Magnetic Properties of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Induced by Dopant Configurations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene
2.2. Investigation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elemental Analysis Using SEM/EDS
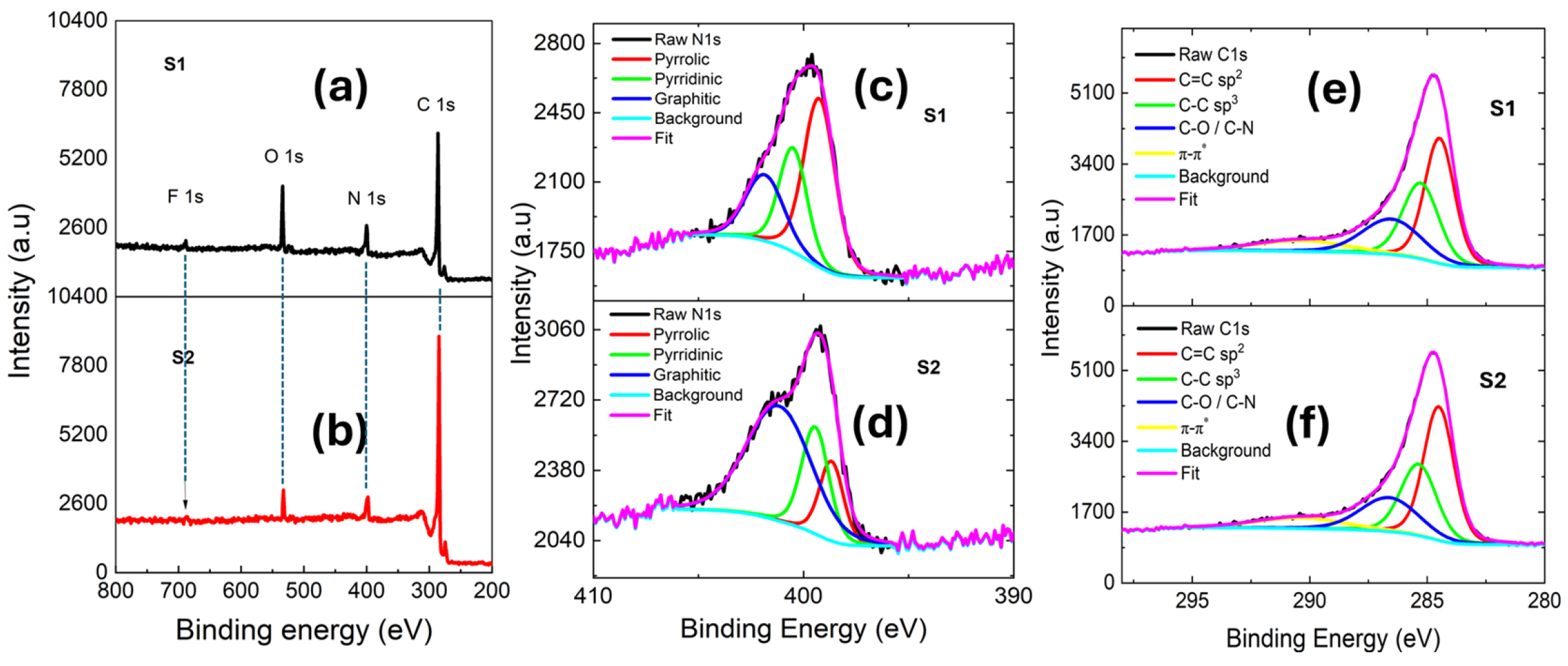
3.2. XPS Characterization of Elemental and Chemical States
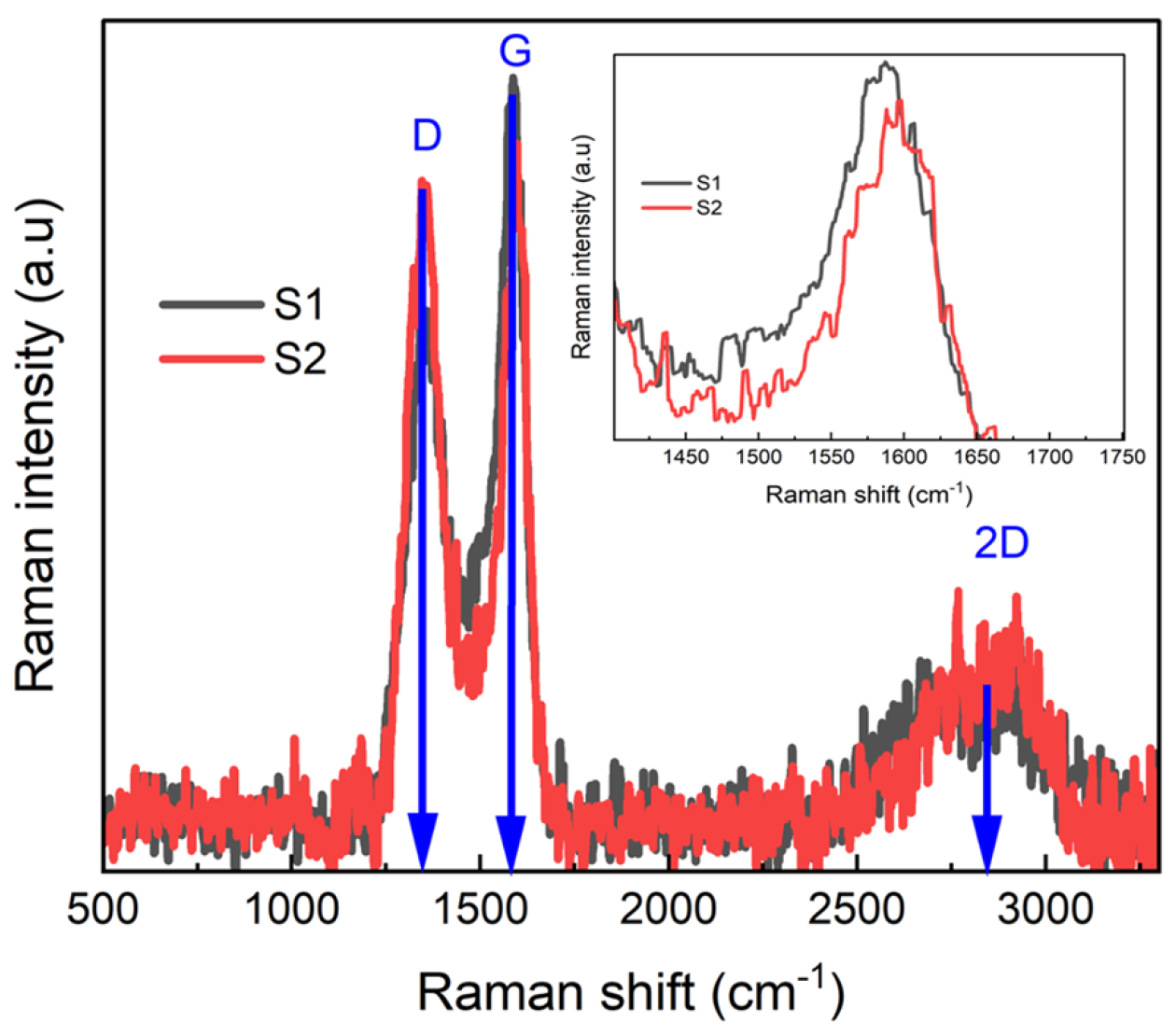
3.3. Raman Analysis of Structural Properties
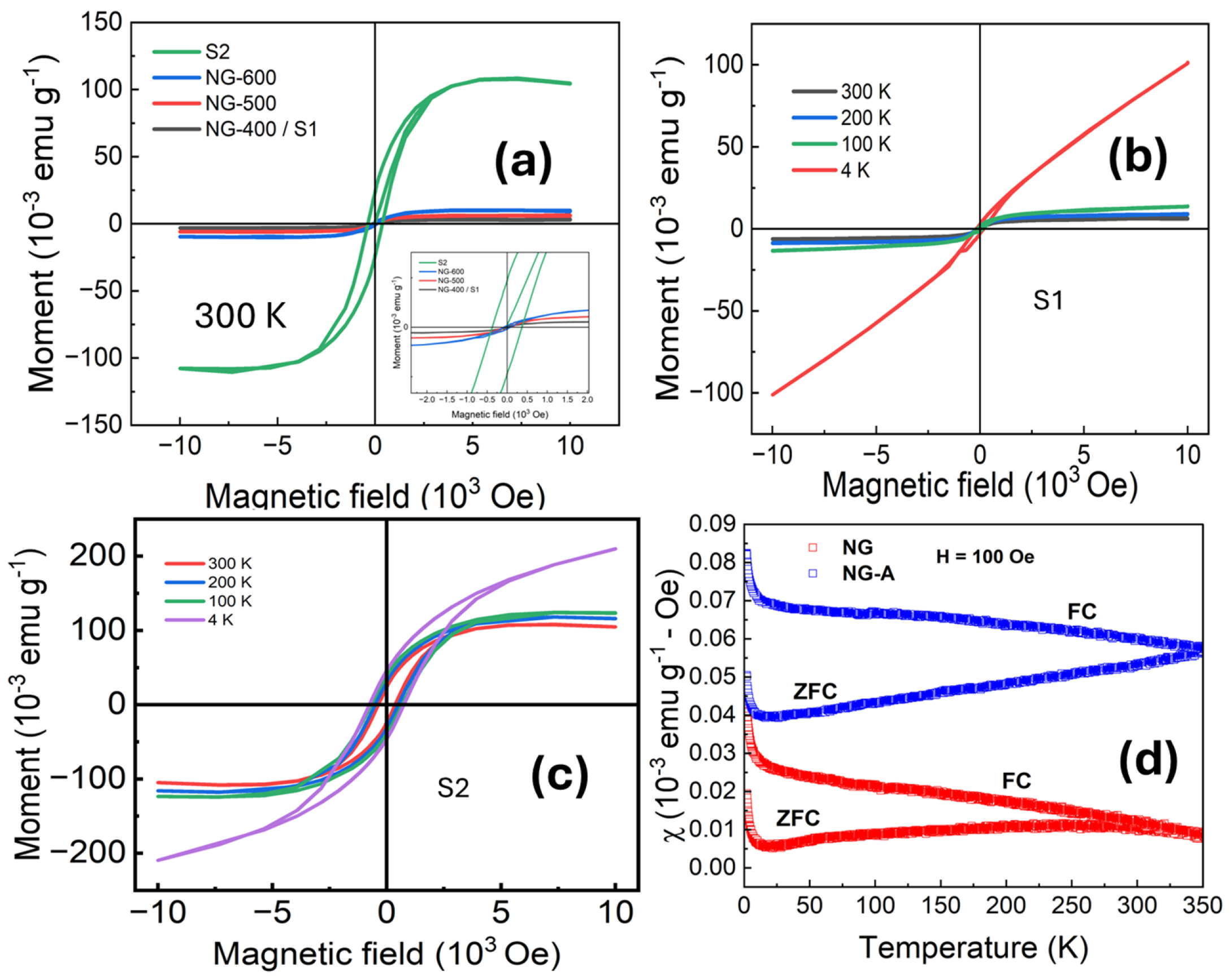
3.4. Magnetic Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rutkauskas, A.V.; Lis, O.N.; Kichanov, S.E.; Lukin, E.V.; Abdurakhimov, B.A.; Rymski, G.S.; Zhaludkevich, A.L.; Makoed, I.I.; Kozlenko, D.P.; Mutali, A. Magnetite Nanoparticles Doped with Rare Earth Ions: Synthesis, Structural, and Magnetic Properties. J. Nanopart. Res. 2025, 27, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, R.; Kabir, M. Ferromagnetism in Nitrogen-doped Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 115442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błoński, P.; Tuček, J.; Sofer, Z.; Mazánek, V.; Petr, M.; Pumera, M.; Otyepka, M.; Zbořil, R. Doping with Graphitic Nitrogen Triggers Ferromagnetism in Graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Nair, A.K.; Ray, S.J.; Yi, J.; Vinu, A.; Kumar, P. Microwave Flash Synthesis of Phosphorus and Sulphur Ultradoped Graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Di, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Y.; Tang, N. Graphitic-nitrogen-enhanced Ferromagnetic Couplings in Nitrogen-doped Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 094406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivas, D.; Suvarna, T.; Lavanya, G.; Vardhani, C.P. Evidence of Ferromagnetism in Boron Doped Graphene Oxide Synthesized by Hydrothermal Method. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 92, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Wu, H.C.; Yu, D.P.; Liao, Z. Magnetic Moments in Graphene with Vacancies. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Pama, S.; Cimatu, L.K.; Jadwisienczak, W.M. Converting Fluorinated Graphite to Nitridated Graphene for Room-Temperature Magnetic Applications. In Proceedings of the 67th EMC, Session: Graphene Synthesis and Devices, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA, 25–27 June 2025. Will be published in J. Elect Mater. (In review). [Google Scholar]
- Vaseem, M.; Ghaffar, F.A.; Farooqui, M.F.; Shamim, A. Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-based Magnetic Ink Development for Fully Printed Tunable Radio-frequency Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Singh, J.; Verma, V.; Kumar, R. Harnessing the Duality of Magnetism and Conductivity: A Review of Oxide-based Dilute Magnetic Semiconductors. Phys. B 2025, 696, 416596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Shi, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, X. Facilitative Preparation of Graphene/Cellulose Aerogels with Tunable Microwave Absorption Properties for Ultra-lightweight Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 679, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Mondal, S.; Banerjee, A.