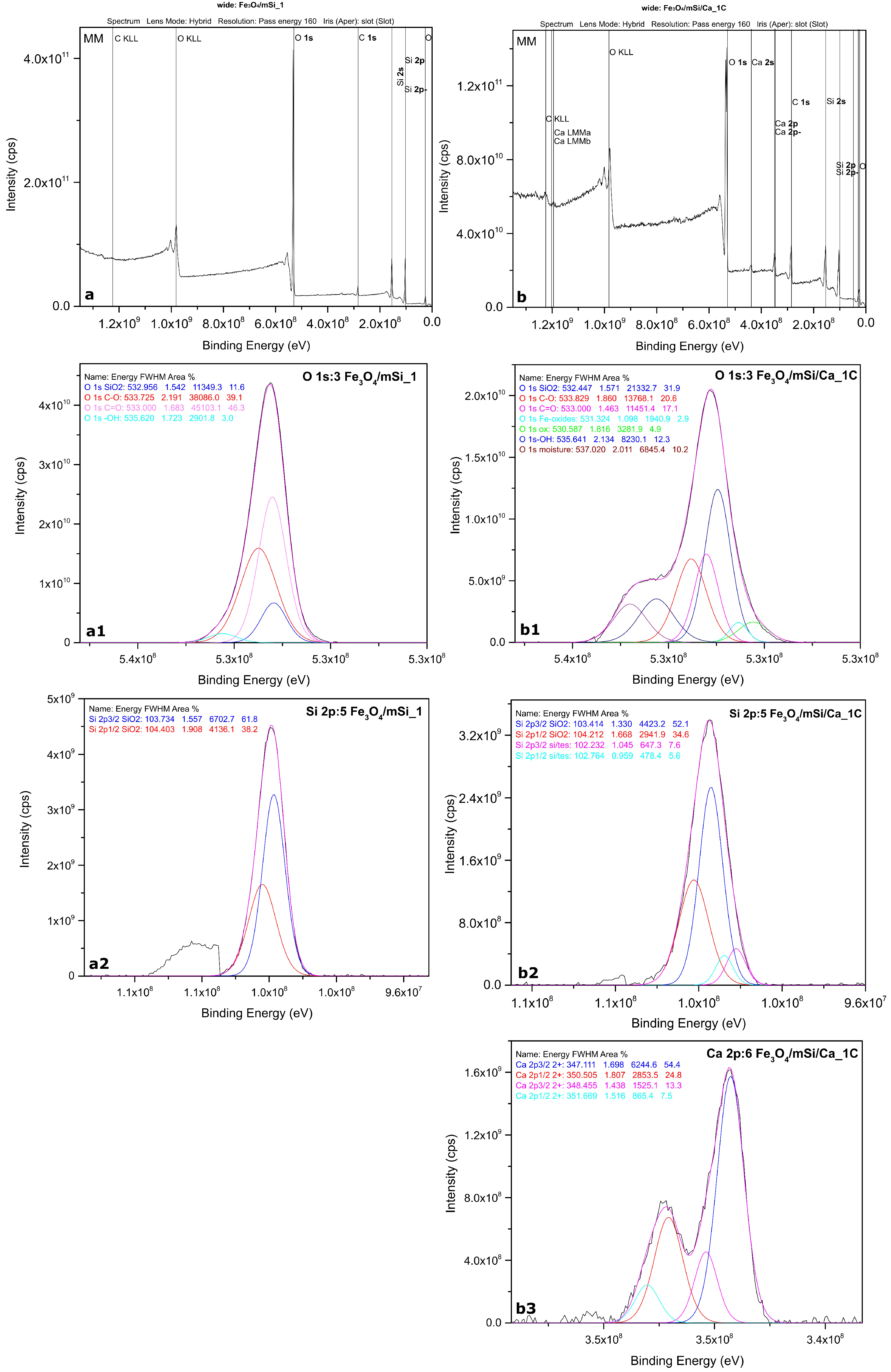
3.2. XPS
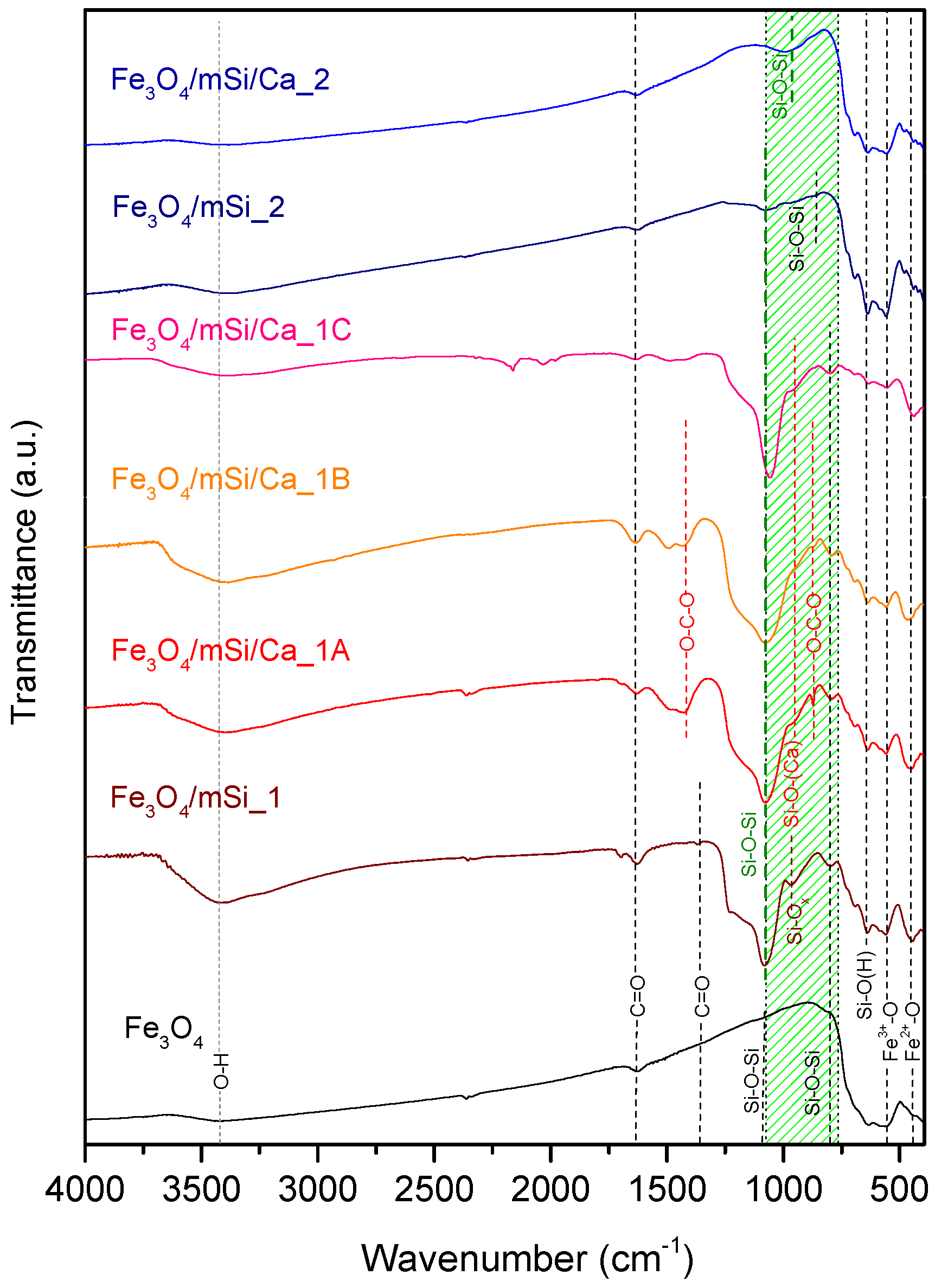
3.3. FTIR
3.4. VSM
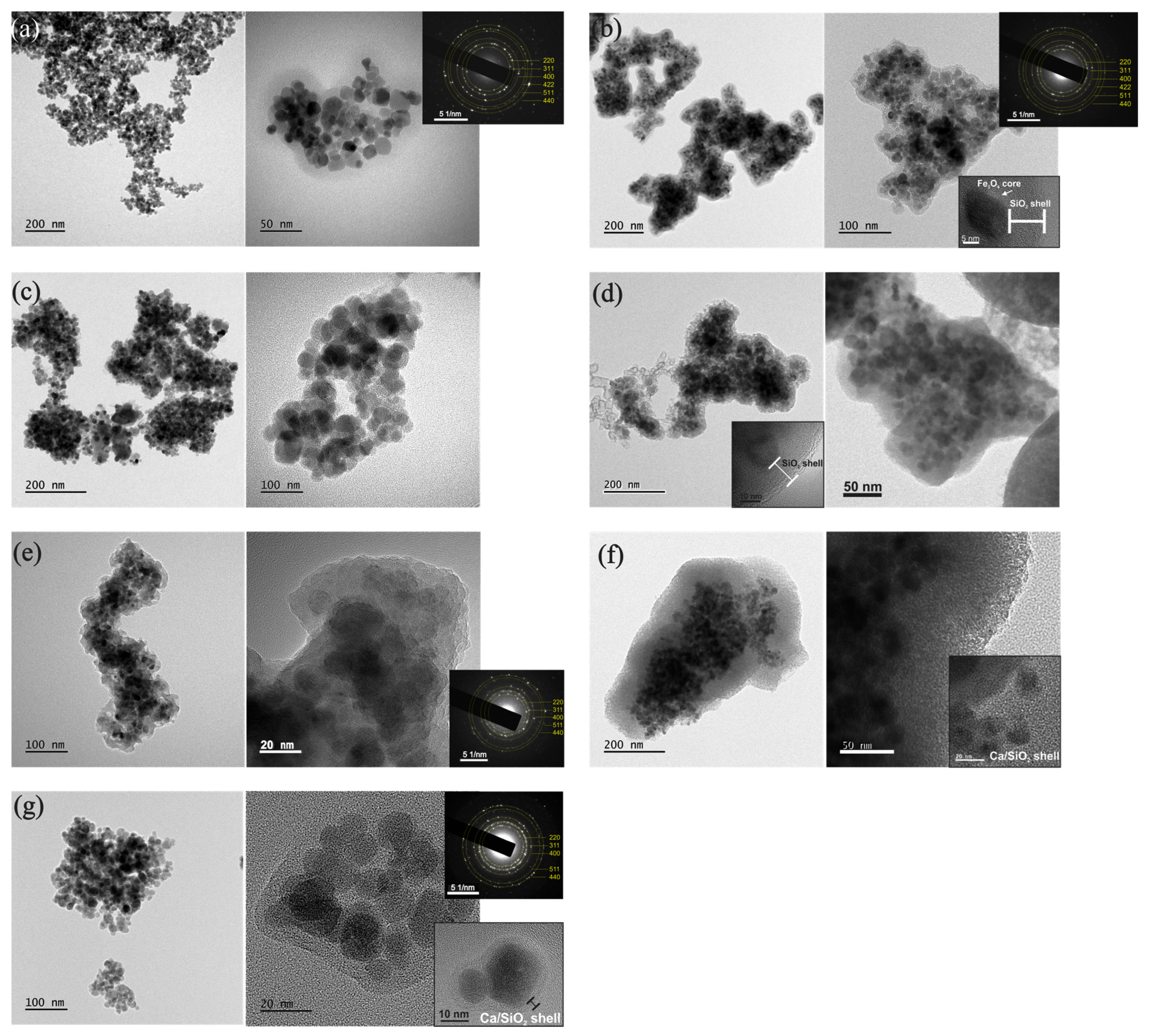
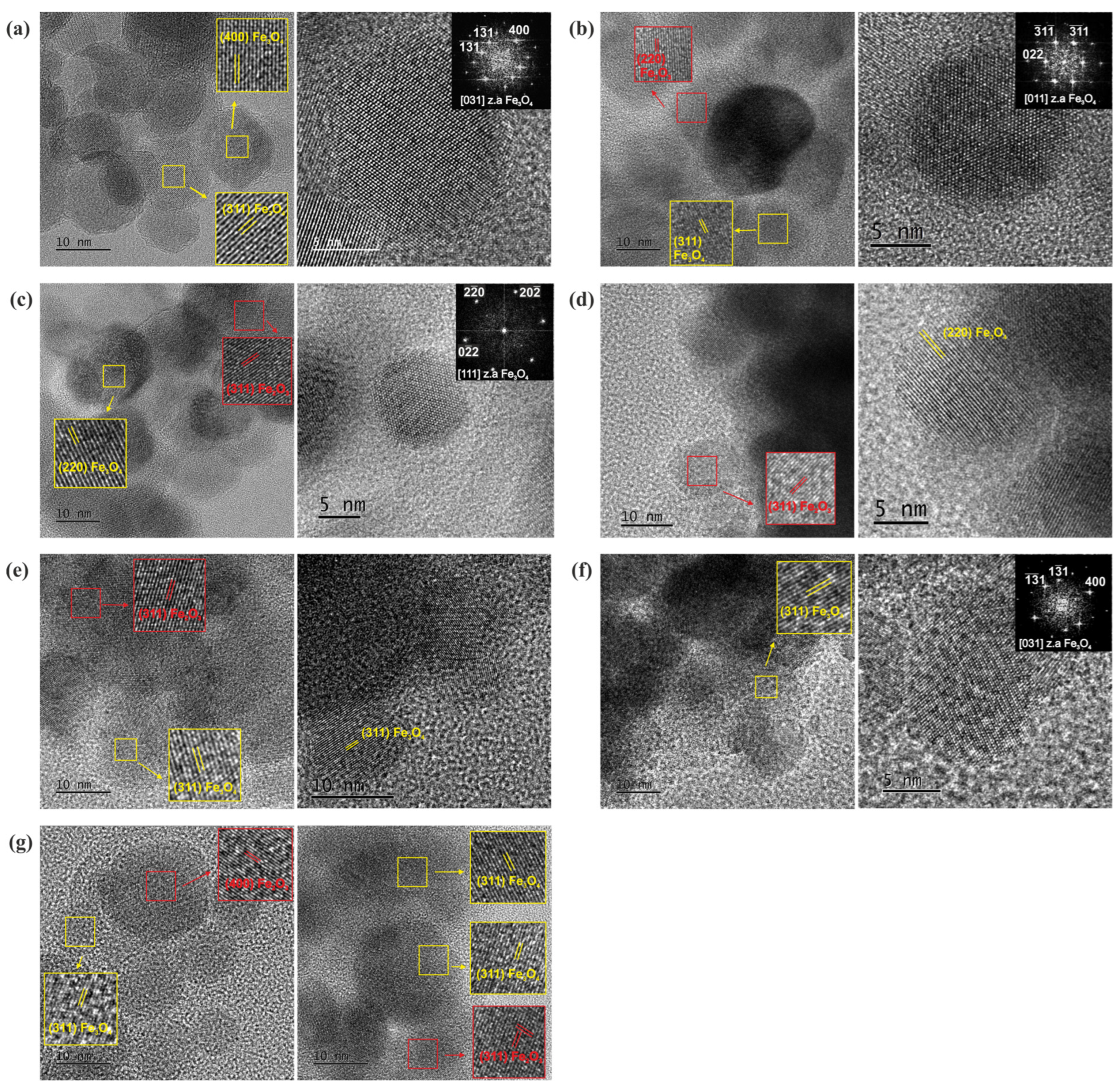
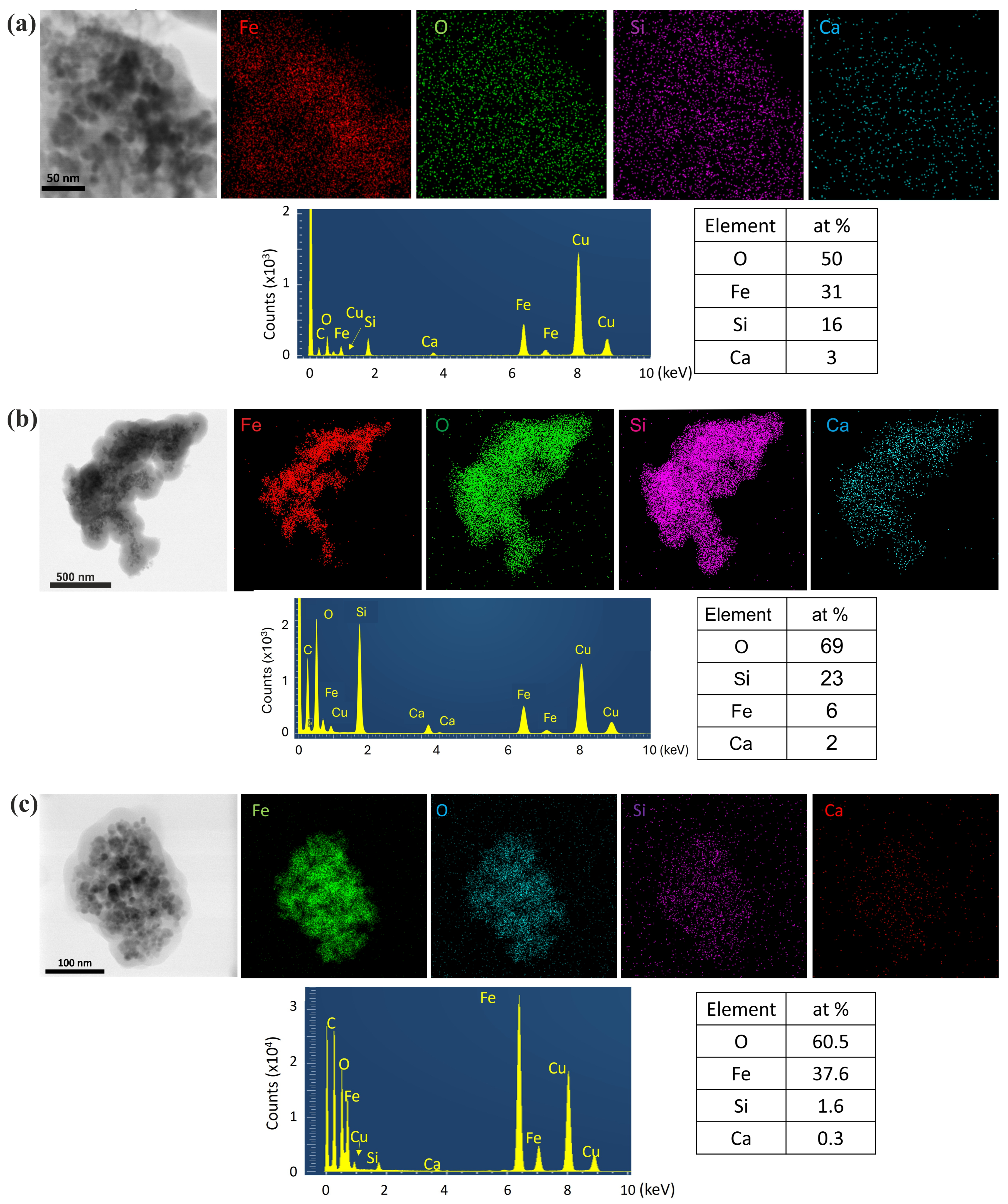
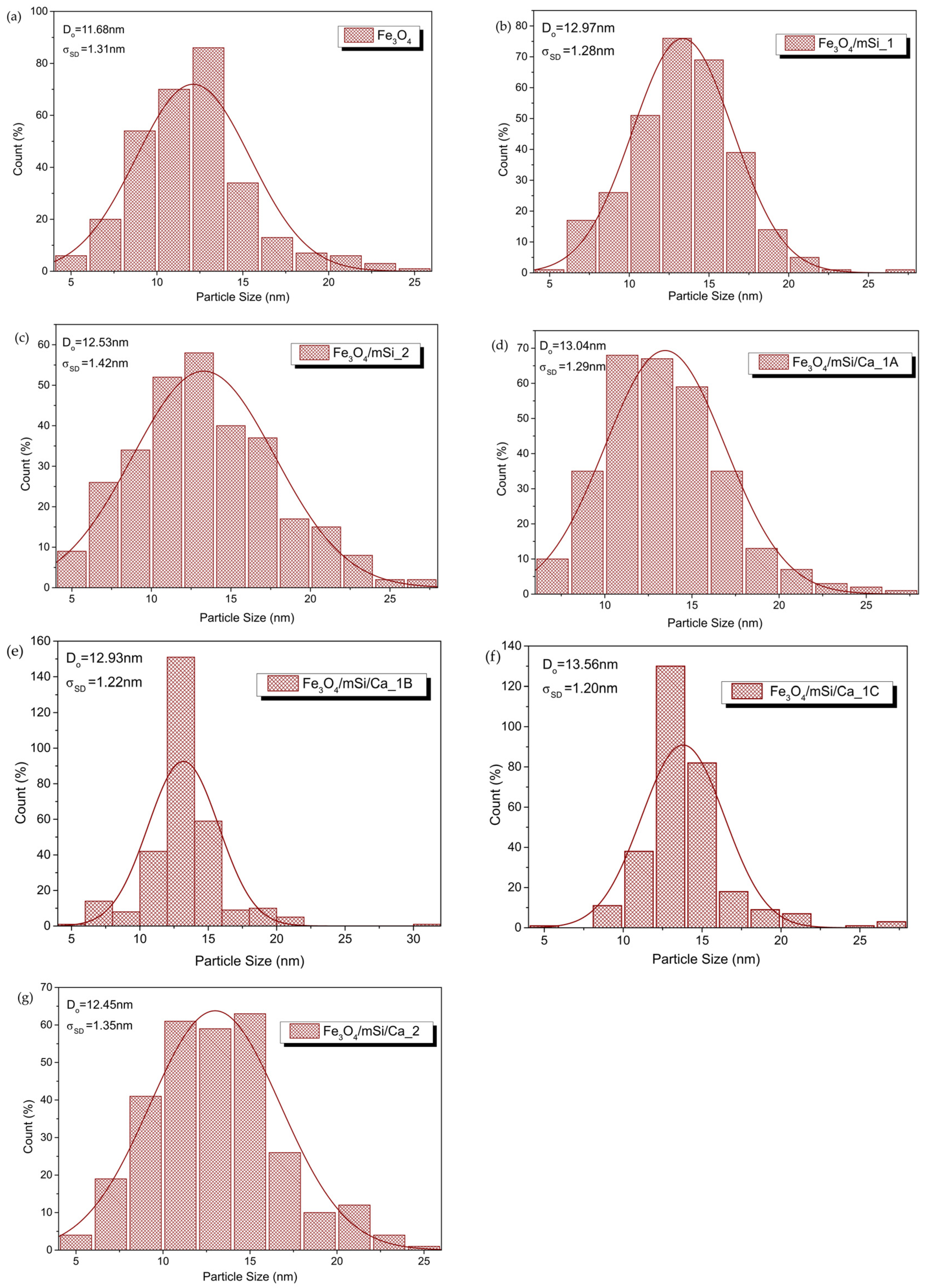
3.5. TEM
3.5.1. Morphology, Structure and Composition of NPs
3.5.2. Size Distribution
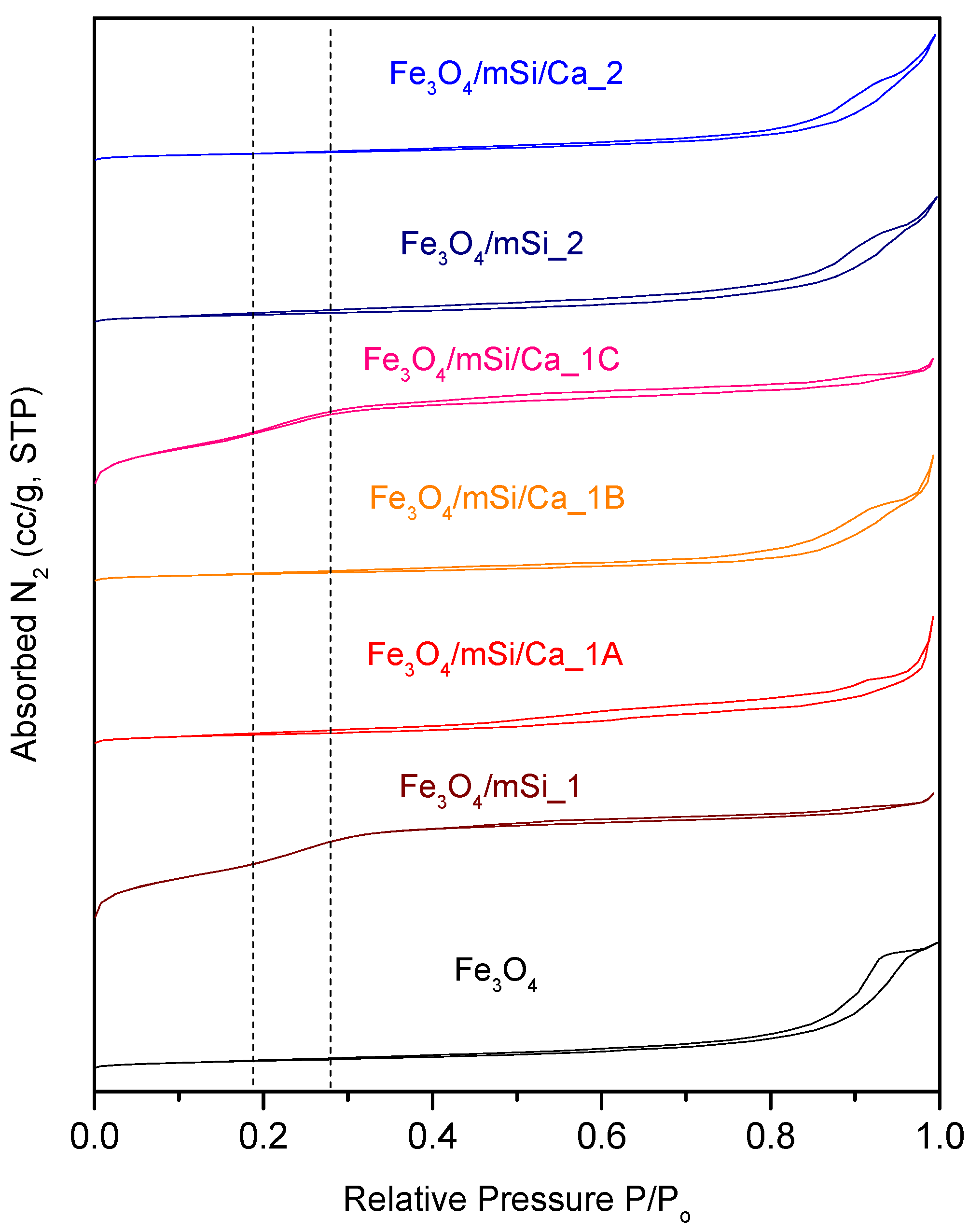
3.6. BET Analysis
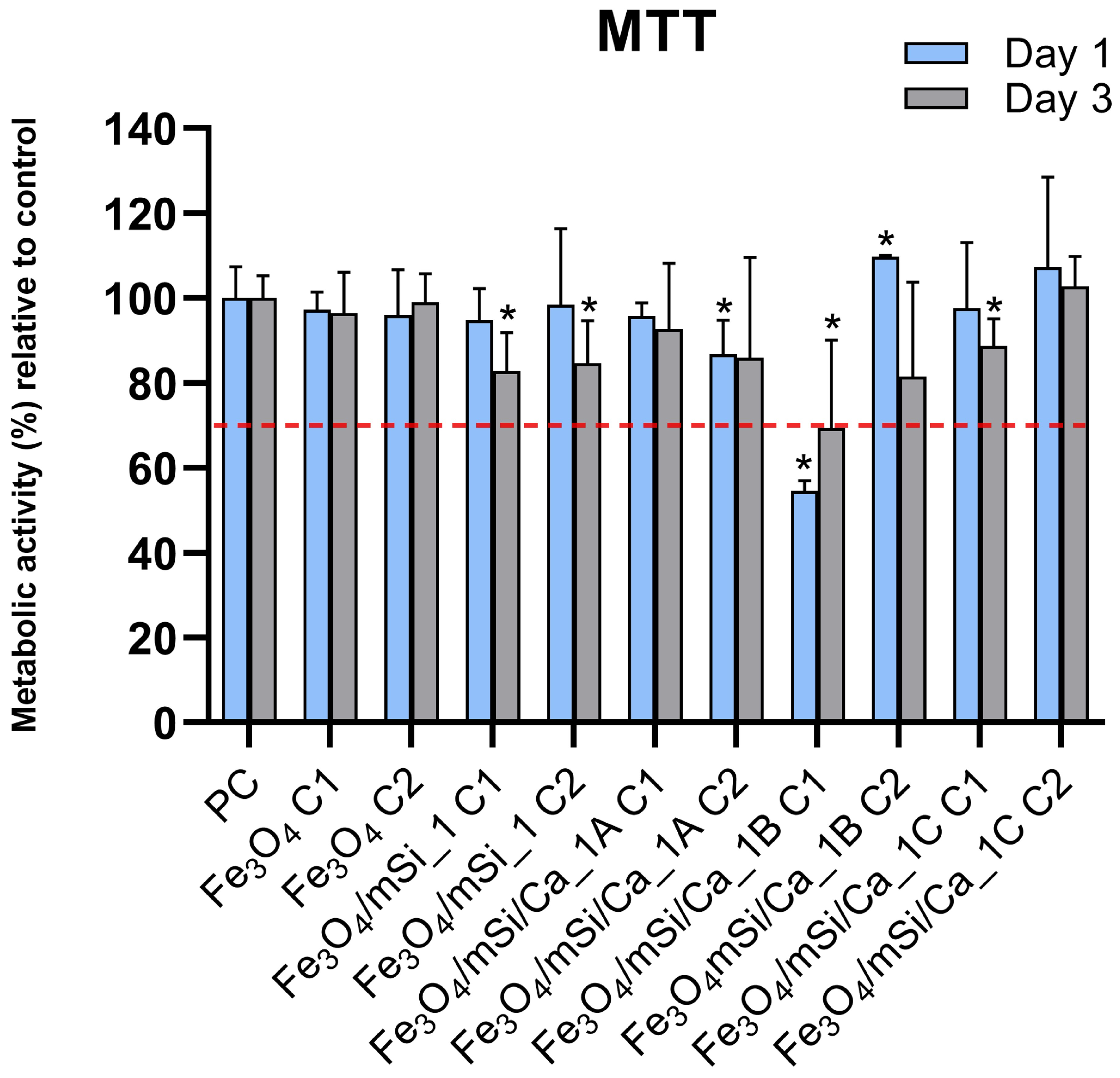
3.7. Cytotoxicity
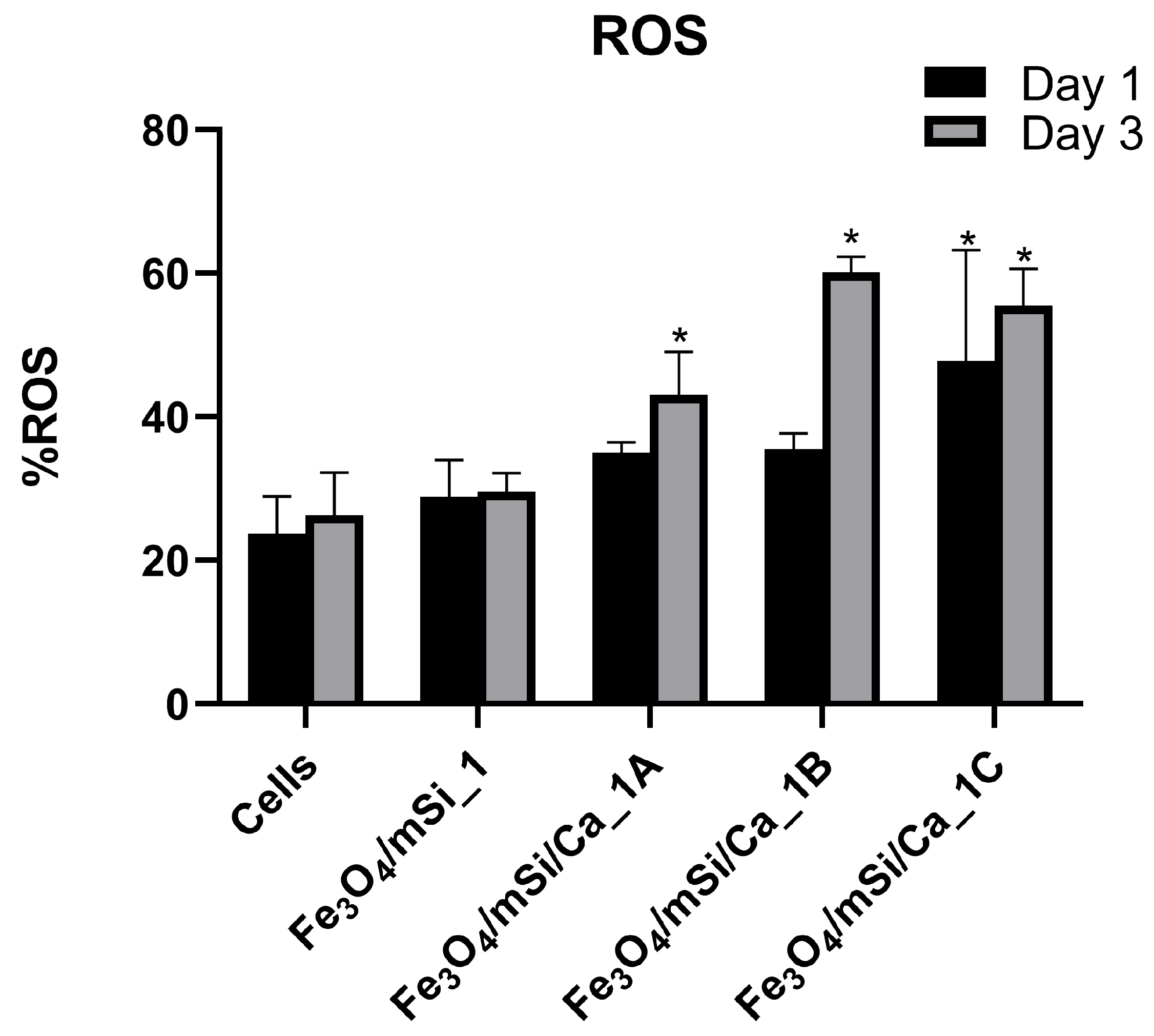
3.8. ROS Generation Evaluation
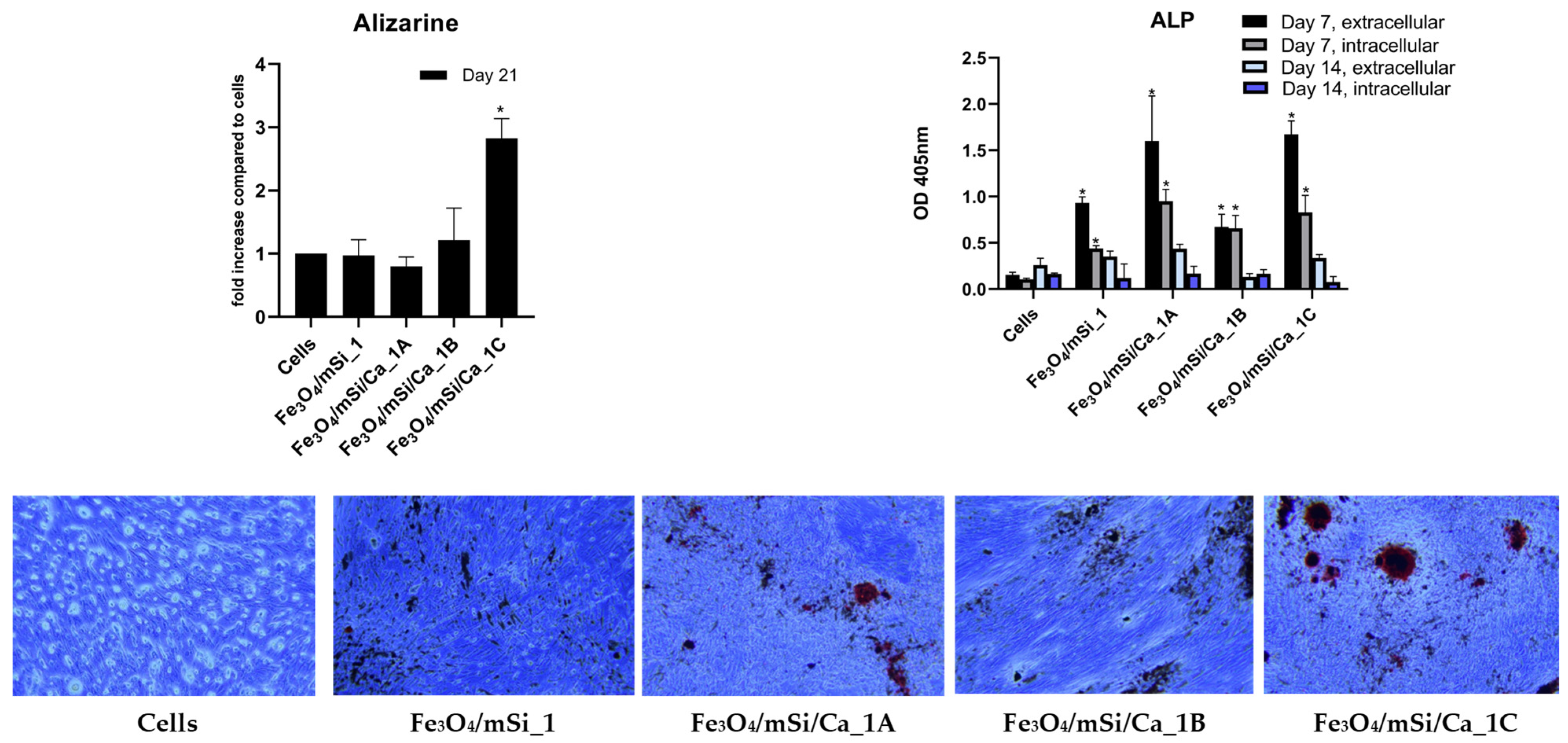
3.9. Osteogenic Differentiation
4. Discussion
4.1. Core–Shell Formation
4.2. Characterization Results
4.3. Magnetic Properties
4.4. Mesoporous Structure
4.5. Cytotoxicity—Osteogenic Potential and ROS Analysis
4.6. Comparative Analysis and Selection of the Optimum Synthesis Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Fe3O4 | Magnetite |
| Fe2O3 | Maghemite |
| mSiO2 | Mesoporous Silica |
| Ca2+ | Calcium Ions |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| MNPs | Magnetic Nanoparticles |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 | Hydroxyapatite |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| FeCl3•6H2O | Ferric Chloride Hexahydrate |
| FeSO4•7H2O | Ferrous Chloride Tetrahydrate |
| NH4OH | Ammonium Hydroxide |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl Orthosilicate |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide |
| CH3CH2OH | Ethanol |
| Ca(NO3)2•4H2O | Calcium Nitrate Tetrahydrate |
| C6H15NO3 | Triethanolamine |
| C6H5Cl or CB | Chlorobenzene |
| dd-H2O | Double-Distilled Water |
| Ar | Argon Gas |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared |
| KBr | Potassium Bromide |
| VSM | Vibrating Sample Magnetometer |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| HRTEM | High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Minimal Essential Medium |
| HGFs | Human Gingival Fibroblasts |
| hPDLCs | Human Periodontal Ligament Cells |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| fcc | Face-centered Cubic |
| BET | Brunauer-Emmett-Teller theory |
| BJH | Barrett–Joyner–Halenda |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| ARS | Alizarin Red Staining |
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase Activity |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| ART | Artemisin |
| PC | Positive Control |
References
