MnO2-Modified Carboxylated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Effective Extraction of Organochlorine Pesticides from Environmental Water Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Synthesis of CGO and MnO2@CGO
2.3.1. Synthesis of CGO
2.3.2. Synthesis of MnO2@CGO Nanocomposite
2.4. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.5. Optimization of µ-SPE Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
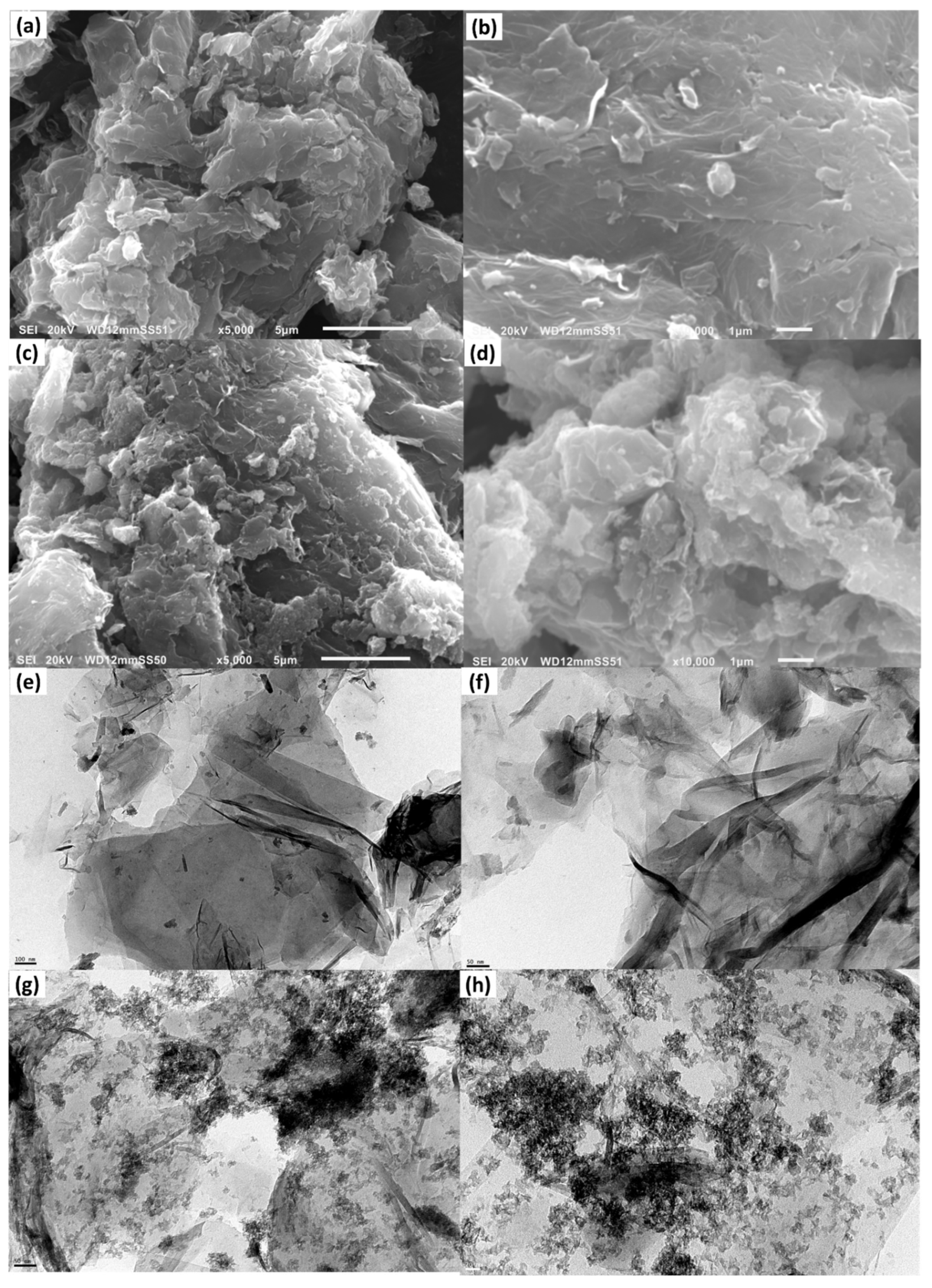
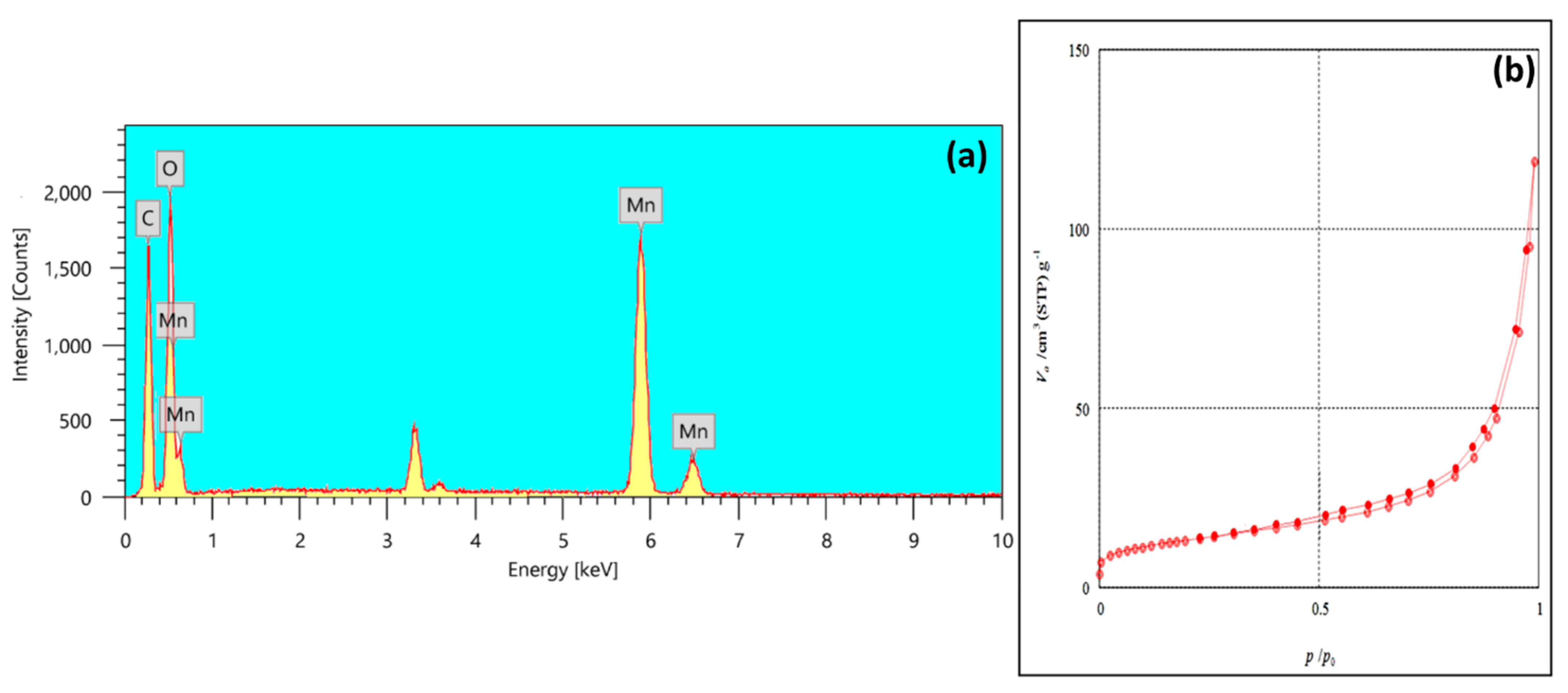
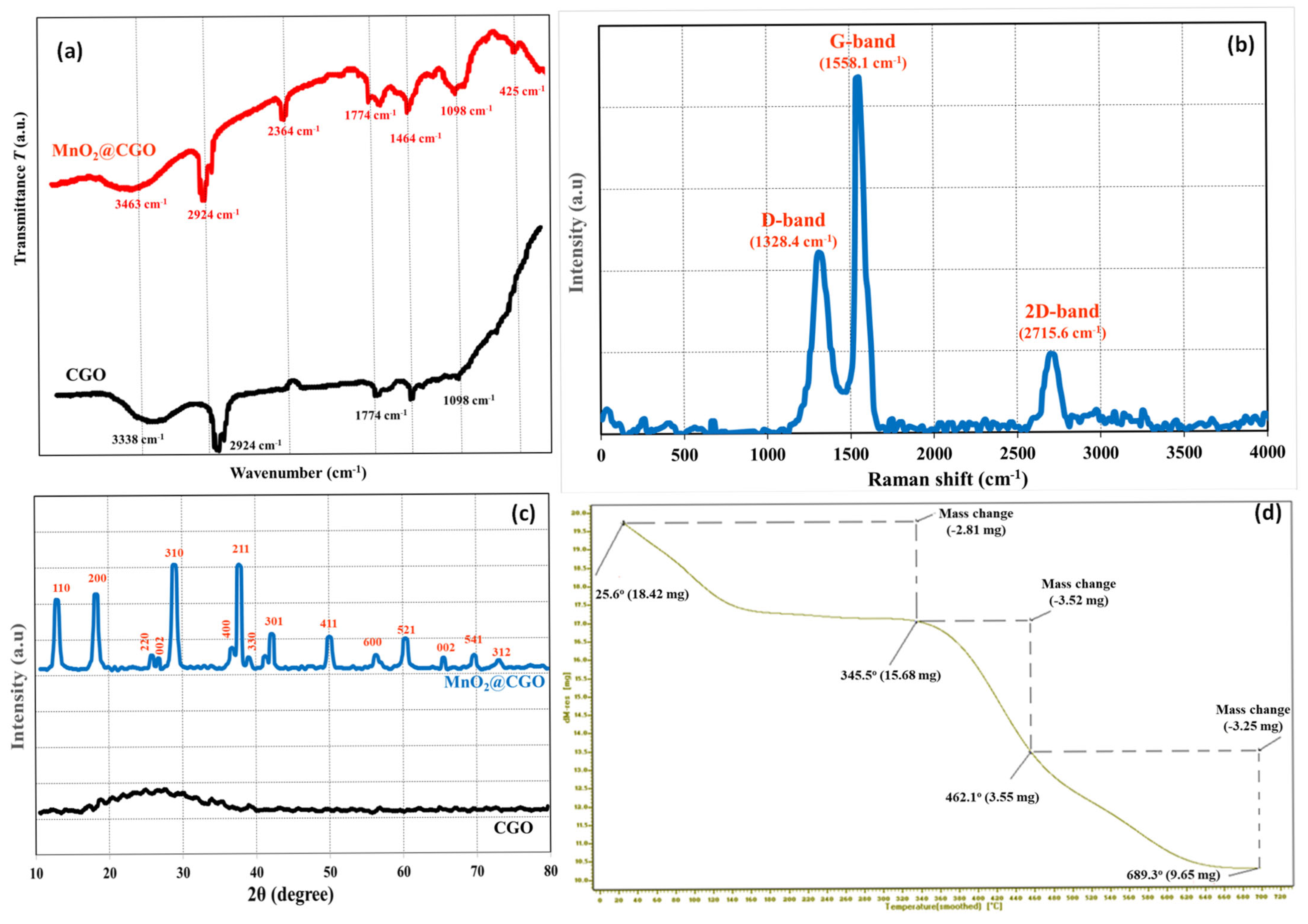
3.1. Characterization of the MnO2@CGO Nanocomposite
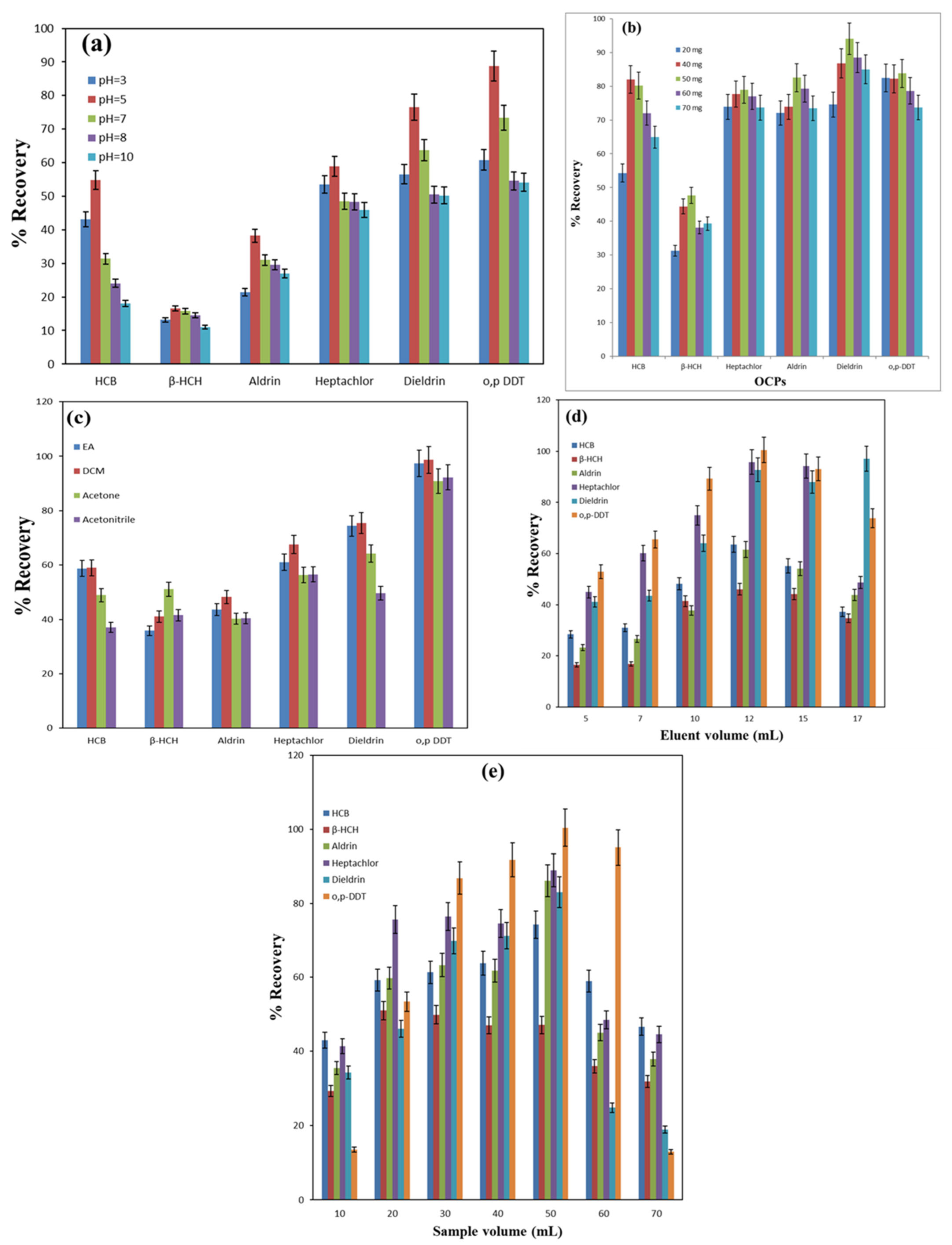
3.2. Optimization of µ-SPE of OCPs by MnO2@CGO Nanosorbent
3.2.1. Impact of pH
3.2.2. Impact of Nanosorbent Amount
3.2.3. Impact of Eluting Solvent
3.2.4. Effect of Eluent Volume
3.2.5. Effect of Sample Volume
3.3. Method Validation
3.3.1. Linearity
3.3.2. Sensitivity
3.3.3. Accuracy and Precision
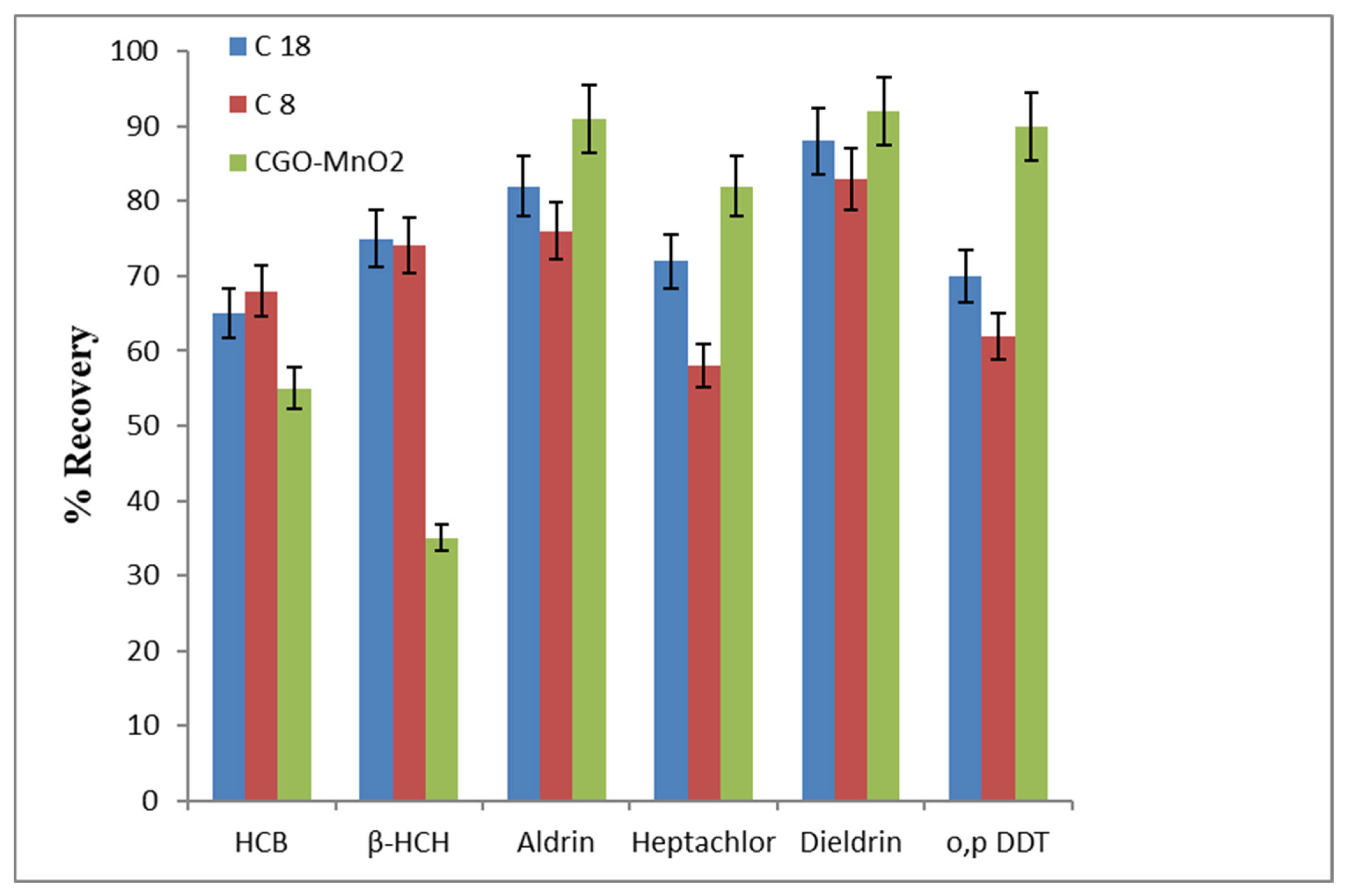
3.4. Comparison of µ-SPE Performance of MnO2@CGO with C8 and C18 Sorbents
3.5. Reusability of the CGO@MnO2 Nanosorbent
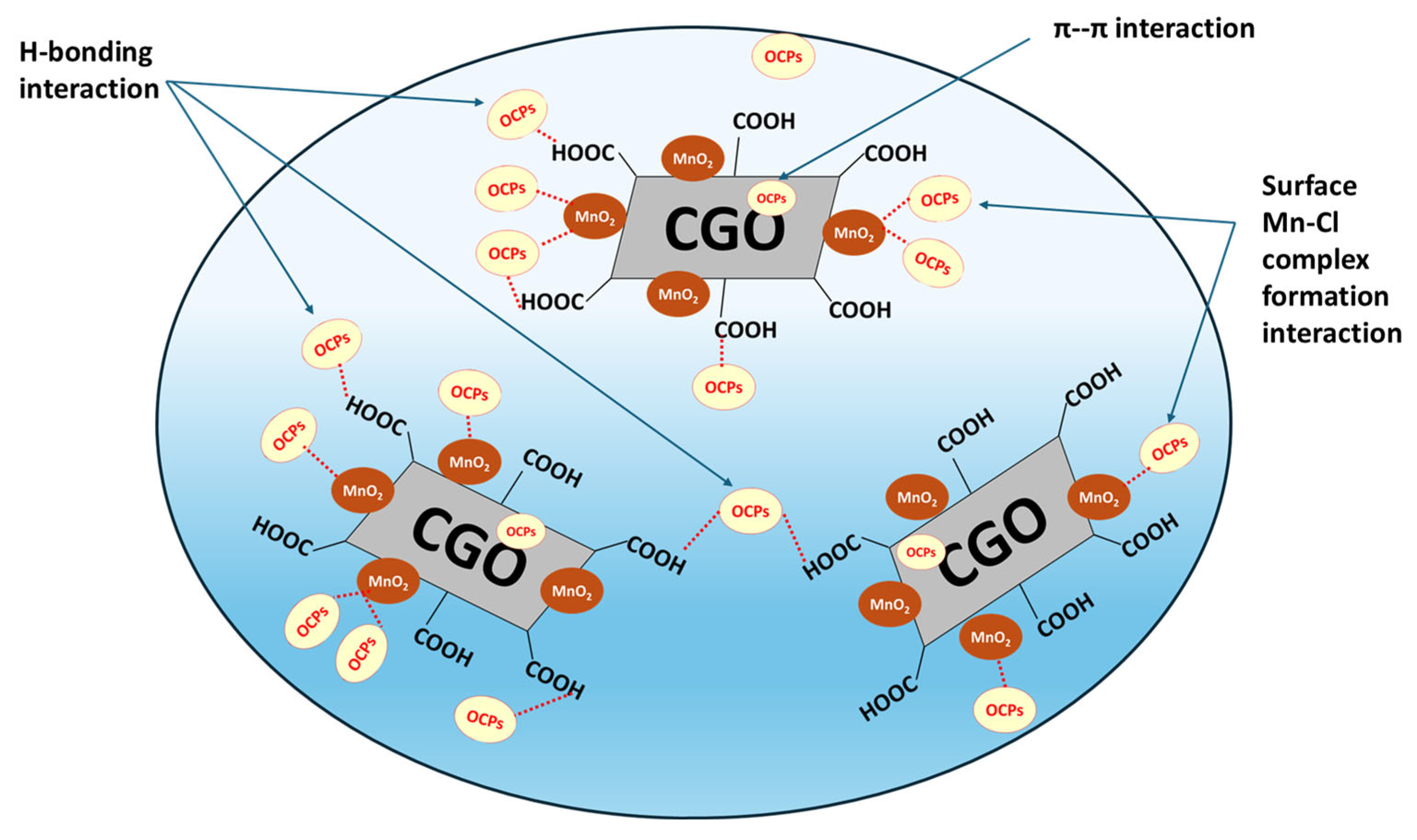
3.6. Mechanism of Adsorptive Extraction of OCPs by MnO2@CGO Nanocomposite
3.7. Analytical Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organisation. UN-Water. In UN-Water Global Analysis and Assessment of Sanitation and Drinking-Water (GLAAS); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Critical review on hazardous pollutants in water environment: Occurrence, monitoring, fate, removal technologies and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, B.H.S. Perspectives on general aspects of pollution toxicology. Afr. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 13, 240–292. Available online: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajce/article/view/240589 (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Yan, Y.; Yang, Y. Revealing the synergistic spatial effects in soil heavy metal pollution with explainable machine learning models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Pu, Y.; Tian, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, T.; Tao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Sun, X.; Mei, S. Concentrations of organochlorine pesticides in umbilical cord blood and related lifestyle and dietary intake factors among pregnant women of the Huaihe River basin in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hansen, S.; Rautio, A.; Dumas, P.; Odland, J.Ø. Assessment of genotoxicity and oxidative stress in pregnant women contaminated to organochlorine pesticides and its correlation with pregnancy outcome. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.; Gong, J.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Yao, F.-B.; Guo, M.; Ou, X.