The Implantable Electrode Co-Deposited with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
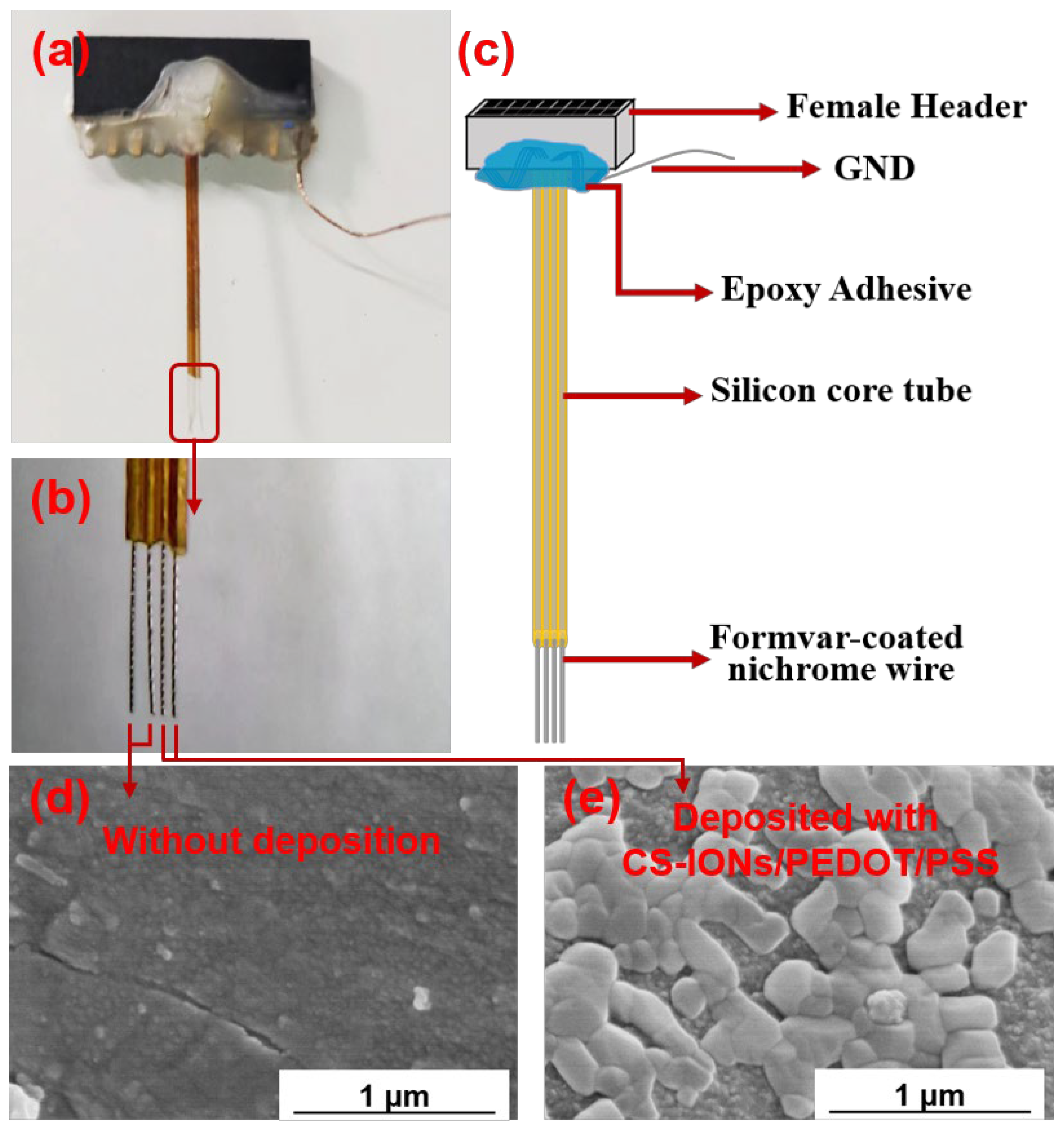
2.2. Materials and Structure of Electrodes
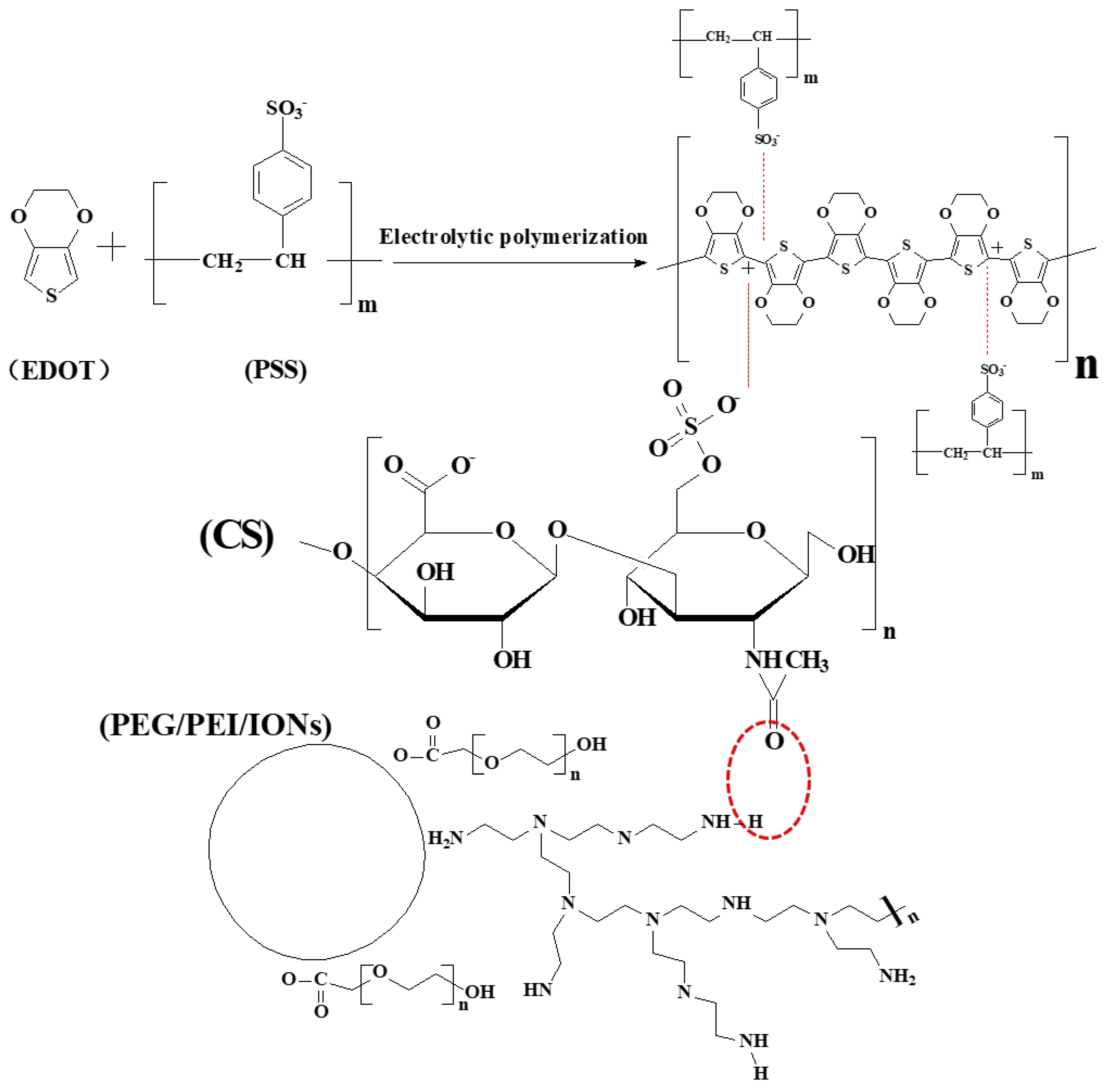
2.3. Surface Modification of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Deposition of CS-IONs/PEDOT/PSS
2.4. Electrode Implantation and Recording of Electrophysiological Signals
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Deposition of CS-IONs/PEDOT/PSS on the Electrode Using the Electrochemistry Method and the Electrodeposition Mechanism
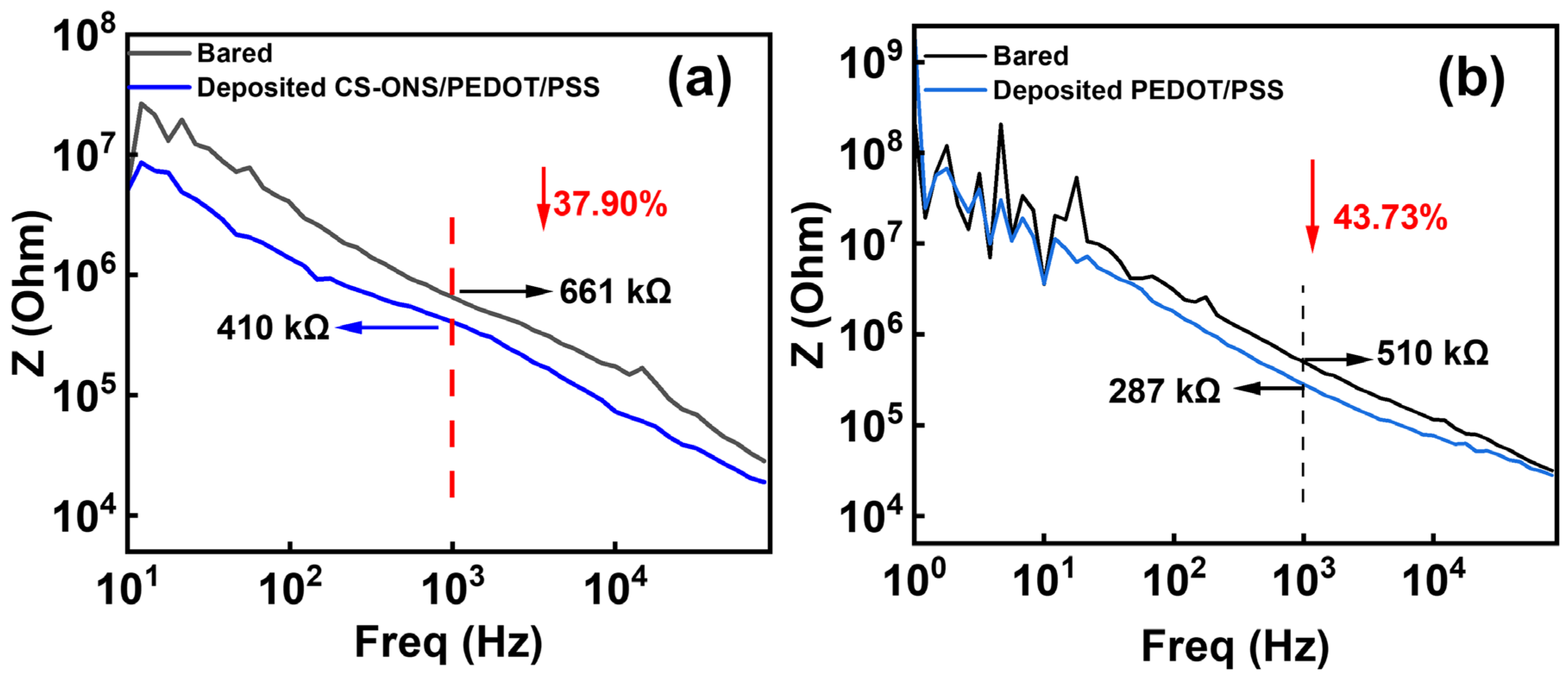
3.2. Characterization of the Coating and Electrical Performance of the Electrodes
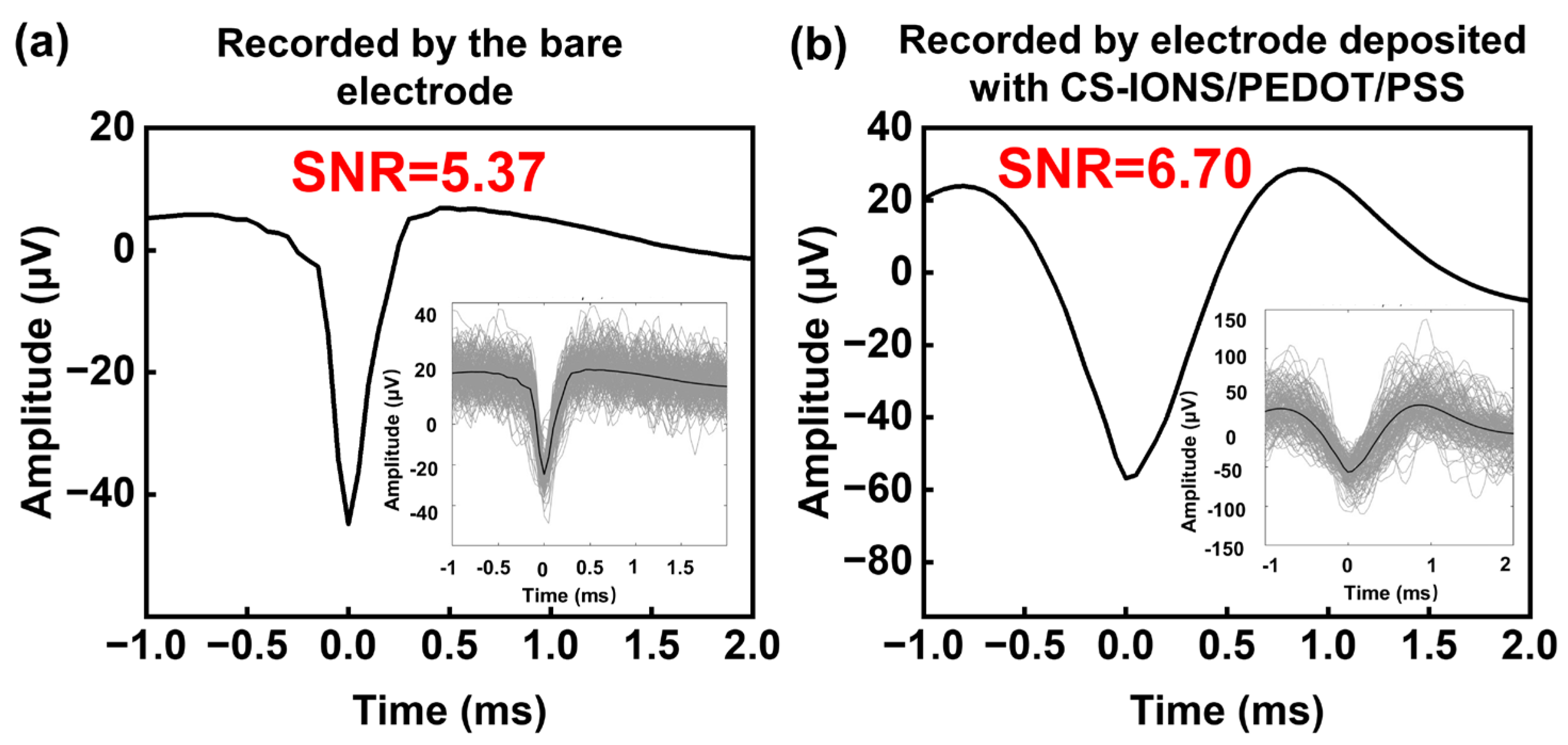
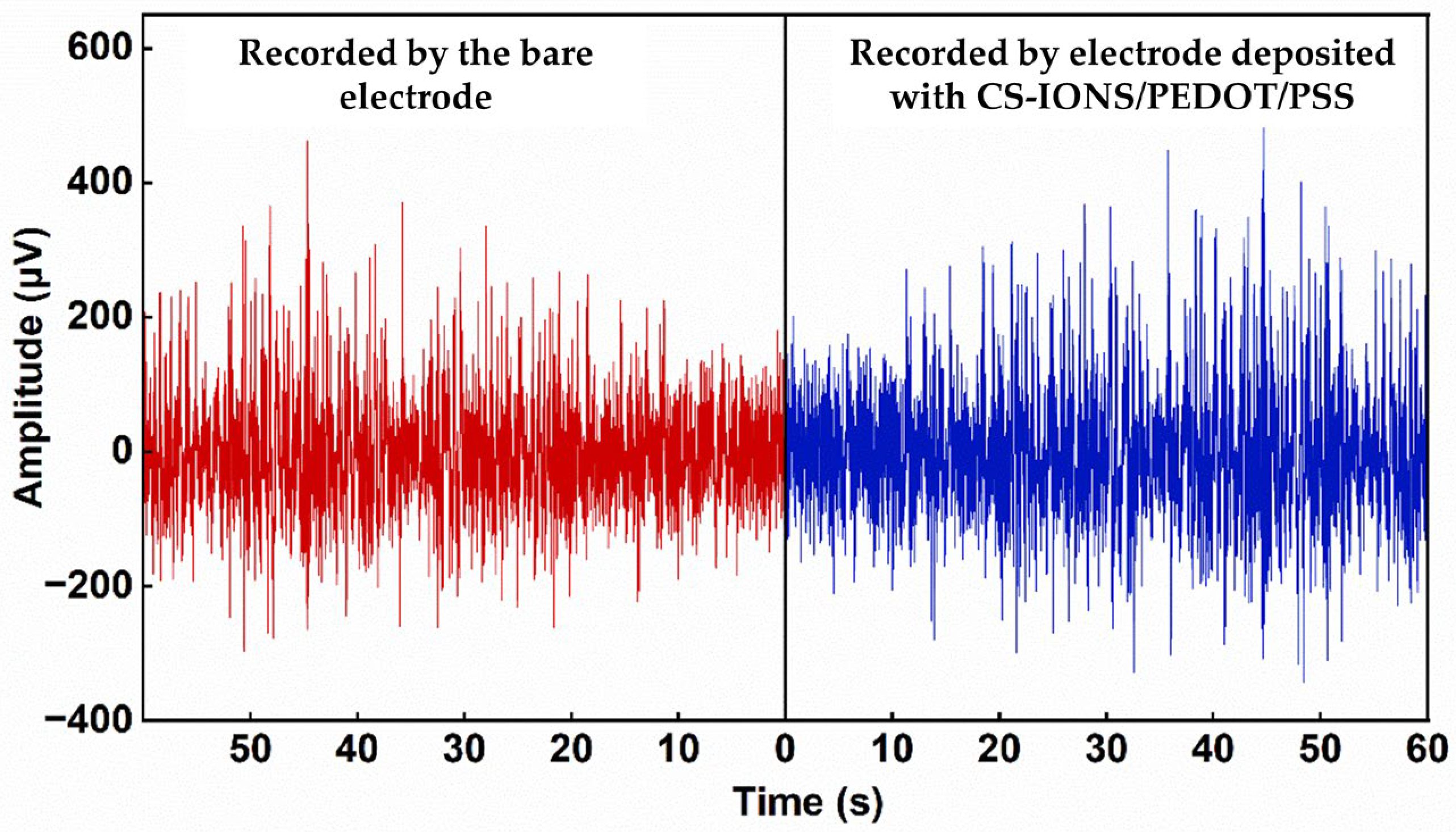
3.3. Evaluation of Neuronal Signal Quality Obtained by the Implanted Electrodes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Materials and Biomedical Applications of Implantable Electronic Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2200853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Huang, Z. Challenges and Opportunities of Implantable Neural Interfaces: From Material, Electrochemical and Biological Perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, M.; Choi, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Cha, G.D. Soft Bioelectronics for Neuroengineering: New Horizons in the Treatment of Brain Tumor and Epilepsy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 13, 2303563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Yao, L.; Yao, P.; Li, L.; Ding, P.; Liang, S.; Liu, C.; Xue, N. An iEEG Recording and Adjustable Shunt-Current Conduction Platform for Epilepsy Treatment. Biosensors 2022, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, H. Tissue-Matchable and Implantable Batteries Toward Biomedical Applications. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.H.; Ha, J.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.N.; Kim, S.; Yea, J.; Lee, H.; Oh, S.; et al. Highly Deformable Double-Sided Neural Probe with All-in-One Electrode System for Real-Time In Vivo Detection of Dopamine for Parkinson’s Disease. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2311436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Ji, X.; Ma, Q.; Paulsen, B.D.; Tropp, J.; Rivnay, J. Direct quantification of ion composition and mobility in organic mixed ionic-electronic conductors. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, S.T.; Rao, A.; Malliaras, G.G. The relationship between ionic-electronic coupling and transport in organic mixed conductors. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, T.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Pei, R. Implantable Neural Microelectrodes: How to Reduce Immune Response. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 2762–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.H.; Song, J.-K.; Kim, D.-H.; Son, D. Soft Implantable Bioelectronics. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, R.; Jiang, J.; Hao, S.; Fang, B.; Zhang, J.; Bai, H.; Peng, B.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Implantable neural electrodes: From preparation optimization to application. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 6550–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Ji, B.; Guo, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, J. Fabrication and Characterization of Micro-Nano Electrodes for Implantable BCI. Micromachines 2019, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, M.K.U.; Tong, W.; Pingle, H.; Kingshott, P.; Needham, K.; Shivdasani, M.N.; Fallon, J.B.; Seligman, P.; Ibbotson, M.R.; Prawer, S.; et al. Laminin coated diamond electrodes for neural stimulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 118, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, G.; Niu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Carbon-Based Fiber Materials as Implantable Depth Neural Electrodes. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 771980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurke, J.; Naegele, T.E.; Hilton, S.; Pezone, R.; Curto, V.F.; Barone, D.G.; List-Kratochvil, E.J.W.; Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Malliaras, G.G. Hybrid fabrication of multimodal intracranial implants for electrophysiology and local drug delivery. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.L.; Jiang, S.; Jang, E.; Niu, L.; Li, L.; Jia, X.; Tong, R. Implantable optical fibers for immunotherapeutics delivery and tumor impedance measurement. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Li, L. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Substrate Structure on Electrochemical Performance and Stability of Electrodeposited Platinum and Iridium Oxide Coatings for Neural Electrodes. Micromachines 2024, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, T.; Lan, T.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Deng, J.; Kong, D.; Yang, S.; Shen, Z. Platinum Black/Gold Nanoparticles/Polyaniline Modified Electrochemical Microneedle Sensors for Continuous In Vivo Monitoring of pH Value. Polymers 2023, 15, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, K.-C.; Chan, T.-Y.; Yu, T.-C.; Tao, Y.-J.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-F.; Ohta, J.; Chen, P.-C.; Wu, P.-W. A robust bendable IrOx thin film via mild alkaline solution process for neuron stimulating electrodes. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 44, 103785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Chung, T.-W.; Wu, P.-W.; Chen, P.-C. A cost-effective fabrication of iridium oxide films as biocompatible electrostimulation electrodes for neural interface applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahi, M.E.E.; Rizu, M.I.; Tina, F.W.; Huang, Z.; Nag, A.; Afsarimanesh, N. Recent Advancements in Graphene-Based Implantable Electrodes for Neural Recording/Stimulation. Sensors 2023, 23, 9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lv, S.; Shang, Y.; Guan, S.; Tian, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H. Free-Standing Carbon Nanotube Embroidered Graphene Film Electrode Array for Stable Neural Interfacing. Nano Lett. 2023, 24, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y. Implantable polypyrrole bioelectrodes inducing anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization for long-term in vivo signal recording. Acta Biomater. 