- Wu, A.; Ou, P.; Zeng, L. Biomedical Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Nano 2010, 5, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Webster, T.J. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications and Challenges. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8760–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Singh, S.; Karakoti, A.S. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Current Trends and Future Aspects in Diagnostics and Nanomedicine. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 20, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolucci, E.; Maria, A.; Galletti, R.; Antonetti, C.; Marracci, M.; Tellini, B.; Piccinelli, F. Chemical and Magnetic Properties Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Pisa, Italy, 11–14 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi-Achachelouei, M.; Knopf-Marques, H.; Ribeiro da Silva, C.E.; Barthès, J.; Bat, E.; Tezcaner, A.; Vrana, N.E. Use of Nanoparticles in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh Chaudhuri, R.; Paria, S. Core/Shell Nanoparticles: Classes, Properties, Synthesis Mechanisms, Characterization, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2373–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Sarkar, S.; Jagajjanani Rao, K.; Paria, S. Core/Shell Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 8–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bhateria, R. Core–Shell Nanostructures: A Simplest Two-Component System with Enhanced Properties and Multiple Applications. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2459–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamos, D.; Krestou, A.; Papagiannaki, M.; Maropoulos, S. An Overview of the Production of Magnetic Core–Shell Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Metals 2022, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatunga, D.C.; Godakanda, V.U.; de Silva, R.M.; de Silva, K.M.N. Recent Developments in the Use of Organic–Inorganic Nanohybrids for Drug Delivery. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, Z.; Rezvani, H.; Keshavarz Moraveji, M. Core–Shell Nanoparticles Used in Drug Delivery-Microfluidics: A Review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 18280–18295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Shi, R.; Liu, H. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutthavas, P.; Tahmasebi Birgani, Z.; Habibovic, P.; van Rijt, S. Calcium Phosphate-Coated and Strontium-Incorporated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Can Effectively Induce Osteogenic Stem Cell Differentiation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, X.; Liang, J.; Shi, J. Preparation of Mesoporous Calcium Doped Silica Spheres with Narrow Size Dispersion and Their Drug Loading and Degradation Behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 102, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Liu, Y.; Qi, S.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Huang, L.; Sun, L.B. Calcium Oxide-Modified Mesoporous Silica Loaded onto Ferriferrous Oxide Core: Magnetically Responsive Mesoporous Solid Strong Base. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 526, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, M.; Jiang, X.; Lv, R.; Mao, C. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Coated with Mesoporous Shells for Pb(II) Removal from Blood. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antarnusa, G.; Jayanti, P.D.; Denny, Y.R.; Suherman, A. Utilization of Co-Precipitation Method on Synthesis of Fe3O4/PEG with Different Concentrations of PEG for Biosensor Applications. Materialia 2022, 25, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, W.; Fink, A.; Ernst Bohn, D. Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paswan, S.K.; Kumari, S.; Kar, M.; Singh, A.; Pathak, H.; Borah, J.P.; Kumar, L. Optimization of Structure-Property Relationships in Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles Annealed at Different Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 151, 109928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeli, K.; Athanasiadou, A.; Makridis, A.; Malletzidou, L.; Vourlias, G.; Kontonasaki, E.; Lymperaki, E.; Angelakeris, M. Synthesis and characterization of a novel multifunctional magnetic bioceramic nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 24650–24659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeli, K.; Tsamesidis, I.; Theocharidou, A.; Malletzidou, L.; Rhoades, J.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Likotrafiti, E.; Chrissafis, K.; Lialiaris, T.; Papadopoulou, L.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Calcium-Silicate Nanobioceramics with Magnesium: Effect of Heat Treatment on Biological, Physical and Chemical Properties. Ceramics 2021, 4, 628–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamesidis, I.; Gkiliopoulos, D.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Lymperaki, E.; Papoulia, C.; Reybier, K.; Perio, P.; Paraskevopoulos, K.M.; Kontonasaki, E.; Theocharidou, A. Effect of Artemisinin-Loaded Mesoporous Cerium-Doped Calcium Silicate Nanopowder on Cell Proliferation of Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakiou, E.A.; Lazaridou, M.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Michopoulou, A.; Tsamesidis, I.; Liverani, L.; Arango-Ospina, M.; Beketova, A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Kontonasaki, E.; et al. Poly(Glycerol Succinate) as Coating Material for 1393 Bioactive Glass Porous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsamesidis, I.; Theocharidou, A.; Beketova, A.; Bousnaki, M.; Chatzimentor, I.