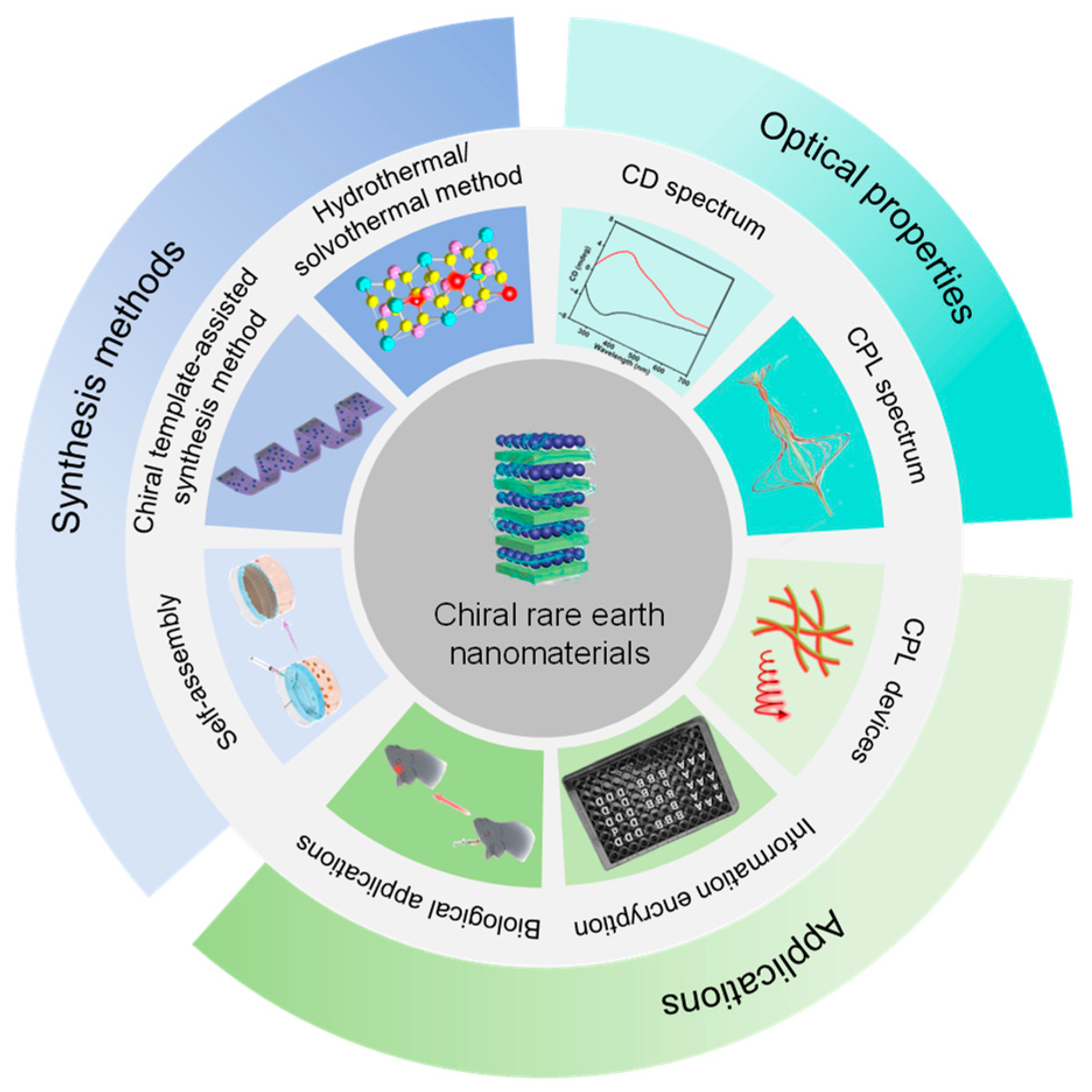
Chiral Rare Earth Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Potential Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
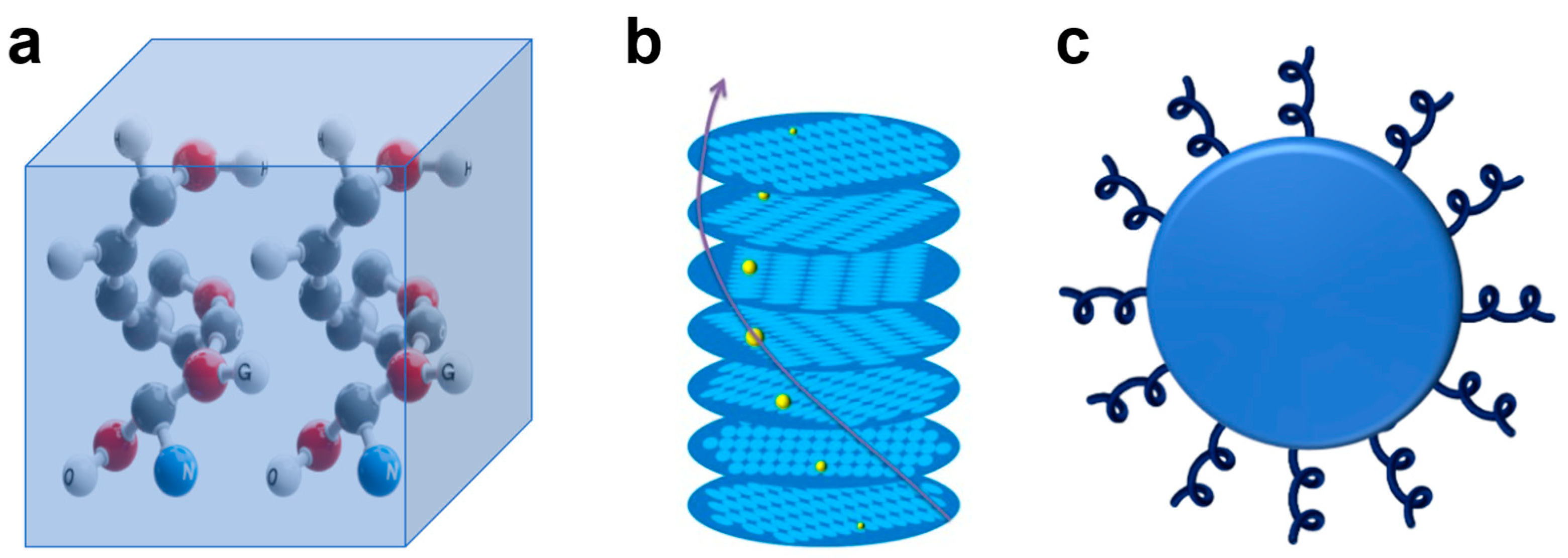
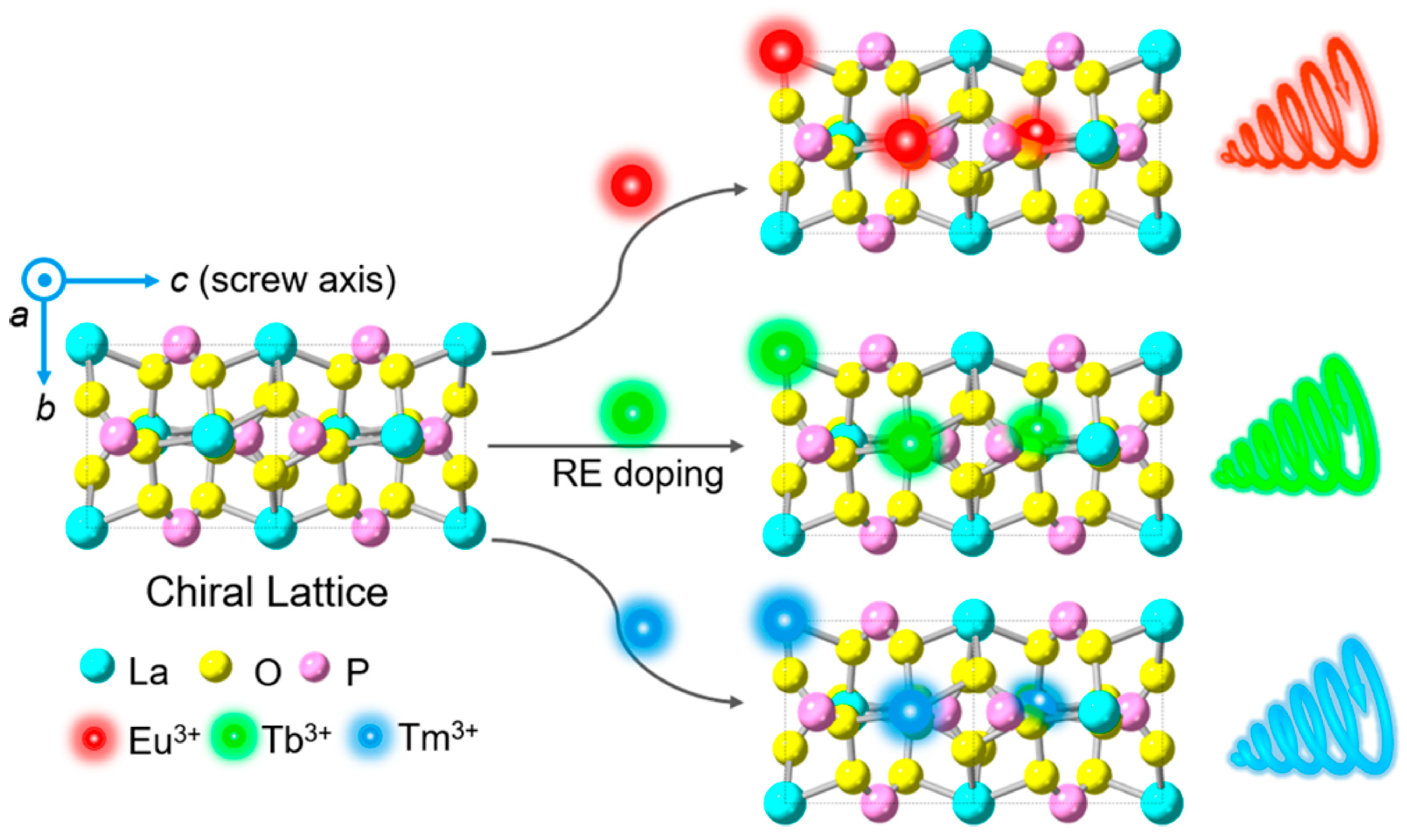
2. The Origin of Chirality
3. Synthesis Methods
3.1. Hydrothermal/Solvothermal Method
3.2. Chiral Template-Assisted Synthesis Method
3.2.1. Co-Assemble with Chiral MOFs Template
3.2.2. Chiral Liquid-Crystalline Template-Assisted Synthesis Method
3.2.3. Chiral Gel-Assisted Synthesis Method
3.2.4. Chiral Silica-Assisted Synthesis Method
3.2.5. Chiral Layered Structure-Assisted Synthesis Method

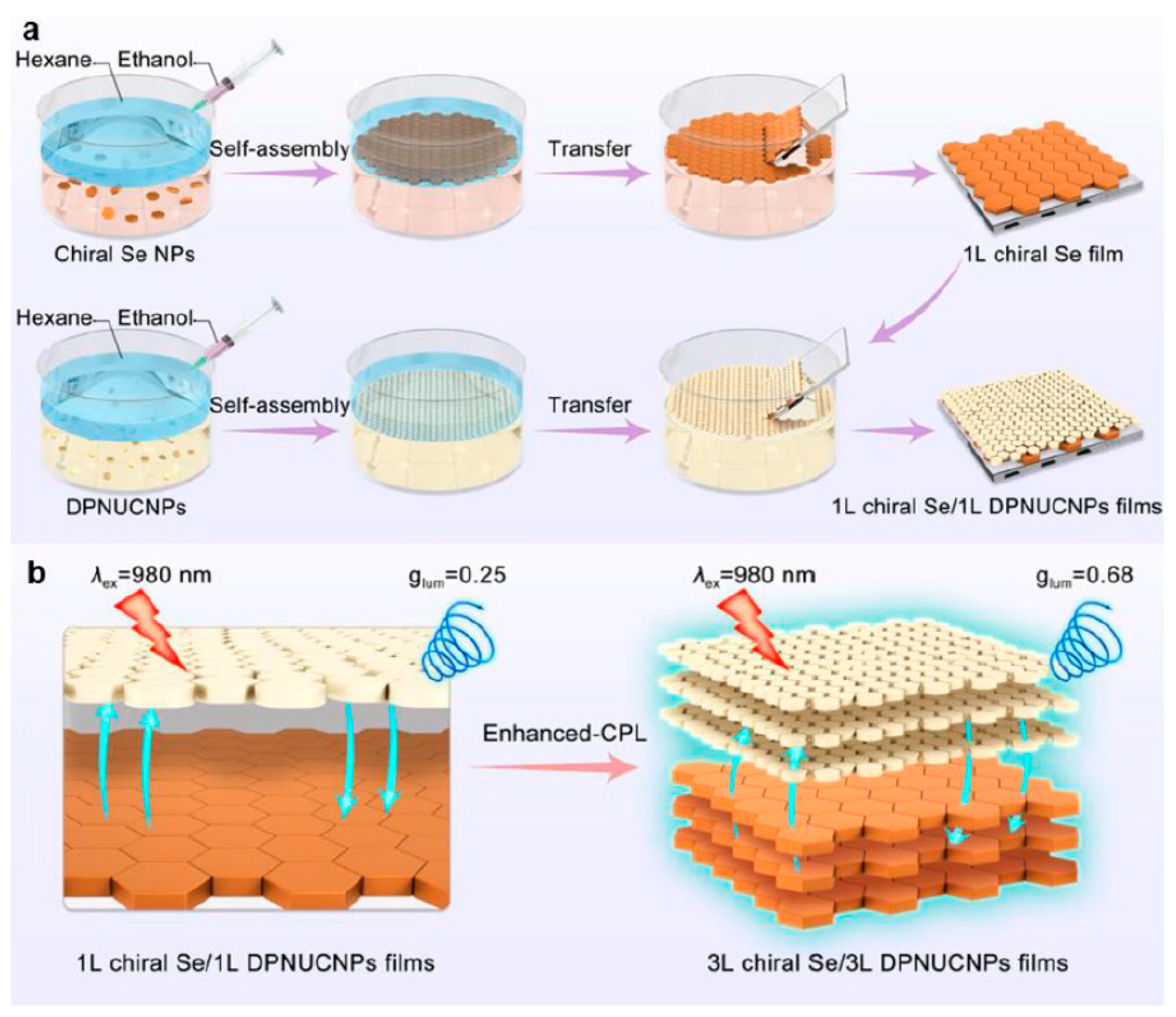
3.3. Self-Assembly Method
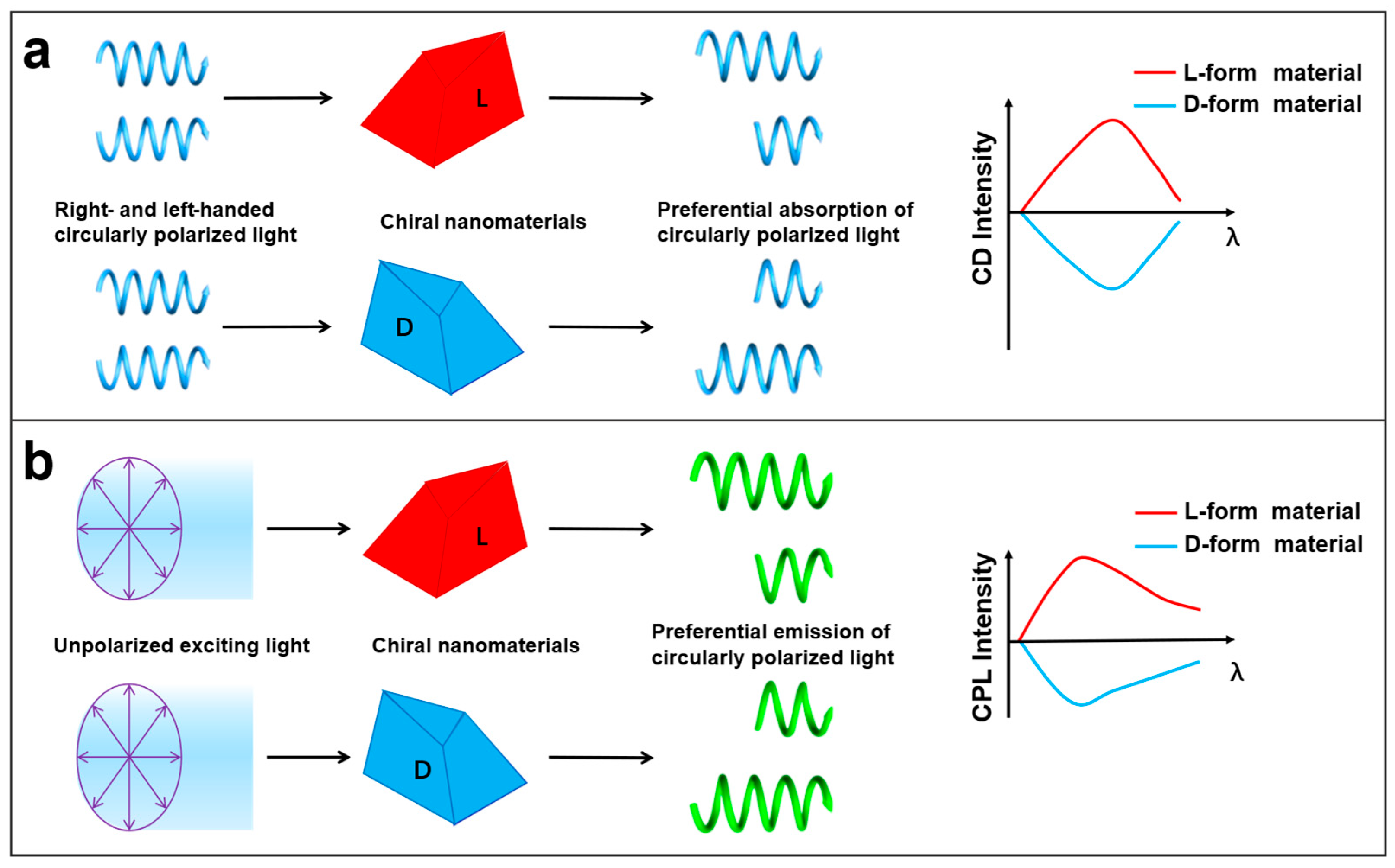
4. Chiroptical Properties
4.1. Basic Concepts Related to CD and CPL
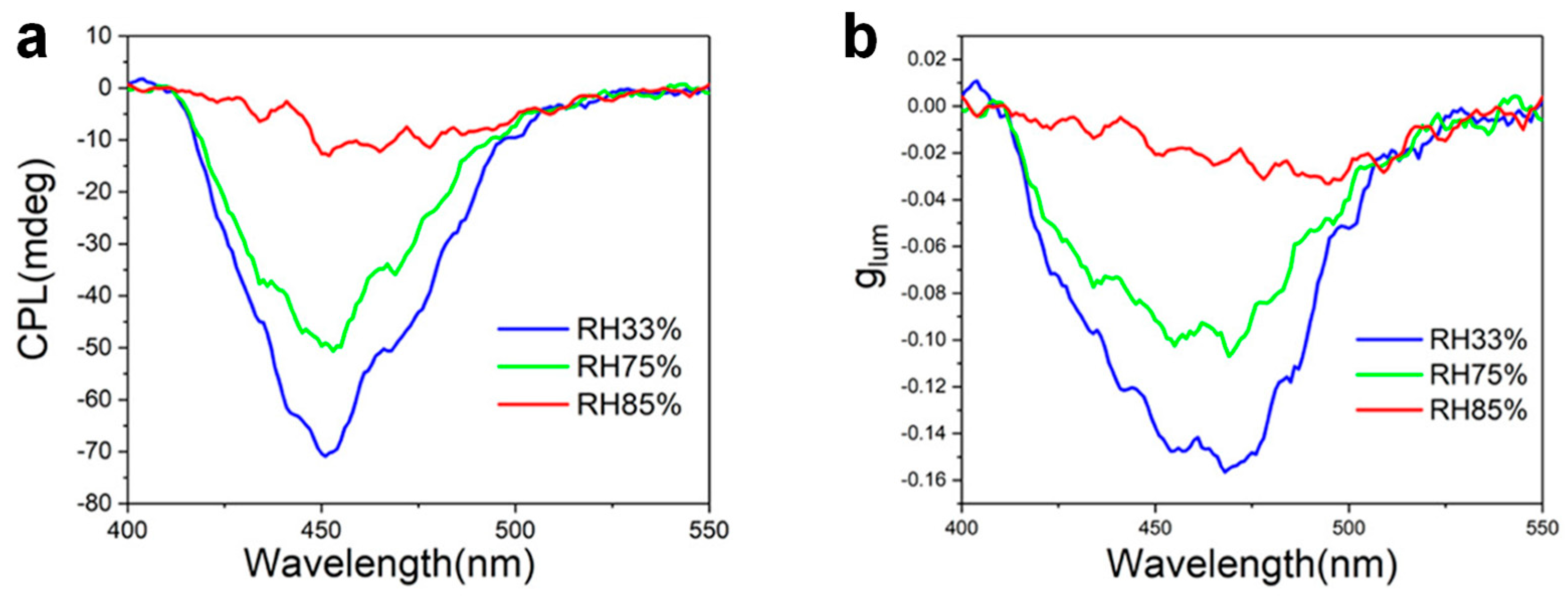
4.2. Chiroptical of Chiral Nanomaterials
5. Potential Applications
5.1. Circularly Polarized Light-Emitting Devices
5.2. Optical Anti-Counterfeiting and Information Encryption
5.3. Drug Delivery, Therapy, and Bioimaging
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Q. Circularly polarized luminescence from organic micro-/nano-structures. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, T.T.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Wei, M.; de Arquer, F.P.G.; Todorović, P.; Tian, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; et al. Regioselective magnetization in semiconducting nanorods. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandula, J.S.; Rayala, V.P.K.; Pullapanthula, R. Chirality: An inescapable concept for the pharmaceutical, bio-pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. Sep. Sci. Plus 2023, 6, 2200131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.U.; Li, J.J.; Liu, X.; Siddique, A.; Shi, Y.X.; Hou, M.; Yang, K.; Nosheen, F.; Cui, X.Y.; Zheng, G.C.; et al. Chiral metal nanostructures: Synthesis, properties and applications. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 2489–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Qin, P.; Zhang, S.; Yung, K.K.L.; Huang, Z. Recent advances in inorganic chiral nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Duan, Y. Chiral mesostructured Yb3+, Er3+ codoped CeO2 with upconverted circularly polarized luminescence. Chem. Eur. J. 2025, 31, e202403836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotov, N.A.; Liz-Marzan, L.M.; Weiss, P.S. Chiral nanostructures: New twists. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12457–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Song, J.; Wu, Q.; Lv, H. Chiral carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probe for rapid chiral recognition of isoleucine enantiomers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhina, M.V.; Maslov, V.G.; Baranov, A.V.; Fedorov, A.V.; Orlova, A.O.; Purcell-Milton, F.; Govan, J.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Intrinsic chirality of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and quantum rods. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohgha, U.; Deol, K.K.; Porter, A.G.; Bartko, S.G.; Choi, J.K.; Leonard, B.M.; Varga, K.; Kubelka, J.; Muller, G.; Balaz, M. Ligand induced circular dichroism and circularly polarized luminescence in CdSe quantum dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11094–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Haynie, B.E.; Tohgha, U.; Pap, L.; Elliott, K.W.; Leonard, B.M.; Dzyuba, S.V.; Varga, K.; Kubelka, J.; Balaz, M. Chirality inversion of CdSe and CdS quantum dots without changing the stereochemistry of the capping ligand. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3809–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Ahn, J.; Moon, J. Chiral perovskites for next-generation photonics: From chirality transfer to chiroptical activity. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q. Chiral metal halide perovskites toward room temperature spin light-emitting diodes: Insights and perspectives. Chem. Phys. Rev. 2025, 6, 021303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mao, B.; Vardeny, Z.V. Chirality induced spin selectivity in chiral hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 159, 091002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y. Chiral lead halide perovskite nanocrystals: Construction strategies and photophysical properties. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2023, 6, 2300178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Huang, Y.; Dong, S.; Bai, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Chao, M.; Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Geng, D.; et al. A chiral nanocomplex for multitarget therapy to alleviate neuropathology and rescue alzheimer’s cognitive deficits. Small 2023, 19, 2303530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhao, L. Ion-pairing chirality transfer in atropisomeric biaryl-centered gold clusters. CCS Chem. 2021, 2, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Emerging chirality in nanoscience. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2930–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Moshe, A.; Maoz, B.M.; Govorov, A.O.; Markovich, G. Chirality and chiroptical effects in inorganic nanocrystal systems with plasmon and exciton resonances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7028–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crassous, J. Chiral transfer in coordination complexes: Towards molecular materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Du, Y.; Yan, C. Ultrathin 2D rare-earth nanomaterials: Compositions, syntheses, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, P.P. Stable two-coordinate, open-shell (d1–d9) transition metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3482–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, P.Z.; Yan, C.H. Upconversion of rare earth nanomaterials. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2015, 66, 619–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. A mini-review on recent progress of new sensitizers for luminescence of lanthanide doped nanomaterials. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, P.; He, M.; Yuan, X.; Fang, Z.; Li, Z. Rare earth-based nanomaterials in electrocatalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 489, 215204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Sang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Duan, P.; Liu, M. Optically active upconverting nanoparticles with induced circularly polarized luminescence and enantioselectively triggered photopolymerization. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Choi, W.J.; Jeong, U.; Jung, W.; Hwang, I.; Park, K.H.; Ko, S.G.; Park, S.M.; Kotov, N.A.; Yeom, J. Recent advances in chiral nanomaterials with unique electric and magnetic properties. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yue, X.; Ding, Q.; Lin, H.; Xu, C.; Li, S. Chiral inorganic nanomaterials for biological applications. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 2541–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, P. Recent advances in circularly polarized luminescence of chiral rare earth nanomaterials. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2024, 54, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Kotov, N.A. Circular polarized light emission in chiral inorganic nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2108431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.L.; Chen, Y.; Du, Y.; Long, G. The first chiral cerium halide towards circularly-polarized luminescence in the UV region. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Fu, W.; Wang, P.P. Multicolor circularly polarized luminescence from inorganic crystalline nanostructures induced by atomic chirality. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 4384–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Liu, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, F.; Chen, X. Helically assembled rare earth fluoride nanoparticles with multicolor circularly polarized luminescence for high-security anti-counterfeiting. Aggregate 2025, 6, e70042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.; Long, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wen, Y.; et al. Chiral inorganic nanostructured BiOCl co-doped with Er3+/Yb3+ exhibits circularly polarized luminescence and enhanced upconversion luminescence. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 30436–30442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Valenzuela, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Feng, W.; Li, Q. Liquid crystal-templated chiral nanomaterials: From chiral plasmonics to circularly polarized luminescence. Light-Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francés-Soriano, L.; Zaballos-García, E.; Pérez-Prieto, J. Up-and down-shifting nanomaterials with chiroptical responses: Origin of their chiroptical activity and applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2300337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Tan, L.; Wang, P. Chiral inorganic nanomaterials for photo (electro) catalytic conversion. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 16326–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M.; Ferry, V.E. Circular dichroism of CdSe nanocrystals bound by chiral carboxylic acids. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12240–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R. The nose as a stereochemist. Enantiomers and odor. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4099–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Moshe, A.; Govorov, A.O.; Markovich, G. Enantioselective synthesis of intrinsically chiral mercury sulfide nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hananel, U.; Ben-Moshe, A.; Diamant, H.; Markovich, G. Spontaneous and directed symmetry breaking in the formation of chiral nanocrystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11159–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Lu, X.; Shen, C.; Ke, Y.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q. Au nanorod helical superstructures with designed chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, F.; Han, Z.; Shang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.; Li, N.; Ding, B. Strong light–matter interactions in chiral plasmonic–excitonic systems assembled on DNA origami. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3573–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzyk, A.; Schreiber, R.; Zhang, H.; Govorov, A.O.; Liedl, T.; Liu, N. Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Urbas, A.M.; Li, Q. Nature-inspired emerging chiral liquid crystal nanostructures: From molecular self-assembly to DNA mesophase and nanocolloids. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1801335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, S.; Guo, J.; Li, Q. Circularly polarized luminescent self-organized helical superstructures: From materials and stimulus-responsiveness to applications. Aggregate 2021, 2, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.P.; Prévôt, M.E.; Üstünel, Ş.; Ogolla, T.; Nemati, A.; Shadpour, S.; Hegmann, T. Recent progress at the interface between nanomaterial chirality and liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2021, 9, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Xu, D.; Lu, Z.; Liu, K. Chiral self-assembly of nanoparticles induced by polymers synthesized via reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.T.; Yang, C.Y.; Xie, Z.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Hung, Y.C.; Ho, R.M. Gold nanohelices for chiral plasmonic films by templated electroless plating. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2002133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, M.; Wu, B.; Zhu, L. Chirality transfer in carbon dot-composited sol–gel systems for excitation-dependent circularly polarized luminescence. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8965–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Duan, P.; Huo, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, M. Endowing perovskite nanocrystals with circularly polarized luminescence. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.H.; Jeon, J.; Kim, H.; Jaworski, J.; Jung, J.H. Chiral arrangement of achiral Au nanoparticles by supramolecular assembly of helical nanofiber templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6446–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.; Pescitelli, G.; Di Bari, L. Chiroptical properties in thin films of π-conjugated systems. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10145–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniappan, S.; Jadhav, A.B.; Kumar, J. Template assisted generation of chiral luminescence in organic fluorophores. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 557650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohgha, U.; Varga, K.; Balaz, M. Achiral CdSe quantum dots exhibit optical activity in the visible region upon post-synthetic ligand exchange with D-or L-cysteine. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, D.E.; Kitchen, J.A.; Albrecht, M.; Faulkner, S.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Near infrared (NIR) lanthanide emissive langmuir–blodgett monolayers formed using Nd (III) directed self-assembly synthesis of chiral amphiphilic ligands. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11506–11515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, X.; Hu, S.; Yang, F.; Zhong, J. Rare-earth nanocrystalline scintillators for biomedical application: A review. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 16936–16950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.S.; Dong, X.Y.; Niu, Y.Y.; Zang, S.Q. Multiple responsive CPL switches in an enantiomeric pair of perovskite confined in lanthanide MOFs. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gu, Z.G.; Zhang, J. Chiral-induced ultrathin covalent organic frameworks nanosheets with tunable circularly polarized luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 7245–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Xiao, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J. Tunable chiroptical application by encapsulating achiral lanthanide complexes into chiral MOF thin films. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulidis, A.P.; Antypov, D.; Whitehead, G.F.; Carrington, E.J.; Adams, D.J.; Berry, N.G.; Darling, G.R.; Dyer, M.S.; Rosseinsky, M.J. Chemical control of structure and guest uptake by a conformationally mobile porous material. Nature 2019, 565, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Han, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Duan, P. Enhanced circularly polarized luminescence from reorganized chiral emitters on the skeleton of a zeolitic imidazolate framework. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 5032–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Chen, X.M. Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal–organic frameworks: Zinc (II) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1557–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Han, J.; Jin, X.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Duan, P.; Liu, M. Dual-mode induction of tunable circularly polarized luminescence from chiral metal-organic frameworks. Research 2020, 2020, 6452123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Han, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Duan, P. Multi-light-responsive upconversion-and-downshifting-based circularly polarized luminescent switches in chiral metal–organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Enhanced circularly polarized luminescence in rare-earth MOFs via framework chirality and host–guest energy transfer. Polyoxometalates 2025, 4, 9140095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Miao, X.; Liu, Y.J.; Fan, Q.; Wang, K.; Luo, D.; Sun, X.W. Circularly polarized luminescence from semiconductor quantum rods templated by self-assembled cellulose nanocrystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Yu, X.; Wei, L.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Y. Cellulose nanocrystal films with NIR-II circularly polarized light for cancer detection applications. ACS Nano 2022, 17, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Hamad, W.Y.; MacLachlan, M.J. Near-IR-sensitive upconverting nanostructured photonic cellulose films. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1600514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Biesold, G.M.; Lee, H.; Bukharina, D.; Lin, Z.; Tsukruk, V.V. Dynamic chiro-optics of bio-inorganic nanomaterials via seamless co-assembly of semiconducting nanorods and polysaccharide nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Crne, M.; Park, J.O.; Srinivasarao, M. Structural origin of circularly polarized iridescence in jeweled beetles. Science 2009, 325, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.H.; Kleinlogel, S.; Cronin, T.; Caldwell, R.; Loeffler, B.; Siddiqi, A.; Goldizen, A.; Marshall, J. Circular polarization vision in a stomatopod crustacean. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, M.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Liu, S. Tunable upconverted circularly polarized luminescence in cellulose nanocrystal based chiral photonic films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23512–23519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, M. Self-Assembly of hierarchical chiral nanostructures based on metal–benzimidazole interactions: Chiral nanofibers, nanotubes, and microtubular flowers. Small 2016, 34, 4743–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, M.; Hung, C.T.; Shi, X.L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, R.H.; Li, W.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, D. Chiral skeletons of mesoporous silica nanospheres to mitigate alzheimer’s β-amyloid aggregation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7810–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; He, Z.; Yin, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Multichiral mesoporous silica screws with chiral differential mucus penetration and mucosal adhesion for oral drug delivery. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 16166–16183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delclos, T.; Aimé, C.; Pouget, E.; Brizard, A.; Huc, I.; Delville, M.H.; Oda, R. Individualized silica nanohelices and nanotubes: Tuning inorganic nanostructures using lipidic self-assemblies. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Liu, X.L.; Tsunega, S.; Nakajima, E.; Abe, S.; Nakashima, T.; Kawai, T.; Jin, R.H. Circularly polarized luminescence from inorganic materials: Encapsulating guest lanthanide oxides in chiral silica hosts. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6519–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Battie, Y.; Kimura, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Pranee, P.; Wang, H.; Pouget, P.; Nlate, S.; Sagawa, T.; Oda, R. Chiral perovskite nanocrystal growth inside helical hollow silica nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, W.; Okazaki, Y.; Battie, Y.; Brocard, L.; Decossas, M.; Pouget, E.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Kauffmann, B.; Pathan, S.; et al. Optically active perovskite CsPbBr3 nanocrystals helically arranged on inorganic silica nanohelices. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 8453–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Sang, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, S.; Guo, J.; Duan, P.; Liu, M. Steering nanohelix and upconverted circularly polarized luminescence by using completely achiral components. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhao, T.; Duan, P.; Liu, M. Circularly polarized luminescence in nanoassemblies: Generation, amplification, and application. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1900110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyuki, M.; Ren-Hua, J. High-temperature-resistant chiral silica generated on chiral crystalline templates at neutral pH and ambient conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2012, 51, 5862–5865. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; He, W.; Yin, J.J. Surface structure-dependent molecular oxygen activation of BiOCl single-crystalline nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15750–15753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Lanthanide-based luminescent hybrid materials. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4283–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, S.; Yu, J.; Parker, D. Engineering emissive europium and terbium complexes for molecular imaging and sensing. Dalton Trans. 2006, 23, 2757–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseeva, S.V.; Bünzli, J.C.G. Lanthanide luminescence for functional materials and bio-sciences. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 189–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangsun, H.; Xu, L.; Qu, A.; Xu, C.; Kuang, H.; Hao, C. Generating strong circularly polarized luminescence from self-assembled films of chiral selenium nanoparticles and upconversion nanoparticles. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202419884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.T.; Kuppe, C.; Hooper, D.C.; Sibilia, C.; Centini, M.; Valev, V.K. Chirality and chiroptical effects in metal nanostructures: Fundamentals and current trends. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizar, N.S.; Sujith, M.; Swathi, K.; Sissa, C.; Painelli, A.; Thomas, K.G. Emergent chiroptical properties in supramolecular and plasmonic assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11208–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, J.; Kim, M.; Yang, Y.; Badloe, T.; Ni, J.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, C.W.; Rho, J. Electromagnetic chirality: From fundamentals to nontraditional chiroptical phenomena. Light-Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, M.; Schadt, M. Linearly polarized light with axial symmetry generated by liquid-crystal polarization converters. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1948–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, L.; Todorov, T.; Ivanov, M.T.; Andruzzi, F.; Hvilsted, S.; Ramanujam, P.S. Polarization holographic gratings in side-chain azobenzene polyesters with linear and circular photoanisotropy. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 3835–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trippe, S. Polarization and polarimetry: A review. J. Korean Astron. Soc. 2014, 1401, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Guo, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, W. Recent progress on circularly polarized luminescent materials for organic optoelectronic devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warning, L.A.; Miandashti, A.R.; McCarthy, L.A.; Zhang, Q.; Landes, C.F.; Link, S. Nanophotonic approaches for chirality sensing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15538–15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, M.; Coccia, C.; Malavasi, L. Chiral 2D and quasi-2D hybrid organic inorganic perovskites: From fundamentals to applications. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Carnerero, E.M.; Agarrabeitia, A.R.; Moreno, F.; Maroto, B.L.; Muller, G.; Ortiz, M.J.; de la Moya, S. Circularly polarized luminescence from simple organic molecules. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13488–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, R.; Evans, N.H.; Parker, D. Lanthanide complexes as chiral probes exploiting circularly polarized luminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7673–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, D.; Duan, J.; Sang, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Terbium–aspartic acid nanocrystals with chirality-dependent tunable fluorescent properties. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Luminescent chiral lanthanide (III) complexes as potential molecular probes. Dalton Trans. 2009, 44, 9692–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Duan, P. Electric-field-regulated energy transfer in chiral liquid crystals for enhancing upconverted circularly polarized luminescence through steering the photonic bandgap. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, M.; Han, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Duan, P. A new strategy to achieve enhanced upconverted circularly polarized luminescence in chiral perovskite nanocrystals. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, T.; Wang, H.; Gull, S.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Chiral europium halides with high-performance magnetic field tunable red circularly polarized luminescence at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.E.; Robert, P. Circularly polarized lanthanide luminescence for advanced security inks. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Wada, S.; Islam, M.D.J.; Saita, K.; Gon, M.; Fushimi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Maeda, S.; Hasegawa, Y. Chiral lanthanide lumino-glass for a circularly polarized light security device. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, T.K.; Barbosa, H.P.; Dos Santos, L.F.; Lima, K.d.O.; de Matos, P.A.; Tsubone, T.M.; Gonçalves, R.R.; Ferrari, J.L. Upconversion rare earths nanomaterials applied to photodynamic therapy and bioimaging. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1035449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y. Rare earth-doped nanocrystals for bioimaging in the near-infrared region. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 8596–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Ming, J.; Yun, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. An extended NIR-II superior imaging window from 1500 to 1900 nm for high-resolution in vivo multiplexed imaging based on lanthanide nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202311883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y. Rare earth-doped nanoparticles for near-infrared II image-guided photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 11008–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Tan, L.; Wen, Z.; Fan, D.; Hui, J.; Wang, P.P. Chiral inorganic nanomaterials: Harnessing chirality-dependent interactions with living entities for biomedical applications. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 11107–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qu, X. Recent progress on molecular recognition and modulation of nucleic acids using chiral rare-earth complexes. Prog. Chem. 2013, 25, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H.; Kotov, N.A.; Xu, C. Propeller-like nanorod-upconversion nanoparticle assemblies with intense chiroptical activity and luminescence enhancement in aqueous phase. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5907–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hu, R.; Men, Y.; Li, J.; Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Feng, D. Impact of photo-irradiation on the optical and spin properties of chiral CdS quantum dot films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 151902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, P.; Men, Y.; Jiang, M.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Feng, D. Light-induced photoluminescence enhancement in chiral CdSe quantum dot films. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 160, 161102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Chirality | Chirality Origin | CPL-Active System | Maximum glum | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic | Chiral lattice | GdPO4:Eu3+ phosphate | 1.1 × 10−1 | [32] |
| Chiral lattice | NaYF4:Eu3+ phosphate | 4 × 10−1 | [41] | |
| Non-intrinsic | Chiral helical nanotubes | NaYF4:Yb/Tm UCNPs | 5.48 × 10−3 | [26] |
| Helical silica | CeF3:Tb3+ nanoparticles | 4.7 × 10−3 | [33] | |
| Chiral MOF | NaYF4:Yb/Er UCNPs | 1.2 × 10−2 | [65] | |
| Cellulose nanocrystal | NaYF4:Tm/Yb UCNPs | 1.56 × 10−1 | [74] | |
| Chiral nematic liquid crystal | UCNPs and CsPbBr3 NCs | 1.1 | [103] | |
| Chiral MOF | DAEC and UCNP-Tm | 7.8 × 10−2 | [66] | |
| Chiral CsPbBr3 NCs | NaYF4:Yb/Tm UCNPs | 5.0 × 10−3 | [104] | |
| BTABA | NaYF4:Yb/Er nanoparticles | 1.2 × 10−2 | [82] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Liang, P.; Zhao, H.; Hu, R.; Xu, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y. Chiral Rare Earth Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Potential Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171321
Zhao L, Liang P, Zhao H, Hu R, Xu Y, Chen F, Wang X, Yao Y. Chiral Rare Earth Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Potential Applications. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(17):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171321
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lei, Pan Liang, Hua Zhao, Rongrong Hu, Yangyang Xu, Fangfang Chen, Xianghu Wang, and Yunhua Yao. 2025. "Chiral Rare Earth Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Potential Applications" Nanomaterials 15, no. 17: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171321
APA StyleZhao, L., Liang, P., Zhao, H., Hu, R., Xu, Y., Chen, F., Wang, X., & Yao, Y. (2025). Chiral Rare Earth Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Potential Applications. Nanomaterials, 15(17), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15171321





