Enhanced Killing of Colon Cancer Cells by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Ellagic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
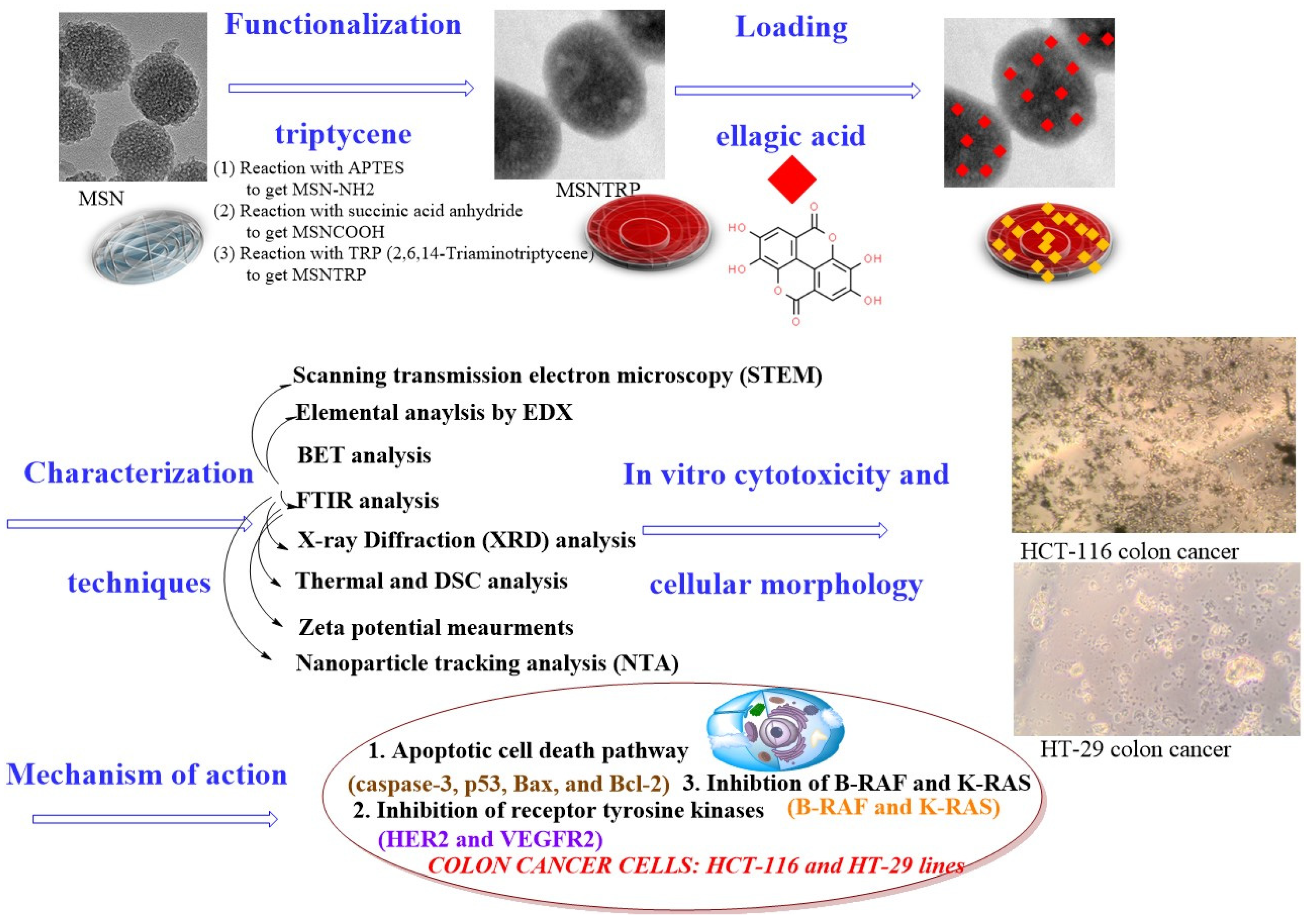
2.1. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Synthesis, Modification, and Functionalization with Triptycene
2.2. Nanoformulation Preparation
2.3. Nanostructure Characterization Techniques
2.4. Cell Cultures, In Vitro Cytotoxicity, and Anticancer Mechanism Evaluation and Gene Expression Profiling
2.4.1. Cell Cultures
2.4.2. In Vitro Studies
2.4.3. Anticancer Mechanism Evaluation
2.4.4. Gene Expression Profiling by RT-qPCR
2.5. Extraction of Protein and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
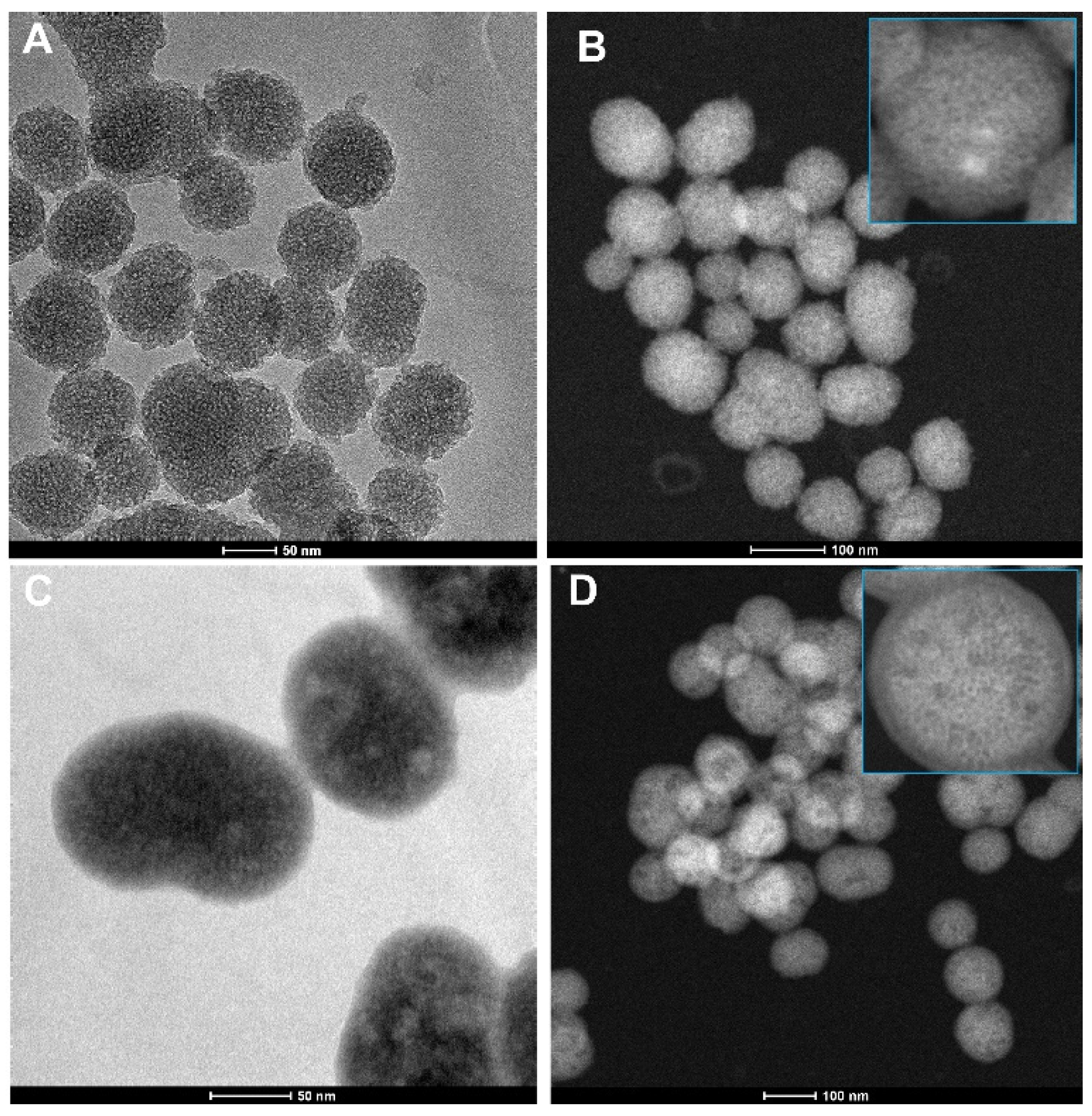
3.1. Microscopical Observations
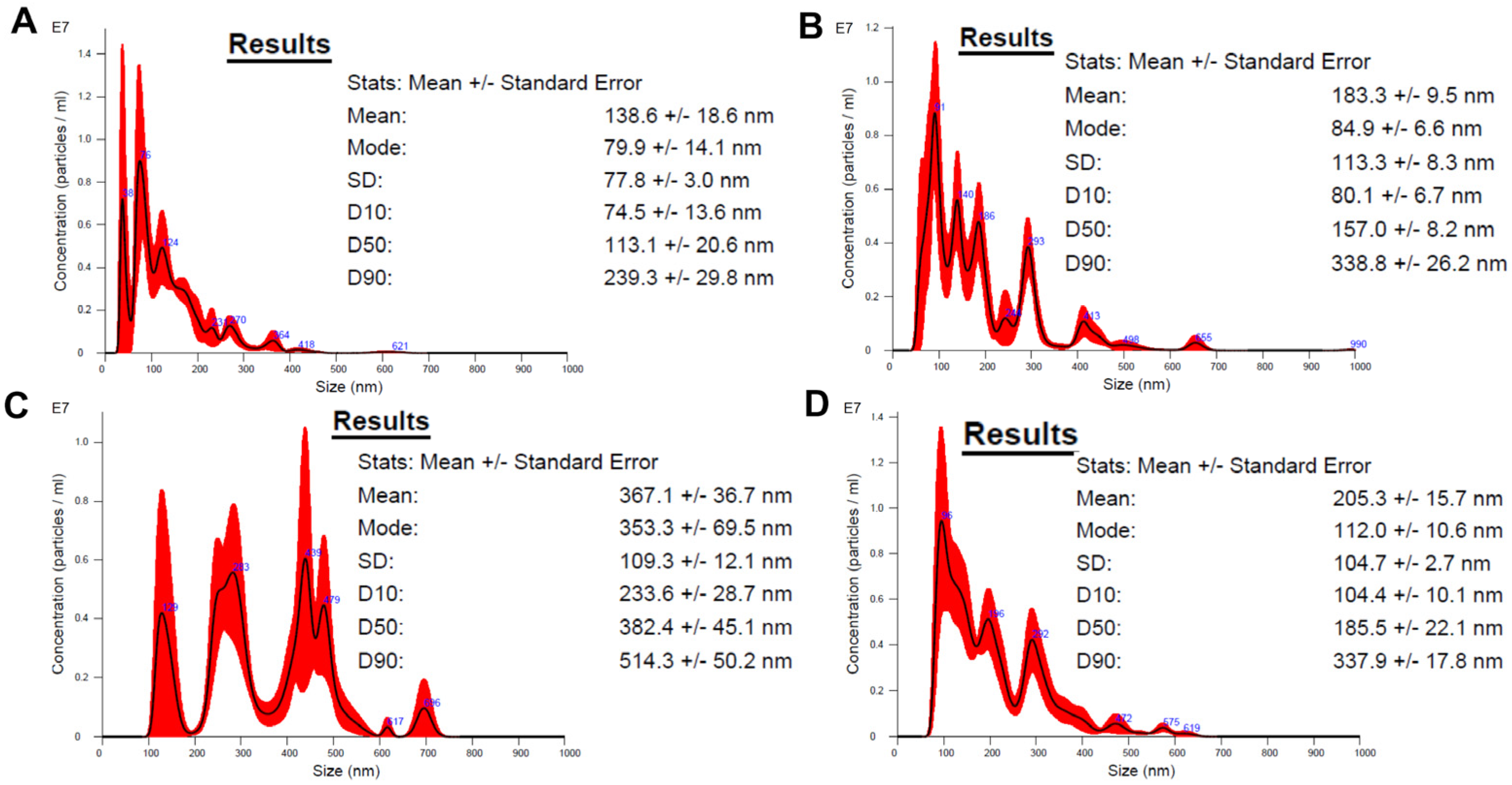
3.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
3.3. Elemental Analysis
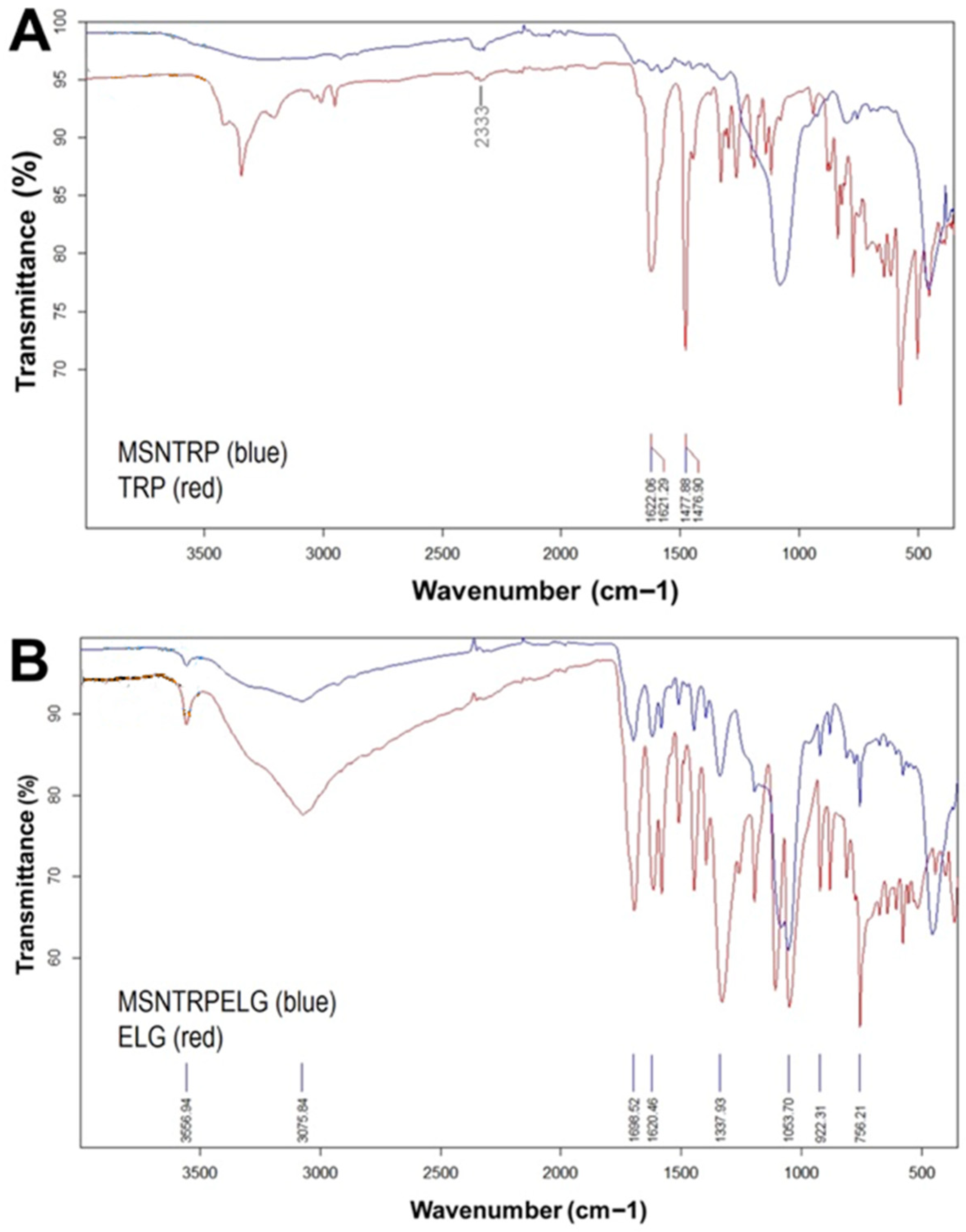
3.4. FTIR-ATR Analysis
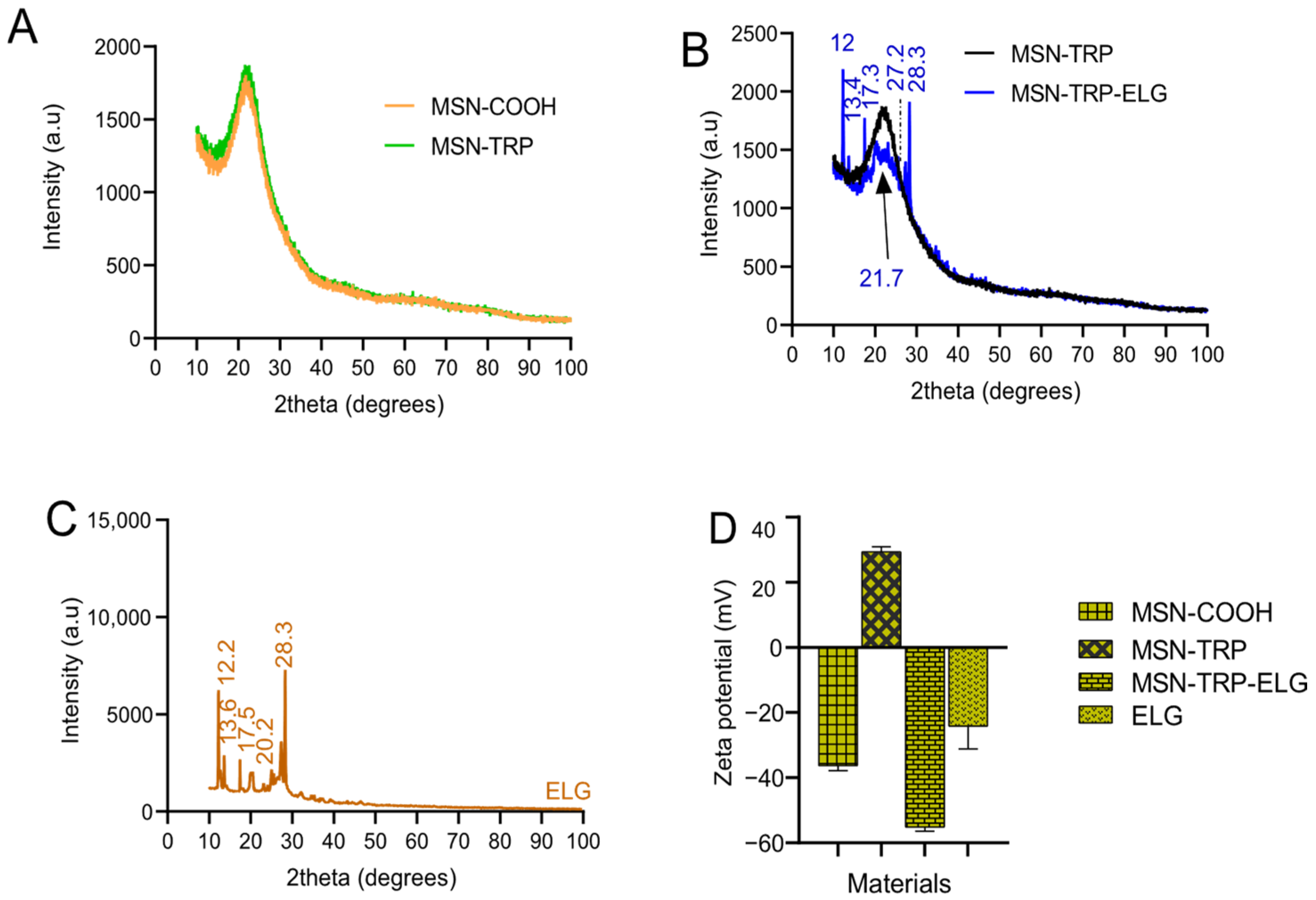
3.5. XRD Analysis
3.6. Zeta Potential Analysis
3.7. Simultaneous Thermal Analysis (STA) and Specific Surface Area
3.8. Loading Efficiency
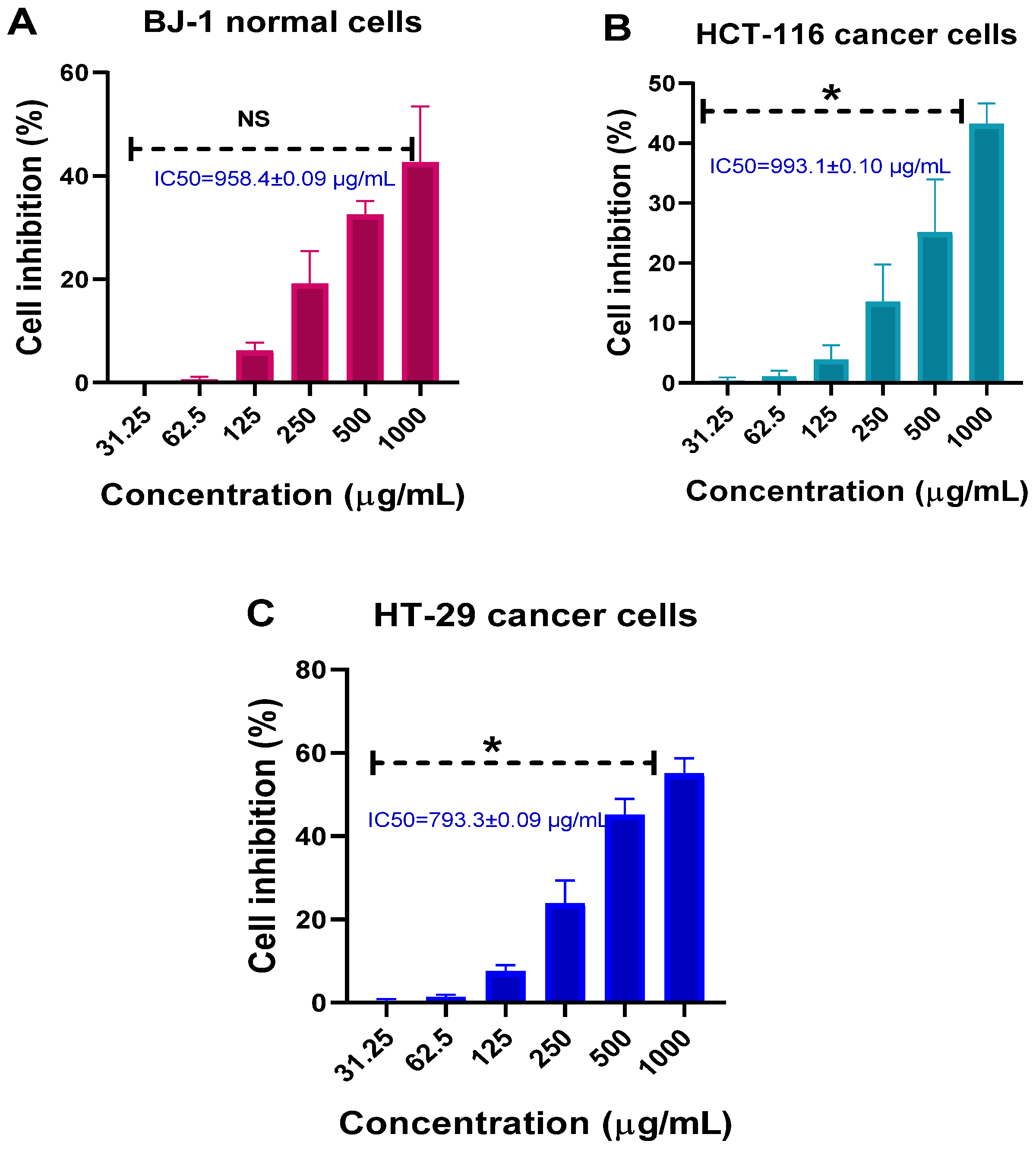
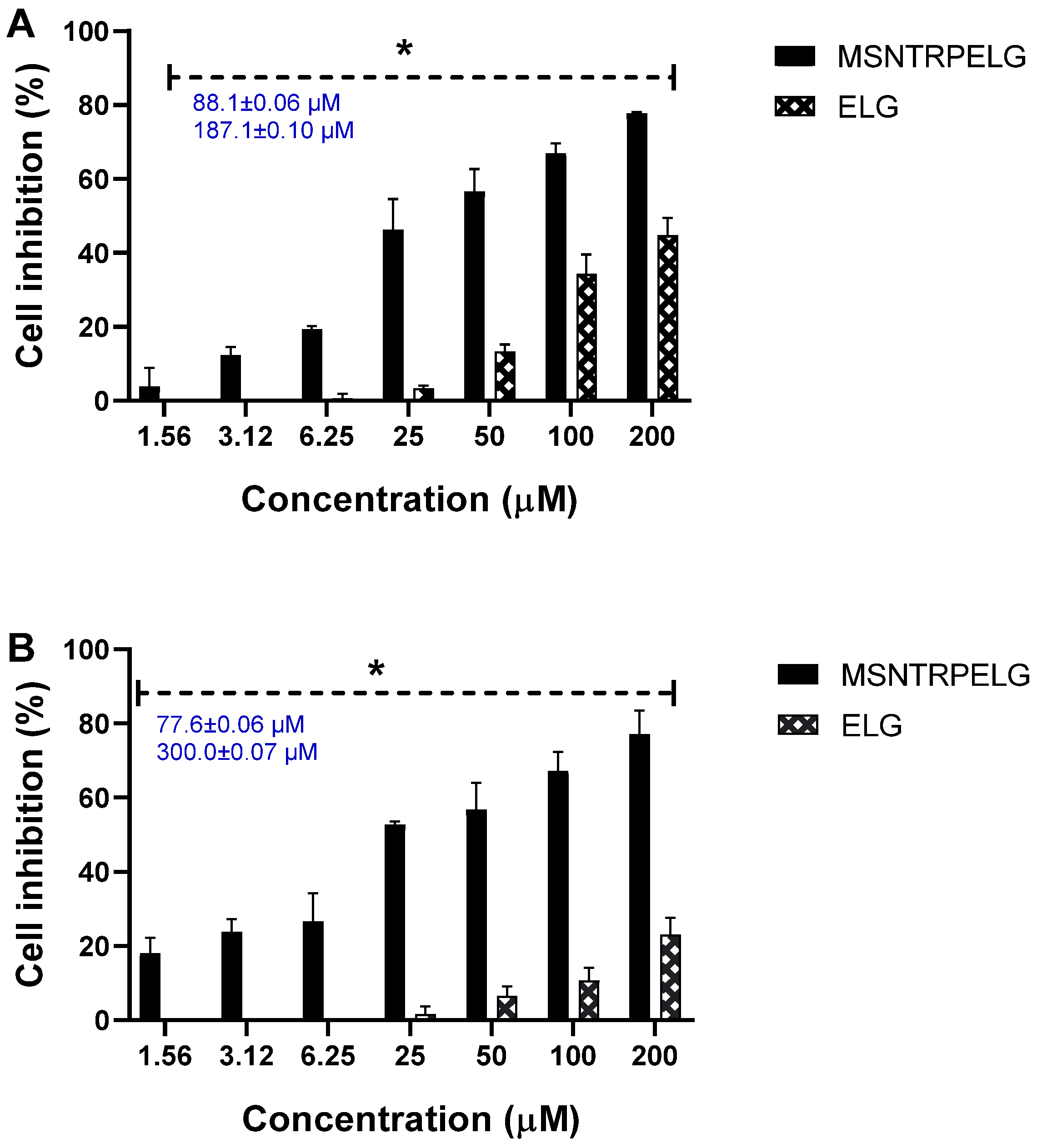
3.9. Cytotoxicity and Anticancer Effects
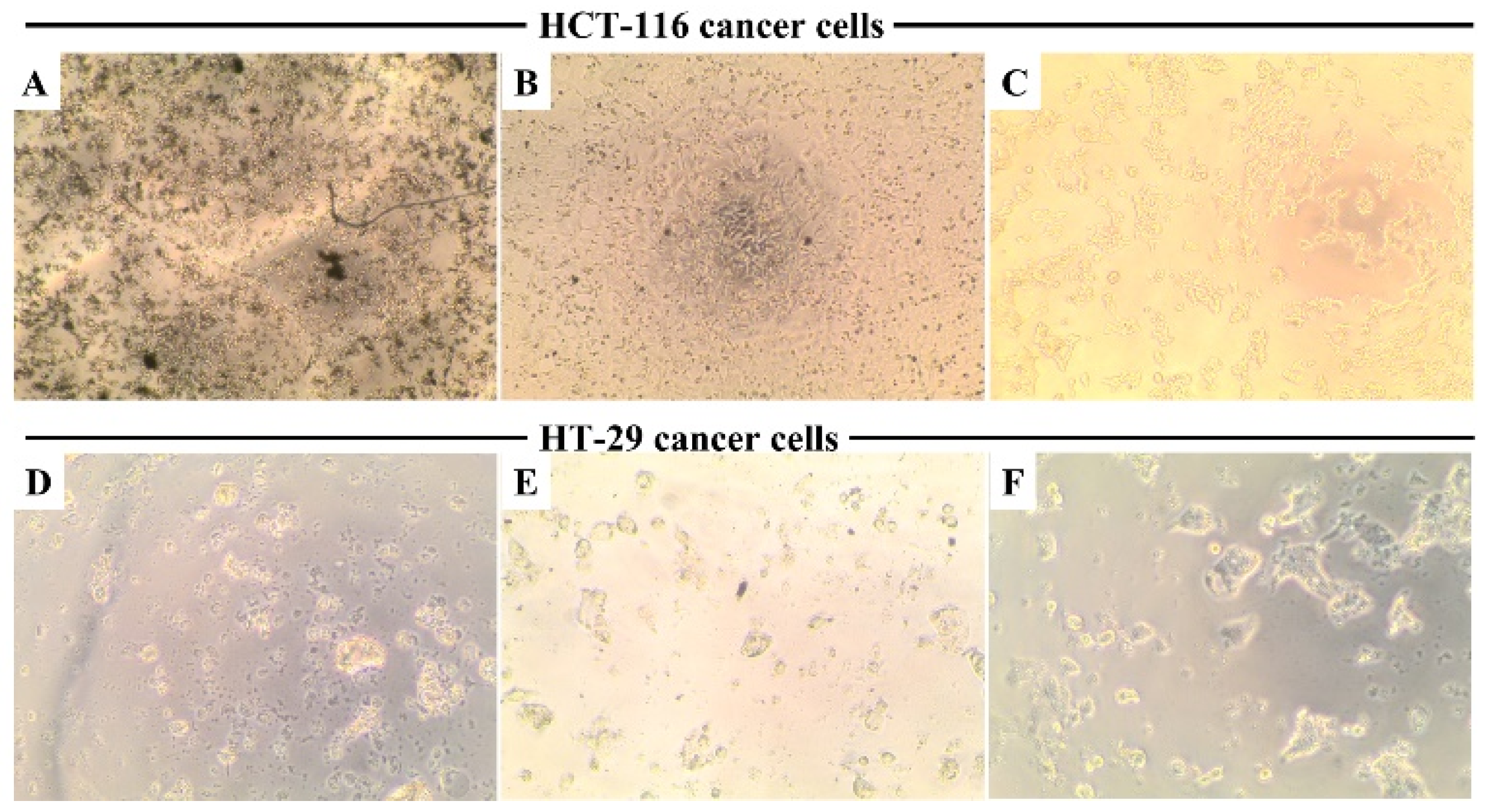
3.10. Cellular Morphology Observation
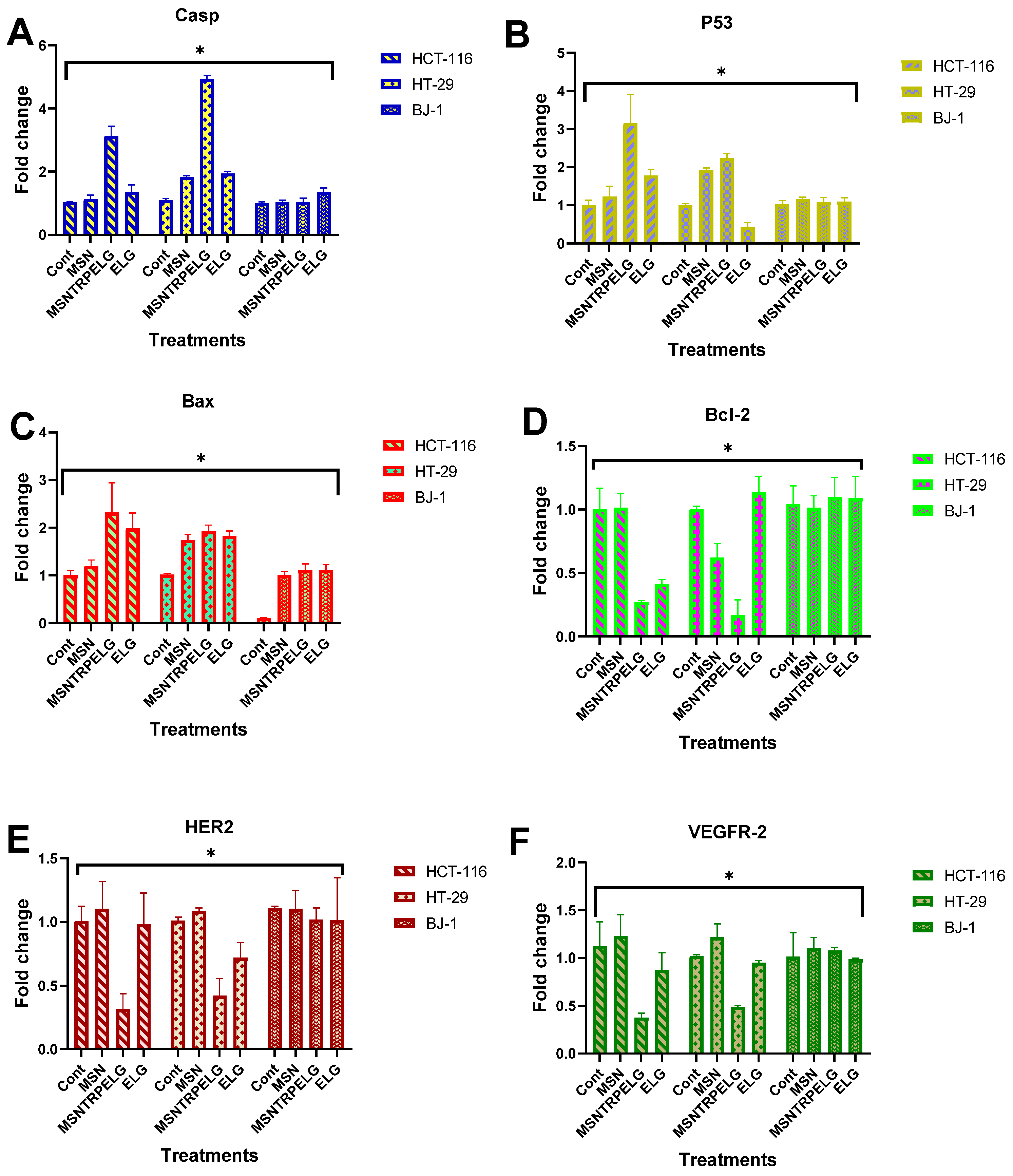
3.11. Evaluation of the Mechanism of Action
Apoptotic Cell Death Pathway
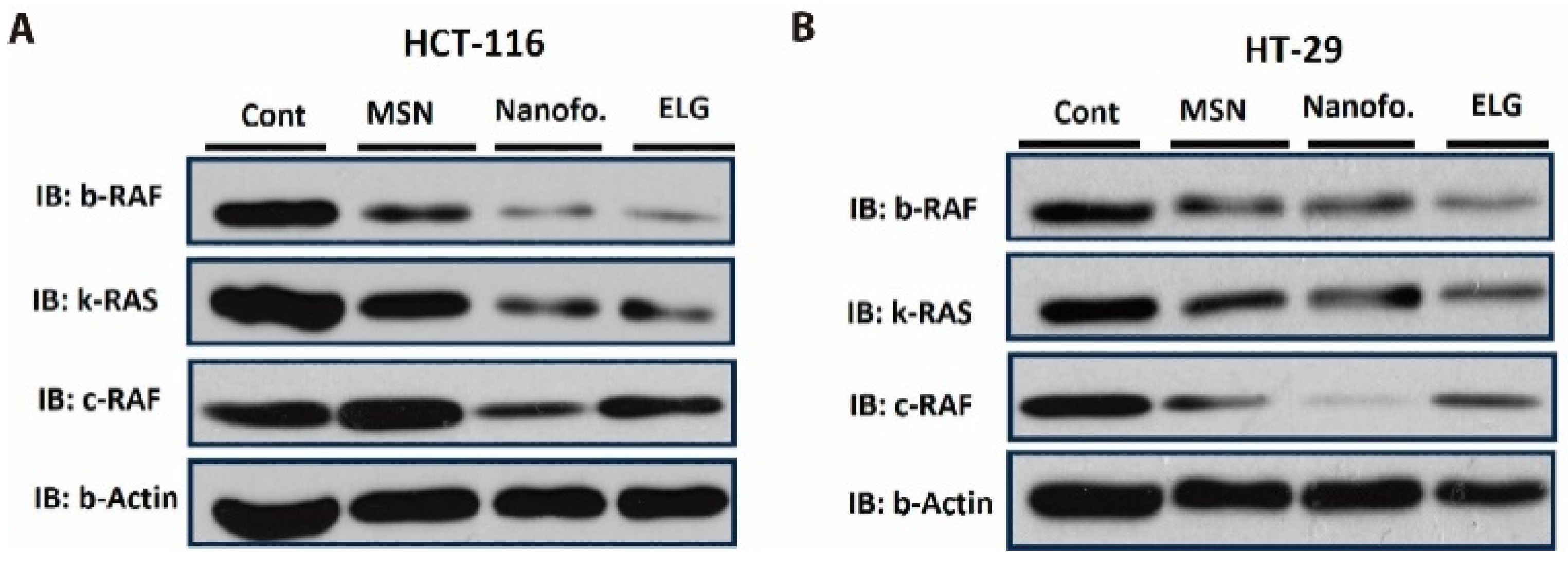
3.12. Inhibition of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
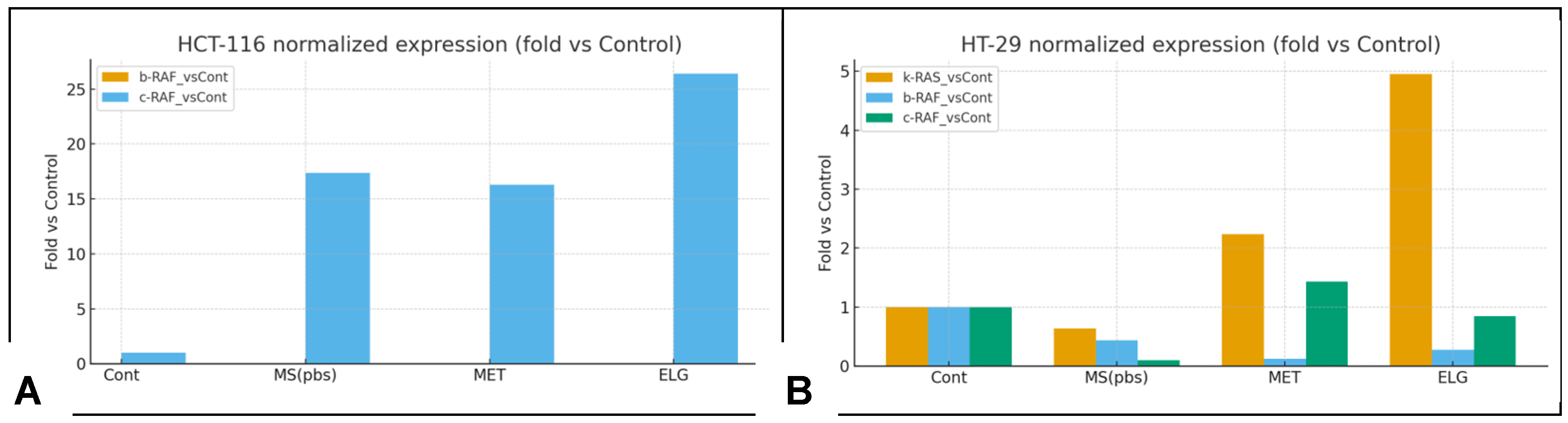
3.13. Inhibition of B-RAF and K-RAS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BJ-1 | human fibroblast cell line |
| B-RAF | B-Raf proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase |
| C-RAF | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase |
| DTG | derivative thermogravimetry |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| EDX | energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| ELG | ellagic acid |
| FE-SEM | field-emission scanning electron microscopy |
| FTIR-ATR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy with attenuated total reflectance |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HCT-116, HT-29 | human colon cancer cell lines |
| IC50 | half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| K-RAS | K-Ras proto-oncogene GTPase |
| MAPK/ERK | mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway |
| MCF-7 | human breast cancer cell line |
| MSN | mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| MSNCOOH | carboxyl-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| MSNTRP | triptycene-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| MSNTRPELG | triptycene-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with ellagic acid |
| MTT assay | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay |
| NTA | nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| PEG | poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PI3K/AKT | phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway |
| PLGA | poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PLGA-PEG | poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymer |
| RAF/RAS | proto-oncogene signalling pathway |
