Investigation of Viscoelastic Properties of Macrophage Membrane–Cytoskeleton Induced by Gold Nanorods in Leishmania Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Parasite Strains
2.2. Chemical Reagents and Solutions
2.3. Cell Culture and Parasite Maintenance Protocols
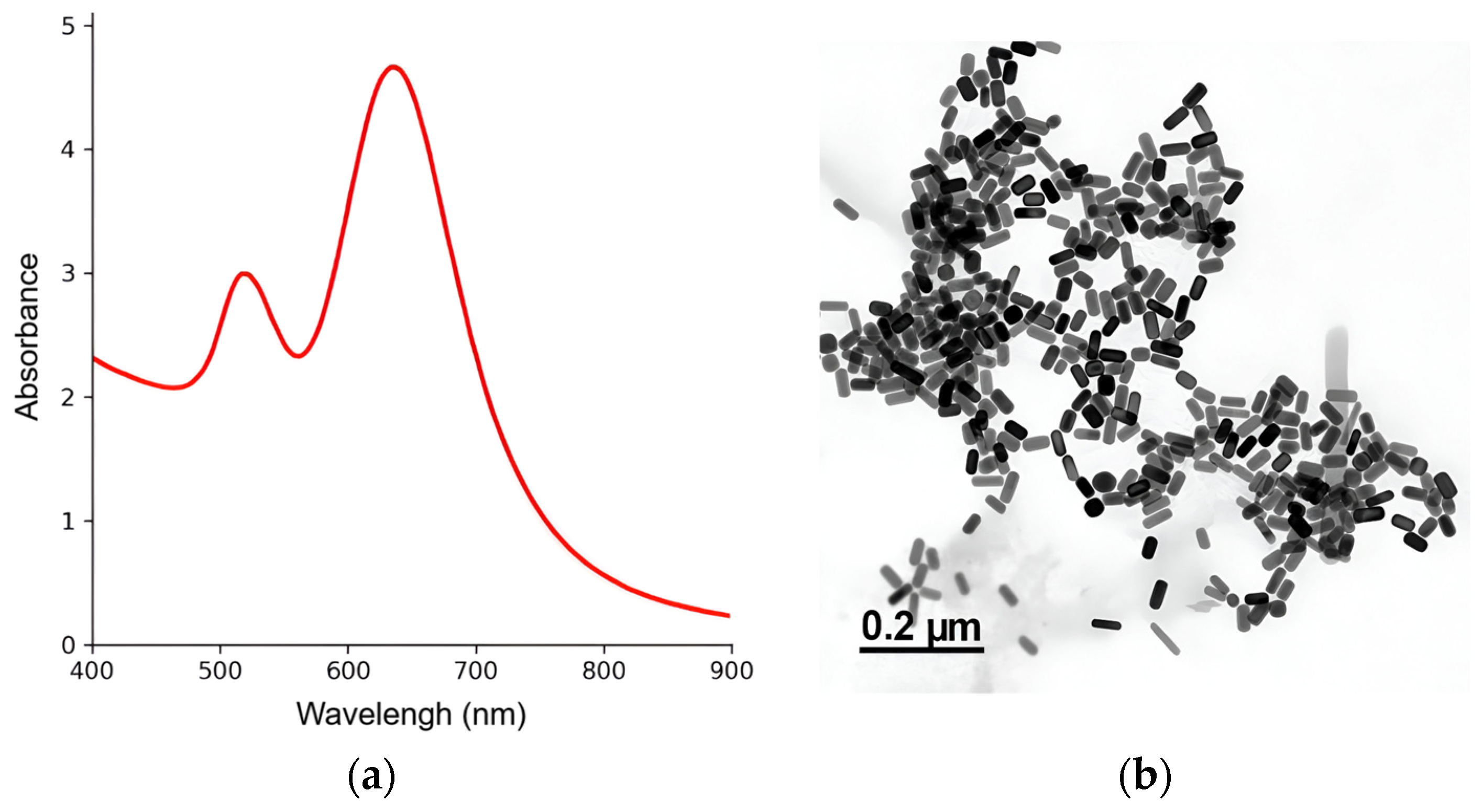
2.4. Gold Nanorod Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization
2.5. Microscopy Equipment and Imaging Setup
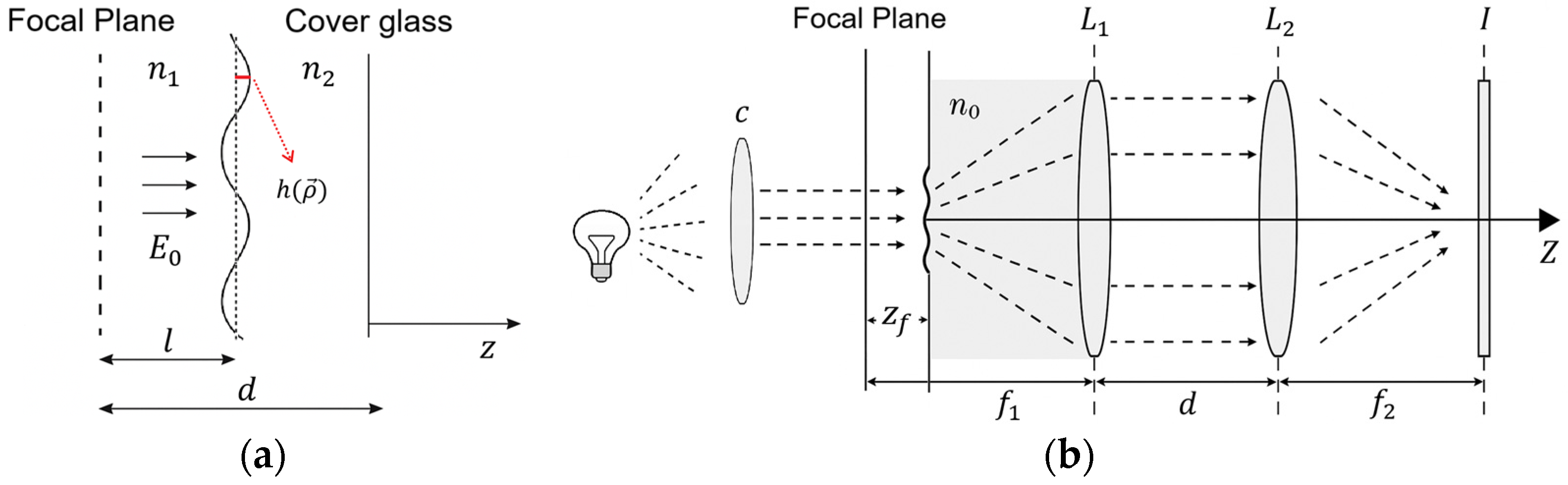
2.6. Defocusing Microscopy
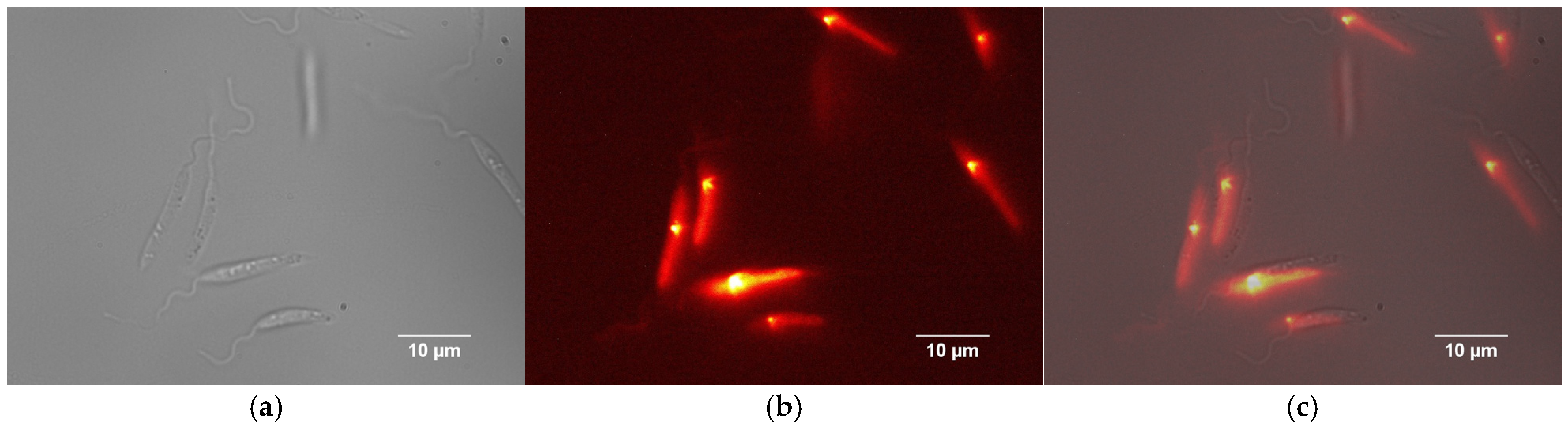
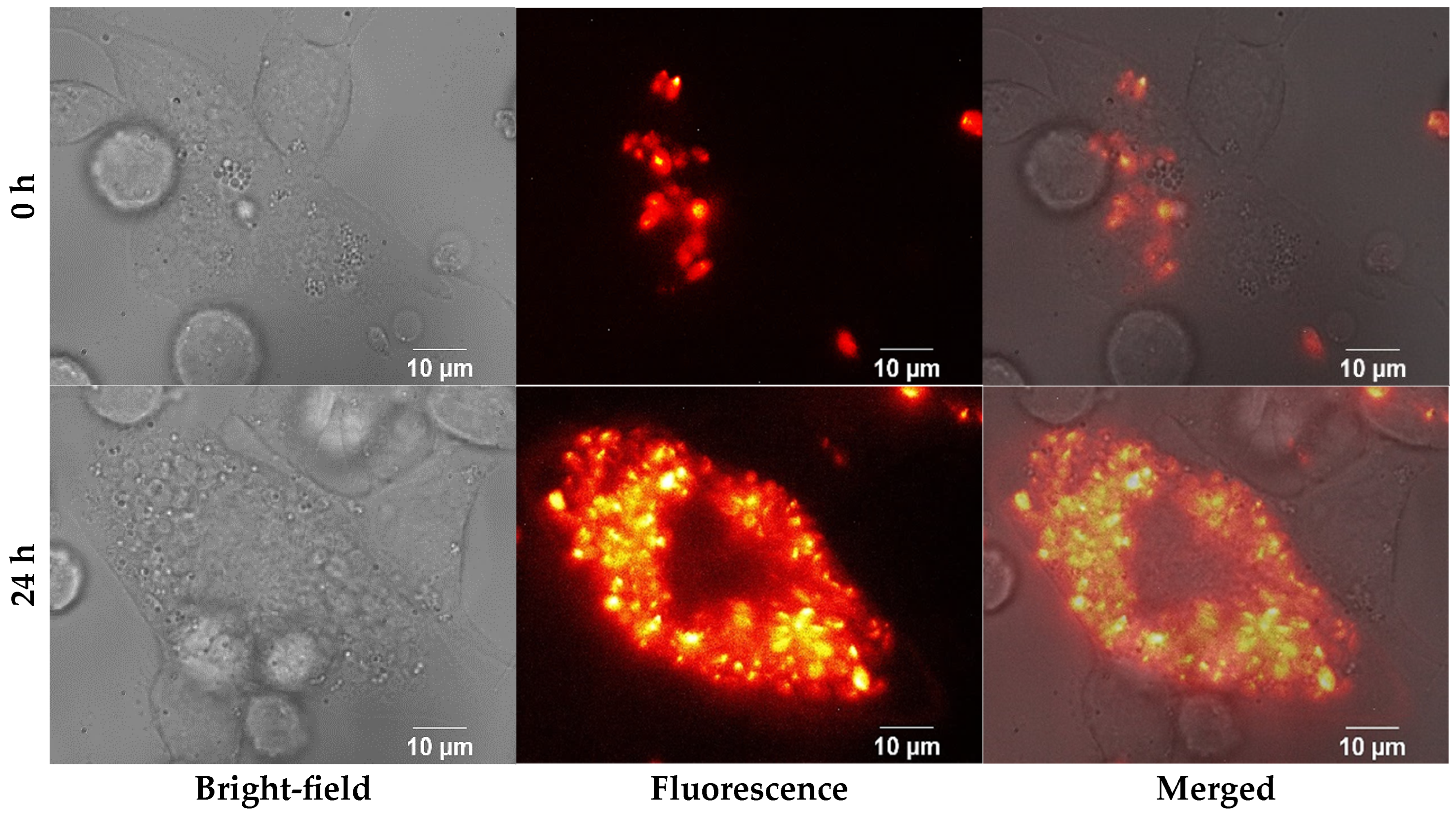
2.7. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.8. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. GNRs Syntheses and Physicochemical Characterizations
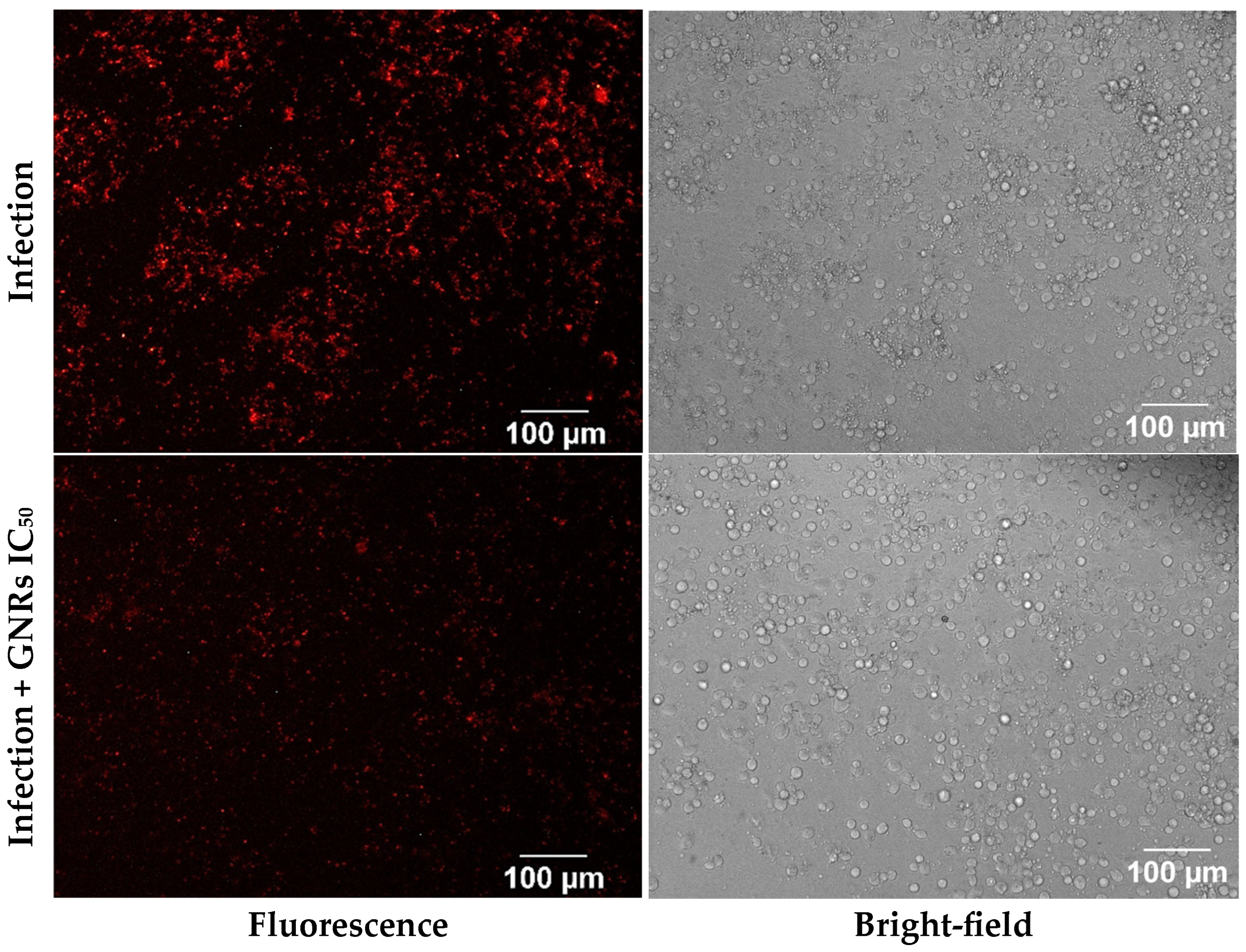
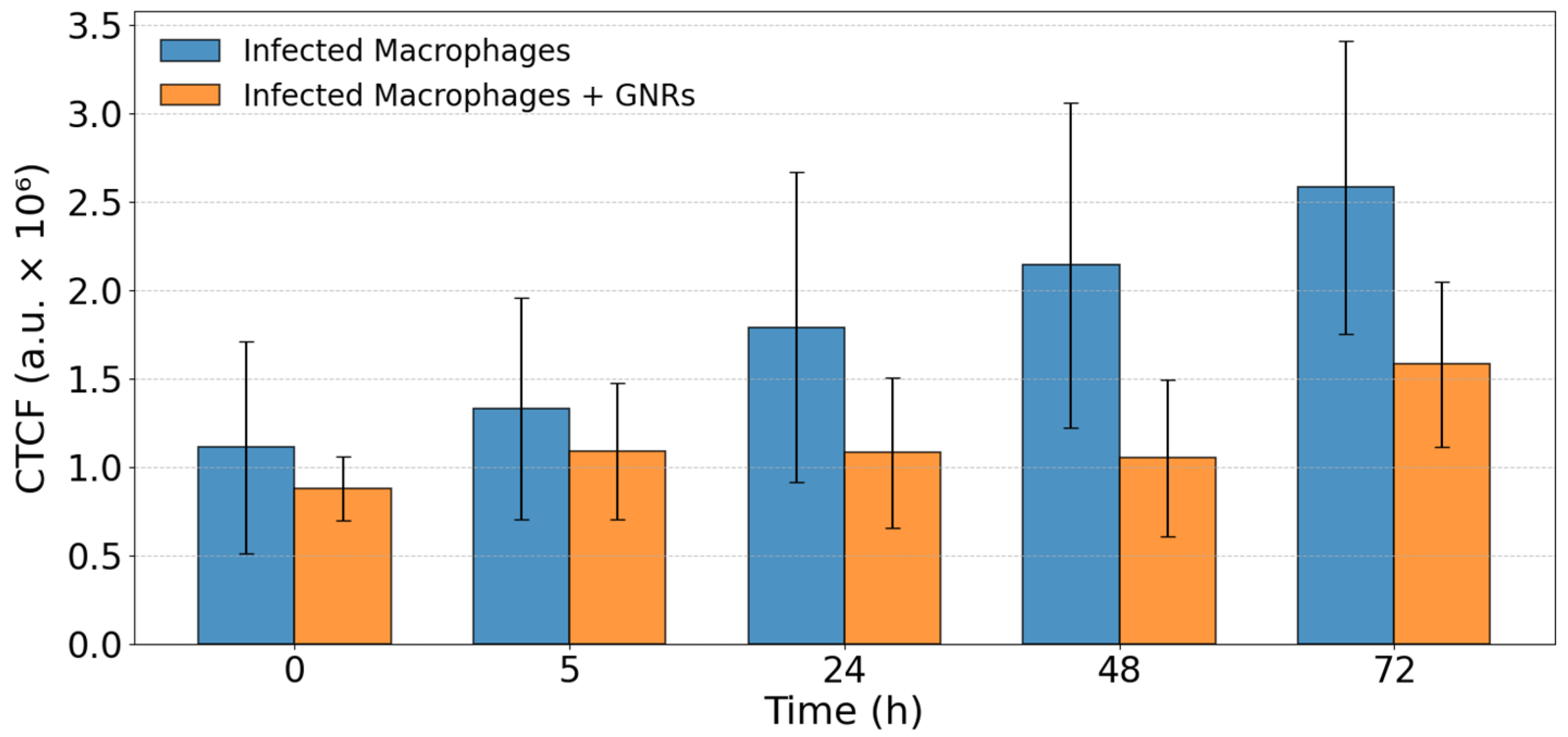
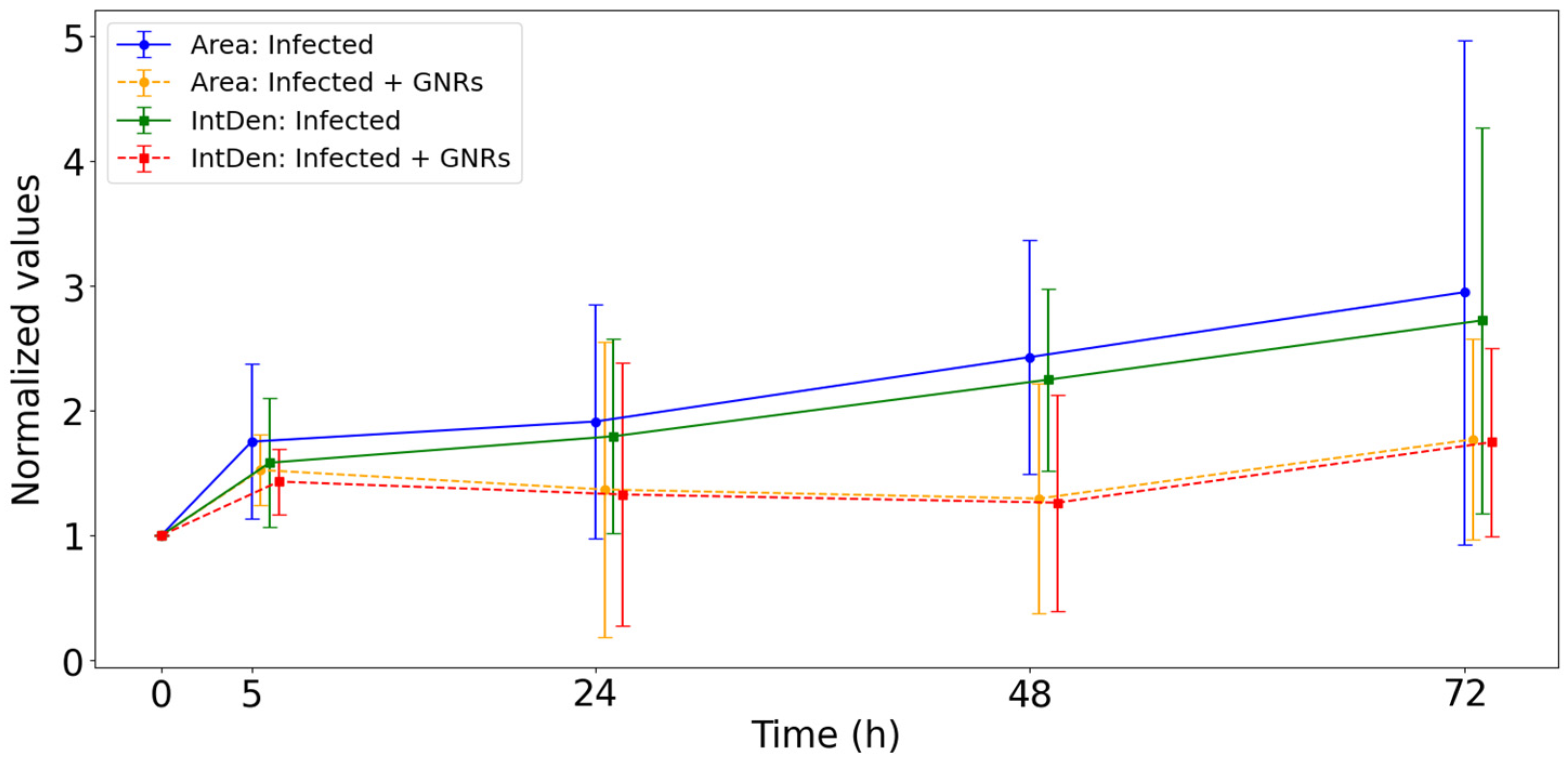
3.2. Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis
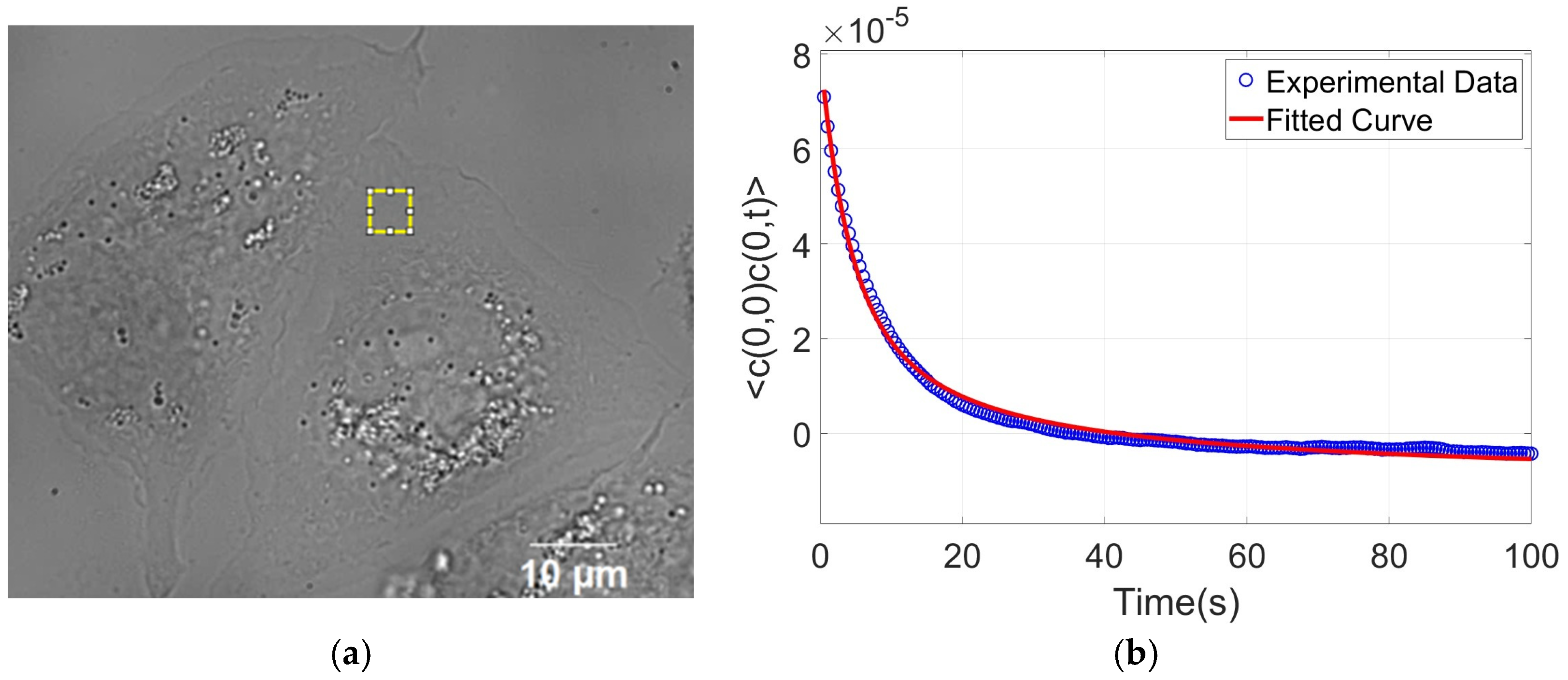
3.3. Defocusing Microscopy Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| AgNO3 | Silver nitrate |
| AR | Aspect ratio |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CL | Cutaneous Leishmaniasis |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| CTAFs | Contrast temporal autocorrelation functions |
| CTCF | Corrected total cell fluorescence |
| DM | Defocusing microscopy |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| GNRs | Gold nanorods |
| HAuCl4 | Chloroauric acid |
| IntDen | Integrated Density |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| Kc | Bending modulus |
| Macrophages | |
| NA | Numerical aperture |
| NaBH4 | Sodium borohydride |
| oxLDLs | Oxidized low-density lipoproteins |
| PFS | Perfect Focus System |
| PMA | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
| RFP | Red fluorescent protein |
| SI | Selectivity index |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| Viscosity | |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Rafique, A.; Sani, S.S.; Sultana, S.; Sultana, T.; Ashraf, A.; Mahmood, M.S. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. In Leishmania Parasites-Epidemiology, Immunopathology and Hosts; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-1-83768-311-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Wei, Y.; Ullah, S.; Shah, S.I.; Nasir, F.; Shah, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Tahir, K.; Khan, U.A.; Yuan, Q. Synthesis of Phytochemicals-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biological Activities against Bacteria and Leishmania. