Silicon-on-Silica Microring Resonators for High-Quality, High-Contrast, High-Speed All-Optical Logic Gates
Abstract
1. Introduction
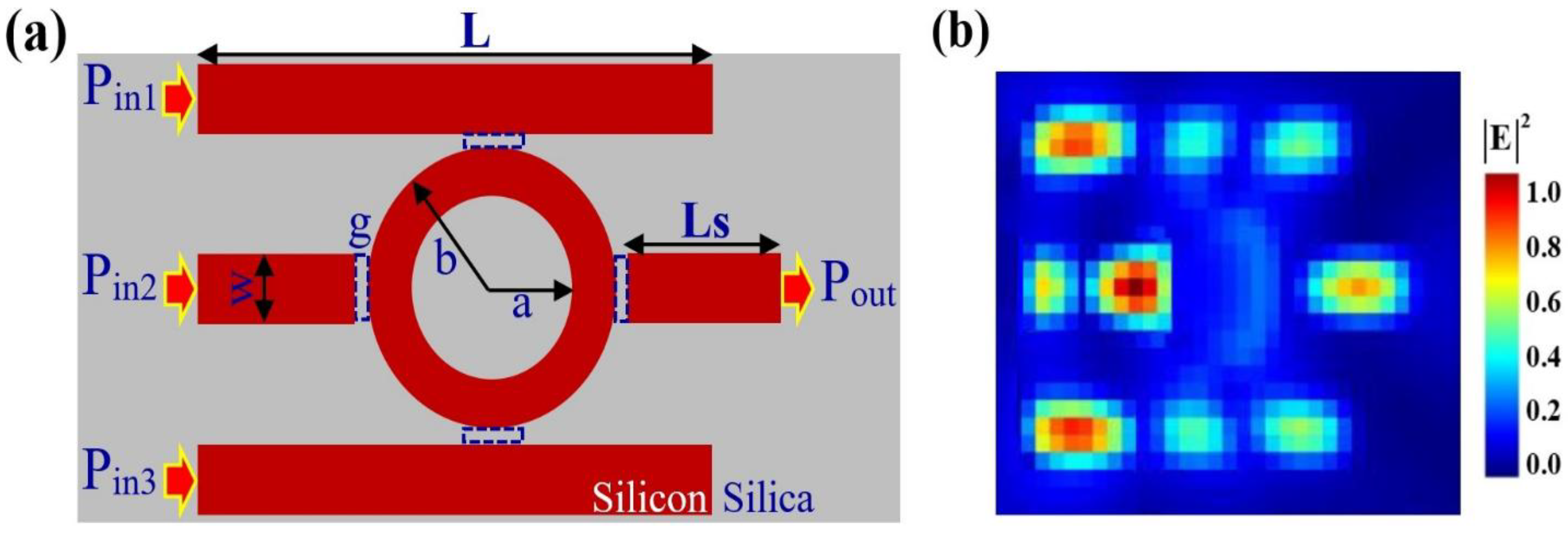