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Dielectric and Piezoelectric Augmentation in Self-poled Magnetic Fe3O4/poly (vinylidene fluoride) Composite Nanogenerators. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebrekers, T.; Kroemer, O.; Majidi, C. Soft Magnetic Skin for Continuous Deformation Sensing. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, S.; Migita, K.; Sugano, S. Soft Magnetic Powdery Sensor for Tactile Sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shang, W.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Tan, R.; Shen, Y. An Agglutinate Magnetic Spray Transforms Inanimate Objects into Millirobots for Biomedical Applications. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eabc8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ze, Q.; Kuang, X.; Wu, S.; Wong, J.; Montgomery, S.M.; Zhang, R.; Kovitz, J.M.; Yang, F.; Qi, H.L.; Zhao, R. Magnetic Shape Memory Polymers with Integrated Multifunctional Shape Manipulation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.S.; Sondhi, K.; Mills, S.C.; Andrew, J.S.; Fan, Z.H.; Nishida, T.; Arnold, D.P. Screen-Printable and Stretchable Hard Magnetic Ink Formulated from Barium Hexaferrite Nanoparticle. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2020, 8, 12133–12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, H. Graphene-based Materials for Adsorptive Removal of Pollutants from Water and Underlying Interaction Mechanism. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 289, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Prakash, A.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Agarrwal, A.; Bahadur, D. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide-reduced Graphene Oxide Nanohybrid-a Vehicle for Targeted Drug Delivery and Hyperthermia Treatment of Cancer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 448, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idisi, D.O.; Oke, J.A.; Benecha, E.M.; Moloi, S.J.; Ray, S.C. Magnetic Properties of Graphene Oxide Functionalized with Au and Fe2O3 Nanoparticles: A Comparative Study. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 5037–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D. Practical Quantum Computing Potential in Graphene Layers. IEEE Spectrum. 2024. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/practical-quantum-computing-bilayered-graphene (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Avsar, A.; Ochoa, H.; Guinea, F.; Özyilmaz, B.; van Wees, B.J.; Vera-Marun, I.J. Colloquium: Spintronics in graphene and other two-dimensional materials. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.L.; Nine, M.J.; Hassan, K.; Tung, T.T.; Tran, D.N.H.; Losic, D. Graphene-Based Sorbents for Multipollutants Removal in Water: A Review of Recent Progress. Adv. Fun. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Yang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Hu, B. 3D Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Composites: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. ChemNanoMat 2025, 11, e202400675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, P.; Lei, D.Y.; Li, W.; Bai, J.; Ren, Z.; Xu, X. Searching for Magnetism in Pyrrolic N-doped Graphene Synthesized via Hydrothermal Reaction. Carbon 2015, 84, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wei, B.; Xu, F.; Fei, W. Magnetic Properties of N-doped Graphene with High Curie Temperature. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xu, Q. Room Temperature Ferromagnetism in N2 Plasma Treated Graphene Oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Tang, N.; Wan, X.; Liu, F.; Lv, L.; Du, Y. Increased Magnetization of Reduced Graphene Oxide by Nitrogen-doping. Carbon 2013, 60, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Ray, S.C.; Strydom, A.M. Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Nitrogen Functionalized Graphene-oxide. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 79, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, D.; Feng, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X. Facilely Synthesized N-doped Graphene Sheets and Its Ferromagnetic Origin. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3841–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyulasaryan, H.; Tolchina, D.; Avakyan, L.; Srabionyan, V.; Bugaev, L.; Kozakov, A.; Nikolskiy, A.; Pankov, I.; Tsaturyan, A.; Emelyanov, A.; et al. Ferromagnetism and Structural Features of N-Doped Graphene Clusters in Carbon Structures. Univ. Notre Dame 2024, Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, P.; Mach, R.; Otyepka, M. Spectroscopic Fingerprints of Graphitic, Pyrrolic, Pyridinic, and Chemisorbed Nitrogen in N-doped Graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 10695–10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Christodoulou, C.; Nardi, M.V.; Koch, N.; Kläui, M.; Sachdev, H.; Müllen, K. Tuning the Magnetic Properties of Carbon by Nitrogen Doping of its Graphene Domains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 137, 7678–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dang, J.; Zhao, X.; Nagase, S. Formation Mechanisms of Graphitic-N: Oxygen Reduction and Nitrogen Doping of Graphene Oxides. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 5673–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šedajová, V.; Bakandritsos, A.; Błoński, P.; Medveď, M.; Langer, R.; Zaoralová, D.; Ugolotti, J.; Dzíbelová, J.; Jakubec, P.; Kupka, V.; et al. Nitrogen Doped Graphene with Diamond-like Bonds Achieves Unprecedented Energy Density at High Power in a Symmetric Sustainable Supercapacitor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Qin, R.; Lai, W.; Ou, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Nitrogen-doping Chemical Behavior of Graphene Materials with Assistance of Defluorination. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbu, C.I.; Feng, X.; Dada, N.S.; Bishop, G.W. Screen-Printed Soft-Nitrided Carbon Electrodes for Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. Sensors 2019, 19, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.; Durai, M.; Sengottaiyan, C.h.; Ahn, Y.-H. Effective Chemical Vapor Deposition and Characterization of N-Doped Graphene for High Electrochemical Performance. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.; Ahmed, M.S.; Kim, Y.B. Nitrogen-rich Graphitic-carbon@graphene as a Metal-free Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiansyah, A.; Sunnardianto, G.K.; Pradanawati, S.A.; Aditya, D.M.; Kida, T.; Liu, T.-Y. Investigating the Impact of Nitrogen-doping on the Characteristics and Performance of Reduced Graphene Oxide for Lithium-ion Batteries Anode Through Experimental and Theoretical Study. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, H.; Huang, B.; Ji, D.; Li, G.; Zhao, X. Precisely Engineered Nitrogen Dopants in Pd/NC Catalysts: Synergistic Pyridinic–Pyrrolic–Graphitic Triad for Alkaline Methanol Electrooxidation. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13211–13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, D. A Review on C1s XPS-Spectra for Some Kinds of Carbon Materials. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorio, A.; Lucchese, M.M.; Stavale, F.; Martins Ferreira, E.H.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Capaz, R.B.; Achete, C.A.; Cancado, L.G. Raman study of ion-induced defects in N-layer graphene: The relation between D band and defect density. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17446–17456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cançado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Ferreira, E.H.M.; Stavale, F.; Achete, C.A.; Capaz, R.B.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Lombardo, A.; Kulmala, T.S.; Ferrari, A.C. Quantifying Defects in Graphene via Raman Spectroscopy at Different Excitation Energies. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3190–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gong, Q.; Kang, H.; Ji, S.; Li, Z.; Kim, J.M.; Song, Y.J. Synthesis of N-doped Graphene Film with Tunable Graphitic and Pyridinic Doping Content. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 144, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Cheong, H. Raman Spectroscopy for Characterization of Graphene. In Raman Spectroscopy for Nanomaterials Characterization; Kumar, C.S.S.R., Ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 215–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madito, M.J. Revisiting the Raman Disorder Band in Graphene-based Materials: A Critical Review. Vib. Spectrosc. 