2023, 168, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Li, H.; Pu, A.; Li, W.; Ban, K.; Xu, L. Hybrid assembly of polymeric nanofiber network for robust and electronically conductive hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, K.; Zhong, C.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y. Fabrication and modification of implantable optrode arrays for in vivo optogenetic applications. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 4, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Mishra, V.S.; Reddy, P.C.; Lochab, B. Multifunctional Multicomponent Highly Biocompatible pH-Responsive Iron-Oxide Embedded Nanodiamond Cargo for Artesunate to Inhibit Cancer Growth. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Dong, J.; Zhang, B. Increasing the Particle Size and Magnetic Property of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Through a Segregated Nucleation and Growth Process. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.; Zhang, B.L.; Pan, R.; Wang, S.; Yan, X.J.; Tan, J. Surface Modification with Chondroitin Sulfate Targets Nanoparticles to the Neuronal Cell Membrane in the Substantia Nigra. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Zhang, B.L.; Su, L.C.; Yang, B.N. Attachment of streptavidin-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles to the PC-12 cell membrane. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 045014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.C.; Zhang, B.L.; Huang, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.; Tan, J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine and their distribution in the brain after injection in the rat substantia nigra. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 81, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.-R.; Zeng, J.-F.; Jia, Q.-J.; Du, J.; Shen, L.; Gao, M.-Y. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-an Important Cornerstone of MR Molecular Imaging of Tumors. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2012, 28, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, A.; Fernandez-Afonso, Y.; Guedes, G.; Guisasola, E.; Gutierrez, L.; Cortajarena, A.L. Engineered Protein-Driven Synthesis of Tunable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as T1 and T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 10832–10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Chi, X.; Ni, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Octapod iron oxide nanoparticles as high-performance T2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.N.; Chou, N.; Jang, J.-W.; Choe, H.K.; Kim, S. A 3D flexible neural interface based on a microfluidic interconnection cable capable of chemical delivery. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Oliva, N.; del Valle, J.; Delgado-Martinez, I.; Mueller, M.; Stieglitz, T.; Navarro, X. Long-Term Functionality of Transversal Intraneural Electrodes Is Improved by Dexamethasone Treatment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Zhang, B.L.; Wang, S. Synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with different particle sizes and its magneto-calorific effects under alternating current magnetic field. J. Mater. Eng. 2019, 47, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ognjanovic, M.; Stankovic, D.M.; Jacimovic, Z.K.; Kosovic-Perutovic, M.; Dojcinovic, B.; Antic, B. The effect of surface-modifier of magnetite nanoparticles on electrochemical detection of dopamine and heating efficiency in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 884, 161075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Eom, T.; Kim, M.-K.; Yang, S.-G.; Shim, B.S. Durable soft neural micro-electrode coating by an electrochemical synthesis of PEDOT:PSS/graphene oxide composites. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 313, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, R.; Chen, A.X.; Polat, B.; Becerra, L.L.; Runser, R.; Zamanimeymian, B.; Choudhary, K.; Lipomi, D.J. Intrinsically Stretchable Block Copolymer Based on PEDOT:PSS for Improved Performance in Bioelectronic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4823–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S. Materials aspects of PEDOT:PSS for neuromorphic organic electrochemical transistors. Flex. Print. Electron. 