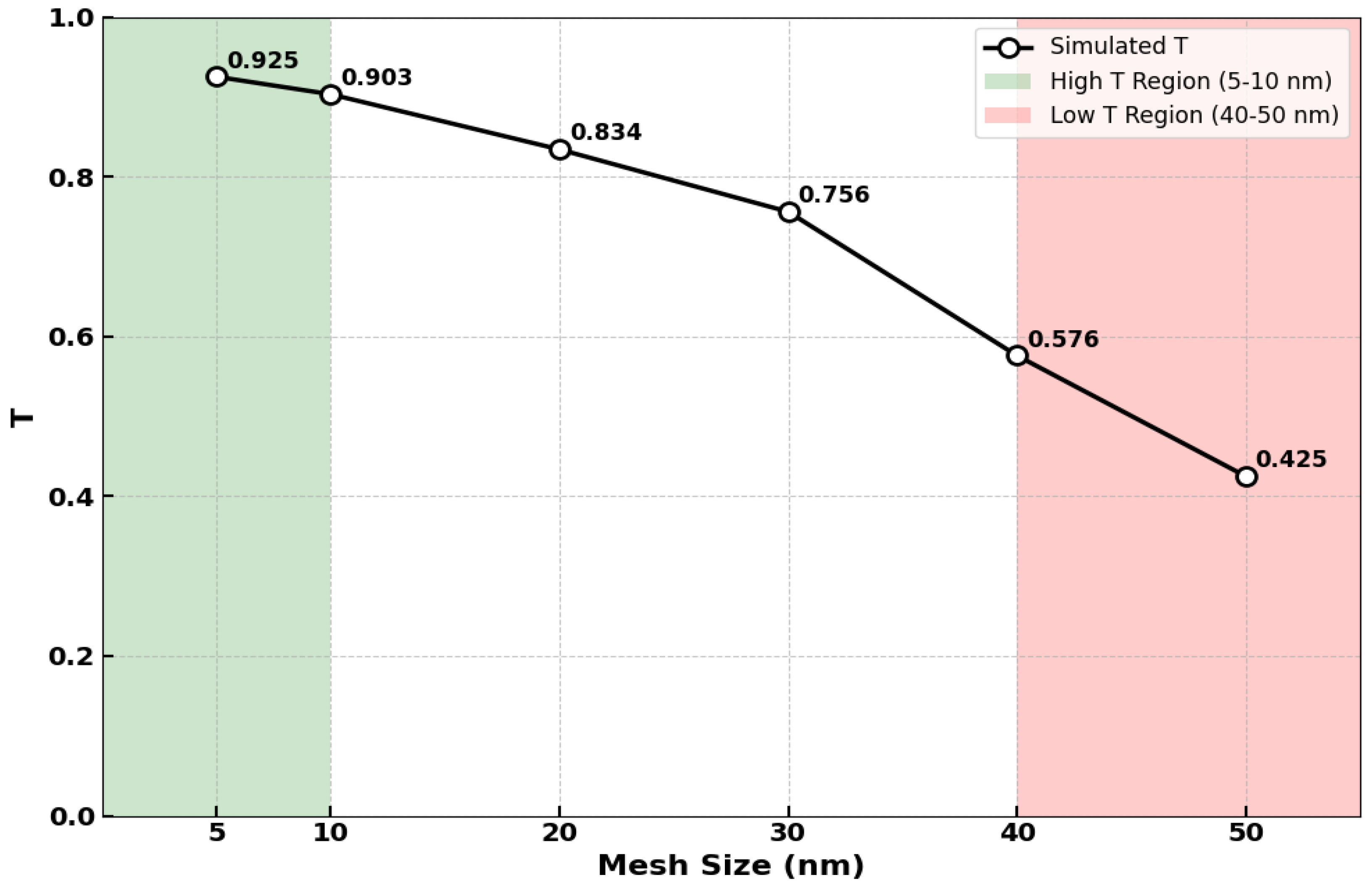
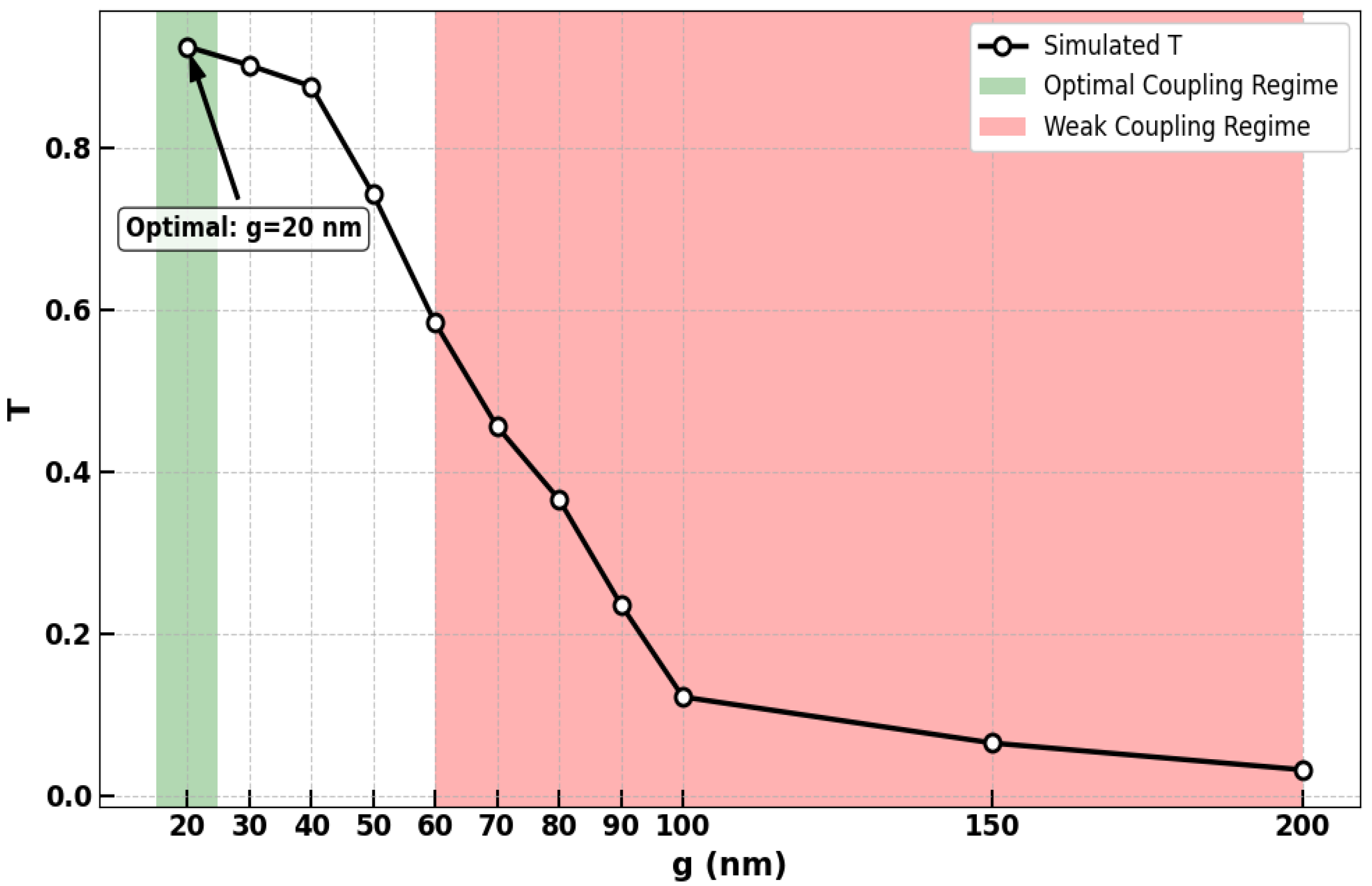
2. Device Design and Simulation Methodology
3. Operating Principle and Reconfigurable Framework
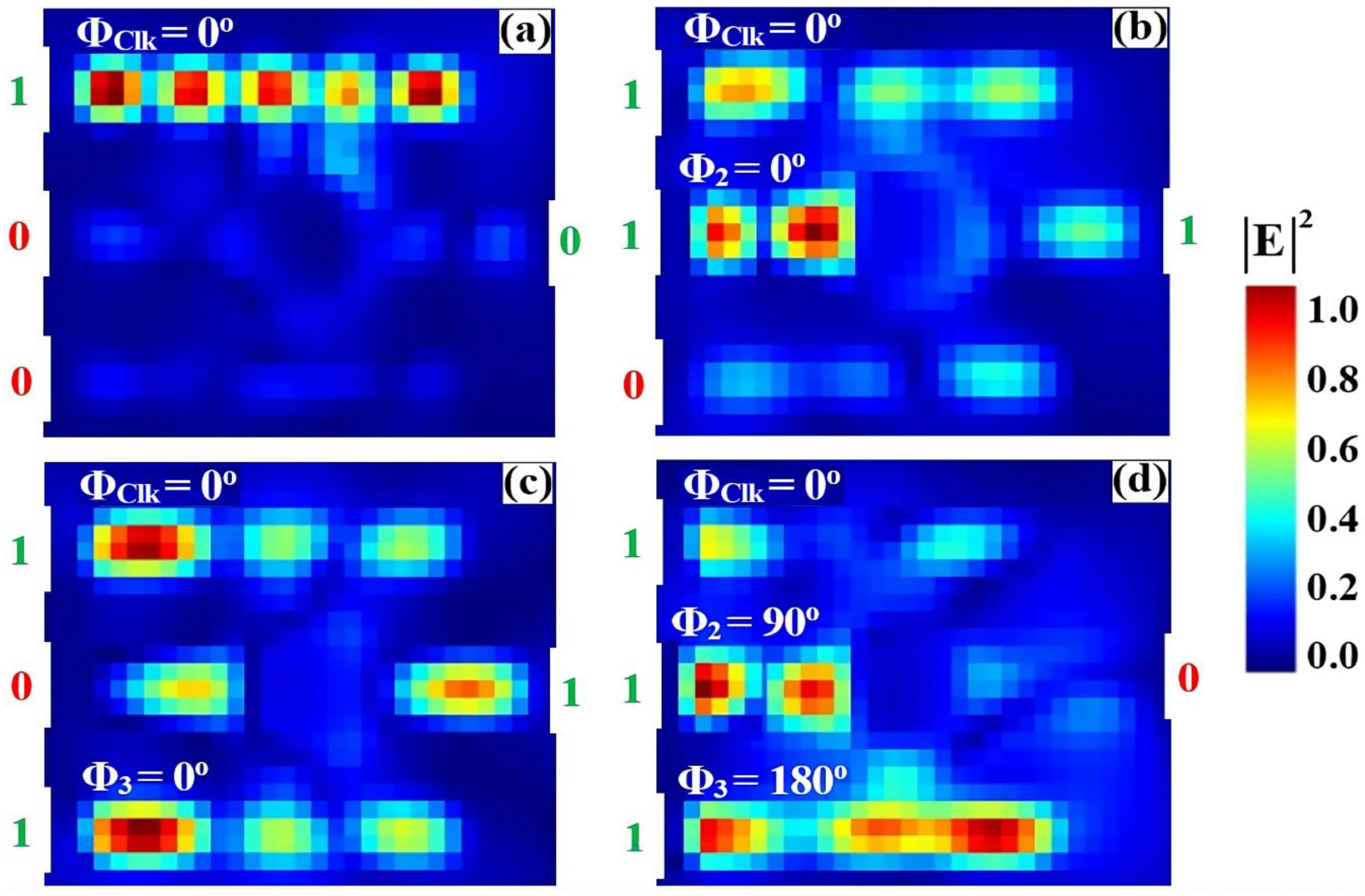
