Nematic Alignment of Composite Silver-Coated Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Composite NR–Uniaxial Nematic CNC Systems
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Numerical Simulation Approach Based on the Onsager Excluded-Volume Model
3. Results and Discussions
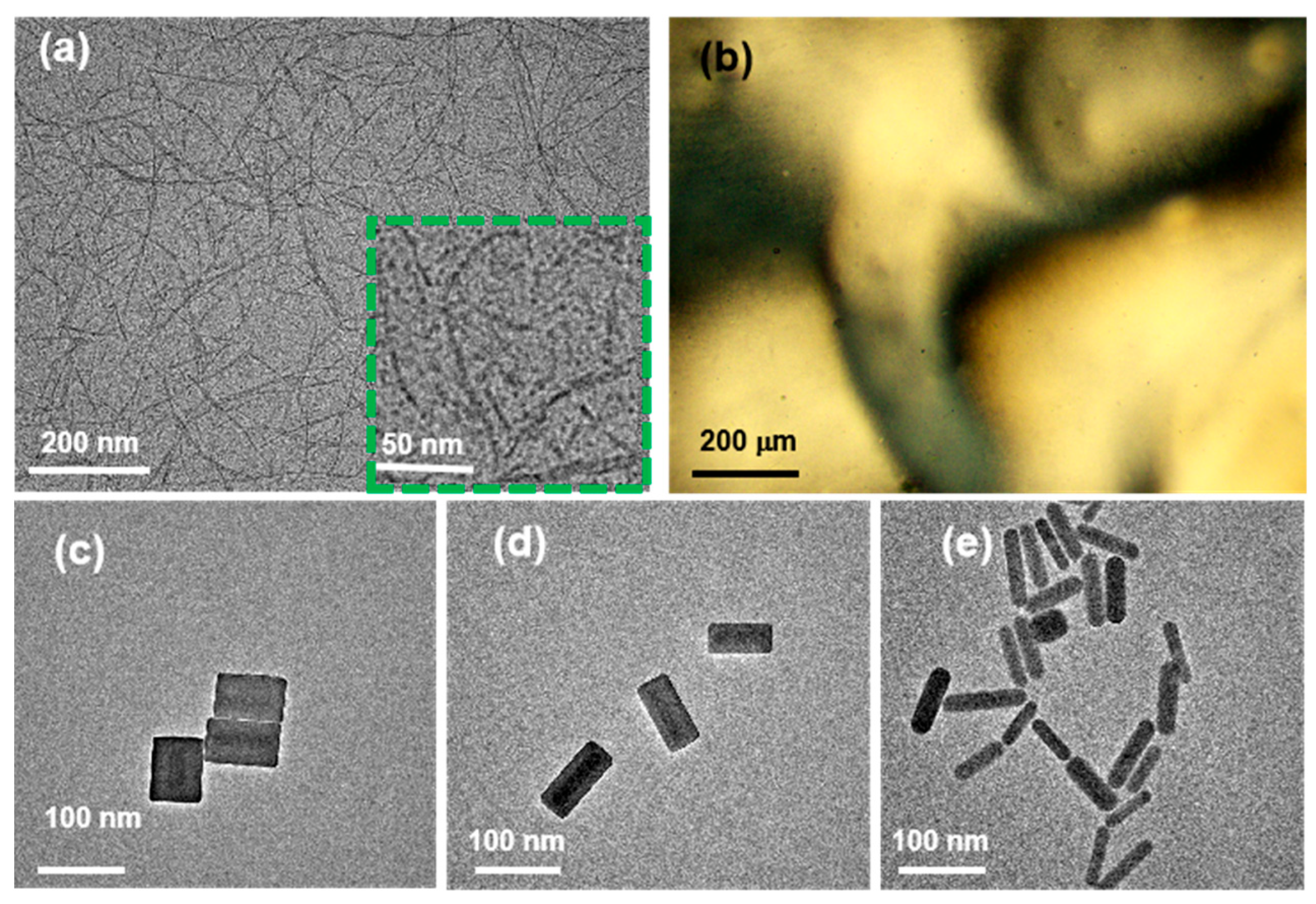
3.1. Self-Assembly Behavior of Composite NR–CNCs
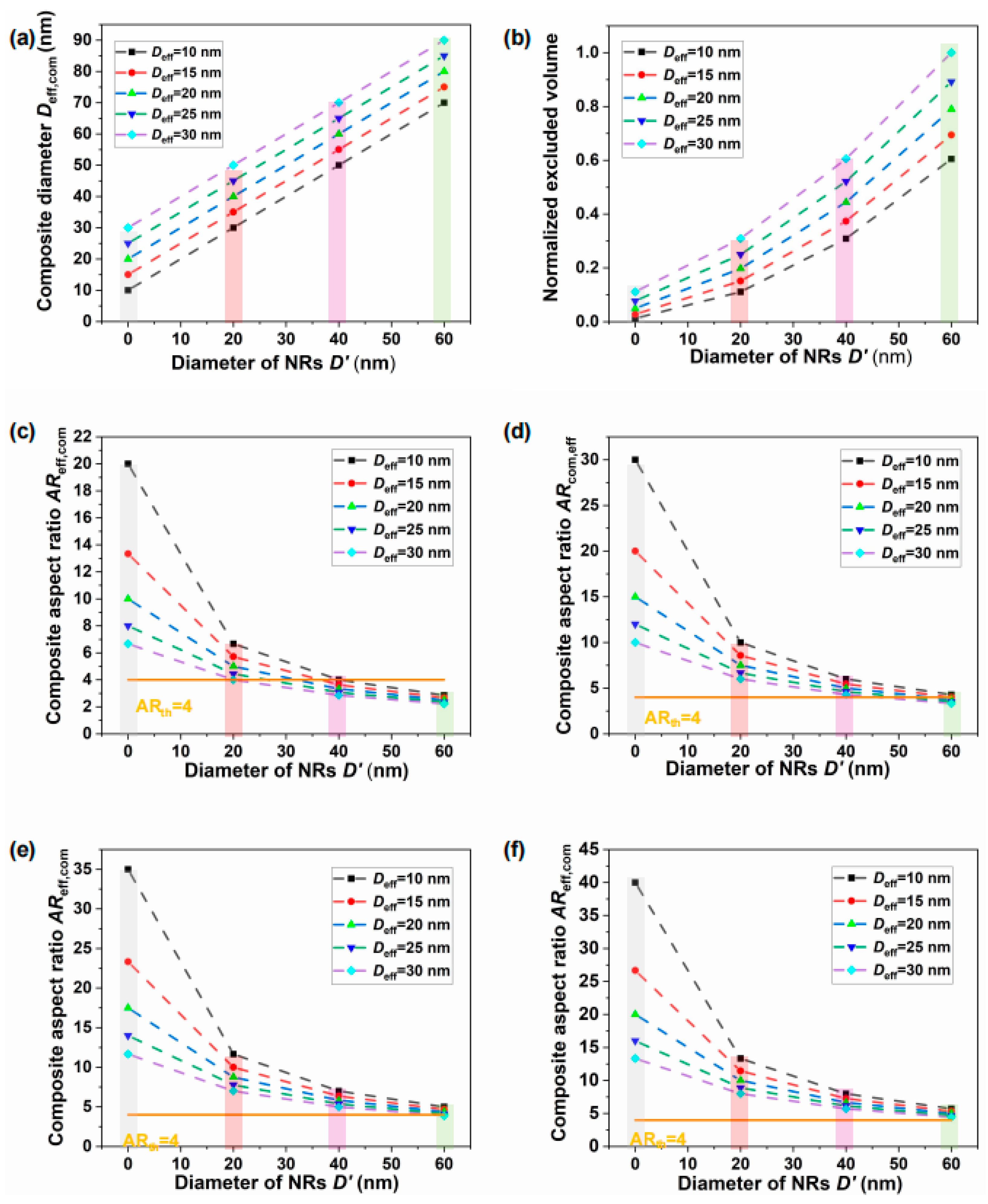
3.2. Composite Effective Excluded-Volume Model
3.3. Influence Mechanism of pH and Aspect Ratio on the Self-Assembly of Composite NR–Uniaxial Nematic CNC Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, X.; Wang, Q. Self-Assembly of Chiral Plasmonic Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10499–10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Valenzuela, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Feng, W.; Li, Q. Liquid crystal-templated chiral nanomaterials: From chiral plasmonics to circularly polarized luminescence. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Al-Zangana, S. Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Phases from Anisotropic Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Mundoor, H.; Yuan, Y.; Smalyukh, I.I. Metal Nanoparticle Dispersion, Alignment, and Assembly in Nematic Liquid Crystals for Applications in Switchable Plasmonic Color Filters and E-Polarizers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.-W.; Rodarte, A.L.; Som, M.; Arya, G.; Tao, A.R. Colloidal plasmonic nanocomposites: From fabrication to optical function. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3100–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi, M.M.; Sandberg, M.; Olsson, R.T.; Pedersen, J.; Benselfelt, T.; Wohlert, J. Wood and Cellulose: The Most Sustainable Advanced Materials for Past, Present, and Future Civilizations. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2415787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.N.; Almeida, P.L.; Monge, N.; Aguirre, L.E.; Reis, D.; de Oliveira, C.L.; Neto, A.M.; Pieranski, P.; Godinho, M.H. Mind the Microgap in Iridescent Cellulose Nanocrystal Films. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Schütz, C.; Salajkova, M.; Noh, J.; Hyun Park, J.; Scalia, G.; Bergström, L. Cellulose nanocrystal-based materials: From liquid crystal self-assembly and glass formation to multifunctional thin films. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Ji, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, H. All-Cellulose-Based Flexible Photonic Films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck-Candanedo, S.; Viet, D.; Gray, D.G. Induced phase separation in cellulose nanocrystal suspensions containing ionic dye species. Cellulose 2006, 13, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.M.; Kimura, T.; Revol, J.-F.; Gray, D.G. Effects of Ionic Strength on the Isotropic−Chiral Nematic Phase Transition of Suspensions of Cellulose Crystallites. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M. Plant bling: Cellulose that sparkles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frka-Petesic, B.; Vignolini, S. So much more than paper. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Evans, J.; Wang, N.; Guo, T.; He, S. pH dependence of the chirality of nematic cellulose nanocrystals. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, N.; Guo, T.; Evans, J.; He, S. Preparation of optical waveplates from cellulose nanocrystal nematics on patterned polydimethylsiloxane substrates. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 4614–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, C.; Agthe, M.; Fall, A.B.; Gordeyeva, K.; Guccini, V.; Salajkova, M.; Plivelic, T.S.; Lagerwall, J.P.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Bergstrom, L. Rod Packing in Chiral Nematic Cellulose Nanocrystal Dispersions Studied by Small-Angle X-ray Scattering and Laser Diffraction. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6507–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Boott, C.E.; MacLachlan, M.J. Understanding the Self-Assembly of Cellulose Nanocrystals-Toward Chiral Photonic Materials. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukach, A.; Thérien-Aubin, H.; Querejeta-Fernández, A.; Pitch, N.; Chauve, G.; Méthot, M.; Bouchard, J.; Kumacheva, E. Coassembly of Gold Nanoparticles and Cellulose Nanocrystals in Composite Films. Langmuir 2015, 31, 5033–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsowitz, K.E.; Qi, H.; Hamad, W.Y.; MacLachlan, M.J. Free-standing mesoporous silica films with tunable chiral nematic structures. Nature 2010, 468, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, O.; Tran, A.; Lewis, L.; Hamad, W.Y.; MacLachlan, M.J. Unwinding a spiral of cellulose nanocrystals for stimuli-responsive stretchable optics. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, C.; Huang, H. Recent advances in structural color display of cellulose nanocrystal materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 22, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Li, C.Y.; Pan, J.T.; Ji, Y.E.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.X.; Lu, Y.Q. Self-assembled liquid crystal architectures for soft matter photonics. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Campbell, M.G.; Evans, J.S.; Smalyukh, I.I. Orientationally ordered colloidal co-dispersions of gold nanorods and cellulose nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7178–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speranza, A.; Sollich, P. Simplified Onsager theory for isotropic–nematic phase equilibria of length polydisperse hard rods. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 5421–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.G.; Liu, Q.; Sanders, A.; Evans, J.S.; Smalyukh, I.I. Preparation of Nanocomposite Plasmonic Films Made from Cellulose Nanocrystals or Mesoporous Silica Decorated with Unidirectionally Aligned Gold Nanorods. Materials 2014, 7, 3021–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, A.J.; Funk, A.J.; Liu, Q.; De La Cruz, J.A.; Sheetah, G.H.; Fleury, B.; Smalyukh, I.I. Plasmonic metamaterial gels with spatially patterned orientational order via 3D Printing. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 20558–20563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, N.; Lei, Q.; Evans, J.; He, S. Aligning silver nanowire films with cellulose nanocrystal nematics. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 3321–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Jaquet, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Gerhard, C.; Zhang, K. Structural colors by synergistic birefringence and surface plasmon resonance. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16832–16839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Song, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, K. Designable Multiple Structural Colors Using Alkaline Periodate Oxidated Cellulose Nanocrystals and Gold Nanorods. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2200615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles. J. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 627–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkerkerker, H.N.W.; Coulon, P.; Van Der Haegen, R.; Deblieck, R. On the isotropic-liquid crystal phase separation in a solution of rodlike particles of different lengths. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3427–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.A.L.; Bollmann, J.; Lee, H.W.; Zhou, Y. Accurate representation of interference colours (Michel–Lévy chart): From rendering to image colour correction. J. Microsc. 