-M. Remediation of organochlorine pesticides contaminated lake sediment using activated carbon and carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temoka, C.; Wang, J.; Bi, Y.; Deyerling, D.; Pfister, G.; Henkelmann, B.; Schramm, K.-W. Concentrations and mass fluxes estimation of organochlorine pesticides in three gorges reservoir with virtual organisms using in situ PRC-based sampling rate. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, A.; Ali, U.; Mahmood, A.; Chaudhry, M.J.I.; Syed, J.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Jones, K.C.; Malik, R.N. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the Indus River catchment area, Pakistan: Status, soil-air exchange and black carbon mediated distribution. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.H.B.; Cavalcante, R.; Duaví, W.C.; Fernandes, G.M.; Nascimento, R.F.; Queiroz, M.E.L.R.; VMendonca, K. The legacy of organochlorine pesticide usage in a tropical semi-arid region (Jaguaribe River, Ceará, Brazil): Implications of the influence of sediment parameters on occurrence, distribution and fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Kameya, T.; Urano, K. Environmental management of pesticidal POPs in China: Past, present and future. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Sun, K.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, S.; Jia, L. Assessment of organochlorine pesticide residues in water, sediment, and fish of the Songhua River, China. Environ. Forensic 2014, 15, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wu, F.; He, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. Ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in surface waters of Lake Taihu, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 2013, 19, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, P.; Jiang, R.; Zhu, F.; Luan, T.; Ouyang, G. Monitoring of persistent organic pollutants in seawater of the Pearl River Estuary with rapid on-site active SPME sampling technique. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Liu, Q. Sources, concentrations and risk factors of organochlorine pesticides in soil, water and sediment in the Yellow River estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qi, S.; Yao, J.; Yang, D.; Xing, X.; Liu, H.; Qu, C. Contamination characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in multimatrix sampling of the Hanjiang River basin, southeast China. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, W. Distribution characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in soil, water, and sediment from the Bahe River, China. Environ. Forensic 2016, 17, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, X.; Mustavich, L.F.; Li, B.-L. Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günter, A.; Balsaa, P.; Werres, F.; Schmidt, T.C. Influence of the drying step within disk-based solid-phase extraction both on the recovery and the limit of quantification of organochlorine pesticides in surface waters including suspended particulate matter. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1450, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochennec, M.; Martin, D.E.; Laulier, B.; Baudouard, A.; Tierce, P.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Parinet, J.; Colombano, S. Ultrasound-assisted removal of organochlorine pesticide chlordecone from aqueous matrices. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 40, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hou, G.; Liu, F.; Luo, X. Records of human activities in sediments from the old Yellow River estuary, China: Concentrations, sources, and ecological risks of organochlorine pesticides. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 393, 127135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulizadeh, M.A.; Movassaghghazani, M.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides from honey samples in a narrow-bore tube prior to HPLC analysis. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 33896–33904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Fang, Y.; Mao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Song, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, R. Organochlorine pesticides: Occurrence and spatial distribution of residues, toxicity, and toxic mechanisms. Toxicology 2025, 515, 154134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altınışık Tağaç, A.; Erdem, P.; Seyhan Bozkurt, S.; Merdivan, M. Utilization of montmorillonite nanocomposite incorporated with natural biopolymers and benzyl functionalized dicationic imidazolium based ionic liquid coated fiber for solid-phase micro-extraction of organochlorine pesticides prior to GC/MS and GC/ECD. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1185, 339075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Chang, Q.; Pang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Solid-phase microextraction of eleven organochlorine pesticides from fruit and vegetable samples by a coated fiber with boron nitride modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Pandey, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.P. Iron nanoparticles decorated hierarchical carbon fiber forest for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of multi-pesticide residues from water samples. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olutona, G.O.; Ayano, S.A.; Obayomi-Davies, O. Organochlorine pesticide in water and bottom sediment from Aiba reservoir (southwestern Nigeria). Chem. Ecol. 2014, 30, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Albadri, A.; Aissa, M.A.B.; Modwi, A.; Saleh, S.M. High poisonous Cd ions removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 nanocomposite: Description and adsorption mechanism. Inorganics 2023, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, L.; Pei, Z.; Li, C.; Lv, J.; Xie, J.; Wen, B.; Zhang, S. Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics of Cr(III) on graphene oxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Zetterlund, P.B. Strategies for reduction of graphene oxide–a comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadil, Y.; Dinh, L.N.M.; Yap, M.O.Y.; Kuchel, R.P.; Yao, Y.; Omura, T.; Aregueta-Robles, U.A.; Song, N.; Huang, S.; Jasinski, F.; et al. Ambient-temperature waterborne polymer/rGO nanocompositefilms: Effect of rGO distribution on electrical conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 48450–48458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, M.; Hussain, Z.; Gao, L.; Asif, M.; Hanif, S.; Qin, Z.; Abbas, M.Q.; Zhou, A. Recent advances in graphene oxide and metal oxides composites synthesis and their applications in wastewater treatment: Removal of dyes, heavy metals, and pharmaceutical contaminants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 376, 133944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Kuntail, J.; Kumar, U.; Sinha, I. Co-adsorption mechanism of organic pollutants on NiFe2O4/GO nanostructures: Experimental and molecular dynamics studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munusamy, N.; Natarajan, S.B.; Chen, T.; Sengodan, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, S. 2D-layer of Graphene Oxide Incorporated with Transition Metal atoms of MnSnO2 for the Electrochemical detection of anti-androgen drug Nilutamide in Environmental samples. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, A.B.; Dara, A.; Taheri, H.S. Efficacious removal of mercury metal in food industry sewerage utilizing reduced graphene oxide adsorbent composited with magnetic nanoparticles. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 52, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Selective and fast removal and determination of β-lactam antibiotics in aqueous solution using multiple templates imprinted polymers based on magnetic hybrid carbon material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, M.A.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M. Multifunctional carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene oxide/polyaniline hybrid thin film for adsorptive removal of Cu(II) and oxytetracycline antibiotic from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Das, J.; Debnath, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Saha, B. Polyaniline-graphite on cellulose substrate: A flexible, low-cost, use-and-throw sensor for glucose concentration detection. Cellulose 2023, 30, 6423–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Debnath, A.; Deb, K.; Saha, B. Pressure Sensors Painted on Flexible Cellulose Substrates from Polyaniline-Based Conductive Ink. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 2988–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Das, J.; Deb, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Saha, B. A low-cost flexible material system made of PANI/graphite for resistive detection and quantitative determination of urea. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 301, 127573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Debnath, A.; Bera, A.; Sarkar, K.; Debnath, A.; Saha, B. Polyaniline encapsulated graphite: A sensitive system for resistive detection of methanol. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 16, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, A.Y.; Medhat, A.S. Dodecyl sulphate functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanosorbent for the investigation of fast and efficient removal of aqueous malachite green. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 63, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, A.A.; Albishri, H.M. Solvothermal synthesis of EDTA-functionalized magnetite-carboxylated graphene oxide nanocomposite as a potential magnetic solid phase extractor of p-phenylenediamine from environmental samples. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooladi, E.; Razavizadeh, B.M.; Noori, M.; Kakooei, S. Application of carboxylic acid-functionalized of graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in milk. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, T.T.; Tran, M.L.; Nguyen, C.H. Carboxylated graphene oxide: Characterization change and enhanced adsorption capacity towards Pb2+ and Cu2+ in wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 426, 127312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Qian, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Single-crystal α-MnO2nanorods: Synthesis and electrochemical properties. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 115616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barudžija, T.; Cvjetićanin, N.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Mojović, M.; Mitrić, M. Vibrational and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopic studies of β-MnO2 and α-K MnO2 nanorods. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ranasinghe, J.C.; Chatterjee, A.; Huang, S. Recent advances on Raman spectroscopy of graphene: Towards biosensing applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 318, 129281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, S.; Nawaz, T.; Durrani, M.A.; Ali, A.; Saher, S.; Khan, M.A.Z.; Egilmez, M.; Samreen, A.; Mustafa, F. Performance evaluation of graphene oxide–MnO2 nanocomposite for alkaline membrane fuel cell. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2021, 2, e2100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, P.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, D. Facile synthesis and strongly microstructure-dependent electrochemical properties of graphene/manganese dioxide composites for supercapacitors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Cheng, J.; Matsadiq, G.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, M. Application of dispersive Liquid–Liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet multi-residue method for the simultaneous determination of polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine, and pyrethroid pesticides in aqueous sample. CLEAN Soil. Air Water 2012, 40, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Gonzalo, A.; Sánchez-Uría, J.E.; Segovia-García, E.; Sanz-Medel, A. Selected ion storage versus tandem 325 MS/MS for organochlorine pesticides determination in drinking waters with SPME and GC-MS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2012, 92, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Han, Q.; Wang, X. Graphene Oxide−MNO2 nanocomposites for supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, S.; Tor, A.; Aydin, M.E. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles to Residue Analysis of Organochlorine Pesticides in Water Samples by GC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölgyessy, P.; Vrana, B.; Šilhárová, K. An improved method for determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediment by ultrasonic solvent extraction followed by stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to TD–GC-MS. Chromatographia 2012, 76, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Chen, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Qin, J.; Wang, S. Multi-residue determination of organophosphorus and organochlorine pesticides in environmental samples using solid-phase extraction with cigarette filter followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, A.A.; Khan, Z.A. High performance Zr-MnO2@reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for efficient and simultaneous remediation of arsenates As(V) from environmental water samples. J. Mol. Liquids. 2021, 334, 116427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, A.A.; Basha, M.T.; Al-Raimi, D.S.; Aljadaani, A.H.; Zainy, F.M.A. Synergistic impact of Cu and MnO2 nanoparticles in Cu/MnO2/chitosan/graphene oxide hybrid nanocomposite for improved antibacterial activity and fast adsorption of environmentally relevant anionic and cationic dyes from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 1, 144839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harthy, E.; Shaker, M.A.; Yakout, A.A. Synergetic Enhancement of Copper and Manganese Dioxide Nanoparticles With the Biobased Chitosan-crosslinked-graphene Nanocomposite for Potential Adsorptive Remediation of Tetracycline Antibiotics From Food Samples. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 112930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, A.A.; Alshutairi, A.M.; Albishri, H.M.; Alshitari, W.H.; Basha, M.T. Cu-nanoparticles@ graphene nanocomposite: A robust and efficient nanocomposite for micro-solid phase extraction of trace aflatoxins in different foodstuffs. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, A.A.; Alshitari, W.; Akhdhar, A. Synergistic effect of Cu-nanoparticles and β-cyclodextrin functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite on the adsorptive remediation of tetracycline antibiotics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
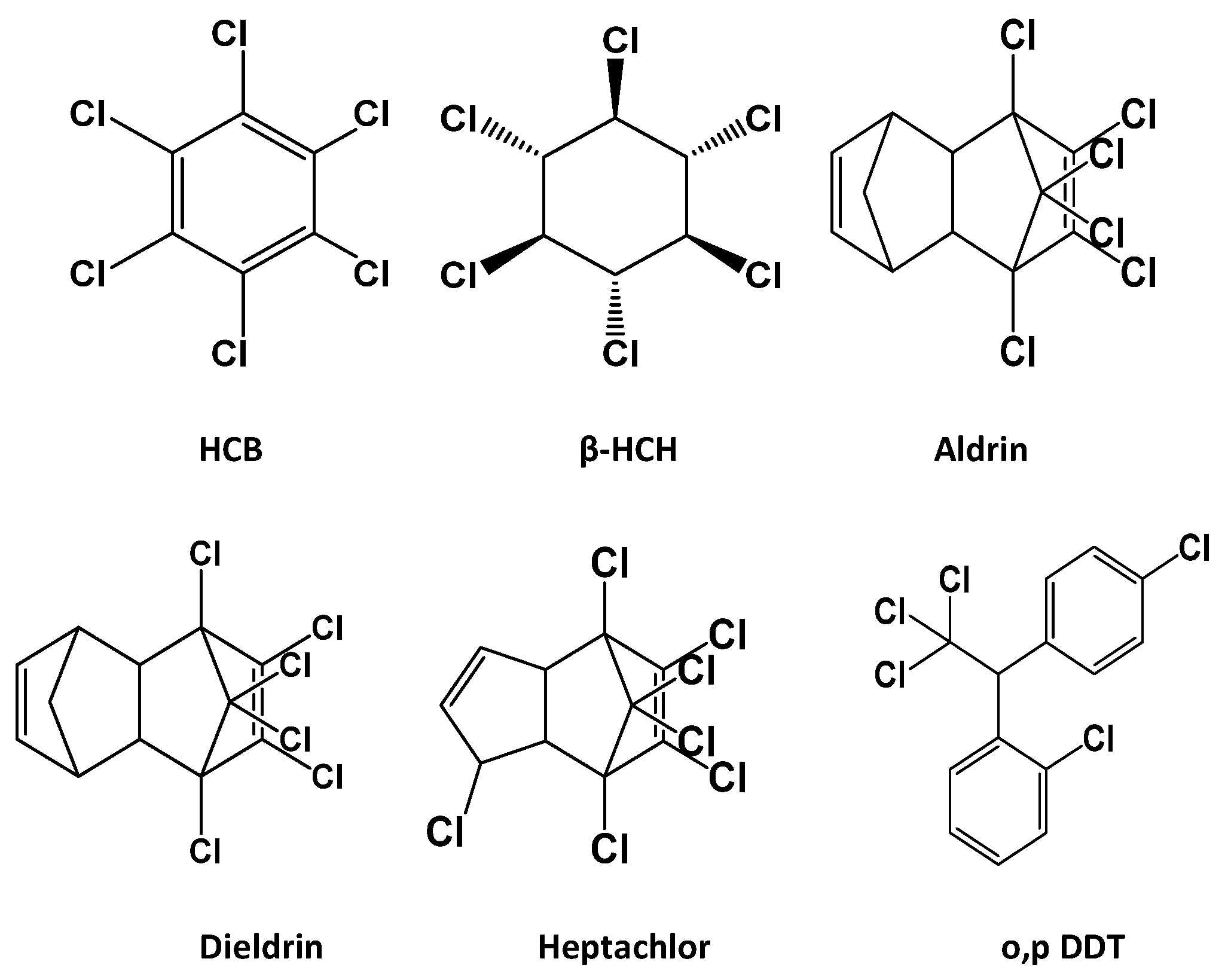
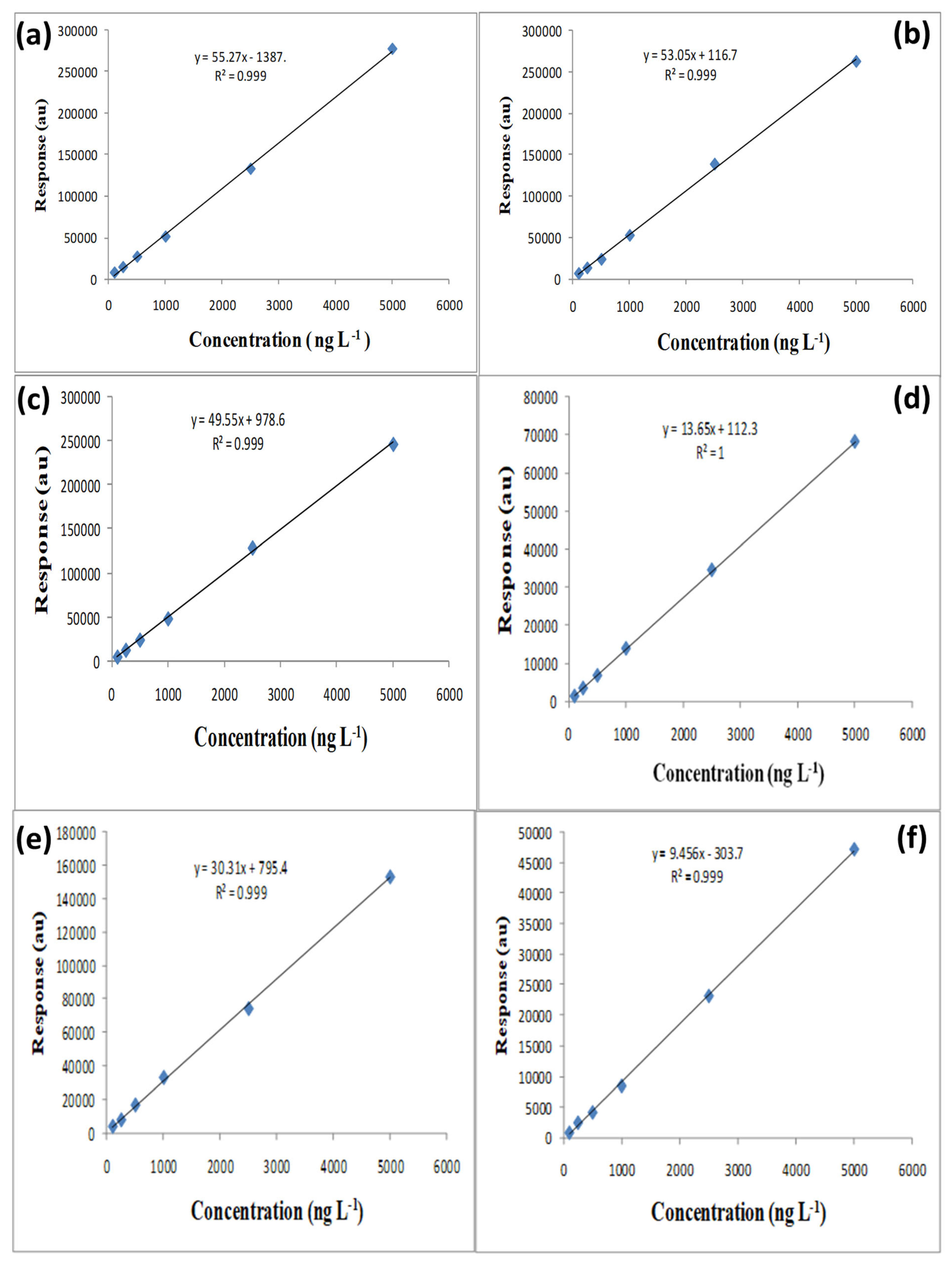
| OCP | Linear Range (μg L−1) | R2 | Regression Equation | LOQ (μg L−1) | LOD (μg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCB | 0.1–5.0 | 0.999 | Y = 53.05x + 116.7 | 10.0 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.5 |
| β-HCH | 0.1–5.0 | 0.998 | Y = 9.456x − 303.7 | 25.0 ± 1.5 | 12.5 ± 1.5 |
| Aldrin | 0.1–5.0 | 0.999 | Y = 12.85x + 599.6 | 25.0 ± 1.5 | 7.5 ± 1.5 |
| Heptachlor | 0.1–5.0 | 1.000 | Y = 55.27x + 138.7 | 25.0 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 1.0 |
| Dieldrin | 0.1–5.0 | 0.999 | Y = 30.31x + 795.4 | 20.0 ± 0.9 | 10.0 ± 0.9 |
| o,p-DDT | 0.1–5.0 | 0.998 | Y = 49.55x + 978.6 | 20.0 ± 0.8 | 7.5 ± 0.8 |
| OCP | Accuracy Percentage Recovery, %R | Precision % RSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 (0.25 μg L−1) | C2 (2.50 μg L−1) | C1 (0.25 μg L−1) | C2 (2.50 μg L−1) | |
| HCB | 70.16 ± 5.04 | 66.54 ± 2.00 | 5.36 | 4.01 |
| β-HCH | 34.51 ± 3.28 | 42.24 ± 5.90 | 8.7 | 3.17 |
| Aldrin | 90.2 ± 3.03 | 96.5 ± 6.09 | 3.05 | 1.15 |
| Heptachlor | 96.57 ± 3.25 | 91.84 ± 4.33 | 3.46 | 4.73 |
| Dieldrin | 95.79 ± 4.68 | 95.56 ± 1.88 | 2.89 | 3.28 |
| o,p-DDT | 99.65 ± 3.99 | 95.30 ± 3.50 | 6.06 | 1.71 |
| Method | Adsorbent Type | LOD (μg L−1) | Extraction Time (min) | % Recovery | % RSD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLLME | Organic solvent droplets | 1.81–3 | 2 | 90–105 | 7.6–10.4 | [51] |
| SPME | PDMS a PDMS/DVB b | 0.2–6.6 | 45 | 79–108 | ≤14 | [52] |
| MSPE | HLB-MPNPs c | 6–48 | 60 | 63.0–97.4 | 2.7–4.5 | [54] |
| SBSE | PDMS | 2.3–25.2 | 120 | 46.8–64.4 | ≤12.1 | [55] |
| SPE | Cigarette filter | 200 | - | 76.4–103.6 | 2.0–13.6 | [56] |
| µ-SPE | MnO2-CGO | 5–12.5 | 15 | 54.6–99.7 | 1.7–8.7 | The present work |
| OCPs | Spiked Conc. (μg L−1) | Percentages Recovery (% R) * ± % RSD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| River Water | Tap Water | Agricultural Wastewater Sample | |||
| Sample 1 (Abees Farm) | (Sample 2) Kafr-El Dawar Farm | ||||