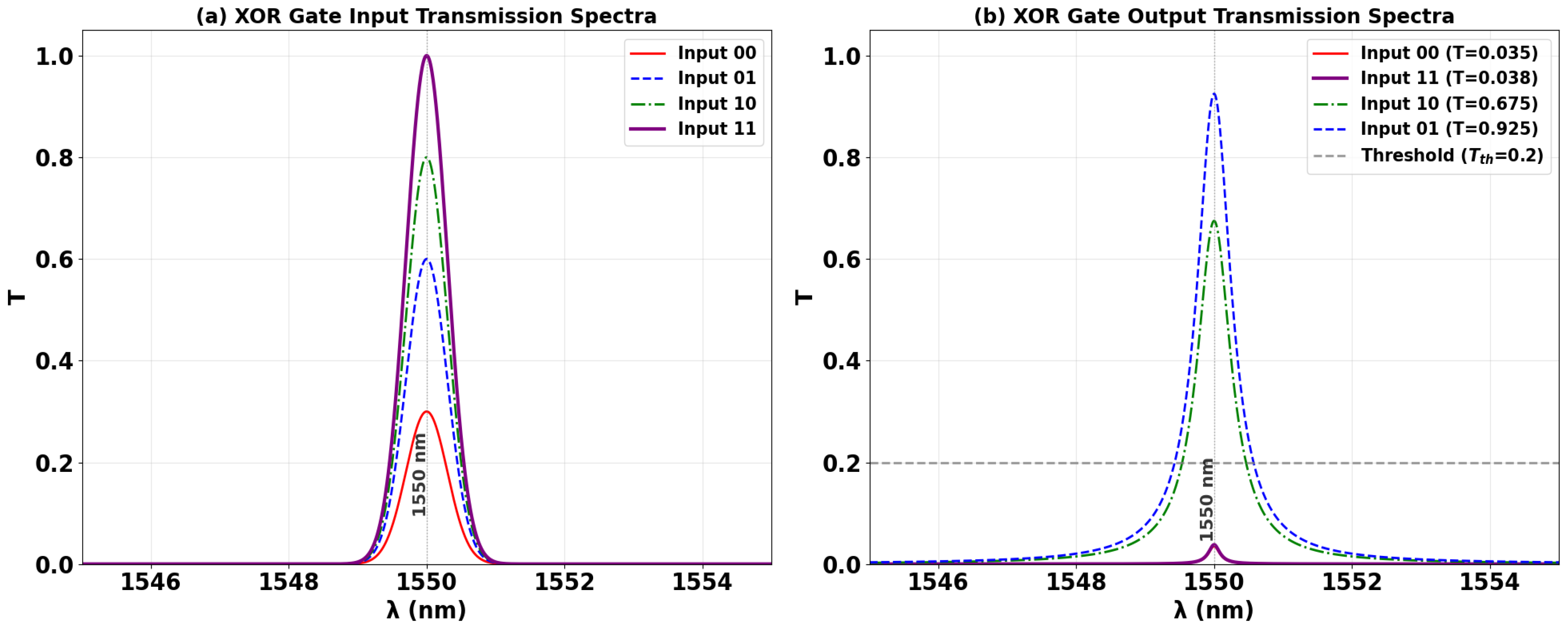
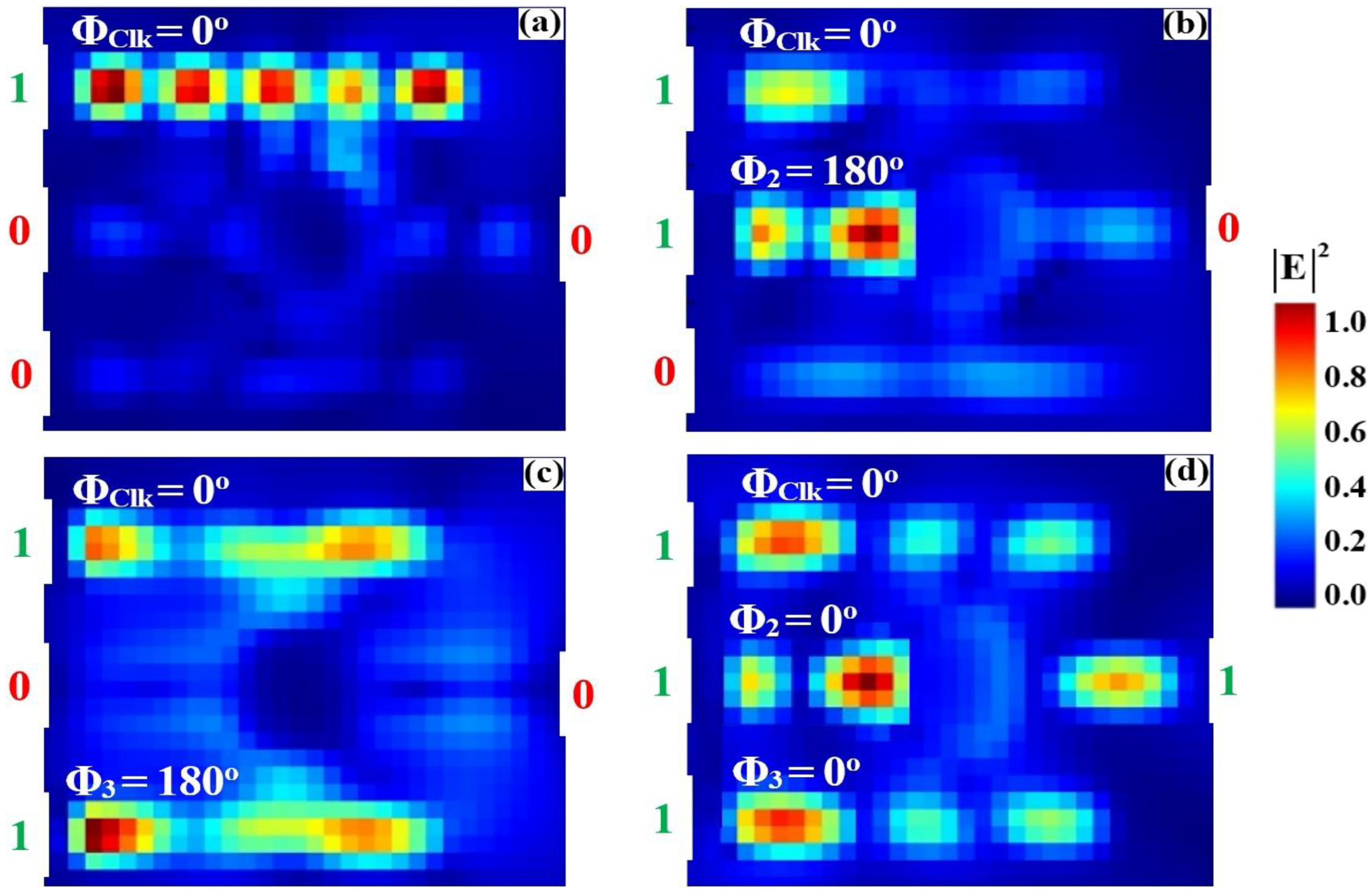
3.1. XOR
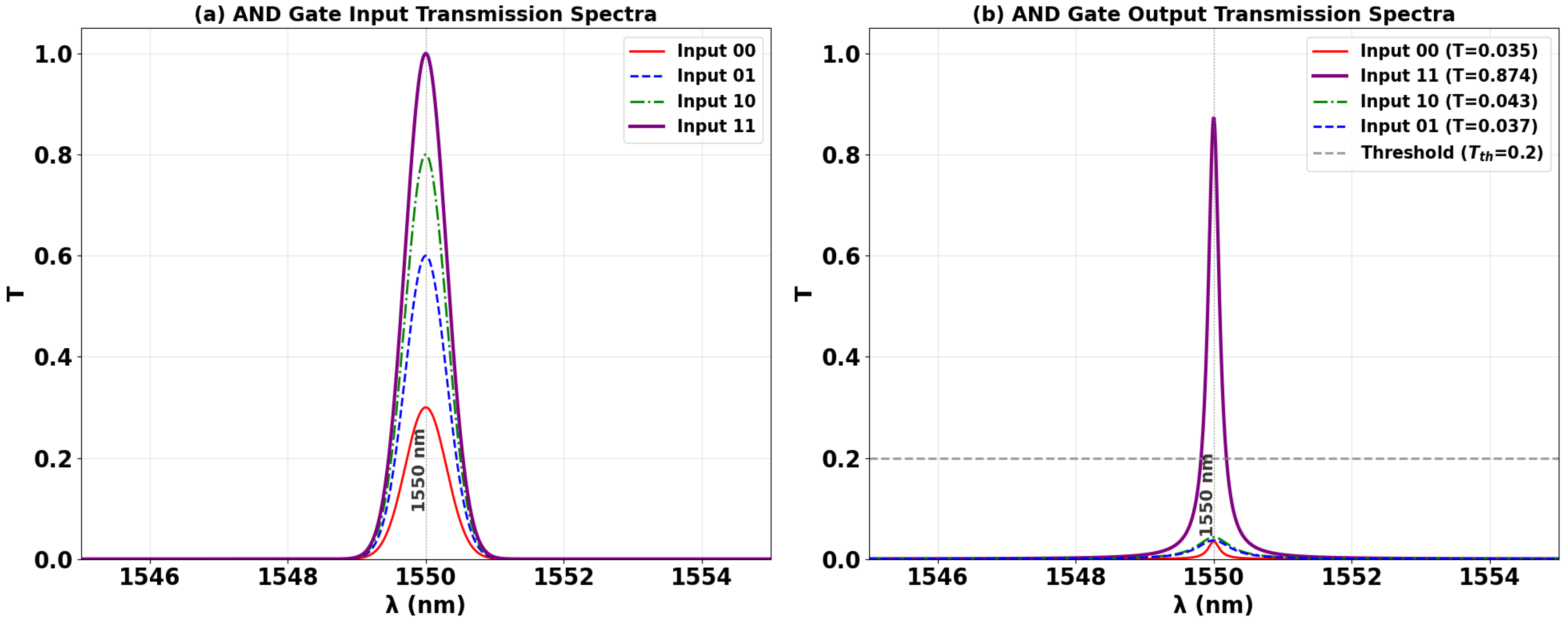
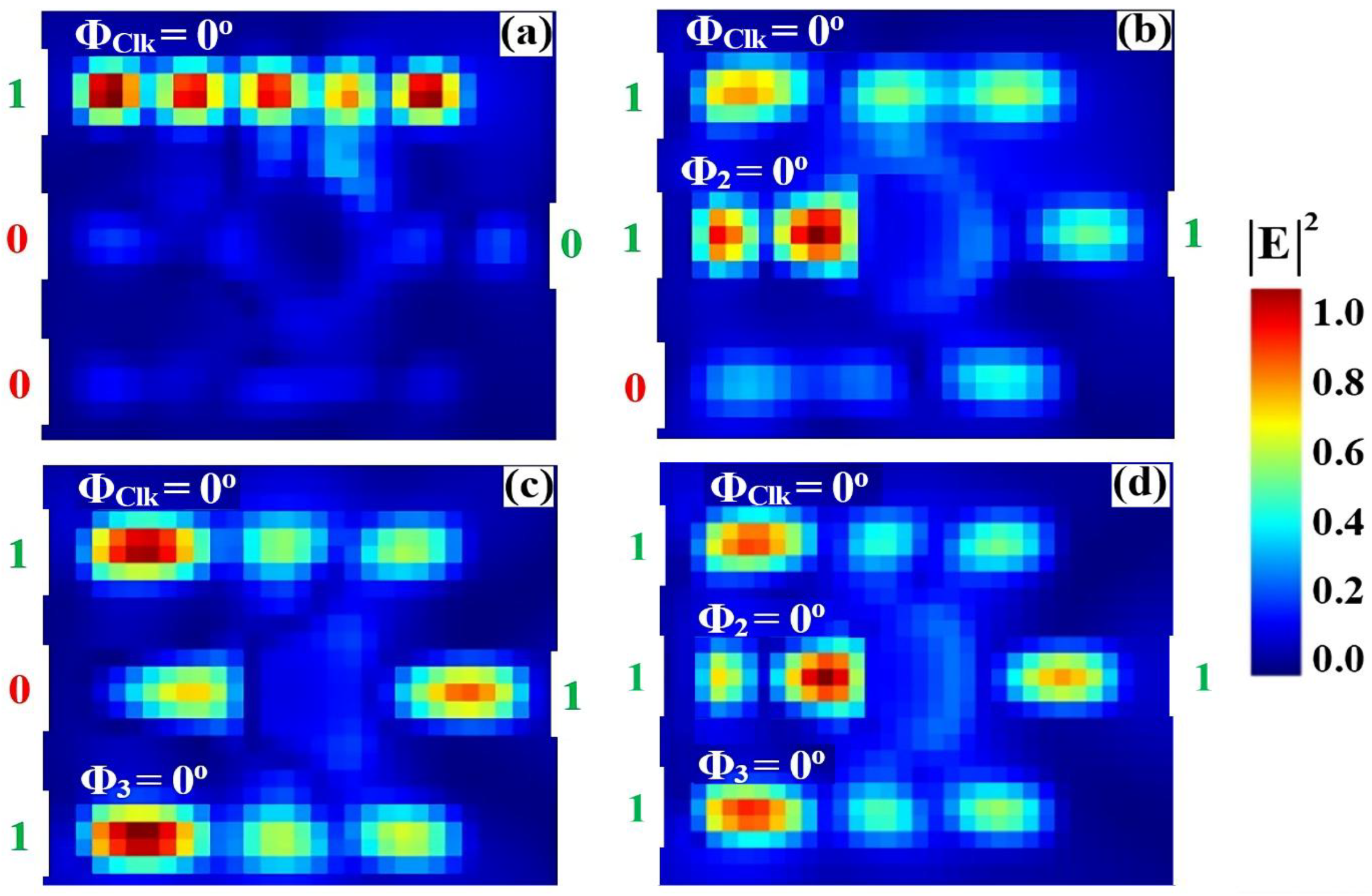