2025, 139, 103814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solati, N.; Çankaya, M.; Kahraman, A.; Şimşek, K.; Titus, C.J.; Lee, S.J.; Nordlund, D.; Ogasawara, H.; Tekin, A.; Kaya, S. Pyridinic Nitrogen Induced Compressed Bilayer Graphene for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Mater. Today Ener. 2023, 35, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar, G.; Jin, J.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Costa, P.M.F.J. Chemical Vapor Deposition-grown Nitrogen-doped Graphene’s Synthesis, Characterization and Applications. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2022, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehra, M.S.; Narang, V.; Geddam, U.K.; Stefaniak, A.B. Correlation between X-ray diffraction and Raman spectra of 16 commercial graphene-based materials and their resulting classification. Carbon 2017, 111, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sherbini, A.S.; Bakr, M.; Ghoneim, I.; Saad, M. Exfoliation of Graphene Seets via High Energy Wet Milling of Graphite in 2-ethylhexanol and Kerosene. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ju, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Oiang, Y.; Qian, Y. One-pot Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nitrogen-doped Graphene as High-performance Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Lian, K.Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Qio, Q.; Jiang, J.; Deng, M.; Luo, Y. Unraveling the Formation Mechanism of Graphitic Nitrogen-doping in Thermally Treated Graphene with Ammonia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, J.; Wei, J.; Hou, H. Insights Into Nitrogen-doped Carbon for Oxygen Reduction: The Role of Graphitic and Pyridinic Nitrogen Species. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2023, 24, e202200734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Sanyal, B. Effect of the Number of Nitrogen Dopants on the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Graphitic and Pyridinic N-doped Graphene: A Density-functional Study. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18371–18380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, V.V.; Prezhdo, O.V. Nitrogen–Nitrogen Bonds Undermine Stability of N-doped Graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11688–11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Woo, S.I.; Jung, Y. On the Mechanism of Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Nitrogen-doped Graphene Nanoribbons. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 17505–17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quílez-Bermejo, J.; Pérez-Rodríguez, S.; Canevesi, R.; Torres, D.; Morallón, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V. Easy Enrichment of Graphitic Nitrogen to Prepare Highly Catalytic Carbons for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Carbon 2022, 196, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupska, M.; Ilnicka, A.; Lukaszewicz, J.P. The Effect of Nitrogen Species on the Catalytic Properties of N-doped Graphene. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Hirohito, O.; Jadwisienczak, W.M. Probing the Room-temperature Electronic Properties of Nitrogen-doped Graphene Using XAS/XES/XMCD for Magnetic Ink Applications in Flexible Electronics, 2025 SLAC Proposal No. S-XV-ST-6960. SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. SLAC experiments are scheduled for November of 2025.