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Maquiaveli, C.; da Silva, E.R.; Hild de Jesus, B.; Oliveira Monteiro, C.E.; Rodrigues Navarro, T.; Pereira Branco, L.O.; Souza dos Santos, I.; Figueiredo Reis, N.; Portugal, A.B.; Mendes Wanderley, J.L.; et al. Design and Synthesis of New Anthranyl Phenylhydrazides: Antileishmanial Activity and Structure–Activity Relationship. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.F.; Gonçalves-Oliveira, L.F.; Souza-Silva, F.; De Castro Côrtes, L.M.; Finkelstein, L.C.; Dias-Lopes, G.; Patricio, B.F.D.C.; Lima, C.G.D.S.; Rocha, H.V.A.; Da Silva, F.D.C.; et al. Efficacy of the Treatment Using a Microemulsion Loaded with Epoxy-α-Lapachone in Combination with Meglumine Antimoniate against Murine Infection by Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2024, 24, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge-Maillo, B.; López-Vélez, R. Therapeutic Options for Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis and New World Cutaneous and Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis. Drugs 2013, 73, 1889–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.G.L.; Cardoso, J.M.G.; Alcântara, L.O.N.d.; Santos, L.d.C.R.d.; Dutra, A.L.V.; Carvalho, F.O.F.d.; Rocha, L.d.A.; Guedes, A.B.G.d.S.; Aniszewski, R.V.L.; Soares, P.A.B.; et al. Medication Options in the Treatment of Cutaneous American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis. In Multidisciplinary Perspectives: Integrating Knowledge; Seven Editora: São José dos Pinhais, Brazil, 2024; pp. 997–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, T.; Fischer, M.; Schliemann, S.; Elsner, P. Treatment of Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis—A Systematic Review. JDDG J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2024, 22, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, A.C.P.; Ladeira, L.O.; Do Camo, P.H.F.; Amorim, J.M.; Monte-Neto, R.L.; Santos, D.A.; Tunes, L.G.; Castilho, R.O.; Moreira, P.O.; Ferreira, D.C.; et al. Changes in Antiparasitical Activity of Gold Nanorods According to the Chosen Synthesis. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 242, 108367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Diez, J.; Souiade, L.; Manzaneda-González, V.; Sánchez-Díez, M.; Megias, D.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Ramírez-Castillejo, C.; Serrano-Olmedo, J.; Ramos-Gómez, M. Effectiveness of Gold Nanorods of Different Sizes in Photothermal Therapy to Eliminate Melanoma and Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komsthöft, T.; Bovone, G.; Bernhard, S.; Tibbitt, M.W. Polymer Functionalization of Inorganic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 37, 100849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Thompson, L.B.; Boulos, S.P.; Sisco, P.N.; Murphy, C.J. Gold Nanorods: Their Potential for Photothermal Therapeutics and Drug Delivery, Tempered by the Complexity of Their Biological Interactions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Song, J. Plasmonic Anisotropic Gold Nanorods: Preparation and Biomedical Applications. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6372–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 6th ed.; Chapter 10 (Membrane Structure), Chapter 24 (The Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems); W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-73536-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzveig, H.M. Cell Membrane Biophysics with Optical Tweezers. Eur. Biophys. J. 2018, 47, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchtefeld, I. Studying Cell Membrane Tension and Mechanosensation during Mechanical Stimulation. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, M.; Alapan, Y.; Jia, H.; Varga, A.G.; Angelino, K.; Aslan, M.; Sayin, I.; Han, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Micro and Nano-Scale Technologies for Cell Mechanics. Nanobiomedicine 2014, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-H.; Aroush, D.R.-B.; Asnacios, A.; Chen, W.-C.; Dokukin, M.E.; Doss, B.L.; Durand-Smet, P.; Ekpenyong, A.; Guck, J.; Guz, N.V.; et al. A Comparison of Methods to Assess Cell Mechanical Properties. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, F.; Zembrzycki, K.; Nakielski, P.; Pawłowska, S.; Kowalewski, T.A. Atomic Force Microscopy Combined with Optical Tweezers (AFM/OT). Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 025904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, K.; Pelling, A.E. Investigating Cell Mechanics with Atomic Force Microscopy. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20140970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, J.W.; Conchello, J.-A. Fluorescence Microscopy. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubaid, F.; Brown, C.M. Less Is More: Longer Exposure Times with Low Light Intensity Is Less Photo-Toxic. Microsc. Today 2017, 25, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, A.; Ojha, N.K. Excitation Light-Induced Phototoxicity during Fluorescence Imaging. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icha, J.; Weber, M.; Waters, J.C.; Norden, C. Phototoxicity in Live Fluorescence Microscopy, and How to Avoid It. BioEssays 2017, 39, 1700003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bai, B.; Ryu, D.; Liu, T.; Lee, C.; Luo, Y.; Lee, M.J.; Huang, L.; Shin, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Quantitative Phase Imaging Methods for Life Sciences. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, P.M.S.; Siman, L.; Amaral, F.T.; Agero, U.; Mesquita, O.N. Total Three-Dimensional Imaging of Phase Objects Using Defocusing Microscopy: Application to Red Blood Cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 251107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agero, U.; Monken, C.H.; Ropert, C.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Mesquita, O.N. Cell Surface Fluctuations Studied with Defocusing Microscopy. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 051904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himbert, S.; D’Alessandro, A.; Qadri, S.M.; Majcher, M.J.; Hoare, T.; Sheffield, W.P.; Nagao, M.; Nagle, J.F.; Rheinstädter, M.C. The Bending Rigidity of the Red Blood Cell Cytoplasmic Membrane. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Canneyt, K.; Verdonck, P. Mechanics of Biofluids in Living Body. In Comprehensive Biomedical Physics: Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 10, pp. 39–53. ISBN 978-0-444-53633-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Yamabe, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, T.; Tada, K. Establishment and Characterization of a Human Acute Monocytic Leukemia Cell Line (THP-1). Int. J. Cancer 1980, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.G.; Hsu, A.; Mandell, M.A.; Roediger, B.; Hoeller, C.; Mrass, P.; Iparraguirre, A.; Cavanagh, L.L.; Triccas, J.A.; Beverley, S.M.; et al. Migratory Dermal Dendritic Cells Act as Rapid Sensors of Protozoan Parasites. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.N.; Corrêa, C.M.; Melo, M.N.; Beverley, S.M.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Madureira, A.P.; Soares, R.P. An Alternative in Vitro Drug Screening Test Using Leishmania Amazonensis Transfected with Red Fluorescent Protein. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.P.P.; Macedo, M.E.; Ropert, C.; Gontijo, N.F.; Almeida, I.C.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Pimenta, P.F.P.; Turco, S.J. Leishmania Chagasi: Lipophosphoglycan Characterization and Binding to the Midgut of the Sand Fly Vector Lutzomyia Longipalpis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2002, 121, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, I.; Pouzet, C.; Brulas, M.; Bauza, E.; Botto, J.M.; Domloge, N. Evaluation of THP-1 cell line as an in vitro model for long-term safety assessment of new molecules. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, G.; Dumas, C.; Sereno, D.; Wu, Y.; Singh, A.K.; Tremblay, M.J.; Ouellette, M.; Olivier, M.; Papadopoulou, B. Episomal and Stable Expression of the Luciferase Reporter Gene for Quantifying leishmania spp. Infections in Macrophages and in Animal Models. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2000, 110, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amlabu, W.E.; Antwi, C.A.; Awandare, G.; Gwira, T.M. Elucidating the Possible Mechanism of Action of Some Pathogen Box Compounds against Leishmania Donovani. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Lan, S.; Rong, L.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B. Seedless Synthesis of Gold Nanorods Using Resveratrol as a Reductant. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 165601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, A.C.P.; Orlando Ladeira, L.; Mosqueira, L.; Magalhães Paniago, R.; Oliveira Castilho, R.; Amorim, J.M.; Pessoa, E.S.; Nuncira, J.; Faraco, A.A.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanorods Using the Natural Products Resveratrol, Gallic Acid, and a Purified Fraction of Stryphnodendron Obovatum by Seedless Method. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L.; Wolf, E.; Meystre, P. Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics. Am. J. Phys. 1996, 64, 1438–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Fresnel diffraction. In Introduction to Fourier Optics, 4th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 4; pp. 57–85. ISBN 978-0-07-023776-6. [Google Scholar]
- Glionna, G.; Oliveira, C.K.; Siman, L.G.; Moyses, H.W.; Prado, D.M.U.; Monken, C.H.; Mesquita, O.N. Tomography of Fluctuating Biological Interfaces Using Defocusing Microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 193701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Open Lab Book. Measuring Cell Fluorescence Using ImageJ. Available online: https://theolb.readthedocs.io/en/latest/imaging/measuring-cell-fluorescence-using-imagej.html (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- de Menezes, J.P.B.; Koushik, A.; Das, S.; Guven, C.; Siegel, A.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Losert, W.; Andrews, N.W. Leishmania Infection Inhibits Macrophage Motility by Altering F-Actin Dynamics and the Expression of Adhesion Complex Proteins. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Kima, P.E. The Leishmania Parasitophorous Vacuole Membrane at the Parasite-Host Interface. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2019, 92, 511–521. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6747952/ (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Couto, N.F.; Rezende, L.; Fernandes-Braga, W.; Alves, A.P.; Agero, U.; Alvarez-Leite, J.; Damasceno, N.R.T.; Castro-Gomes, T.; Andrade, L.O. OxLDL Alterations in Endothelial Cell Membrane Dynamics Leads to Changes in Vesicle Trafficking and Increases Cell Susceptibility to Injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Hussain, S.; Paul, J.; Mukherjee, B. Linking Membrane Fluidity with Defective Antigen Presentation in Leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 2021, 43, e12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyaz, E.; Tandon, R.; Beg, M.A.; Dey, R.; Puri, N.; Salotra, P.; Nakhasi, H.L.; Selvapandiyan, A. Proteome Profile of Leishmania Donovani Centrin1−/−Parasite-Infected Human Macrophage Cell Line and Its Implications in Determining Possible Mechanisms of Protective Immunity. Microbes Infect. 