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Gkiliopoulos, D.; Kontonasaki, E. Artemisinin Loaded Cerium-Doped Nanopowders Improved In Vitro the Biomineralization in Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, A.; Farjami Shayesteh, S.; Salouti, M.; Boustani, K. Effect of Annealing Temperature on Magnetic Phase Transition in Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 379, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dib, F.I.; Mohamed, D.E.; El-Shamy, O.A.A.; Mishrif, M.R. Study the Adsorption Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles in the Presence of Different Synthesized Surfactants for Heavy Metal Ions Removal. Egypt. J. Pet. 2020, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Liverani, L.; Theocharidou, A.; Tsamesidis, I.; Lazaridou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Beketova, A.; Pappa, C.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Anastasiou, A.D.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Mg-and Sr-Doped Nanoparticles for Moxifloxacin Drug Delivery in Promising Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Lazaridou, M.; Papoulia, C.; Tsamesidis, I.; Chrissafis, K.; Vourlias, G.; Paraskevopoulos, K.M.; Bikiaris, D.; Kontonasaki, E. Electrospun PLGA Membranes with Incorporated Moxifloxacin-Loaded Silica-Based Mesoporous Nanocarriers for Periodontal Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, S.M.; Ghoshoon, M.B.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y.; Dehshahri, A.; Ebrahiminezhad, A. Impacts of Magnetic Immobilization on the Recombinant Proteins Structure Produced in Pichia Pastoris System. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Turki, T.; Boubakri, A.; Ben Amor, M.; Mzoughi, N. Study of Cadmium Adsorption onto Calcite Using Full Factorial Experiment Design. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 83, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Preparation, Surface Functionalization and Application of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 281, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D. Extension of the Stöber Method to Construct Mesoporous SiO2 and TiO2 Shells for Uniform Multifunctional Core–Shell Structures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wu, R.; Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Shen, M.; Xu, W.; Huang, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Gao, C.; et al. Nonstoichiometric Wollastonite Bioceramic Scaffolds with Core–Shell Pore Struts and Adjustable Mechanical and Biodegradable Properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 88, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Guo, L.; Zheng, T.; Cai, Q.; Yang, X. Formation of Core–Shell Structured Calcium Silicate Fiber via Sol–Gel Electrospinning and Controlled Calcination. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 23975–23983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketova, A.