| Element | Line Type | Apparent Concentration | Intensity Correction | K-Ratio | wt. % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | ||
| Carbon | K series | 112.02 | 112.90 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 1.12022 | 1.12897 | 85.38 | 89.56 |
| Nitrogen | K series | 4.59 | 2.77 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.00817 | 0.00493 | 11.59 | 7.86 |
| Oxygen | K series | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.00241 | 0.00219 | 2.46 | 2.36 |
| Fluorine | K series | 0.44 | 0.31 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.00085 | 0.00060 | 0.56 | 0.22 |
| Sample | C at.% | O at.% | F at.% | N at.% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG-400 (S1) | 58.3 | 27.2 | 2.6 | 11.9 | ||
| %NPyrrolic | %NPyridinic | %NGraphitic | ||||
| 49.3 | 27.2 | 23.5 | ||||
| NG-500 | 65.1 | 20.2 | 2.2 | 12.5 | ||
| %NPyrrolic | %NPyridinic | %NGraphitic | ||||
| 37.5 | 36.3 | 26.2 | ||||
| NG-600 | 75.2 | 10.6 | 1.5 | 12.7 | ||
| %NPyrrolic | %NPyridinic | %NGraphitic | ||||
| 30.5 | 41.2 | 28.3 | ||||
| S2 | 89.7 | 4.6 | 0.2 | 5.5 | ||
| %NPyrrolic | %NPyridinic | %NGraphitic | ||||
| 15.6 | 23.8 | 60.6 | ||||
| Sample | N (at.%) | Ms (10−3 emug−1) | Hc (103 Oe) | Mr (10−3 emug−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG-400 (S1) | 11.9 | 3.06 | 0.04 | 0.29 |
| NG-500 | 12.5 | 5.09 | 0.15 | 0.79 |
| NG-600 | 12.7 | 11.80 | 0.15 | 0.79 |
| S2 | 5.5 | 129.81 | 0.75 | 23.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborty, M.; Jensen, G.; Ingram, D.C.; Stinaff, E.; Jadwisienczak, W.M. Magnetic Properties of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Induced by Dopant Configurations. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221694
Chakraborty M, Jensen G, Ingram DC, Stinaff E, Jadwisienczak WM. Magnetic Properties of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Induced by Dopant Configurations. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(22):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221694
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborty, Madhuparna, Gregory Jensen, David C. Ingram, Eric Stinaff, and Wojciech M. Jadwisienczak. 2025. "Magnetic Properties of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Induced by Dopant Configurations" Nanomaterials 15, no. 22: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221694
APA StyleChakraborty, M., Jensen, G., Ingram, D. C., Stinaff, E., & Jadwisienczak, W. M. (2025). Magnetic Properties of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Induced by Dopant Configurations. Nanomaterials, 15(22), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221694






