A Novel Zn-Cu Bimetallic Mixed-Component MOFs Composite for Efficient CO2 Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Gas Adsorption and Desorption Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs
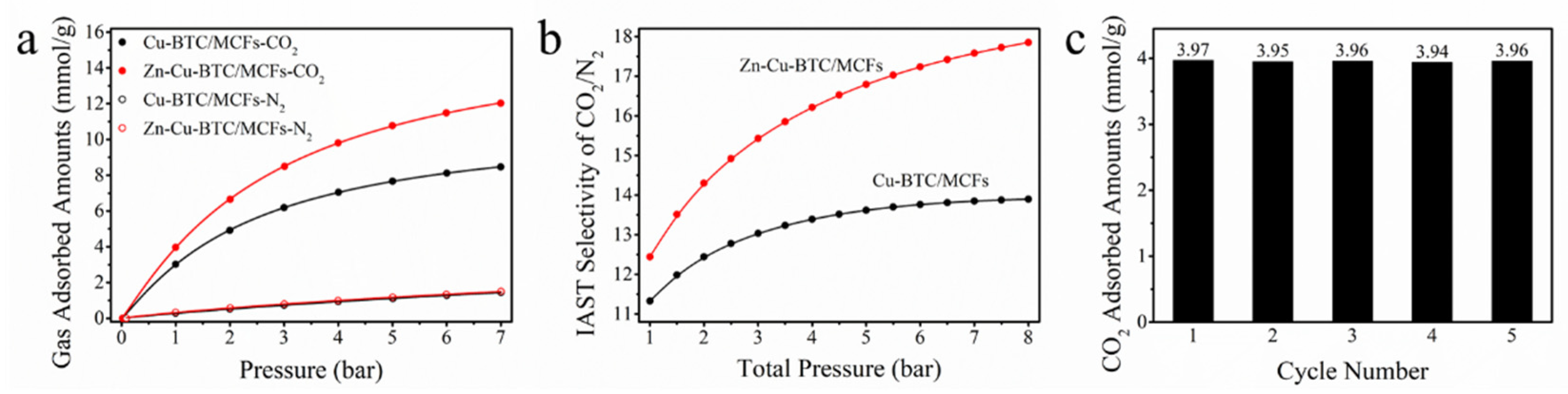
3.2. Gas Adsorption Isotherms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, S.; Tao, Z.; Yang, C.; Hanif, A.; Li, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Gu, Q.; Shang, J. Facile synthesis of CuBTC and its graphene oxide composites as efficient adsorbents for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, A.-V.; Petrescu, L. Membrane technology applied to steel production: Investigation based on process modelling and environmental tools. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpooya, M.; Esfilar, R.; Moosavian, S.M.A. Introducing a novel air separation process based on cold energy recovery of LNG integrated with coal gasification, transcritical carbon dioxide power cycle and cryogenic CO2 capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.K.; Yoon, T.-U.; Bae, Y.-S.; Jhung, S.H. Metal-organic framework MIL-101 loaded with polymethacrylamide with or without further reduction: Effective and selective CO2 adsorption with amino or amide functionality. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, W.; Miao, J.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. Enhanced separation performance of a novel composite material GrO@MIL-101 for CO2/CH4 binary mixture. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slostowski, C.; Marre, S.; Dagault, P.; Babot, O.; Toupance, T.; Aymonier, C. CeO2 nanopowders as solid sorbents for efficient CO2 capture/release processes. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 20, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, D. Vacuum pressure swing adsorption process with carbon molecular sieve for CO2 separation from biogas. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 54, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hillesheim, P.C.; Mahurin, S.M.; Wang, C.; Tian, C.; Brown, S.; Luo, H.; Veith, G.M.; Han, K.S.; Hagaman, E.W.; et al. Efficient CO2 capture by porous, nitrogen-doped carbonaceous adsorbents derived from task-specific ionic liquids. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, E.; Huang, R.; Wang, J.; Hao, Y.; Hao, X. Encapsulated HKUST-1 nanocrystal with enhanced vapor stability and its CO2 adsorption at low partial pressure in unitary and binary systems. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, M.; Talaie, M.R.; Sabzyan, H.; Aghamiri, S.; Chen, P. Evaluating equilibrium and kinetics of CO2 and N2 adsorption into amine-functionalized metal-substituted MIL-101 frameworks using molecular simulation. Fuel 2022, 308, 121965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, M.; Li, G.; Li, H. Selective binding and removal of guests in a microporous metal-organic framework. Nature 1995, 378, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, F.; Lin, R.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y. Enabling photocatalytic hydrogen production over Fe-based MOFs by refining band structure with dye sensitization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Singhal, J.; Lee, H.K.; Chae, K.H. Drug delivery of paracetamol by metal-organic frameworks (HKUST-1): Improvised synthesis and investigations. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbalkan, H.C.; Haslak, Z.P.; Altintas, C.; Uzun, A.; Keskin, S. Assessing CH4/N2 separation potential of MOFs, COFs, IL/MOF, MOF/Polymer, and COF/Polymer composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hao, X.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Y.; Niu, B.; Li, C. Flexible H2S sensors: Fabricated by growing NO2-UiO-66 on electrospun nanofibers for detecting ultralow concentration H2S. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 573, 151446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, S.S.-Y.; Lo, S.M.-F.; Charmant, J.P.H.; Orpen, A.G.; Williams, I.D. A Chemically Functionalizable Nanoporous Material [Cu3(TMA)2(H2O)3]n. Science 1999, 283, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Zou, W.; Wan, H.; Dong, L.; Guan, G. Layer-by-layer self-assembly of hierarchical flower-like HKUST-1-based composite over amino-tethered SBA-15 with synergistic enhancement for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Komarneni, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z. Extremely enhanced CO2 uptake by HKUST-1 metal-organic framework via a simple chemical treatment. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2014, 183, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; Dai, W.