| RTKs | receptor tyrosine kinases |
| STA | simultaneous thermal analysis |
| STEM | scanning transmission electron microscopy |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| TRP | triptycene |
| VEGFR2 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Huang, M.; Lu, J.-J.; Ding, J. Natural Products in Cancer Therapy: Past, Present and Future. Nat. Prod. Bioprospecting 2021, 11, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, S. Natural products as anticancer agents and enhancing their efficacy by a mechanism-based precision approach. Explor. Drug Sci. 2024, 2, 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A.; Koliada, A.; Zayachkivska, A.; Lushchak, O. Nanodelivery of Natural Antioxidants: An Anti-aging Perspective. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, H.; Lu, L.; Li, M.; Han, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Enhanced Solubility and Antitumor Activity of Annona Squamosa Seed Oil via Nanoparticles Stabilized with TPGS: Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Su, R.; Nie, S.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Application of nanotechnology in improving bioavailability and bioactivity of diet-derived phytochemicals. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, L.; Pastor, E.R.; Stone, T.; Mousa, S.A. Emerging Nanopharmaceuticals and Nanonutraceuticals in Cancer Management. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouAitah, K.; Lojkowski, W. Delivery of Natural Agents by Means of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres as a Promising Anticancer Strategy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Zong, G.-f.; Wang, X.; Yue, B.-j.; Cheng, P.; Tao, R.-z.; Li, X.; Wei, Z.-h.; Lu, Y. Promises of natural products as clinical applications for cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2025, 1880, 189241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, B.; Jain, S.K. Semisynthesis: Bridging natural products and novel anticancer therapies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 12, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Martorell, M.; Valdes, S.E.; Belwal, T.; Tejada, S.; Sureda, A.; Kamal, M.A. Flavonoids nanoparticles in cancer: Treatment, prevention and clinical prospects. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 69, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, D.A.; Elkhodairy, K.A.; Teleb, M.; Elzoghby, A.O. Nanomedicine-based approaches for improved delivery of phyto-therapeutics for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, D.M.; El-Sayed, M.; Reda, A.; Fang, J.Y.; Khattab, S.N.; Elzoghby, A.O. Recent advances in herbal combination nanomedicine for cancer: Delivery technology and therapeutic outcomes. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Lojkowski, W. Nanomedicine as an Emerging Technology to Foster Application of Essential Oils to Fight Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Chiu, T.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hu, S.H.; Chen, S.Y. Magnetic core-shell nanocapsules with dual-targeting capabilities and co-delivery of multiple drugs to treat brain gliomas. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Farghali, A.A.