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Kontonasaki, E.; Giourieva, V.; Smits, K.; Stepanova, V.; Tsamesidis, I.; Choudhary, R.; Rubenis, K.; Eiduks, T.V.; et al. Zn containing mesoporous bioglasses with enhanced textural and antibacterial properties produced by three modifications of the sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2025, 36, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.A.; Essien, E.R.; Kaufmann, E.E. A New Route to Sol–Gel Crystalline Wollastonite Bioceramic. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 6, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, C.; Yun, J.Y.; Jang, J. Designed synthesis of SiO2/TiO2 core/shell structure as light scattering material for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4815–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaria, A.; Soulé, S.; Hallali, N.; Ojo, W.S.; Mirjolet, M.; Fuks, G.; Cornejo, A.; Allouche, J.; Dupin, J.C.; Martinez, H.; et al. Silica Coated Iron Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Interface Control, Magnetic and Hyperthermia Properties. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 32146–32156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaraju, P.L.; Meka, A.K.; Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Jambhrunkar, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Yu, M.; Yu, C. Asymmetric Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Head-Tail Structures Enhance Hemocompatibility and Maturation of Immune Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6321–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, P.; Sztorch, B.; Martyła, A.; Czapik, A.; Stodolny, M.; Przekop, R.E. Metallic Calcium as a Precursor for Sol–Gel Synthesis of CaCO3-SiO2 and CaO-SiO2 Systems. Ceramics 2021, 4, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.M.; Xu, S.C.; Li, G.H. Fe3O4@SiO2 Core/Shell Nanoparticles: The Silica Coating Regulations with a Single Core for Different Core Sizes and Shell Thicknesses. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4572–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterary, S.S.; Alkhamees, A. Synthesis, Surface Modification, and Characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2core@shell Nanostructure. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, B.N.; Shi, C.W. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Self-Assembly of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles with the Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 5453–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, W.; Song, X. Multifunctional Triple-Porous Fe3O4@SiO2 Superparamagnetic Microspheres for Potential Hyperthermia and Controlled Drug Release. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32049–32057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, P.; Batlle-Brugal, B.; Roca, A.G.; Iglesias, O.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J.; Labarta, A.; Batlle, X. Surfactant Effects in Magnetite Nanoparticles of Controlled Size. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, e756–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Oh, Y.; Phan, T.T.V.; Mondal, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Modified Mesoporous Silica Hybrid for PH-Responsive Drug Delivery and Magnetic Hyperthermia Applications. J. Porous Mater. 2018, 25, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Mao, F.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Bai, Z. Sulfhydryl-Modified Fe3O4@SiO2 Core/Shell Nanocomposite: Synthesis and Toxicity Assessment in Vitro. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14983–14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, W.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xiong, Y.; Lai, W.; Xu, H.; Wei, H. Size Dependent Biodistribution and Toxicokinetics of Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles in Mice. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, E.; Hwang, H.-M. In Vitro Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Different Coatings and Different Sizes in A3 Human T Lymphocytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4475–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, N.; Geng, X.; Meng, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Osteogenic Capacity and Cytotherapeutic Potential of Periodontal Ligament Cells for Periodontal Regeneration in Vitro and in Vivo. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Kang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Chai, Y. Regeneration of Large Bone Defects Using Mesoporous Silica Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles during Distraction Osteogenesis. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, A.; Xue, J.; Deb, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Bone Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, P.; Johansson, A.; Jugdaohsingh, R.; Powell, J.J.; Magnusson, C.; Davila, M.; Westerlund, A.; Ransjö, M. Soluble Silica Stimulates Osteogenic Differentiation and Gap Junction Communication in Human Dental Follicle Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xynos, I.D.; Edgar, A.J.; Buttery, L.D.K.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Ionic Products of Bioactive Glass Dissolution Increase Proliferation of Human Osteoblasts and Induce Insulin-like Growth Factor II MRNA Expression and Protein Synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marycz, K.; Sobierajska, P.; Wiglusz, R.; Idczak, R.; Nedelec, J.-M.; Fal, A.; Kornicka-Garbowska, K. Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Under Static Magnetic Field Improve Osteogenesis via RUNX-2 and Inhibit Osteoclastogenesis by the Induction of Apoptosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10127–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, Y.; Golovkin, A.; Malashicheva, A.; Korolev, D.; Gorshkov, A.; Gareev, K.; Afonin, M.; Galagudza, M. In Vitro Toxicity of FemOn, FemOn-SiO2 Composite, and SiO2-FemOn Core–Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, R.; Sivakumaran, G.; Mallén, J.; Lindén, M. Superparamagnetic Core–Mesoporous Silica Shell Nanoparticles with Tunable Extra- and Intracellular Dissolution Rates. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Composition |
|---|---|
| Fe3O4 | magnetic core FeCl3•6H2O 98%, FeSO4•7H2O 98%, NH4OH 25% |
| Fe3O4/mSi_1 | Silica shell TEOS:Ca2+ → 100:0 TEOS, CTAB, NH3 25 wt%, CH3CH2OH |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1A | Silica shell Ca-enriched TEOS:Ca2+ → 60:40 TEOS, CTAB, NH3 25 wt%, CH3CH2OH, Ca(NO3)2•4H2O |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1B | Silica shell Ca-enriched TEOS:Ca2+ → 90:10 TEOS, CTAB, NH3 25 wt%, CH3CH2OH, Ca(NO3)2•4H2O |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1C | Silica shell Ca-enriched (wet impregnation) TEOS:Ca2+ → 60:40 TEOS, CTAB, NH3 25 wt%, CH3CH2OH, Ca(NO3)2•4H2O |
| Fe3O4/mSi_2 | Silica shell TEOS:Ca2+ → 100:0 TEOS, CTAB, C6H15NO3, C6H5Cl |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_2 | Silica shell Ca-enriched TEOS:Ca2+ → 60:40 TEOS, CTAB, C6H15NO3, C6H5Cl, Ca(NO3)2•4H2O |
| Fe3O4/mSi_1 | |||||||||
| State #0 | Etch Time | 0.00 s | |||||||
| Peak | Type | Position | FWHM | Raw Area | RSF | Atomic | Atomic | Mass | |
| BE (eV) | (eV) | (cps eV) | Mass | Conc % | Conc % | ||||
| C 1s | Reg | 284.720 | 2.001 | 2867.1 | 0.278 | 12.011 | 6.51 | 4.33 | |
| O 1s | Reg | 533.120 | 2.032 | 100,069.5 | 0.780 | 15.999 | 75.05 | 66.55 | |
| Fe 2p | Reg | 711.070 | 0.274 | 1377.6 | 2.957 | 55.846 | 0.26 | 0.80 | |
| Si 2p | Reg | 103.920 | 1.870 | 9052.6 | 0.328 | 28.086 | 18.19 | 28.32 | |
| Ca 2p | Reg | 352.670 | 0.000 | 0.0 | 1.833 | 40.078 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1C | |||||||||
| State #0 | Etch Time | 0.00 s | |||||||
| Peak | Type | Position | FWHM | Raw Area | RSF | Atomic | Atomic | Mass | |
| BE (eV) | (eV) | (cps eV) | Mass | Conc % | Conc % | ||||
| C 1s | Reg | 284.770 | 2.741 | 8620.8 | 0.278 | 12.011 | 22.62 | 15.22 | |
| O 1s | Reg | 532.870 | 2.307 | 67,094.5 | 0.780 | 15.999 | 58.18 | 52.17 | |
| Fe 2p | Reg | 711.220 | 1.377 | 2813.8 | 2.957 | 55.846 | 0.61 | 1.90 | |
| Si 2p | Reg | 103.470 | 1.902 | 7088.3 | 0.328 | 28.086 | 16.47 | 25.92 | |