2024, 26, 105340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.C.; Agero, U.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Mesquita, O.N. Measuring Optical and Mechanical Properties of a Living Cell with Defocusing Microscopy. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietuch, A.; Brückner, B.R.; Schneider, D.; Tarantola, M.; Rosman, C.; Sönnichsen, C.; Janshoff, A. Mechanical Properties of MDCK II Cells Exposed to Gold Nanorods. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hartmann, R.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; Yang, F.; Soenen, S.J.H.; Manshian, B.B.; Franz, J.; Valdeperez, D.; Pelaz, B.; Feliu, N.; et al. Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles Induce Changes in Cellular and Subcellular Morphology. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7807–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, M.; Kandy, S.K.; Graber, Z.T.; Baumgart, T.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Crocker, J.C. Probing Lipid Membrane Bending Mechanics Using Gold Nanorod Tracking. Phys. Rev. Res. 2022, 4, L012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Pang, W.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Qi, H.; Yang, K.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y. Bidirectional Regulation of Cell Mechanical Motion via a Gold Nanorods-Acoustic Streaming System. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8427–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesaragandla, B.; Komaragiri, Y.; Schlüter, R.; Otto, O.; Delcea, M. The Impact of Cell Culture Media on the Interaction of Biopolymer-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles with Cells: Mechanical and Toxicological Properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grala, M.; Kołodziejczyk, A.M.; Białkowska, K.; Walkowiak, B.; Komorowski, P. Assessment of the Influence of Gold Nanoparticles Stabilized with PAMAM Dendrimers on HUVEC Barrier Cells. Micron 2023, 168, 103430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 p value: *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; - - - mean;
p value: *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; - - - mean;
 median; ○ out-liers;
median; ○ out-liers;
 Healthy group;
Healthy group;
 Healthy + GNRs group;
Healthy + GNRs group;
 Infected group;
Infected group;
 Infected + GNRs group.