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Stefanek, A.; Gierlotka, S.; Opalinska, A.; Allayeh, A.K.; Ciach, T.; Lojkowski, W. Folic acid-conjugated mesoporous silica particles as nanocarriers of natural prodrugs for cancer targeting and antioxidant action. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26466–26490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahein, S.A.; Aboul-Enein, A.M.; Higazy, I.M.; Abou-Elella, F.; Lojkowski, W.; Ahmed, E.R.; Mousa, S.A.; AbouAitah, K. Targeted anticancer potential against glioma cells of thymoquinone delivered by mesoporous silica core-shell nanoformulations with pH-dependent release. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5503–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouAitah, K.; Hassan, H.A.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Gohar, L.; Shaker, O.G.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Opalinska, A.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Targeted Nano-Drug Delivery of Colchicine against Colon Cancer Cells by Means of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Cancers 2020, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Stefanek, A.; Higazy, I.M.; Janczewska, M.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Chodara, A.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Szałaj, U.; Shahein, S.A.; Aboul-Enein, A.M.; et al. Effective Targeting of Colon Cancer Cells with Piperine Natural Anticancer Prodrug Using Functionalized Clusters of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouAitah, K.; Allayh, A.K.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Shaker, Y.M.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Lojkowski, W. Nanoformulation Composed of Ellagic Acid and Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Inactivates DNA and RNA Viruses. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerio, A.P.; Fontanari, C.; Borducchi, E.; Keller, A.C.; Russo, M.; Soares, E.G.; Albuquerque, D.A.; Faccioli, L.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of Lafoensia pacari and ellagic acid in a murine model of asthma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 580, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Hawthorne, S. Ellagic acid, pomegranate and prostate cancer—A mini review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.H.; Kown, T.Y.; Oh, G.T.; Park, W.F.; Park, S.I.; Park, S.K.; Lee, Y.I. The flavonoid ellagic acid from a medicinal herb inhibits host immune tolerance induced by the hepatitis B virus-e antigen. Antivir. Res. 2006, 72, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, E.L.; Zografov, N.N.; Simeonova, L.S. Comparative study on the antioxidant capacities of synthetic influenza inhibitors and ellagic acid in model systems. Biomed. Pharmacother 2016, 83, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, P.N.; Witkowski, B.; Olagnier, D.; Nicolau, M.L.; Garcia-Alvarez, M.C.; Berry, A.; Benoit-Vical, F. In vitro and in vivo properties of ellagic acid in malaria treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Kasukabe, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Niitsu, N.; Okabe-Kado, J. Ellagic acid, a natural polyphenolic compound, induces apoptosis and potentiates retinoic acid-induced differentiation of human leukemia HL-60 cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2010, 92, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjaeraa, C.; Nånberg, E. Effect of ellagic acid on proliferation, cell adhesion and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2009, 63, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, J.H. Antioxidant and apoptosis-inducing activities of ellagic acid. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 3601–3606. [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg, J.H.; Schuck, A.G.; Reiss, S.E.; Wolf, B.J.; Fertel, S.R.; Zuckerbraun, H.L.; Babich, H. Ellagic Acid, a Dietary Polyphenol, Selectively Cytotoxic to HSC-2 Oral Carcinoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadinejad, A.; Mohajeri, T.; Aleyaghoob, G.; Heidarian, F.; Kazemi Oskuee, R. Ellagic acid as a potent anticancer drug: A comprehensive review on in vitro, in vivo, in silico, and drug delivery studies. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2323–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyer, H.S.; Warri, A.M.; Woode, D.R.; Hilakivi-Clarke, L.; Clarke, R. Influence of Berry Polyphenols on Receptor Signaling and Cell-Death Pathways: Implications for Breast Cancer Prevention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5693–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Bo, W.; Zhou, Y.; Dang, S.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Liu, M. Multiple effects of ellagic acid on human colorectal carcinoma cells identified by gene expression profile analysis. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Yadav, M.; Chauhan, R.; Basniwal, R.K.; Pathak, V.M.; Ranjan, A.; Kapardar, R.K.; Srivastav, R.; Tuli, H.S.; Ramniwas, S.; et al. Exploring the Potential of Ellagic Acid in Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Oncol. Ther. 2024, 12, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Sánchez, M.A.; Dávalos, A.; González-Sarrías, A.; Casas-Agustench, P.; Visioli, F.; Monedero-Saiz, T.; García-Talavera, N.V.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.B.; Sánchez-Álvarez, C.; García-Albert, A.M.; et al. MicroRNAs expression in normal and malignant colon tissues as biomarkers of colorectal cancer and in response to pomegranate extracts consumption: Critical issues to discern between modulatory effects and potential artefacts. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesalma, S.; Sudhandiran, G. Ellagic acid prevents rat colon carcinogenesis induced by 1, 2 dimethyl hydrazine through inhibition of AKT-phosphoinositide-3 kinase pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 660, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ye, C.; Qing, X.; Liu, S.; Lv, X.; Wang, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y. Multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor nanoparticle delivery systems for cancer therapy. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marslin, G.; Revina, A.M.; Khandelwal, V.K.M.; Balakumar, K.; Prakash, J.; Franklin, G.; Sheeba, C.J. Delivery as nanoparticles reduces imatinib mesylate-induced cardiotoxicity and improves anticancer activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, F.; Lamas, S.; Osório, H.; Aguiar, P.; Freitas, D.; Gärtner, F.; Sarmento, B.; Reis, C.A.; Gomes, J. Nanoparticles targeting Sialyl-Tn for efficient tyrosine kinase inhibitor delivery in gastric cancer. Acta Biomater. 