3.2. AND
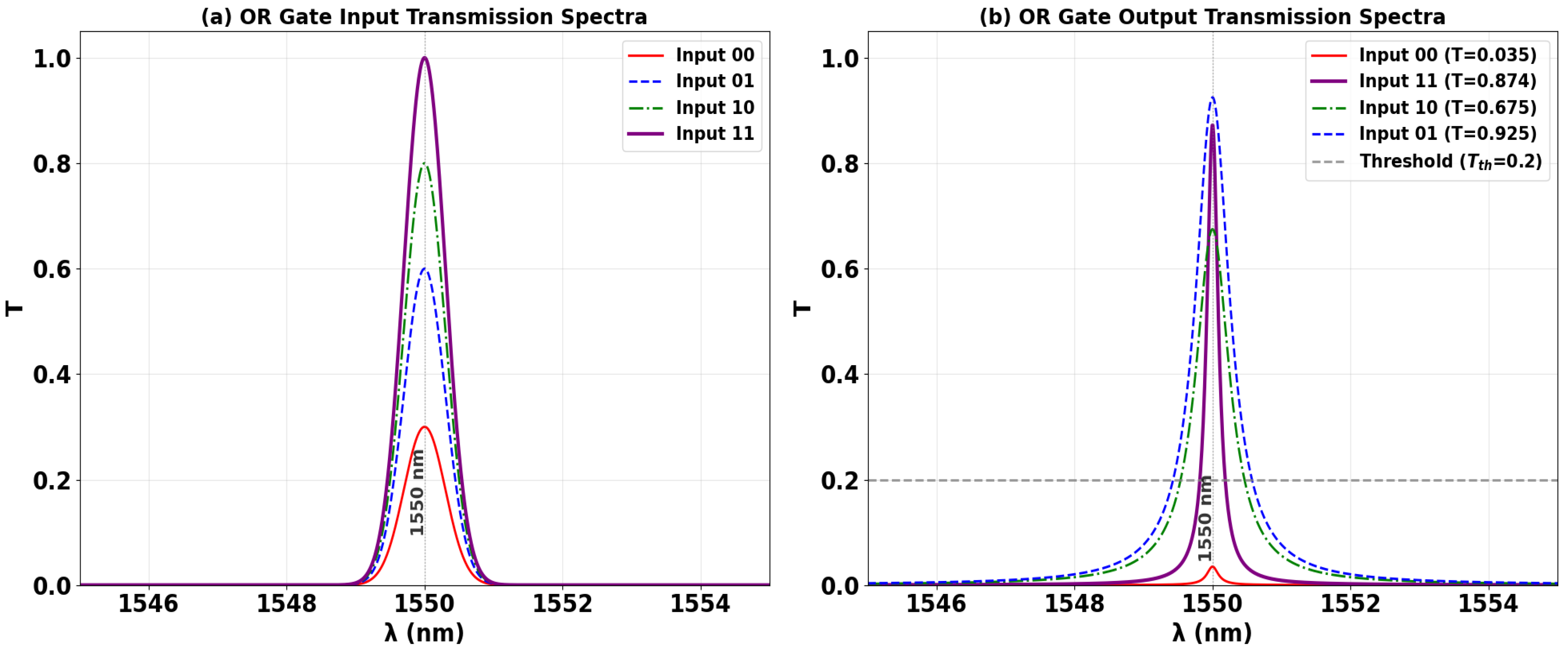
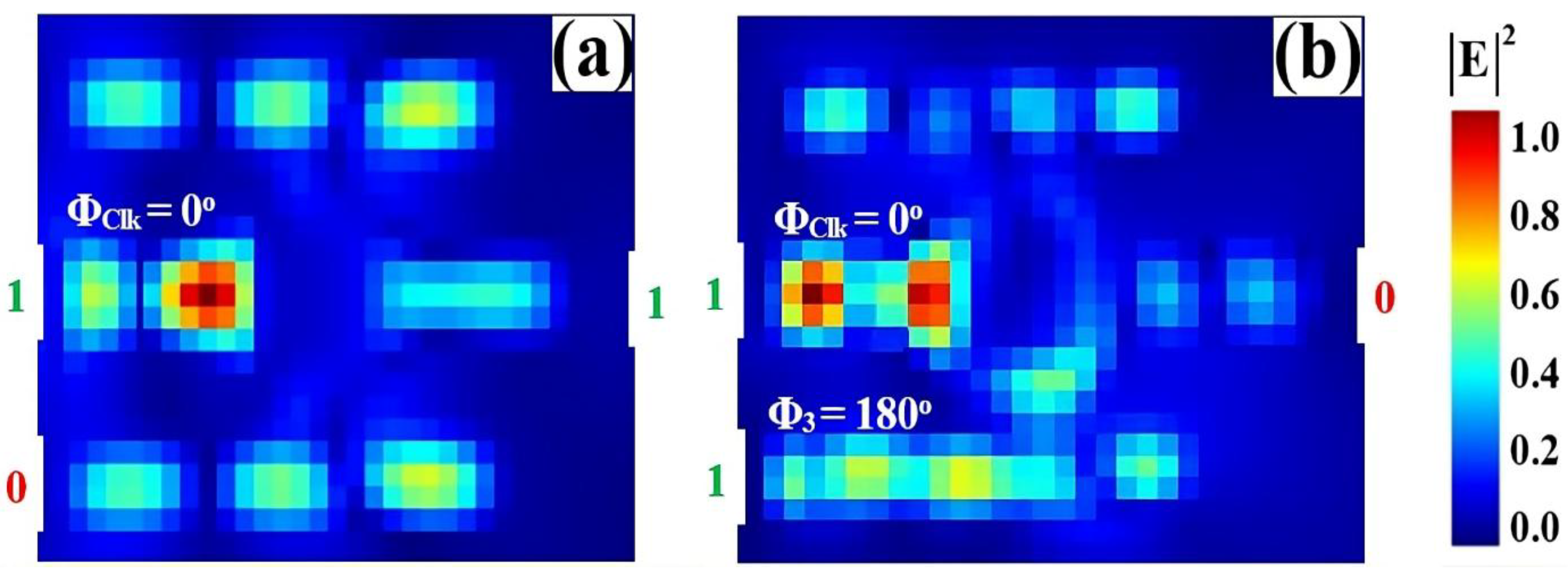
3.3. OR
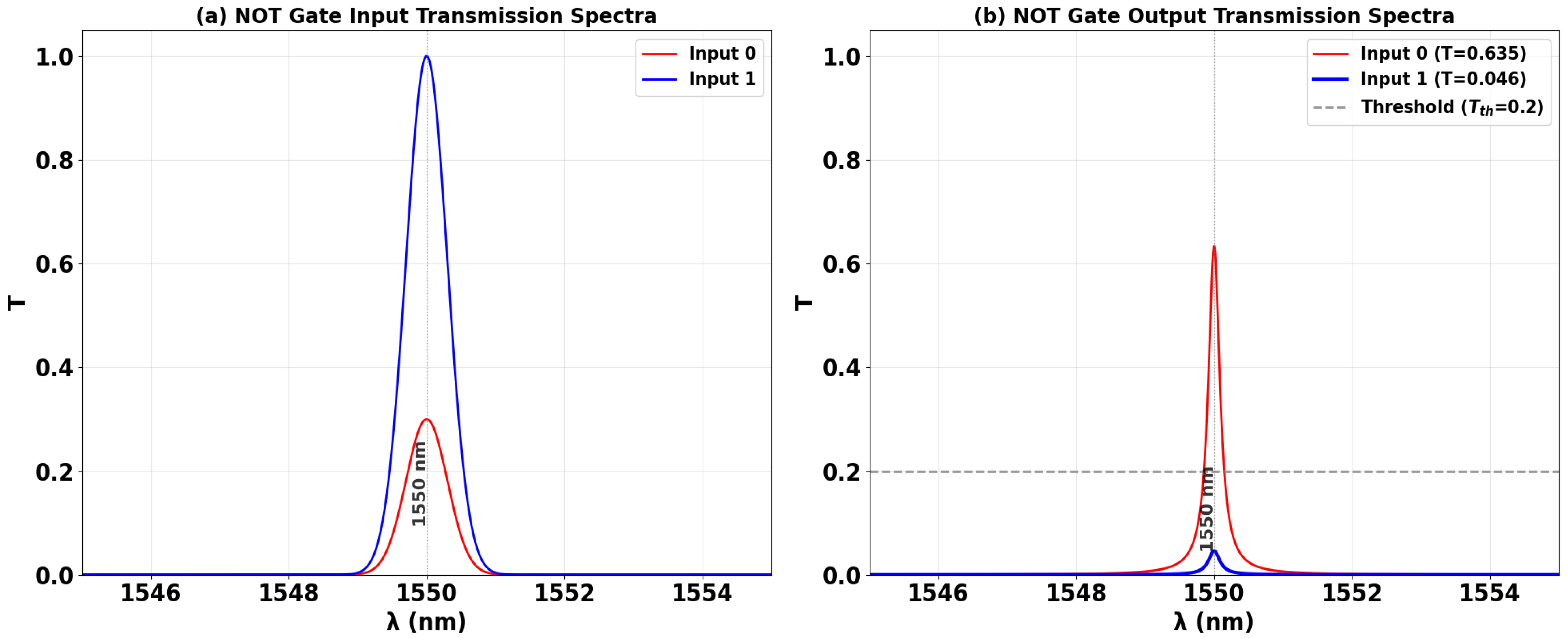
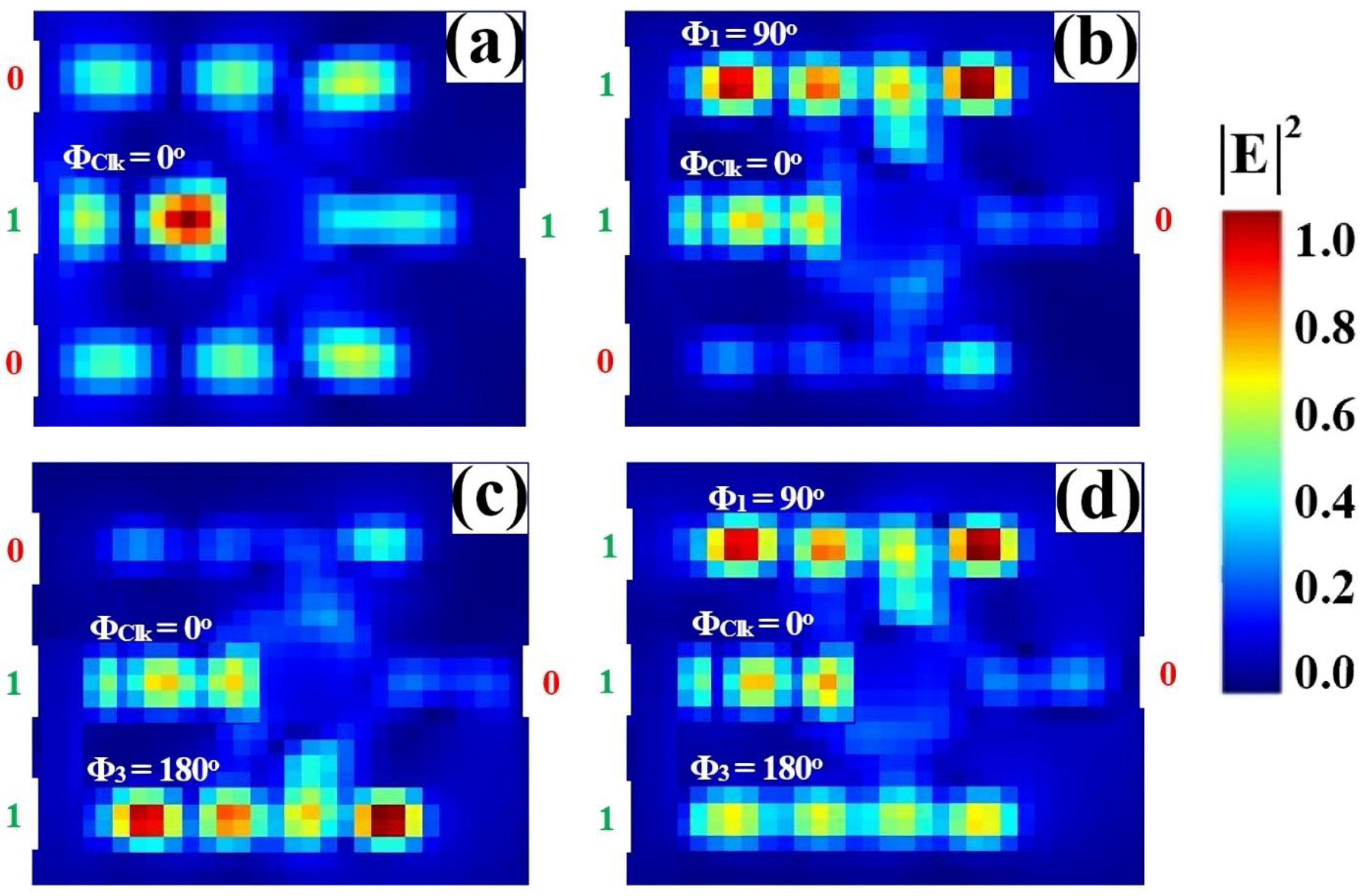
3.4. NOT