2018, 269, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K. Van der Waals Forces: A Handbook for Biologists, Chemists, Engineers, and Physicists. By V Adrian Parsegian. Q. Rev. Biol. 2006, 81, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroege, G.J.; Lekkerkerker, H.N.W. Theory of the isotropic-nematic-nematic phase separation for a solution of bidisperse rodlike particles. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 3601–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


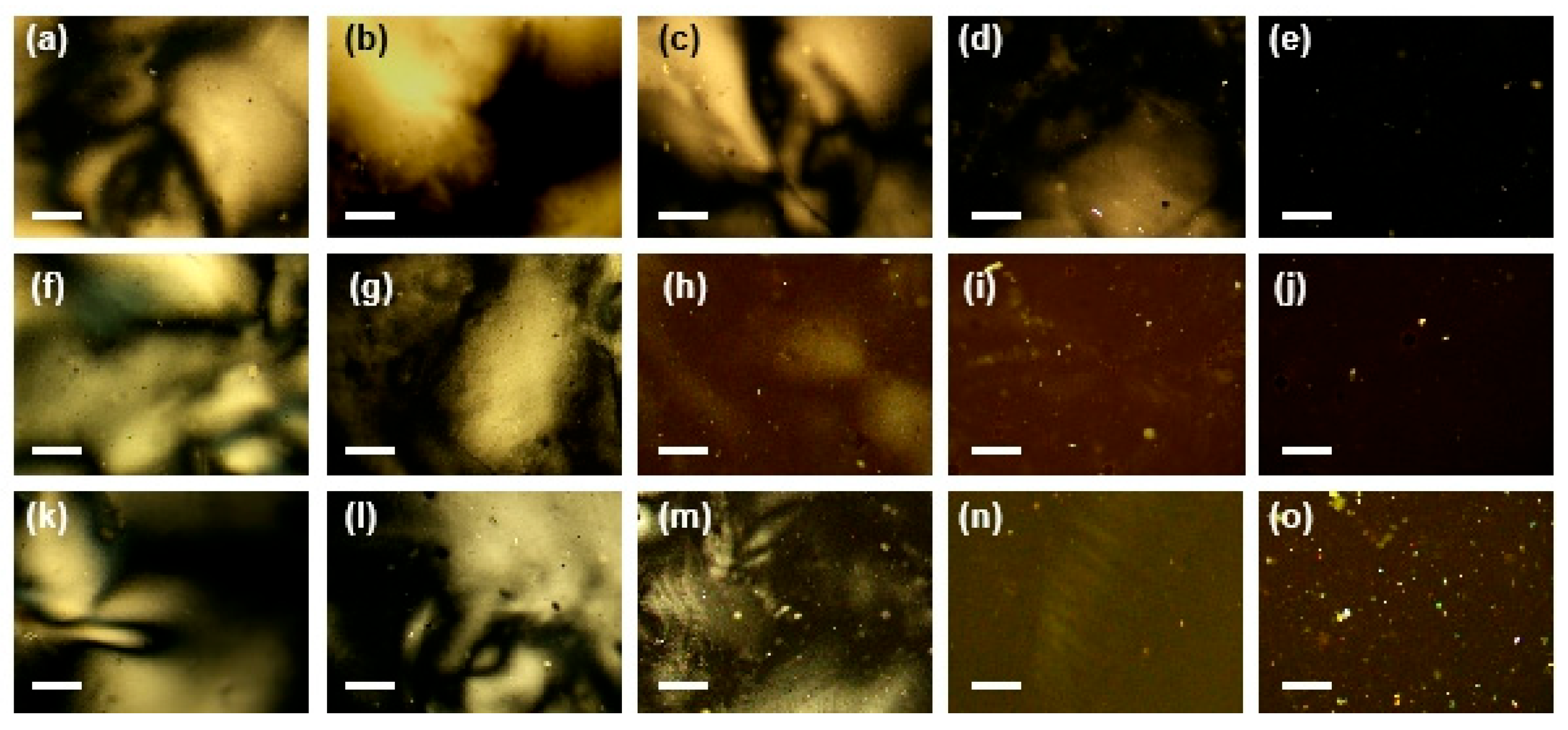


| Composite System | NR1-Ne1 | NR2-Ne1 | NR3-Ne1 | NR1-Ne2 | NR2-Ne2 | NR3-Ne2 | NR1-Ne3 | NR2-Ne3 | NR3-Ne3 | NR1-Ne4 | NR2-Ne4 | NR3-Ne4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 11.49 | 11.49 | 11.49 | 11.83 | 11.83 | 11.83 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 12.03 | 12.03 | 12.03 |
| Aspect ratio | 1.3 | 2 | 3.4 | 1.3 | 2 | 3.4 | 1.3 | 2 | 3.4 | 1.3 | 2 | 3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Evans, J.; Gao, B.; Shen, G.; He, S.; Yu, W. Nematic Alignment of Composite Silver-Coated Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201594
Li C, Evans J, Gao B, Shen G, He S, Yu W. Nematic Alignment of Composite Silver-Coated Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(20):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201594
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chenxi, Julian Evans, Bo Gao, Guancheng Shen, Sailing He, and Weixing Yu. 2025. "Nematic Alignment of Composite Silver-Coated Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals" Nanomaterials 15, no. 20: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201594
APA StyleLi, C., Evans, J., Gao, B., Shen, G., He, S., & Yu, W. (2025). Nematic Alignment of Composite Silver-Coated Gold Nanorods and Cellulose Nanocrystals. Nanomaterials, 15(20), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201594






