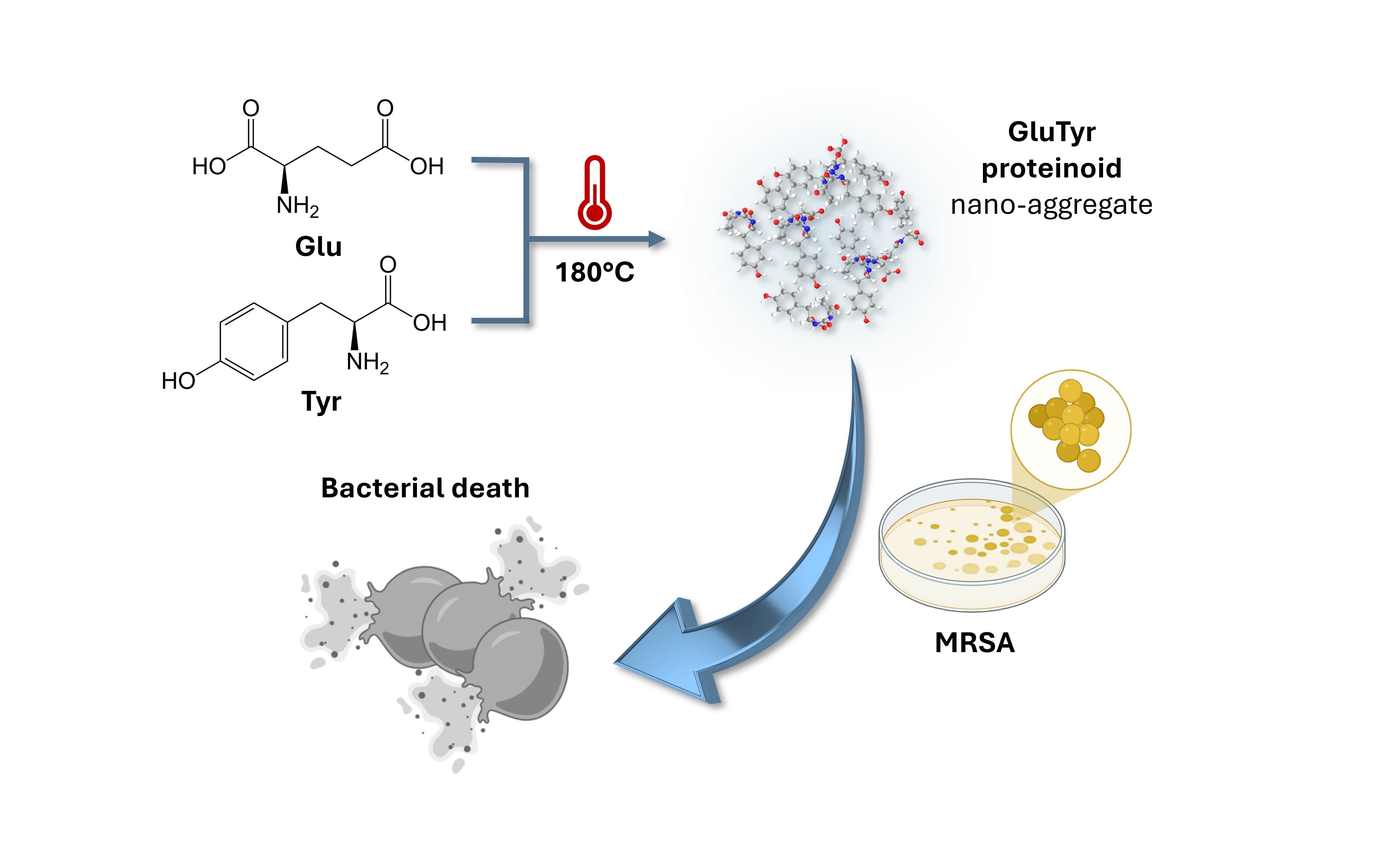
Antimicrobial Proteinoid Nanostructures via Thermal Condensation of L-Glutamic Acid and L-Tyrosine
Abstract
Share and Cite
Cadeddu, M.; Adams, J.R.G.; La Ragione, R.; Whelligan, D.K.; Stolojan, V.; Bernardi, N.; Smyrnias, I.; Poddesu, B.; Cugia, G.; De Forni, D.; et al. Antimicrobial Proteinoid Nanostructures via Thermal Condensation of L-Glutamic Acid and L-Tyrosine. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241846
Cadeddu M, Adams JRG, La Ragione R, Whelligan DK, Stolojan V, Bernardi N, Smyrnias I, Poddesu B, Cugia G, De Forni D, et al. Antimicrobial Proteinoid Nanostructures via Thermal Condensation of L-Glutamic Acid and L-Tyrosine. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(24):1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241846
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadeddu, Marta, James R. G. Adams, Roberto La Ragione, Daniel K. Whelligan, Vlad Stolojan, Nadia Bernardi, Ioannis Smyrnias, Barbara Poddesu, Giulia Cugia, Davide De Forni, and et al. 2025. "Antimicrobial Proteinoid Nanostructures via Thermal Condensation of L-Glutamic Acid and L-Tyrosine" Nanomaterials 15, no. 24: 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241846
APA StyleCadeddu, M., Adams, J. R. G., La Ragione, R., Whelligan, D. K., Stolojan, V., Bernardi, N., Smyrnias, I., Poddesu, B., Cugia, G., De Forni, D., Malfatti, L., Carboni, D., Pinna, A., & Innocenzi, P. (2025). Antimicrobial Proteinoid Nanostructures via Thermal Condensation of L-Glutamic Acid and L-Tyrosine. Nanomaterials, 15(24), 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241846