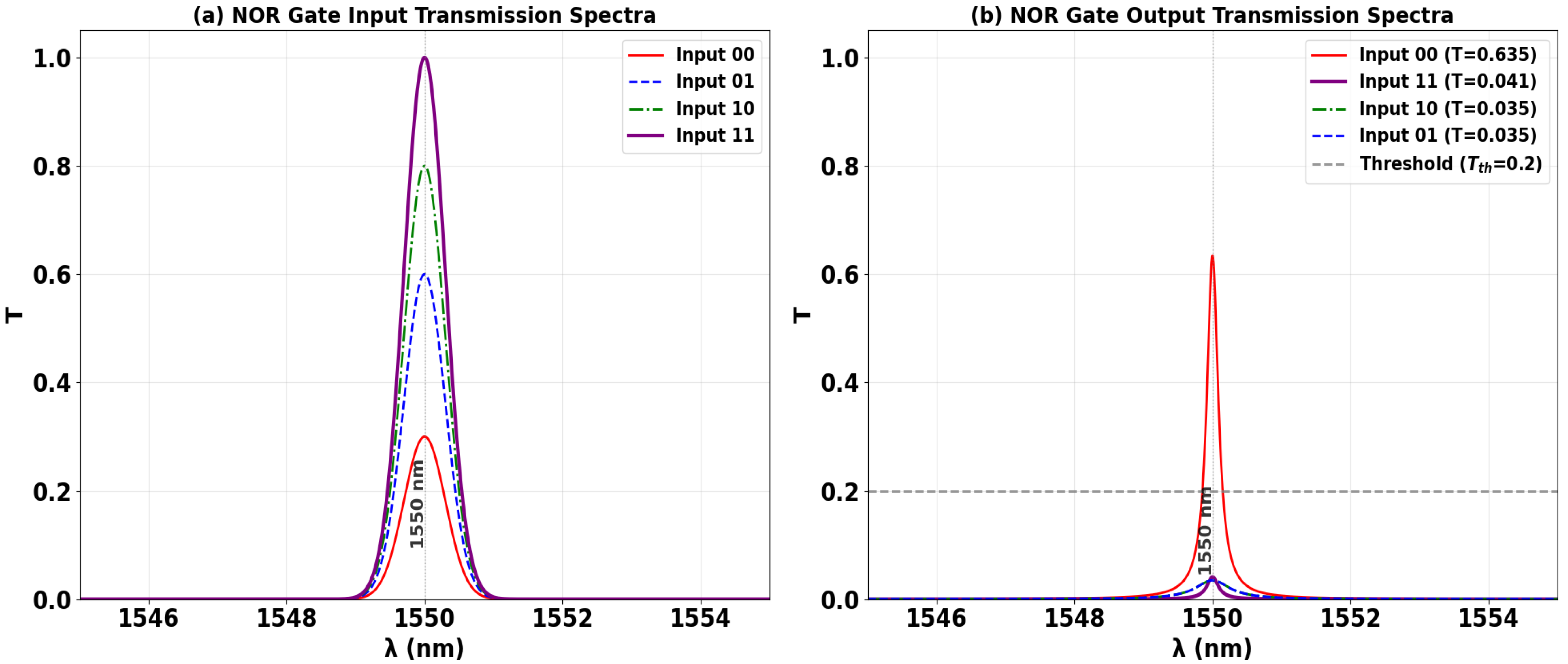
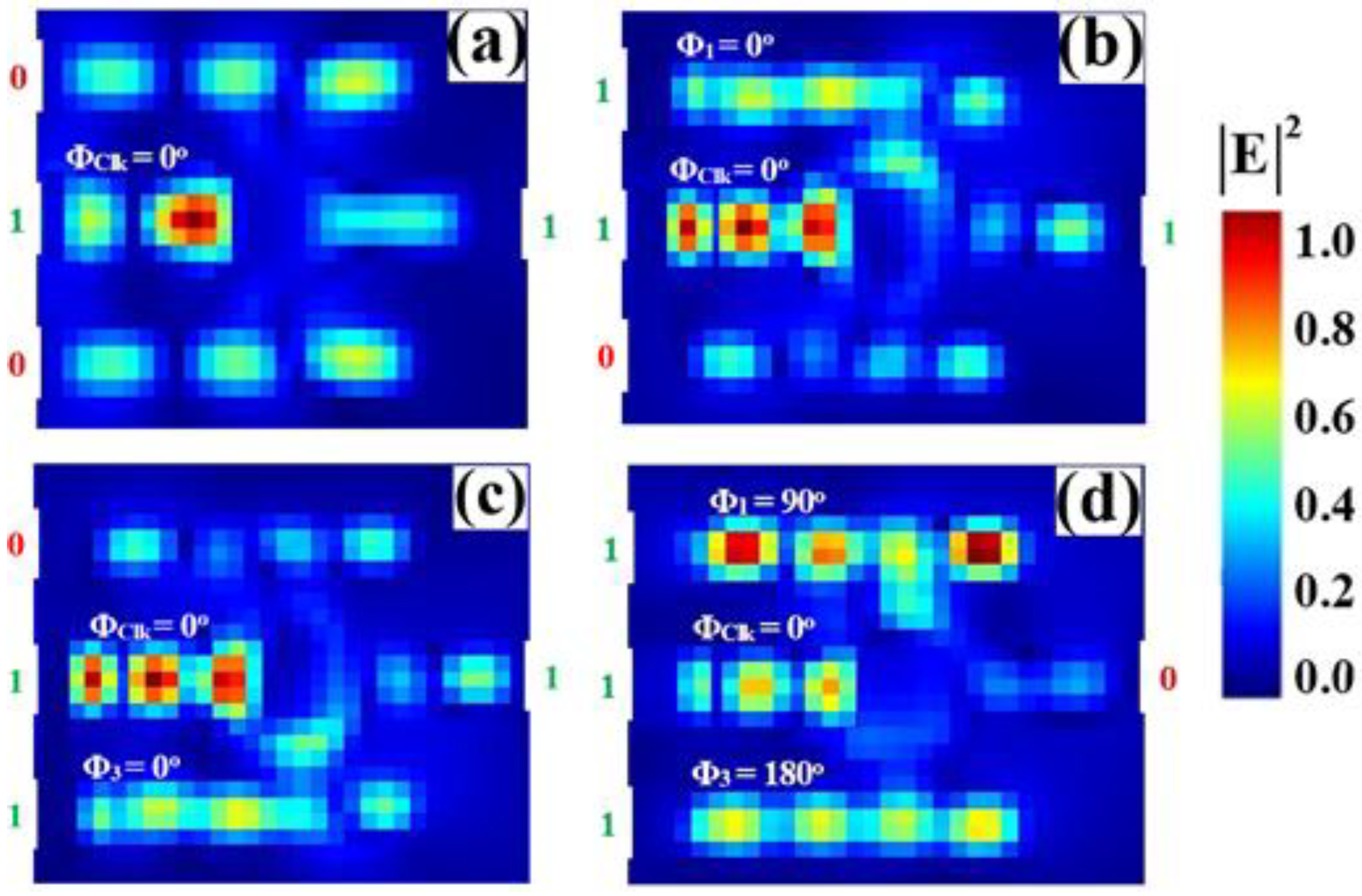
3.5. NOR
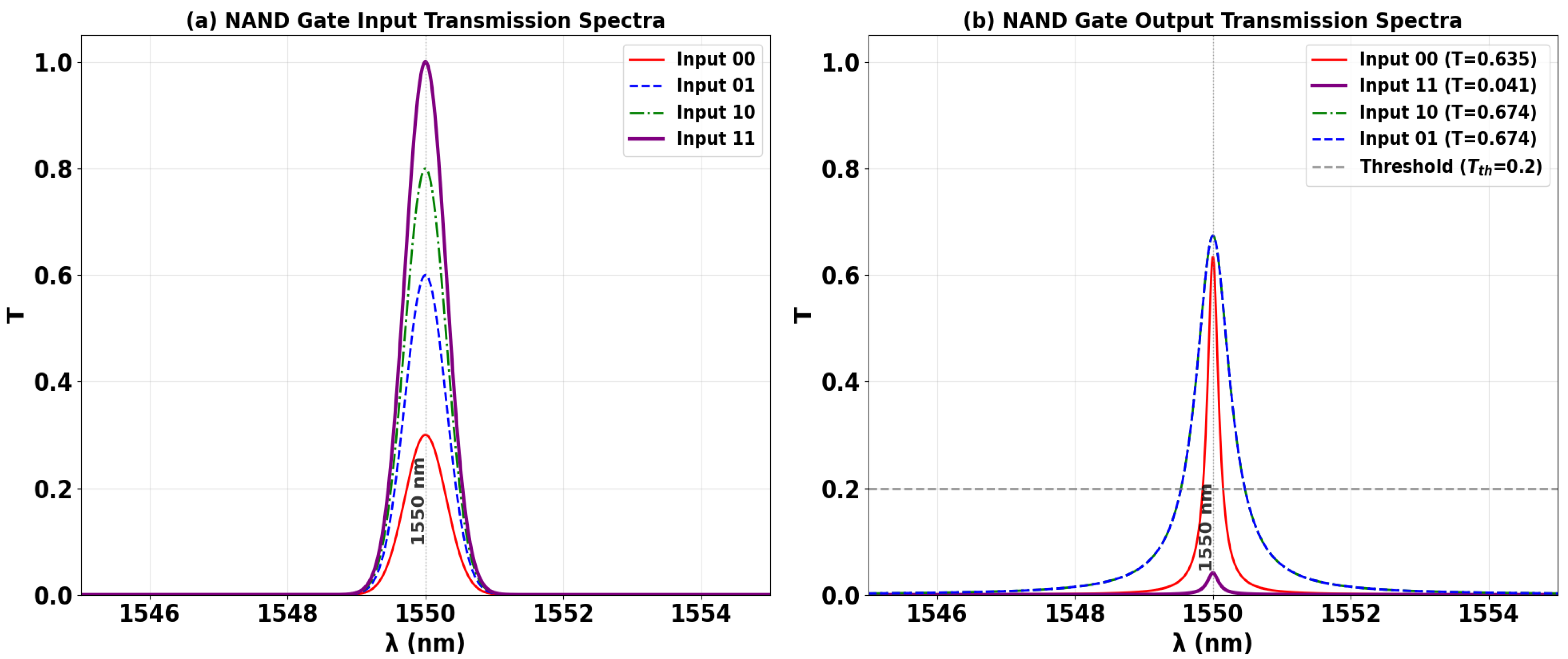
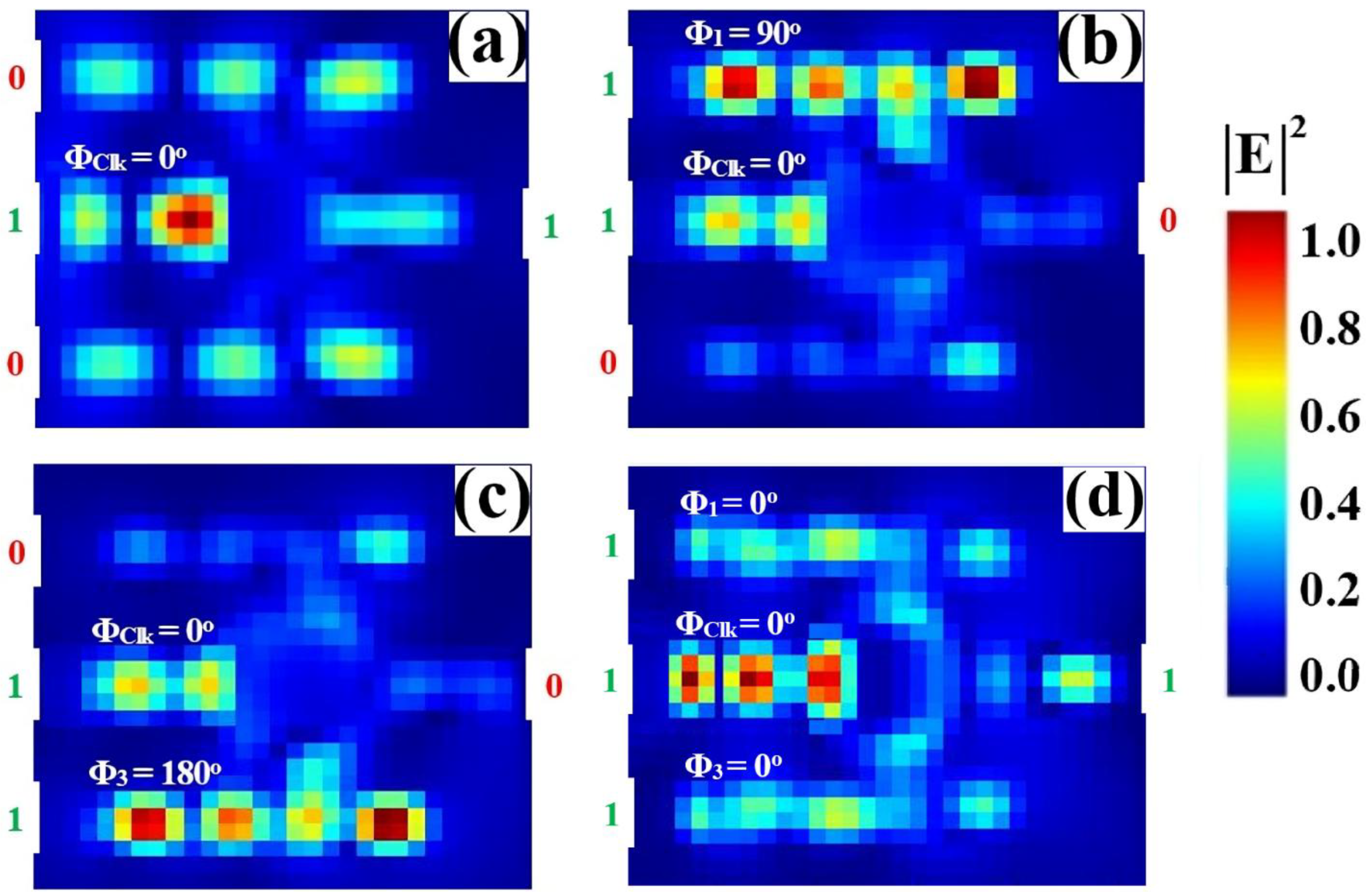
3.6. NAND