2024, 9, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, D.; del Agua, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Mecerreyes, D. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) Derivatives: Innovative Conductive Polymers for Bioelectronics. Polymers 2017, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivnay, J.; Inal, S.; Collins, B.A.; Sessolo, M.; Stavrinidou, E.; Strakosas, X.; Tassone, C.; Delongchamp, D.M.; Malliaras, G.G. Structural control of mixed ionic and electronic transport in conducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, J.; Krischek, C.; Harisch, G. Modulation of camp-dependent protein kinase by derivatives of chondroitin sulfate. Life Sci. 1997, 60, PL201–PL206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oommen, O.P.; Duehrkop, C.; Nilsson, B.; Hilborn, J.; Varghese, O.P. Multifunctional hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate nanoparticles: Impact of glycosaminoglycan presentation on receptor mediated cellular uptake and immune activation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20614–20624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, H.; Kawahara, S.; Tsutsumi, N.; Miyamoto, N. Quantification of orally administered chondroitin sulfate oligosaccharides in human plasma and urine. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Shi, S.; Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Duan, F.; Li, Y. Surface composite modification of anion exchange membrane by electrodeposition and self-polymerization for improved antifouling performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lee, D.; Koo, H.Y.; Maeng, S. Chemically modified graphene/PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite films for hydrogen gas sensing. Carbon 2015, 81, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chua, M.H.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, J. High-performance PEDOT:PSS-based thermoelectric composites. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.H.; Lu, Y.; Wei, P.F.; Deng, C.S.; Li, X.J. Progress in Devices and Materials for Implantable Multielectrode Arrays. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2020, 36, 2007004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, V.; Giera, B.; Karnes, J.J.; Stratmann, N.; Schaufler, V.; Li, Y.; Rehbock, C.; Barcikowski, S. Electrophoretic Deposition of Platinum Nanoparticles using Ethanol-Water Mixtures Significantly Reduces Neural Electrode Impedance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 022504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodart, C.; Rossetti, N.; Hagler, J.E.; Chevreau, P.; Chhin, D.; Soavi, F.; Schougaard, S.B.; Amzica, F.; Cicoira, F. Electropolymerized Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) Coatings for Implantable Deep-Brain-Stimulating Microelectrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17226–17233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyakumura, T.; Aregueta-Robles, U.; Duan, W.; Villalobos, J.; Adams, W.K.; Poole-Warren, L.; Fallon, J.B. Improving Deep Brain Stimulation Electrode Performance in vivo Through Use of Conductive Hydrogel Coatings. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 761525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cao, M.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, L.; Hu, J.; et al. The high and low molecular weight forms of hyaluronan have distinct effects on CD44 clustering. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Chadar, R.; Sheikh, A.; Rizg, W.Y.; Safhi, A.Y. CD44-Targeted Nanocarrier for Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 800481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
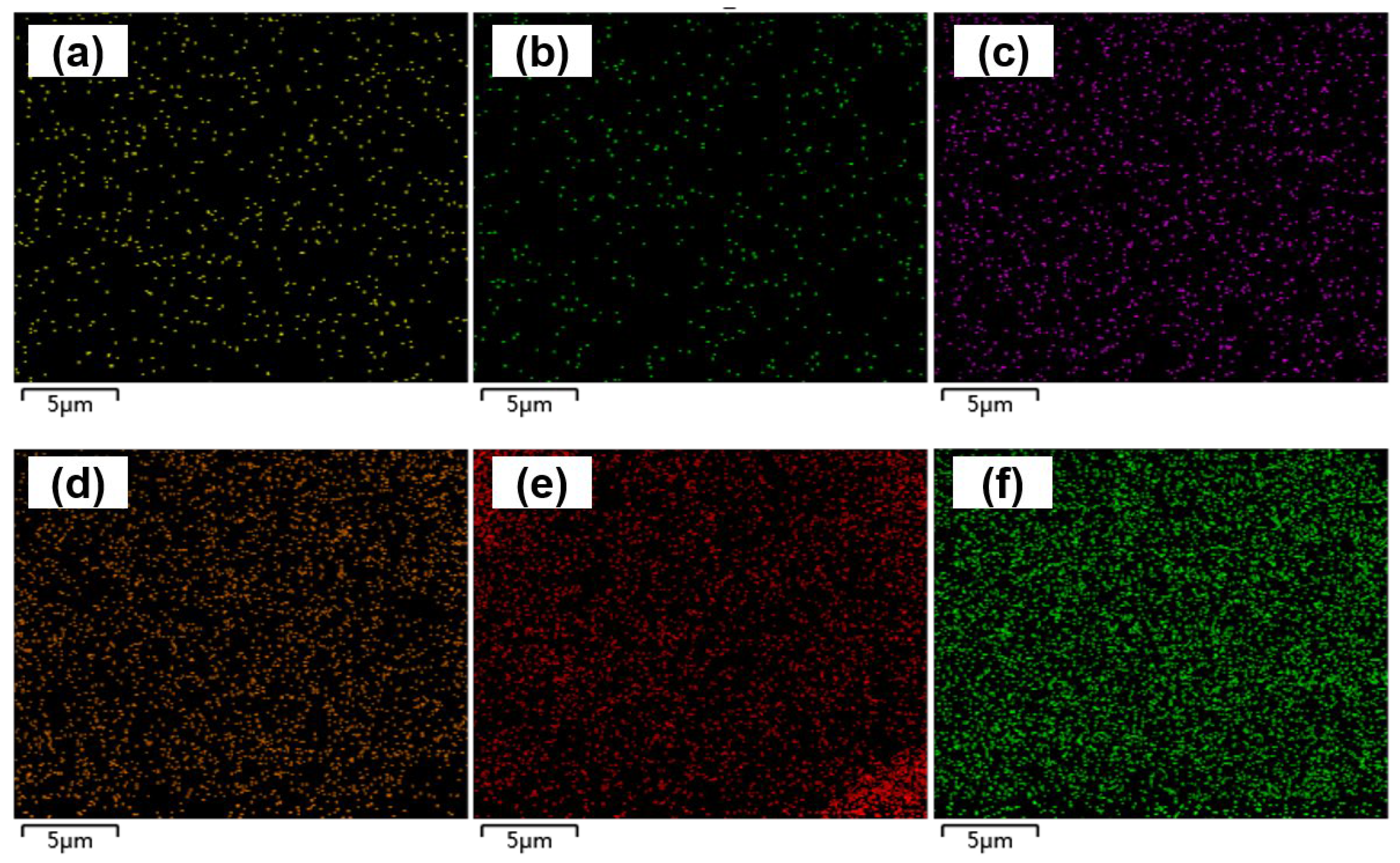
| Element | wt % | at % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Electrode Tip | Electrode Tip Deposited with CS-IONs/PEDOT/PSS | Bare Electrode Tip | Electrode Tip Deposited with CS-IONs/PEDOT/PSS | |
| C | 7.65 | 40.13 | 28.04 | 60.83 |