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H. Enhanced adsorption of dibenzothiophene with zinc/copper-based metal-organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21044–21050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Q. Bimetallic Metal–Organic Frameworks for Gas Storage and Separation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, Z.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, M.Y.; Shahid, M. Emerging trends in N-based metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for CO2 sequestration and catalytic conversion into value-added products: An integrated strategy for clean energy solutions. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2026, 548, 217190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Fan, S.; Matus, E.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Li, L.; Xiao, F. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of CO2 on mesocellular foams modified HKUST-1: Experiment and simulation. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 44, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Min, X.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Zhao, F. In-situ synthesis of highly dispersed Cu-CuxO nanoparticles on porous carbon for the enhanced persulfate activation for phenol degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Zhao, N.; Zhan, H.; Xiao, F.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. Phase transition of silica in the TMB-P123-H2O-TEOS quadru-component system: A feasible route to different mesostructured materials. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 433, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, J.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Dietrich, A.M. Insights into metal-organic frameworks HKUST-1 adsorption performance for natural organic matter removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 126918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Li, P.; Zhong, J. Facile preparation of low-cost HKUST-1 with lattice vacancies and high-efficiency adsorption for uranium. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, W. Bisphenol S degradation via persulfate activation under UV-LED using mixed catalysts: Synergistic effect of Cu-TiO2 and Zn-TiO2 for catalysis. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Du, W.; Shi, D.; Ning, W.; Lu, X.; Hou, Z. Metal-organic framework derived Cu/ZnO catalysts for continuous hydrogenolysis of glycerol. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 203, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Rehman, A.U.; Kan, K.; Li, L.; Shi, K. Synthesis; characterization, and ammonia gas sensing properties of Co3O4@CuO nanochains. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 52, 3757–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Sugahara, T.; Shimada, M. Facile fabrication of HKUST-1 thin films and free-standing MWCNT/HKUST-1 film using a spray-assisted method. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 312, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Ying, W.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Peng, X. Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS threaded HKUST-1 thin films. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13865–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raganati, F.; Gargiulo, V.; Ammendola, P.; Alfe, M.; Chirone, R. CO2 capture performance of HKUST-1 in a sound assisted fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shang, J.; Zhou, L.; Dong, W.; He, D. HKUST-1 and its graphene oxide composites: Finding an efficient adsorbent for SO2 capture. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 323, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, F.; Zhong, Q. Alkali metal cation doping of metal-organic framework for enhancing carbon dioxide adsorption capacity. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Lima, E.C.; Juang, R.-S.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Chao, H.-P. Thermodynamic parameters of liquid–phase adsorption process calculated from different equilibrium constants related to adsorption isotherms: A comparison study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yin, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Song, Q.; Zhao, N.; Xiao, F.; Wei, W. Numerical Simulation of CO2 Adsorption on K-Based Sorbent. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 4283–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, K. Synthesis of polybenzoxazine based nitrogen-rich porous carbons for carbon dioxide capture. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6534–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Song, Q.; Lin, J.; Li, G.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lee, C.-S.; Tang, C. In Situ Cu-Loaded Porous Boron Nitride Nanofiber as an Efficient Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7454–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, O.; Joseph, B.; Kuhn, J.N. CO2 separation from biogas using PEI-modified crosslinked polymethacrylate resin sorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 103, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, M.V.; Masoumifard, N.; Hu, Y.; Han, J.; Kleitz, F.; Fontaine, F.G. Designed Synthesis of Mesoporous Solid-Supported Lewis Acid-Base Pairs and Their CO2 Adsorption Behaviors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2018, 10, 13199–13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Y.; Najafi, M.; Khalili, S.; Jahanshahi, M.; Peyravi, M. Assembly of amine-functionalized graphene oxide for efficient and selective adsorption of CO2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 270, 124788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Sanz, R.; Orcajo, G.; Briones, D.; Yángüez, V. Amino-impregnated MOF materials for CO2 capture at post-combustion conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 142, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Bustam, M.A.; Assiri, M.A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Sagir, M.; Kareem, F.A.A.; Elkhalifah, A.E.I.; Mukhtar, A.; Gonfa, G. Synthesis, and characterization of metal-organic frameworks-177 for static and dynamic adsorption behavior of CO2 and CH4. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2019, 288, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lv, D.; Wu, J.; Xiao, J.; Xi, H.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z. A new MOF-505@GO composite with high selectivity for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sorbents | SBET (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Vmicro (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-BTC/MCFs | 1412 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 4.1 |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs | 1529 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 4.4 |
| Sorbents | Langmuir–Freundlich | AARD (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | n | R2 | ||
| Cu-BTC/MCFs-CO2 | 11.223 | 0.368 | 0.913 | 0.9998 | 0.1521 |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs-CO2 | 16.419 | 0.317 | 0.899 | 0.9999 | 0.2099 |
| Cu-BTC/MCFs-N2 | 6.440 | 0.045 | 1.046 | 0.9993 | 0.4939 |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs-N2 | 6.213 | 0.054 | 1.104 | 0.9987 | 0.3301 |
| Solid Materials | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (bar) | CO2 Adsorption Capacity (mmol/g) | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu@BNNF | 25 | 1 | 2.77 | [38] |
| 30PEI-HP2MGL | 25 | 1 | 2.70 | [39] |
| Ti-SBA-15 | 25 | 1 | 1.20 | [40] |
| GO-MPD | 25 | 1 | 0.91 | [41] |
| MIL-53(Al) | 45 | 1 | 1.14 | [42] |
| MOF-177 | 25 | 1 | 1.03 | [43] |
| MOF-505@5GO | 25 | 1 | 3.94 | [44] |
| Cu-BTC/MCFs | 25 | 1 | 3.14 | This work |
| Cu-BTC/MCFs | 35 | 1 | 3.02 | This work |
| Cu-BTC/MCFs | 45 | 1 | 2.65 | This work |
| Cu-BTC/MCFs | 55 | 1 | 2.43 | This work |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs | 25 | 1 | 4.05 | This work |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs | 35 | 1 | 3.97 | This work |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs | 45 | 1 | 3.82 | This work |
| Zn-Cu-BTC/MCFs | 55 | 1 | 3.60 | This work |
| Zn-BTC/MCFs | 35 | 1 | 0.30 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Yan, F.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M. A Novel Zn-Cu Bimetallic Mixed-Component MOFs Composite for Efficient CO2 Capture. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231777
Zhao H, Li L, Li J, Yan F, Wang W, Zhao M. A Novel Zn-Cu Bimetallic Mixed-Component MOFs Composite for Efficient CO2 Capture. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231777
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Haihong, Lei Li, Jiaxin Li, Feiqi Yan, Wenhao Wang, and Mingxia Zhao. 2025. "A Novel Zn-Cu Bimetallic Mixed-Component MOFs Composite for Efficient CO2 Capture" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231777
APA StyleZhao, H., Li, L., Li, J., Yan, F., Wang, W., & Zhao, M. (2025). A Novel Zn-Cu Bimetallic Mixed-Component MOFs Composite for Efficient CO2 Capture. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231777