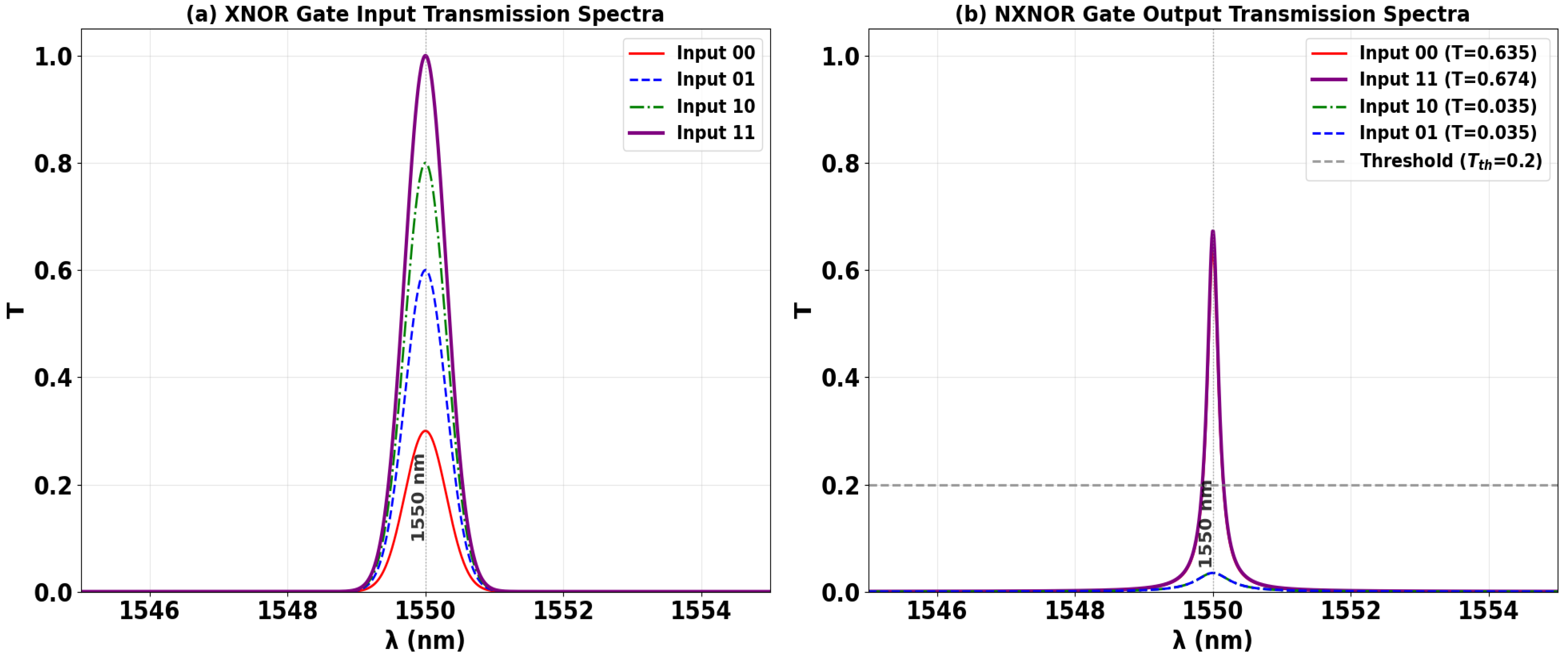
3.7. XNOR
4. Performance Comparison
- Refractive-index contrast engineering between core and cladding to enhance confinement and reduce unwanted losses.