| HCB | 0.0 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.25 | 69.31 ± 5.68 | 72.86 ± 5.68 | 62.85 ± 5.68 | 67.41 ± 5.68 | |
| 2.50 | 55.80 ± 3.65 | 57.64 ± 3.65 | 52.90 ± 3.65 | 52.54 ± 3.65 | |
| β-HCH | 0.0 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.25 | 62.64 ± 2.20 | 64.57 ± 2.20 | 63.50 ± 2.20 | 65.63 ± 2.20 | |
| 2.50 | 34.74 ± 4.86 | 37.03 ± 4.68 | 33.92 ± 4.68 | 32.20 ± 4.68 | |
| Aldrin | 0.0 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.25 | 84.48 ± 5.27 | 87.41 ± 5.27 | 85.69 ± 5.27 | 84.21 ± 5.27 | |
| 2.50 | 93.27 ± 1.95 | 90.12 ± 1.95 | 80.71 ± 1.95 | 82.87 ± 1.95 | |
| Heptachlor | 0.0 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.25 | 87.50 ± 3.62 | 87.50 ± 3.62 | 84.50 ± 3.62 | 88.73 ± 3.62 | |
| 2.50 | 93.40 ± 5.92 | 97.72 ± 5.92 | 87.90 ± 5.92 | 90.95 ± 5.92 | |
| Dieldrin | 0.0 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.25 | 91.86 ± 1.74 | 89.9 ± 1.74 | 88.08 ± 1.74 | 87.03 ± 1.74 | |
| 2.50 | 90.24 ± 3.58 | 90.74 ± 3.58 | 84.9 ± 3.58 | 83.15 ± 3.58 | |
| o,p-DDT | 0 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 0.25 | 91.08 ± 2.77 | 99.81 ± 2.77 | 86.45 ± 2.77 | 84.07 ± 2.77 | |
| 2.50 | 94.60 ± 4.90 | 97.17 ± 4.90 | 92.31 ± 4.90 | 91.42 ± 4.90 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaker, M.A.; Alshitari, W.H.; Aljadaani, A.H.; Zainy, F.M.A.; Al-Raimi, D.S.; Mahmoud, M.F.; El Husseiny, A.F.; Khalil, T.E.; Yakout, A.A. MnO2-Modified Carboxylated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Effective Extraction of Organochlorine Pesticides from Environmental Water Samples. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231757
Shaker MA, Alshitari WH, Aljadaani AH, Zainy FMA, Al-Raimi DS, Mahmoud MF, El Husseiny AF, Khalil TE, Yakout AA. MnO2-Modified Carboxylated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Effective Extraction of Organochlorine Pesticides from Environmental Water Samples. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231757
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaker, Medhat A., Wael H. Alshitari, Abeer H. Aljadaani, Faten M. Ali Zainy, Doaa S. Al-Raimi, Mustafa F. Mahmoud, Amel F. El Husseiny, Tarek E. Khalil, and Amr A. Yakout. 2025. "MnO2-Modified Carboxylated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Effective Extraction of Organochlorine Pesticides from Environmental Water Samples" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231757
APA StyleShaker, M. A., Alshitari, W. H., Aljadaani, A. H., Zainy, F. M. A., Al-Raimi, D. S., Mahmoud, M. F., El Husseiny, A. F., Khalil, T. E., & Yakout, A. A. (2025). MnO2-Modified Carboxylated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Effective Extraction of Organochlorine Pesticides from Environmental Water Samples. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231757