Infected + GNRs group.
 p value: *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; - - - mean;
p value: *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; - - - mean;
 median; ○ out-liers;
median; ○ out-liers;
 Healthy group;
Healthy group;
 Healthy + GNRs group;
Healthy + GNRs group;
 Infected group;
Infected group;
 Infected + GNRs group.
Infected + GNRs group.
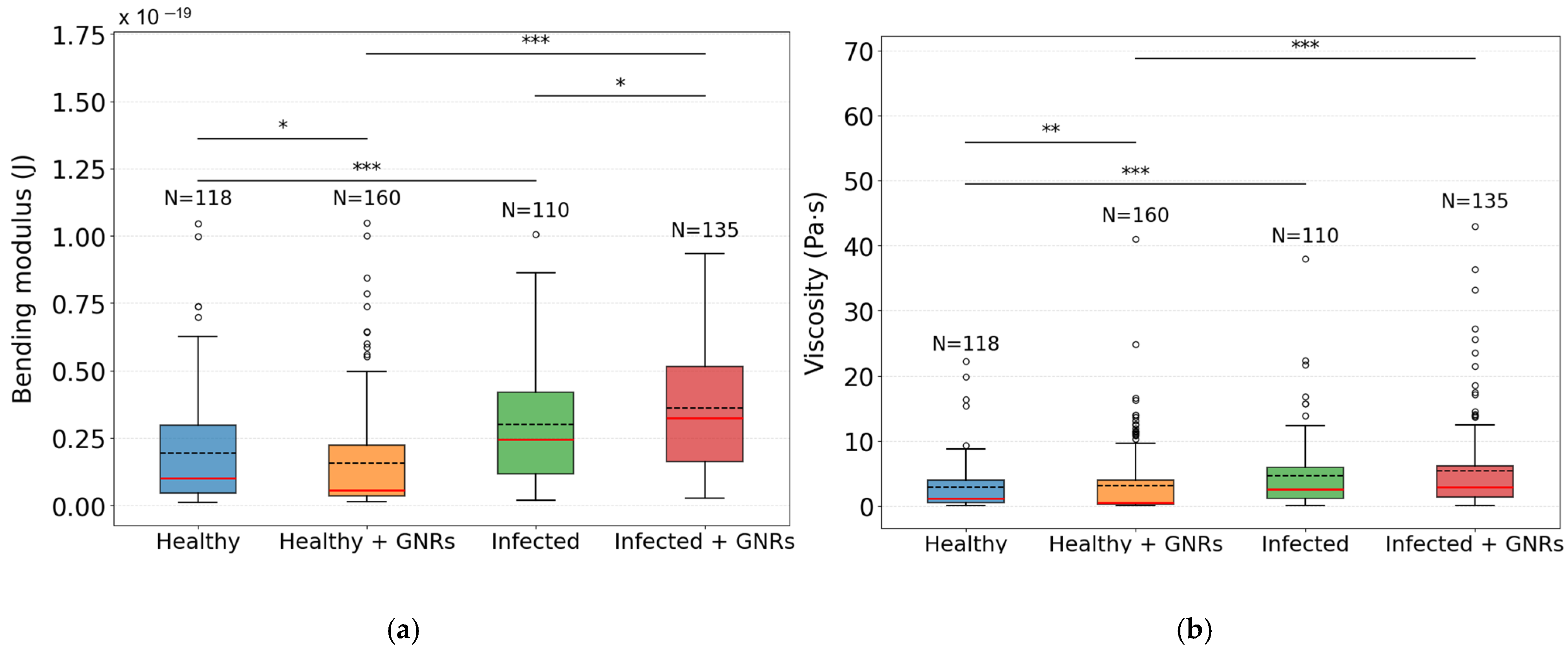
| (J) | Median × 10−20 | IQR × 10−20 |
| Healthy | 1.00 | 2.54 |
| Infected | 2.46 | 3.02 |
| Healthy + GNRs | 0.55 | 1.86 |
| Infected + GNRs | 3.24 | 3.53 |
| (Pa·s) | Median | IQR |
| Healthy | 1.23 | 3.48 |
| Infected | 2.55 | 4.77 |
| Healthy + GNRs | 0.57 | 3.79 |
| Infected + GNRs | 2.92 | 4.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pertence, M.L.B.; Guedes, M.V.; Barcelos, R.C.; Rugani, J.N.; Soares, R.P.; Cruz, J.L.V.; de Sousa, A.M.; do Monte-Neto, R.L.; Siman, L.G.; Lage, A.C.P.; et al. Investigation of Viscoelastic Properties of Macrophage Membrane–Cytoskeleton Induced by Gold Nanorods in Leishmania Infection. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171373
Pertence MLB, Guedes MV, Barcelos RC, Rugani JN, Soares RP, Cruz JLV, de Sousa AM, do Monte-Neto RL, Siman LG, Lage ACP, et al. Investigation of Viscoelastic Properties of Macrophage Membrane–Cytoskeleton Induced by Gold Nanorods in Leishmania Infection. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(17):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171373
Chicago/Turabian StylePertence, Maria L. B., Marina V. Guedes, Rosimeire C. Barcelos, Jeronimo N. Rugani, Rodrigo P. Soares, Joyce L. V. Cruz, Alessandra M. de Sousa, Rubens L. do Monte-Neto, Livia G. Siman, Anna C. P. Lage, and et al. 2025. "Investigation of Viscoelastic Properties of Macrophage Membrane–Cytoskeleton Induced by Gold Nanorods in Leishmania Infection" Nanomaterials 15, no. 17: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171373
APA StylePertence, M. L. B., Guedes, M. V., Barcelos, R. C., Rugani, J. N., Soares, R. P., Cruz, J. L. V., de Sousa, A. M., do Monte-Neto, R. L., Siman, L. G., Lage, A. C. P., & Agero, U. (2025). Investigation of Viscoelastic Properties of Macrophage Membrane–Cytoskeleton Induced by Gold Nanorods in Leishmania Infection. Nanomaterials, 15(17), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171373