- Precise tuning of coupling gaps and cavity geometry to sharpen resonance peaks and improve the ON/OFF intensity ratio.
- Minimization of propagation and scattering losses through high-quality fabrication and smooth sidewalls.
- Advanced material engineering, such as controlled doping or hybrid integration with low-loss dielectrics.
- CMOS compatibility and low loss: The all-dielectric SoS platform avoids metal-induced absorption, exhibits thermal stability, and is fully compatible with mature CMOS processes, providing a cost-effective route for mass production and seamless integration with electronics.
- Design uniformity, modularity, and scalability: The common microring-based resonant mechanism across all seven logic gates allows straightforward replication, cascading, and reconfiguration without individual gate redesign. This modular approach facilitates scaling to multi-gate systems and complex photonic logic networks, in contrast to PhC [69,70,71,72,73] and plasmonic designs [68,74,75,76], which often require extensive redesign for each gate.
- High-speed operation: The 55 Gb/s data rate, while slightly below the theoretical maximum of certain PhC structures [69,73], significantly surpasses several experimental demonstrations (e.g., 0.31 Gb/s [74] and 20 Gb/s [75]), meeting the requirements of modern optical interconnects and computing systems.
- Advanced functionality: Compared to inverse-designed ultra-compact photonic gates [77], the SoS microring platform provides a robust, easily fabricated, and modular solution suitable for large-scale integration, maintaining performance uniformity across all seven logic gates.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| FDTD | finite-difference time-domain |
| AOLGs | all-optical logic gates |
| CR | contrast ratio |
| Si | silicon |
| SiO2 | silicon dioxide |
| CMOS | complementary metal-oxide semiconductor |
| T | normalized transmission |
| Q | quality factor |
| TE | transverse electric mode |
| b | ring outer radius |
| a | ring inner radius |
| w | ring width |
| g | coupling gap |
| Clk | clock signal |
| CI | constructive interference |
| DI | destructive interference |
| τₚ | photon lifetime |
| λ | operating wavelength |
| FWHM | full width at half maximum |
References
- Miller, D.A.B. Rationale and challenges for optical interconnects to electronic chips. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 728–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soref, R. The past, present, and future of silicon photonics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2006, 12, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, G.T.; Knights, A.P. Silicon Photonics: An Introduction; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pavesi, L.; Lockwood, D.J. (Eds.) Silicon Photonics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, B.; Fathpour, S. Silicon photonics. J. Light. Technol. 2006, 24, 4600–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipson, M. Guiding, modulating, and emitting light on silicon—Challenges and opportunities. J. Light. Technol. 2005, 23, 4222–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulbe, M.; Kumar, S. Role of Nonlinear Optics in Big data transmission and Next Generation Computing Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 10–11 January 2019; pp. 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, H.J.; Dolev, S. Why future supercomputing requires optics. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batten, C.; Joshi, A.; Orcutt, J.; Khilo, A.; Moss, B.; Holzwarth, C.W.; Popovic, M.A.; Li, H.; Smith, H.I.; Hoyt, J.L.; et al. Building many-core processor-to-DRAM networks with monolithic CMOS silicon photonics. IEEE Micro 2009, 29, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, D.; Manning, R.J.; Blow, K.J.; Ellis, A.D.; Kelly, A.E.; Nesset, D.; Phillips, I.D.; Poustie, A.J.; Rogers, D.C. Nonlinear optics for high-speed digital information processing. Science 1999, 286, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.W. Nonlinear Optics, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, V.R.; Barrios, C.A.; Panepucci, R.R.; Lipson, M. All-optical control of light on a silicon chip. Nature 2004, 431, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr-Jones, T.; Hochberg, M.; Scherer, A. Photodetection in silicon beyond the band edge with surface states. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, G.T.; Mashanovich, G.; Gardes, F.Y.; Thomson, D.J. Silicon optical modulators. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, W.; De Heyn, P.; Van Vaerenbergh, T.; De Vos, K.; Kumar Selvaraja, S.; Claes, T.; Dumon, P.; Bienstman, P.; Van Thourhout, D.; Baets, R. Silicon microring resonators. Laser Photonics Rev. 2012, 6, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Haus, H.A.; Foresi, J.; Laine, J.-P. Microring resonator channel dropping filters. J. Light. Technol. 1997, 15, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryniewicz, J.V.; Absil, P.P.; Little, B.E.; Wilson, R.; Ho, P.-T. Higher order filter response in coupled microring resonators. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2000, 12, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, A. Critical coupling and its control in optical waveguide-ring resonator systems. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2002, 14, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, A. Universal relations for coupling of optical power between microresonators and dielectric waveguides. Electron. Lett. 2000, 36, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, C.K.; Zhao, J.H. Optical Filter Design and Analysis: A Signal Processing Approach; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kaalund, C.J.; Peng, G.-D. Pole-Zero Diagram Approach to the Design of Ring Resonator-Based Filters for Photonic Applications. J. Lightwave Technol. 2004, 22, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, F.; Bianchi, A.; Stracca, S.; Sabella, R. Silicon photonics for telecom and datacom applications. In Silicon Photonics III; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Schmidt, B.; Pradhan, S.; Lipson, M. Micrometre-scale silicon electro-optic modulator. Nature 2005, 435, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Densmore, A.; Xu, D.-X.; Waldron, P.; Janz, S.; Cheben, P.; Lapointe, J.; Delage, A.; Lamontagne, B.; Schmid, J.H.; Post, E. A silicon-on-insulator photonic wire based evanescent field sensor. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2006, 18, 2520–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Olio, F.; Passaro, V.M.N. Optical sensing by optimized silicon slot waveguides. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 4977–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, T.A.; Cao, W.; Kim, Y.; Li, J.; Goldhar, J.; Ho, P.-T.; Lee, C.H. All-optical switching in a laterally coupled microring resonator by carrier injection. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2003, 15, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Lipson, M. All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbavlis, T.; Zoiros, K.E.; Hatziefremidis, A.; Avramopoulos, H.; Occhi, L.; Guekos, G.; Hansmann, S.; Burkhard, H.; Dall’ARa, R. 10 Gbit/s all-optical Boolean XOR with SOA fibre Sagnac gate. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 1650–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, B.G.; Byun, Y.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, S.; Woo, D. All-optical NAND gate using cross-gain modulation in semiconductor optical amplifiers. Electron. Lett. 2005, 41, 1027–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, V.V.; Rautert, J.; Mikhrin, V.S.; Gubenko, A.E. Bit Error Rate in WDM Data Transmission Links With Semiconductor Optical Amplifier. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 43, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, M.J. Wideband semiconductor optical amplifier steady-state numerical model. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2001, 37, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.; Zoiros, K.E.; Chen, W. High-performance all-optical logic gates with D-shaped silicon-on-silica waveguides. J. Opt. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.; Wang, Z.; Zoiros, K.E. High-Performance All-Optical Logic Gates Based on Silicon Racetrack and Microring Resonators. Electronics 2025, 14, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W. High-contrast and high-speed optical logic operations using silicon microring resonators. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotb, A.; Zoiros, K.E. High-Speed All-Optical Encoder and Comparator at 120 Gb/s Using a Carrier Reservoir Semiconductor Optical Amplifier. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotb, A.; Zoiros, K.E.; Chen, W. All-Optical Encryption and Decryption at 120 Gb/s Using Carrier Reservoir Semiconductor Optical Amplifier-Based Mach–Zehnder Interferometers. Micromachines 2025, 16, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osgood, R.M.; Panoiu, N.C.; Dadap, J.I.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Hsieh, I.-W.; Dulkeith, E.; Green, W.M.; Vlasov, Y.A. Engineering nonlinearities in nanoscale optical systems: Physics and applications in dispersion-engineered silicon nanophotonic wires. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2009, 1, 162–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulkeith, E.; Vlasov, Y.A.; Chen, X.; Panoiu, N.C.; Osgood, J.R.M. Self-phase-modulation in submicron silicon-on-insulator photonic wires. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 5524–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, Q. Proposal for all-optical switchable OR/XOR logic gates using sum-frequency generation. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2007, 19, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, M.; Shinya, A.; Mitsugi, S.; Kira, G.; Kuramochi, E.; Tanabe, T. Optical bistable switching action of Si high-Q photonic-crystal nanocavities. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 2678–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; McCutcheon, M.W.; Burgess, I.B.; Lončar, M. Ultra-high-Q TE/TM dual-polarized photonic crystal nanocavities. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2694–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenila, C.; Aarthi, V.P.M.B.; Sampson, J.; Ravikumar, G.K.; Kannan, H. Design and Analysis of Silicon Photonic Waveguides and Optical Micro-Ring Resonator for Next-Generation Computing, Communication and Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 14–15 March 2024; pp. 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, G.; Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L. Experimental demonstration of a reconfigurable electro-optic directed logic circuit using cascaded carrier-injection micro-ring resonators. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, M.A.; Barwicz, T.; Watts, M.R.; Rakich, P.T.; Socci, L.; Ippen, E.P.; Kärtner, F.X.; Smith, H.I. Multistage high-order microring-resonator add-drop filters. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2571–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Samara-Rubio, D.; Morse, M.; Liu, A.; Hodge, D.; Rubin, D.; Keil, U.D.; Franck, T. High speed silicon Mach-Zehnder modulator. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, R.; Ramos, F.; Martínez, J.M. All-optical flip-flop based on a single SOA-MZI. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2005, 17, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubkjaer, K.E. Semiconductor optical amplifier-based all-optical gates for high-speed optical processing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Sekaric, L.; Vlasov, Y. Ultracompact optical buffers on a silicon chip. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, M.; Johnson, T.J.; Painter, O. Beyond the Rayleigh scattering limit in high-Q silicon microdisks: Theory and experiment. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 1515–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabus, D.G. Integrated Ring Resonators: The Compendium; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, K.S. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1966, 14, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenger, J.P. A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 114, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Cahill, L.W. The design of wavelength selective switches and filters based on SOI microring resonators. In Proceedings of the 2007 Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications, Bangkok, Thailand, 18–20 October 2007; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manipatruni, S.; Preston, K.; Chen, L.; Lipson, M. Ultra-low voltage, ultra-small mode volume silicon microring modulator. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 18235–18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M. Ultra-high Q planar silicon microdisk resonators for chip-scale silicon photonics. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 4694–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, A.; Dali, P.P.; Janyani, V.; Tanabe, T.; Singh, G. All Optical Scalable Logic Gates Using Si3N4 Microring Resonators. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2016, 22, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.; Zoiros, K.E.; Guo, C. High-performance all-optical logic operations using Ψ-shaped silicon waveguides at 1.55 μm. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.; Zoiros, K.E.; Li, W. Silicon-on-silica waveguides-based all-optical logic gates. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 035517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liao, L.; Rubin, D.; Nguyen, H.; Ciftcioglu, B.; Chetrit, Y.; Izhaky, N.; Paniccia, M. High-speed optical modulation based on carrier depletion in a silicon waveguide. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelusi, M.D.; Luan, F.; Magi, E.; Lamont, M.R.E.; Moss, D.J.; Eggleton, B.J.; Sanghera, J.S.; Shaw, L.B.; Aggarwal, I.D. High bit rate all-optical signal processing in a fiber photonic wire. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 11506–11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Duan, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Zhong, F.; et al. On-chip optoelectronic logic gates operating in the telecom band. Nat. Photonics 2024, 18, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soref, R.; Bennett, B. Electrooptical effects in silicon. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1987, 23, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, W.; Dumon, P.; Van Thourhout, D.; Baets, R. Compact wavelength-selective functions in silicon-on-insulator photonic wires. J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2006, 12, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, L.; Ding, Y.; Cusano, A.; Fan, J.A.; Hu, Q.; Wang, K.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. Optical meta-waveguides for integrated photonics and beyond. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taflove, A.; Hagness, S.C. Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method, 3rd ed.; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, G.P. Fiber-Optic Communication Systems, 4th ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kita, S.; Nozaki, K.; Takata, K.; Shinya, A.; Notomi, M. Ultrashort low-loss Ψ gates for linear optical logic on Si photonics platform. Commun. Phys. 2020, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, H.K.; Al-Janabi, A.K.; Al-abassi, S.A.W.; Abusiba, N.A.H.A.; Al-Fatlawi, N.A.H.Q. Plasmonic logic gates based on dielectric–metal–dielectric design with two optical communication bands. Optik 2020, 223, 165416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Kalra, Y.; Sinha, R.K. Design of all-optical logic gates in photonic crystal waveguides. Optik 2015, 126, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachana, M.; Swarnakar, S.; Krishna, S.V.; Kumar, S. Design and analysis of an optical three-input AND gate using a photonic crystal fiber. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, N.H.; Swarnakar, S.; Krishna, S.V.; Kumar, S. Design and analysis of a photonic crystal-based all-optical 3-input OR gate for high-speed optical processing. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.G.S.; Swarnakar, S.; Palacharla, V.; Raju, K.S.R.; Kumar, S. Design of all-optical AND, OR, and XOR logic gates using photonic crystals for switching applications. Photon. Netw. Commun. 2021, 41, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, T.S.; Mohammed, N.A.; El-Rabaie, E.M. Ultra-high bit rate all-optical AND/OR logic gates based on photonic crystal with multi-wavelength simultaneous operation. J. Mod. Opt. 2019, 66, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Optical interferometric logic gates based on metal slot waveguide network realizing whole fundamental logic operations. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Gong, Q. Compact all-optical interferometric logic gates based on one-dimensional metal–insulator–metal structures. Opt. Commun. 2014, 313, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, M.J.; Raheema, M.N.; Alwahib, A.A. Nanoscale plasmonic logic gates design by using an elliptical resonator. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 4080–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neseli, B.; Yilmaz, Y.A.; Kurt, H.; Turduev, M. Inverse design of ultra-compact photonic gates for all-optical logic operations. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 215107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 (Clk) | Pin2 | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| XOR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | 13.41 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.675 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.925 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.038 | ||
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 (Clk) | Pin2 | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| AND | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | 13.58 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.043 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.037 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.874 | ||
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 (Clk) | Pin2 | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| OR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | 13.72 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.675 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.925 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.874 | ||
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin2 (Clk) | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| NOT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.635 | 11.40 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.046 | ||
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 | Pin2 (Clk) | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| NOR | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.635 | 13.35 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.035 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.041 | ||
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 | Pin2 (Clk) | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| NAND | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.635 | 12.10 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.674 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.674 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.041 | ||
| Logic Gate | Input Signals | Output Logic | T | CR (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 | Pin2 (Clk) | Pin3 | Pout | |||
| XNOR | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.635 | 12.72 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.035 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.035 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.674 | ||
| Logic Gates | Waveguide | Materials | Size (µm2) | Speed (Gb/s) | λ (nm) | Metric (dB) | Exp./Sim. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AND, NAND | Silicon micro-ring resonators | Si/SiO2 | 5 µm radius | 0.310 | 1550.7 | ER ~ 10 | Exp. | [27] |
| XOR, AND, OR, NOT, NOR, XNOR, NAND | Silicon microrings waveguide | Si/SiO2 | 1.30 × 1.35 | 199.80 | 1550 | CR = 12.02–15.85 | Sim. | [50] |
| AND, NOR, XNOR | Si photonics platform | Si | 3 µm long | 20 | 1550 | CR > 10 | Exp. | [67] |
| NOT, OR, AND, NOR, NAND, XOR, XNOR | Dielectric-metal-dielectric plasmonic waveguide | Silver/Teflon | - | - | 900–1330 | ER > 20 | Sim. | [68] |
| AND, XOR, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XNOR | PhC waveguides | Si/Air | 5.28 × 5.28 | 976 | 1550 | CR = 5.42–9.59 | Sim. | [69] |
| AND, XOR, XNOR | T-shaped PhC waveguides | Si/Air | 8.4 × 5.4 | >30,000 | 1550 | CR = 8.29–33.05 | Sim. | [70,71,72] |
| AND, OR | 2D PhC design | Si/Air | 19.8 × 12.6 | >4740 | 1520 | CR = 9.74 and 17.95 | Sim. | [73] |
| NOT, XOR, AND, OR, NOR, NAND, XNOR | Metal slot waveguide | Silver/SiO2 | 1.5 × 2.36 | - | 632.8 | CR = 6–16 | Exp. | [74] |
| NOT, XOR, AND, OR, NOR, NAND, XNOR | Metal-insulator-metal structures | Air/Silver | 5.33 × 0.42 | - | 632.8 | CR = 15 | Sim. | [75] |
| AND, NAND, OR, XOR, NOR, XNOR, NOT | Plasmonic logic gate design | Silver/SiO2 | 0.25 × 0.25 | - | 850 | CR = 4.14–14.46 | Sim. | [76] |
| AND, OR, NOT, NAND | Inverse design on silicon platforms | Si/SiO2 | 1.0 × 1.5 | - | 1300 | CR = 0.5–5.79 | Sim. | [77] |
| XOR, AND, OR, NOT, NOR, XNOR, NAND | Silicon racetrack and ring resonator | Si/SiO2 | 1.42 × 1.08 | 55 | 1550 | CR = 11.40–13.72 | Sim. | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotb, A.; Hatziefremidis, A.; Zoiros, K.E. Silicon-on-Silica Microring Resonators for High-Quality, High-Contrast, High-Speed All-Optical Logic Gates. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221736
Kotb A, Hatziefremidis A, Zoiros KE. Silicon-on-Silica Microring Resonators for High-Quality, High-Contrast, High-Speed All-Optical Logic Gates. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(22):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221736
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotb, Amer, Antonios Hatziefremidis, and Kyriakos E. Zoiros. 2025. "Silicon-on-Silica Microring Resonators for High-Quality, High-Contrast, High-Speed All-Optical Logic Gates" Nanomaterials 15, no. 22: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221736
APA StyleKotb, A., Hatziefremidis, A., & Zoiros, K. E. (2025). Silicon-on-Silica Microring Resonators for High-Quality, High-Contrast, High-Speed All-Optical Logic Gates. Nanomaterials, 15(22), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221736