2023, 170, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirersa, W.B.; Getachew, G.; Wibrianto, A.; Rasal, A.S.; Gurav, V.S.; Zakki Fahmi, M.; Chang, J.Y. Molybdenum-oxo-sulfide quantum dot-based nanocarrier: Efficient generation of reactive oxygen species via photo/chemodynamic therapy and stimulus-induced drug release. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2023, 647, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, G.G.; Chen, Y.-C.; Ciou, S.-Y.; Hsu, S.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-Y. Hypoxia-Targeted-Therapy: Mussel-inspired hollow polydopamine nanocarrier containing MoS2 nanozyme and tirapazamine with anti-angiogenesis property for synergistic tumor therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 685, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, F.M.; Shaker, M.A. Enhanced anticancer activity and oral bioavailability of ellagic acid through encapsulation in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7405–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, O.M.; Bekhit, A.A.; Khattab, S.N.; Helmy, M.W.; Abdel-Ghany, Y.S.; Teleb, M.; Elzoghby, A.O. Synthesis of lactoferrin mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pemetrexed/ellagic acid synergistic breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Ghosh, S.; Kumar, P.; Basu, B.; Nagpal, K. Ellagic acid-loaded, tween 80-coated, chitosan nanoparticles as a promising therapeutic approach against breast cancer: In-vitro and in-vivo study. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, F.; Alavizadeh, S.H.; Kalantari, M.R.; Hoseini, S.J.; Farshchi, H.K.; Jaafari, M.R.; Doagooyan, M.; Bemidinezhad, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Sahebkar, A.; et al. Ellagic acid nanoliposomes potentiate therapeutic effects of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin in melanoma: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 93, 105396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.; Santini, C.; Bardasi, C.; Cerma, K.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Spallanzani, A.; Andrikou, K.; Cascinu, S.; Gelsomino, F. BRAF-Mutated Colorectal Cancer: Clinical and Molecular Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Biphase Stratification Approach to Three-Dimensional Dendritic Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, A.; Duan, R.; Zahid, F.; Dong, C.; Wang, B.; Hong, F.; Ou, X.; Jia, Y.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Dual stimuli-responsive nano-vehicles for controlled drug delivery: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles end-capped with natural chitosan. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13268–13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Soliman, A.A.F.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Nassrallah, A.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Co-Delivery System of Curcumin and Colchicine Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Promotes Anticancer and Apoptosis Effects. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelenein, M.G.; El-Rashedy, A.A.; Awad, H.M.; El Farargy, A.F.; Nassar, I.F.; Nassrallah, A. Synthesis, molecular modeling Insights, and anticancer assessment of novel polyfunctionalized Pyridine congeners. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 141, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboul-Soud, M.A.M.; Ashour, A.E.; Challis, J.K.; Ahmed, A.F.; Kumar, A.; Nassrallah, A.; Alahmari, T.A.; Saquib, Q.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Al-Sheikh, Y.; et al. Biochemical and Molecular Investigation of In Vitro Antioxidant and Anticancer Activity Spectrum of Crude Extracts of Willow Leaves Salix safsaf. Plants 2020, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaad, H.I.; Zhou, L.; Carroll, R.J.; Wu, G. Rapid publication-ready MS-Word tables for one-way ANOVA. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, W.A.; Wahyuningsih, S.; Gomez-Ruiz, S.; Wibowo, F.R. Drug loading ability and release study of various size small mesoporous silica nanoparticle as drug carrier. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2190, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarara, T.E.; Miller, D.P.; Weers, A.E.; Muliadi, A.; Tso, J.; Eliahu, A.; Weers, J.G. Formulation of Dry Powders for Inhalation Comprising High Doses of a Poorly Soluble Hydrophobic Drug. Front. Drug Deliv. 2022, 2, 862336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta Potential Measurement. In Characterization of Nanoparticles Intended for Drug Delivery; McNeil, S.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiadis, S.H.; Chrissopoulou, K.; Stratakis, E.; Kavatzikidou, P.; Kaklamani, G.; Ranella, A. How the Physicochemical Properties of Manufactured Nanomaterials Affect Their Performance in Dispersion and Their Applications in Biomedicine: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzard, R.H.; Siddig, L.A.; Abdelhamid, A.S.; Alzamly, A. Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Coupling of Neat Benzylamine over a Bi-Ellagate Metal–Organic Framework. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36689–36696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, G.; Sharma, M.; Dahiya, S.; Chhikara, A.; Chopra, M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Radical Scavenging Ability of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Nanogels. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 695138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Piotrowska, U.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; El-Desoky, A.H.H.; Lojkowski, W. Enhanced Activity and Sustained Release of Protocatechuic Acid, a Natural Antibacterial Agent, from Hybrid Nanoformulations with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Primavera, R.; Wilson, R.J.; Thakor, A.S.; Kevadiya, B.D. Cellular uptake and retention of nanoparticles: Insights on particle properties and interaction with cellular components. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourian, P.; Yazdani, G.; Ashraf, S.S.; Frounchi, M.; Mashayekhan, S.; Kiani, S.; Kakkar, A. Effect of Physico-Chemical Properties of Nanoparticles on Their Intracellular Uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccari, G.; Baldassari, S.; Ailuno, G.; Turrini, F.; Alfei, S.; Caviglioli, G. Formulation Strategies to Improve Oral Bioavailability of Ellagic Acid. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, B.; Jeon, H.; Kim, D.; Kang, D.; Kim, K.R. Effect of fibroblast co-culture on the proliferation, viability and drug response of colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, N.; Långbacka, E.; Özliseli, E.; Mattsson, J.; Mahran, A.; Suleymanova, I.; Sahlgren, C.