| N | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| O | 0.40 | 23.59 | 1.09 | 26.84 |
| S | 0.00 | 2.58 | 0.00 | 1.47 |
| Cr | 19.00 | 10.04 | 16.10 | 3.52 |
| Fe | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.65 | 0.10 |
| Ni | 72.14 | 23.34 | 54.12 | 7.24 |
| Group Number | Bared Area | Deposited Area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.57897 × 10−9 | 3.7035 × 10−9 |
| 2 | 1.6846 × 10−10 | 3.16217 × 10−9 |
| 3 | 1.3739 × 10−10 | 5.4120 × 10−10 |
| 4 | 1.69545 × 10−9 | 4.06069 × 10−9 |
| 5 | 5.4148 × 10−11 | 2.39552 × 10−9 |
| 6 | 8.1638 × 10−11 | 4.5103 × 10−10 |
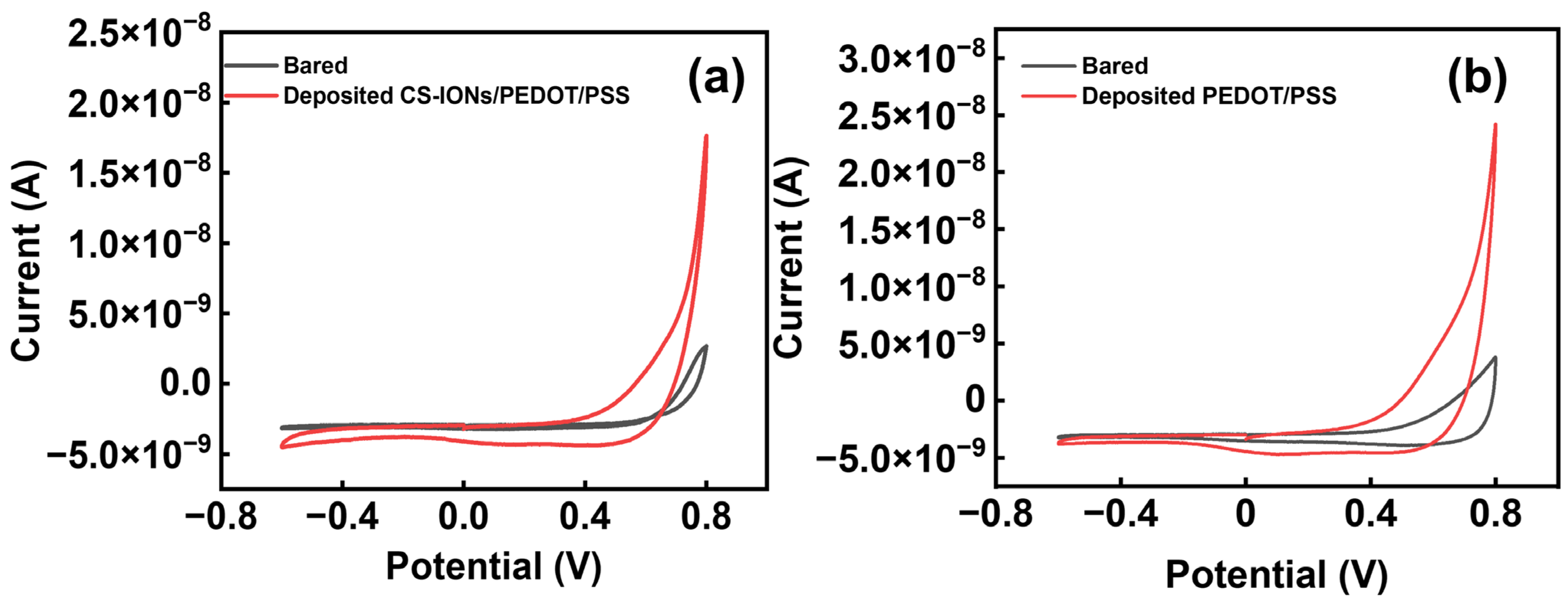
| Charge Density of the Bare Electrode (c/cm2) | Charge Density of the Electrode Deposited with CS-IONs/PEDOT/PSS (c/cm2) | Percentage Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.37 × 10−3 | 6.08 × 10−2 | 97.95 |
| Frequency (Hz) | PSD of the Bare Electrode (dB) | PSD of the Electrode Deposited with CS-IONs/PEDOT/PSS (dB) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26.90 | 27.26 |
| 2 | 24.95 | 25.52 |
| 4 | 20.87 | 21.60 |
| 8 | 18.35 | 19.63 |
| 16 | 13.56 | 14.94 |
| 32 | 7.85 | 9.21 |
| 64 | 1.37 | 2.52 |
| 128 | −5.17 | −4.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, B. The Implantable Electrode Co-Deposited with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191511
Liu Y, Wu H, Wang S, Yang Q, Zhang B. The Implantable Electrode Co-Deposited with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(19):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191511
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yiyang, Hui Wu, Sheng Wang, Quanwei Yang, and Baolin Zhang. 2025. "The Implantable Electrode Co-Deposited with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS" Nanomaterials 15, no. 19: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191511
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wu, H., Wang, S., Yang, Q., & Zhang, B. (2025). The Implantable Electrode Co-Deposited with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS. Nanomaterials, 15(19), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191511