| Ca 2p | Reg | 347.220 | 2.190 | 5412.2 | 1.833 | 40.078 | 2.13 | 4.78 | |
| Sample | MS [Am2/kg] |
|---|---|
| Fe3O4 | 63.0 |
| Fe3O4/mSi_1 | 39.5 |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1A | 60.00 |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1B | 32.3 |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1C | 18.7 |
| Fe3O4/mSi_2 | 54.1 |
| Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_2 | 30.4 |
| Fe3O4 | Fe3O4/mSi_1 | Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1A | Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1B | Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_1C | Fe3O4/mSi_2 | Fe3O4/mSi/Ca_2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Area (m2/g) | 85 | 355.4 | 125.9 | 49.489 | 463.3 | 100.4 | 82.6 |
| Pore Diameter (nm) | 25 | 2.52 | - | 16.0–30.1 (absorption) | - | 18.7 (absorption) | 29.5 (absorption) |
| 18.7 (desorption) | 2.18 (desorption) | 19.1 (desorption) | 18.2 (desorption) | ||||
| Total pore volume (cc/g) | 0.38 | 0.409 | 0.5563 | 0.278 | 0.415 | 0.5042 | 0.4621 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kordonidou, D.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Florini, N.; Tsamesidis, I.; Kazeli, K.; Gkiliopoulos, D.; Vourlias, G.; Angelakeris, M.; Komninou, P.; Patsalas, P.; et al. Calcium-Enriched Magnetic Core–Shell Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Potential Application in Bone Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241904
Kordonidou D, Pouroutzidou GK, Florini N, Tsamesidis I, Kazeli K, Gkiliopoulos D, Vourlias G, Angelakeris M, Komninou P, Patsalas P, et al. Calcium-Enriched Magnetic Core–Shell Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Potential Application in Bone Regeneration. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(24):1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241904
Chicago/Turabian StyleKordonidou, Despoina, Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Nikoletta Florini, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Konstantina Kazeli, Dimitrios Gkiliopoulos, George Vourlias, Makis Angelakeris, Philomela Komninou, Panos Patsalas, and et al. 2025. "Calcium-Enriched Magnetic Core–Shell Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Potential Application in Bone Regeneration" Nanomaterials 15, no. 24: 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241904
APA StyleKordonidou, D., Pouroutzidou, G. K., Florini, N., Tsamesidis, I., Kazeli, K., Gkiliopoulos, D., Vourlias, G., Angelakeris, M., Komninou, P., Patsalas, P., & Kontonasaki, E. (2025). Calcium-Enriched Magnetic Core–Shell Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Potential Application in Bone Regeneration. Nanomaterials, 15(24), 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241904