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Åkerfelt, M.; Nees, M. Surface Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Means to Introduce Inherent Cancer-Targeting Ability in a 3D Tumor Microenvironment. Small Sci. 2024, 4, 2400084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igaz, N.; Bélteky, P.; Kovács, D.; Papp, C.; Rónavári, A.; Szabó, D.; Gácser, A.; Kónya, Z.; Kiricsi, M. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug-Delivery to Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 3079–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Park, D.W.; Kwon, J.E.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, T.; Kim, I.; Kang, S.C.; Chi, K.W. Investigation of the biological and anti-cancer properties of ellagic acid-encapsulated nano-sized metalla-cages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wan, K.; Fan, D.; Wang, D. Novel oral administrated ellagic acid nanoparticles for enhancing oral bioavailability and anti-inflammatory efficacy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, F.; Hassan, A.; Klaab, Z.; Abdulla, S.; Pizzi, A.P. Tannin Nanoparticles (NP99) Enhances the Anticancer Effect of Tamoxifen on ER+ Breast Cancer Cells. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 2077–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-Y.; Peng, S.-F.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lu, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-C.; Shieh, T.-M.; Wu, T.-S.; Tu, M.-G.; Chen, M.Y.; Yang, J.-S. Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through regulation of the function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in cisplatin-resistant CAR human oral cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Tripathi, A.K.; Parveen, A. PLGA-Quercetin Nano-Formulation Inhibits Cancer Progression via Mitochondrial Dependent Caspase-3,7 and Independent FoxO1 Activation with Concomitant PI3K/AKT Suppression. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Zheng, M.; He, H.; Wu, T. Anti-Tumor and Anti-Metastasis Effects of Berbamine-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles on Pancreatic Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 3097–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harakeh, S.; Akefe, I.O.; Saber, S.H.; alamri, T.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Al-Jaouni, S.; Tashkandi, H.; Qari, M.; Moulay, M.; Aldahlawi, A.; et al. Nanoformulated 3′-diindolylmethane modulates apoptosis, migration, and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Zamanian, M.Y.; Jalal, S.M.; Noraldeen, S.A.M.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Oudaha, K.H.; Obaid, R.F.; Almulla, A.F.; Bazmandegan, G.; Kamiab, Z. A comprehensive review on Ellagic acid in breast cancer treatment: From cellular effects to molecular mechanisms of action. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 7458–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Xiang, D.; Lian, X.; Wu, C.; Quan, J. Ellagic acid inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in melanoma via EGFR pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, B.; Kim, J.; Sui, G.; Shi, J. Small Molecule Compounds of Natural Origin Target Cellular Receptors to Inhibit Cancer Development and Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-sonbaty, S.M.; Moawed, F.S.M.; Kandil, E.I.; M Tamamm, A. Antitumor and Antibacterial Efficacy of Gallium Nanoparticles Coated by Ellagic Acid. Dose-Response 2022, 20, 15593258211068998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, C.; Fakih, M. Targeting KRASG12C-Mutated Advanced Colorectal Cancer: Research and Clinical Developments. OncoTargets Ther. 2022, 15, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Qi, Y.; Miyako, E. Nanoformulation of the K-Ras(G12D)-inhibitory peptide KS-58 suppresses colorectal and pancreatic cancer-derived tumors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Target Gene | Forward/Reverse |
|---|---|
| P53 | Forward primer 5′-GCTCTGACTGTACCACCATCC-3′ Reverse primer 5′-CTCTCGGAACATCTCGAAGCG-3′ |
| Caspase-3 | Forward primer 5′-CTCTCGGAACATCTCGAAGCG-3′ Reverse primer 5′-CAAACTTTTTCAGAGGGGATCG-3′ |
| Bax | Forward primer 5′-AAGCTGAGCGAGTGTCTCCGGCG-3′ Reverse primer 5′-CAGATGCCGGTTCAGGTACTCAGTC-3′ |
| Bcl-2 | Forward primer 5′-CTCGTCGCTACCGTCGTGACTTGG-3′ Reverse primer 5′-CAGATGCCGGTTCAGGTACTCAGTC-3′ |
| VEGFR-2 | Forward primer 5′-CGTCCGCAAGTGTAAGAA-3′ Reverse primer 5′-AGCAAAAACCCTGTGATT-3′ |
| HER2 | Forward primer 5′-AGAGTCACCAGCCTCTGCAT-3′ Reverse primer 5′ -GCAACTCCCAGCTTCACTTT-3′ |
| GAPDH | Forward primer 5′-CGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGTC-3′ Reverse primer 5′-AGCCTTCTCCATGGTCGTGA-3′ |
| Nanoformulation | a SSA | b Weight Loss | c Total Drug Loading (TDL) | d Entrapment Efficiency (EE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSNCOOH | 85.0 | 20.4 | - | - |
| MSNTRP | 30.3 | 32.1 | 11.7 (TRP) | - |
| MSNTRPELG | 22.2 | 57.1 | 25.0 (ELG) | 62.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AbouAitah, K.; Nassrallah, A.; Soliman, A.A.F.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Chudoba, T.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Kim, B.S.; Łojkowski, W. Enhanced Killing of Colon Cancer Cells by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Ellagic Acid. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201547
AbouAitah K, Nassrallah A, Soliman AAF, Swiderska-Sroda A, Chudoba T, Smalc-Koziorowska J, Kim BS, Łojkowski W. Enhanced Killing of Colon Cancer Cells by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Ellagic Acid. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(20):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201547
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbouAitah, Khaled, Amr Nassrallah, Ahmed A. F. Soliman, Anna Swiderska-Sroda, Tadeusz Chudoba, Julita Smalc-Koziorowska, Beom Soo Kim, and Witold Łojkowski. 2025. "Enhanced Killing of Colon Cancer Cells by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Ellagic Acid" Nanomaterials 15, no. 20: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201547
APA StyleAbouAitah, K., Nassrallah, A., Soliman, A. A. F., Swiderska-Sroda, A., Chudoba, T., Smalc-Koziorowska, J., Kim, B. S., & Łojkowski, W. (2025). Enhanced Killing of Colon Cancer Cells by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Ellagic Acid. Nanomaterials, 15(20), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201547










